US20150211638A1 - Mechanical seal - Google Patents
Mechanical seal Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20150211638A1 US20150211638A1 US14/407,372 US201314407372A US2015211638A1 US 20150211638 A1 US20150211638 A1 US 20150211638A1 US 201314407372 A US201314407372 A US 201314407372A US 2015211638 A1 US2015211638 A1 US 2015211638A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- cartridge
- fixed
- sealing ring
- inner cylinder
- bellows
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/36—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member connected by a diaphragm or bellow to the other member
- F16J15/363—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member connected by a diaphragm or bellow to the other member the diaphragm or bellow being made of metal
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/3436—Pressing means
- F16J15/3452—Pressing means the pressing force resulting from the action of a spring
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/3436—Pressing means
- F16J15/3448—Pressing means the pressing force resulting from fluid pressure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/3464—Mounting of the seal
- F16J15/348—Pre-assembled seals, e.g. cartridge seals
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/38—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member sealed by a packing
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a mechanical seal used, e.g., as a shaft-sealing device in a pump or the like.
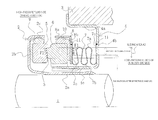
- FIG. 7 An inside-format mechanical seal in which a sealed fluid that may leak from the outer circumference of a sealing face to the inner circumference direction is sealed, wherein: an annular rotation-side sealing ring 53 provided, via a sleeve 51 and a cup gasket 52 , on the side of a rotating shaft 50 for driving a pump impeller (not shown) on the high-pressure fluid-side, so as to be capable of rotating integrally with the rotating shaft 50 ; and an annular fixed-side sealing ring 55 provided, via a bellows 57 in a cartridge 56 , to a housing 54 Document of the pump in a non-rotating state so as to be capable of axial movement, are caused by the bellows 57 and a coiled wave spring 58 axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring 55 to slide against each other in intimate contact at respective sealing faces S which have been mirror-surface-finished by lapping or the like (hereafter referred to as “
- Patent Document 2 discloses an invention of a mechanical seal in which, as shown in FIG. 8 , a fixed-side sealing ring 62 is attached to a housing 61 , a rotation-side sealing ring 63 is provided to a shaft which is rotatably supported by the housing 61 , and the fixed-side sealing ring 62 and the rotation-side sealing ring 63 are in elastic contact with each other so as to be capable of sliding, wherein a fixing claw 64 a is formed on the right end of a metal bellows 64 so that the metal bellows 64 supports the fixed-side sealing ring 62 so as to be capable of axial movement, the fixing claw 64 a is bent and the fixed-side sealing ring 62 is supported at the right-end interior of the metal bellows 64 , and the left end of the metal bellows 64 is directly fixed to the housing 61 (hereafter referred to as “prior art 2”; see Patent Citation 2).
- the bellows 57 being made from rubber presents problems such as degradation or tearing of the bent part. Problems are also presented in that an urging member such as the coiled wave spring 58 and an attaching member such as the driving band 60 are required, increasing the number of components.
- the present invention was devised in order to resolve the problems presented by the prior art, it being an object thereof to provide a mechanical seal in which degradation or tearing of a bellows does not occur, the spring constant of the bellows is reduced, and the fluctuation in the load due to stretching and contracting of the bellows is reduced.
- assembly of [a mechanical seal] through integrating the rotation-side and the fixed-side normally necessitates increasing the inside diameter of the bellows in order to secure sufficient space, which changes the pressure-receiving area of the bellows and results in a fluctuation in the balance value; an object of the present invention is to provide a mechanical seal in which the fluctuation in the balance value in such an instance is minimized.
- a mechanical seal according to the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to said sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge;
- the mechanical seal being characterized in that: the bellows is made from a metal; and the metal bellows has one end fixed to a case for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case or the cartridge.
- the metal bellows exclusively plays a role of axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, and is formed as a separate body with respect to the case, the cartridge, or the like. Therefore, the plate thickness of the metal bellows can be reduced, the spring constant of the metal bellows can be reduced, and a change in load with respect to the amount of stretching and contracting of the metal bellows can be reduced. Therefore, even when the rotation-side sealing ring is axially displaced, the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring can be kept stable, and the pressure at the sealing face can be maintained at an optimum value. In addition, the tolerance of the length of attachment of the metal bellows can be relaxed.
- the metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan. Also, the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used. Furthermore, the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests. Also, the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- a mechanical seal according to the first aspect of the present invention is characterized in that: the metal bellows comprises a bellows part in which crest parts and trough parts are alternately formed, and a disc-shaped flange part extending radially outwards from the trough part at each end of the bellows part; and the bellows part is formed by molding or welding so that the outer diameter of the flange parts is greater than the diameter of the crest parts, and the inner diameter of the flange parts is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of the trough parts. According to this characteristic, it is possible to easily fix the metal bellows to the case and the cartridge and to prevent the sealed fluid from leaking.
- a mechanical seal according to the first or second aspect of the present invention is characterized in that: fixing of the metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge is performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part of the metal bellows.
- fixing of the metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge is performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part of the metal bellows.
- a mechanical seal according to any of the first through third aspects of the present invention is characterized in that the rotation-side sealing ring is fixed to the sleeve via a cup gasket, and the cup gasket is provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of the rotation-side sealing ring. According to this characteristic, it is possible to prevent the cup gasket from detaching, even when the pressure of a high-pressure fluid acts on the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket.
- a mechanical seal of the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to the sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge; the mechanical seal being characterized in that:
- the bellows is made from a metal
- the metal bellows has one end fixed to a gasket for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the cartridge.
- the metal bellows is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- a mechanical seal according to the fifth aspect of the present invention is characterized in that a band is attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows fitting into the gasket holding the fixed-side sealing ring. This characteristic makes it possible for the fitting between the metal bellows and the cup gasket to be made more reliable.
- a mechanical seal of the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to the sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge;
- the mechanical seal being characterized in that: the bellows is made from a metal; and the metal bellows has one end directly fixed to the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the cartridge.
- a mechanical seal according to any of first through seventh aspects of the present invention is characterized in being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of the sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of the cartridge, thereby preventing the cartridge and the sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
- a portion of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to the fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part;
- the bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge.
- the present invention has the following beneficial effects.
- the metal bellows having one end fixed to a case for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case or the cartridge, result in the metal bellows exclusively playing a role of axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, and being formed separately from the case, the cartridge, or the like. Therefore, the plate thickness of the metal bellows can be reduced, the spring constant of the metal bellows can be reduced, and a change in load with respect to the amount of stretching and contracting of the metal bellows can be reduced.
- the rotation-side sealing ring is axially displaced, the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring can be kept stable, and the pressure at the sealing face can be maintained at an optimum value.
- the tolerance of the length of attachment of the metal bellows can be relaxed.
- using a metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan.
- the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used.
- the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests.
- the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- the metal bellows comprising a bellows part in which crest parts and trough parts are alternately formed, and a disc-shaped flange part extending radially outwards from the trough part at each end of the bellows part; and the bellows part being formed by molding or welding so that the outer diameter of the flange parts is greater than the diameter of the crest parts, and the inner diameter of the flange parts is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of the trough parts, result in it being possible to easily fix the metal bellows to the case and the cartridge and to prevent the sealed fluid from leaking.
- the metal bellows having one end fixed to a gasket for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, whereby the metal bellows is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- a band being attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows fitting into the gasket holding the fixed-side sealing ring makes it possible for the fitting between the metal bellows and the cup gasket to be made more reliable.
- the metal bellows having one end directly fixed to the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge results in it being possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the axial length of the mechanical seal.
- the mechanical seal ⁇ being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of the sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of the cartridge, thereby preventing the cartridge and the sleeve from axial detachment, wherein: a portion of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to the fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and the bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge, results in it being possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value, reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face, and suppress an increase in the spring constant of the bellows, without increasing the outer diameter of the bell
- FIG. 1 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a first example of the present invention
- FIG. 2 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a second example of the present invention
- FIG. 3 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a third example of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a fourth example of the present invention.
- FIG. 5 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a fifth example of the present invention.
- FIG. 6 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a sixth example of the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to prior art 1;
- FIG. 8 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to prior art 2.
- FIG. 9 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a reference example for illustrating the mechanical seal according to the fifth and sixth examples of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 A description will now be given for a mechanical seal according to a first example of the present invention.
- the present invention is applied to an inside-type mechanical seal of a format in which a fluid trying to leak from the outer circumference of the sealing face to the inner circumference direction is sealed.
- the left side corresponds to the high-pressure fluid side (sealed fluid side) and the right side corresponds to the low-pressure fluid side (atmosphere side).
- the mechanical seal according to the present invention is a mechanical seal comprising a sleeve 2 fixed to a rotating shaft 1 , and a cartridge 4 fixed to a housing 3 ; a rotation-side sealing ring 5 being provided to the sleeve 2 ; and a fixed-side sealing ring 6 , which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring 5 , and a bellows 7 for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring 6 being provided to the cartridge 4 ;
- the mechanical seal being mainly characterized in that: the bellows 7 is made from a metal;
- the metal bellows 7 has one end fixed to a case 8 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and another end fixed to the cartridge 4 , and has a plate thickness set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case 8 or the cartridge 4 .
- a pump impeller (not shown) is fixed to the high-pressure-fluid side of the rotating shaft 1 , and the shaft-sealing part between the inner diameter side of the housing 3 and the outer diameter side of the rotating shaft 1 of the pump has the mechanical seal of the present invention installed thereto and sealed.
- the sleeve 2 has: an inner cylinder part 2 a fitted to the rotating shaft 1 ; a disc part 2 b extending in the outer diameter direction from the high-pressure-fluid side of the inner cylinder part 2 a ; and an outer cylinder part 2 c extending from the outer diameter side of the disc part 2 b to the low-pressure-fluid side.
- the sleeve 2 supports the rotation-side sealing ring 5 to the low-pressure-fluid side having a substantially C-shaped cross-section via a cup gasket 9 .
- the cup gasket 9 is provided across the outer circumferential surface and the side opposite the sealing face of the rotation-side sealing ring 5 . Therefore, even when the pressure of the high-pressure fluid acts on the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket 9 , the cup gasket 9 will not detach.
- the cartridge 4 is made from, e.g., a metal, and has: an outer cylinder part 4 a fitting into the inner circumference of the housing 3 ; a disc part 4 b extending radially inwards from the low-pressure-fluid side of the outer cylinder part 4 a ; and an inner cylinder part 4 c extending to the high-pressure-fluid side along the rotating shaft from the inner diameter part of the 4 b .
- the cartridge 4 supports, via the metal bellows 7 , the fixed-side sealing ring 6 to the high-pressure-fluid side having a substantially C-shaped cross-section so as to be capable of axially moving.
- the cartridge 4 is formed as a cartridge format capable of being attached to and detached from the housing 3 .
- the plate thickness of the cartridge 4 is, e.g., in the instance of a metal cartridge, approximately 0.4 mm.
- the outer circumferential surface and the side opposite the sealing face of the fixed-side sealing ring 6 are held by the case 8 via a cup gasket 10 .
- the case 8 is made, e.g., from a metal, has a substantially inverse L-shaped cross-section having an outer cylinder part 8 a and a disc part 8 b , holds the fixed-side sealing ring 6 to the high-pressure-fluid side via the cup gasket 10 , and is fixed, at the low-pressure-fluid side of the disc part 8 b , to one end of the metal bellows 7 .
- the plate thickness of the case 8 is, in the instance of a metal case, approximately 0.4 mm.
- the cup gaskets 9 and 10 are capable of elastically deforming, and is [made from a material] selected from, e.g., rubber, a resin, or a metal.
- the metal bellows 7 has one end fixed to the disc part 8 b of the metal case 8 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and another end fixed to the disc part 4 b of the metal cartridge 4 by welding or other means.
- the metal bellows 7 is formed as a separate body with respect to the case 8 and the cartridge 4 .
- a disc-shaped flange part 7 c extending from a trough part 7 b of the bellows 7 is provided at each axial end part of the bellows 7 , the inner diameter of the flange parts 7 c , 7 c is formed so as to be substantially the same as or slightly larger than the trough parts 7 b of the bellows 7 , and the outer diameter of the flange parts 7 c is formed so as to be larger than the crest parts 7 a of the bellows 7 .
- the flange parts 7 c , 7 c at both ends of the bellows 7 are fixed to the disc part 8 b of the case 8 and the disc part 4 b of the cartridge 4 , [respectively].
- [the flange parts 7 c ] are welded or fused to the case 8 and the cartridge 4 at each position 11 located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part 7 c formed so as to be greater than the outer diameter of the crest parts 7 a of the bellows 7 . It thereby becomes possible to easily fix the bellows 7 to the case 8 and the cartridge 4 and prevent the sealed fluid from leaking.
- the disc part 8 b of the case 8 extends slightly further towards the inner diameter side than the flange part 7 c of the bellows 7 , and supports the entire flange part 7 c of the bellows 7 , whereby the action and the spring constant of the bellows 7 are made more stable, and sealing performance is maintained.
- the metal bellows 7 are made from a molded bellows formed by molding or a welded bellows formed by welding.
- the plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 is set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the metal case 8 or the metal cartridge 4 .
- the plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 is set to approximately 0.1 mm, and formed so as to be significantly less than the plate thickness of the case 8 or the cartridge 4 .
- Reducing the plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 reduces the spring constant of the bellows 7 and reduces the change in load in relation to the amount of stretching and contacting of the bellows 7 .
- reducing the change in load in relation to the amount of stretching and contracting of the bellows 7 stabilizes the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring 6 , even when the rotation-side sealing ring 5 is axially displaced, making it possible to maintain the pressure at the sealing face at an optimum value.
- the metal bellows 7 has two crests; however, the number of crests can be changed as required, e.g., to three crests if the load in relation to the amount of stretching and contacting of the bellows 7 is reduced, or to one crest if the axial length is reduced.
- the effective diameter of the metal bellows 7 (i.e., the diameter midway between the inner and outer diameters) and the positional relationship of the sealing face S in the radial direction are set so that a force F 1 pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side of the sealing face and a force F 2 pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side opposite the sealing face are balanced at a given relationship.
- a force F 1 pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side of the sealing face and a force F 2 pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side opposite the sealing face are balanced at a given relationship.
- a 1 represents the pressure-receiving area of the metal bellows 7 at which pressure from the sealed fluid is received (i.e., the pressure-receiving area at which the pressure from the sealed fluid is received by the bellows 7 for pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side of the sealing face, represented by the area between the effective diameter of the bellows 7 and the outer diameter of the sealing face S; the same definition applies hereafter) and A 2 represents the sliding area between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6 , the balance value represented by the ratio A 1 /A 2 is set to a range of 50% ⁇ balance value ⁇ 100%.
- the balance value can be changed through setting the balance diameter (effective diameter) and the sliding area, and is normally set so as to be larger if the pressure of the sealed fluid is higher and smaller if the pressure of the sealed fluid is lower.
- a metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan. Also, the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used. Furthermore, the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests. Also, the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- FIG. 2 differs from the first example shown in FIG. 1 in having the metal bellows formed so as to also function as the case.
- other configurations are the same as those in the first example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided.
- a bellows 15 comprises a stretchable bellows part in which crest parts 15 a and trough parts 15 b are alternately formed, a disc-shaped flange part 15 c extending from a trough part 15 b of the bellows 15 is provided at each axial end part of the bellows 15 , the inner diameter of the flange parts 15 c , 15 c is formed so as to be substantially the same as or slightly larger than the trough parts 15 b of the bellows 15 , and the outer diameter of the flange parts 15 c is formed so as to be larger than the crest parts 15 a of the bellows 15 .
- the flange part 15 c of the bellows 15 on the side towards the cartridge 4 is fixed to the disc part 4 b of the cartridge 4 .
- An outer cylinder part 15 d is formed continuously on the flange part 15 c on the side towards the fixed-side sealing ring 6 so as to fit with the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket 10 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6 , and the outer cylinder part 15 d and the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket 10 fit to each other elastically.
- the flange part 7 c of the bellows 15 on the side towards the cartridge 4 is welded only [at a position located] slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter, and the flange part 15 c on the side towards the fixed-side sealing ring 6 is elastically joined to the side surface of the cup gasket 10 , it is possible for the inner circumferential parts of the flange parts 15 c of the bellows 15 to separate from the disc part 4 b of the cartridge 4 and the side surface of the cup gasket 10 , and it is possible to obtain a stable sealing performance and excellent tracking performance with respect to the eccentricity of the rotating shaft 1 .
- the material constituting the metal bellows 15 and the method for forming the bellows 15 are the same as those for the metal bellows 7 in the first example.
- the plate thickness of the metal bellows 15 is set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the metal cartridge 4 .
- the metal bellows 15 is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- the third example differs from the second example shown in FIG. 2 in that a band is attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows.
- other configurations are the same as those in the second example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided.
- a band 16 is attached on the outer circumference of the outer cylinder part 15 d of the metal bellows 15 .
- the band 16 squeezes the outer cylinder part 15 d radially inwards so as to act against the radially outward elastic force of the cup gasket 10 .
- the band 16 comprises, e.g.: a hose-band-type [element] made from a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming and configured so that the diameter is decreased by tightening, by screwing, the circumferential-direction bonding part; a plate-clip-type [element] (one-touch hose clamp) similarly made from a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming and configured so as to be capable of being operated in the diameter-expanding direction at one touch against the elastic force acting in the contracting direction; or a C-ring-type [element] in which a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming is cut at one location.
- a hose-band-type [element] made from a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming and configured so that the diameter is decreased by tightening, by screwing, the circumferential-direction bonding part
- a plate-clip-type [element] one-touch hose clamp
- the band 16 squeezes the outer cylinder part 15 d radially inwards against the radially outward elastic force of the cup gasket 10 , therefore making the fitting between the outer cylinder part 15 d of the bellows 15 and the cup gasket 10 more reliable.
- the fourth example, shown in FIG. 4 differs from the first example shown in FIG. 1 in that the flange part of the metal bellows and the fixed-side sealing ring are directly fixed; however, other configurations are the same as those in the first example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided.
- the metal bellows 7 can be directly welded to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 without using the case 8 and the cup gasket 10 shown in FIG. 1 .
- the flange parts 7 c , 7 c at both ends of the bellows 7 are fixed to the disc part 4 b of the cartridge 4 and side 6 a opposite the sealing face of the fixed-side sealing ring 6 .
- the bellows is directly welded or fused to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and the cartridge 4 at each position 11 located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part 7 c formed so as to be greater than the outer diameter of the crest parts 7 a of the bellows 7 .
- Examples of materials constituting the fixed-side sealing ring 6 include stainless steel (SUS304), a sintered metal, a superhard alloy, or silicon carbide (SiC). Fixing can be performed by welding if the material constituting the fixed-side sealing ring 6 is stainless steel (SUS304) or a sintered metal, or by brazing if the material is a superhard alloy or silicon carbide (SiC).
- the case 8 and the cup gasket 10 as shown in FIG. 1 are not used; therefore, it is possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the axial length of the mechanical seal.
- the fifth example, shown in FIG. 5 differs from the first through fourth examples shown in FIG. 1 through 4 in being a “fixed-side/rotation-side-crimped” integrated type in which the cartridge and the sleeve can be prevented from axial detachment.
- Other configurations, such as the balance value being set to a range of 50% ⁇ balance value 100% ⁇ , are the same as those in the aforementioned examples, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided.
- FIG. 9 is a reference example for illustrating the mechanical seal according to the firth example of the present invention.
- the mechanical seal ⁇ is of a type in which a distal end 2 d of the inner cylinder part 2 a of the sleeve 2 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with the inner cylinder part 4 c of the cartridge 4 , thereby preventing the cartridge 4 and the sleeve 2 from axial detachment, wherein:
- the inner cylinder part 4 c of the cartridge 4 is provided with a stepped part 4 d which engages with the distal end 2 d of the inner cylinder part 2 a of the sleeve 2 .
- the stepped part 4 d is formed by a portion of the inner cylinder part 4 c on the side towards the disc part 4 b being shaped so as to expand in diameter.
- the distal end 2 d having a diameter expanded by crimping, of the inner cylinder part 2 a is fitted into the expanded-diameter portion of the inner cylinder part 4 c , and the distal end 2 d and the stepped part 4 d engage with each other.
- Increasing the outer diameter of the bellows 7 would increase the pressure-receiving area A 1 and also increases the balance value. However, increasing the outer diameter of the bellows 7 would present problems of impeding the task of welding the bellows 7 to the cartridge 4 or other metal components and increasing the outer diameter of the mechanical seal, and is therefore not practical.
- FIG. 5 is a vertical cross-section view showing the principal part of the mechanical seal.
- the dashed lines in FIG. 5 indicate the cross-section of a rotation locking part provided to a part of the circumferential direction of the fixed-side sealing ring 6
- solid lines indicate the cross-section of a portion other than the rotation locking part.
- the solid lines indicate a rotation locking part and the dashed lines indicate a portion other than the rotation locking part, in contrast to FIG. 5 .
- a portion of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 on the side towards a disc part 40 b is expanded in diameter, an expanded diameter part 40 e is formed, and a stepped part 40 d is provided.
- the stepped part 40 d which engages with the distal end 20 d of the inner cylinder part 20 a of the sleeve 20 , is provided.
- the distal end 20 d having a diameter expanded by crimping, of the inner cylinder part 20 a of the sleeve 20 engages with the stepped part 40 d of the inner cylinder part 40 c , whereby the cartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 are prevented from axial detachment, and the fixed side and the rotation side are integrated.
- the metal bellows 30 has an outer diameter identical to that in the above reference example, and has an inner diameter, at a portion located on the side of the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the stepped part 40 d of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 , formed so as to be smaller than the inner diameter of the portion located on the opposite side to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the stepped part 40 d of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 .
- the metal bellows 30 is shaped so that the inner diameter side is stepped in cross-section.
- the portion of the bellows 30 having a larger inner diameter may be hereafter referred to as a large inner diameter part 30 - 1 and the portion having a smaller inner diameter may be hereafter referred to as a small inner diameter part 30 - 2 .
- the large inner diameter part 30 - 1 of the bellows 30 has the same effective diameter as that in the above reference example; therefore, the pressure-receiving area A 1 - 1 represented by the area between the effective diameter and the outer diameter of the sealing face S is smaller, and the balance value is also smaller.
- the small inner diameter part 30 - 2 of the bellows 30 has a smaller effective diameter than that of the large inner diameter part 30 - 1 ; therefore, the pressure-receiving area A 1 - 2 represented by the area between the effective diameter and the outer diameter of the sealing face S is larger, and the balance value is also larger. Therefore, the overall balance value of the bellows 30 is larger than that of the bellows shown in FIG.
- ⁇ the mechanical seal ⁇ is of a type in which the distal end 20 d of the inner cylinder part 20 of the sleeve 20 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 , thereby preventing the cartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 from axial detachment, wherein:
- the bellows 30 is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side relative to the stepped part 40 d of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the stepped part 40 d . Therefore, compared to an instance in which the outer diameter of the bellows is the same and the inner diameter is increased in a uniform manner, the balance value is greater, a decrease in the balance value can be suppressed, and the amount of leakage at the sealing face S can be reduced. It is also possible to suppress an increase in the spring constant of the bellows 30 .
- [the present example] has a beneficial effect of it being possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value, reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face, and suppress an increase in the spring constant of the bellows 30 , without increasing the outer diameter of the bellows.
- the sixth example shown in FIG. 6 is similar to the fifth example shown in FIG. 5 in being a “fixed-side/rotation-side-crimped” integrated type in which the cartridge and the sleeve can be prevented from axial detachment, but differs from the fifth example shown in FIG. 5 in having the balance value set so as to exceed 100%. In the following description, descriptions that overlap with those for the fifth example will not be provided.
- a 1 represents the pressure-receiving area of the metal bellows 30 at which pressure from the sealed fluid is received (i.e., the average value between the pressure-receiving area A 1 - 1 and the pressure-receiving area A 1 - 1 ) and A 2 represents the sliding area between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6
- the balance value represented by the ratio A 1 /A 2 is set so as to exceed 100%.
- the small inner diameter part 30 - 2 of the bellows 30 has a smaller effective diameter than that of the large inner diameter part 30 - 1 , therefore making it possible to suppress an increase in size of the sealing face between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6 .
- ⁇ the mechanical seal ⁇ is of a type in which the distal end 20 d of the inner cylinder part 20 of the sleeve 20 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 , thereby preventing the cartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 from axial detachment, wherein: a portion of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 located on the opposite axial-direction side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part 40 d ; and the bellows 30 is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side relative to the stepped part 40 d of the inner cylinder part 40 c of the cartridge 40 is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the stepped part 40 d .
- the present example has a prominent effect of enabling the balance value to be set so as to exceed 100% and avoid an increase in size of the mechanical seal without significantly increasing the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6 .
- the cartridge 4 and the case 8 are formed from a metal.
- the material is not limited to a metal, and any material having a high corrosion resistance can be used, e.g., a plastic.
- the fixing with the metal bellows may be performed, e.g., by adhesion using an adhesive or bonding using laser.
- the present invention can be applied to any balance value.
- the balance value is set as appropriate according to factors such as the pressure and the type of the sealed fluid.
- the effect of the present invention was described using examples of instances in which the outer diameter of the bellows is the same in order to facilitate comprehension, this is not provided by way of limitation. Even when there is a fluctuation in the outer diameter of the bellows 30 , the effect of the present invention can be obtained.
- the technical significance is in reducing the inner diameter of a portion of the bellows 30 and thereby preventing the balance value from decreasing and suppressing an increase in the size of the rotating ring and the fixed ring in a type [of mechanical seal] in which the fixed side and the rotation side are integrated.
- the balance value when, as in the fifth example, [the balance value] is within the range of 50% ⁇ balance value ⁇ 100%, the balance value is prevented form decreasing, and when, as in the sixth example, the balance value exceeds 100%, an increase in the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring and the fixed-side sealing ring is suppressed and an increase in size of the mechanical seal is avoided.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Mechanical Sealing (AREA)
- Diaphragms And Bellows (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
- Sealing Devices (AREA)
Abstract
To provide a mechanical seal in which degradation or tearing of a bellows does not occur, the spring constant of the bellows is reduced, and the fluctuation in the load due to stretching and contracting of the bellows is reduced.
An inside-type mechanical seal includes a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing. A rotation-side sealing ring is provided to the sleeve. A fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring is provided to the cartridge. The bellows is made from a metal; and the metal bellows has one end fixed to a case for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge. The plate thickness of the metal bellows is set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case or the cartridge.
Description
- The present invention relates to a mechanical seal used, e.g., as a shaft-sealing device in a pump or the like.
- One conventionally known type of a mechanical seal is, as shown in
FIG. 7 , an inside-format mechanical seal in which a sealed fluid that may leak from the outer circumference of a sealing face to the inner circumference direction is sealed, wherein: an annular rotation-side sealing ring 53 provided, via asleeve 51 and acup gasket 52, on the side of a rotatingshaft 50 for driving a pump impeller (not shown) on the high-pressure fluid-side, so as to be capable of rotating integrally with the rotatingshaft 50; and an annular fixed-side sealing ring 55 provided, via abellows 57 in acartridge 56, to ahousing 54 Document of the pump in a non-rotating state so as to be capable of axial movement, are caused by thebellows 57 and acoiled wave spring 58 axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring 55 to slide against each other in intimate contact at respective sealing faces S which have been mirror-surface-finished by lapping or the like (hereafter referred to as “prior art 1”; see, e.g., Patent Document 1). Thebellows 57 in the mechanical seal in this prior art is made from rubber, and has one end attached to thefixed ring 55 via acase 59 and the other end attached to a cartridgeinner cylinder part 56 via adriving band 60. -
Patent Document 2 discloses an invention of a mechanical seal in which, as shown inFIG. 8 , a fixed-side sealing ring 62 is attached to ahousing 61, a rotation-side sealing ring 63 is provided to a shaft which is rotatably supported by thehousing 61, and the fixed-side sealing ring 62 and the rotation-side sealing ring 63 are in elastic contact with each other so as to be capable of sliding, wherein afixing claw 64 a is formed on the right end of ametal bellows 64 so that themetal bellows 64 supports the fixed-side sealing ring 62 so as to be capable of axial movement, thefixing claw 64 a is bent and the fixed-side sealing ring 62 is supported at the right-end interior of themetal bellows 64, and the left end of themetal bellows 64 is directly fixed to the housing 61 (hereafter referred to as “prior art 2”; see Patent Citation 2). - However, in
prior art 1, thebellows 57 being made from rubber presents problems such as degradation or tearing of the bent part. Problems are also presented in that an urging member such as thecoiled wave spring 58 and an attaching member such as thedriving band 60 are required, increasing the number of components. - In
prior art 2, since the structure is one in which thefixed ring 62 is directly supported by themetal bellows 64 and themetal bellows 64 is directly fixed to thehousing 61 such that themetal bellows 64 functions also as a cartridge, a problem is presented in that themetal bellows 64 must have the same thickness as that of a cartridge or a case, resulting in an increase in the spring constant of themetal bellows 64. -
- Patent Document 1: Japanese Laid-Open Patent Application No. 2000-74226 (
page 3, FIG. 2) - Patent Document 2: Japanese Patent No. 2956862 (
page 5, FIG. 5) - The present invention was devised in order to resolve the problems presented by the prior art, it being an object thereof to provide a mechanical seal in which degradation or tearing of a bellows does not occur, the spring constant of the bellows is reduced, and the fluctuation in the load due to stretching and contracting of the bellows is reduced. In addition, assembly of [a mechanical seal] through integrating the rotation-side and the fixed-side normally necessitates increasing the inside diameter of the bellows in order to secure sufficient space, which changes the pressure-receiving area of the bellows and results in a fluctuation in the balance value; an object of the present invention is to provide a mechanical seal in which the fluctuation in the balance value in such an instance is minimized.
- In order to achieve the following objects, first, a mechanical seal according to the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to said sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge; the mechanical seal being characterized in that: the bellows is made from a metal; and the metal bellows has one end fixed to a case for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case or the cartridge. According to this characteristic, the metal bellows exclusively plays a role of axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, and is formed as a separate body with respect to the case, the cartridge, or the like. Therefore, the plate thickness of the metal bellows can be reduced, the spring constant of the metal bellows can be reduced, and a change in load with respect to the amount of stretching and contracting of the metal bellows can be reduced. Therefore, even when the rotation-side sealing ring is axially displaced, the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring can be kept stable, and the pressure at the sealing face can be maintained at an optimum value. In addition, the tolerance of the length of attachment of the metal bellows can be relaxed. In addition, using a metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan. Also, the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used. Furthermore, the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests. Also, the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- Second, a mechanical seal according to the first aspect of the present invention is characterized in that: the metal bellows comprises a bellows part in which crest parts and trough parts are alternately formed, and a disc-shaped flange part extending radially outwards from the trough part at each end of the bellows part; and the bellows part is formed by molding or welding so that the outer diameter of the flange parts is greater than the diameter of the crest parts, and the inner diameter of the flange parts is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of the trough parts. According to this characteristic, it is possible to easily fix the metal bellows to the case and the cartridge and to prevent the sealed fluid from leaking.
- Third, a mechanical seal according to the first or second aspect of the present invention is characterized in that: fixing of the metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge is performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part of the metal bellows. According to this characteristic, it is possible for the inner circumferential part of the flange part of the metal bellows to separate from the case and the cartridge, and it is possible to obtain a stable sealing performance and excellent tracking performance with respect to the eccentricity of the rotating shaft. In addition, the metal bellows can be fixed in a reliable manner without using a special attachment member.
- Fourth, a mechanical seal according to any of the first through third aspects of the present invention is characterized in that the rotation-side sealing ring is fixed to the sleeve via a cup gasket, and the cup gasket is provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of the rotation-side sealing ring. According to this characteristic, it is possible to prevent the cup gasket from detaching, even when the pressure of a high-pressure fluid acts on the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket.
- Fifth, a mechanical seal of the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to the sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge; the mechanical seal being characterized in that:
- the bellows is made from a metal; and
- the metal bellows has one end fixed to a gasket for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the cartridge.
- According to this characteristic, the metal bellows is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- Sixth, a mechanical seal according to the fifth aspect of the present invention is characterized in that a band is attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows fitting into the gasket holding the fixed-side sealing ring. This characteristic makes it possible for the fitting between the metal bellows and the cup gasket to be made more reliable.
- Seventh, a mechanical seal of the present invention is an inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to the sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to the cartridge; the mechanical seal being characterized in that: the bellows is made from a metal; and the metal bellows has one end directly fixed to the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the cartridge. According to this characteristic, it is possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the axial length of the mechanical seal. Alternatively, instead of reducing the axial length of the mechanical seal, it is also possible to increase the number of crests of the metal bellows.
- Eighth, a mechanical seal according to any of first through seventh aspects of the present invention is characterized in being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of the sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of the cartridge, thereby preventing the cartridge and the sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
- a portion of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to the fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
- the bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge.
- According to this characteristic, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value, reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face, and suppress an increase in the spring constant of the bellows, without increasing the outer diameter of the bellows. In addition, it is possible to suppress an increase in the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring and the fixed-side sealing ring and avoid an increase in size of the mechanical seal, even when the balance value is set so as to exceed 100%.
- The present invention has the following beneficial effects.
- (1) Having the bellows be made from a metal, the metal bellows having one end fixed to a case for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the case or the cartridge, result in the metal bellows exclusively playing a role of axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, and being formed separately from the case, the cartridge, or the like. Therefore, the plate thickness of the metal bellows can be reduced, the spring constant of the metal bellows can be reduced, and a change in load with respect to the amount of stretching and contracting of the metal bellows can be reduced. Therefore, even when the rotation-side sealing ring is axially displaced, the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring can be kept stable, and the pressure at the sealing face can be maintained at an optimum value. In addition, the tolerance of the length of attachment of the metal bellows can be relaxed. In addition, using a metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan. Also, the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used. Furthermore, the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests. Also, the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- (2) The metal bellows comprising a bellows part in which crest parts and trough parts are alternately formed, and a disc-shaped flange part extending radially outwards from the trough part at each end of the bellows part; and the bellows part being formed by molding or welding so that the outer diameter of the flange parts is greater than the diameter of the crest parts, and the inner diameter of the flange parts is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of the trough parts, result in it being possible to easily fix the metal bellows to the case and the cartridge and to prevent the sealed fluid from leaking.
- (3) Fixing of the metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge being performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of the flange part of the metal bellows results in it being possible for the inner circumferential part of the flange part of the metal bellows to separate from the case and the cartridge, and it being possible to obtain a stable sealing performance and excellent tracking performance with respect to the eccentricity of the rotating shaft. In addition, the metal bellows can be fixed in a reliable manner without using a special attachment member.
- (4) The rotation-side sealing ring being fixed to the sleeve via a cup gasket, and the cup gasket being provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of the rotation-side sealing ring, result in it being possible to prevent the cup gasket from detaching, even when the pressure of a high-pressure fluid acts on the outer circumferential surface of the cup gasket.
- (5) The metal bellows having one end fixed to a gasket for holding the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge, whereby the metal bellows is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- (6) A band being attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows fitting into the gasket holding the fixed-side sealing ring makes it possible for the fitting between the metal bellows and the cup gasket to be made more reliable.
- (7) The metal bellows having one end directly fixed to the fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to the cartridge results in it being possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the axial length of the mechanical seal. Alternatively, instead of reducing the axial length of the mechanical seal, it is also possible to increase the number of crests of the metal bellows.
- (8) {The mechanical seal} being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of the sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of the cartridge, thereby preventing the cartridge and the sleeve from axial detachment, wherein: a portion of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to the fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and the bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of the cartridge, results in it being possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value, reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face, and suppress an increase in the spring constant of the bellows, without increasing the outer diameter of the bellows. In addition, it is possible to suppress an increase in the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring and the fixed-side sealing ring and avoid an increase in size of the mechanical seal, even if the balance value is set so as to exceed 100%.
-
FIG. 1 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a first example of the present invention; -
FIG. 2 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a second example of the present invention; -
FIG. 3 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a third example of the present invention; -
FIG. 4 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a fourth example of the present invention; -
FIG. 5 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a fifth example of the present invention; -
FIG. 6 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according to a sixth example of the present invention; -
FIG. 7 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according toprior art 1; -
FIG. 8 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a mechanical seal according toprior art 2; and -
FIG. 9 is a vertical cross-section view showing a principal part of a reference example for illustrating the mechanical seal according to the fifth and sixth examples of the present invention. - Embodiments for carrying out this invention will now be described by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings. The examples are not intended to limit the dimensions, material, shape, relative arrangement, and other attributes of constituent components to those set forth in the examples unless expressly specified otherwise.
- A description will now be given for a mechanical seal according to a first example of the present invention. The present invention is applied to an inside-type mechanical seal of a format in which a fluid trying to leak from the outer circumference of the sealing face to the inner circumference direction is sealed. In
FIG. 1 , the left side corresponds to the high-pressure fluid side (sealed fluid side) and the right side corresponds to the low-pressure fluid side (atmosphere side). - The mechanical seal according to the present invention is a mechanical seal comprising a
sleeve 2 fixed to arotating shaft 1, and acartridge 4 fixed to ahousing 3; a rotation-side sealing ring 5 being provided to thesleeve 2; and a fixed-side sealing ring 6, which slides against the rotation-side sealing ring 5, and abellows 7 for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring 6 being provided to thecartridge 4; the mechanical seal being mainly characterized in that: thebellows 7 is made from a metal; - and the metal bellows 7 has one end fixed to a
case 8 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and another end fixed to thecartridge 4, and has a plate thickness set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of thecase 8 or thecartridge 4. - For example, a pump impeller (not shown) is fixed to the high-pressure-fluid side of the
rotating shaft 1, and the shaft-sealing part between the inner diameter side of thehousing 3 and the outer diameter side of therotating shaft 1 of the pump has the mechanical seal of the present invention installed thereto and sealed. - The
sleeve 2 has: aninner cylinder part 2 a fitted to therotating shaft 1; adisc part 2 b extending in the outer diameter direction from the high-pressure-fluid side of theinner cylinder part 2 a; and anouter cylinder part 2 c extending from the outer diameter side of thedisc part 2 b to the low-pressure-fluid side. Thesleeve 2 supports the rotation-side sealing ring 5 to the low-pressure-fluid side having a substantially C-shaped cross-section via acup gasket 9. Thecup gasket 9 is provided across the outer circumferential surface and the side opposite the sealing face of the rotation-side sealing ring 5. Therefore, even when the pressure of the high-pressure fluid acts on the outer circumferential surface of thecup gasket 9, thecup gasket 9 will not detach. - The
cartridge 4 is made from, e.g., a metal, and has: anouter cylinder part 4 a fitting into the inner circumference of thehousing 3; adisc part 4 b extending radially inwards from the low-pressure-fluid side of theouter cylinder part 4 a; and aninner cylinder part 4 c extending to the high-pressure-fluid side along the rotating shaft from the inner diameter part of the 4 b. Thecartridge 4 supports, via the metal bellows 7, the fixed-side sealing ring 6 to the high-pressure-fluid side having a substantially C-shaped cross-section so as to be capable of axially moving. Thecartridge 4 is formed as a cartridge format capable of being attached to and detached from thehousing 3. The plate thickness of thecartridge 4 is, e.g., in the instance of a metal cartridge, approximately 0.4 mm. - The outer circumferential surface and the side opposite the sealing face of the fixed-
side sealing ring 6 are held by thecase 8 via acup gasket 10. Thecase 8 is made, e.g., from a metal, has a substantially inverse L-shaped cross-section having anouter cylinder part 8 a and adisc part 8 b, holds the fixed-side sealing ring 6 to the high-pressure-fluid side via thecup gasket 10, and is fixed, at the low-pressure-fluid side of thedisc part 8 b, to one end of the metal bellows 7. The plate thickness of thecase 8 is, in the instance of a metal case, approximately 0.4 mm. Thecup gaskets - The metal bellows 7 has one end fixed to the
disc part 8 b of themetal case 8 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and another end fixed to thedisc part 4 b of themetal cartridge 4 by welding or other means. In other words, the metal bellows 7 is formed as a separate body with respect to thecase 8 and thecartridge 4. - In a
bellows 7 comprising a stretchable bellows part in whichcrest parts 7 a andtrough parts 7 b are alternately formed, a disc-shapedflange part 7 c extending from atrough part 7 b of thebellows 7 is provided at each axial end part of thebellows 7, the inner diameter of theflange parts trough parts 7 b of thebellows 7, and the outer diameter of theflange parts 7 c is formed so as to be larger than thecrest parts 7 a of thebellows 7. Theflange parts bellows 7 are fixed to thedisc part 8 b of thecase 8 and thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4, [respectively]. When the fixing is performed, [theflange parts 7 c] are welded or fused to thecase 8 and thecartridge 4 at eachposition 11 located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of theflange part 7 c formed so as to be greater than the outer diameter of thecrest parts 7 a of thebellows 7. It thereby becomes possible to easily fix thebellows 7 to thecase 8 and thecartridge 4 and prevent the sealed fluid from leaking. Thedisc part 8 b of thecase 8 extends slightly further towards the inner diameter side than theflange part 7 c of thebellows 7, and supports theentire flange part 7 c of thebellows 7, whereby the action and the spring constant of thebellows 7 are made more stable, and sealing performance is maintained. Since welding is only performed [at a position located] slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of theflange part 7 c of thebellows 7, it is possible for the inner circumferential parts of theflange parts 7 c of thebellows 7 to separate from thedisc part 8 b of thecase 8 and thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4, and it is possible to obtain a stable sealing performance and excellent tracking performance with respect to the eccentricity of therotating shaft 1. - Typical examples of the material constituting the metal bellows 7 include SUS304, SUS316L, AM350, and Inconel 625. The metal bellows 7 is made from a molded bellows formed by molding or a welded bellows formed by welding. The plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 is set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of the
metal case 8 or themetal cartridge 4. For example, the plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 is set to approximately 0.1 mm, and formed so as to be significantly less than the plate thickness of thecase 8 or thecartridge 4. - Reducing the plate thickness of the metal bellows 7 reduces the spring constant of the
bellows 7 and reduces the change in load in relation to the amount of stretching and contacting of thebellows 7. Thus, reducing the change in load in relation to the amount of stretching and contracting of thebellows 7 stabilizes the axial urging force on the fixed-side sealing ring 6, even when the rotation-side sealing ring 5 is axially displaced, making it possible to maintain the pressure at the sealing face at an optimum value. There is also a benefit in that the tolerance of the length of attachment of thebellows 7 can be relaxed. InFIG. 1 , the metal bellows 7 has two crests; however, the number of crests can be changed as required, e.g., to three crests if the load in relation to the amount of stretching and contacting of thebellows 7 is reduced, or to one crest if the axial length is reduced. - The effective diameter of the metal bellows 7 (i.e., the diameter midway between the inner and outer diameters) and the positional relationship of the sealing face S in the radial direction are set so that a force F1 pressing the fixed-
side sealing ring 6 towards the side of the sealing face and a force F2 pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side opposite the sealing face are balanced at a given relationship. In the instance of the example shown inFIG. 1 , if A1 represents the pressure-receiving area of the metal bellows 7 at which pressure from the sealed fluid is received (i.e., the pressure-receiving area at which the pressure from the sealed fluid is received by thebellows 7 for pressing the fixed-side sealing ring 6 towards the side of the sealing face, represented by the area between the effective diameter of thebellows 7 and the outer diameter of the sealing face S; the same definition applies hereafter) and A2 represents the sliding area between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6, the balance value represented by the ratio A1/A2 is set to a range of 50%≦balance value≦100%. The balance value can be changed through setting the balance diameter (effective diameter) and the sliding area, and is normally set so as to be larger if the pressure of the sealed fluid is higher and smaller if the pressure of the sealed fluid is lower. - Using a metal bellows instead of a conventional rubber bellows prevents degradation or tearing of the bellows and makes it possible to increase the lifespan. Also, the number of components for attachment can be reduced compared to instances in which a rubber bellows is used. Furthermore, the spring constant of the bellows can be freely set by the material, the plate thickness, or the number of crests. Also, the balance value can be set to an optimum value.
- Next, a description will be given for a mechanical seal according to a second example of the present invention with reference to
FIG. 2 . The second example, shown inFIG. 2 , differs from the first example shown inFIG. 1 in having the metal bellows formed so as to also function as the case. However, other configurations are the same as those in the first example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided. - In
FIG. 2 , a bellows 15 comprises a stretchable bellows part in whichcrest parts 15 a andtrough parts 15 b are alternately formed, a disc-shapedflange part 15 c extending from atrough part 15 b of thebellows 15 is provided at each axial end part of thebellows 15, the inner diameter of theflange parts trough parts 15 b of thebellows 15, and the outer diameter of theflange parts 15 c is formed so as to be larger than thecrest parts 15 a of thebellows 15. Theflange part 15 c of thebellows 15 on the side towards thecartridge 4 is fixed to thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4. Anouter cylinder part 15 d is formed continuously on theflange part 15 c on the side towards the fixed-side sealing ring 6 so as to fit with the outer circumferential surface of thecup gasket 10 for holding the fixed-side sealing ring 6, and theouter cylinder part 15 d and the outer circumferential surface of thecup gasket 10 fit to each other elastically. When theflange part 15 c on the side towards thecartridge 4 is fixed to thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4, [theflange part 15 c] is welded or fused to thecartridge 4 at aposition 11 located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of theflange part 15 c formed so as to be greater than the outer diameter of thecrest parts 15 a of thebellows 15. It thereby becomes possible to easily fix thebellows 15 to thecartridge 4 and thecup gasket 10 and prevent the sealed fluid from leaking. Since theflange part 7 c of thebellows 15 on the side towards thecartridge 4 is welded only [at a position located] slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter, and theflange part 15 c on the side towards the fixed-side sealing ring 6 is elastically joined to the side surface of thecup gasket 10, it is possible for the inner circumferential parts of theflange parts 15 c of thebellows 15 to separate from thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4 and the side surface of thecup gasket 10, and it is possible to obtain a stable sealing performance and excellent tracking performance with respect to the eccentricity of therotating shaft 1. - The material constituting the metal bellows 15 and the method for forming the
bellows 15 are the same as those for the metal bellows 7 in the first example. The plate thickness of the metal bellows 15 is set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of themetal cartridge 4. - In the present second example, the metal bellows 15 is formed so as to also function as a case, making it possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the number of welded locations.
- Next, a description will be given for a mechanical seal according to a third example of the present invention with reference to
FIG. 3 . The third example, shown inFIG. 3 , differs from the second example shown inFIG. 2 in that a band is attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of the metal bellows. However, other configurations are the same as those in the second example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided. - In
FIG. 3 , aband 16 is attached on the outer circumference of theouter cylinder part 15 d of the metal bellows 15. Theband 16 squeezes theouter cylinder part 15 d radially inwards so as to act against the radially outward elastic force of thecup gasket 10. Theband 16 comprises, e.g.: a hose-band-type [element] made from a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming and configured so that the diameter is decreased by tightening, by screwing, the circumferential-direction bonding part; a plate-clip-type [element] (one-touch hose clamp) similarly made from a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming and configured so as to be capable of being operated in the diameter-expanding direction at one touch against the elastic force acting in the contracting direction; or a C-ring-type [element] in which a ring-shaped flat plate capable of elastically deforming is cut at one location. - In the present third example, the
band 16 squeezes theouter cylinder part 15 d radially inwards against the radially outward elastic force of thecup gasket 10, therefore making the fitting between theouter cylinder part 15 d of thebellows 15 and thecup gasket 10 more reliable. - Next, a mechanical seal according to a fourth example of the present invention will be described with reference to
FIG. 4 . The fourth example, shown inFIG. 4 , differs from the first example shown inFIG. 1 in that the flange part of the metal bellows and the fixed-side sealing ring are directly fixed; however, other configurations are the same as those in the first example, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided. - If the fixed-
side sealing ring 6 is made from a material that can be metal-welded, the metal bellows 7 can be directly welded to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 without using thecase 8 and thecup gasket 10 shown inFIG. 1 . InFIG. 4 , theflange parts bellows 7 are fixed to thedisc part 4 b of thecartridge 4 and side 6 a opposite the sealing face of the fixed-side sealing ring 6. When the fixing is performed, [the bellows] is directly welded or fused to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 and thecartridge 4 at eachposition 11 located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of theflange part 7 c formed so as to be greater than the outer diameter of thecrest parts 7 a of thebellows 7. - Examples of materials constituting the fixed-
side sealing ring 6 include stainless steel (SUS304), a sintered metal, a superhard alloy, or silicon carbide (SiC). Fixing can be performed by welding if the material constituting the fixed-side sealing ring 6 is stainless steel (SUS304) or a sintered metal, or by brazing if the material is a superhard alloy or silicon carbide (SiC). - In the present fourth example, the
case 8 and thecup gasket 10 as shown inFIG. 1 are not used; therefore, it is possible to reduce the number of components and reduce the axial length of the mechanical seal. Alternatively, instead of reducing the axial length of the mechanical seal, it is also possible to increase the number of crests of the metal bellows 7. - Next, a description will be given for a mechanical seal according to a fifth example of the present invention with reference to
FIGS. 5 and 9 . The fifth example, shown inFIG. 5 , differs from the first through fourth examples shown inFIG. 1 through 4 in being a “fixed-side/rotation-side-crimped” integrated type in which the cartridge and the sleeve can be prevented from axial detachment. Other configurations, such as the balance value being set to a range of 50%≦balance value 100%≦, are the same as those in the aforementioned examples, and descriptions that overlap will not be provided. -
FIG. 9 is a reference example for illustrating the mechanical seal according to the firth example of the present invention. {The mechanical seal} is of a type in which adistal end 2 d of theinner cylinder part 2 a of thesleeve 2 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with theinner cylinder part 4 c of thecartridge 4, thereby preventing thecartridge 4 and thesleeve 2 from axial detachment, wherein: - the
inner cylinder part 4 c of thecartridge 4 is provided with a steppedpart 4 d which engages with thedistal end 2 d of theinner cylinder part 2 a of thesleeve 2. The steppedpart 4 d is formed by a portion of theinner cylinder part 4 c on the side towards thedisc part 4 b being shaped so as to expand in diameter. Thedistal end 2 d, having a diameter expanded by crimping, of theinner cylinder part 2 a is fitted into the expanded-diameter portion of theinner cylinder part 4 c, and thedistal end 2 d and the steppedpart 4 d engage with each other. - As shown in
FIG. 9 , in order to provide a steppedpart 4 d to theinner cylinder part 4 c of thecartridge 4, it is necessary to have the inner diameter of thebellows 7 be larger than the inner diameter of the bellows in first through fourth examples and provide a given gap with respect to theinner cylinder part 4 c. If the inner diameter of thebellows 7 is increased, assuming the outer diameter to be uniform, the effective diameter will increase, and the pressure-receiving area A1 on which thebellows 7 receives pressure from the sealed fluid will decrease; therefore, a problem is presented in that the balance value=A1/A2 (where A2 is the area of the sealing face) will decrease and the amount of leakage will increase. Increasing the outer diameter of thebellows 7 would increase the pressure-receiving area A1 and also increases the balance value. However, increasing the outer diameter of thebellows 7 would present problems of impeding the task of welding thebellows 7 to thecartridge 4 or other metal components and increasing the outer diameter of the mechanical seal, and is therefore not practical. - The mechanical seal according to the fifth embodiment of the present invention resolves the problems presented by the reference example, and
FIG. 5 is a vertical cross-section view showing the principal part of the mechanical seal. The dashed lines inFIG. 5 indicate the cross-section of a rotation locking part provided to a part of the circumferential direction of the fixed-side sealing ring 6, and solid lines indicate the cross-section of a portion other than the rotation locking part. In the first through fourth examples inFIG. 1 through 4 , the solid lines indicate a rotation locking part and the dashed lines indicate a portion other than the rotation locking part, in contrast toFIG. 5 . - In
FIG. 5 , in order to prevent acartridge 40 and a sleeve 20 from axial detachment by expanding the diameter of adistal end 20 d of aninner cylinder part 20 a of the sleeve 20 and causing thedistal end 20 d to engage with aninner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40, a portion of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40 on the side towards adisc part 40 b is expanded in diameter, an expandeddiameter part 40 e is formed, and a steppedpart 40 d is provided. The steppedpart 40 d, which engages with thedistal end 20 d of theinner cylinder part 20 a of the sleeve 20, is provided. Thedistal end 20 d, having a diameter expanded by crimping, of theinner cylinder part 20 a of the sleeve 20 engages with the steppedpart 40 d of theinner cylinder part 40 c, whereby thecartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 are prevented from axial detachment, and the fixed side and the rotation side are integrated. - The metal bellows 30 has an outer diameter identical to that in the above reference example, and has an inner diameter, at a portion located on the side of the fixed-
side sealing ring 6 relative to the steppedpart 40 d of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40, formed so as to be smaller than the inner diameter of the portion located on the opposite side to the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the steppedpart 40 d of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40. In other words, the metal bellows 30 is shaped so that the inner diameter side is stepped in cross-section. - In order to facilitate description, the portion of the
bellows 30 having a larger inner diameter may be hereafter referred to as a large inner diameter part 30-1 and the portion having a smaller inner diameter may be hereafter referred to as a small inner diameter part 30-2. - The large inner diameter part 30-1 of the
bellows 30 has the same effective diameter as that in the above reference example; therefore, the pressure-receiving area A1-1 represented by the area between the effective diameter and the outer diameter of the sealing face S is smaller, and the balance value is also smaller. In contrast, the small inner diameter part 30-2 of thebellows 30 has a smaller effective diameter than that of the large inner diameter part 30-1; therefore, the pressure-receiving area A1-2 represented by the area between the effective diameter and the outer diameter of the sealing face S is larger, and the balance value is also larger. Therefore, the overall balance value of thebellows 30 is larger than that of the bellows shown inFIG. 9 in which the outer diameter is the same and a step is not present (reference example), and it is possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value and reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face S. In addition, it is also possible to suppress an increase in the spring constant of thebellows 30. - In the present example, {the mechanical seal} is of a type in which the
distal end 20 d of the inner cylinder part 20 of the sleeve 20 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40, thereby preventing thecartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 from axial detachment, wherein: - a portion of the
inner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40 located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to the fixed-sidesealing ring side 6 is expanded in diameter and provided with the steppedpart 40 d; and - the
bellows 30 is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side relative to the steppedpart 40 d of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40 is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the steppedpart 40 d. Therefore, compared to an instance in which the outer diameter of the bellows is the same and the inner diameter is increased in a uniform manner, the balance value is greater, a decrease in the balance value can be suppressed, and the amount of leakage at the sealing face S can be reduced. It is also possible to suppress an increase in the spring constant of thebellows 30. In other words, [the present example] has a beneficial effect of it being possible to suppress a decrease in the balance value, reduce the amount of leakage at the sealing face, and suppress an increase in the spring constant of thebellows 30, without increasing the outer diameter of the bellows. - Next, a description will be given for a mechanical seal according to a sixth example of the present invention with reference to
FIG. 6 . The sixth example shown inFIG. 6 is similar to the fifth example shown inFIG. 5 in being a “fixed-side/rotation-side-crimped” integrated type in which the cartridge and the sleeve can be prevented from axial detachment, but differs from the fifth example shown inFIG. 5 in having the balance value set so as to exceed 100%. In the following description, descriptions that overlap with those for the fifth example will not be provided. - In the sixth example shown in
FIG. 6 , if A1 represents the pressure-receiving area of the metal bellows 30 at which pressure from the sealed fluid is received (i.e., the average value between the pressure-receiving area A1-1 and the pressure-receiving area A1-1) and A2 represents the sliding area between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6, the balance value represented by the ratio A1/A2 is set so as to exceed 100%. - In order to set the balance value so as to exceed 100%, it is necessary to have the inner diameter of the sealing face between the rotation-
side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6 be larger than the balance diameter (effective diameter) of thebellows 30. Therefore, a problem is presented in that if the balance diameter of thebellows 30 is uniform, the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6 will increase, and the size of the mechanical seal will increase. According to the present example 6, the small inner diameter part 30-2 of thebellows 30 has a smaller effective diameter than that of the large inner diameter part 30-1, therefore making it possible to suppress an increase in size of the sealing face between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6. - In the present example, {the mechanical seal} is of a type in which the
distal end 20 d of the inner cylinder part 20 of the sleeve 20 is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40, thereby preventing thecartridge 40 and the sleeve 20 from axial detachment, wherein: a portion of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40 located on the opposite axial-direction side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side is expanded in diameter and provided with a steppedpart 40 d; and thebellows 30 is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring 6 side relative to the steppedpart 40 d of theinner cylinder part 40 c of thecartridge 40 is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring 6 relative to the steppedpart 40 d. Therefore, compared to an instance in which the outer diameter of the bellows is the same and the inner diameter is increased in a uniform manner, even if the balance value is set so as to exceed 100%, it is possible to suppress an increase in the inner diameter of the sealing face between the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6. In other words, [the present example] has a prominent effect of enabling the balance value to be set so as to exceed 100% and avoid an increase in size of the mechanical seal without significantly increasing the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring 5 and the fixed-side sealing ring 6. - While embodiments of the present invention have been described above on the basis of examples, the specific configurations are not limited to those according to the examples, and the present invention includes instances in which a variety of modifications and additions have been made without departing from the scope of the present invention.
- For example, in the aforementioned examples, descriptions have been given with regards to instances in which the mechanical seal of the present invention is applied to a pump. However, this is not provided by way of limitation; [the mechanical seal of the present invention] can be applied, e.g., to a compressor, a submersible motor, or other industrial machinery.
- In the aforementioned examples, descriptions have been given with regards to instances in which the
cartridge 4 and thecase 8 are formed from a metal. However, [the material] is not limited to a metal, and any material having a high corrosion resistance can be used, e.g., a plastic. In such an instance, the fixing with the metal bellows may be performed, e.g., by adhesion using an adhesive or bonding using laser. - As can be seen by the fact that, e.g., descriptions were given for instances in which the balance value is set to a range of 50%≦balance value≦100% in the first through fifth examples and a description was given for an instance in which the balance value exceeds 100% in the sixth example, the present invention can be applied to any balance value. The balance value is set as appropriate according to factors such as the pressure and the type of the sealed fluid.
- For example, in the fifth and sixth examples, the effect of the present invention was described using examples of instances in which the outer diameter of the bellows is the same in order to facilitate comprehension, this is not provided by way of limitation. Even when there is a fluctuation in the outer diameter of the
bellows 30, the effect of the present invention can be obtained. In short, the technical significance is in reducing the inner diameter of a portion of thebellows 30 and thereby preventing the balance value from decreasing and suppressing an increase in the size of the rotating ring and the fixed ring in a type [of mechanical seal] in which the fixed side and the rotation side are integrated. - In other words, when, as in the fifth example, [the balance value] is within the range of 50%≦balance value≦100%, the balance value is prevented form decreasing, and when, as in the sixth example, the balance value exceeds 100%, an increase in the diameters of the rotation-side sealing ring and the fixed-side sealing ring is suppressed and an increase in size of the mechanical seal is avoided.
-
-
- 1 Rotating shaft
- 2 Sleeve
- 3 Housing
- 4 Cartridge
- 5 Rotation-side sealing ring
- 6 Fixed-side sealing ring
- 7 Metal bellows
- 8 Case
- 9 Cup gasket
- 10 Cup gasket
- 15 Metal bellows
- 16 Band
- 20 Sleeve
- 30 Metal bellows
- 40 Cartridge
Claims (20)
1. An inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to said sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against said rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to said cartridge; wherein:
said bellows is made from a metal; and
said metal bellows has one end fixed to a case for holding said fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to said cartridge, the plate thickness of said metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of said case or said cartridge.
2. The mechanical seal according to claim 1 , wherein: said metal bellows comprises a bellows part in which crest parts and trough parts are alternately formed, and a disc-shaped flange part extending radially outwards from said trough part at each end of the bellows part; and said bellows part is formed by molding or welding so that the outer diameter of said flange parts is greater than the diameter of said crest parts, and the inner diameter of said flange parts is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of said trough parts.
3. The mechanical seal according to claim 1 , wherein the fixing of said metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge is performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of said flange part of said metal bellows.
4. The mechanical seal according to claim 1 , wherein said rotation-side sealing ring is fixed to said sleeve via a cup gasket, and said cup gasket is provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of said rotation-side sealing ring.
5. An inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to said sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against said rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to said cartridge; wherein:
said bellows is made from a metal; and
said metal bellows has one end fixed to a gasket for holding said fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to said cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of said cartridge.
6. The mechanical seal according to claim 5 , wherein a band is attached on an outer circumference of an outer cylinder part of said metal bellows fitting into said gasket holding said fixed-side sealing ring.
7. An inside-type mechanical seal comprising a sleeve fixed to a rotating shaft, and a cartridge fixed to a housing; a rotation-side sealing ring being provided to said sleeve; and a fixed-side sealing ring, which slides against said rotation-side sealing ring, and a bellows for axially urging the fixed-side sealing ring, being provided to said cartridge; wherein:
said bellows is made from a metal; and
said metal bellows has one end directly fixed to said fixed-side sealing ring and another end fixed to said cartridge, the plate thickness of the metal bellows being set so as to be smaller than the plate thickness of said cartridge.
8. The mechanical seal according to claim 1 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
9. The mechanical seal according to claim 2 , wherein the fixing of said metal bellows to the metal case and the metal cartridge is performed by welding or fusing at each position located slightly further towards the inner diameter side relative to the outer diameter of said flange part of said metal bellows.
10. The mechanical seal according to claim 2 , wherein said rotation-side sealing ring is fixed to said sleeve via a cup gasket, and said cup gasket is provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of said rotation-side sealing ring.
11. The mechanical seal according to claim 3 , wherein said rotation-side sealing ring is fixed to said sleeve via a cup gasket, and said cup gasket is provided across an outer circumferential surface and a side opposite the sealing face of said rotation-side sealing ring.
12. The mechanical seal according to claim 2 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
13. The mechanical seal according to claim 3 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
14. The mechanical seal according to claim 4 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
15. The mechanical seal according to claim 5 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
16. The mechanical seal according to claim 6 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
17. The mechanical seal according to claim 7 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
18. The mechanical seal according to claim 9 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
19. The mechanical seal according to claim 10 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
20. The mechanical seal according to claim 11 , being of a type in which a distal end of an inner cylinder part of said sleeve is expanded in diameter by crimping and caused to engage with an inner cylinder part of said cartridge, thereby preventing said cartridge and said sleeve from axial detachment, wherein:
a portion of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge located on the opposite axial-direction side relative to said fixed-side sealing ring side is expanded in diameter and provided with a stepped part; and
said bellows is formed so that the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the fixed-side sealing ring side relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge is smaller than the inner diameter of a portion positioned on the opposite side from the fixed-side sealing ring relative to the stepped part of the inner cylinder part of said cartridge.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-222233 | 2012-10-04 | ||
| JP2012222233 | 2012-10-04 | ||
| PCT/JP2013/076968 WO2014054745A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2013-10-03 | Mechanical seal |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/076968 A-371-Of-International WO2014054745A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2013-10-03 | Mechanical seal |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/159,049 Division US9581248B2 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2016-05-19 | Mechanical seal |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20150211638A1 true US20150211638A1 (en) | 2015-07-30 |
Family
ID=50435064
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/407,372 Abandoned US20150211638A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2013-10-03 | Mechanical seal |
| US15/159,049 Active US9581248B2 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2016-05-19 | Mechanical seal |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/159,049 Active US9581248B2 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2016-05-19 | Mechanical seal |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20150211638A1 (en) |
| EP (2) | EP2853788B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6116575B2 (en) |
| CN (2) | CN105864432B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2014054745A1 (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9927030B2 (en) * | 2014-01-17 | 2018-03-27 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| US20180269743A1 (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2018-09-20 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Liquid-cooled electric machine |
| US20180328211A1 (en) * | 2015-10-22 | 2018-11-15 | Man Diesel & Turbo Se | Dry Gas Seal And Turbomachine Having A Dry Gas Seal |
| US20190211816A1 (en) * | 2016-08-23 | 2019-07-11 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Liquid supply system |
| US10662798B2 (en) | 2015-10-22 | 2020-05-26 | Man Energy Solutions Se | Dry gas sealing system, and turbomachine comprising a dry gas sealing system |
| US11187326B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2021-11-30 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| US11371616B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2022-06-28 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106662254B (en) * | 2014-07-24 | 2019-06-18 | 伊格尔工业股份有限公司 | Mechanical sealing member |
| CN105202193B (en) * | 2015-10-23 | 2017-05-17 | 宁波方力密封件有限公司 | Mechanical seal for compressor |
| US10012315B2 (en) * | 2016-05-23 | 2018-07-03 | United Technologies Corporation | Seal assembly |
| DE102016211816B4 (en) * | 2016-06-30 | 2018-02-22 | Eagleburgmann Germany Gmbh & Co. Kg | Mechanical seal assembly with coated bellows unit |
| US11473680B2 (en) | 2016-07-12 | 2022-10-18 | John Crane Inc. | Non-collapsible flexible sealing membrane and seal assembly for rotary shaft equipment |
| ES2934247T3 (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2023-02-20 | Crane John Inc | Non-collapsible flexible sealing membrane and sealing kit for rotating shaft equipment |
| CN110050150B (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2022-02-01 | 伊格尔工业股份有限公司 | Mechanical sealing element |
| JP6855295B2 (en) * | 2017-03-17 | 2021-04-07 | Nok株式会社 | Sealing device |
| BR112019022649B1 (en) * | 2017-05-18 | 2022-08-30 | Sulzer Management Ag | MECHANICAL SEAL |
| EP3643949B1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2023-05-03 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| US10563772B2 (en) | 2017-11-13 | 2020-02-18 | General Electric Company | Seal assembly and an associated method thereof |
| WO2019163726A1 (en) * | 2018-02-21 | 2019-08-29 | イーグル工業株式会社 | Mechanical seal |
| JP6900348B2 (en) * | 2018-05-23 | 2021-07-07 | 株式会社鷺宮製作所 | Welded structure and valve gear |
| US11293329B2 (en) | 2019-10-15 | 2022-04-05 | Cummins Inc. | Integrated bellows gasket |
| FR3104225B1 (en) * | 2019-12-05 | 2023-01-13 | Eaton Intelligent Power Ltd | Mechanical seal with welded bellows |
| WO2023228943A1 (en) * | 2022-05-25 | 2023-11-30 | イーグル工業株式会社 | Mechanical tool |
Citations (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2100220A (en) * | 1935-12-04 | 1937-11-23 | Gen Electric | Shaft seal |
| US2392763A (en) * | 1943-10-12 | 1946-01-08 | Carl D Peterson | Fluid seal |
| US2610874A (en) * | 1946-08-12 | 1952-09-16 | Crane Packing Co | Driving means for fluid seals |
| GB1007552A (en) * | 1960-11-01 | 1965-10-13 | Garrett Corp | Improvements relating to seals |
| US4136887A (en) * | 1977-10-04 | 1979-01-30 | Borg-Warner Corporation | Bellows type mechanical seal |
| US4193756A (en) * | 1978-03-08 | 1980-03-18 | Tosco Corporation | Seal assembly and method for providing a seal in a rotary kiln |
| US4261581A (en) * | 1980-04-14 | 1981-04-14 | Durametallic Corporation | Mechanical seal with improved face ring mounting |
| US4378119A (en) * | 1980-07-24 | 1983-03-29 | Crane Packing Limited | Mechanical face seals with special bellows |
| US4691927A (en) * | 1986-12-01 | 1987-09-08 | A. W. Chesterton Company | Temperature-compensating mechanical face seal |
| US5011166A (en) * | 1989-04-24 | 1991-04-30 | John Crane Uk Limited | Mechanical face seals |
| US5797602A (en) * | 1996-10-10 | 1998-08-25 | Pac-Seal Inc. International | Mechanical seal for water pump of heavy duty vehicle |
| US5893564A (en) * | 1997-05-23 | 1999-04-13 | Meritor Heavy Vehicle Systems, Llc | Mechanical face seal assembly |
| US5954341A (en) * | 1996-07-30 | 1999-09-21 | John Crane Sealol Inc. | Bellows seal with drive collar for reverse pressure capability |
| US6341781B1 (en) * | 1998-04-15 | 2002-01-29 | Burgmann Dichtungswerke Gmbh & Co. Kg | Sealing element for a face seal assembly |
| US20020113375A1 (en) * | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-22 | Gennady Ruderman | Pressure differential sealing device |
| US20030006560A1 (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2003-01-09 | Dahlheimer John C. | Bellows face seal assembly |
| WO2010113932A1 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | イーグル工業株式会社 | Bellows type mechnical seal |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1222843B (en) * | 1961-05-09 | 1966-08-11 | Huettenwerk Oberhausen Ag | Oven sealing for rotary tubes |
| US4365816A (en) * | 1980-10-29 | 1982-12-28 | Eg&G Sealol, Inc. | Self-damping bellows seal assembly |
| JPS6154553A (en) | 1984-08-23 | 1986-03-18 | Fujitsu Ltd | Channel start control system |
| JPS6150863U (en) * | 1984-09-07 | 1986-04-05 | ||
| JPS6322369Y2 (en) * | 1984-09-14 | 1988-06-20 | ||
| FR2594519B1 (en) * | 1986-02-17 | 1990-01-12 | Leonetti Bernard | MECHANICAL SEALING FOR A ROTATING SHAFT AND ITS MANUFACTURING METHOD |
| JPS6353959A (en) | 1986-08-22 | 1988-03-08 | Mitsui Haitetsuku:Kk | Lead frame for semiconductor device and manufacture thereof |
| JPH0211659Y2 (en) * | 1986-09-29 | 1990-03-27 | ||
| GB8906901D0 (en) * | 1989-03-28 | 1989-05-10 | Crane John Uk Ltd | Mechanical face seals |
| JP2956862B2 (en) | 1991-12-04 | 1999-10-04 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | mechanical seal |
| JPH09144536A (en) * | 1995-11-27 | 1997-06-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | Seal device for water pump |
| GB9606815D0 (en) * | 1996-03-30 | 1996-06-05 | Crane John Uk Ltd | Mechanical face seals |
| JPH1162890A (en) * | 1997-08-28 | 1999-03-05 | Toyota Motor Corp | Mechanical seal of water pump |
| JP2000074226A (en) * | 1998-08-27 | 2000-03-14 | Eagle Ind Co Ltd | Mechanical seal |
| US6398223B1 (en) * | 2000-08-21 | 2002-06-04 | John Crane Inc. | Mechanical face seal |
| JP2006057725A (en) * | 2004-08-19 | 2006-03-02 | Eagle Ind Co Ltd | Mechanical sealing device |
| WO2007142177A1 (en) * | 2006-06-08 | 2007-12-13 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| CN201209669Y (en) * | 2008-06-10 | 2009-03-18 | 浙江东新密封有限公司 | Mechanical seal for automobile engine cooling water pump |
| CN202251961U (en) * | 2011-09-20 | 2012-05-30 | 宁波精科机械密封件制造有限公司 | Mechanical sealing device |
| ITTO20130352A1 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2014-10-31 | Umbra Meccanotecnica | MECHANICAL SEAL |
-
2013
- 2013-10-03 JP JP2014539823A patent/JP6116575B2/en active Active
- 2013-10-03 EP EP13843315.6A patent/EP2853788B1/en active Active
- 2013-10-03 EP EP16186342.8A patent/EP3159583B1/en active Active
- 2013-10-03 WO PCT/JP2013/076968 patent/WO2014054745A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-10-03 US US14/407,372 patent/US20150211638A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-10-03 CN CN201610301197.1A patent/CN105864432B/en active Active
- 2013-10-03 CN CN201380030374.1A patent/CN104379974B/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-05-19 US US15/159,049 patent/US9581248B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2100220A (en) * | 1935-12-04 | 1937-11-23 | Gen Electric | Shaft seal |
| US2392763A (en) * | 1943-10-12 | 1946-01-08 | Carl D Peterson | Fluid seal |
| US2610874A (en) * | 1946-08-12 | 1952-09-16 | Crane Packing Co | Driving means for fluid seals |
| GB1007552A (en) * | 1960-11-01 | 1965-10-13 | Garrett Corp | Improvements relating to seals |
| US4136887A (en) * | 1977-10-04 | 1979-01-30 | Borg-Warner Corporation | Bellows type mechanical seal |
| US4193756A (en) * | 1978-03-08 | 1980-03-18 | Tosco Corporation | Seal assembly and method for providing a seal in a rotary kiln |
| US4261581A (en) * | 1980-04-14 | 1981-04-14 | Durametallic Corporation | Mechanical seal with improved face ring mounting |
| US4378119A (en) * | 1980-07-24 | 1983-03-29 | Crane Packing Limited | Mechanical face seals with special bellows |
| US4691927A (en) * | 1986-12-01 | 1987-09-08 | A. W. Chesterton Company | Temperature-compensating mechanical face seal |
| US5011166A (en) * | 1989-04-24 | 1991-04-30 | John Crane Uk Limited | Mechanical face seals |
| US5954341A (en) * | 1996-07-30 | 1999-09-21 | John Crane Sealol Inc. | Bellows seal with drive collar for reverse pressure capability |
| US5797602A (en) * | 1996-10-10 | 1998-08-25 | Pac-Seal Inc. International | Mechanical seal for water pump of heavy duty vehicle |
| US5893564A (en) * | 1997-05-23 | 1999-04-13 | Meritor Heavy Vehicle Systems, Llc | Mechanical face seal assembly |
| US6341781B1 (en) * | 1998-04-15 | 2002-01-29 | Burgmann Dichtungswerke Gmbh & Co. Kg | Sealing element for a face seal assembly |
| US20020113375A1 (en) * | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-22 | Gennady Ruderman | Pressure differential sealing device |
| US20030006560A1 (en) * | 2001-05-18 | 2003-01-09 | Dahlheimer John C. | Bellows face seal assembly |
| WO2010113932A1 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | イーグル工業株式会社 | Bellows type mechnical seal |
| US20120013076A1 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2012-01-19 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Bellows type mechanical seal |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9927030B2 (en) * | 2014-01-17 | 2018-03-27 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| US20180269743A1 (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2018-09-20 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Liquid-cooled electric machine |
| US20180328211A1 (en) * | 2015-10-22 | 2018-11-15 | Man Diesel & Turbo Se | Dry Gas Seal And Turbomachine Having A Dry Gas Seal |
| US10662798B2 (en) | 2015-10-22 | 2020-05-26 | Man Energy Solutions Se | Dry gas sealing system, and turbomachine comprising a dry gas sealing system |
| US20190211816A1 (en) * | 2016-08-23 | 2019-07-11 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Liquid supply system |
| US11187326B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2021-11-30 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
| US11371616B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2022-06-28 | Eagle Industry Co., Ltd. | Mechanical seal |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105864432B (en) | 2018-02-13 |
| JPWO2014054745A1 (en) | 2016-08-25 |
| EP3159583A1 (en) | 2017-04-26 |
| US9581248B2 (en) | 2017-02-28 |
| CN104379974B (en) | 2017-05-10 |
| EP3159583B1 (en) | 2020-09-09 |
| CN105864432A (en) | 2016-08-17 |
| JP6116575B2 (en) | 2017-04-19 |
| EP2853788A1 (en) | 2015-04-01 |
| EP2853788B1 (en) | 2018-08-01 |
| US20160281856A1 (en) | 2016-09-29 |
| EP2853788A4 (en) | 2016-03-16 |
| CN104379974A (en) | 2015-02-25 |
| WO2014054745A1 (en) | 2014-04-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9581248B2 (en) | Mechanical seal | |
| JP5216084B2 (en) | Lip type seal | |
| US8256772B2 (en) | Lip type seal | |
| KR101500478B1 (en) | Lip type seal | |
| JP5374591B2 (en) | Lip type seal | |
| JPWO2007102267A1 (en) | Sealing device | |
| CN101501373B (en) | Shaft seal device | |
| JPWO2014030742A1 (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP6405389B2 (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP5016423B2 (en) | Lip type seal | |
| US20140377057A1 (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP6031753B2 (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP2015203489A (en) | seal ring and sealing device | |
| EP2815158B1 (en) | Slide ring seal | |
| JP6143018B2 (en) | Sealing device | |
| US20190195366A1 (en) | Mechanical Seal and Device with Such a Mechanical Seal | |
| JP3196643U (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP2006057646A (en) | Sealing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: EAGLE INDUSTRY CO., LTD., JAPAN Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:ITADANI, MASATOSHI;SHINOMIYA, TAKASHI;OGAWA, YOSHIHIRO;SIGNING DATES FROM 20140214 TO 20140218;REEL/FRAME:034571/0593 |
|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |