US20100251299A1 - System and Method to Send Information Identifying Reccomended Media Content Items - Google Patents
System and Method to Send Information Identifying Reccomended Media Content Items Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20100251299A1 US20100251299A1 US12/413,822 US41382209A US2010251299A1 US 20100251299 A1 US20100251299 A1 US 20100251299A1 US 41382209 A US41382209 A US 41382209A US 2010251299 A1 US2010251299 A1 US 2010251299A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- media content
- computing device
- item
- content items
- recording
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
- H04N21/482—End-user interface for program selection
- H04N21/4826—End-user interface for program selection using recommendation lists, e.g. of programs or channels sorted out according to their score
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/432—Content retrieval operation from a local storage medium, e.g. hard-disk
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/433—Content storage operation, e.g. storage operation in response to a pause request, caching operations
- H04N21/4334—Recording operations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/45—Management operations performed by the client for facilitating the reception of or the interaction with the content or administrating data related to the end-user or to the client device itself, e.g. learning user preferences for recommending movies, resolving scheduling conflicts
- H04N21/458—Scheduling content for creating a personalised stream, e.g. by combining a locally stored advertisement with an incoming stream; Updating operations, e.g. for OS modules ; time-related management operations
- H04N21/4583—Automatically resolving scheduling conflicts, e.g. when a recording by reservation has been programmed for two programs in the same time slot
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/45—Management operations performed by the client for facilitating the reception of or the interaction with the content or administrating data related to the end-user or to the client device itself, e.g. learning user preferences for recommending movies, resolving scheduling conflicts
- H04N21/466—Learning process for intelligent management, e.g. learning user preferences for recommending movies
- H04N21/4668—Learning process for intelligent management, e.g. learning user preferences for recommending movies for recommending content, e.g. movies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
- H04N21/472—End-user interface for requesting content, additional data or services; End-user interface for interacting with content, e.g. for content reservation or setting reminders, for requesting event notification, for manipulating displayed content
- H04N21/47202—End-user interface for requesting content, additional data or services; End-user interface for interacting with content, e.g. for content reservation or setting reminders, for requesting event notification, for manipulating displayed content for requesting content on demand, e.g. video on demand
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
- H04N21/478—Supplemental services, e.g. displaying phone caller identification, shopping application
- H04N21/4788—Supplemental services, e.g. displaying phone caller identification, shopping application communicating with other users, e.g. chatting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/47—End-user applications
- H04N21/482—End-user interface for program selection
- H04N21/4825—End-user interface for program selection using a list of items to be played back in a given order, e.g. playlists
Definitions
- the present disclosure is generally related to sending information identifying recommended media content items.
- a user may desire to send information identifying recommended media content items to one or more recipients.
- a teacher may desire to send information identifying recommended media content items to students.
- the user may identify recommended media content items and deliver a hardcopy or an email that includes information identifying the recommenced media content items to particular recipients.
- Each recipient may then review the recommended media content items and determine how to view each item. For example, each recipient may manually schedule a recording of media content items at a digital video recorder, manually select video on demand items, and manually schedule download of downloadable media content. When a recipient is not technically knowledgeable, the recipient may encounter difficulties viewing each recommended media content item.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a first particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a second particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items
- FIG. 3 is a flow diagram of a first particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items
- FIG. 4 is a flow diagram of a second particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items
- FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of a third particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items.
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram of an illustrative embodiment of a general computer system.
- a method includes accessing an electronic program guide (EPG) at a computing device (e.g. at a set-top box device or a personal computer).
- the method includes identifying recommended media content items using the EPG.
- the method further includes selecting addresses of one or more recipients and sending information identifying the recommended media content items to the selected addresses.
- EPG electronic program guide
- a method in another particular embodiment, includes receiving information identifying recommended media content items at a computing device. The method includes receiving a user selection selecting at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items. When the at least one item of media content is a scheduled broadcast program, the method includes automatically scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content at a media recorder device. When the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, the method includes automatically placing the at least one item of media content in an on demand queue.
- a computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to send a first graphical user interface (GUI) to a first computing device.
- GUI graphical user interface
- the first GUI enables selection of recommended media content items and enables access to an electronic program guide (EPG).
- EPG electronic program guide
- the computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to receive, via the first GUI, selections identifying recommended media content items.
- the computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to receive, via the first GUI, addresses of recipients.
- the computer-readable storage medium further includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to send the information identifying the recommended media content items to the addresses of the recipients.
- a system in another particular embodiment, includes a first computing device to access an electronic program guide (EPG) to identify recommended media content items based on selections from the EPG and to send information identifying the recommended media content items to addresses associated with selected recipients.
- EPG electronic program guide
- the EPG includes information identifying scheduled media content and on demand media content.
- FIG. 1 a block diagram of a first particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items is depicted and generally designated 100 .
- the system 100 includes a first computing device 102 coupled to a media content server 104 via a network 106 .
- An electronic program guide (EPG) 108 may also be coupled to the network 106 .
- EPG electronic program guide
- the first computing device 102 is operable to access the EPG 108 and to create information identifying recommended media content items 118 using the EPG 108 .
- the first computing device 102 is further operable to send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to selected addresses 120 of recipients. For example, a teacher may identify recommended media content items and send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to students.
- the first computing device 102 may be a mobile telephony device, a personal digital assistant (PDA) device, a personal computing device, a set-top box (STB) device, other computing device, or any combination thereof.
- the first computing device 102 may include address data 154 from which a sender 116 may select the selected addresses 120 .
- the address data 154 may include addresses associated with recipients that the sender 116 selects to receive the information identifying recommended media content items 118 .
- the sender 116 may modify the address data 154 by entering recipient address data 150 at the first computing device 102 .
- a particular address from the address data 154 may be a phone number, an email address, an Internet Protocol (IP) address, other address, or any combination thereof.
- IP Internet Protocol
- the address data 154 may include an address of the recipient 136 that is associated with a mobile telephony device.
- the sender 116 uses a remote control device 156 to interact with the first computing device 102 .
- the remote control device 156 may be used to interact with the STB device to create the information identifying recommended media content items 218 , to select recipients 152 and to send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 of the selected recipients 152 .
- the remote control device 156 enables the sender 116 to browse the EPG 108 to identify recommended media content items by selecting media content items from the EPG 108 .
- the remote control device 156 may also enable the sender 116 to select recipients 152 from the address data 154 .
- the remote control device 156 may enable the sender 116 to add, delete, or modify a recipient and an address associated with the recipient.
- the media content server 104 is operable to provide media content to various devices, such as the first computing device 102 , the second computing device 110 , the third computing device 112 , and the download device 114 .
- the media content server 104 may include various types of media content, including scheduled media content 160 , on demand media content 162 , and downloadable media content 164 .
- the scheduled media content 160 may include media content, such as television programs or movies, scheduled for broadcast at a particular date and time.
- the on demand media content 162 may include media content that may be streamed upon request from the media content server 104 to one or more of the devices 102 , 110 , 112 , and 114 .
- the downloadable media content 164 may include media content that may be download from the media content server 104 to one or more of the devices 102 , 110 , 112 , and 114 .
- the media content server 104 is illustrated as a single server in FIG. 1 , in various embodiments the media content sever 104 may include a plurality of servers.
- the plurality of servers may be a part of a particular service provider network or each server may belong to a separate service provider network.
- the second computing device 110 is associated with one of the selected addresses 120 and receives the information identifying recommended media content items 118 .
- the second computing device 110 may display the information identifying recommended media content items 118 at a display device 122 as displayed recommended media content 124 .
- the second computing device 110 may be a personal computer, a personal digital assistant (PDA), a mobile telephony device, a set-top box device, other computing device, or any combination thereof.
- PDA personal digital assistant
- the second computing device 110 is further operable to receive a user selection 128 from a recipient 136 .
- the user selection 128 may select at least one item from the displayed recommended media content 124 .
- the second computing device 110 may automatically make the media content associated with the user selection 128 available for playback at the third computing device 112 .
- the second computing device 110 may automatically schedule a recording of scheduled media content 160 , automatically schedule a download of downloadable media content 164 , and automatically place on demand media content 162 in a queue.
- the third computing device 112 may be a digital video recorder (DVR) device, personal computing device, STB device, other computing device, or any combination thereof.
- DVR digital video recorder
- the second computing device 110 may instruct the third computing device 112 to automatically schedule recording of the selected media content at the third computing device 112 .
- the recipient 136 may view the displayed recommended media content 124 at the display device 122 of a mobile telephony device, and the user selection 128 may cause the mobile telephony device to automatically schedule recording of the selected media content at a DVR device.
- the on demand media content item may be automatically placed in an on demand queue 132 of the third computing device 112 .
- the download device 114 may automatically place the selected media content item in a download queue 134 of the download device 114 .
- the download device may be a personal computing device or a STB device.
- the sender 116 may access the EPG 108 at the first computing device 102 .
- the sender 116 may identify recommended media content items by selecting media content items using the EPG 108 . Further, the sender 116 may select one or more addresses from the address data 154 , such as an address associated with the recipient 136 .
- the first computing device 102 may send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 associated with the selected recipients 152 .
- the information identifying recommended media content items 118 may be received at the second computing device 110 when the second computing device 110 is associated with an address of the selected addresses 120 .
- the second computing device 110 may display the displayed recommended media content 124 at the display device 122 .
- the recipient 136 may provide the user selection 128 , selecting at least one item of media content from the displayed recommended media content 124 .
- the recipient 136 may select program A from displayed recommended media content 124 .
- the second computing device 110 may receive the user selection 128 and automatically schedule at least one item of media content from the displayed recommended media content 124 for recording at the third computing device 112 .
- the third computing device 112 may be a media recorder device such as a DVR.
- the displayed recommended media content 124 may include a user selectable option to select (e.g., accept) all of the recommended media content. For example, when the recipient 136 accepts items from the information identifying the recommended media content items 118 , all of the media content of the displayed recommended media content 124 may be automatically scheduled for recording at the third computing device 112 .
- the second computing device 110 may determine whether a selected item of media content is the schedule media content 160 , the downloadable media content 164 , or the on demand media content 162 and perform an appropriate action to provide the selected item of media content for playback. For example, when the user selection 128 includes a scheduled program from the scheduled media content 160 , the second computing device 110 may automatically schedule recording of the scheduled program at the third computing device 112 . In a particular embodiment, the second computing device 110 automatically schedules recording of a scheduled program by accessing the EPG 108 . When the user selection 128 includes the on demand media content 162 , the second computing device 110 may automatically place the on demand media content 162 in an on demand queue 132 associated with the third computing device 112 .
- the second computing device 110 may send a request to purchase the on demand media content to the media content server 104 , and in response the media content server 104 may place the on demand media content 162 in the on demand items queue 132 associated with the third computing device 112 .
- the second computing device 110 may automatically schedule the downloadable media content 164 for download at the download device 114 .
- the download device 114 is integrated with the third computing device 112 .
- the download device 114 may be internal to the STB.
- the download device 114 is a device separate from the third computing device 112 .
- the third computing device 112 may be a set-top box device while the download device 114 may be a personal computing device.
- scheduling a download of at least one item of media content at the download device 114 includes setting a priority of the item of media content and placing the item of media content in the download queue 134 associated with the download device 114 .
- the second computing device 110 may perform appropriate actions to make each selected item of media content available to the recipient 136 .
- the second computing device 110 may automatically identify a second presentation of a program associated with either the previously scheduled recording 126 or associated with the selected media content.
- the second computing device 110 may prompt the recipient 136 to select which of the second presentations to record.
- the information identifying recommended media content items 118 may include a program X that is scheduled at the same time as a program A in the scheduled recordings 112 .
- the second computing device 110 may automatically determine a second presentation of either program X or program A.
- the second computing device 110 may prompt the recipient 136 to select from among the second alternatives.
- the second computing device 110 may receive a second user selection 130 and schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device 112 .
- the sender 116 can efficiently send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 of one or more recipients.
- a teacher may create the information identifying recommended media content items 118 and send the information identifying recommended media content items 118 to students.
- An example of information identifying recommended media content items 118 is a list of content item titles.
- each of the recipients of the information identifying recommended media content items 118 may select only those media content items that they wish to view and the second computing device 110 performs various actions to automatically make the selected items available.
- the second computing device 110 automatically determines whether a particular media content item is scheduled media content 160 , downloadable media content 164 , or on demand media content 164 and then takes an appropriate action to make the particular media content available to the recipient 136 . In this way, the recipient 136 can automatically obtain multiple media content items from the information identifying recommended media content items 118 via a single selection.
- FIG. 2 a block diagram of a second particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items is depicted and generally designated 200 .
- the system 200 includes a first computing device 202 coupled to a media content server 204 via a network 206 .
- an electronic program guide (EPG) 208 is also coupled to the network 206 .
- EPG electronic program guide
- the media content server 204 is operable to provide media content to various devices, such as the first computing device 202 , the second computing device 210 , and the third computing device 212 .
- the media content server 204 may include various types of media content, such as scheduled media content, on demand media content, downloadable media content, other media content, or any combination thereof.
- the media content server 204 is illustrated as a single server in FIG. 2 , in various embodiments the media content server 204 may include a plurality of servers.
- the plurality of servers may be a part of a particular service provider network, or each server may belong to a separate service provider network.
- the recommendation server 270 is operable to send first data 280 representing a first graphical user interface (GUI) 242 to the first computing device 202 and is operable to send second data 282 representing a second GUI 224 to the second computing device 210 .
- the recommendation server 270 includes a processor 272 , an input/output interface 274 , and a memory 276 .
- the memory 276 includes operational instructions 278 that are executable by the processor 272 to perform the various functions of the recommendation server 270 .
- the first computing device 202 is operable to receive the first data 280 from the recommendation server 270 and to display the first GUI 242 at a first display device 240 .
- the first GUI 242 may include one or more of a scheduled program listing 244 , a video on demand listing 246 , and a downloadable content listing 248 .
- the functions described as being performed by the first computing device 202 are performed by a combination of the first computing device 202 and the recommendation server 270 .
- the first computing device 202 may access the EPG 208 via the recommendation server 270 .
- a sender 216 may use the first GUI 242 to create information identifying recommended media content items 218 .
- the sender 216 may create the information identifying recommended media content items 218 by accessing the EPG 208 via the first GUI 242 .
- the first computing device 202 is operable to receive, via the first GUI 242 , a selection of selected media content 250 to create the information identifying recommended media content items 218 .
- the first computing device 202 is further operable to receive, via the first GUI 242 , a selection of selected recipients 252 and to identify the selected addresses 220 associated with the selected recipients 252 .
- the first computing device 202 is further operable to send the information identifying recommended media content items 218 to the selected addresses 220 .
- the first computing device 202 may be a mobile telephony device, a personal computing device, a personal digital assistant (PDA) device, a set-top box (STB) device, or any other computing device.
- PDA personal digital assistant
- STB set-top box
- the second computing device 210 is operable to receive second data 282 from the recommendation server 270 and to display the second GUI 224 at a second display device 222 .
- the second GUI 224 may display the information identifying recommended media content items 218 at the second display device 224 .
- the second computing device 210 may be associated with one of the selected addresses 220 associated with the selected recipients 252 .
- the functions described as being performed by the second computing device 210 are performed by a combination of the second computing device 210 and the recommendation server 270 .
- the second computing device 210 may send a message to the recommendation server 270 requesting the recommendation server 270 to provide a selected media content items for download.
- the second computing device 210 may enable a recipient 236 to select, via the second GUI 224 , at least one item of media content from the second GUI 224 .
- the second computing device 210 is operable to receive a user selection 228 via the second GUI 224 .
- the user selection 228 may select at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommended media content items 218 .
- the second computing device 210 is operable to automatically schedule recording of the selected item of media content at the third computing device 212 .
- the third computing device 212 may be a personal computing device, a STB device, a DVR device, or other computing device. In a particular embodiment, the third computing device 212 is integrated with the second computing device 210 .
- the third computing device 212 is a different device that is independent of the second computing device 210 .
- the user selection 228 may select one or more of the items of recommended media content displayed at the second GUI 224 . In a particular embodiment, the user selection 228 may select all of the recommended media content via a “select all” selection.
- the second computing device 210 is further operable to automatically determine whether scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the third computing device 212 .
- the second computing device 210 is operable to automatically identify a second presentation of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording or the at least one item of media content.
- the second computing device 210 is further operable to automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device 212 .
- the information identifying recommended media content items 218 may identify a program X that is scheduled for recording at the same time that a program A is scheduled for recording.
- the second computing device 210 may automatically identify a second presentation of either program X or program A and automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device 112 .
- the second computing device 210 may automatically perform various actions to make each selected item of media content available to the recipient 236 .
- the second computing device 210 may automatically schedule recording of at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommended media content items 218 at the third computing device 212 when the selected media content includes a scheduled program.
- the second computing device 210 may automatically identify at least one item of media content in an active content list 232 associated with the third computing device 212 when the selected item of media content includes on demand media content.
- the second computing device 210 may automatically schedule download of the selected item of media content at the third computing device 212 when the selected item of media content includes downloadable media content.
- the selected media content item may be automatically placed in a download queue 234 associated with the third computing device 212 .
- the recommendation server 270 may send the first data 280 to the first computing device 202 for display at the first display device 240 .
- the first computing device 202 may display, via the first GUI 242 , the information identifying recommended media content items 218 and selected addresses 220 of selected recipients 252 .
- the first computing device 202 may send the information identifying recommended media content items 218 to the selected addresses 220 .
- a computing device associated with each of the selected addresses 220 may receive the information identifying recommended media content items 218 .
- the selected addresses 220 may include an address associated with the second computing device 210 .
- the second computing device 210 may receive the information identifying recommended media content items 218 and display the information identifying recommended media content items 218 via the second GUI 224 , at the second display device 222 .
- the second computing device 210 may, via the second GUI 224 , receive a user selection 228 of one or more of the items of the recommended media content 224 .
- the second computing device 210 may automatically make the selected one or more items of media content available for playback at the third computing device 212 .
- the item of media content when the item of media content is a scheduled program, the item of media content may be automatically scheduled for recording at the third computing device 212 .
- the selected item of media content includes on demand media content
- the selected item of media content may be automatically identified in the active content list 232 associated with the third computing device 212 .
- the downloadable media content may be automatically scheduled for download at the third computing device 212 .
- the downloadable media content may be placed in the download queue 234 associated with the third computing device 212 .
- the recipient 236 may receive the information identifying recommended media content items 218 , select one or more items of the recommended media content, and have the selections automatically made available for playback at the third computing device 212 .
- the recipient 236 does not have to determine whether a particular item from the information identifying recommended media content items 218 is downloadable media content or video-on demand media content or scheduled media content.
- the second computing device 210 determines how each selected item of media content may be obtained for viewing and automatically schedules recording of scheduled programs, automatically places on demand items in the active content list 232 , and automatically places downloadable media content items in the download queue 234 .
- the second computing device 210 By receiving and performing various actions after receiving the user selection 228 , the second computing device 210 makes selected items from the information identifying recommended media content items 218 available to the recipient 236 . In this way, the amount of effort required to make each selected item of media content available to the recipient 236 is reduced.
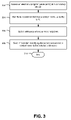
- FIG. 3 is a flow diagram of a first particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items.
- the method may be performed by a computing device, such as the first computing device 102 of FIG. 1 , the first computing device 202 of FIG. 2 , or the recommendation server 270 of FIG. 2 .
- the method begins by accessing an electronic program guide (EPG) at a computing device, at 302 .
- EPG electronic program guide
- recommended media content items are identified using the EPG.
- an address of one or more recipients is selected.
- information identifying the recommended media content is sent to the selected addresses.
- the sender 116 may access the EPG 108 via the first computing device 102 to create the recommended media content items 118 .
- the sender 116 may use the first computing device 102 to select selected recipients 152 and send the recommended media content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 .
- the method ends at 310 .
- a sender can access an EPG to easily identify recommended media content items from scheduled programs, on demand media content, and downloadable media content, and can send information identifying the recommended media content to one or more recipients.
- FIG. 4 is a flow diagram of a second particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items. The method may be performed by the second computing device 110 of FIG. 1 , the second computing device 210 of FIG. 2 , or the recommendation server 270 of FIG. 2 .
- the method begins by receiving information identifying recommended media content items at a computing device, at 402 .
- a user selection is received selecting at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items.
- the at least one item of media content is automatically placed in an on demand queue.
- the at least one item of media content includes downloadable media content
- the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled for download at a media download device.
- recording of the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled at a media recorder in response to the user selection. For example, in FIG.
- the second computing device 210 may receive the information identifying recommended media content items 218 , receive the user selection 228 selecting at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommended media content items 218 , and make the at least one item of media content available to the recipient 236 .
- a determination may be made whether scheduling a recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the media recorder device. Proceeding to 414 , a second presentation of one of the programs associated with the previously scheduled recording and the at least one item of media content may be automatically identified. Advancing to 416 , a second user selection may be received indicating that the second presentation should be scheduled for recording. Continuing to 418 , the second presentation may be scheduled for recording at the media recorder. The method ends at 420 . Thus, a recipient can select at least one item of media content from information identifying recommended media content items and have the selected at least one item of media content automatically made available for viewing.
- FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of a third particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items. The method may be performed by the first computing device 102 of FIG. 1 , the second computing device 110 of FIG. 1 , the first computing device 202 of FIG. 2 , the second computing device 210 of FIG. 2 , or the recommendation server 270 of FIG. 2 .
- the method begins by sending a first graphical user interface (GUI) to a first computing device, at 502 .
- the first GUI may be used to identify recommended media content items.
- the first GUI may enable access to an electronic program guide (EPG).
- EPG electronic program guide
- selections identifying recommended media content items are received via the first GUI.
- addresses of recipients are received via the first GUI.
- information identifying the recommended media content items is sent to the addresses of the recipients.
- the recommendation server 270 sends the first GUI 242 to the first computing device 202 .
- the recommendation server 270 may receive the information identifying recommended media content items 218 and the selected addresses 220 via the first GUI 242 .
- a second GUI is sent to a second computing device.
- the second GUI enables selection of at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items.
- a user selection may be received via the second GUI selecting the at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items.
- a determination may be made whether the at least one item of media content is available as a scheduled program, an on demand program, or via a download.
- data may be sent to a third computing device that causes the third computing device to schedule recording of the at least one item of media content, at 516 .
- a determination may be made whether scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the third computing device.
- a second presentation of one of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording and the at least one item of media content may be identified.
- the data sent to the third computing device may cause the third computing device to automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device. The method ends at 526 .
- the at least one item of media content may be automatically identified in an active content list associated with the third computing device, at 522 .
- the method ends at 526 .
- a download of the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled at the third computing device, at 524 .
- the method then ends at 526 .
- the computer system 600 includes a set of instructions that can be executed to cause the computer system 600 to perform any one or more of the methods or computer based functions disclosed herein.
- the computer system 600 or any portion thereof, may be connected, e.g., using a network, to other computer systems or peripheral devices.
- the computer system 600 may operate in the capacity of a computing device, such as the first computing device 102 of FIG. 1 , the second computing device 110 of FIG. 1 , the third computing device 112 of FIG. 1 , the download device 114 of FIG. 1 , the first computing device 202 of FIG. 2 , the second computing device 210 of FIG. 2 , the third computing device 212 of FIG. 2 , and the recommendation server 270 of FIG. 2 .
- a computing device such as the first computing device 102 of FIG. 1 , the second computing device 110 of FIG. 1 , the third computing device 112 of FIG. 1 , the download device 114 of FIG. 1 , the first computing device 202 of FIG. 2 , the second computing device 210 of FIG. 2 , the third computing device 212 of FIG. 2 , and the recommendation server 270 of FIG. 2 .
- the computer system 600 can also be implemented as or incorporated into various devices, such as a personal computer (PC), a tablet PC, a personal digital assistant (PDA), a mobile device, a palmtop computer, a laptop computer, a desktop computer, a communications device, a network router, a wireless telephone, a land-line telephone, a control system, a camera, a scanner, a facsimile machine, a printer, a pager, a personal trusted device, a web appliance, a switch or bridge, or any other machine capable of executing a set of instructions (sequential or otherwise) that specify actions to be taken by that machine.
- the computer system 600 can be implemented using electronic devices that provide voice, video or data communication.
- the term “system” shall also be taken to include any collection of systems or sub-systems that individually or jointly execute a set, or multiple sets, of instructions to perform one or more computer functions.
- the computer system 600 may include a processor 602 , e.g., a central processing unit (CPU), a graphics-processing unit (GPU), or both. Moreover, the computer system 600 can include a main memory 604 and a static memory 606 that can communicate with each other via a bus 608 . As shown, the computer system 600 may further include a video display unit 610 , such as a liquid crystal display (LCD), a cathode ray tube (CRT) display, an organic light emitting diode (OLED), a flat panel display, a solid-state display, or a projection display.
- LCD liquid crystal display
- CRT cathode ray tube
- OLED organic light emitting diode
- the computer system 600 may include an input device 612 , such as a keyboard or a remote control, and a cursor control device 614 , such as a mouse or a remote control.
- the computer system 600 can also include a disk drive unit 616 , a signal generation device 618 , such as a speaker, and a network interface device 620 .
- the disk drive unit 616 may include a computer-readable medium 622 in which one or more sets of instructions 624 , e.g. software, can be embedded. Further, the instructions 624 may embody one or more of the methods or logic as described herein. In a particular embodiment, the instructions 624 may reside completely, or at least partially, within the main memory 604 , the static memory 606 , and/or within the processor 602 during execution by the computer system 600 . The main memory 604 and the processor 602 also may include computer-readable media.
- dedicated hardware implementations such as application specific integrated circuits, programmable logic arrays and other hardware devices, can be constructed to implement one or more of the methods described herein.
- Applications that may include the apparatus and systems of various embodiments can broadly include a variety of electronic and computer systems.
- One or more embodiments described herein may implement functions using two or more specific interconnected hardware modules or devices with related control and data signals that can be communicated between and through the modules, or as portions of an application-specific integrated circuit. Accordingly, the present system encompasses software, firmware, and hardware implementations.
- the methods described herein may be implemented by software programs executable by a computer system.
- implementations can include distributed processing, component/object distributed processing, and parallel processing.
- virtual computer system processing can be constructed to implement one or more of the methods or functionality as described herein.
- the present disclosure contemplates a computer-readable medium that includes instructions 624 or receives and executes instructions 624 so that a device connected to a network 626 can communicate voice, video or data over the network 626 . Further, the instructions 624 may be transmitted or received over the network 626 via the network interface device 620 .
- While the computer-readable medium is shown to be a single medium, the term “computer-readable medium” includes a single medium or multiple media, such as a centralized or distributed database, and/or associated caches and servers that store one or more sets of instructions.
- the term “computer-readable medium” shall also include any medium that is capable of storing, or encoding a set of instructions for execution by a processor or that cause a computer system to perform any one or more of the methods or operations disclosed herein.
- the computer-readable medium can include a solid-state memory such as a memory card or other package that houses one or more non-volatile read-only memories. Further, the computer-readable medium can be a random access memory or other volatile re-writable memory. Additionally, the computer-readable medium can include a magneto-optical or optical medium, such as a disk or tapes or other storage device to capture carrier wave signals such as a signal communicated over a transmission medium. A digital file attachment to an email or other self-contained information archive or set of archives may be considered equivalent to a tangible storage medium.
- the disclosure is considered to include any one or more of a computer-readable storage medium and other equivalents and successor media, in which data or instructions may be stored.
- software that implements the disclosed methods may optionally be stored on a tangible storage medium, such as: a magnetic medium, such as a disk or tape; a magneto-optical or optical medium, such as a disk; or a solid state medium, such as a memory card or other package that houses one or more read-only (non-volatile) memories, random access memories, or other re-writable (volatile) memories.
- inventions of the disclosure may be referred to herein, individually and/or collectively, by the term “invention” merely for convenience and without intending to voluntarily limit the scope of this application to any particular invention or inventive concept.
- inventions merely for convenience and without intending to voluntarily limit the scope of this application to any particular invention or inventive concept.
- specific embodiments have been illustrated and described herein, it should be appreciated that any subsequent arrangement designed to achieve the same or similar purpose may be substituted for the specific embodiments shown.
- This disclosure is intended to cover any and all subsequent adaptations or variations of various embodiments. Combinations of the above embodiments, and other embodiments not specifically described herein, will be apparent to those of skill in the art upon reviewing the description.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
A method includes accessing an electronic program guide (EPG). The method includes identifying recommended media content items using the EPG and selecting one or more addresses of recipients. The method further includes sending information identifying recommended media content items to the selected addresses.
Description
- The present disclosure is generally related to sending information identifying recommended media content items.
- A user may desire to send information identifying recommended media content items to one or more recipients. For example, a teacher may desire to send information identifying recommended media content items to students. The user may identify recommended media content items and deliver a hardcopy or an email that includes information identifying the recommenced media content items to particular recipients. Each recipient may then review the recommended media content items and determine how to view each item. For example, each recipient may manually schedule a recording of media content items at a digital video recorder, manually select video on demand items, and manually schedule download of downloadable media content. When a recipient is not technically knowledgeable, the recipient may encounter difficulties viewing each recommended media content item.
-
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a first particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items; -
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a second particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items; -
FIG. 3 is a flow diagram of a first particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items; -
FIG. 4 is a flow diagram of a second particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items; -
FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of a third particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items; and -
FIG. 6 is a block diagram of an illustrative embodiment of a general computer system. - In a particular embodiment, a method includes accessing an electronic program guide (EPG) at a computing device (e.g. at a set-top box device or a personal computer). The method includes identifying recommended media content items using the EPG. The method further includes selecting addresses of one or more recipients and sending information identifying the recommended media content items to the selected addresses.
- In another particular embodiment, a method includes receiving information identifying recommended media content items at a computing device. The method includes receiving a user selection selecting at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items. When the at least one item of media content is a scheduled broadcast program, the method includes automatically scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content at a media recorder device. When the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, the method includes automatically placing the at least one item of media content in an on demand queue.
- In another particular embodiment, a computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to send a first graphical user interface (GUI) to a first computing device. The first GUI enables selection of recommended media content items and enables access to an electronic program guide (EPG). The computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to receive, via the first GUI, selections identifying recommended media content items. The computer-readable storage medium includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to receive, via the first GUI, addresses of recipients. The computer-readable storage medium further includes operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to send the information identifying the recommended media content items to the addresses of the recipients.
- In another particular embodiment, a system includes a first computing device to access an electronic program guide (EPG) to identify recommended media content items based on selections from the EPG and to send information identifying the recommended media content items to addresses associated with selected recipients. The EPG includes information identifying scheduled media content and on demand media content.
- Referring to
FIG. 1 , a block diagram of a first particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items is depicted and generally designated 100. Thesystem 100 includes afirst computing device 102 coupled to amedia content server 104 via anetwork 106. An electronic program guide (EPG) 108, asecond computing device 110, athird computing device 112, and adownload device 114 may also be coupled to thenetwork 106. - The
first computing device 102 is operable to access theEPG 108 and to create information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 using theEPG 108. Thefirst computing device 102 is further operable to send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to selectedaddresses 120 of recipients. For example, a teacher may identify recommended media content items and send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to students. Thefirst computing device 102 may be a mobile telephony device, a personal digital assistant (PDA) device, a personal computing device, a set-top box (STB) device, other computing device, or any combination thereof. Thefirst computing device 102 may includeaddress data 154 from which asender 116 may select theselected addresses 120. Theaddress data 154 may include addresses associated with recipients that thesender 116 selects to receive the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118. Thesender 116 may modify theaddress data 154 by enteringrecipient address data 150 at thefirst computing device 102. A particular address from theaddress data 154 may be a phone number, an email address, an Internet Protocol (IP) address, other address, or any combination thereof. For example, theaddress data 154 may include an address of therecipient 136 that is associated with a mobile telephony device. - In a particular embodiment, the
sender 116 uses aremote control device 156 to interact with thefirst computing device 102. For example, when thefirst computing device 102 is a STB device, theremote control device 156 may be used to interact with the STB device to create the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218, to selectrecipients 152 and to send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to the selectedaddresses 120 of the selectedrecipients 152. In a particular embodiment, theremote control device 156 enables thesender 116 to browse theEPG 108 to identify recommended media content items by selecting media content items from theEPG 108. Theremote control device 156 may also enable thesender 116 to selectrecipients 152 from theaddress data 154. Theremote control device 156 may enable thesender 116 to add, delete, or modify a recipient and an address associated with the recipient. - The
media content server 104 is operable to provide media content to various devices, such as thefirst computing device 102, thesecond computing device 110, thethird computing device 112, and thedownload device 114. Themedia content server 104 may include various types of media content, including scheduledmedia content 160, ondemand media content 162, anddownloadable media content 164. For example, the scheduledmedia content 160 may include media content, such as television programs or movies, scheduled for broadcast at a particular date and time. The ondemand media content 162 may include media content that may be streamed upon request from themedia content server 104 to one or more of thedevices downloadable media content 164 may include media content that may be download from themedia content server 104 to one or more of thedevices media content server 104 is illustrated as a single server inFIG. 1 , in various embodiments themedia content sever 104 may include a plurality of servers. For example, the plurality of servers may be a part of a particular service provider network or each server may belong to a separate service provider network. - In a particular embodiment, the
second computing device 110 is associated with one of the selectedaddresses 120 and receives the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118. Thesecond computing device 110 may display the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 at adisplay device 122 as displayed recommendedmedia content 124. Thesecond computing device 110 may be a personal computer, a personal digital assistant (PDA), a mobile telephony device, a set-top box device, other computing device, or any combination thereof. Thesecond computing device 110 is further operable to receive auser selection 128 from arecipient 136. Theuser selection 128 may select at least one item from the displayed recommendedmedia content 124. In response to theuser selection 128, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically make the media content associated with theuser selection 128 available for playback at thethird computing device 112. For example, in response to theuser selection 128, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically schedule a recording of scheduledmedia content 160, automatically schedule a download ofdownloadable media content 164, and automatically place ondemand media content 162 in a queue. Thethird computing device 112 may be a digital video recorder (DVR) device, personal computing device, STB device, other computing device, or any combination thereof. - When the
user selection 128 selects a scheduled program, thesecond computing device 110 may instruct thethird computing device 112 to automatically schedule recording of the selected media content at thethird computing device 112. For example, therecipient 136 may view the displayed recommendedmedia content 124 at thedisplay device 122 of a mobile telephony device, and theuser selection 128 may cause the mobile telephony device to automatically schedule recording of the selected media content at a DVR device. When theuser selection 128 selects an on demand media content item, the on demand media content item may be automatically placed in an ondemand queue 132 of thethird computing device 112. When theuser selection 128 selects a downloadable media content item, thedownload device 114 may automatically place the selected media content item in adownload queue 134 of thedownload device 114. In a particular embodiment, the download device may be a personal computing device or a STB device. - In operation, the
sender 116 may access theEPG 108 at thefirst computing device 102. Thesender 116 may identify recommended media content items by selecting media content items using theEPG 108. Further, thesender 116 may select one or more addresses from theaddress data 154, such as an address associated with therecipient 136. Thefirst computing device 102 may send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 associated with the selectedrecipients 152. The information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 may be received at thesecond computing device 110 when thesecond computing device 110 is associated with an address of the selected addresses 120. Thesecond computing device 110 may display the displayed recommendedmedia content 124 at thedisplay device 122. Therecipient 136 may provide theuser selection 128, selecting at least one item of media content from the displayed recommendedmedia content 124. For example, therecipient 136 may select program A from displayed recommendedmedia content 124. Thesecond computing device 110 may receive theuser selection 128 and automatically schedule at least one item of media content from the displayed recommendedmedia content 124 for recording at thethird computing device 112. For example, thethird computing device 112 may be a media recorder device such as a DVR. The displayed recommendedmedia content 124 may include a user selectable option to select (e.g., accept) all of the recommended media content. For example, when therecipient 136 accepts items from the information identifying the recommendedmedia content items 118, all of the media content of the displayed recommendedmedia content 124 may be automatically scheduled for recording at thethird computing device 112. - The
second computing device 110 may determine whether a selected item of media content is theschedule media content 160, thedownloadable media content 164, or the ondemand media content 162 and perform an appropriate action to provide the selected item of media content for playback. For example, when theuser selection 128 includes a scheduled program from the scheduledmedia content 160, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically schedule recording of the scheduled program at thethird computing device 112. In a particular embodiment, thesecond computing device 110 automatically schedules recording of a scheduled program by accessing theEPG 108. When theuser selection 128 includes the ondemand media content 162, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically place the ondemand media content 162 in an ondemand queue 132 associated with thethird computing device 112. For example, thesecond computing device 110 may send a request to purchase the on demand media content to themedia content server 104, and in response themedia content server 104 may place the ondemand media content 162 in the ondemand items queue 132 associated with thethird computing device 112. When theuser selection 128 includes thedownloadable media content 164, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically schedule thedownloadable media content 164 for download at thedownload device 114. In a particular embodiment, thedownload device 114 is integrated with thethird computing device 112. For example, when the third computing device is a STB, thedownload device 114 may be internal to the STB. In another particular embodiment, thedownload device 114 is a device separate from thethird computing device 112. For example, thethird computing device 112 may be a set-top box device while thedownload device 114 may be a personal computing device. In a particular embodiment, scheduling a download of at least one item of media content at thedownload device 114 includes setting a priority of the item of media content and placing the item of media content in thedownload queue 134 associated with thedownload device 114. In this way, thesecond computing device 110 may perform appropriate actions to make each selected item of media content available to therecipient 136. - When the
user selection 128 conflicts with one or more scheduledrecordings 126 at thethird computing device 112, thesecond computing device 110 may automatically identify a second presentation of a program associated with either the previously scheduledrecording 126 or associated with the selected media content. Thesecond computing device 110 may prompt therecipient 136 to select which of the second presentations to record. For example, the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 may include a program X that is scheduled at the same time as a program A in the scheduledrecordings 112. Thesecond computing device 110 may automatically determine a second presentation of either program X or program A. Thesecond computing device 110 may prompt therecipient 136 to select from among the second alternatives. Thesecond computing device 110 may receive asecond user selection 130 and schedule the second presentation for recording at thethird computing device 112. - Thus, the
sender 116 can efficiently send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to the selected addresses 120 of one or more recipients. For example, a teacher may create the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 and send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 to students. An example of information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 is a list of content item titles. In addition, each of the recipients of the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 may select only those media content items that they wish to view and thesecond computing device 110 performs various actions to automatically make the selected items available. Furthermore, thesecond computing device 110 automatically determines whether a particular media content item is scheduledmedia content 160,downloadable media content 164, or ondemand media content 164 and then takes an appropriate action to make the particular media content available to therecipient 136. In this way, therecipient 136 can automatically obtain multiple media content items from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 118 via a single selection. - Referring to
FIG. 2 , a block diagram of a second particular embodiment of a system to send information identifying recommended media content items is depicted and generally designated 200. Thesystem 200 includes afirst computing device 202 coupled to amedia content server 204 via anetwork 206. In the illustrated embodiment, an electronic program guide (EPG) 208, asecond computing device 210, athird computing device 212, and arecommendation server 270 are also coupled to thenetwork 206. - The
media content server 204 is operable to provide media content to various devices, such as thefirst computing device 202, thesecond computing device 210, and thethird computing device 212. Themedia content server 204 may include various types of media content, such as scheduled media content, on demand media content, downloadable media content, other media content, or any combination thereof. Although themedia content server 204 is illustrated as a single server inFIG. 2 , in various embodiments themedia content server 204 may include a plurality of servers. For example, the plurality of servers may be a part of a particular service provider network, or each server may belong to a separate service provider network. - The
recommendation server 270 is operable to sendfirst data 280 representing a first graphical user interface (GUI) 242 to thefirst computing device 202 and is operable to sendsecond data 282 representing asecond GUI 224 to thesecond computing device 210. In the embodiment illustrated, therecommendation server 270 includes aprocessor 272, an input/output interface 274, and amemory 276. Thememory 276 includesoperational instructions 278 that are executable by theprocessor 272 to perform the various functions of therecommendation server 270. - The
first computing device 202 is operable to receive thefirst data 280 from therecommendation server 270 and to display thefirst GUI 242 at afirst display device 240. Thefirst GUI 242 may include one or more of a scheduled program listing 244, a video ondemand listing 246, and adownloadable content listing 248. In a particular embodiment, the functions described as being performed by thefirst computing device 202 are performed by a combination of thefirst computing device 202 and therecommendation server 270. For example, thefirst computing device 202 may access theEPG 208 via therecommendation server 270. - A
sender 216 may use thefirst GUI 242 to create information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218. For example, thesender 216 may create the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 by accessing theEPG 208 via thefirst GUI 242. Thefirst computing device 202 is operable to receive, via thefirst GUI 242, a selection of selectedmedia content 250 to create the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218. Thefirst computing device 202 is further operable to receive, via thefirst GUI 242, a selection of selectedrecipients 252 and to identify the selected addresses 220 associated with the selectedrecipients 252. Thefirst computing device 202 is further operable to send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 to the selected addresses 220. Thefirst computing device 202 may be a mobile telephony device, a personal computing device, a personal digital assistant (PDA) device, a set-top box (STB) device, or any other computing device. - The
second computing device 210 is operable to receivesecond data 282 from therecommendation server 270 and to display thesecond GUI 224 at asecond display device 222. For example, thesecond GUI 224 may display the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 at thesecond display device 224. Thesecond computing device 210 may be associated with one of the selected addresses 220 associated with the selectedrecipients 252. In a particular embodiment, the functions described as being performed by thesecond computing device 210 are performed by a combination of thesecond computing device 210 and therecommendation server 270. For example, thesecond computing device 210 may send a message to therecommendation server 270 requesting therecommendation server 270 to provide a selected media content items for download. Thesecond computing device 210 may enable arecipient 236 to select, via thesecond GUI 224, at least one item of media content from thesecond GUI 224. Thesecond computing device 210 is operable to receive auser selection 228 via thesecond GUI 224. Theuser selection 228 may select at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218. After receiving theuser selection 228, thesecond computing device 210 is operable to automatically schedule recording of the selected item of media content at thethird computing device 212. Thethird computing device 212 may be a personal computing device, a STB device, a DVR device, or other computing device. In a particular embodiment, thethird computing device 212 is integrated with thesecond computing device 210. In another particular embodiment, thethird computing device 212 is a different device that is independent of thesecond computing device 210. Theuser selection 228 may select one or more of the items of recommended media content displayed at thesecond GUI 224. In a particular embodiment, theuser selection 228 may select all of the recommended media content via a “select all” selection. - The
second computing device 210 is further operable to automatically determine whether scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at thethird computing device 212. Thesecond computing device 210 is operable to automatically identify a second presentation of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording or the at least one item of media content. Thesecond computing device 210 is further operable to automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at thethird computing device 212. For example, the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 may identify a program X that is scheduled for recording at the same time that a program A is scheduled for recording. Thesecond computing device 210 may automatically identify a second presentation of either program X or program A and automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at thethird computing device 112. - The
second computing device 210 may automatically perform various actions to make each selected item of media content available to therecipient 236. For example, thesecond computing device 210 may automatically schedule recording of at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 at thethird computing device 212 when the selected media content includes a scheduled program. Thesecond computing device 210 may automatically identify at least one item of media content in anactive content list 232 associated with thethird computing device 212 when the selected item of media content includes on demand media content. Thesecond computing device 210 may automatically schedule download of the selected item of media content at thethird computing device 212 when the selected item of media content includes downloadable media content. For example, the selected media content item may be automatically placed in adownload queue 234 associated with thethird computing device 212. - In operation, the
recommendation server 270 may send thefirst data 280 to thefirst computing device 202 for display at thefirst display device 240. Thefirst computing device 202 may display, via thefirst GUI 242, the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 and selectedaddresses 220 of selectedrecipients 252. Thefirst computing device 202 may send the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 to the selected addresses 220. - A computing device associated with each of the selected addresses 220 may receive the information identifying recommended
media content items 218. For example, the selected addresses 220 may include an address associated with thesecond computing device 210. Thesecond computing device 210 may receive the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 and display the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 via thesecond GUI 224, at thesecond display device 222. Thesecond computing device 210 may, via thesecond GUI 224, receive auser selection 228 of one or more of the items of the recommendedmedia content 224. Thesecond computing device 210 may automatically make the selected one or more items of media content available for playback at thethird computing device 212. For example, when the item of media content is a scheduled program, the item of media content may be automatically scheduled for recording at thethird computing device 212. When the selected item of media content includes on demand media content, the selected item of media content may be automatically identified in theactive content list 232 associated with thethird computing device 212. When the item of media content includes downloadable media content, the downloadable media content may be automatically scheduled for download at thethird computing device 212. For example, the downloadable media content may be placed in thedownload queue 234 associated with thethird computing device 212. - Thus, the
recipient 236 may receive the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218, select one or more items of the recommended media content, and have the selections automatically made available for playback at thethird computing device 212. Therecipient 236 does not have to determine whether a particular item from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 is downloadable media content or video-on demand media content or scheduled media content. Instead, thesecond computing device 210 determines how each selected item of media content may be obtained for viewing and automatically schedules recording of scheduled programs, automatically places on demand items in theactive content list 232, and automatically places downloadable media content items in thedownload queue 234. By receiving and performing various actions after receiving theuser selection 228, thesecond computing device 210 makes selected items from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 available to therecipient 236. In this way, the amount of effort required to make each selected item of media content available to therecipient 236 is reduced. -
FIG. 3 is a flow diagram of a first particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items. The method may be performed by a computing device, such as thefirst computing device 102 ofFIG. 1 , thefirst computing device 202 ofFIG. 2 , or therecommendation server 270 ofFIG. 2 . - The method begins by accessing an electronic program guide (EPG) at a computing device, at 302. Moving to 304, recommended media content items are identified using the EPG. Advancing to 306, an address of one or more recipients is selected. Proceeding to 308, information identifying the recommended media content is sent to the selected addresses. For example, in
FIG. 1 , thesender 116 may access theEPG 108 via thefirst computing device 102 to create the recommendedmedia content items 118. Thesender 116 may use thefirst computing device 102 to select selectedrecipients 152 and send the recommendedmedia content items 118 to the selected addresses 120. The method ends at 310. - Thus, a sender can access an EPG to easily identify recommended media content items from scheduled programs, on demand media content, and downloadable media content, and can send information identifying the recommended media content to one or more recipients.
-
FIG. 4 is a flow diagram of a second particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items. The method may be performed by thesecond computing device 110 ofFIG. 1 , thesecond computing device 210 ofFIG. 2 , or therecommendation server 270 ofFIG. 2 . - The method begins by receiving information identifying recommended media content items at a computing device, at 402. Moving to 404, a user selection is received selecting at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items. Advancing to 406, when the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, the at least one item of media content is automatically placed in an on demand queue. Proceeding to 408, when the at least one item of media content includes downloadable media content, the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled for download at a media download device. Moving to 410, when the at least one item of media content is a scheduled program, recording of the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled at a media recorder in response to the user selection. For example, in
FIG. 2 , thesecond computing device 210 may receive the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218, receive theuser selection 228 selecting at least one item of media content from the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218, and make the at least one item of media content available to therecipient 236. - Advancing to 412, a determination may be made whether scheduling a recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the media recorder device. Proceeding to 414, a second presentation of one of the programs associated with the previously scheduled recording and the at least one item of media content may be automatically identified. Advancing to 416, a second user selection may be received indicating that the second presentation should be scheduled for recording. Continuing to 418, the second presentation may be scheduled for recording at the media recorder. The method ends at 420. Thus, a recipient can select at least one item of media content from information identifying recommended media content items and have the selected at least one item of media content automatically made available for viewing.
-
FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of a third particular embodiment of a method to send information identifying recommended media content items. The method may be performed by thefirst computing device 102 ofFIG. 1 , thesecond computing device 110 ofFIG. 1 , thefirst computing device 202 ofFIG. 2 , thesecond computing device 210 ofFIG. 2 , or therecommendation server 270 ofFIG. 2 . - The method begins by sending a first graphical user interface (GUI) to a first computing device, at 502. The first GUI may be used to identify recommended media content items. The first GUI may enable access to an electronic program guide (EPG). Moving to 504, selections identifying recommended media content items are received via the first GUI. Moving to 506, addresses of recipients are received via the first GUI. Advancing to 508, information identifying the recommended media content items is sent to the addresses of the recipients. For example, in
FIG. 2 , therecommendation server 270 sends thefirst GUI 242 to thefirst computing device 202. Therecommendation server 270 may receive the information identifying recommendedmedia content items 218 and the selected addresses 220 via thefirst GUI 242. - Proceeding to 510, a second GUI is sent to a second computing device. The second GUI enables selection of at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items. Proceeding to 512, a user selection may be received via the second GUI selecting the at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items. Proceeding to 514, a determination may be made whether the at least one item of media content is available as a scheduled program, an on demand program, or via a download. When the at least one item of media content includes a scheduled program, at 514, data may be sent to a third computing device that causes the third computing device to schedule recording of the at least one item of media content, at 516. Proceeding to 518, before sending the data, a determination may be made whether scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the third computing device. Moving to 520, when scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with the previously scheduled recording, a second presentation of one of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording and the at least one item of media content may be identified. The data sent to the third computing device may cause the third computing device to automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device. The method ends at 526.
- When the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, at 514, the at least one item of media content may be automatically identified in an active content list associated with the third computing device, at 522. The method ends at 526.
- When the at least one item of media content includes downloadable media content, at 514, a download of the at least one item of media content may be automatically scheduled at the third computing device, at 524. The method then ends at 526.
- Referring to
FIG. 6 , an illustrative embodiment of a general computer system is shown and is designated 600. Thecomputer system 600 includes a set of instructions that can be executed to cause thecomputer system 600 to perform any one or more of the methods or computer based functions disclosed herein. Thecomputer system 600, or any portion thereof, may be connected, e.g., using a network, to other computer systems or peripheral devices. - In a networked deployment, the
computer system 600 may operate in the capacity of a computing device, such as thefirst computing device 102 ofFIG. 1 , thesecond computing device 110 ofFIG. 1 , thethird computing device 112 ofFIG. 1 , thedownload device 114 ofFIG. 1 , thefirst computing device 202 ofFIG. 2 , thesecond computing device 210 ofFIG. 2 , thethird computing device 212 ofFIG. 2 , and therecommendation server 270 ofFIG. 2 . Thecomputer system 600 can also be implemented as or incorporated into various devices, such as a personal computer (PC), a tablet PC, a personal digital assistant (PDA), a mobile device, a palmtop computer, a laptop computer, a desktop computer, a communications device, a network router, a wireless telephone, a land-line telephone, a control system, a camera, a scanner, a facsimile machine, a printer, a pager, a personal trusted device, a web appliance, a switch or bridge, or any other machine capable of executing a set of instructions (sequential or otherwise) that specify actions to be taken by that machine. In a particular embodiment, thecomputer system 600 can be implemented using electronic devices that provide voice, video or data communication. Further, while asingle computer system 600 is illustrated, the term “system” shall also be taken to include any collection of systems or sub-systems that individually or jointly execute a set, or multiple sets, of instructions to perform one or more computer functions. - As illustrated in
FIG. 6 , thecomputer system 600 may include aprocessor 602, e.g., a central processing unit (CPU), a graphics-processing unit (GPU), or both. Moreover, thecomputer system 600 can include amain memory 604 and astatic memory 606 that can communicate with each other via abus 608. As shown, thecomputer system 600 may further include avideo display unit 610, such as a liquid crystal display (LCD), a cathode ray tube (CRT) display, an organic light emitting diode (OLED), a flat panel display, a solid-state display, or a projection display. Additionally, thecomputer system 600 may include aninput device 612, such as a keyboard or a remote control, and acursor control device 614, such as a mouse or a remote control. Thecomputer system 600 can also include adisk drive unit 616, asignal generation device 618, such as a speaker, and anetwork interface device 620. - In a particular embodiment, as depicted in
FIG. 6 , thedisk drive unit 616 may include a computer-readable medium 622 in which one or more sets ofinstructions 624, e.g. software, can be embedded. Further, theinstructions 624 may embody one or more of the methods or logic as described herein. In a particular embodiment, theinstructions 624 may reside completely, or at least partially, within themain memory 604, thestatic memory 606, and/or within theprocessor 602 during execution by thecomputer system 600. Themain memory 604 and theprocessor 602 also may include computer-readable media. - In an alternative embodiment, dedicated hardware implementations, such as application specific integrated circuits, programmable logic arrays and other hardware devices, can be constructed to implement one or more of the methods described herein. Applications that may include the apparatus and systems of various embodiments can broadly include a variety of electronic and computer systems. One or more embodiments described herein may implement functions using two or more specific interconnected hardware modules or devices with related control and data signals that can be communicated between and through the modules, or as portions of an application-specific integrated circuit. Accordingly, the present system encompasses software, firmware, and hardware implementations.
- In accordance with various embodiments of the present disclosure, the methods described herein may be implemented by software programs executable by a computer system. Further, in an exemplary, non-limited embodiment, implementations can include distributed processing, component/object distributed processing, and parallel processing. Alternatively, virtual computer system processing can be constructed to implement one or more of the methods or functionality as described herein.
- The present disclosure contemplates a computer-readable medium that includes
instructions 624 or receives and executesinstructions 624 so that a device connected to anetwork 626 can communicate voice, video or data over thenetwork 626. Further, theinstructions 624 may be transmitted or received over thenetwork 626 via thenetwork interface device 620. - While the computer-readable medium is shown to be a single medium, the term “computer-readable medium” includes a single medium or multiple media, such as a centralized or distributed database, and/or associated caches and servers that store one or more sets of instructions. The term “computer-readable medium” shall also include any medium that is capable of storing, or encoding a set of instructions for execution by a processor or that cause a computer system to perform any one or more of the methods or operations disclosed herein.
- In a particular non-limiting, exemplary embodiment, the computer-readable medium can include a solid-state memory such as a memory card or other package that houses one or more non-volatile read-only memories. Further, the computer-readable medium can be a random access memory or other volatile re-writable memory. Additionally, the computer-readable medium can include a magneto-optical or optical medium, such as a disk or tapes or other storage device to capture carrier wave signals such as a signal communicated over a transmission medium. A digital file attachment to an email or other self-contained information archive or set of archives may be considered equivalent to a tangible storage medium. Accordingly, the disclosure is considered to include any one or more of a computer-readable storage medium and other equivalents and successor media, in which data or instructions may be stored. It should also be noted that software that implements the disclosed methods may optionally be stored on a tangible storage medium, such as: a magnetic medium, such as a disk or tape; a magneto-optical or optical medium, such as a disk; or a solid state medium, such as a memory card or other package that houses one or more read-only (non-volatile) memories, random access memories, or other re-writable (volatile) memories.
- Although the present specification describes components and functions that may be implemented in particular embodiments with reference to particular standards and protocols, the invention is not limited to such standards and protocols. For example, standards for Internet and other packet switched network transmission (e.g., TCP/IP, UDP/IP, HTML, HTTP, MPEG, SMPTE, H.264) represent examples of the state of the art. Such standards are periodically superseded by faster or more efficient equivalents having essentially the same functions. Accordingly, replacement standards and protocols having the same or similar functions as those disclosed herein are considered equivalents thereof.
- The illustrations of the embodiments described herein are intended to provide a general understanding of the structure of the various embodiments. The illustrations are not intended to serve as a complete description of all of the elements and features of apparatus and systems that utilize the structures or methods described herein. Many other embodiments may be apparent to those of skill in the art upon reviewing the disclosure. Other embodiments may be utilized and derived from the disclosure, such that structural and logical substitutions and changes may be made without departing from the scope of the disclosure. Accordingly, the disclosure and the figures are to be regarded as illustrative rather than restrictive.
- One or more embodiments of the disclosure may be referred to herein, individually and/or collectively, by the term “invention” merely for convenience and without intending to voluntarily limit the scope of this application to any particular invention or inventive concept. Moreover, although specific embodiments have been illustrated and described herein, it should be appreciated that any subsequent arrangement designed to achieve the same or similar purpose may be substituted for the specific embodiments shown. This disclosure is intended to cover any and all subsequent adaptations or variations of various embodiments. Combinations of the above embodiments, and other embodiments not specifically described herein, will be apparent to those of skill in the art upon reviewing the description.
- The Abstract of the Disclosure is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. In addition, in the foregoing Detailed Description, various features may be grouped together or described in a single embodiment for the purpose of streamlining the disclosure. This disclosure is not to be interpreted as reflecting an intention that the claimed embodiments require more features than are expressly recited in each claim. Rather, as the following claims reflect, inventive subject matter may be directed to less than all of the features of any of the disclosed embodiments. Thus, the following claims are incorporated into the Detailed Description, with each claim standing on its own as defining separately claimed subject matter.
- The above-disclosed subject matter is to be considered illustrative, and not restrictive, and the appended claims are intended to cover all such modifications, enhancements, and other embodiments, which fall within the scope of the present invention. Thus, to the maximum extent allowed by law, the scope of the present invention is to be determined by the broadest permissible interpretation of the following claims and their equivalents, and shall not be restricted or limited by the foregoing detailed description.
Claims (25)
1. A computer implemented method, comprising:
accessing an electronic program guide (EPG) at a computing device;
identifying recommended media content items using the EPG;
selecting one or more addresses of recipients; and
sending information identifying the recommended media content items to the selected addresses.
2. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items is scheduled for recording at a media recorder device associated with the recipient.
3. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein all of the recommended media content items are scheduled for recording at a media recorder device associated with at least one of the recipients in response to receiving a user selection selecting all items of the recommended media content items.
4. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items is automatically scheduled for download at a media recorder device.
5. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein the computing device comprises a mobile telephony device.
6. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein at least one of the addresses is associated with a mobile telephony device.
7. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein at least one of the addresses is associated with a set-top box device.
8. The computer implemented method of claim 1 , wherein at least one of the addresses comprises an email address.
9. A computer implemented method comprising:
receiving information identifying recommended media content items at a computing device;
receiving a user selection of at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items;
when the at least one item of media content is a scheduled program, automatically scheduling recording of the at least one item of media content at a media recorder device; and
when the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, automatically placing the at least one item of media content in an on demand items queue.
10. The computer implemented method of claim 9 , further comprising automatically scheduling a download of the at least one item of media content at a media download device in response to the user selection when the at least one item of media content includes downloadable media content.
11. The computer implemented method of claim 10 , wherein scheduling the at least one item of media content for download comprises:
setting a priority of the at least one item of media content; and
placing the at least one item of media content in a download queue.
12. The computer implemented method of claim 9 , further comprising:
determining whether scheduling a recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the media recorder device; and
automatically identifying a second presentation of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording or the at least one item of media content.
13. The computer implemented method of claim 12 , further comprising:
receiving a second user selection indicating that the second presentation should be scheduled for recording; and
scheduling the second presentation for recording at the media recorder.
14. The computer implemented method of claim 9 , wherein scheduling a recording of the at least one item of media content comprises accessing an electronic program guide.
15. The computer implemented method of claim 9 , wherein the computing device comprises a set-top box (STB) device.
16. A computer-readable storage medium comprising operational instructions that, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to:
send a first graphical user interface (GUI) to a first computing device, wherein the first GUI enables selection of recommended media content items, and wherein the first GUI enables access to an electronic program guide (EPG);
receive, via the first GUI, selections identifying recommended media content items;
receive, via the first GUI, addresses of recipients; and
send information identifying the recommended media content items to the addresses of the recipients.
17. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 16 , further comprising operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to send a second GUI to a second computing device, wherein the second GUI enables selection of at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items.
18. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 16 , further comprising operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to:
receive, via the second GUI, a user selection of at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items; and
send data to a third computing device, wherein the data causes the third computing device to schedule recording of the at least one item of media content.
19. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 18 , further comprising operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to:
before sending the data, determine whether scheduling a recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with a previously scheduled recording at the third computing device; and
when scheduling the recording of the at least one item of media content would conflict with the previously scheduled recording, identify a second presentation of a program associated with the previously scheduled recording or the at least one item of media content, wherein the data sent to the third computing device causes the third computing device to automatically schedule the second presentation for recording at the third computing device.
20. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 17 , further comprising operational instructions that, when executed by the processor, cause the processor to:
receive, via the second GUI, a user selection selecting all of the recommended media content items;
when the at least one item of media content includes a scheduled program, automatically instruct a third computing device to record at least one item of media content from the recommended media content items;
when the at least one item of media content includes on demand media content, automatically identify the at least one item of media content in an active content list associated with the third computing device; and
when the at least one item of media content includes downloadable media content, automatically instruct the third computing device to schedule download of the at least one item of media content at the third computing device.
21. A system, comprising:
a first computing device, to access an electronic program guide (EPG), to identify recommended media content based on selections from the EPG, and to send information identifying the recommended media content to addresses associated with selected recipients;
wherein the EPG includes data identifying scheduled media content and on demand media content.
22. The system of claim 21 , wherein the first computing device is responsive to a remote control device to enable a user to browse the EPG and to identify the recommended media content by selecting media content items from the EPG.
23. The system of claim 22 , wherein the remote control device is further operable to enable the user to select the recipients from a set of recipients.
24. The system of claim 22 , wherein the remote control device is further operable to enable the user to add a recipient and an address associated with the recipient to the set of recipients.
25. The system of claim 21 , further comprising:
a second computing device associated with one of the addresses to receive the information identifying the recommended media content and to automatically make the media content items associated with the user selection available for playback at a set-top box (STB) device.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/413,822 US20100251299A1 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2009-03-30 | System and Method to Send Information Identifying Reccomended Media Content Items |
| US13/467,310 US9137580B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2012-05-09 | System and method to send information identifying recommended media content items |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/413,822 US20100251299A1 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2009-03-30 | System and Method to Send Information Identifying Reccomended Media Content Items |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/467,310 Division US9137580B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2012-05-09 | System and method to send information identifying recommended media content items |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20100251299A1 true US20100251299A1 (en) | 2010-09-30 |
Family
ID=42785968
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/413,822 Abandoned US20100251299A1 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2009-03-30 | System and Method to Send Information Identifying Reccomended Media Content Items |
| US13/467,310 Active US9137580B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2012-05-09 | System and method to send information identifying recommended media content items |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/467,310 Active US9137580B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2012-05-09 | System and method to send information identifying recommended media content items |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20100251299A1 (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090279847A1 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-12 | Sony Corporation | Program accumulation apparatus, program accumulation reservation method, and program |
| US20110107370A1 (en) * | 2009-11-03 | 2011-05-05 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | System for media program management |
| US20120257583A1 (en) * | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Securus Technologies, Inc. | Distribution of Broadcast Content to Controlled-Environment Facilities |
| US8495699B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2013-07-23 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Distributed content analysis network |
| US8881209B2 (en) * | 2012-10-26 | 2014-11-04 | Mobitv, Inc. | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| US8904421B2 (en) | 2009-06-30 | 2014-12-02 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Shared multimedia experience including user input |
| US20150026746A1 (en) * | 2012-01-24 | 2015-01-22 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Method and IPTV Server for Enabling Playout of One or More Media Objects |
| US20160007058A1 (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2016-01-07 | TCL Research America Inc. | System and method for video program recognition |
| US20160142745A1 (en) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-19 | KBA2 Inc. | Management system to predict signal strength and bit rate |
| EP3160101A4 (en) * | 2014-06-18 | 2018-02-21 | Huizhou TCL Mobile Communication Co., Ltd. | Multi-media resource management method, cloud server and electronic device |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101867800A (en) * | 2009-04-15 | 2010-10-20 | 华为技术有限公司 | Program recommending method, terminal equipment and network system |
| MX338614B (en) * | 2009-09-03 | 2016-04-22 | Opentv Inc | System and method to provide gift media. |
| EP2537334A1 (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2012-12-26 | Thomson Licensing | Automatic clip generation on set top box |
| US10652592B2 (en) | 2017-07-02 | 2020-05-12 | Comigo Ltd. | Named entity disambiguation for providing TV content enrichment |
| US10939146B2 (en) | 2018-01-17 | 2021-03-02 | Comigo Ltd. | Devices, systems and methods for dynamically selecting or generating textual titles for enrichment data of video content items |
Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030005448A1 (en) * | 2001-06-27 | 2003-01-02 | Karin Axelsson | Cross-device sharing of reminders |
| US20050022251A1 (en) * | 2002-07-30 | 2005-01-27 | Kensuke Ohnuma | Information processing system, information processing device and method, recording medium, and program |
| US20050149987A1 (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-07 | Gilles Boccon-Gibod | Television viewing communities |
| US20060109854A1 (en) * | 2004-11-22 | 2006-05-25 | Cancel Ramon C | Systems and methods to share information between digital video recorders |
| US20060161950A1 (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2006-07-20 | Mitsubishi Kabushiki Kaisha | Program recommending apparatus, program recommended apparatus, and program recommending system |
| US20070124795A1 (en) * | 1998-08-26 | 2007-05-31 | United Video Properties Inc. | Television message system |
| US20070220554A1 (en) * | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-20 | Tivo Inc. | Recommended recording and downloading guides |
| US20080098436A1 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2008-04-24 | Sbc Knowledge Ventures, L.P. | Top recording events list for media device |
| US20090094643A1 (en) * | 2007-01-23 | 2009-04-09 | Cox Communications, Inc. | Providing a Customized User Interface |
| US20090119715A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-07 | Microsoft Corporation | Alternate source conflict resolution |
| US20100064325A1 (en) * | 2008-08-26 | 2010-03-11 | Alex Fishman | Community-based recommendation engine |
| US20100229212A1 (en) * | 2008-02-04 | 2010-09-09 | Jian Liu | Method and terminal for sharing information in iptv service system |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7603684B1 (en) * | 1998-05-19 | 2009-10-13 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Program guide system with video-on-demand browsing |
-
2009
- 2009-03-30 US US12/413,822 patent/US20100251299A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2012
- 2012-05-09 US US13/467,310 patent/US9137580B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20070124795A1 (en) * | 1998-08-26 | 2007-05-31 | United Video Properties Inc. | Television message system |
| US20030005448A1 (en) * | 2001-06-27 | 2003-01-02 | Karin Axelsson | Cross-device sharing of reminders |
| US20050022251A1 (en) * | 2002-07-30 | 2005-01-27 | Kensuke Ohnuma | Information processing system, information processing device and method, recording medium, and program |
| US20050149987A1 (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-07 | Gilles Boccon-Gibod | Television viewing communities |
| US20060161950A1 (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2006-07-20 | Mitsubishi Kabushiki Kaisha | Program recommending apparatus, program recommended apparatus, and program recommending system |
| US20060109854A1 (en) * | 2004-11-22 | 2006-05-25 | Cancel Ramon C | Systems and methods to share information between digital video recorders |
| US20070220554A1 (en) * | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-20 | Tivo Inc. | Recommended recording and downloading guides |
| US20080098436A1 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2008-04-24 | Sbc Knowledge Ventures, L.P. | Top recording events list for media device |
| US20090094643A1 (en) * | 2007-01-23 | 2009-04-09 | Cox Communications, Inc. | Providing a Customized User Interface |
| US20090119715A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-07 | Microsoft Corporation | Alternate source conflict resolution |
| US20100229212A1 (en) * | 2008-02-04 | 2010-09-09 | Jian Liu | Method and terminal for sharing information in iptv service system |
| US20100064325A1 (en) * | 2008-08-26 | 2010-03-11 | Alex Fishman | Community-based recommendation engine |
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090279847A1 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-12 | Sony Corporation | Program accumulation apparatus, program accumulation reservation method, and program |
| US8781303B2 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2014-07-15 | Sony Corporation | Program accumulation apparatus, program accumulation reservation method, and program |
| US8495699B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2013-07-23 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Distributed content analysis network |
| US9843843B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2017-12-12 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Distributed content analysis network |
| US9078019B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2015-07-07 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Distributed content analysis network |
| US10112109B2 (en) | 2009-06-30 | 2018-10-30 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Shared multimedia experience including user input |
| US8904421B2 (en) | 2009-06-30 | 2014-12-02 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Shared multimedia experience including user input |
| US20110107370A1 (en) * | 2009-11-03 | 2011-05-05 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | System for media program management |
| US9794611B2 (en) | 2009-11-03 | 2017-10-17 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | System for media program management |
| US9462318B2 (en) * | 2009-11-03 | 2016-10-04 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | System for media program management |
| US9332014B2 (en) * | 2011-04-05 | 2016-05-03 | Securus Technologies, Inc. | Distribution of broadcast content to controlled-environment facilities |
| US9866607B2 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2018-01-09 | Securus Technologies, Inc. | Distribution of broadcast content to controlled-environment facilities |
| US20120257583A1 (en) * | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Securus Technologies, Inc. | Distribution of Broadcast Content to Controlled-Environment Facilities |
| US9544630B2 (en) * | 2012-01-24 | 2017-01-10 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Method and IPTV server for enabling playout of one or more media objects |
| US20150026746A1 (en) * | 2012-01-24 | 2015-01-22 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Method and IPTV Server for Enabling Playout of One or More Media Objects |
| US11567973B2 (en) | 2012-10-26 | 2023-01-31 | Tivo Corporation | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| US10885063B2 (en) | 2012-10-26 | 2021-01-05 | Mobitv, Inc. | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| US11960509B2 (en) | 2012-10-26 | 2024-04-16 | Tivo Corporation | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| US8881209B2 (en) * | 2012-10-26 | 2014-11-04 | Mobitv, Inc. | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| US10095767B2 (en) | 2012-10-26 | 2018-10-09 | Mobitv, Inc. | Feedback loop content recommendation |
| EP3160101A4 (en) * | 2014-06-18 | 2018-02-21 | Huizhou TCL Mobile Communication Co., Ltd. | Multi-media resource management method, cloud server and electronic device |
| US10708330B2 (en) | 2014-06-18 | 2020-07-07 | Huizhou Tcl Mobile Communication Co., Ltd | Multimedia resource management method, cloud server and electronic apparatus |
| US9432702B2 (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2016-08-30 | TCL Research America Inc. | System and method for video program recognition |
| US20160007058A1 (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2016-01-07 | TCL Research America Inc. | System and method for video program recognition |
| US20160142745A1 (en) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-19 | KBA2 Inc. | Management system to predict signal strength and bit rate |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9137580B2 (en) | 2015-09-15 |
| US20120222073A1 (en) | 2012-08-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9137580B2 (en) | System and method to send information identifying recommended media content items | |
| US8281337B2 (en) | System and method to display media content and an interactive display | |
| US8705944B2 (en) | System and method of recording media content | |
| US7899305B2 (en) | Digital video recorder having skip-to-interval-from-end button | |
| US10939177B2 (en) | System for presenting media content | |
| US8904414B2 (en) | System and method of delivering video content | |
| US8595757B2 (en) | System and method of sharing media content | |
| US8949914B2 (en) | System and method of delivering video content | |
| US8621529B2 (en) | System and method of receiving over-the-air television content | |
| US10187695B2 (en) | Notification of media content of interest | |
| US9137490B2 (en) | System and method for video transmission scheduling | |
| US20090193482A1 (en) | System and Method of Scheduling Recording of Media Content | |
| WO2008054562A2 (en) | System and method of media selection and media content distribution | |
| US20100031296A1 (en) | System and Method for Using Short Message Service Text Messaging to Schedule a Recording of a Television Program | |
| JP2007028589A (en) | System and method for transmitting photographs from set top box | |
| US9961405B2 (en) | Systems and methods of processing programming wish list data | |
| US8209719B2 (en) | System for presenting status information associated with a media content processor | |
| US20110072456A1 (en) | System and Method for Substituting Broadband Delivered Advertisements for Expired Advertisements | |
| US8555320B2 (en) | System and method to record media content | |
| US20090010618A1 (en) | System and method of storing video content | |
| US8826331B2 (en) | Systems and methods to schedule recording of media content | |
| US20100131998A1 (en) | Multimedia Frame Capture | |
| US9172902B2 (en) | Media recorder that selects when to record media content that is available at multiple times | |
| US20090282435A1 (en) | Video Program Sequenced Output | |
| US20140112635A1 (en) | System and Method for Recording Clips of Media Content |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: AT&T INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY I, L.P., NEVADA Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SCOTT, CHARLES;WHITE, SCOTT;MUKERJI, ANKUR;SIGNING DATES FROM 20090325 TO 20090327;REEL/FRAME:022468/0036 |
|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |