US20050053361A1 - Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, apparatus for reproducing AV data in interactive mode - Google Patents
Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, apparatus for reproducing AV data in interactive mode Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20050053361A1 US20050053361A1 US10/902,274 US90227404A US2005053361A1 US 20050053361 A1 US20050053361 A1 US 20050053361A1 US 90227404 A US90227404 A US 90227404A US 2005053361 A1 US2005053361 A1 US 2005053361A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- enhanced navigation
- profile information
- data
- audio
- reproducing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 130
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/102—Programmed access in sequence to addressed parts of tracks of operating record carriers
- G11B27/105—Programmed access in sequence to addressed parts of tracks of operating record carriers of operating discs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/19—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier
- G11B27/28—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording
- G11B27/30—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording on the same track as the main recording
- G11B27/3027—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording on the same track as the main recording used signal is digitally coded
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/19—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier
- G11B27/28—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording
- G11B27/32—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording on separate auxiliary tracks of the same or an auxiliary record carrier
- G11B27/322—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording on separate auxiliary tracks of the same or an auxiliary record carrier used signal is digitally coded
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/19—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier
- G11B27/28—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording
- G11B27/32—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel by using information detectable on the record carrier by using information signals recorded by the same method as the main recording on separate auxiliary tracks of the same or an auxiliary record carrier
- G11B27/327—Table of contents
- G11B27/329—Table of contents on a disc [VTOC]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B27/00—Editing; Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Monitoring; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/10—Indexing; Addressing; Timing or synchronising; Measuring tape travel
- G11B27/34—Indicating arrangements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11B—INFORMATION STORAGE BASED ON RELATIVE MOVEMENT BETWEEN RECORD CARRIER AND TRANSDUCER
- G11B2220/00—Record carriers by type
- G11B2220/20—Disc-shaped record carriers
- G11B2220/25—Disc-shaped record carriers characterised in that the disc is based on a specific recording technology
- G11B2220/2537—Optical discs
- G11B2220/2562—DVDs [digital versatile discs]; Digital video discs; MMCDs; HDCDs
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus and method for reproducing audio/video (AV) data in interactive mode, and an information storage medium therefor.
- AV audio/video
- Interactive DVDs that can be reproduced in an interactive mode using a conventional personal computer (PC).
- An interactive DVD refers to a DVD in which interactive data is recoded in addition to recorded DVD-Video data.
- Interactive DVDs are reproduced in either of two modes. One mode is a video mode in which only DVD-Video data is reproduced, such as with an ordinary DVD.
- the other mode is an interactive mode in which DVD-Video data is reproduced together with a markup document and is displayed through a display window of the markup document. If the interactive mode is selected by a user, a web browser embedded in the PC parses and displays a markup document recorded on the interactive DVD. In the display window defined by the markup document, DVD-Video data selected by the user is displayed.
- the DVD-Video data is a film
- the film is reproduced in the display window of the markup document and in the remaining part the script, synopsis, photos of actors, and other related additional information of the film can be displayed. Additional information is also displayed in synchronism with a title (AV data). For example, when an actor is displayed on an AV screen, interactive data containing career information on the actor is reproduced and displayed.
- Interactive data includes markup documents written in markup languages, script codes manufactured using files inside the markup documents or separate files and linked to the markup documents, audio files, animation files, and image files linked to the markup documents and reproduced together with the markup documents.
- a variety of functions can be added to a user interface in interactive mode.
- the range of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode in each reproducing apparatus can be varied.
- the invention provides an information storage medium having a data structure for being reproduced adaptively in a variety of reproducing apparatuses having different ranges of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in an interactive mode, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode therefor.
- the invention also provides an information storage medium having a data structure having a high compatibility, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode therefor.
- an information storage medium storing interactive data for reproducing audio/video (AV) data in an interactive mode, wherein the interactive data is displayed together with an AV screen obtained from the AV data and provides additional information related to the AV screen; and profile information indicating a version of the interactive data.
- AV audio/video
- the interactive data may include a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected, and the profile information may be recorded in the startup file.
- the profile information may be referred to so that interactive data that can be reproduced by a reproducing apparatus for reproducing the AV data in the interactive mode is selected.
- an information storage medium storing a plurality of ENAV applications manufactured with a plurality of versions so that AV data is reproduced in an interactive mode; and profile information that is referred to so that one is selected from the plurality of ENAV applications.
- the profile information may be recorded using an element for linking loading information file contained in an ENAV application corresponding to a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected.
- the loading information file may indicate position information of ENAV files belonging to a corresponding ENAV application.
- an apparatus for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode includes an AV reproducing engine which decodes AV data; and an ENAV engine which has player profile information indicating a version of a supportable ENAV application and interprets and executes an ENAV application selected by referring to the player profile information so that the AV data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
- the player profile information may be stored as a system parameter.
- a method for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode includes reading profile information indicating a version of interactive data; selecting and reading the interactive data manufactured with a version that can be supported by a reproducing apparatus, by referring to the read profile information; and interpreting and executing the read interactive data.
- the reading profile information may include opening a startup file that is initially read when interactive mode is selected, and reading the profile information.
- the reading profile information may include reading the profile information from the startup file recorded using an element for linking loading information file contained in a corresponding ENAV application or reading profile information indicating versions of a plurality of ENAV applications manufactured with a plurality of versions so that AV data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
- the selecting and reading the interactive data may include reading a version of an ENAV application that can be supported by the reproducing apparatus, from player profile information stored as a system parameter or reading ENAV files belonging to the ENAV application by referring to the loading information file indicating position information of ENAV files belonging to a corresponding to an ENAV application.
- FIG. 1 schematically shows a structure of a reproducing system according to an embodiment of the invention
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an embodiment of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention.
- FIG. 3 schematically shows a volume space of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a directory structure of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention.
- FIG. 5 shows the relation between AV data recorded on an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram of a reproducing apparatus according to an embodiment of the invention.
- FIG. 7 is an example of a startup file startup.mls according to an embodiment of the invention.
- FIG. 8 shows a system parameter table in which profile information is recorded, according to an embodiment of the invention.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a data structure of profile information recorded as a system parameter of FIG. 8 ;
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a method for reproducing AV data in interactive mode according to an embodiment of the invention.
- interactive data refers to data that is needed in reproducing audio/video data AV in an interactive mode.
- Interactive data includes markup documents written in markup languages and/or script codes, script code files linked to the markup documents or separately provided, program files, audio files, animation files, and image files which are resource files linked to the markup documents and displayed together with the markup documents.
- the interactive data serves as an application program that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode and simultaneously serves as additional contents provided together with AV data.
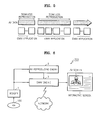
- FIG. 1 schematically shows a structure of a reproducing system according to an embodiment of the invention.
- the reproducing system includes an Enhanced Audio/video (ENAV) disc 100 that is an information storage medium for supporting an interactive mode according to a reproducing apparatus 200 , a displaydevice 300 , and a controller 400 that is a user input apparatus.
- the controller 400 receives a control command from the user and transmits the command to the reproducing apparatus 200 .
- the reproducing apparatus 200 reproduces AV data recorded on the ENAV disc 100 in the interactive mode.
- the display device 300 may be a television and the controller 400 may be a remote controller.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 If the ENAV disc 100 is placed on a DVD drive provided to the reproducing apparatus 200 and the user selects the interactive mode, the reproducing apparatus 200 reproduces corresponding AV data in the interactive mode and transmits the data to the display device 300 . On the display device 300 , an interactive screen and an AV screen embedded in the interactive screen obtained from the interactive data is displayed together.
- Interactive mode refers to a mode in which AV data is displayed together with interactive data.
- AV data is displayed in a display window defined in a markup document such that an AV screen is displayed embedded in an interactive screen.
- the AV screen may be a screen displayed on the display device 300 by reproducing DVD-Video data recorded on the ENAV disc 100 using the reproducing apparatus 200 , and the interactive screen indicates a screen displayed on the TV 300 after the interactive data recorded on the ENAV disc 100 is interpreted and executed using the reproducing apparatus 200 .
- Video mode is a mode in which AV data is reproduced such that only an AV screen obtained by reproducing corresponding AV data is displayed.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 may support both the interactive mode and the video mode.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 can receive/transmit AV data and/or interactive data from/to a network or an Internet connection.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 has a system parameter table in which system parameters SPRMs are set, and the system parameter table has player profile information.
- the player profile information indicates the range of interactive data supported by the reproducing apparatus 200 .
- the player profile information is the same as version information of interactive data supported by the reproducing apparatus 200 .
- the version of interactive data may be, for example, a version of document type definition (DTD) of markup languages used to make ENAV files, a version of program languages used to make ENAV files, a version of languages used to implement one ENAV application or a version of specifications in which restriction conditions of a variety of resource files linked to markup documents.
- DTD document type definition
- Profile information indicates whether a version of stored interactive data is also recorded on the ENAV disc 100 .
- the meaning of profile information is the same as the meaning of player profile information, except that, unlike the player profile information, the profile information is recorded on the ENAV disc 100 and indicates corresponding interactive data.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 reads the profile information recorded on the ENAV disc 100 , compares the profile information with its own player profile information as a system parameter and reproduces AV data in the interactive mode using interactive data selected according to a comparison result.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an ENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention.
- interactive data is recorded on the ENAV disc 100 to correspond to profile information.
- interactive data # 1 corresponding to profile information # 1 is recorded on the ENAV disc 100
- interactive data # 2 corresponding to profile information # 2 is recorded on the ENAV disc 100
- interactive data #n corresponding to profile information #n is recorded on the ENAV disc 100 (where n is an integer number).
- the profile information # 1 , # 2 , . . . , #n are recorded on the ENAV disc 100 separately with the interactive data # 1 , # 2 , . . . , and #n and may be linked to the interactive data # 1 , # 2 , . . . , and #n or included as a part of the interactive data # 1 , # 2 , . . . , and #n.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 supports all of the interactive data # 1 , # 2 , . . . , and #n.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 reproduces the interactive data # 1 .
- the reproducing apparatus 200 can reproduce the interactive data # 2 and the interactive data # 1 , selectively.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 can set the interactive data # 2 to be reproduced as default.
- FIG. 3 schematically shows a volume space of the ENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention.
- the volume space of the ENAV disc 100 comprises a volume and file structure region in which information on volume and file is recorded, a DVD-Video data region in which AV data, i.e., a video title is recorded as a DVD-Video format, an ENAV file region in which ENAV files for supporting an interactive mode are recorded, and an other data region.
- Video_ts.ifo includes reproduction control information for the entire video title recorded on the ENAV disc 100
- vts — 01 — 0.ifo includes reproduction control information for a first video title
- vts — 01 — 0.vob, vts — 01 — 1.vob, etc. which are AV data for constituting a video title, are recorded in the DVD-Video data region.
- Vts — 01 — 0.vob, vts — 01 — 1.vob, and so on are video titles, i.e., video objects.
- Vobu in which a navigation pack, a video pack, and an audio pack are packed, is included in each vob.
- a detailed configuration thereof is described in a DVD-Video standard ‘DVD-Video for Read Only Memory Disc 1.0’.
- An ENAV application comprised of a plurality of ENAV files is stored in the ENAV file region.
- a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected, and a markup document corresponding to a selected video title are recorded as ENAV files.
- the interactive data is recorded as a plurality of ENAV files.
- the ENAV files are referred to as markup documents, script code files, program files, style sheets for defining styles of markup documents, audio files, animation files, and image files which are resource files linked to the markup documents and displayed together with the markup documents, as previously described.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a directory structure of the ENAV disc according to an aspect of the invention.
- a root directory includes a DVD video directory video_ts and an ENAV directory DVD_ENAV in which ENAV data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode is recorded.
- the data described with reference to FIG. 2 that is, video_ts.ifo, vts — 01 — 0.ifo, vts — 01 — 0.vob, vts — 01 — 1.vob, etc., are stored in the DVD video directory video_ts.
- Data described with reference to FIG. 2 that is, a startup file startup.mls and other ENAV files are stored in the ENAV directory DVD_ENAV.
- FIG. 5 shows the relation between AV data recorded on the ENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention.
- each ENAV application corresponds to AV data of which there is seamless reproduction.
- Each ENAV application is a set of a plurality of ENAV files.
- a corresponding ENAV application is buffered before AV data of the corresponding ENAV application is reproduced in an interactive mode.
- an ENAV application corresponding to AV data is buffered prior to reproducing the AV data in the interactive mode.
- Each ENAV application contains one loading information file. Position information on ENAV files that are needed in reproducing corresponding AV data in the interactive mode is recorded in the loading information file.
- the position information on the ENAV files contains position information on ENAV files that should be buffered before a corresponding ENAV application is launched, that is, position information on ENAV files that should be preloaded.
- Postloading refers to a buffering of a predetermined ENAV file after a corresponding ENAV application is launched. Not every ENAV file is required to be postloaded. When there is the need for postloading, position information on an ENAV file that should be postloaded is recorded in the loading information file.
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram of a reproducing apparatus 200 according to an aspect of the invention.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 comprises a reader 1 , an AV reproducing engine 2 , and an ENAV engine 3 .
- the reader 1 reads AV data, i.e., DVD-Video data and ENAV files, recorded on the ENAV disc 100 in response to a control signal generated from the ENAV engine 3 .
- AV data i.e., DVD-Video data and ENAV files
- the AV reproducing engine 2 reproduces AV data read by the reader 2 .
- AV data is recorded as DVD-Video data; therefore, the AV reproducing engine 2 is used as a DVD-Video reproducing engine to reproduce DVD-Video data.
- the AV reproducing engine 2 communicates with the ENAV engine 3 through an application program interface (API). For example, a property indicating the operating state of the AV reproducing engine 2 is transmitted to the ENAV engine 3 , and a trigger is transmitted to the ENAV engine 3 .
- API application program interface
- Trigger refers to when a film, e.g., ‘Star Wars’ is reproduced in the interactive mode, if a battle scene is displayed on an AV screen and a corresponding quiz is displayed on an interactive screen, this case is transmitted to the ENAV engine 3 before and/or after a time where the battle scene is displayed.
- a film e.g., ‘Star Wars’
- the ENAV engine 3 reproduces ENAV files.
- the ENAV engine 3 verifies, interprets and executes a markup document as one ENAV file so that DVD-Video data recorded on the ENAV disc 100 is reproduced in the interactive mode.
- the ENAV engine 3 combines a reproduced DVD-Video stream with the interpreted markup document and outputs the result to the display device 300 .
- an interactive screen in which an AV screen is embedded is displayed on the display device 300 .
- the ENAV engine 3 may include a variety of plug-in units. By using plug-in units, files having a variety of formats contained in a markup document or linked to the markup document are able to be opened.
- the ENAV engine 3 is able to call the MICROSOFT WINDOWS Media Player.
- the ENAV engine 3 is able to access the network and call information, such as ENAV files.
- the ENAV engine 3 reads profile information recorded on a startup file, compares the profile information with player profile information recorded in a system parameter table, and selects a corresponding loading information file according to a comparison result.
- a list of ENAV files that should be buffered in advance and/or during a reproduction operation for seamless reproduction is recorded in the loading information file.
- the ENAV engine 3 buffers ENAV files according to the selected loading information file in a buffer (not shown) provided to the ENAV engine 3 , interprets and executes an initial file.
- FIG. 7 is an example of a startup file startup.mls according to an aspect of the invention.
- a startup file startup.m which is a markup document written in markup languages, includes two elements. One element is a ‘walledgarden’ element, and the other element is a ‘loadinginfo’ element.
- the ‘walledgarden’ element for example, links a walled garden list file that enumerates a list of accessible files according to a region of a network that can be accessed through the inserted ENAV disc 100 or a parental level.
- the ‘walledgarden’ element is not always recorded in a startup file.
- the ‘loadinginfo’ element links a loading information file, so as to load an ENAV application, which is a set of ENAV files that are needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode.
- the ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates position information of ENAV files belonging to the ENAV application.
- condition information for selecting one from a plurality of ENAV applications is recorded. More specifically in FIG. 7 , the condition information for selecting an ENAV application is recorded using properties ‘name’ and ‘value’ recorded in the ‘condition’ element.
- two ‘loadinginfo’ elements exist in the startup file.
- Reference A indicates a portion in which a first ‘loadinginfo’ element is recorded
- Reference B indicates a portion in which a second ‘loadinginfo’ element is recorded.
- An ENAV application referred to by the first ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates that values of properties ‘name’ and ‘value’, which are each properties of the ‘condition’ element included in a corresponding ‘loadinginfo’ element, are recorded as ‘profile’ and ‘01’, respectively, such that profile information of an ENAV file included in a corresponding ENAV application is ‘01’.
- Version information on the ENAV file for constituting an ENAV application referred to by the second ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates ‘00’.
- the profile information ‘00’ includes markup documents corresponding to DVD-ML 1.0, which are basic specifications for an ENAV application and JPEG and PNG as resource files linked to the markup documents
- the profile information ‘01’ may be extended specifications including markup documents or resource files manufactured by adding flash and JAVA languages to the contents of the profile information ‘00’.
- restriction conditions of ENAV files are only defined at a divergence point where one of a plurality of ENAV applications should be initially executed, that is, all of the ENAV applications are manufactured according to the same restriction conditions.
- an ENAV file since an ENAV file has only one profile information, it is not necessary to select an ENAV application according to profile information.
- profile information is recorded by considering a version of specifications by which an addition and a deletion of a variety of future resource files are defined, and the profile information is included in a startup file so that contents manufactured using a plurality of versions are manufactured when an information storage medium is manufactured.
- FIG. 8 shows a system parameter table in which profile information is recorded, according to an aspect of the invention.
- the system parameter table is stored in the reproducing apparatus 200 .
- system parameters 0 through 20 are each implemented as a shape in which player profile information is added to the system parameter table according to system parameters (SPRMs) defined in DVD specifications for read-only disc part 3 video specifications.
- SPRMs system parameters
- a value having a fixed length of 2 bytes is stored in each system parameter, and each system parameter has an integer value of 16-bits.
- system parameters SPRMs 11 to 21 are referred to as player parameters.
- Each player parameter has only a read property.
- Detailed descriptions of the system parameters SPRMs 0 to 20 have no direct relation with the invention; therefore, a detailed description is not provided.
- the system parameters SPRMs 21 to 24 stored in the system parameter table are reserved, and the player profile information is recorded as a player profile code in the system parameter SPRM 21 .
- the system parameter SPRM 21 is recorded to have only a read property.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a data structure of profile information recorded as a system parameter of FIG. 8 .
- the player profile information is recorded as 2 bits of 2 bytes allocated to the SPRM 21 . Thus, the remaining 14 bits are reserved, and other information may be recorded therein.
- the SPRM 21 includes 00b as a basic value.
- 00b refers to player profile information according to basic specifications of DVD-Video in which interactive data is further recorded.
- an expanded version of the player profile information may be defined as 01b, 10b, and 11 b.
- a reproducing apparatus for supporting a new version ‘01b’ selects and reproduces loading information file ‘loadinginfomation1.1di’ indicating position information of an ENAV application recorded in the startup file of FIG. 7 according to a new version, by referring to profile information ‘01b’ recorded in the SPRM 21 .
- a reproducing apparatus for supporting a previous version ‘00b’ selects and reproduces loading information file ‘loadinginfomation2.1di’ indicating position information of an ENAV application corresponding to a previous version ‘00b’ in the startup file of FIG. 7 so that the previous version ‘00b’ is added to the version information ‘00b’ recorded in the SPRM 21 of the reproducing apparatus.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a method for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode according to an aspect of the invention.
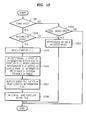
- the reproducing apparatus 200 checks a startup file stored in the DVD_ENAV directory and determines whether the inserted disc is the ENAV disc 100 (operation 1001 ). If the startup file is not found, the reproducing apparatus 200 determines the inserted disc as a conventional DVD-Video disc (operation 1002 ) and reproduces AV data in a video mode (operation 1003 ) or simply does not reproduce the disc.
- the reproducing apparatus 200 recognizes the inserted disc is the ENAV disc 100 (operation 1001 ), and if a user selects video mode, the reproducing apparatus 200 reproduces AV data in the video mode (operation 1003 ). If the user selects an interactive mode (operation 1004 ), the reproducing apparatus 200 reads the startup file (operation 1005 ), reads profile information recorded in the startup file, and reads a loading information file added to the player profile information recorded in the system parameter table (operation 1006 ). The reproducing apparatus then buffers an ENAV file listed in the read loading information file (operation 1007 ), interprets and executes an initial file and reproduces the selected AV data in the interactive mode (operation 1008 ).
- the above-described reproducing method can be embodied as a computer program to be read by a computer. Codes and code segments for constituting the computer program can be easily deciphered by a computer programmer.
- the computer program is stored in computer readable media, read and executed by the computer, thereby implementing the reproducing method.
- the computer readable media includes media such as, magnetic recording media, optical data storage units, carrier waves, etc.
- an information storage medium in which interactive data having a data structure that can be adaptively reproduced in a variety of reproducing apparatuses having different ranges of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode are included. Further, the information storage medium in which interactive data with a data structure having a high compatibility is recorded can be manufactured, and a user can have a wider range of selection.
Landscapes
- Signal Processing For Digital Recording And Reproducing (AREA)
- Management Or Editing Of Information On Record Carriers (AREA)
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
Abstract
An apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in an interactive mode including an audio/video reproducing engine that decodes audio/video data; and an enhanced navigation engine that has player profile information indicating a version of a supportable enhanced navigation application and interprets and executes an enhanced navigation application that is selected by referring to the player profile information so that the audio/video data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
Description
- This application claims the priorities of Korean Patent Application Nos. 2003-56722, filed on Aug. 16, 2003,2003-61571, filed on Sep. 3, 2003, and 2003-61572, field on Sep. 3, 2003, in the Korean Intellectual Property Office, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference.
- 1. Field of the Invention
- The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for reproducing audio/video (AV) data in interactive mode, and an information storage medium therefor.
- 2. Description of the Related Art
- Interactive DVDs that can be reproduced in an interactive mode using a conventional personal computer (PC). An interactive DVD refers to a DVD in which interactive data is recoded in addition to recorded DVD-Video data. Interactive DVDs are reproduced in either of two modes. One mode is a video mode in which only DVD-Video data is reproduced, such as with an ordinary DVD. The other mode is an interactive mode in which DVD-Video data is reproduced together with a markup document and is displayed through a display window of the markup document. If the interactive mode is selected by a user, a web browser embedded in the PC parses and displays a markup document recorded on the interactive DVD. In the display window defined by the markup document, DVD-Video data selected by the user is displayed.
- For example, if the DVD-Video data is a film, the film is reproduced in the display window of the markup document and in the remaining part the script, synopsis, photos of actors, and other related additional information of the film can be displayed. Additional information is also displayed in synchronism with a title (AV data). For example, when an actor is displayed on an AV screen, interactive data containing career information on the actor is reproduced and displayed.
- Interactive data includes markup documents written in markup languages, script codes manufactured using files inside the markup documents or separate files and linked to the markup documents, audio files, animation files, and image files linked to the markup documents and reproduced together with the markup documents. In order to reflect a user's demands, a variety of functions can be added to a user interface in interactive mode. Thus, when there is a reproducing apparatus for supporting the interactive mode, the range of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode in each reproducing apparatus can be varied.
- The invention provides an information storage medium having a data structure for being reproduced adaptively in a variety of reproducing apparatuses having different ranges of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in an interactive mode, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode therefor.
- The invention also provides an information storage medium having a data structure having a high compatibility, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode therefor.
- According to an aspect of the invention, there is an information storage medium storing interactive data for reproducing audio/video (AV) data in an interactive mode, wherein the interactive data is displayed together with an AV screen obtained from the AV data and provides additional information related to the AV screen; and profile information indicating a version of the interactive data.
- The interactive data may include a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected, and the profile information may be recorded in the startup file.
- The profile information may be referred to so that interactive data that can be reproduced by a reproducing apparatus for reproducing the AV data in the interactive mode is selected.
- According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided an information storage medium storing a plurality of ENAV applications manufactured with a plurality of versions so that AV data is reproduced in an interactive mode; and profile information that is referred to so that one is selected from the plurality of ENAV applications.
- The profile information may be recorded using an element for linking loading information file contained in an ENAV application corresponding to a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected.
- The loading information file may indicate position information of ENAV files belonging to a corresponding ENAV application.
- According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided an apparatus for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode. The apparatus includes an AV reproducing engine which decodes AV data; and an ENAV engine which has player profile information indicating a version of a supportable ENAV application and interprets and executes an ENAV application selected by referring to the player profile information so that the AV data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
- The player profile information may be stored as a system parameter.
- According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a method for reproducing AV data in an interactive mode. The method includes reading profile information indicating a version of interactive data; selecting and reading the interactive data manufactured with a version that can be supported by a reproducing apparatus, by referring to the read profile information; and interpreting and executing the read interactive data.
- The reading profile information may include opening a startup file that is initially read when interactive mode is selected, and reading the profile information.
- The reading profile information may include reading the profile information from the startup file recorded using an element for linking loading information file contained in a corresponding ENAV application or reading profile information indicating versions of a plurality of ENAV applications manufactured with a plurality of versions so that AV data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
- The selecting and reading the interactive data may include reading a version of an ENAV application that can be supported by the reproducing apparatus, from player profile information stored as a system parameter or reading ENAV files belonging to the ENAV application by referring to the loading information file indicating position information of ENAV files belonging to a corresponding to an ENAV application.
- Additional aspects and/or advantages of the invention will be set forth in part in the description which follows and, in part, will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention.
- The above objects and advantages of the present invention will become more apparent by describing in detail preferred embodiments thereof with reference to the attached drawings in which:
-
FIG. 1 schematically shows a structure of a reproducing system according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an embodiment of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 3 schematically shows a volume space of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a directory structure of an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 5 shows the relation between AV data recorded on an ENAV disc according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 6 is a block diagram of a reproducing apparatus according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 7 is an example of a startup file startup.mls according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 8 shows a system parameter table in which profile information is recorded, according to an embodiment of the invention; -
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a data structure of profile information recorded as a system parameter ofFIG. 8 ; and -
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a method for reproducing AV data in interactive mode according to an embodiment of the invention. - Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein like reference numerals refer to the like elements throughout. The embodiments are described below to explain the present invention by referring to the figures.
- In the present invention, ‘interactive data’ refers to data that is needed in reproducing audio/video data AV in an interactive mode. Interactive data includes markup documents written in markup languages and/or script codes, script code files linked to the markup documents or separately provided, program files, audio files, animation files, and image files which are resource files linked to the markup documents and displayed together with the markup documents. In other words, the interactive data serves as an application program that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode and simultaneously serves as additional contents provided together with AV data.
-
FIG. 1 schematically shows a structure of a reproducing system according to an embodiment of the invention. Referring toFIG. 1 , the reproducing system includes an Enhanced Audio/video (ENAV)disc 100 that is an information storage medium for supporting an interactive mode according to a reproducingapparatus 200, adisplaydevice 300, and acontroller 400 that is a user input apparatus. Thecontroller 400 receives a control command from the user and transmits the command to the reproducingapparatus 200. The reproducingapparatus 200 reproduces AV data recorded on the ENAVdisc 100 in the interactive mode. Thedisplay device 300 may be a television and thecontroller 400 may be a remote controller. - If the ENAV
disc 100 is placed on a DVD drive provided to the reproducingapparatus 200 and the user selects the interactive mode, the reproducingapparatus 200 reproduces corresponding AV data in the interactive mode and transmits the data to thedisplay device 300. On thedisplay device 300, an interactive screen and an AV screen embedded in the interactive screen obtained from the interactive data is displayed together. - ‘Interactive mode’ refers to a mode in which AV data is displayed together with interactive data. In other words, AV data is displayed in a display window defined in a markup document such that an AV screen is displayed embedded in an interactive screen. The AV screen may be a screen displayed on the
display device 300 by reproducing DVD-Video data recorded on theENAV disc 100 using the reproducingapparatus 200, and the interactive screen indicates a screen displayed on theTV 300 after the interactive data recorded on theENAV disc 100 is interpreted and executed using the reproducingapparatus 200. - ‘Video mode’ is a mode in which AV data is reproduced such that only an AV screen obtained by reproducing corresponding AV data is displayed. The reproducing
apparatus 200 may support both the interactive mode and the video mode. In addition, the reproducingapparatus 200 can receive/transmit AV data and/or interactive data from/to a network or an Internet connection. - In particular, the reproducing
apparatus 200 has a system parameter table in which system parameters SPRMs are set, and the system parameter table has player profile information. The player profile information indicates the range of interactive data supported by the reproducingapparatus 200. In other words, the player profile information is the same as version information of interactive data supported by the reproducingapparatus 200. The version of interactive data may be, for example, a version of document type definition (DTD) of markup languages used to make ENAV files, a version of program languages used to make ENAV files, a version of languages used to implement one ENAV application or a version of specifications in which restriction conditions of a variety of resource files linked to markup documents. - Profile information indicates whether a version of stored interactive data is also recorded on the
ENAV disc 100. The meaning of profile information is the same as the meaning of player profile information, except that, unlike the player profile information, the profile information is recorded on theENAV disc 100 and indicates corresponding interactive data. - If a user selects the interactive mode, the reproducing
apparatus 200 reads the profile information recorded on theENAV disc 100, compares the profile information with its own player profile information as a system parameter and reproduces AV data in the interactive mode using interactive data selected according to a comparison result. -
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing anENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 2 , interactive data is recorded on theENAV disc 100 to correspond to profile information. For example, as illustrated inFIG. 2 ,interactive data # 1 corresponding to profileinformation # 1 is recorded on theENAV disc 100,interactive data # 2 corresponding to profileinformation # 2 is recorded on theENAV disc 100, and interactive data #n corresponding to profile information #n is recorded on the ENAV disc 100 (where n is an integer number). - The
profile information # 1, #2, . . . , #n are recorded on theENAV disc 100 separately with theinteractive data # 1, #2, . . . , and #n and may be linked to theinteractive data # 1, #2, . . . , and #n or included as a part of theinteractive data # 1, #2, . . . , and #n. - If the player profile information recorded in the
recording apparatus 200 is theprofile information # 2, not only theinteractive data # 2 corresponding to theprofile information # 2 but also theinteractive data # 1 corresponding to theprofile information # 1 can be reproduced. Similarly, if the player profile information recorded in therecording apparatus 200 is the profile information #n, the reproducingapparatus 200 supports all of theinteractive data # 1, #2, . . . , and #n. - Thus, if the player profile information is the
profile information # 1, the reproducingapparatus 200 reproduces theinteractive data # 1. However, if the player profile information is theprofile information # 2, the reproducingapparatus 200 can reproduce theinteractive data # 2 and theinteractive data # 1, selectively. Of course, the reproducingapparatus 200 can set theinteractive data # 2 to be reproduced as default. -
FIG. 3 schematically shows a volume space of theENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 3 , the volume space of theENAV disc 100 comprises a volume and file structure region in which information on volume and file is recorded, a DVD-Video data region in which AV data, i.e., a video title is recorded as a DVD-Video format, an ENAV file region in which ENAV files for supporting an interactive mode are recorded, and an other data region. - Various information is recorded n the ENAV disk. For example, ‘video_ts.ifo’ includes reproduction control information for the entire video title recorded on the
ENAV disc 100, vts—01—0.ifo includes reproduction control information for a first video title, and vts—01—0.vob, vts—01—1.vob, etc., which are AV data for constituting a video title, are recorded in the DVD-Video data region. Vts—01—0.vob, vts—01—1.vob, and so on are video titles, i.e., video objects. Vobu, in which a navigation pack, a video pack, and an audio pack are packed, is included in each vob. A detailed configuration thereof is described in a DVD-Video standard ‘DVD-Video for Read Only Memory Disc 1.0’. - An ENAV application comprised of a plurality of ENAV files is stored in the ENAV file region. In other words, a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected, and a markup document corresponding to a selected video title are recorded as ENAV files. In this way, the interactive data is recorded as a plurality of ENAV files. The ENAV files are referred to as markup documents, script code files, program files, style sheets for defining styles of markup documents, audio files, animation files, and image files which are resource files linked to the markup documents and displayed together with the markup documents, as previously described.
-
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a directory structure of the ENAV disc according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 4 , a root directory includes a DVD video directory video_ts and an ENAV directory DVD_ENAV in which ENAV data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode is recorded. - The data described with reference to
FIG. 2 , that is, video_ts.ifo, vts—01—0.ifo, vts—01—0.vob, vts—01—1.vob, etc., are stored in the DVD video directory video_ts. Data described with reference toFIG. 2 , that is, a startup file startup.mls and other ENAV files are stored in the ENAV directory DVD_ENAV. -
FIG. 5 shows the relation between AV data recorded on theENAV disc 100 according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 5 , each ENAV application corresponds to AV data of which there is seamless reproduction. Each ENAV application is a set of a plurality of ENAV files. In order to have seamless reproduction of AV data, a corresponding ENAV application is buffered before AV data of the corresponding ENAV application is reproduced in an interactive mode. In other words, an ENAV application corresponding to AV data is buffered prior to reproducing the AV data in the interactive mode. - Each ENAV application contains one loading information file. Position information on ENAV files that are needed in reproducing corresponding AV data in the interactive mode is recorded in the loading information file. The position information on the ENAV files contains position information on ENAV files that should be buffered before a corresponding ENAV application is launched, that is, position information on ENAV files that should be preloaded.
- Since preloading is performed on each ENAV application, seamless reproduction is guaranteed for AV data corresponding to each ENAV application. As such, a contents maker should make contents so that one ENAV application corresponds with one volume of a video title and one chapter of a video title in order to have a seamless reproduction.
- Postloading refers to a buffering of a predetermined ENAV file after a corresponding ENAV application is launched. Not every ENAV file is required to be postloaded. When there is the need for postloading, position information on an ENAV file that should be postloaded is recorded in the loading information file.
-
FIG. 6 is a block diagram of a reproducingapparatus 200 according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 6 , the reproducingapparatus 200 comprises areader 1, anAV reproducing engine 2, and anENAV engine 3. - The
reader 1 reads AV data, i.e., DVD-Video data and ENAV files, recorded on theENAV disc 100 in response to a control signal generated from theENAV engine 3. - The
AV reproducing engine 2 reproduces AV data read by thereader 2. In the present aspect of the invention, AV data is recorded as DVD-Video data; therefore, theAV reproducing engine 2 is used as a DVD-Video reproducing engine to reproduce DVD-Video data. TheAV reproducing engine 2 communicates with theENAV engine 3 through an application program interface (API). For example, a property indicating the operating state of theAV reproducing engine 2 is transmitted to theENAV engine 3, and a trigger is transmitted to theENAV engine 3. Trigger, for example, refers to when a film, e.g., ‘Star Wars’ is reproduced in the interactive mode, if a battle scene is displayed on an AV screen and a corresponding quiz is displayed on an interactive screen, this case is transmitted to theENAV engine 3 before and/or after a time where the battle scene is displayed. - The
ENAV engine 3 reproduces ENAV files. In particular, theENAV engine 3 verifies, interprets and executes a markup document as one ENAV file so that DVD-Video data recorded on theENAV disc 100 is reproduced in the interactive mode. In addition, theENAV engine 3 combines a reproduced DVD-Video stream with the interpreted markup document and outputs the result to thedisplay device 300. As such, an interactive screen in which an AV screen is embedded is displayed on thedisplay device 300. TheENAV engine 3 may include a variety of plug-in units. By using plug-in units, files having a variety of formats contained in a markup document or linked to the markup document are able to be opened. For example, in order to reproduce AV data for a MICROSOFT WINDOWS Media Player, theENAV engine 3 is able to call the MICROSOFT WINDOWS Media Player. In addition, theENAV engine 3 is able to access the network and call information, such as ENAV files. - In particular, according to an aspect of the invention, the
ENAV engine 3 reads profile information recorded on a startup file, compares the profile information with player profile information recorded in a system parameter table, and selects a corresponding loading information file according to a comparison result. A list of ENAV files that should be buffered in advance and/or during a reproduction operation for seamless reproduction is recorded in the loading information file. TheENAV engine 3 buffers ENAV files according to the selected loading information file in a buffer (not shown) provided to theENAV engine 3, interprets and executes an initial file. -
FIG. 7 is an example of a startup file startup.mls according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 7 , a startup file startup.mis which is a markup document written in markup languages, includes two elements. One element is a ‘walledgarden’ element, and the other element is a ‘loadinginfo’ element. - The ‘walledgarden’ element, for example, links a walled garden list file that enumerates a list of accessible files according to a region of a network that can be accessed through the inserted
ENAV disc 100 or a parental level. The ‘walledgarden’ element is not always recorded in a startup file. - The ‘loadinginfo’ element links a loading information file, so as to load an ENAV application, which is a set of ENAV files that are needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode. In other words, the ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates position information of ENAV files belonging to the ENAV application. In
FIG. 7 , by using a ‘condition’ element included in the ‘loadinginfo’ element, condition information for selecting one from a plurality of ENAV applications is recorded. More specifically inFIG. 7 , the condition information for selecting an ENAV application is recorded using properties ‘name’ and ‘value’ recorded in the ‘condition’ element. - As shown in
FIG. 7 , two ‘loadinginfo’ elements exist in the startup file. Reference A indicates a portion in which a first ‘loadinginfo’ element is recorded, and Reference B indicates a portion in which a second ‘loadinginfo’ element is recorded. An ENAV application referred to by the first ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates that values of properties ‘name’ and ‘value’, which are each properties of the ‘condition’ element included in a corresponding ‘loadinginfo’ element, are recorded as ‘profile’ and ‘01’, respectively, such that profile information of an ENAV file included in a corresponding ENAV application is ‘01’. Version information on the ENAV file for constituting an ENAV application referred to by the second ‘loadinginfo’ element indicates ‘00’. If the profile information ‘00’ includes markup documents corresponding to DVD-ML 1.0, which are basic specifications for an ENAV application and JPEG and PNG as resource files linked to the markup documents, the profile information ‘01’ may be extended specifications including markup documents or resource files manufactured by adding flash and JAVA languages to the contents of the profile information ‘00’. - In a conventional reproducing apparatus, restriction conditions of ENAV files are only defined at a divergence point where one of a plurality of ENAV applications should be initially executed, that is, all of the ENAV applications are manufactured according to the same restriction conditions. However, according to an aspect of the invention, since an ENAV file has only one profile information, it is not necessary to select an ENAV application according to profile information. However, profile information is recorded by considering a version of specifications by which an addition and a deletion of a variety of future resource files are defined, and the profile information is included in a startup file so that contents manufactured using a plurality of versions are manufactured when an information storage medium is manufactured.
-
FIG. 8 shows a system parameter table in which profile information is recorded, according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 8 , the system parameter table is stored in the reproducingapparatus 200. Considering compatibility,system parameters 0 through 20 are each implemented as a shape in which player profile information is added to the system parameter table according to system parameters (SPRMs) defined in DVD specifications for read-only disc part 3 video specifications. For example, a value having a fixed length of 2 bytes is stored in each system parameter, and each system parameter has an integer value of 16-bits. In particular, system parameters SPRMs 11 to 21 are referred to as player parameters. Each player parameter has only a read property. Detailed descriptions of the system parameters SPRMs 0 to 20 have no direct relation with the invention; therefore, a detailed description is not provided. - The system parameters SPRMs 21 to 24 stored in the system parameter table are reserved, and the player profile information is recorded as a player profile code in the system parameter SPRM 21. In the present aspect of the invention, for example, the system parameter SPRM 21 is recorded to have only a read property.
-
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a data structure of profile information recorded as a system parameter ofFIG. 8 . Referring toFIG. 9 , the player profile information is recorded as 2 bits of 2 bytes allocated to the SPRM 21. Thus, the remaining 14 bits are reserved, and other information may be recorded therein. - The SPRM 21 includes 00b as a basic value. 00b refers to player profile information according to basic specifications of DVD-Video in which interactive data is further recorded. For examples, an expanded version of the player profile information may be defined as 01b, 10b, and 11b.
- If basic player profile information (e.g., ‘00b’) is upgraded and recorded together with an ENAV DVD in which interactive data of a previous version is together recorded, for lower compatibility with interactive data of a new version (e.g., ‘01b’), a reproducing apparatus for supporting a new version ‘01b’ selects and reproduces loading information file ‘loadinginfomation1.1di’ indicating position information of an ENAV application recorded in the startup file of
FIG. 7 according to a new version, by referring to profile information ‘01b’ recorded in the SPRM 21. However, a reproducing apparatus for supporting a previous version ‘00b’ selects and reproduces loading information file ‘loadinginfomation2.1di’ indicating position information of an ENAV application corresponding to a previous version ‘00b’ in the startup file ofFIG. 7 so that the previous version ‘00b’ is added to the version information ‘00b’ recorded in the SPRM 21 of the reproducing apparatus. - A method of reproducing AV data in an interactive mode using the reproducing apparatus having the above-described structure is described below with reference to
FIG. 10 .FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a method for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode according to an aspect of the invention. Referring toFIG. 10 , if theENAV disc 100 is loaded into the reproducingapparatus 200, the reproducingapparatus 200 checks a startup file stored in the DVD_ENAV directory and determines whether the inserted disc is the ENAV disc 100 (operation 1001). If the startup file is not found, the reproducingapparatus 200 determines the inserted disc as a conventional DVD-Video disc (operation 1002) and reproduces AV data in a video mode (operation 1003) or simply does not reproduce the disc. - If the startup file is found, the reproducing
apparatus 200 recognizes the inserted disc is the ENAV disc 100 (operation 1001), and if a user selects video mode, the reproducingapparatus 200 reproduces AV data in the video mode (operation 1003). If the user selects an interactive mode (operation 1004), the reproducingapparatus 200 reads the startup file (operation 1005), reads profile information recorded in the startup file, and reads a loading information file added to the player profile information recorded in the system parameter table (operation 1006). The reproducing apparatus then buffers an ENAV file listed in the read loading information file (operation 1007), interprets and executes an initial file and reproduces the selected AV data in the interactive mode (operation 1008). - The above-described reproducing method can be embodied as a computer program to be read by a computer. Codes and code segments for constituting the computer program can be easily deciphered by a computer programmer. In addition, the computer program is stored in computer readable media, read and executed by the computer, thereby implementing the reproducing method. The computer readable media includes media such as, magnetic recording media, optical data storage units, carrier waves, etc.
- As described above, according to an aspect of the invention, an information storage medium, in which interactive data having a data structure that can be adaptively reproduced in a variety of reproducing apparatuses having different ranges of interactive data that is needed in reproducing AV data in the interactive mode, and a method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in the interactive mode are included. Further, the information storage medium in which interactive data with a data structure having a high compatibility is recorded can be manufactured, and a user can have a wider range of selection.
- While this invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to preferred embodiments thereof, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
- Although a few embodiments of the present invention have been shown and described, it would be appreciated by those skilled in the art that changes may be made in these embodiments without departing from the principles and spirit of the invention, the scope of which is defined in the claims and their equivalents.
Claims (13)
1. An apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in an interactive mode, comprising:
an audio/video reproducing engine that decodes audio/video data; and
an enhanced navigation engine that has player profile information indicating a version of a supportable enhanced navigation application and interprets and executes an enhanced navigation application that is selected by referring to the player profile information so that the audio/video data is reproduced in the interactive mode.
2. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 1 , wherein the player profile information is stored as a system parameter.
3. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 1 , further comprising a reader that reads the enhanced navigation application from an information storage medium, wherein the enhanced navigation engine selects the enhanced navigation application by referring to the player profile information and profile information that are recorded in a startup file that is initially read when the interactive mode is selected and indicates a version of the enhanced navigation application.
4. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 1 , wherein a plurality of enhanced navigation applications are manufactured with a plurality of versions and the profile information of each enhanced navigation application is stored in an information storage medium, and the enhanced navigation engine selects one from the plurality of enhanced navigation applications by referring to the profile information.
5. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 1 , wherein the enhanced navigation engine refers to the profile information recorded using an element for linking a loading information file included in a corresponding enhanced navigation application.
6. An apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in an interactive mode, the apparatus comprising:
a reader to read the audio/video data;
an audio/video reproducing unit to reproduce the audio/video data read by the reader; and
an enhanced navigation unit connected with the audio/video reproducing unit to reproduce enhanced navigation files,
wherein the reader reads audio visual data in response to a control signal from the enhanced navigation unit.
7. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 6 , wherein the enhanced navigation unit verifies, interprets, and executes a markup document as one enhanced navigation file in order to reproduce the audio/video data recorded on the enhanced navigation storage medium in the interactive mode.
8. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 7 , wherein the enhanced navigation unit combines the reproduced audio/video data with an interpreted markup document and outputs the result in the interactive mode to a display device.
9. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 6 , wherein the enhanced navigation unit further comprises a plurality of plug-in units to enable the enhanced navigation unit to read a variety of formats included in a markup document or connected to a markup document.
10. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 6 , wherein the enhanced navigation unit reads profile information recorded on an enhanced navigation storage medium to determine a version of interactive data that is stored on the enhanced navigation storage medium, compares the read profile information with player profile information, the player profile information indicates a range of the interactive data supported by a reproducing apparatus, and reproduces audio/video data stored on the enhanced navigation storage medium in the interactive mode using the interactive data that is supported by the reproducing apparatus according to the comparison result.
11. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 10 , wherein the enhanced navigation unit selectively reproduces previously recorded interactive data from the enhanced navigation storage medium when, according to the comparison result, the player profile information is the same as the profile information corresponding to particular interactive data.
12. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 6 , wherein a plurality of enhanced navigation applications having a plurality of versions and profile information are stored in the information storage medium, and the enhanced navigation engine selects one from the plurality of enhanced navigation applications by referring to the profile information.
13. The apparatus for reproducing audio/video data in the interactive mode of claim 6 , further comprising a system parameter table to store player profile information and system parameters.
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR2003-56722 | 2003-08-16 | ||
| KR1020030056722A KR100565057B1 (en) | 2003-08-16 | 2003-08-16 | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, method and apparatus thereof |
| KR1020030061572A KR100584574B1 (en) | 2003-09-03 | 2003-09-03 | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information |
| KR1020030061571A KR100584573B1 (en) | 2003-09-03 | 2003-09-03 | Reproducing method of information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information |
| KR2003-61572 | 2003-09-03 | ||
| KR2003-61571 | 2003-09-03 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20050053361A1 true US20050053361A1 (en) | 2005-03-10 |
Family
ID=36203847
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/902,274 Abandoned US20050053361A1 (en) | 2003-08-16 | 2004-07-30 | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, apparatus for reproducing AV data in interactive mode |
| US10/902,252 Expired - Fee Related US7653288B2 (en) | 2003-08-16 | 2004-07-30 | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, method for reproducing AV data in interactive mode |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/902,252 Expired - Fee Related US7653288B2 (en) | 2003-08-16 | 2004-07-30 | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, method for reproducing AV data in interactive mode |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20050053361A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1656675A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4839214B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0411850A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2531336C (en) |
| HK (1) | HK1090166A1 (en) |
| MY (1) | MY141451A (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI263983B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2005017897A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110314113A1 (en) * | 2010-06-21 | 2011-12-22 | Takurou Noda | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020002563A1 (en) * | 1999-08-23 | 2002-01-03 | Mary M. Bendik | Document management systems and methods |
| KR100574823B1 (en) * | 2003-03-07 | 2006-04-28 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for managing animation chunk data and attribute information for interactive optical disc |
| JP4438527B2 (en) * | 2004-06-18 | 2010-03-24 | ソニー株式会社 | Information management method, information reproducing apparatus, and information management apparatus |
| US8280233B2 (en) * | 2005-01-28 | 2012-10-02 | Panasonic Corporation | Reproduction device, program, reproduction method |
| CN101238518B (en) * | 2005-08-09 | 2013-03-20 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Recording method, reproducing apparatus and method |
| KR20070042072A (en) * | 2005-10-17 | 2007-04-20 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Reproducing apparatus and video data storing method |
| US7600686B2 (en) | 2005-11-30 | 2009-10-13 | Microsoft Corporation | Media content menu navigation and customization |
| US20070124764A1 (en) * | 2005-11-30 | 2007-05-31 | Microsoft Corporation | Media content menu navigation and customization |
| US8307403B2 (en) * | 2005-12-02 | 2012-11-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Triggerless interactive television |
| KR20090017386A (en) * | 2007-08-13 | 2009-02-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Information storage medium, reproducing apparatus, and reproducing method |
| US7877687B2 (en) * | 2007-08-16 | 2011-01-25 | Yahoo! Inc. | Persistent visual media player |
| US8893203B2 (en) * | 2007-08-17 | 2014-11-18 | Phoenix Myrrh Technology Pty Ltd. | Method and system for content delivery |
| EP2451151B1 (en) | 2010-11-08 | 2014-08-13 | Deluxe Media Inc. | Method and apparatus for use in controlling the playback of contents related with a recorded content. |
| CN111988667B (en) * | 2020-08-18 | 2022-06-21 | 视若飞信息科技(上海)有限公司 | Intelligent terminal media player management method and system |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020088011A1 (en) * | 2000-07-07 | 2002-07-04 | Lamkin Allan B. | System, method and article of manufacture for a common cross platform framework for development of DVD-Video content integrated with ROM content |
| US20030012558A1 (en) * | 2001-06-11 | 2003-01-16 | Kim Byung-Jun | Information storage medium containing multi-language markup document information, apparatus for and method of reproducing the same |
| US20030093816A1 (en) * | 2001-10-25 | 2003-05-15 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Storage medium adaptable to changes in screen aspect ratio and reproducing method thereof |
| US20030161615A1 (en) * | 2002-02-26 | 2003-08-28 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Enhanced navigation system using digital information medium |
| US20030206710A1 (en) * | 2001-09-14 | 2003-11-06 | Ferman Ahmet Mufit | Audiovisual management system |
| US20040126095A1 (en) * | 2002-08-14 | 2004-07-01 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Optical disk apparatus and optical disk processing method and optical disk |
| US20050114396A1 (en) * | 2003-03-14 | 2005-05-26 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd | Method of reproducing an information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player startup information |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1108612C (en) * | 1996-04-12 | 2003-05-14 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Multimedium optical disk storing image titles in such manner that whether they need AV functions for reproduction can be instantly judged, and apparatus for and method of reproducing the same |
| US6076166A (en) * | 1997-01-17 | 2000-06-13 | Philips Electronics North America Corporation | Personalizing hospital intranet web sites |
| US6580870B1 (en) * | 1997-11-28 | 2003-06-17 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Systems and methods for reproducing audiovisual information with external information |
| US6735625B1 (en) * | 1998-05-29 | 2004-05-11 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | System and method for automatically determining whether a product is compatible with a physical device in a network |
| US6529526B1 (en) * | 1998-07-13 | 2003-03-04 | Thomson Licensing S.A. | System for processing programs and program content rating information derived from multiple broadcast sources |
| JP2000067522A (en) | 1998-08-25 | 2000-03-03 | Sony Corp | Information reproducing device/method, information recording device and its method, providing medium and recording medium |
| US20050166232A1 (en) * | 1999-04-21 | 2005-07-28 | Lamkin Allan B... | Presentation of media content from multiple media sources |
| US7178106B2 (en) * | 1999-04-21 | 2007-02-13 | Sonic Solutions, A California Corporation | Presentation of media content from multiple media sources |
| JP2001344951A (en) | 2000-05-30 | 2001-12-14 | Toshiba Corp | Information reproducing device and information reproducing method |
| US20020099829A1 (en) * | 2000-11-27 | 2002-07-25 | Richards Kenneth W. | Filter proxy system and method |
| ES2261527T3 (en) | 2001-01-09 | 2006-11-16 | Metabyte Networks, Inc. | SYSTEM, PROCEDURE AND APPLICATION OF SOFTWARE FOR DIRECT ADVERTISING THROUGH A GROUP OF BEHAVIOR MODELS, AND PROGRAMMING PREFERENCES BASED ON BEHAVIOR MODEL GROUPS. |
| TWI224316B (en) * | 2001-06-14 | 2004-11-21 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | Information storage medium containing preload information, apparatus and method for reproducing therefor |
| JP3785983B2 (en) * | 2001-10-05 | 2006-06-14 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Digital information recording apparatus and information recording / reproducing apparatus |
| AU2003217514A1 (en) | 2002-04-16 | 2003-11-03 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Information storage medium for recording interactive contents version information, recording and reproducing method thereof |
| US7665110B2 (en) * | 2002-05-14 | 2010-02-16 | Lg Electronics Inc. | System and method for synchronous reproduction of local and remote content in a communication network |
| JP3971346B2 (en) * | 2002-06-24 | 2007-09-05 | 株式会社東芝 | Moving picture reproducing apparatus, schedule data, moving picture reproducing method, and program |
| KR100574823B1 (en) * | 2003-03-07 | 2006-04-28 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for managing animation chunk data and attribute information for interactive optical disc |
| KR100930353B1 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2009-12-08 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | How to handle connection request of disc player |
| JP2004296065A (en) * | 2003-03-10 | 2004-10-21 | Toshiba Corp | Information recording medium, information reproducing device and method |
| KR100565056B1 (en) | 2003-08-14 | 2006-03-30 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in interactive mode and information storage medium thereof |
-
2004
- 2004-07-30 US US10/902,274 patent/US20050053361A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2004-07-30 US US10/902,252 patent/US7653288B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-08-12 EP EP04774305A patent/EP1656675A4/en not_active Ceased
- 2004-08-12 MY MYPI20043280A patent/MY141451A/en unknown
- 2004-08-12 CA CA2531336A patent/CA2531336C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-08-12 JP JP2006523131A patent/JP4839214B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-08-12 BR BRPI0411850-2A patent/BRPI0411850A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-08-12 WO PCT/KR2004/002025 patent/WO2005017897A1/en active Application Filing
- 2004-08-13 TW TW093124317A patent/TWI263983B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2006
- 2006-09-27 HK HK06110746.0A patent/HK1090166A1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020088011A1 (en) * | 2000-07-07 | 2002-07-04 | Lamkin Allan B. | System, method and article of manufacture for a common cross platform framework for development of DVD-Video content integrated with ROM content |
| US20030012558A1 (en) * | 2001-06-11 | 2003-01-16 | Kim Byung-Jun | Information storage medium containing multi-language markup document information, apparatus for and method of reproducing the same |
| US20030206710A1 (en) * | 2001-09-14 | 2003-11-06 | Ferman Ahmet Mufit | Audiovisual management system |
| US20030093816A1 (en) * | 2001-10-25 | 2003-05-15 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Storage medium adaptable to changes in screen aspect ratio and reproducing method thereof |
| US20030161615A1 (en) * | 2002-02-26 | 2003-08-28 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Enhanced navigation system using digital information medium |
| US20040126095A1 (en) * | 2002-08-14 | 2004-07-01 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Optical disk apparatus and optical disk processing method and optical disk |
| US20050114396A1 (en) * | 2003-03-14 | 2005-05-26 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd | Method of reproducing an information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player startup information |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110314113A1 (en) * | 2010-06-21 | 2011-12-22 | Takurou Noda | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| US9674130B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2017-06-06 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| US10643367B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2020-05-05 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| US11151768B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2021-10-19 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| US11670034B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2023-06-06 | Interdigital Ce Patent Holdings, Sas | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MY141451A (en) | 2010-04-30 |
| TWI263983B (en) | 2006-10-11 |
| TW200511244A (en) | 2005-03-16 |
| EP1656675A1 (en) | 2006-05-17 |
| EP1656675A4 (en) | 2009-02-18 |
| CA2531336A1 (en) | 2005-02-24 |
| JP4839214B2 (en) | 2011-12-21 |
| US7653288B2 (en) | 2010-01-26 |
| BRPI0411850A (en) | 2006-08-29 |
| HK1090166A1 (en) | 2006-12-15 |
| US20050053360A1 (en) | 2005-03-10 |
| WO2005017897A1 (en) | 2005-02-24 |
| CA2531336C (en) | 2012-10-02 |
| JP2007503068A (en) | 2007-02-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7596579B2 (en) | Method of reproducing an information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player startup information | |
| US7653288B2 (en) | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, method for reproducing AV data in interactive mode | |
| US7493552B2 (en) | Method to display a mark-up document according to a parental level, method and apparatus to reproduce the mark-up document in an interactive mode, and a data storage medium therefor | |
| US7650063B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for reproducing AV data in interactive mode, and information storage medium thereof | |
| US20090154901A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for reproducing data | |
| JP4559412B2 (en) | Information recording medium recorded with data structure adaptively reproducible by player startup information, and reproducing method and apparatus thereof | |
| US20050094973A1 (en) | Moving picture reproducing apparatus in which player mode information is set, reproducing method using the same, and storage medium | |
| KR100565057B1 (en) | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information, method and apparatus thereof | |
| US20050089314A1 (en) | Information storage medium with search information file recorded thereon, method and reproducing apparatus for reproducing the information storage medium | |
| RU2316062C2 (en) | Information storage carrier having a data structure for adaptive reproduction in accordance with player profile information, method for reproduction of av-data in interactive mode | |
| KR100584574B1 (en) | Information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information | |
| KR100584573B1 (en) | Reproducing method of information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player profile information | |
| RU2313138C2 (en) | Information storage carrier having a data structure for adaptive reproduction of reproduction means according to launch information, method and device for reproduction of carrier | |
| EP1772868A2 (en) | A method to display a mark-up document according to a parental level, method and apparatus to reproduce the mark-up document in an interactive mode, and a data storage medium therefor | |
| TW200425077A (en) | Method of reproducing an information storage medium having data structure for being reproduced adaptively according to player startup information |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO., LTD., KOREA, REPUBLIC OF Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:JUNG, KIL-SOO;PARK, SUNG-WOOK;REEL/FRAME:016013/0671 Effective date: 20041122 |
|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |