KR810001731B1 - Quart crystal vibriator - Google Patents
Quart crystal vibriator Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR810001731B1 KR810001731B1 KR7701789A KR770001789A KR810001731B1 KR 810001731 B1 KR810001731 B1 KR 810001731B1 KR 7701789 A KR7701789 A KR 7701789A KR 770001789 A KR770001789 A KR 770001789A KR 810001731 B1 KR810001731 B1 KR 810001731B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- vibrator
- electrode
- quartz crystal
- electrodes
- crystal vibrator
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Piezo-Electric Or Mechanical Vibrators, Or Delay Or Filter Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
Description
제1도는 종래의 진동자의 커트각을 도시한 것이고,1 shows a cut angle of a conventional vibrator,
제2도는 종래의 실시예를 표면에서 본 도면,2 is a surface view of a conventional embodiment,
제3도는 종래의 실시예를 이면에서 본 도면,3 is a view of a conventional embodiment from the back,
제4도는 종래의 실시예의 내부 전계(電界)를 표시하기 위한 단면도,4 is a sectional view for displaying an internal electric field of a conventional embodiment,
제5도는 수정진동자를 사용한 발진회로의 일예를 보인 회로도,5 is a circuit diagram showing an example of an oscillation circuit using a crystal oscillator,
제6도는 부가용량에 의한 발진주파수의 변화를 나타낸 그라프도,6 is a graph showing a change in oscillation frequency due to additional capacitance;
제7도는 본 발명의 진동자를 표면에서 본 사시도,Figure 7 is a perspective view of the vibrator of the present invention from the surface,
제8도는 본 발명의 진동자를 이면에서 본 사시도,8 is a perspective view from the back of the vibrator of the present invention,
제9도는 본 발명의 진동자의 단면도,9 is a cross-sectional view of the vibrator of the present invention,
제10도는 각종 진동자의 단면도이고, 화살표는 전계의 방향을 표시하고 있다.10 is a cross-sectional view of various vibrators, and arrows indicate directions of electric fields.
제11도는 본 발명의 진동자의 제법예를 표시한 사시도,11 is a perspective view showing a manufacturing example of the vibrator of the present invention,
제12도는 본 발명에 의한 수정진동자의 등가회로도.12 is an equivalent circuit diagram of a crystal oscillator according to the present invention.
본 발명은 포토 에칭제법에 의한 박판상의 수정 진동자의 측면에도 전극을 부여하므로서 특성의 향상과 제법의 합리화를 기함을 목적으로 한다.An object of this invention is to provide the electrode also to the side surface of a thin crystal crystal vibrator by the photo-etching method, and to aim at the improvement of a characteristic and the rationalization of a manufacturing method.
수정진동자의 제조에 포토 에칭기술을 적용하므로서 진동자는 대폭으로 소형화되고 또 저가격화되었다.By applying the photo etching technique to the production of the crystal oscillator, the vibrator has been greatly miniaturized and inexpensive.
그러나 투성면에서는 종래의 기계가공에 의한 후형(厚型)의 것에는 약간 미달했다.However, in the permeable surface, it was slightly below the thick type by the conventional machining.
본 발명은 신규의 전극배치와 고정법의 조합에 의하여 기계가공에 의한 것에 대등한 성능을 얻으려고 하는 것으로서, 이하 도면을 따라 설명한다.The present invention intends to obtain a performance comparable to that by machining by a combination of a novel electrode arrangement and a fixing method, which will be described below with reference to the drawings.
제1도에서 보는 바와같이 본 발명에 관계되는 음차형(音叉型) 진동자(2)는 두께 0.2mm 이하의 얇은 수정판/으로 포토에침법을 사용하여서 만들어진다. 이 수정판 /은 X축의 주위로 α(0°-10°), 이어서 Y1축의 주위로 B(70°-90°)회전시켜서 얻어진다.As shown in FIG. 1, the
이하에 있어서는 설명의 간략화를 위하여 α는 0°β는 90°로 취한다.In the following description, alpha is 0 ° beta is 90 ° for the sake of simplicity.
제2, 3, 4도는 종래의 수정진동자의 표면과 이면 및 단면도이며 이 음차의 표리각면에는 각기 2극성의 전극(3), (5) 및 (4), (6)이 설치되어 있고 각 차(叉)에 있어서 한편은 다른편을 둘러싸도록 배치되어 있다.2, 3, and 4 are the front, back, and cross-sectional views of a conventional crystal oscillator, each of which has bipolar electrodes (3), (5), (4), and (6) on each side of the tuning fork. In (i), one side is arrange | positioned so that the other side may be enclosed.
제4도는 내부 전계의 상황을 설명하기 위한 도면이고 표리의 대향하는 전극대(電極對)(3), (5)와 (4), (6)은 각기 같은 극성에 연결된다. 이 때문에 내부에는 화살표로 표시한 것처럼 X축에 평행한 전계가 발생하여 이 음차는 굴곡운동을 한다.4 is a view for explaining the situation of the internal electric field, and opposing
제2도에 있어서 진동자(2)는 전극 리이드를 겸한 리이드 선(11), (12)에 합금, 땜잡 등의 도전성이 있는 물질로 첩착되어 있다. 구멍(7), (8)애눈 도전계(導電劑)(9), (10)이 주입되어 있고, 표면과 이면의 전극간의 전기적 접속이 이루어진다.In FIG. 2, the
상기 제조방법에 의하면 한번에 수 10개의 진동자가 배취 생산되기 때문에 종래의 후현진동자를 기계적으로 가공하는 방법에 비하여 공정상의 대폭적인 합리화를 기할 수 있고 코스트 다운이 가능하다. 또 상기한 진동자는 길이 5mm 폭 1.5mm 이하로 하는 것이 용이하므로 단순한 지지방법과 상호관련하여 대폭적인 소형화가 가능하다.According to the above manufacturing method, since several ten vibrators are batch-produced at a time, the process can be greatly rationalized and the cost can be reduced compared to the conventional method of mechanically processing the rear-side vibrator. In addition, since the vibrator can easily be 5 mm long and 1.5 mm wide or less, it is possible to greatly reduce the size of the vibrator in connection with a simple supporting method.
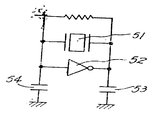
제5도는 수정진동자를 사용한 발진회로의 일예이고 (5)는 수정진동자, (52)는 C-MOS 트랜지스터를 사용한 인버어터, (53)은 드레인용량, (54)는 게이트용량을 나타내고 있다.5 shows an example of an oscillation circuit using a crystal oscillator, 5 denotes a crystal oscillator, 52 denotes an inverter using a C-MOS transistor, 53 denotes a drain capacitance, and 54 denotes a gate capacitance.
제6도는 드레인 혹은 게이트 용량을 변화시켰을 때, 발진주파수가 어떻게 변화되는가를 나타내고 있고, (55)는 등가 직렬용량이 1×10-15F, 56은 등가 직렬용량이 2×10-15F의 진등자의 경우이다.6 shows how the oscillation frequency changes when the drain or gate capacitance is changed. (55) shows an equivalent series capacitance of 1 × 10 -15 F, and 56 shows an equivalent series capacitance of 2 × 10 -15 F. It is the case of a senior.
제조상의 관점으로서는, 상기한 주파수 가변폭은 도리수 있는대로 넓은 것이 바람직하다. 제2도∼4도에서 설명한 진동자에 있어서 등가직렬 용량은 1×10-15F 정도이고 더욱 더 개량된 것이 바람직하다.From a manufacturing viewpoint, it is preferable that said frequency variable width is as wide as possible. In the vibrator described in FIGS. 2 to 4, the equivalent series capacitance is about 1x10 -15 F, and it is preferable to further improve.
제7, 8, 9도는 각기 본 발명에 관한 진동자(14)의 표면, 이면, 단면도이다. 진동자(14)의 커트 각 및 제조방법, 형상은 먼저 설명한 종래의 것과 본질적으로 같은 것이다. 도면에 있어서 (15),(15'),(16),(16')는 측면에 부여된 전극이고, 음창의 에지에 있어서 전극(17),(20) 및 (18),(19)와 통한다. 단면도에서 보는 바와 같이, 이 진동자 내부에는 X방향의 전계가 유효하게 가동하기 때문에, 제3도의 경우와 비교하여서 효율이 높고, 등가직렬용량도 커진다. 우리들의 시험의 결과로는 종래 예의 약 2배의 값이 얻어졌다.7, 8, and 9 are front, back, and sectional views of the
수정진동자는 등가회로로 치환하면 제12도와 같이 코일 L1과 등가 직열용량 C1과 저항 R1및 병열용량 Co로 표시한다.When the quartz crystal oscillator is replaced with an equivalent circuit, the coil L 1 , the equivalent series capacitance C 1 , the resistance R 1, and the parallel capacitance Co are represented as shown in FIG. 12.
CL는 부하용량으로 제5도의 53,54에 상당한다.C L corresponds to the load capacity of 53,54 in FIG.
그때에는, 공진주파수 F는 차식으로 표시하는 것이 일반적으로 알려져 있다.At that time, it is generally known that the resonance frequency F is expressed by the following equation.
이 식에 의하면, CL의 증가에 따라 주파수 f가 지수관수적으로 변화하는 것을 알 수 있다.According to this equation, it can be seen that the frequency f changes exponentially with increasing C L.
또한 서술과 같이 수전진동자의 측면에 전극을 형성하면 등가직열용량 G가 거의 2배가 되고, 그 결과 CL의 변화에 대하여, 주파수 f의 변화량이 많아지는 것이 명백하게 된다.As described above, when the electrode is formed on the side surface of the power receiving oscillator, the equivalent direct heat capacity G is almost doubled, and as a result, it becomes clear that the amount of change in the frequency f increases with respect to the change in C L.
그때, CL값의 설정을 주파수 f의 변화랑이 큰 곳에서 실시함으로서 측면전극이 없는 종래의 수정진동자에 비교해서 공진주파수를 맞추워 넣기에 대하여 허용범위를 거의 2배로 할 수가 있다.At this time, by setting the C L value at a large variation in the frequency f, the allowable range can be nearly doubled for the resonant frequency to be matched with that of a conventional crystal oscillator without side electrodes.
다음에 본 진동자의 특징을 다른 진동자와 비교하여 제10도를 따라 설명하기로 한다. A도에 표시하는 것은 종래의 기계가공에 의한 후형의 진동자이고, 전계는 표리의 전극과 측면의 전극사이에 발생된다.Next, the characteristics of the present vibrator will be described with reference to FIG. 10 in comparison with other vibrators. Shown in FIG. A is a thick vibrator by conventional machining, and an electric field is generated between the front and back electrodes and the side electrodes.
이 진동자의 전기적 특성은 우수하고 현재 가장 널리 사용되고 있는, B도는 이 진동자의 전극구조를 박형의 진동자에 적용한 예이다. 이 경우에 측면 전극이 작기 때문에 발새오디는 전계의 효율이 나쁘고 실용성이 적다. C도에 표시하는 것은 이미 설명한 것이나, 측면전극을 폐지하고 대신에 표리의 주변부에 전극을 설치한 것으로 생각된다. E도는 C도의 전극구조를 후형의 진동자에 적용한 것이고, 두껍기 때문에 전계는 내부까지 도달하지 않고 효율이 불량하다.The electrical characteristics of the vibrator are excellent and the most widely used presently, B is an example of applying the electrode structure of the vibrator to a thin vibrator. In this case, since the side electrodes are small, the germination audio has a low electric field efficiency and low practicality. Although it is already demonstrated to display in FIG. C, it is thought that the side electrode was removed and the electrode was provided in the periphery of the front and back instead. E is the electrode structure of C is applied to a thick vibrator, and because it is thick, the electric field does not reach the inside and the efficiency is poor.
D도는 B도와 C도의 장점을 취한 것으로서 내부전계는 표리의 외주부의 전극과 측면의 전극의 효과에 따라 대단히 효과에 따라 대단히 효과적으로 인가된다. 이 효과는 후형의 진동자로는 전혀 불가능하고, 포토에침에 의한 박형 진동자에 있어서 비로소 가능한 것이다.Fig. D takes the advantages of Fig. B and C. The internal electric field is applied very effectively according to the effect of the electrode on the outer peripheral part of the front and back and the side electrode. This effect is impossible at all with a thick vibrator, and is only possible with a thin vibrator by photo-etching.
본 발명에 있어서는 표리 전극간의 통전은 이미 취해져 있으므로 종래와 같은 구멍은 없다. 따라서 본 진동자를 부착할 때에는 기밀단자(23)을 관통하는 2개의 리이드선(21),(22)에 첩착하기만 하면 되고 종래와 비교하여서 간단하다.In the present invention, since energization between the front and back electrodes is already taken, there is no hole as in the prior art. Therefore, when attaching this vibrator, it only needs to adhere to the two
제11도는 본 발명에 관한 진동자의 제법예를 나타낸 도면이다.11 is a diagram showing an example of the method of manufacturing a vibrator according to the present invention.
도면에 있어서 (24)는 1장의 수정판으로 형성되며, 표면 및 이면의 전극이 부여된 다수의 진동자중 2개이고 이들은 틀(25)와 연결되어서 서로 분리되는 것을 방지하고 있다. 실제로는 수 10개의 진동자가 연걸되고 있는 것이지만, 도면의 간략화를 위해 일부분을 발취하여 확대도시한 것이다. (26),(27)은 금속판 등으로 만들어진 마스크이고 구멍(28),(28')이 뚫어져 있다. 중앙의 구멍(28')는 약간 폭이 넓고, 좌우의 차(叉)에 걸쳐서 뚫려있다. 이들 2매의 마스크로 진동자를 협지하여 저항가열 혹은 스패터링 등으로 금속막을 증착하면 진동자의 에지부분 및 측면에 전극막이 형성된다. 또 진동자의 마스크는 증발원에 대하여 기울어지도록 하고, 혹은 반전시키는 것이 바람직하다.In the figure, 24 is formed of a single crystal plate, which is two of a plurality of vibrators provided with electrodes on the front and back thereof, which are connected to the mold 25 to prevent them from being separated from each other. In reality, ten or more vibrators are connected, but parts are extracted and enlarged for simplification of the drawings.
본 발명에 있어서 측면전극은 음차의 측면전체에 설치할 필요는 업속, 굴곡 변형이 있는 부분에만 설치하여도 된다. 또 측면 전극은 4개의 측면 전부에 부여하는 것이 바람직하지만, 그중 몇 개를 생략해도 무방하다.In the present invention, the side electrode may be provided only at the portion having up speed and bending deformation if it is necessary to be installed on the entire side of the tuning fork. Moreover, although it is preferable to provide a side electrode to all four side surfaces, you may abbreviate some of them.
본 발명에 있어서는, 종래는 표리 양면에만 있었던 전극을 측면에도 만드는 셈이지만, 이 때문에 진동자를 일일이 정렬시킬 필요는 없으며, 수 10개의 진동자가 일체전으로 만들어진 수정의 틀을 개재하여서 연결된 상태로 처리할 수 있으므로, 공전이 합리적이고 한 개당의 공수도 근소하므로, 여기에서도 본 진동자의 제법의 특징이 잘 나타나 있다.In the present invention, the electrodes conventionally existed only on both sides of the front and back are also made on the side, but for this reason, it is not necessary to align the vibrators one by one. Since the revolving is reasonable and the number of maneuvers per piece is few, the characteristics of the manufacturing method of this vibrator are well shown here.
이미 기술한 바와 같이 본 발명에 의하면 등가 직렬용랑은 2×10-15F이므로 제6도에 있어서 (56)의 곡선이 얻어지고, 종래의 박형진동자의 거의 2배의 가변변위가 얻어진다. 이 때문에 본 발명의 진동자 사용하면, 진동자 제조공정에 있어서의 공진주파수의 맞추워 넣기에 대한 허용범위가 거의 종래의 2배로 되기 때문에 제조가 용이하고 수율(收率)도 대폭으로 향상된다. 또 시계 등에 조립된 후에의 보도(步度) 조정도 용이한 것이다.As described above, according to the present invention, since the equivalent series melt is 2 x 10 -15 F, the curve of (56) is obtained in FIG. 6, and nearly twice the variable displacement of the conventional thin oscillator is obtained. For this reason, when using the vibrator of this invention, since the permissible range for fitting of the resonant frequency in a vibrator manufacturing process becomes nearly twice conventional, manufacture is easy and a yield improves significantly. Moreover, the sidewalk adjustment after being assembled to a watch etc. is also easy.
이들의 특징은 측면전극을 만드는 공수의 증가를 상살하고도 남음이 있는 것이며 본 발명이 진동자의 소형, 고성능, 저가격화에 기여되는 것도 크고 특히 팔목시계용으로서 최적이다.The characteristics of these are that the increase in the number of man-hours to make the side electrode, and the present invention contributes to the small size, high performance, low price of the vibrator, and is particularly suitable for wrist watches.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR7701789A KR810001731B1 (en) | 1977-08-02 | 1977-08-02 | Quart crystal vibriator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR7701789A KR810001731B1 (en) | 1977-08-02 | 1977-08-02 | Quart crystal vibriator |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR810001731B1 true KR810001731B1 (en) | 1981-11-07 |
Family
ID=19204692
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR7701789A KR810001731B1 (en) | 1977-08-02 | 1977-08-02 | Quart crystal vibriator |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR810001731B1 (en) |
-
1977
- 1977-08-02 KR KR7701789A patent/KR810001731B1/en active
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3969641A (en) | Quartz crystal vibrator | |
| US4099078A (en) | Quartz crystal tuning fork with three electrodes on each major tine face | |
| US4468584A (en) | Unidirectional flexure type tuning fork crystal vibrator | |
| JP2001223553A (en) | Ultra-thin piezoelectric resonator | |
| JPS5925486B2 (en) | piezoelectric vibrator container | |
| US4421621A (en) | Quartz crystal oscillator | |
| US4005321A (en) | Quartz crystal vibrator mounting | |
| GB2002955B (en) | Oscillator assembly | |
| US3944862A (en) | X-cut quartz resonator using non overlaping electrodes | |
| KR810001731B1 (en) | Quart crystal vibriator | |
| GB918127A (en) | Improvements in or relating to electromechanical filters | |
| GB2024503A (en) | Piezo-electric resonator | |
| JPH0233392Y2 (en) | ||
| US6937119B1 (en) | High frequency apparatus | |
| JPS6223489B2 (en) | ||
| JPS5818810B2 (en) | Onsagata Atsuddenkuyokushindoushi | |
| JPS6145505Y2 (en) | ||
| JPH0637567A (en) | Electrode forming method for thick system crystal resonator | |
| JPH0265503A (en) | Microstrip antenna | |
| JPS6216573B2 (en) | ||
| GB1353408A (en) | Electronic timepiece | |
| JPH089935Y2 (en) | Quartz crystal electrode structure | |
| JPS6048925B2 (en) | Support structure of tuning fork crystal resonator | |
| GB608986A (en) | Improvements in or relating to the mounting of piezo-electric quartz crystal elements | |
| JPS5833721B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of tuning fork type piezoelectric vibrator |