KR20220025477A - Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback - Google Patents
Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20220025477A KR20220025477A KR1020200106227A KR20200106227A KR20220025477A KR 20220025477 A KR20220025477 A KR 20220025477A KR 1020200106227 A KR1020200106227 A KR 1020200106227A KR 20200106227 A KR20200106227 A KR 20200106227A KR 20220025477 A KR20220025477 A KR 20220025477A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- client
- eeg
- interface
- data
- brain wave
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/369—Electroencephalography [EEG]
- A61B5/375—Electroencephalography [EEG] using biofeedback
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/369—Electroencephalography [EEG]
- A61B5/372—Analysis of electroencephalograms
- A61B5/374—Detecting the frequency distribution of signals, e.g. detecting delta, theta, alpha, beta or gamma waves
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/40—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the nervous system
- A61B5/4058—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the nervous system for evaluating the central nervous system
- A61B5/4064—Evaluating the brain
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M21/00—Other devices or methods to cause a change in the state of consciousness; Devices for producing or ending sleep by mechanical, optical, or acoustical means, e.g. for hypnosis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/60—Protecting data
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/60—Protecting data
- G06F21/602—Providing cryptographic facilities or services
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/70—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to mental therapies, e.g. psychological therapy or autogenous training
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M2230/00—Measuring parameters of the user
- A61M2230/08—Other bio-electrical signals
- A61M2230/10—Electroencephalographic signals
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Developmental Disabilities (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Social Psychology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Bioethics (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명의 기술적 사상은 뉴로피드백에 관한 것으로서, 자세하게는 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법 및 시스템에 관한 것이다.The technical idea of the present invention relates to neurofeedback, and more particularly, to a method and system for testing and training based on neurofeedback.
뉴로피드백(neurofeedback)은 1934년 영국 캠브리지대학교에서 처음으로 발견된 이후 지속적으로 연구되고 개발된 뇌과학의 중요한 학문분야로서, 뇌의 항상성 자기조절 능력을 강화시키고, 이에 따라 뇌와 인체의 건강을 증진하거나 그 기능을 강화하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이와 같은 뉴로피드백을 위하여, 피험자로부터 뇌파를 정확하게 측정하는 것이 요구될 수 있고, 측정된 뇌파로부터 유용한 정보를 피험자에게 제공하는 요구될 수 있다. 전자의 요건을 위하여 높은 성능의 뇌파 측정 장치가 필요할 수 있는 한편, 후자의 요건을 위하여 고도의 알고리즘 및 방대한 양의 수집된 데이터의 처리가 필요할 수 있다.Neurofeedback is an important field of brain science that has been continuously researched and developed since it was first discovered at the University of Cambridge in England in 1934. or to enhance its function. For such neurofeedback, it may be required to accurately measure EEG from the subject, and it may be required to provide useful information to the subject from the measured EEG. For the former requirement, a high-performance EEG measurement device may be required, while for the latter requirement, a high-level algorithm and processing of a large amount of collected data may be required.
본 발명의 기술적 사상은, 뉴로피드백을 위한 뇌파 처리의 높은 계산 복잡도를 효율적으로 해소하고, 높은 편의성 및 보안성을 제공할 수 있는 방법 및 시스템을 제공한다.The technical idea of the present invention provides a method and system that can efficiently solve the high computational complexity of brain wave processing for neurofeedback and provide high convenience and security.
상기와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위하여, 본 발명의 기술적 사상의 일측면에 따른 시스템은, 네트워크를 통해서 제1 클라이언트로부터, 제1 클라이언트의 식별 정보, 피험자의 생체 정보, 피험자의 뇌파를 측정함으로써 생성된 뇌파 데이터를 수신하는 제1 인터페이스, 유효한(valid) 제1 클라이언트들의 정보를 저장하는 인증 시스템과의 통신을 제공하는 제2 인터페이스, 및 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 인증 시스템에 식별 정보를 제공하고, 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 제1 클라이언트의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성하고, 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 제1 클라이언트에 출력 데이터를 제공하는 뇌파 처리부를 포함할 수 있다.In order to achieve the above object, the system according to one aspect of the technical idea of the present invention is generated by measuring the identification information of the first client, the biometric information of the subject, and the brain wave of the subject from the first client through a network. A first interface for receiving EEG data, a second interface for providing communication with an authentication system that stores information of valid first clients, and a second interface for providing identification information to the authentication system through the second interface, the authentication system It may include an EEG processing unit that generates output data based on the biometric information and EEG data of the first client authenticated by , and provides the output data to the first client through the first interface.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 제1 인터페이스는, 네트워크를 통해서 제2 클라이언트로부터 피험자의 뉴로피드백(neurofeedback)을 위한 설정을 수신할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 제1 클라이언트의 식별 정보에 대응하는 설정을 식별하고, 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 제1 클라이언트에 식별된 설정을 제공할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first interface may receive a setting for neurofeedback of a subject from a second client through a network, and the EEG processing unit corresponds to the identification information of the first client The identified setting may be identified, and the identified setting may be provided to the first client through the first interface.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 설정은, 훈련 프로토콜, 훈련 프로그램의 종류, 훈련 프로그램의 순서, 훈련 프로그램의 실행 시간, 훈련 프로그램의 조건, 훈련 프로그램의 난이도, 훈련 횟수, 훈련 프로그램의 등급 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the setting may be selected from among a training protocol, a type of training program, an order of a training program, an execution time of the training program, conditions of the training program, difficulty of the training program, the number of training sessions, and a grade of the training program. It may include at least one.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 제1 인터페이스는, 제2 클라이언트로부터 출력 데이터에 대한 의견을 수신할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 의견을 제1 클라이언트에 제공할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first interface may receive an opinion on the output data from the second client, and the brain wave processing unit may provide the opinion to the first client through the first interface.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 시스템은 설정 및 의견을 저장하는 데이터베이스와 통신을 제공하는 제3 인터페이스를 더 포함할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 제1 클라이언트의 식별 정보에 대응하는 설정 및 의견을 데이터베이스로부터 획득할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the system may further include a third interface for providing communication with a database for storing settings and opinions, and the EEG processing unit, settings and opinions corresponding to the identification information of the first client can be obtained from the database.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 뇌파 처리부는, 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여, 기초율동 지수, 자기조절 지수, 주의 지수, 활성 지수, 감성 지수, 항스트레스 지수, 좌우 뇌균형 지수, 뇌지수를 포함하는 복수의 지수들을 생성할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the EEG processing unit, based on biometric information and EEG data, basic rhythm index, self-regulation index, attention index, activity index, emotional index, anti-stress index, left and right brain balance index, brain A plurality of exponents including the exponent can be created.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 제1 인터페이스는, 제1 클라이언트로부터 분석 파라미터를 더 수신할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 복수의 지수들 중 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택하고, 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함하는 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first interface may further receive an analysis parameter from the first client, and the EEG processing unit selects at least one index among a plurality of indexes based on the analysis parameter, Output data including at least one index may be generated.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 제2 인터페이스는, 인증 시스템으로부터 식별 정보에 대응하는 분석 파라미터를 더 수신할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 복수의 지수들 중 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택하고, 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함하는 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the second interface may further receive an analysis parameter corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system, and the EEG processing unit, based on the analysis parameter, includes at least one index among the plurality of indexes. may be selected, and output data including at least one index may be generated.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 제1 인터페이스는, 제1 클라이언트로부터 하드웨어 키를 포함하는 등록 요청을 더 수신할 수 있고, 하드웨어 키를 검증하고, 검증된 하드웨어 키에 응답하여 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 인증 시스템에 제1 클라이언트의 등록을 요청하고, 인증 시스템으로부터 제공된 암호화 키를 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 제1 클라이언트에 제공할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first interface may further receive a registration request including a hardware key from the first client, verify the hardware key, and configure the second interface in response to the verified hardware key. Through this, a registration of the first client may be requested from the authentication system, and an encryption key provided from the authentication system may be provided to the first client through the first interface.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터는, 암호화 키에 기초하여 암호화될 수 있고, 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 인증 시스템으로부터 식별 정보에 대응하는 복호화 키를 수신하고, 복호화 키에 기초하여 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 복호화될 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, biometric information and brain wave data may be encrypted based on an encryption key, receive a decryption key corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system through the second interface, and based on the decryption key Thus, biometric information and EEG data can be decoded.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 생체 정보는, 피험자의 나이, 시력, 신장, 체중, 혈액형, 아이큐, 혈압, 혈당, 질병, 복용약 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the biometric information may include at least one of a subject's age, eyesight, height, weight, blood type, IQ, blood pressure, blood sugar, disease, and medication.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 복수의 피험자들에 대한 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 저장하는 데이터베이스와의 통신을 제공하는 제3 인터페이스를 더 포함할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부는, 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 제1 클라이언트의 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를 제3 인터페이스를 통해서 데이터베이스로부터 획득하고, 참조 데이터에 기초하여 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, it may further include a third interface that provides communication with a database for storing identification information and EEG data for a plurality of subjects, and the EEG processing unit is authenticated by the authentication system The reference data corresponding to the biometric information of the first client may be obtained from the database through the third interface, and output data may be generated by processing the EEG data based on the reference data.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 뇌파 처리부는, 인증된 제1 클라이언트의 생체 정보, 뇌파 데이터 및 출력 데이터 중 적어도 하나를 제3 인터페이스를 통해서 데이터베이스에 저장할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the EEG processing unit may store at least one of biometric information, EEG data, and output data of the authenticated first client in the database through the third interface.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 뇌파 처리부는, 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터의 복수의 샘플들에 의해서 학습된 기계 학습 모델을 포함하고, 인증된 제1 클라이언트의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 기계 학습 모델에 제공하고, 기계 학습 모델로부터 출력 데이터의 적어도 일부를 획득할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the EEG processing unit includes a machine learning model learned by a plurality of samples of identification information and EEG data, and uses the biometric information and EEG data of the authenticated first client as a machine learning model. and may obtain at least a portion of the output data from the machine learning model.
본 발명의 기술적 사상의 일측면에 따른 뇌파 처리 방법은, 네트워크를 통해서 클라이언트로부터, 클라이언트의 식별 정보, 피험자의 생체 정보, 피험자의 뇌파를 측정함으로써 생성된 뇌파 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 유효한 클라이언트들의 정보를 저장하는 인증 시스템에 식별 정보를 제공하는 단계, 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 클라이언트의 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를 데이터베이스로부터 수신하는 단계, 참조 데이터에 기초하여 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성하는 단계, 및 출력 데이터를 클라이언트에 제공하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The brain wave processing method according to one aspect of the present invention comprises the steps of receiving, from a client, the client's identification information, the subject's biometric information, and the brain wave data generated by measuring the subject's brain wave, through a network, effective client information Providing identification information to an authentication system storing and providing the output data to the client.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 뇌파 처리 방법은, 클라이언트로부터 하드웨어 키를 포함하는 등록 요청을 수신하는 단계, 하드웨어 키를 검증하고, 검증된 하드웨어 키에 응답하여 인증 시스템에 클라이언트의 등록을 요청하는 단계, 및 인증 시스템으로부터 제공된 암호화 키를 클라이언트에 제공하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an EEG processing method includes receiving a registration request including a hardware key from a client, verifying the hardware key, and requesting registration of the client from the authentication system in response to the verified hardware key and providing the encryption key provided from the authentication system to the client.
본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라, 인증 시스템으로부터 식별 정보에 대응하는 복호화 키를 수신하는 단계, 및 복호화 키에 기초하여 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 복호화하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the method may further include receiving a decryption key corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system, and decrypting the biometric information and EEG data based on the decryption key.
본 발명의 기술적 사상에 따른 방법 및 시스템에 의하면, 높은 계산 복잡도의 동작을 클라이언트로부터 해방시킬 수 있고, 이에 따라 뉴로피드백을 위한 테스트 및 트레이닝 서비스가 광범위하고 용이하게 구축될 수 있다.According to the method and system according to the technical idea of the present invention, it is possible to release the operation of high computational complexity from the client, and accordingly, a test and training service for neurofeedback can be extensively and easily constructed.
또한, 본 발명의 기술적 사상에 따른 방법 및 시스템에 의하면, 클라이언트의 식별 정보와 피험자의 개인 정보가 분리됨으로써, 개인 정보 유출의 위험이 감소할 수 있고, 높은 보안성이 달성될 수 있다.In addition, according to the method and system according to the technical idea of the present invention, by separating the identification information of the client and the personal information of the subject, the risk of personal information leakage can be reduced and high security can be achieved.
본 발명의 실시예들에서 얻을 수 있는 효과는 이상에서 언급한 효과들로 제한되지 아니하며, 언급되지 아니한 다른 효과들은 이하의 본 발명의 실시예들에 대한 기재로부터 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 명확하게 도출되고 이해될 수 있다. 즉, 본 발명을 실시함에 따른 의도하지 아니한 효과들 역시 본 발명의 실시예들로부터 당해 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 도출될 수 있다.Effects obtainable in the embodiments of the present invention are not limited to the above-mentioned effects, and other effects not mentioned are common in the art to which the present invention belongs from the description of the embodiments of the present invention below. It can be clearly derived and understood by those with knowledge. That is, unintended effects of practicing the present invention may also be derived by a person of ordinary skill in the art from the embodiments of the present invention.
도 1은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템을 나타내는 블록도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템을 나타내는 블록도이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템을 나타내는 블록도이다.1 is a block diagram showing an EEG processing system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a block diagram illustrating an EEG processing system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a block diagram illustrating an EEG processing system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
이하, 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 대해 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명의 실시예는 당 업계에서 평균적인 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 보다 완전하게 설명하기 위하여 제공되는 것이다. 본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 개시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 각 도면을 설명하면서 유사한 참조부호를 유사한 구성요소에 대해 사용한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The embodiments of the present invention are provided to more completely explain the present invention to those of ordinary skill in the art. Since the present invention may have various changes and may have various forms, specific embodiments will be illustrated in the drawings and described in detail. However, this is not intended to limit the present invention to the specific disclosed form, it should be understood to include all modifications, equivalents and substitutes included in the spirit and scope of the present invention. In describing each figure, like reference numerals are used for like elements.
본 출원에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수개의 표현을 포함한다. 본 출원에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 명세서 상에 기재된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성 요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The terms used in the present application are only used to describe specific embodiments, and are not intended to limit the present invention. The singular expression includes the plural expression unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. In the present application, terms such as “comprise” or “have” are intended to designate that a feature, number, step, operation, component, part, or a combination thereof described in the specification exists, but one or more other features It should be understood that the existence or addition of numbers, steps, operations, components, parts or combinations thereof is not precluded in advance.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 갖는다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가지는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 아니하는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.Unless defined otherwise, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Terms such as those defined in a commonly used dictionary should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the meaning in the context of the related art, and unless explicitly defined in the present application, it should be interpreted in an ideal or excessively formal meaning doesn't happen
이하 도면 및 설명에서, 하나의 블록으로 표시 또는 설명되는 구성요소는 하드웨어 블록 또는 소프트웨어 블록일 수 있다. 예를 들면, 구성요소들 각각은 서로 신호를 주고 받는 독립적인 하드웨어 블록일 수도 있고, 또는 적어도 하나의 프로세서에서 실행되는 소프트웨어 블록일 수도 있다.In the drawings and description below, a component indicated or described as one block may be a hardware block or a software block. For example, each of the components may be an independent hardware block that sends and receives signals to and from each other, or may be a software block executed by at least one processor.
도 1은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템을 나타내는 블록도이다. 도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 네트워크(5)에 접속할 수 있고, 네트워크(5)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)와 통신할 수 있다. 또한, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 인증(authentication) 시스템(7) 및 데이터베이스(9)와 통신할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 도 1에 도시된 바와 상이하게, 인증 시스템(7) 및 데이터베이스(9)가 네트워크(5)에 접속할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 네트워크(5)를 통해서 인증 시스템(7) 및 데이터베이스(9)와 통신할 수도 있다.1 is a block diagram illustrating an EEG processing system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1 , the brain
제1 클라이언트(2)는 피험자(1)의 뇌파를 측정함으로써 뇌파 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 피험자(1)는, 본 출원의 출원인이 특허권자로 있는 등록특허공보 제10-2126002호에 개시된 뇌파 측정 장치를 착용할 수 있고, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 뇌파 측정 장치로부터 복수의 채널들을 통해서 감지되는 신호들을 수신할 수 있다. 또한, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 피험자(1)로부터 입력된 생체 정보, 예컨대 나이, 시력, 신장, 체중, 혈액형, 아이큐, 혈압, 혈당, 질병, 복용약 등을 수신할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 데스크탑 컴퓨터, 랩탑 컴퓨터와 같은 퍼스널 컴퓨터일 수 있고, 뇌파 측정 장치와 통신가능하게 연결될 수 있다. 또한, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 네트워크(5)를 통해서 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)으로부터 제공되는 출력 데이터를 피험자(1)에게, 예컨대 디스플레이, 프린트 등을 통해 제공할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 데이터는 시간의 흐름에 따라 복수의 채널들을 통해서 뇌파를 감지함으로써 생성된 일련의 샘플들을 포함할 수 있고, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 네트워크(5)를 통해서 뇌파 데이터를 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 제공할 수 있다.The
제1 클라이언트(2)는 뉴로피드백(neurofeedback)을 피험자(1)에게 제공할 수 있다. 뉴로피드백은 "신경 바이오피드백"으로서 지칭될 수도 있고, 뇌파를 측정하여 이 신호를 선택적으로 자신의 뇌와 피드백함으로써 뇌의 항상성 자기조절 능력을 향상시키는 기법을 지칭할 수 있다. 뉴로피드백은 뇌과학의 중요한 분야로서 많은 연구가 진행되고 있고, 새로운 훈련기법들이 제안되고 있고 새로운 사실들이 발견되고 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌가 사용하면 할수록 발달되고 필요에 따라 스스로 신경망을 발달시키는 특성인 뇌의 가소성(plasticity)이 발견되었으며, 신경세포, 즉 뉴런 역시 끊임없이 새롭게 생성된다는 신경신생(neurogenesis)이 발견되었다. 이에 따라, 새로운 뇌 세포가 지속적으로 만들어질 수 있고, 학습에 의해서 새로운 신경망이 생성됨으로써 뇌는 끊임없이 발달할 수 있으며, 뉴로피드백은 이러한 뇌의 특성을 극대화시킬 수 있다. 제1 클라이언트(2)는 네트워크(5)를 통해서 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)과 통신할 수 있고, 후술되는 바와 같이 전문가(3)가 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 설정한 바에 따라 피험자(1)에 뉴로피드백을 제공할 수 있다. 제1 클라이언트(2)는 다양한 출력 장치들, 예컨대 디스플레이 장치, 스피커 등을 통해서 피험자(1)에 피드백을 제공할 수도 있고, 뇌파 측정 장치에 포함된 출력 장치들을 통해서 피드백(예컨대, 소리, 진동 등)이 제공되도록 뇌파 측정 장치와 통신할 수도 있다.The
제1 클라이언트(2)는 비제한적인 예시로서, 데스크탑 컴퓨터, 랩탑 컴퓨터, 스마트폰, 태블릿(tablet) PC 등과 같이 피험자(1) 자신의 컴퓨터일 수다. 또한, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 전문가(3)와 함께 있는 공간에 설치될 수 있고, 예컨대 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 제공하는 센터나 기관에서 운영되는 컴퓨팅 시스템(예컨대, 키오스크)일 수도 있고, 피험자(1)의 건강 검진 항목들 중 하나로서 뉴로피드백을 제공하는 건강 검진 센터에서 운영되는 컴퓨팅 시스템일 수도 있고, 의료기관에서 운영되는 컴퓨팅 시스템일 수도 있다. 본 명세서에서, 다른 언급이 없는 한, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 피험자(1) 자신의 컴퓨터인 것으로 가정되나, 본 발명의 예시적 실시예들이 이에 제한되지 아니하는 점은 이해될 것이다.The
전문가(3)는 제2 클라이언트(4) 및 네트워크(5)에 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 접속할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 전문가(1)는 피험자(1)와 관계된 숙련된 상담자, 의사 등이 될 수 있고, 피험자(1)의 뉴로피드백을 위한 다양한 설정들을 제2 클라이언트(4)를 통해서 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 제공할 수 있다. 제1 클라이언트(2)와 유사하게, 제2 클라이언트(4)는 비제한적인 예시로서, 데스크탑 컴퓨터, 랩탑 컴퓨터, 스마트폰, 태블릿(tablet) PC 등과 같이 피험자(1) 자신의 컴퓨터일 수 있다. 또한, 제2 클라이언트(4)는 제1 클라이언트(2)와 동일한 공간에 있을 수도 있고, 원거리에 있을 수도 있다. 또한, 일부 실시예들에서, 피험자(1) 및 전문가(3)가 동일 장소에 있는 경우, 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)는 동일할 수도 있다. 즉, 제1 클라이언트(2), 제2 클라이언트(4) 및 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 네트워크(5)에 접속할 수 있고, 예컨대 네트워크(5)는 인터넷과 같은 광역 네트워크일 수 있으며, 이에 따라 제1 클라이언트(2), 제2 클라이언트(4) 및 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)의 물리적 거리는 제한이 없을 수 있다. The
뉴로피드백을 위한 뇌파 처리(또는 뇌파 신호/데이터 처리)는 높은 계산 복잡도를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파는 델타(약 0.1 ~ 3Hz, 깊은 수면 상태), 세타(약 4 ~ 7Hz, 수면 상태), 알파(약 8 ~ 12Hz, 휴식 상태), SMR(약 12 ~ 15Hz, 각성 상태), 저베타(약 13 ~20Hz, 활성 상태), 고베타(약 21 ~ 30Hz, 활성, 흥분, 스트레스 상태), 감마(약 31Hz 이상, 활성, 정보결합 상태) 등과 같이 다양한 종류로 분류될 수 있고, 종류별 처리 알고리즘이 상이할 수 있다. 후술되는 바와 같이, 뉴로피드백에 의해서 취득된 피험자(1)의 뇌파는, 자신으로부터 이전에 측정된 뇌파뿐만 아니라 데이터베이스(9)에 수집되어 저장된 방대한 양의 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여 처리될 수 있다. 이에 따라, 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)에서 뉴로피드백에 기초한 뇌파 처리를 수행하는 것은 현실적으로 용이하지 아니할 수 있고, 뉴로피드백에 기반한 서비스의 구축을 용이하지 아니하게 할 수 있다.EEG processing (or EEG signal/data processing) for neurofeedback may have high computational complexity. For example, brain waves are delta (about 0.1 to 3 Hz, deep sleep state), theta (about 4 to 7 Hz, sleep state), alpha (about 8 to 12 Hz, resting state), SMR (about 12-15 Hz, awake state) , low beta (about 13 to 20 Hz, active state), high beta (about 21 to 30 Hz, active, excited, stressed state), and gamma (about 31 Hz or higher, active, information binding state), etc. , a processing algorithm for each type may be different. As will be described later, the brainwaves of the subject 1 acquired by neurofeedback may be processed based on a vast amount of brainwave data collected and stored in the
이하에서, 도면들을 참조하여 후술되는 바와 같이, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 네트워크(5)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)와 통신할 수 있고, 제2 클라이언트(4)에 의한 설정에 기초하여 뉴로피드백에 의해서 피험자(1)의 뇌파를 측정함으로써 생성된 뇌파 데이터를 제1 클라이언트(2)로부터 수신하여 원격에서 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)에 제공할 수 있다. 이에 따라, 높은 계산 복잡도의 뇌파 처리는, 제1 클라이언트(2)보다 높은 성능의 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에서 효율적으로 수행될 수 있다. 또한, 뇌파 처리에 요구되는 피험자(1)의 뇌파 데이터 및 생체 정보는 제1 클라이언트(2)의 인증을 위한 식별 정보와 분리될 수 있고, 이에 따라 개인 정보 유출 등의 문제가 해소될 수 있고, 높은 보안성이 달성될 수 있다. 결과적으로, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 뉴로피드백에 기반한 서비스들을 광범위하고 용이하게 구축하게 할 수 있다.Hereinafter, as described below with reference to the drawings, the brain
도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은 제1 인터페이스(11), 제2 인터페이스(12), 제3 인터페이스(13) 및 뇌파 처리부(15)를 포함할 수 있다. 제1 인터페이스(11)는 네트워크(5)에 대한 접속을 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 제공할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 제1 인터페이스(11)는 네트워크(5)를 통해서, 제1 클라이언트(2)로부터 제1 클라이언트(2)의 식별 정보, 피험자(1)의 생체 정보, 피험자(1)의 뇌파 데이터를 수신할 수 있고, 제2 클라이언트(4)로부터 제2 클라이언트(4)의 식별 정보, 전문가(3)의 생체 정보, 피험자(1)에 대한 전문가(3)의 설정 정보 등을 수신할 수 있다. 또한, 제1 인터페이스(11)는 뇌파 처리부(15)로부터 제공되는 출력 데이터를 네트워크(5)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)에 제공할 수 있다.1 , the
제2 인터페이스(12)는 인증 시스템(7)에 대한 액세스를 제공할 수 있다. 인증 시스템(7)은 유효한(valid) 클라이언트들의 정보를 저장할 수 있고, 인증 시스템(7)은 저장된 정보에 기초하여 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)를 인증할 수 있다. 또한, 인증 시스템(7)은 도 3 및 도 4를 참조하여 후술되는 바와 같이, 데이터의 암호화/복호화에 사용되는 비밀 키를 생성할 수도 있다. 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)이 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)를 직접 인증하는 대신, 별도의 인증 시스템(7)이 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)를 인증할 수 있고, 이에 따라 피험자(1)의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터의 처리는 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)의 인증과 분리될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 피험자(1)의 생체 정보는 피험자(1)를 식별할 수 있는 어떠한 정보도 포함하지 아니할 수 있는 한편, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 자신의 고유한 식별 정보(예컨대, 도 4의 하드웨어 키)를 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 제공함으로써 인증될 수 있다. 제2 인터페이스(12)는 로컬 네트워크를 통해서 인증 시스템(7)과 통신할 수도 있고, 일대일 접속을 통해서 인증 시스템(7)과 통신할 수도 있다.The
제3 인터페이스(13)는 데이터베이스(9)에 대한 액세스를 제공할 수 있다. 데이터베이스(9)는 복수의 피험자들의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 제1 클라이언트(2)로부터 제공된 피험자(1)의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터, 그리고 이에 대응하는 출력 데이터가 데이터베이스(9)에 저장될 수 있다. 도 1에 도시된 바와 상이하게, 제1 클라이언트(2)가 네트워크(5)를 통해서 데이터베이스(9)에 액세스하고 제1 클라이언트(2)가 데이터베이스(9)에 저장된 데이터에 기초하여 뇌파 처리를 수행하는 것을 고려할 수 있으나, 데이터베이스(9)에 저장된 방대한 양의 데이터를 처리하기 위한 하드웨어/소프트웨어가 제1 클라이언트(2)에 구현되는 것은 용이하지 아니할 수 있고, 제1 클라이언트(2)의 운영 주체로 하여금 높은 비용을 발생시킬 수 있다. 또한, 전문가(3)로 하여금 피험자(1)에게 적합한 설정을 제1 클라이언트(2)에 하도록 하는 것은, 피험자(1) 및 전문가(3)가 동일한 공간에 있는 경우에만 가능할 수 있다. 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)은, 높은 보안성을 바탕으로, 낮은 비용으로도 구현될 수 있는 제1 클라이언트(2) 및 제2 클라이언트(4)에 뇌파 처리 결과를 제공함으로써 뉴로피드백에 기반한 서비스의 구축을 용이하게 할 수 있다.The
뇌파 처리부(15)는 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 유용한 정보를 포함하는 뇌파 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제1 인터페이스(11)를 통해서, 제1 클라이언트(2)의 식별 정보, 피험자(1)의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 수신할 수 있다. 또한, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제1 인터페이스(11)를 통해서 제2 클라이언트(2)의 식별 정보, 전문가(3)가 제공하는 설정 정보를 수신할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)의 식별 정보를 인증 시스템(7)에 제공함으로써 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)를 인증할 수 있는 한편, 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)의 인증이 성공한 경우, 피험자(1)의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. The
일부 실시예들에서, 데이터 베이스(9)는 피험자(1)가 뉴로피드백 훈련을 통해서 생성한 뇌파 데이터 및 훈련의 성취도를 저장할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 훈련에 따른 피험자(1)의 뇌파 및 성취도 변화를 분석할 수 있다. 또한, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 분석 결과에 기초하여 피험자(1)의 뉴로피드백 효과를 파악할 수 있고, 이를 바탕으로 전문가(3) 및/또는 뇌파 처리부(15)는 향후 피험자(1)의 훈련 방법과 방향을 결정할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제2 클라이언트(4)로부터 전문가(3)가 피험자(1)에 대하여 정의한 설정들을 수신할 수 있고, 이를 데이터베이스(9)에 저장할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 전문가(3)는 제2 클라이언트(4)를 통해서, 훈련 프로토콜, 훈련 프로그램의 종류, 훈련 프로그램의 순서, 훈련 프로그램의 실행 시간, 훈련 프로그램의 조건, 훈련 프로그램의 난이도, 훈련 횟수, 훈련 프로그램의 등급 등을 피험자(1)를 위하여 설정할 수 있다. 뇌파 처리부(15)는 데이터베이스(9)에 저장된 설정에 기초하여 뉴로피드백이 수행되도록, 제1 클라이언트(2)의 식별 정보에 대응하는 설정을 식별할 수 있고, 제1 클라이언트(2)에 식별된 설정들을 제공할 수 있으며, 제1 클라이언트(2)는 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)으로부터 제공된 설정에 따라 피험자(1)에게 뉴로피드백을 제공할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 전문가(3)는 제2 클라이언트(4)를 통해서 피험자(1)의 뇌파 데이터 및/또는 뇌파 데이터로부터 뇌파 처리부(15)가 생성한 데이터 등을 확인할 수 있고, 피험자(1)의 뇌파 데이터 및/또는 성취도를 분석함으로써 본인의 의견(comment)을 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)에 제공할 수 있다. 뇌파 처리부(15)는 전문가(3)로부터 제공된 의견을 데이터베이스(9)에 저장할 수 있고, 제1 클라이언트(2)의 식별 정보에 대응하는 의견을 식별할 수 있으며, 식별된 의견을 제1 클라이언트(2)를 통해서 피험자(1)에게 제공할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 피험자(1)의 BQ 보고서, 훈련 결과 보고서가 전문가(3)에 의해서 작성될 수 있으며, 데이터베이스(9)에 저장될 수 있고, 피험자(1)에게 제공될 수 있다.In some embodiments, the
일부 실시예들에서, 데이터베이스(9)는, 복수의 피험자들에 의해서 수집된 뇌파 데이터에서, 다양한 조건들(예컨대, 연령 등)에 대응하는 전술된 지수들의 통계값(예컨대, 평균, 산포)을 저장할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 피험자(1)의 생체 정보에 대응하는 통계값에 기초하여 뇌파 데이터를 분석함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 데이터에 포함된 시간 도메인의 샘플들은, 예컨대 푸리에 변환을 통해서 주파수 도메인으로 변환될 수 있고, 주파수 도메인에서 뇌파가 분석될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 주파수 도메인에서 피크들, 최대 피크값, 좌우 상관도(coherence) 등이 검출될 수 있고, 검출된 값들에 기초하여 후술되는 지수들이 산출될 수 있다.In some embodiments, the
뇌파 처리부(15)는 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 기초율동 지수, 자기조절 지수, 주의 지수, 활성 지수, 감성 지수, 항스트레스 지수, 좌우 뇌균형 지수, 뇌지수 증을 포함하는 다양한 지수들을 포함하는 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 기초율동은, 눈을 감고 가성상태로 안정을 취하고 있을 때 나오는 뇌파로서 연령에 따라 기준이 상이할 수 있고, 뇌발달정도, 노화정도, 안정도를 판단하는데 기초로 사용될 수 있다. 자기조절 지수는, 뇌건강과 활동력의 기본적인 척도로서 기능할 수 있다. 뇌는 각성시에 휴식 상태, 주의력 상태, 집중력 상태의 3가지 상태들을 자율 조절함으로써 활동리듬을 통제할 수 있고, 자기조절 지수는 이와 같은 3가지 상태들에 대한 뇌의 자율조절 능력을 평가하는 값일 수 있다. 주의 지수는, 뇌의 각성 정도와 질병이나 스트레스에 대한 저항력을 나타내는 지수로서, 연령기준에 따라 뇌의 각성 정도가 판단될 수 있다. 활성 지수는, 뇌의 활성 정도를 나타내는 지수로서, 정신적 활동과 사고능력 및 행동성향을 판단하는데 기초로 사용될 수 있다. 감성 지수는, 정서 지수로서 지칭될 수도 있고, 정서적 안정, 불안정 상태를 나타낼 수 있다. 항스트레스 지수(또는 스트레스 지수)는, 내외적 환경 요인으로 인한 육체적 정신적 피로에 대한 저항치를 나타낼 수 있다. 육체적 스트레스는 인체의 긴장과 불안, 흥분 상태를 나타낼 수 있는 한편, 정신적 스트레스는 심리적인 긴장과 불안, 흥분 상태를 나타낼 수 있다. 좌우 균형 뇌지수는, 좌뇌와 우뇌의 균형을 나타내는 지수로서, 균형은 뇌파의 진폭의 대칭 및 위상의 대칭에 기초하여 판단될 수 있다. 뇌지수는 전술된 지수들에 기초하여 뇌의 기능을 종합적으로 평가하는 지수일 수 있고, IQ 또는 EQ와 상이하게 뇌파의 측정 및 뉴로피드백에 기초하여 판단된 뇌의 반응과 조절능력을 나타내는 점에서, 보다 정확하고 폭넓은 정보를 포함할 수 있다.The
일부 실시예들에서, 제1 인터페이스(11)는 네트워크(5)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)로부터 분석 파라미터를 더 수신할 수 있다. 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제1 인터페이스(11)릍 통해서 제공된 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 뇌파 처리 기능들 중 적어도 일부를 선택할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 분석 파라미터에 기초하여, 전술된 지수들 중 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택할 수 있고, 선택된 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함하는 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 인증 시스템(7)은 유효한 클라이언트들 각각이 요구하는 기능들에 대한 정보를 저장할 수 있다. 이에 따라, 인증 시스템(7)은 제2 인터페이스(12)를 통해서 제공된 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)의 식별 정보에 대응하는 분석 파라미터를 제2 인터페이스(12)를 통해서 뇌파 처리부(15)에 제공할 수 있고, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택할 수 있다.In some embodiments, the
도 2는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다. 도 2의 클라이언트(22), 뇌파 처리 시스템(24) 및 인증 시스템(26)은, 도 1의 제1 클라이언트(2), 뇌파 처리 시스템(10) 및 인증 시스템(7)에 대응할 수 있다. 도 1의 제2 클라이언트(4)의 경우, 도 2에서 생체 정보의 전송 및 생체 정보에 대응하는 출력 데이터의 생성이 생략될 수 있고, 도 2에 도시된 바와 유사하게 제2 클라이언트(4)에 대한 인증 역시 수행될 수 있다. 이하에서, 도 2에 대한 설명 중 도 1에 대한 설명과 중복되는 내용은 생략될 것이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. The
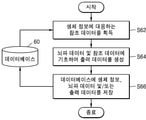
도 2를 참조하면, 단계 S21에서 클라이언트(22)는 피험자의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 획득할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 클라이언트(22)는 피험자가 착용중인 뇌파 측정 장치로부터 뇌파 데이터를 수신할 수 있고, 피험자가 제공하는 입력으로부터 생체 정보를 수신할 수 있다. Referring to FIG. 2 , in step S21 , the
단계 S22에서, 클라이언트(22)는 식별 정보, 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)에 전송할 수 있다. 식별 정보는 클라이언트(22)의 식별 정보로서, 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터의 소유자인 피험자와는 무관할 수 있다. 식별 정보는 클라이언트(22)의 고유한 정보로서, 일부 실시예들에서 도 4를 참조하여 후술되는 바와 같이, 인증 시스템(26)으로부터 발행된 정보를 포함할 수 있다.In step S22 , the
단계 S23에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)은 식별 정보를 인증 시스템(26)에 전송할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)의 뇌파 처리부(예컨대, 도 1의 15)는, 단계 S22에서 제공된 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터가 유효한 클라이언트로부터 제공된 것인지 여부를 판정하기 위하여, 식별 정보를 인증 시스템(26)에 제공할 수 있다.In step S23 , the brain
단계 S24에서, 인증 시스템(26)은 클라이언트(22)의 인증을 시도할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(26)은 유효한 클라이언트들에 대한 정보를 저장할 수 있고, 단계 S23에서 수신된 식별 정보에 기초하여 클라이언트(22)가 유효한 클라이언트인지 여부를 판정할 수 있다. 그 다음에, 단계 S25에서 인증 시스템(26)은 인증 결과를 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)에 전송할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 결과는 클라이언트(22)의 인증 성공 또는 인증 실패를 나타낼 수 있다.In step S24 , the
단계 S26에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)은 인증된 클라이언트(22)가 제공한 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)은, 단계 S25에서 제공된 인증 결과가 클라이언트(22)의 인증 성공을 나타내는 경우, 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 다른 한편으로, 도 2에 도시된 바와 상이하게, 단계 S25에서 제공된 인증 결과가 클라이언트(22)의 인증 실패를 나타내는 경우, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)(또는 뇌파 처리부)은 클라이언트(22)에 인증 실패를 나타내는 데이터를 전송할 수 있고, 출력 데이터를 생성하지 아니할 수 있다.In step S26 , the
단계 S27에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(24)은 출력 데이터를 클라이언트(22)에 전송할 수 있다. 단계 S28에서, 클라이언트(22)는 출력 데이터를 피험자(또는 전문가)에게 제공할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 출력 데이터는 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 생성된 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함할 수도 있고, 클라이언트(22)는 적어도 하나의 지수를 다양한 형태로, 예컨대 수치 및/또는 그래프로 피험자에게 디스플레이할 수 있다.In step S27 , the brain
도 3은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템(30)을 나타내는 블록도이다. 도 1의 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)과 유사하게, 도 3의 뇌파 처리 시스템(30)은 제1 인터페이스(31), 제2 인터페이스(32), 제3 인터페이스(33) 및 뇌파 처리부(35)를 포함할 수 있고, 클라이언트 등록부(37) 및 암호화 엔진(39)을 더 포함할 수 있다. 도 3에 대한 설명에서 뇌파 처리 시스템(30)은 도 1의 제1 클라이언트(2), 제2 클라이언트(4), 인증 시스템(7) 및 데이터베이스(9)와 통신하는 것으로 가정되고, 도 1에 대한 설명과 중복되는 내용은 생략될 것이다.3 is a block diagram illustrating an
클라이언트 등록부(37)는 제1 인터페이스(31) 및 제2 인터페이스(32)와 통신할 수 있다. 이에 따라, 클라이언트 등록부(37)는 제1 인터페이스(31)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)와 통신할 수 있고, 제2 인터페이스(32)를 통해서 인증 시스템(7)과 통신할 수 있다. 클라이언트 등록부(37)는 신규 클라이언트를 유효한 클라이언트로서 인증 시스템(7)에 등록하는 기능을 수행할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 클라이언트 등록부(37)는 제1 인터페이스(31)를 통해서 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)의 등록 요청을 수신할 수 있고, 제2 인터페이스(32)를 통해서 인증 시스템(7)에 제1 클라이언트(2) 및/또는 제2 클라이언트(4)의 등록을 요청할 수 있다. 클라이언트 등록부(37)의 동작의 예시가 도 4를 참조하여 후술될 것이다.The
암호화 엔진(39)은 암호화 키에 기초하여 복호화 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 암호화 엔진(39)은 제2 인터페이스(32)를 통해서 인증 시스템(7)으로부터 복호화 키를 수신할 수 있고, 제1 인터페이스(31)를 통해서 수신된 암호화된 데이터를 복호화 키에 기초하여 복호화할 수 있으며, 복호화된 데이터를 뇌파 처리부(35)에 제공할 수 있다. 암호화 엔진(39)의 동작의 예시가 도 5를 참조하여 후술될 것이다. The
도 4는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다. 구체적으로, 도 4의 순서도는 도 3의 뇌파 처리 시스템(30)의 동작의 예시를 나타낸다. 도 3을 참조하여 전술된 바와 같이, 도 4의 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 클라이언트 등록부를 포함할 수 있고, 클라이언트 등록부는 클라이언트(42)를 유효한 클라이언트로서 인증 시스템(46)에 등록할 수 있다.4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, the flowchart of FIG. 4 shows an example of operation of the brain
도 4를 참조하면, 단계 S41에서 클라이언트(42)는 등록 요청을 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)에 전송할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 등록 요청은 하드웨어 키를 포함할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 도 4의 클라이언트(42)가 도 1의 제1 클라이언트(2)인 경우, 피험자가 착용한 뇌파 측정 장치는 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)의 운영자로부터 공급될 수 있고, 하드웨어 키는 뇌파 측정 장치에 고유한 값을 가질 수 있고, 해당 운영자에 의해서 발행될 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 하드웨어 키는 뇌파 처리 장치의 표면이나 인증서 등에 기입될 수 있고, 피험자(또는 전문가)는 기입된 하드웨어 키를 클라이언트(42)에 입력할 수 있다. 또한, 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 처리 장치는 하드웨어 키를 저장하는 비휘발성 메모리(예컨대, 플래시 메모리, EPROM, OTP 메모리 등)를 포함할 수 있고, 클라이언트(42)는 뇌파 처리 장치로부터 하드웨어 키를 수신할 수도 있다. 또한, 클라이언트(42)가 도 1의 제2 클라이언트(4)인 경우, 전문가(4)는 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)의 운영자로부터 미리 발급된 키를 포함하는 등록 요청을 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)에 전송할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 키는 하드웨어 키로서 USB 메모리 장치, CD 등과 같이 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)의 운영자로부터 제공된 기록매체에 포함될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4 , in step S41 , the
단계 S42에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 하드웨어 키를 검증할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)(또는 클라이언트 등록부)은 단계 S41의 등록 요청에 포함된 하드웨어 키가 정당하게 발행된 것인지 여부를 판단할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 하드웨어 키 리스트에 하드웨어 키가 포함되는 여부를 판단할 수도 있고, 하드웨어 키의 생성시 사용된 알고리즘을 사용하여 하드웨어 키를 검증할 수도 있다. 하드웨어 키의 검증이 성공한 경우, 도 4에 도시된 바와 같이 단계 S43이 후속하여 수행될 수 있는 한편, 하드웨어 키의 검증이 실패한 경우, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 하드웨어 키의 검증 실패를 나타내는 데이터를 클라이언트(42)에 전송할 수 있다.In step S42, the brain
단계 S43에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 인증 시스템(46)에 클라이언트의 등록을 요청할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 단계 S41에서 수신된 하드웨어 키 또는 해당 하드웨어 키로부터 생성된 데이터(예컨대, 다이제스트)를 인증 시스템(46)에 전송할 수 있다. In step S43 , the brain
단계 S44에서, 인증 시스템(46)은 클라이언트(42)를 등록할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(46)은 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)의 요청에 포함된 정보를, 유효한 클라이언트 리스트에 추가할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 인증 시스템(46)은 피험자를 위한 클라이언트(즉, 도 1의 2)의 리스트 및 전문가를 위한 클라이언트(4)의 리스트를 관리할 수 있다. 또한, 인증 시스템(46)은 식별 정보 및 암호화 키를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(46)은 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)의 요청에 포함된 정보에 기초하여 식별 정보 및 암호화 키를 생성할 수 있고, 이에 따라 식별 정보 및 암호화 키는 해당 정보에 바인딩(binding)될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(46)은 비대칭 암호 알고리즘에 기초하여, 공유키(public key) 및 개인키(private key)를 포함하는 키 페어를 생성할 수 있다.In step S44 , the
단계 S45에서, 인증 시스템(46)은 식별 정보 및 암호화 키를 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)에 전송할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(46)은 공유키를 암호화 키로서 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)에 전송할 수 있다. 단계 S46에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)은 식별 정보 및 암호화 키를 클라이언트(42)에 전송할 수 있다. 클라이언트(42)는 단계 S46에서 수신된 식별 정보 및 암호화 키를 저장할 수 있고, 도 2를 참조하여 전술된 바와 같이, 클라이언트(42)가 피험자의 클라이언트인 경우, 피험자의 데이터(즉, 생체 정보, 뇌파 데이터)와 함께 뇌파 처리 시스템(44)에 전송할 수 있다. 클라이언트(42)가 단계 S46에서 수신된 암호화 키를 사용하는 동작의 예시가 도 5를 참조하여 후술될 것이다.In step S45 , the
도 5는 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다. 구체적으로, 도 5의 순서도는 도 3의 뇌파 처리 시스템(30)의 동작의 예시로서 클라이언트(52)가 피험자의 클라이언트(예컨대, 도 1의 2)인 경우를 나타낸다. 도 3을 참조하여 전술된 바와 같이, 도 5의 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)은 암호화 엔진을 포함할 수 있고, 암호화 엔진은 암호화된 데이터를 복호화 키에 기초하여 복호화할 수 있다. 이하에서, 도 5에 대한 설명 중 도 2에 대한 설명과 중복되는 내용은 생략될 것이다.5 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, the flowchart of FIG. 5 illustrates a case in which the
도 5를 참조하면, 단계 S51에서 클라이언트(52)는 피험자의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 암호화할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 클라이언트(52)는 뇌파 측정 장치로부터 획득된 피험자의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를, 도 4의 암호화 키를 사용하여 암호화함으로써 암호화된 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 그 다음에, 단계 S52에서 클라이언트(52)는 암호화된 데이터 및 식별 정보를 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)에 전송할 수 있다. 단계 S53에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)은 식별 정보를 인증 시스템(56)에 전송할 수 있고, 단계 S54에서, 인증 시스템(56)은 식별 정보에 기초하여 클라이언트(52)를 인증할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 5 , in step S51 , the
단계 S55에서, 인증 시스템(56)은 인증 결과 및 복호화 키를 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)에 전송할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 인증 시스템(56)은 인증된 클라이언트(52)에 대응하는 복호화 키를 획득할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 도 4에서 클라이언트 등록시 키 페어가 생성될 수 있고(비대칭형 암호), 도 4의 암호화 키는 키 페어의 공유키일 수 있고, 도 5의 복호화 키는 키 페어의 개인키일 수 있다. 또한, 일부 실시예들에서, 도 4의 암호화 키 및 도 5의 복호화 키는 동일할 수도 있다(대칭형 암호).In step S55 , the
단계 S56에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)은 데이터를 복호화할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)(또는 암호화 엔진)은 단계 S52에서 수신된 암호화된 데이터를, 단계 S55에서 수신된 복호화 키를 사용하여 복호화함으로써 복호화된 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 데이터의 암호화 및 복호화는 임의의 암호화 알고리즘이 사용될 수 있고, 예컨대 Known-PlainText, Chosen-PlainText, Differential, Linear 방식 등과 같은 대칭형 암호화 알고리즘이 채용될 수도 있고, Diffie-Hellman 키 교환, DSS(digital signature standard), ElGamal, ECC, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 등과 같은 비대칭형 암호화 알고리즘이 채용될 수도 있다.In step S56, the brain
단계 S7에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)은 복호화된 데이터에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있고, 단계 S58에서, 뇌파 처리 시스템(54)은 출력 데이터를 클라이언트(52)에 전송할 수 있다. 단계 S59에서, 클라이언트(52)는 피험자에게 출력 데이터를 제공할 수 있다.In step S7 , the brain
도 6은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따라 뉴로피드백에 기초한 테스트 및 트레이닝을 위한 방법을 나타내는 순서도이다. 구체적으로, 도 6의 순서도는 데이터베이스(60)에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성하는 방법의 예시를 나타낸다. 일부 실시예들에서, 도 6의 방법은 도 1의 뇌파 처리부(15)에 의해서 수행될 수 있고, 이하에서 도 6은 도 1을 참조하여 설명될 것이다.6 is a flowchart illustrating a method for testing and training based on neurofeedback according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, the flowchart of FIG. 6 shows an example of a method of generating output data based on the
단계 S62에서, 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를 획득하는 동작이 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 제1 인터페이스(11)를 통해서 수신된 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를, 제3 인터페이스(13)를 통해서 데이터베이스(60)로부터 수신할 수 있다. 일부 실시예들에서, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 피험자(1)의 나이 및/또는 성별이 속하는 범위에 대응하는 뇌파 데이터, 통계 데이터 등을 참조 데이터로서 획득할 수 있다.In step S62, an operation of obtaining reference data corresponding to the biometric information may be performed. For example, the brain
단계 S64에서, 뇌파 데이터 및 참조 데이터에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성하는 동작이 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 참조 데이터에 기초하여 뇌파 데이터를 분석할 수 있고, 분석 결과를 포함하는 출력 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.In step S64, an operation of generating output data based on the EEG data and the reference data may be performed. For example, the brain
단계 S66에서, 데이터베이스에 생체 정보, 뇌파 데이터 및/또는 출력 데이터를 저장하는 동작이 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 뇌파 처리부(15)는 출력 데이터의 생성에 사용된 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 데이터베이스(60)에 저장할 수도 있고, 단계 S64에서 생성된 출력 데이터를 데이터베이스(60)에 저장할 수도 있다. 이에 따라, 데이터베이스(60)에는 피험자(1)를 식별할 수 있는 정보를 제외한, 생체 정보 및 뇌파 정보가 수집될 수 있고, 수집된 데이터는 후속하는 뇌파 데이터의 처리에 사용될 수 있다.In step S66, an operation of storing biometric information, brain wave data, and/or output data in the database may be performed. For example, the
도 7은 본 발명의 예시적 실시예에 따른 뇌파 처리 시스템(70)을 나타내는 블록도이다. 구체적으로, 도 7은 일부 구성요소들로서 뇌파 처리부(75) 및 모델 학습부(76)를 포함하는 뇌파 처리 시스템(70)을 나타낸다. 도 1 등을 참조하여 전술된 바와 같이, 뇌파 처리부(75)는 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 입력 데이터(IN)로서 수신할 수 있고, 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터(OUT)를 생성할 수 있다. 7 is a block diagram illustrating an
도 1의 뇌파 처리 시스템(10)과 비교할 때, 도 7의 뇌파 처리부(75)는 기계 학습 모델(ML)을 포함할 수 있고, 도 7의 뇌파 처리 시스템(70)은 모델 학습부(76)를 더 포함할 수 있다. 기계 학습 모델(ML)은 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터의 복수의 샘플들, 예컨대 도 1의 데이터베이스(9)에 저장된 복수의 피험자들의 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터에 의해서 학습된 상태일 수 있고, 기계 학습 모델(ML)을 실행하도록 설계된 임의의 하드웨어, 예컨대 NPU(neural processing unit)에 의해서 실행될 수 있다. 기계 학습 모델(ML)은 입력 데이터(IN) 또는 입력 데이터(IN)로부터 가공된 데이터를 수신할 수 있고, 수신된 데이터에 응답하여 출력 데이터(OUT)의 적어도 일부를 출력할 수 있다. 기계 학습 모델(ML)은 인공 신경망(artificial neural network), 결정 트리, 서포트 벡터 머신, 회귀 분석(regression analysis), 베이즈 네트워크(Bayesian network), 유전 계획법(genetic algorithm) 등에 기초한 모델일 수 있다.Compared with the
모델 학습부(76)는 입력 데이터(IN) 및 출력 데이터(OUT)에 기초하여 기계 학습 모델(ML)을 훈련시킬 수 있다. 예를 들면, 기계 학습 모델(ML)은 인공 신경망을 포함할 수 있고, 모델 학습부(76)는 역전파(back propagation) 등의 훈련 기법에 기초하여 기계 학습 모델(ML)을 훈련시킬 수 있다. 이에 따라, 뇌파 처리부(75)는 피험자의 생체 정보 및 뇌파 데이터가 재학습될 수 있다. 기계 학습 모델(ML)은, 비제한적인 예시로서 CNN(Convolution Neural Network), R-CNN(Region with Convolution Neural Network), RPN(Region Proposal Network), RNN(Recurrent Neural Network), S-DNN(Stacking-based deep Neural Network), S-SDNN(State-Space Dynamic Neural Network), Deconvolution Network, DBN(Deep Belief Network), RBM(Restricted Boltzmann Machine), Fully Convolutional Network, LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory) Network, Classification Network 등을 포함할 수 있다.The
이상에서와 같이 도면과 명세서에서 예시적인 실시예들이 개시되었다. 본 명세서에서 특정한 용어를 사용하여 실시예들을 설명되었으나, 이는 단지 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 설명하기 위한 목적에서 사용된 것이지 의미 한정이나 특허청구범위에 기재된 본 발명의 범위를 제한하기 위하여 사용된 것은 아니다. 그러므로 본 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이로부터 다양한 변형 및 균등한 타 실시예가 가능하다는 점을 이해할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명의 진정한 기술적 보호범위는 첨부된 특허청구범위의 기술적 사상에 의해 정해져야 할 것이다.Exemplary embodiments have been disclosed in the drawings and specification as described above. Although the embodiments have been described using specific terms in this specification, these are used only for the purpose of explaining the technical idea of the present invention and not used to limit the meaning or the scope of the present invention described in the claims . Therefore, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications and equivalent other embodiments are possible therefrom. Accordingly, the true technical protection scope of the present invention should be defined by the technical spirit of the appended claims.
Claims (17)
유효한(valid) 제1 클라이언트들의 정보를 저장하는 인증 시스템과의 통신을 제공하도록 구성된 제2 인터페이스; 및
상기 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 인증 시스템에 상기 식별 정보를 제공하고, 상기 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여 출력 데이터를 생성하고, 상기 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 제1 클라이언트에 상기 출력 데이터를 제공하도록 구성된 뇌파 처리부를 포함하는 시스템.a first interface, configured to receive, from a first client, identification information of the first client, biometric information of the subject, and EEG data generated by measuring EEG of the subject;
a second interface configured to provide communication with an authentication system that stores information of valid first clients; and
providing the identification information to the authentication system through the second interface, generating output data based on the biometric information and the EEG data of the first client authenticated by the authentication system, and using the first interface and an EEG processor configured to provide the output data to the first client via
상기 제1 인터페이스는, 상기 네트워크를 통해서 제2 클라이언트로부터 상기 피험자의 뉴로피드백(neurofeedback)을 위한 설정을 수신하도록 구성되고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 식별 정보에 대응하는 설정을 식별하고, 상기 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 제1 클라이언트에 식별된 상기 설정을 제공하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.The method according to claim 1,
The first interface is configured to receive settings for neurofeedback of the subject from a second client via the network,
The EEG processing unit is configured to identify a setting corresponding to the identification information of the first client, and provide the identified setting to the first client via the first interface.
상기 설정은, 훈련 프로토콜, 훈련 프로그램의 종류, 훈련 프로그램의 순서, 훈련 프로그램의 실행 시간, 훈련 프로그램의 조건, 훈련 프로그램의 난이도, 훈련 횟수, 훈련 프로그램의 등급 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.3. The method according to claim 2,
The setting comprises at least one of a training protocol, a type of training program, an order of a training program, an execution time of a training program, conditions of a training program, difficulty of a training program, the number of training sessions, and a grade of the training program system.
상기 제1 인터페이스는, 상기 제2 클라이언트로부터 상기 출력 데이터에 대한 의견을 수신하도록 구성되고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 의견을 상기 제1 클라이언트에 제공하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.3. The method according to claim 2,
the first interface is configured to receive an opinion on the output data from the second client;
The EEG processing unit is configured to provide the opinion to the first client via the first interface.
상기 설정 및 상기 의견을 저장하는 데이터베이스와 통신을 제공하도록 구성된 제3 인터페이스를 더 포함하고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 식별 정보에 대응하는 설정 및 의견을 상기 데이터베이스로부터 획득하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.5. The method of claim 4,
a third interface configured to provide communication with a database storing the settings and the comments;
The EEG processing unit is configured to obtain settings and opinions corresponding to the identification information of the first client from the database.
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터에 기초하여, 기초율동 지수, 자기조절 지수, 주의 지수, 활성 지수, 감성 지수, 항스트레스 지수, 좌우 뇌균형 지수, 뇌지수를 포함하는 복수의 지수들을 생성하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.The method according to claim 1,
The brain wave processing unit, based on the biometric information and the brain wave data, a plurality of indices including basic rhythm index, self-regulation index, attention index, activity index, emotional index, anti-stress index, left and right brain balance index, brain index A system configured to generate
상기 제1 인터페이스는, 상기 제1 클라이언트로부터 분석 파라미터를 더 수신하도록 구성되고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 상기 복수의 지수들 중 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택하고, 상기 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함하는 상기 출력 데이터를 생성하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.7. The method of claim 6,
the first interface is configured to further receive an analysis parameter from the first client,
The EEG processing unit is configured to select at least one exponent from among the plurality of exponents based on the analysis parameter, and generate the output data including the at least one exponent.
상기 제2 인터페이스는, 상기 인증 시스템으로부터 상기 식별 정보에 대응하는 분석 파라미터를 더 수신하도록 구성되고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 분석 파라미터에 기초하여 상기 복수의 지수들 중 적어도 하나의 지수를 선택하고, 상기 적어도 하나의 지수를 포함하는 상기 출력 데이터를 생성하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.7. The method of claim 6,
the second interface is configured to further receive an analysis parameter corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system;
The EEG processing unit is configured to select at least one exponent from among the plurality of exponents based on the analysis parameter, and generate the output data including the at least one exponent.
상기 하드웨어 키를 검증하고, 검증된 하드웨어 키에 응답하여 상기 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 인증 시스템에 상기 제1 클라이언트의 등록을 요청하고, 상기 인증 시스템으로부터 제공된 암호화 키를 상기 제1 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 제1 클라이언트에 제공하도록 구성된 클라이언트 등록부를 더 포함하는 시스템.the first interface is configured to further receive a registration request including a hardware key from the first client;
verify the hardware key, request registration of the first client with the authentication system through the second interface in response to the verified hardware key, and send the encryption key provided from the authentication system through the first interface 1 The system further comprising a client registrar configured to provide to clients.
상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터는, 상기 암호화 키에 기초하여 암호화되고,
상기 제2 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 인증 시스템으로부터 상기 식별 정보에 대응하는 복호화 키를 수신하고, 상기 복호화 키에 기초하여 상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터를 복호화하도록 구성된 암호화 엔진을 더 포함하는 시스템.10. The method of claim 9,
The biometric information and the brain wave data are encrypted based on the encryption key,
and an encryption engine configured to receive a decryption key corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system through the second interface, and decrypt the biometric information and the EEG data based on the decryption key.
상기 생체 정보는, 상기 피험자의 나이, 시력, 신장, 체중, 혈액형, 아이큐, 혈압, 혈당, 질병, 복용약 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.The method according to claim 1,
The biometric information may include at least one of age, eyesight, height, weight, blood type, IQ, blood pressure, blood sugar, disease, and medication of the subject.
복수의 피험자들에 대한 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터를 저장하는 데이터베이스와의 통신을 제공하도록 구성된 제3 인터페이스를 더 포함하고,
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 상기 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를 상기 제3 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 데이터베이스로부터 획득하고, 상기 참조 데이터에 기초하여 상기 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.The method according to claim 1,
a third interface configured to provide communication with a database storing brain wave data and identification information for the plurality of subjects;
The brain wave processing unit obtains reference data corresponding to the biometric information of the first client authenticated by the authentication system from the database through the third interface, and processes the brain wave data based on the reference data. A system configured to generate output data.
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 인증된 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 생체 정보, 뇌파 데이터 및 상기 출력 데이터 중 적어도 하나를 상기 제3 인터페이스를 통해서 상기 데이터베이스에 저장하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템13. The method of claim 12,
The EEG processing unit is configured to store at least one of the biometric information, EEG data, and the output data of the authenticated first client in the database through the third interface.
상기 뇌파 처리부는, 식별 정보 및 뇌파 데이터의 복수의 샘플들에 의해서 학습된 기계 학습 모델을 포함하고, 인증된 상기 제1 클라이언트의 상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터를 상기 기계 학습 모델에 제공하고, 상기 기계 학습 모델로부터 상기 출력 데이터의 적어도 일부를 획득하도록 구성된 것을 특징으로 하는 시스템.The method according to claim 1,
The brain wave processing unit includes a machine learning model learned by a plurality of samples of identification information and brain wave data, and provides the biometric information and the brain wave data of the authenticated first client to the machine learning model, and obtain at least a portion of the output data from a machine learning model.
유효한 클라이언트들의 정보를 저장하는 인증 시스템에 상기 식별 정보를 제공하는 단계;
상기 인증 시스템에 의해서 인증된 상기 클라이언트의 상기 생체 정보에 대응하는 참조 데이터를 데이터베이스로부터 수신하는 단계;
상기 참조 데이터에 기초하여 상기 뇌파 데이터를 처리함으로써 출력 데이터를 생성하는 단계; 및
상기 출력 데이터를 상기 클라이언트에 제공하는 단계를 포함하는 뇌파 처리 방법.receiving, from a client, identification information of the client, biometric information of a subject, and EEG data generated by measuring EEG of the subject through a network;
providing the identification information to an authentication system that stores information of valid clients;
receiving reference data corresponding to the biometric information of the client authenticated by the authentication system from a database;
generating output data by processing the brain wave data based on the reference data; and
EEG processing method comprising the step of providing the output data to the client.
상기 클라이언트로부터 하드웨어 키를 포함하는 등록 요청을 수신하는 단계;
상기 하드웨어 키를 검증하고, 검증된 하드웨어 키에 응답하여 상기 인증 시스템에 상기 클라이언트의 등록을 요청하는 단계; 및
상기 인증 시스템으로부터 제공된 암호화 키를 상기 클라이언트에 제공하는 단계를 더 포함하는 뇌파 처리 방법.16. The method of claim 15,
receiving a registration request including a hardware key from the client;
verifying the hardware key and requesting registration of the client from the authentication system in response to the verified hardware key; and
EEG processing method further comprising the step of providing the encryption key provided from the authentication system to the client.
상기 인증 시스템으로부터 상기 식별 정보에 대응하는 복호화 키를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 복호화 키에 기초하여 상기 생체 정보 및 상기 뇌파 데이터를 복호화하는 단계를 더 포함하는 방법.17. The method of claim 16,
receiving a decryption key corresponding to the identification information from the authentication system; and
The method further comprising the step of decrypting the biometric information and the brain wave data based on the decryption key.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200106227A KR102538667B1 (en) | 2020-08-24 | 2020-08-24 | Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback |
| PCT/KR2021/011275 WO2022045727A1 (en) | 2020-08-24 | 2021-08-24 | Method and system for testing and training on basis of neurofeedback |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200106227A KR102538667B1 (en) | 2020-08-24 | 2020-08-24 | Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20220025477A true KR20220025477A (en) | 2022-03-03 |
| KR102538667B1 KR102538667B1 (en) | 2023-06-01 |
Family
ID=80355416
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200106227A KR102538667B1 (en) | 2020-08-24 | 2020-08-24 | Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102538667B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2022045727A1 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130061619A (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-06-11 | 이종훈 | Trainging system and method for developing human resources using neuro mental behavior program |
| KR101633344B1 (en) * | 2015-10-23 | 2016-06-24 | 주식회사 자원메디칼 | Apparatus, server and computer program stored in computer-readable medium for measuring body information |
| KR101699623B1 (en) * | 2015-10-15 | 2017-02-14 | 세종대학교산학협력단 | Game application system for improving the symmetry of the left/light brain activity |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100508885B1 (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2005-08-18 | 림스테크널러지주식회사 | Wireless telemetric system and method for neurofeedback training using parameters of electroencephalogram(EEG) |
| EP2682053A1 (en) * | 2009-06-15 | 2014-01-08 | Brain Computer Interface LLC | A brain-computer interface test battery for the physiological assessment of nervous system health |
| KR20160031187A (en) * | 2014-09-12 | 2016-03-22 | 주식회사 옴니씨앤에스 | System for psychotherapy by using neurofeedback |
-
2020
- 2020-08-24 KR KR1020200106227A patent/KR102538667B1/en active IP Right Grant
-
2021
- 2021-08-24 WO PCT/KR2021/011275 patent/WO2022045727A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130061619A (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-06-11 | 이종훈 | Trainging system and method for developing human resources using neuro mental behavior program |
| KR101699623B1 (en) * | 2015-10-15 | 2017-02-14 | 세종대학교산학협력단 | Game application system for improving the symmetry of the left/light brain activity |
| KR101633344B1 (en) * | 2015-10-23 | 2016-06-24 | 주식회사 자원메디칼 | Apparatus, server and computer program stored in computer-readable medium for measuring body information |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Tuckute G, etc., A framework for closed-loop neurofeedback for real-time EEG decoding. bioRxiv. pp.1~32 (2019.11.11.)* * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102538667B1 (en) | 2023-06-01 |
| WO2022045727A1 (en) | 2022-03-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chan et al. | Challenges and future perspectives on electroencephalogram-based biometrics in person recognition | |
| Ihmig et al. | On-line anxiety level detection from biosignals: Machine learning based on a randomized controlled trial with spider-fearful individuals | |
| Sohankar et al. | E-bias: A pervasive eeg-based identification and authentication system | |
| CN107708525B (en) | Determining health changes of a user using neuro and neuro-mechanical fingerprints | |
| US11700128B2 (en) | Methods and systems for cryptographically secured outputs from telemedicine sessions | |
| US20150304101A1 (en) | Physiological signal-based encryption and ehr management | |
| Zhang et al. | Review on EEG‐Based Authentication Technology | |
| Zhu et al. | Blinkey: A two-factor user authentication method for virtual reality devices | |
| US20200097951A1 (en) | Cryptocurrency system using body activity data | |
| Arslan Tuncer et al. | True random number generation from bioelectrical and physical signals | |
| JP7120994B2 (en) | Subject data management system | |
| KR20230058440A (en) | Electronic device with static artificial intelligence model for external situations including age blocking for vaping and ignition start using data analysis and its operating method | |
| KR20170034618A (en) | Method for User Authentication Using Biometirc Information, Authentication Server and Biometric Device for User Authentication | |
| El-Banby et al. | Security enhancement of the access control scheme in IoMT applications based on fuzzy logic processing and lightweight encryption | |
| Merrill et al. | Is the Future of Authenticity All In Our Heads? Moving passthoughts from the lab to the world | |
| US11904179B2 (en) | Virtual reality headset and system for delivering an individualized therapy session | |
| KR102538667B1 (en) | Method, device and system for test ad training based on neurofeedback | |
| Carr | Evaluating the Usability of Passthought Authentication | |
| Pham | EEG-based person authentication for security systems | |
| US11947648B2 (en) | Electronic device related to user identification, authentication, liveliness, encryption using biometrics technology and methods for operation thereof | |
| Patel et al. | An approach to developing EEG-based person authentication system | |
| Rodriguez | An Electroencephalogram (EEG) Based Biometrics Investigation for Authentication: A Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Approach | |
| US20220366027A1 (en) | Using Continuous Biometric Information Monitoring For Security | |
| Jenkins et al. | Authentication, privacy, security can exploit brainwave by biomarker | |
| Zhu | Bringing" Virtual" to" Reality": Enhancing Security and Usability on VR System and Applications |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right |