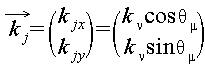KR20200012355A - Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process - Google Patents
Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20200012355A KR20200012355A KR1020180087533A KR20180087533A KR20200012355A KR 20200012355 A KR20200012355 A KR 20200012355A KR 1020180087533 A KR1020180087533 A KR 1020180087533A KR 20180087533 A KR20180087533 A KR 20180087533A KR 20200012355 A KR20200012355 A KR 20200012355A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- face
- eye
- screens
- screen
- pupil
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 79
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 40
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 title abstract description 20
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 title description 2
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 210000001508 eye Anatomy 0.000 claims description 148
- 210000001747 pupil Anatomy 0.000 claims description 63
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 59
- 230000001815 facial effect Effects 0.000 claims description 48
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 claims description 44
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 42
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000002372 labelling Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000004424 eye movement Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 241000287181 Sturnus vulgaris Species 0.000 claims description 8
- 210000005252 bulbus oculi Anatomy 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 206010044565 Tremor Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 19
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 14
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000012706 support-vector machine Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000001179 pupillary effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 210000004709 eyebrow Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 101100498818 Arabidopsis thaliana DDR4 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 241000167854 Bourreria succulenta Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000019693 cherries Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000000887 face Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 206010012239 Delusion Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000228740 Procrustes Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010041349 Somnolence Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013473 artificial intelligence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000868 delusion Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004209 hair Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012886 linear function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000214 mouth Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010606 normalization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001331 nose Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007781 pre-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013519 translation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010792 warming Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/10—Services
- G06Q50/20—Education
- G06Q50/205—Education administration or guidance
-
- G06K9/00221—
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/10—Services
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V40/00—Recognition of biometric, human-related or animal-related patterns in image or video data
- G06V40/10—Human or animal bodies, e.g. vehicle occupants or pedestrians; Body parts, e.g. hands
- G06V40/16—Human faces, e.g. facial parts, sketches or expressions
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Educational Technology (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 CLM과 가버 웨이블렛을 이용한 얼굴 인증 과정을 구비한 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an online lecture monitoring method having a face authentication process using CLM and Gabor wavelets.
오늘날 온라인 강의는 네트워크 기반의 온라인 학습 환경을 통해 원격지에서도 다양한 지식과 학습 경험을 제공할 수 있는 유용한 수단으로 부상하고 있다. 온라인 강의는 수강자가 시간과 공간의 물리적 제약을 극복할 수 있게 함으로써 수강자가 원하는 시간과 장소에서 학습을 가능하게 한다. Today's online courses are emerging as a useful means of providing a variety of knowledge and learning experiences in remote locations through a network-based online learning environment. Online lectures allow learners to overcome the physical constraints of time and space, allowing them to learn at the time and place they want.
이에 수강자 자신의 학습 수준과 목적, 그리고 개인의 여건에 따라 자발적인 학습이 가능하고, 거시적 차원에서는 사회적, 개인적 교육비용을 절감할 수 있는 장점이 있다. 그리고 제한된 교육 자원의 효율적 분배를 통해 비용 대비 효용을 증가시키는 사회적 순기능이 있다. 특히 최근의 온라인 교육은 교육 불평등 해소, 교육 자원의 분배를 통한 사회적 가치 창출을 이루어낼 수 있는 고부가가치 산업으로 평가받고 있다. 이와 같은 흐름 속에 탄생한 것이 바로 Cousera, edX 등으로 대표되는 MOOC(Massive Open Online Courses) 플랫폼이다. Therefore, students can voluntarily learn according to their own learning level, purpose, and individual conditions, and can reduce social and personal education costs at the macro level. And there is a social net function to increase the utility of cost through the efficient distribution of limited educational resources. In particular, recent online education has been evaluated as a high value-added industry that can create social value by reducing educational inequality and distributing educational resources. The birth of this trend is the Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) platform represented by Cousera and edX.
현재 세계적으로 일어나는 이러한 추세에 한국도 동참하여 정부와 대학들의 주도하에 한국형 MOOC(K-MOOC)를 개설하고 각 전문가에게 의뢰하여 온라인 강의 콘텐츠를 업로드 하는 등의 노력을 아끼지 않고 있다. Korea is also participating in this trend that is happening globally, and has made efforts to open Korean-style MOOC (K-MOOC) under the leadership of governments and universities, and to upload online lecture contents to each expert.
그러나 이상과 같은 장점에도 불구하고 현재의 온라인 강의 시스템은 다양한 측면에서 미비한 부분을 보완할 필요가 있다. 여기에는 수강자가 온라인 강의 콘텐츠를 성실하게 수강했는지 여부를 확인할 수 있는 방안이 부재한 것도 포함된다. 예컨대, 온라인 강의를 활용한 역전 학습(inverted learning)의 경우, 수강자가 사전 학습(pre-class) 용도로 제공된 온라인 강의 콘텐츠를 열람하지 않고 본 강의(in-class)에 출석하면, 자연스러운 수업 진행에 방해가 되고 결과적으로는 타인의 학습 효율까지 저하시키는 문제가 있다.However, in spite of the above advantages, the current online lecture system needs to compensate for the deficiencies in various aspects. This includes the lack of a way to determine whether or not participants have taken the online course content in good faith. For example, in the case of inverted learning using online lectures, if the attendees attend the in-class without viewing the online lecture contents provided for pre-class use, There is a problem that hinders and consequently lowers the learning efficiency of others.
따라서, 수강자의 학습을 방해하지 않으면서도 온라인 강의를 정상적으로 열람했는지의 여부를 효과적으로 모니터링할 있는 방안이 강구될 필요가 있다. 이러한 필요성에 부응하기 위해 본 발명의 발명자는 시선 추적 기술을 활용한 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템을 제안한 바 있었다. Therefore, it is necessary to devise a method for effectively monitoring whether or not the online lecture is normally viewed without disturbing the learners. In order to meet this need, the inventor of the present invention has proposed an online lecture monitoring system using gaze tracking technology.
하지만, 이 시스템을 도입하더라도 실제 시청이 아닌 사진이나 인형, 조형물 등을 이용한 허위 시청으로 응시율을 높여 온라인 강의 출석을 인정받는 시청 현혹자(cherry picker)를 차단함에는 한계가 있기 때문에 시선 추적 기반 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템의 종단부에서 안구 운동의 변동량을 조사해 시청 현혹자를 검출함으로써 부당 이용자를 차단할 수 있는 시청 현혹 검출 방법을 또한 제안하였다.However, even if this system is introduced, there is a limit to blocking the cherry picker who is recognized for attending the online lecture by increasing the rate of application by false viewing using pictures, dolls, sculptures, etc., rather than the actual viewing. We also proposed an auditory deception method that can block fraudulent users by detecting fluctuations in eye movement at the end of lecture monitoring systems.
그러나 기존의 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템은 사진이나 인형, 조형물 등을 이용한 허위 시청 시, 조명의 변화나 카메라 노이즈에 의해 미세한 거짓 떨림이 포함되기 때문에 이를 효과적으로 억제함으로써 시청 현혹 검출 성능을 개선할 필요가 있다.However, the existing online lecture monitoring system includes fine false tremors caused by changes in lighting or camera noise when false viewing using photographs, figurines, sculptures, etc., and therefore, needs to be effectively suppressed to improve viewing deception detection performance.
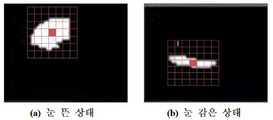
제안된 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템은 본 연구진이 기 제안한 그레이디언트 기반 눈 검출 방법을 통해 얻은 인접 프레임들 간 좌측 및 우측 눈의 중심점 좌표를 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행한 후, 프레임 간 차분합을 이용해 안구 운동의 변동량을 구한다. 이상 변인에 기인한 변화를 억제시키는 칼만 필터의 동작 특성을 효과적으로 이용하고자 한다. The proposed online lecture monitoring system performs Kalman filtering on the coordinates of the left and right eye center points between adjacent frames obtained using the gradient-based eye detection method proposed by the researchers. Find the variation in the movement. It is intended to effectively use the operating characteristics of the Kalman filter to suppress the changes caused by the abnormal variables.
그레이디언트 기반 눈 검출 방법은 PC 캠을 통해 획득한 입력영상으로부터 얼굴 영역을 검출한 후, 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙 및 외곽에서 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 확장 혹은 수렴해 가면서 제한된 화소 수만큼만 양방향으로 동공 영역을 레이블링을 통해 눈 검출 정확도와 연산 속도를 개선하고, 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행해 눈 개폐 여부를 판단할 수 있다. The gradient-based eye detection method detects the face area from the input image acquired through the PC cam, and then expands or converges in two concentric directions originating from the center and the outside of the eye search area, and bidirectionally by a limited number of pixels. The pupil area can be labeled to improve eye detection accuracy and computation speed, and Kalman filtering can be performed on the corrected cumulative mean to determine whether the eye is open or closed.
제안된 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템은 온라인 강의의 성실 시청 여부를 모니터링하고 시청 현혹자의 허위 출석을 방지함으로써 온라인 강의 시스템의 신뢰성과 학습효율성을 제고할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.The proposed online lecture monitoring system is expected to improve the reliability and learning efficiency of the online lecture system by monitoring whether the online lectures are faithfully watched and preventing false attendance by the viewers.
본 발명의 목적은 저가의 PC 캠을 이용하여 수강자의 성실 시청 여부를 감시해 온라인 출석 여부를 효율적이고 신뢰성 있게 관리할 수 있는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법을 제공하는 것이다.An object of the present invention is to provide an online lecture monitoring method that can monitor whether or not the attendees sincerely watch using a low-cost PC cam to efficiently and reliably manage online attendance.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 온라인 출석 여부를 강의 콘텐츠의 재생 중에 화면에 표시함으로써 수강자에게 실시간적으로 피드백을 제공할 수 있도록 한 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide an online lecture monitoring method that provides feedback to learners in real time by displaying whether or not online attendance is displayed on the screen during the playback of lecture contents.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 기존의 온라인 강의 시스템과도 용이하게 결합되어 온라인 강의의 성실 시청 여부를 모니터링하고 허위 출석을 방지함으로써 온라인 강의 시스템의 신뢰성과 학습 효율성을 제고할 수 있는 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide an online lecture monitoring method that can be easily combined with the existing online lecture system to improve the reliability and learning efficiency of the online lecture system by monitoring the integrity of the online lecture and preventing false attendance. To provide.
본 발명의 일 측면에 의하면, 컴퓨터에서 소프트웨어를 동작시키고 파일 열기를 통해 강의 콘텐츠를 선택하여 재생하는 단계; 카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계; 강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠 화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계; 내적 누적 평균을 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 나눠 보정된 내적 누적 평균값을 구하고, 직전 프레임과 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값들을 입력받아 칼만 필터링(Kalman filtering)을 수행해 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값을 갱신하고 이렇게 갱신된 내적 누적 평균과 눈 개폐 임계값을 비교해 눈의 개폐 여부를 판단하는 단계; 및 실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법이 제공된다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer program comprising: operating software on a computer and selecting and playing lecture contents through file opening; Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames; Determining whether the learner stares at the screen; If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner; When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture content screen; The inner cumulative mean is calculated by dividing the inner cumulative mean by the number of gradient vectors, and the Kalman filtering is performed by inputting the corrected inner cumulative mean values of the previous frame and the current frame to perform the corrected inner cumulative mean value of the current frame. Determining whether to open or close the eyes by comparing the updated internal cumulative average and the eye opening and closing threshold value; And in real time, the number of full screens played so far, the number of gaze screens checked by eye tracking, the screen gaze ratio that is the ratio of the number of screens and the number of screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens that are the ratio of dazzle screens and the total screens. An online lecture monitoring method is provided, comprising the step of displaying a final learning rate, which is a ratio of a subtracted number of screens and a total number of screens.
바람직하게, 상기 얼굴 인증 단계는, 다수의 방향과 주파수 성분을 갖는 가버 커널을 생성하는 서브단계; 갤러리 얼굴 영상을 대상으로 사전에 주요 얼굴 특징점들을 추출하는 서브단계; 사전에 오프라인으로 각 얼굴 특징점에서 가버 커널을 이용한 갤러리 특징 벡터를 추출 및 저장하는 서브단계; 온라인으로 추출한 프로브 얼굴 영상의 가버 특징 벡터와 사전에 기 저장된 갤러리 특징 벡터 간의 유사도를 측정하는 서브단계; 상기 프로브 얼굴 영상과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물의 얼굴이 포함되어 있으면 정분류로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정하는 단계; 상기 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴인 정분류된 경우에 한해 정분류 얼굴의 최근접 거리비(Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 구하는 서브단계; 및 상기 최근접 거리비가 인증 임계값보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정하는 서브단계를 포함한다.Preferably, the face authentication step includes: generating a Gabor kernel having a plurality of direction and frequency components; A sub-step of extracting major facial feature points from a gallery face image in advance; Extracting and storing a gallery feature vector using a Gabor kernel at each facial feature point in advance offline; Measuring a similarity between the Gabor feature vector of the online extracted probe face image and a previously stored gallery feature vector; Determining that the gallery face image having the highest similarity with the probe face image includes a face of the same person as the probe face, and determines a misclassification otherwise; A substep of obtaining a nearest neighbor distance ratio only when the gallery face having the most similarity to the probe face is classified as the same face as the probe face; And a substep of determining that face authentication succeeds if the nearest distance ratio is less than an authentication threshold, and otherwise deems unauthorized.
바람직하게, 상기 주요 얼굴 특징점은 CLM(Constrained Local Models)을 이용해 68개를 추출하고, 상기 가버 커널은 8개의 방향 성분과 4개의 주파수 성분을 이용해 40개가 생성되며, 상기 인증 임계값은 0.95일 수 있다.Preferably, the main facial feature points are extracted 68 by using Constrained Local Models (CLM), the Gabor kernel is generated 40 using 8 direction components and 4 frequency components, the authentication threshold value can be 0.95 have.
바람직하게, 상기 눈 개폐 임계값은, 직전 프레임들과 현 프레임의 갱신된 내적 누적 평균값을 소정 프레임 수만큼 누적한 후, 프레임 수로 나눈 구간 평균값을 이용해 구할 수 있으며, 상기 소정 프레임 수는 눈을 감은 프레임을 제외해 뜬 눈 상태로 판단된 70 프레임만으로 계수하고, 상기 눈 개폐 임계값은 상기 구간 평균값에 비례계수 0.8을 곱한 값을 이용할 수 있다.Preferably, the eye opening / closing threshold value is obtained by accumulating the updated internal cumulative average value of the previous frames and the current frame by a predetermined number of frames and dividing the interval by the number of frames. Only the 70 frames determined as the opened eye state excluding the frame may be counted, and the eye open / close threshold value may be a value obtained by multiplying the section average value by a proportional coefficient of 0.8.
본 발명의 다른 측면에 의하면, 컴퓨터에서 소프트웨어를 동작시키고 파일 열기를 통해 강의 콘텐츠를 선택하여 재생하는 단계; 카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계; 강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계; 및 실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하며, 상기 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계는, 이전 프레임과 현재 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 일정 기준치 이하이면 현재 프레임의 눈 중심점을 거짓 떨림으로 간주해 이전 프레임의 값으로 대체하는 서브단계; 연속된 프레임 간에서 상기 거짓 떨림 현상이 제거된 눈 중심점의 수평 및 수직 좌표를 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행한 후, 현재 프레임과 이전 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 상기 일정 기준치 이하이면 눈의 중심점이 변동되지 않은 것으로 판단해 안구 정지 횟수를 증가하는 서브단계; 및 소정 프레임 구간 동안에 상기 안구 정지 횟수가 일정 정지 횟수 이상이면 시청 현혹 상태로 판별하고 그렇지 않으면 정상 시청으로 판별하고, 상기 소정 프레임 구간마다 상기 안구 정지 횟수를 초기화시키면서 시청 현혹 여부를 지속적으로 감시하는 서브단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법이 제공된다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer program comprising the steps of: running software on a computer and selecting and playing lecture content through file opening; Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames; Determining whether the learner stares at the screen; If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner; When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture contents screen; And in real time, the number of full screens played so far, the number of gaze screens checked by eye tracking, the screen gaze ratio that is the ratio of the number of screens and the number of screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens that are the ratio of dazzle screens and the total screens. And displaying a final learning rate, which is a ratio of the total number of screens minus the number of deceptive screens, wherein detecting the viewing deception comprises: a difference between vertical and horizontal coordinates of left and right eye center points between a previous frame and a current frame. Substeps of substituting the eye center point of the current frame as a false tremor if the predetermined threshold value is less than the predetermined reference value; After performing Kalman filtering on the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the eye center point from which the false tremor is removed between successive frames, the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the current frame and the previous frame is the predetermined reference value. A sub-step of determining that the eye's center point is not changed to increase the number of eye stops; And determining that the number of eye stoppages is greater than or equal to a predetermined number of stops during a predetermined frame period, and determining that the viewing is deceptive. Otherwise, the subblock is configured to continuously monitor whether or not viewing is deceptive while initializing the number of eye stops every predetermined frame period. An online lecture monitoring method is provided comprising the steps.
바람직하게, 상기 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계는, 수강자가 정상적으로 영상을 시청하는 경우엔 적색 경고등이 들어오지 않지만, 시청 현혹 상태로 판별되면 적색 경고등을 표시함으로써 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되고 있음을 외부에 경고하는 서브단계; 전체 프레임 중 85% 이상의 구간에서 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되면 고의적 시청 현혹 의도로 최종 판단하고, 상기 최종학습률을 0%로 처리하는 서브단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.Preferably, the detecting of the viewing deception is to warn the outside that it is determined that the viewing deception state by displaying a red warning light when the attendees normally watch the video, but the red warning light does not come in. Substep; If it is determined that the viewing deception state in more than 85% of the entire frame, the final determination to deliberate viewing deception intention, and may further include a sub-step of processing the final learning rate to 0%.
바람직하게, 상기 일정 기준치는 3 픽셀이고, 상기 소정 프레임 구간은 30 프레임이고, 상기 일정 정지 횟수는 29회일 수 있다.Preferably, the predetermined reference value is 3 pixels, the predetermined frame section is 30 frames, and the predetermined number of stops may be 29 times.
본 발명의 다른 측면에 의하면, 컴퓨터에서 소프트웨어를 동작시키고 파일 열기를 통해 강의 콘텐츠를 선택하여 재생하는 단계; 카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계; 상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계; 강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계; 및 실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하며, 상기 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계는, 입력 영상에서 얼굴 영역을 검출하는 서브단계; 상기 검출된 얼굴 영역을 이용하여 좌측 및 우측 눈 탐색 영역을 지정하는 서브단계; 상기 지정된 각 눈 탐색 영역으로부터 동공 후보 영역을 검출하는 서브단계; 상기 검출된 동공 후보 영역 중에서 상기 각 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙과 외곽 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 수렴해가면서 양방향으로 제한된 화소수만큼만을 동공 영역으로 레이블링하는 서브단계; 수평 및 수직 미분 마스크를 이용해 에지 맵을 구하여 에지 여부를 판정하는 서브단계; 및 상기 레이블링된 동공 영역에서 내적 누적 연산을 수행하여 내적 누적값을 산출하여 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출하는 서브단계를 포함하며, 상기 동공 영역으로 레이블링하는 단계에서, 상기 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙에서부터 동심원 확산 방향으로 진행해 가면서 소정의 화소 면적 한도 내에서 동공 영역을 레이블링한 이후, 이렇게 레이블링된 동공 영역이 상기 눈 탐색 영역의 외곽에 접할 경우엔 상기 외곽으로부터 동심원 수축 방향으로 진행해 가면서 상기 레이블링된 동공 면적의 일정 비율 한도 내에서 외곽 인접 영역을 상기 레이블링된 동공 영역에서 제거해 최종 레이블링된 동공 영역으로 지정하고, 상기 내적 누적 연산을 수행하는 단계에서, 상기 최종 레이블링된 동공 영역에서만 정규 변위 벡터를 취해 상기 각 눈 탐색 영역 내 모든 그레이디언트 벡터와의 내적을 구한 후, 누적 연산을 수행하여 내적 누적값을 구하고, 각각의 상기 내적 누적값에 대응되는 역 밝기 가중치를 곱해 내적 누적값을 갱신한 후, 최대 내적 누적값의 위치를 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법이 제공된다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer program comprising the steps of: running software on a computer and selecting and playing lecture content through file opening; Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames; Determining whether the learner stares at the screen; If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner; When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture contents screen; And in real time, the number of full screens played so far, the number of gaze screens checked by eye tracking, the screen gaze ratio that is the ratio of the number of screens and the number of screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens that are the ratio of dazzle screens and the total screens. And displaying a final learning rate, which is a ratio of a subtracted number of screens to a total number of screens, and determining whether to stare at the screen comprises: detecting a face region in an input image; Specifying a left and right eye search region using the detected face region; Detecting a pupil candidate region from each of the designated eye searching regions; Labeling the pupil area of the detected pupil candidate area as only the limited number of pixels in both directions while converging in two concentric directions originating from each of the center and the outside of the eye searching area; A substep of determining an edge by obtaining an edge map using horizontal and vertical differential masks; And a sub-step of performing an inner cumulative calculation in the labeled pupil area to calculate an inner cumulative value and detecting the inner cumulative value, and in the labeling of the pupil area, concentric diffusion from a center of the eye search area. After labeling the pupil area within a predetermined pixel area limit while proceeding in a direction, if the labeled pupil area is in contact with the outer periphery of the eye search area, the labeled pupil area proceeds in the concentric contraction direction from the outer part. In the step of removing the outer adjacent region from the labeled pupil region within the ratio limit and designating it as the final labeled pupil region, and performing the dot accumulation operation, the normal displacement vector is taken only in the final labeled pupil region to search for each eye. All grady in the zone After calculating the dot product with the vector, the cumulative operation is performed to obtain the dot product cumulative value, multiply the inverse brightness weight corresponding to each of the dot product cumulative values to update the dot product cumulative value, and then determine the position of the maximum dot product cumulative value. An online lecture monitoring method is provided that detects at the center of the eye.
바람직하게, 상기 수강자의 동공이 검출되는 경우와 검출되지 않는 경우 각각 다른 색으로 상기 입력 영상의 눈의 영역에 표시하여 눈의 개폐 여부를 판단할 수 있으며, 상기 입력 영상으로부터 얼굴이 검출되지 않을 시, 강의 동영상을 멈추고, 얼굴이 검출될 경우, 그 시점부터 다시 강의를 재생시킬 수 있다.Preferably, when the pupil of the participant is detected and when it is not detected, it may be determined whether the eyes are opened or closed by displaying different colors on the eye region of the input image, and when the face is not detected from the input image. If the video is stopped and a face is detected, the video may be played again from that point on.
바람직하게, 상기 얼굴 영역을 검출하는 단계는, 초기 얼굴 템플릿을 입력 영상의 좌상단 시작점에 중첩해 놓고 겹쳐진 부분과의 상호 상관도(cross correlation)를 구하는 서브단계; 상기 시작점에서부터 한 화소씩 옮겨가면서 상호 상관도가 가장 높은 위치를 얼굴 영역으로 검출하는 서브단계; 및 상호 상관도가 일정 값 이상이면 계속하여 템플릿 정합을 진행하고, 그렇지 않으면 얼굴 영역을 재검출하고 새로운 얼굴 템플릿으로 갱신해 템플릿 정합을 수행하는 서브단계로 이루어질 수 있다.Preferably, the detecting of the face region comprises: a sub-step of overlapping an initial face template with a starting point of an upper left end of an input image and obtaining a cross correlation with an overlapped portion; A sub-step of detecting a position having the highest cross-correlation as a face region while moving by one pixel from the starting point; And if the cross-correlation is equal to or greater than a predetermined value, the template matching may be continuously performed. Otherwise, the template matching may be performed by re-detecting the face region and updating the new face template.
바람직하게, 상기 얼굴 영역이 검출되지 않으면 상호 상관도를 낮춰서 템플릿 정합을 진행하고, 상기 낮춘 상호 상관도에서도 얼굴 영역이 검출되지 않으면 영상에 얼굴 영역이 없다고 판별할 수 있다.Preferably, if the face region is not detected, the template matching may be performed by lowering the cross correlation, and if the face region is not detected even in the lower cross correlation, it may be determined that there is no face region in the image.
상기의 구성에 의하면, 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙 및 외곽에서 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 수렴해 가면서 양방향으로 동공 영역을 레이블링함으로써 눈 검출 정확도를 개선할 수 있다.According to the above configuration, the eye detection accuracy can be improved by labeling the pupil region in both directions while converging in two concentric circles originating from the center and the outer edge of the eye search region, respectively.
또한, 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행해 불특정 외난에 의한 성능 저하를 억제함으로써 기존의 그레이디언트 벡터 필드 기반의 눈 개폐 판단 방법의 성능을 개선할 수 있다.In addition, Kalman filtering is performed on the corrected cumulative inner cumulative average to suppress performance degradation due to unspecified external conditions, thereby improving performance of the conventional gradient vector field-based eye open / closed judgment method.
또한, 시청 현혹 검출 기능을 적용함으로써, 응시 판단 알고리즘의 허점을 분석하여 사람의 얼굴 사진이나 인형, 조형물 등을 이용해 마치 수강자가 강의 콘텐츠를 응시하는 것처럼 현혹해 허위로 온라인 강의 출석을 인정받는 것을 방지할 수 있다.Also, by applying the deception function of viewing, it analyzes the loophole of the gaze determination algorithm and prevents the false attendance of online lectures from being deceived as if the learner gazes at the contents of the lecture using human face photos, figurines, and sculptures. can do.
또한, 카메라를 이용하여 수강자의 성실 시청 여부를 감시해 온라인 출석 여부를 관리할 수 있고 이를 강의 콘텐츠의 재생 중에 화면에 표시함으로써 수강자에게 실시간으로 피드백을 제공할 수 있다.In addition, by using a camera to monitor the attendee's sincerity to watch the online attendance can be managed and display the on-screen during the course content playback can provide feedback to the learner in real time.
도 1(a)은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템의 관리자 모드의 사용자 인터페이스를 나타내고, 도 1(b)은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템의 정상 동작 상태를 나타낸다.
도 2는 본 발명에 따른 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법을 보여주는 순서도이다.
도 3은 정규화 영상 를 대상으로 서로 다른 값으로 임계처리해 구한 이진 영상이다.
도 4는 동공 영역 레이블링을 적용한 예를 보여준다.
도 5는 동공 중심 영역의 국부 블록 마스크를 나타낸다.
도 6은 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 보정한 내적 누적 평균을 이용해 눈 개폐 판단 여부를 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 시스템의 시청 현혹 검출 실험 상황을 예시한 것이다.
도 8은 시청 현혹 검출 시의 최종학습률을 표시하는 예를 보여준다.
도 9는 본 발명의 방법을 적용한 눈 검출 결과를 예시한 것이다.
도 10은 본 발명의 눈 개폐 판단 방법을 이용한 판단 결과 영상을 나타낸 것이다.
도 11은 얼굴 인증 동작 과정을 나타낸 순서도이다.
도 12는 CLM을 이용한 주요 얼굴 특징점의 추출 결과를 나타낸 것이다.
도 13은 FEI Face Database의 1인당 14장씩 촬영한 얼굴 영상 세트를 예시한 것이다. Figure 1 (a) shows the user interface of the administrator mode of the online lecture monitoring system, Figure 1 (b) shows the normal operating state of the online lecture monitoring system.
2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for monitoring online lectures according to the present invention.
3 is a normalized image It is a binary image obtained by thresholding with different values.
4 shows an example in which pupil area labeling is applied.
5 shows a local block mask of the pupil center region.
6 is a graph showing whether the eye is opened or closed by using an internal cumulative average corrected by the number of gradient vectors.
Figure 7 illustrates the situation of deception detection experiment of the system of the present invention.
8 shows an example of displaying a final learning rate at the time of detecting deception of watching.
9 illustrates an eye detection result to which the method of the present invention is applied.
10 is a view showing a determination result image using the eye opening and closing determination method of the present invention.
11 is a flowchart illustrating a face authentication operation process.
12 shows extraction results of major facial feature points using CLM.
FIG. 13 exemplifies a set of face images captured by 14 people in the FEI Face Database.
본 발명에서 사용되는 기술적 용어는 단지 특정한 실시 예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아님을 유의해야 한다. 또한, 본 발명에서 사용되는 기술적 용어는 본 발명에서 특별히 다른 의미로 정의되지 않는 한, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 의미로 해석되어야 하며, 과도하게 포괄적인 의미로 해석되거나 과도하게 축소된 의미로 해석되지 않아야 한다. 또한, 본 발명에서 사용되는 기술적인 용어가 본 발명의 사상을 정확하게 표현하지 못하는 잘못된 기술적 용어일 때에는, 당업자가 올바르게 이해할 수 있는 기술적 용어로 대체되어 이해되어야 할 것이다. 또한, 본 발명에서 사용되는 일반적인 용어는 사전에 정의되어 있는 바에 따라, 또는 전후 문맥상에 따라 해석되어야 하며, 과도하게 축소된 의미로 해석되지 않아야 한다.Technical terms used in the present invention are merely used to describe particular embodiments, it should be noted that it is not intended to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical terms used in the present invention should be interpreted as meanings generally understood by those skilled in the art unless the present invention is defined in any other meaning in the present invention, and is excessively comprehensive. It should not be interpreted in the sense of or in the sense of being excessively reduced. In addition, when the technical terminology used in the present invention is an incorrect technical term that does not accurately express the spirit of the present invention, it should be understood as being replaced by a technical term that can be properly understood by those skilled in the art. In addition, the general terms used in the present invention should be interpreted as defined in the dictionary or according to the context before and after, and should not be interpreted in an excessively reduced sense.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명에 따른 온라인 강의 시스템의 실시 예를 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, with reference to the accompanying drawings will be described in detail an embodiment of an online lecture system according to the present invention.
도 1(a)은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템의 관리자 모드의 사용자 인터페이스를 나타내고, 도 1(b)은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템의 정상 동작 상태를 나타낸다.Figure 1 (a) shows the user interface of the administrator mode of the online lecture monitoring system, Figure 1 (b) shows the normal operating state of the online lecture monitoring system.
화면 인터페이스는 관리자 모드(Admin Mode)와 사용자 모드(User Mode)에 따라 수강자의 입력 영상을 표시하는 영역을 구비할 수 있다The screen interface may include an area for displaying an input image of a participant according to an administrator mode and a user mode.
도 1(a)에서는 관리자 모드에서의 화면 인터페이스를 보여주고 있는데, User Mode 버튼(사용자 모드 전환 버튼)을 누르면, 동작 모드가 관리자 모드에서 사용자 모드로 전환되면서 동시에 User Mode 버튼은 Admin Mode 버튼(관리자 모드 전환 버튼)으로 변경된다. 역으로, 사용자 모드에서 Admin Mode 버튼을 누르면, 동작 모드가 관리자 모드로 전환되면서 동시에 Admin Mode 버튼은 User Mode 버튼으로 변경된다. Figure 1 (a) shows the screen interface in the administrator mode, pressing the User Mode button (user mode switch button), the operation mode is switched from the administrator mode to the user mode while the User Mode button is the Admin Mode button (administrator) Mode switch button). Conversely, if the Admin Mode button is pressed in the user mode, the operation mode is changed to the administrator mode and the Admin Mode button is changed to the User Mode button at the same time.
사용자 모드에서는 수강자의 얼굴 영상을 표시하는 우측 화면과 화면 응시 정보를 표시하는 리스트 박스가 제거되고 콘텐츠 화면과 동작 제어 버튼만 남는다.In the user mode, the right screen displaying the face image of the participant and the list box displaying the screen gaze information are removed and only the content screen and the operation control button remain.
도 1(a)과 같은 사용자 인터페이스상에서 원하는 강의 콘텐츠를 선택해 재생하면 PC 캠을 통해 획득한 입력 영상으로부터 얼굴 영역을 검출한 후, 눈의 위치와 개폐 상태를 감시해 화면 응시율을 계산할 수 있고, 이후 일정 시퀀스 구간에서 인접 화면들 간의 동공 위치 변화가 있는 화면수를 조사함으로써 시청 현혹 상태도 파악할 수 있다. When the desired lecture content is selected and played on the user interface as shown in FIG. 1 (a), the face region is detected from the input image acquired through the PC cam, and then the screen staring rate can be calculated by monitoring the eye position and the open / closed state. By examining the number of screens with a change in pupil position between adjacent screens in a certain sequence section, the deceptive state of viewing can also be identified.
도 1(b)을 보면, 전체 화면을 크기가 다른 4개의 영역으로 분할해 좌측 상단에 콘텐츠 화면을 표시하고, 우측 상단에 입력 영상을 표시하고, 좌측 하단에 각종 기능 버튼을 위치시키며, 우측 하단에 리스트 박스를 표시한다.Referring to FIG. 1 (b), the entire screen is divided into four regions having different sizes to display a content screen on the upper left, an input image on the upper right, and various function buttons are located on the lower left, and the lower right Display a list box.
입력 영상에는 컴퓨터의 전면 카메라를 통해 촬영된 수강자의 입력 영상이 표시되면서 입력영상 위에 얼굴 영역 및 얼굴 특징 요소, 눈의 개폐여부 들의 검출 결과를 표시한다. An input image of the participant photographed through the front camera of the computer is displayed on the input image, and the detection result of the face region, facial feature elements, and whether the eyes are opened or closed is displayed on the input image.
각종 기능 버튼은 기능의 특성에 따라 배치될 수 있는데, 가령 좌측에 기본적인 동영상 플레이를 위한 Open 버튼, Play 버튼, Stop 버튼 및 Pause 버튼이 있고, 우측에 Eye State 버튼, Cherry Picker 동작 버튼, Smart Stay 동작 버튼 및 모드 전환 버튼이 위치한다.Various function buttons can be arranged according to the characteristics of the function. For example, there are Open button, Play button, Stop button and Pause button for basic video play on the left side, Eye State button, Cherry Picker operation button, Smart Stay operation on the right side. The button and the mode switch button are located.
Play 버튼(재생 버튼)과 Pause 버튼(일시정지 버튼)을 통해 강의 콘텐츠의 재생 여부를 제어할 수 있고, Stop 버튼(정지 버튼)을 누르면, 강의 콘텐츠의 재생이 정지되고 전체화면수, 응시화면수, 화면응시율, 시청현혹률 및 최종학습률이 초기화된다. Play button (play button) and Pause button (pause button) can control whether or not the course content is played, press the Stop button (stop button) to stop the course content playback, the number of full screen, the number of screens The screen rate, viewing rate and final learning rate are initialized.
Eye State 버튼(눈 개폐 감시 버튼)을 누르면 그레이디언트 기반의 고속 눈 검출 방법과 적응형 눈 개폐 판단 알고리즘을 이용하여 눈 개폐 판단 결과를 우측 화면상에 표시하는데, 눈을 뜬 경우엔 흰색 원으로 표시하고 눈을 감은 경우엔 적색의 타원으로 표시하고 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 간주해 콘텐츠 화면의 좌상단에 적색 경고등을 표시한다. 그리고 리스트 박스엔 개폐 판단 결과로 눈을 뜬 경우엔 Open Eye로, 눈을 감은 경우엔 Closed Eye로 출력한다.When the Eye State button (eye open / close button) is pressed, the result of the eye open / closed judgment is displayed on the right screen by using the gradient-based high speed eye detection method and the adaptive eye open / closed judgment algorithm. If the display is closed and the eyes are closed, it is indicated by a red ellipse and the red warning light is displayed on the upper left of the content screen in consideration of not staring at the screen. The list box outputs Open Eye if the eyes are opened and Closed Eye if the eyes are closed.
Cherry Picker 버튼은 시청 현혹자(cherry picker)를 검출하기 위한 것으로, 응시 판단 알고리즘의 허점을 분석하여 사람의 얼굴 사진이나 인형을 이용해 마치 수강자가 동영상 콘텐츠를 응시하는 것처럼 현혹해 허위로 온라인 강의 출석을 인정받는 것을 방지하기 위한 기능이다. 입력 영상 시퀀스의 일정 프레임 구간 내에서 동공의 움직임이 없으면 시청 현혹 상황으로 판단하여 출석을 인정하지 않는다.The Cherry Picker button is used to detect cherry pickers, and analyzes the loopholes in the gaze judgment algorithm and uses the face of a person's face or a doll to deceive the lectures as if the participant is staring at the video content. This function is to prevent recognition. If there is no movement of the pupil within a predetermined frame section of the input image sequence, it is determined that the viewing is deceptive and the attendance is not recognized.
Smart Stay 버튼을 누르게 되면 입력 영상의 개폐 판단 여부와 얼굴 유무를 판단하여 우측 화면의 수강자가 강의 콘텐츠를 보고 있을 시에는 정상 재생이 지속되고 일시적으로 응시하지 않거나 눈을 감고 있을 경우에는 재생 상태에서 일시정지 상태로 전환하게 되고 다시 시청을 하게 되면 일시정지 상태에서 재생 상태로 변경하게 된다.When the Smart Stay button is pressed, it judges whether the input image is open or closed and whether there is a face. When the learner on the right screen is watching the lecture contents, the normal playback is continued. When the player enters the stopped state and watches again, the user changes from the pause state to the play state.
리스트 박스에는 실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률, 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률, 눈개폐상태, 및 눈검출시간 등이 표시된다. In the list box, the number of screens that have been played so far, the number of screens that have been checked by eye tracking, the screen viewing rate that is the ratio of the number of screens to the number of screens, and the viewing dazzle rate that is the ratio of the number of screens to the screen The final learning rate, the eye open state, and the eye detection time, which are the ratio of the number of screens minus the number of dazzle screens and the total screens, are displayed.
또한, 최종적으로 하나의 강의 콘텐츠를 모두 시청했을 경우, 가령 팝-업 윈도를 통하여 수강자의 최종 학습률을 표시함으로써 수강자로 하여금 자신이 수강한 온라인 강의 출석의 유효 혹은 무효를 판단할 수 있도록 해준다.In addition, when finally viewing all the contents of a lecture, for example, by displaying the final learning rate of the learner through a pop-up window, the learner can determine the validity or invalidity of the attendance of the online course attended.
도 2는 본 발명에 따른 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법을 보여주는 순서도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for monitoring online lectures according to the present invention.
컴퓨터에서 소프트웨어를 동작시키면 파일 열기를 통해 강의 콘텐츠를 선택하여 재생한다(단계 S21).When the software is operated on the computer, the lecture contents are selected and played by opening the file (step S21).
Open 버튼으로 강의 콘텐츠가 선택되고 Play 버튼으로 재생되면, 좌측 화면에 해당 강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 우측 화면에는 전면 카메라를 통해 촬영한 수강자의 얼굴 영상이 표시된다.When lecture content is selected with the Open button and played with the Play button, the lecture content is played on the left screen, and the face image of the participant photographed through the front camera is displayed on the right screen.
카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출한다(단계 S22).A face is detected from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, a gaze is tracked, and an amount of change in eye movement between frames is examined to detect viewing deception (step S22).
이어, 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단한다(단계 S23).Then, it is determined whether the student stares at the screen (step S23).
판단결과, 강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하고(단계 S24), 이후 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여(단계 S25) 응시 화면수를 증가한다(단계 S26).As a result, if the learner's face and pupil are detected while the lecture contents are being played, the student's face authentication is prevented through the verification of the learner's face (step S24), and then judged whether the viewing is deceptive (step S25). The number of screens is increased (step S26).
반면, 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 스마트 스테이 기능이 활성화되면서(단계 S27) 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 콘텐츠 화면의 좌상단에 적색 경고등이 표시된다(단계 S28).On the other hand, if the face and pupil of the participant are not detected, it is determined that the user does not stare at the screen and the smart stay function is activated (step S27), and the number of non-stare screens is increased and a red warning light is displayed at the upper left of the content screen (step S28).
이후, 강의 콘텐츠 재생이 종료되었는지를 확인하여(단계 S29), 종료되지 않았으면 단계 S22으로 복귀하고, 종료되었으면, 화면 응시율을 계산한다(단계 S30).Thereafter, it is checked whether the lecture content reproduction is finished (step S29), and if not, the process returns to step S22, and if it is finished, the screen gaze rate is calculated (step S30).
이하, 단계 S22에서의 눈 검출과 눈 개폐 판단 및 시청 현혹 검출에 대해 구체적으로 설명한다.Hereinafter, eye detection, eye open / closed judgment and viewing deception detection in step S22 will be described in detail.
<눈 검출><Eye detection>
종래 이중 에지 맵, 동공 후보 영역, 비동공 영역 레이블링, 동공 후보 영역 레이블링을 이용한 방법을 통해 연산 부담을 경감함과 동시에 기존의 방법의 검출 정확도를 개선한 방법들을 이미 제안한 바 있지만, 안정된 시선 추적 기능을 제공하기 위해서는 다소 극단적인 상황에서도 눈 검출 정확도를 좀 더 향상시킬 수 있는 방안이 개발될 필요가 있다. Conventional methods have been proposed to reduce the computational burden and improve the detection accuracy of conventional methods through the method using the dual edge map, pupil candidate region, non-pupillary region labeling, and pupil candidate region labeling. In order to provide a more accurate method, it is necessary to develop a method to further improve eye detection accuracy even in a more extreme situation.
본 발명에서는 이러한 필요성에 부응하기 위해 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙 및 외곽에서 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 수렴해 가면서 양방향으로 동공 영역을 레이블링함으로써 눈 검출 정확도를 개선한 그레이디언트 기반 눈 검출 방법을 제안한다.In order to meet this need, the present invention proposes a gradient-based eye detection method that improves eye detection accuracy by labeling the pupil area in both directions while converging in two concentric directions originating from the center and the outside of the eye search area, respectively. do.
우선, 본 발명의 방법은 Haar 유사 특징과 AdaBoost 알고리즘 그리고 적응형 템플릿 정합을 이용해 입력 영상에서 얼굴 영역을 검출하고, 얼굴의 기하학적 특징을 이용하여 도 3과 같이 좌측과 우측의 눈 탐색 영역을 지정한다.First, the method of the present invention detects a face region from an input image using a Haar-like feature, an AdaBoost algorithm, and adaptive template matching, and designates left and right eye searching regions as shown in FIG. .
다음으로, 눈 탐색 영역의 가우시안 필터링된 역 밝기 영상을 히스토그램 평활화하여 정규화한 후, 임계처리를 통해 동공 후보 영역을 추출한다. Next, the gaussian filtered inverse brightness image of the eye search region is normalized by histogram smoothing, and the pupil candidate region is extracted through threshold processing.
먼저, 식 (1)과 같이 눈 탐색 영역 의 영상 을 구한 후, 가우시안 필터링을 취한다. 를 식 (2)와 같이 히스토그램 평활화를 취한 후, 식 (3)처럼 의 최대값을 이용해 정규화 영상 을 구한다.First, the eye navigation area as shown in equation (1) Video of Then, Gaussian filtering is performed. After histogram smoothing as in Eq. (2), Normalized image using maximum of Obtain
이후, 실험적으로 구한 소정의 임계값을 이용해 동공의 중심을 포함하는 동공 후보 영역과 그 이외의 영역인 비동공 영역으로 구분한다. Thereafter, a predetermined threshold value obtained experimentally is used to classify the pupil candidate region including the center of the pupil and the non-pupillary region, which is another region.
도 3은 정규화 영상 를 대상으로 서로 다른 값으로 임계처리해 구한 이진 영상으로, 상부는 안경을 착용한 경우이고 하부는 안경을 착용하지 않은 경우이다.3 is a normalized image This is a binary image obtained by thresholding different values with respect to the upper part when wearing glasses and the lower part when wearing glasses.
여기서 밝은 곳은 동공의 중심을 포함하는 동공 후보 영역이고, 어두운 곳은 비동공 영역이다. 임계값이 작을수록 비동공 영역의 면적이 점진적으로 증가함을 알 수 있다.Here, the bright place is the pupil candidate area including the center of the pupil, and the dark place is the non-pupillary area. It can be seen that as the threshold is smaller, the area of the non-pupillary region gradually increases.
이후, 눈 탐색 영역 내 에지 화소들의 그레이디언트 벡터와 정규 변위 벡터 간의 내적을 누적한 후 최대 누적값의 위치를 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출한다. 이때, 동공의 중심은 각각 좌우측 눈 탐색 중앙 영역의 저명도 영역 인근에 위치함에 착안하여 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙에서부터 동심원 확장 방향으로 진행해 가면서 소정의 화소 면적 한도 내에서 동공 영역을 레이블링한다. Then, after accumulating the inner product between the gradient vector and the normal displacement vector of the edge pixels in the eye search region, the position of the maximum cumulative value is detected as the center of the left and right eyes. At this time, the center of the pupil is located in the vicinity of the low-brightness region of the left and right eye search center region, respectively, and proceeds in the direction of concentric circles from the center of the eye search region to label the pupil area within a predetermined pixel area limit.
도 4는 동공 영역 레이블링을 적용한 예를 보여준다.4 shows an example in which pupil area labeling is applied.
다음으로, 이렇게 레이블링된 동공 영역이 눈 탐색 영역의 테두리에 접할 경우에는 이 테두리로부터 동심원 수축 방향으로 진행해 가면서 상기 레이블링된 동공 면적의 일정 비율 한도 내에서 테두리 인접 영역을 비동공 영역으로 지정해 제거한다.Next, when the labeled pupil area is in contact with the edge of the eye search area, the border adjacent area is designated as a non-porous area within the predetermined ratio limit of the labeled pupil area while proceeding in the concentric contraction direction from the border.
최종적으로, 전체 눈 탐색 영역이 아닌 도 4(b)의 레이블링된 동공 영역에서만 한정해 내적 누적 연산을 수행한 후 최대 내적 누적값의 위치를 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출한다. Finally, the inner cumulative calculation is limited to only the labeled pupil area of FIG. 4 (b), not the entire eye searching area, and then the position of the maximum inner cumulative value is detected as the center of the left and right eyes.
본 발명의 눈 개폐 판단 방법은 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행해 불특정 외난에 의한 성능 저하를 억제함으로써 기존의 그레이디언트 벡터 필드 기반의 눈 개폐 판단 방법의 성능을 개선할 수 있다.The eye open / close determination method of the present invention can improve the performance of the conventional gradient vector field-based eye open / close determination method by performing Kalman filtering on the corrected cumulative internal mean to suppress performance degradation due to unspecified external disturbances.
도 5는 동공 중심 영역의 국부 블록 마스크를 나타낸다.5 shows a local block mask of the pupil center region.
눈 개폐 여부를 판단하기 위해 좌측 및 우측 눈 탐색 영역에서 최대 내적 누적값의 위치를 중심으로 소정 화소 크기(예컨대, 7×7 화소 크기)의 국부 블록 마스크를 지정한 후, 이 블록 마스크에 포함된 화소의 내적 누적값을 합산한 다음에 블록 마스크의 크기로 나눠 평균을 구한다. In order to determine whether the eyes are opened or closed, a local block mask having a predetermined pixel size (for example, 7 × 7 pixel size) is specified around the positions of the maximum inner cumulative values in the left and right eye search areas, and then the pixels included in the block mask. Calculate the mean by summing the inner cumulative values of and dividing by the size of the block mask.
이후 이 내적 누적 평균을 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 나눈 값과 눈 개폐 임계값을 비교해 눈 개폐 여부를 판단한다.Thereafter, the inner cumulative average is divided by the number of gradient vectors and the eye open / close threshold is determined to determine whether the eye is open or closed.
통계적으로 동일한 사람의 동공 영역에서 구한 내적 누적 평균의 크기는 도 5와 같이 눈을 뜨면 커지고 감으면 작아진다. 또한, 같은 조건일 때 그 값은 안경 착용 시에 커지고 눈과 동공의 크기에 비례해 커진다. 하지만, 내적 누적 평균은 개인 간의 편차가 심하기 때문에 단순히 이 값을 기준으로 눈 개폐 여부를 판단하면 일정 수준 이하로 오분류 확률을 낮추기 어렵다. Statistically, the magnitude of the internal cumulative mean obtained in the pupil region of the same person is larger when the eyes are opened and smaller when the eyes are closed as shown in FIG. 5. Also, under the same conditions, the value increases when the glasses are worn and increases in proportion to the size of the eyes and the pupils. However, since the internal cumulative average is severely different among individuals, it is difficult to reduce the probability of misclassification below a certain level simply by determining whether eyes are opened or closed based on this value.
하나의 내적 누적값은 동공 후보 영역의 각 정규 변위 벡터와 눈 탐색 영역 내 모든 그레이디언트 벡터들을 곱해 누적하는 방식으로 계산되므로 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수가 많을수록 내적 누적값이 상대적으로 커진다. 즉, 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수는 내적값을 누적하는 연산 횟수이다. Since the inner cumulative value is calculated by multiplying each normal displacement vector of the pupil candidate area with all the gradient vectors in the eye search area, the larger the number of the gradient vectors, the larger the inner cumulative value becomes. That is, the number of gradient vectors is the number of operations that accumulate the dot product.
따라서, 식 (4)와 같이 내적 누적 평균 을 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수 로 나눠 보정된 내적 누적 평균 을 구함으로써 이러한 편차를 효과적으로 줄일 수 있다. Therefore, the cumulative inner product mean as in equation (4) Number of gradient vectors Cumulative internal mean corrected by This variation can be effectively reduced by
이때, 각 프레임 단위로 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 그대로 사용할 수도 있다. 하지만 식 (5)처럼 일정 구간의 직전 프레임들과 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값들을 대상으로 칼만 필터링(Kalman filtering)을 수행해 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 갱신하면, 노이즈나 비정상적인 동작에 따른 악영향을 적절하게 억제해 안정된 동작을 유도할 수 있다. 본 발명의 방법은 현 프레임을 포함해 5프레임 단위로 칼만 필터링을 수행해 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 갱신한다.In this case, the internal cumulative average corrected for each frame unit may be used as it is. However, if Kalman filtering is performed on the corrected cumulative cumulative mean values of the previous frame and the current frame in a certain section as shown in Equation (5), the corrected cumulative inner cumulative mean of the current frame is updated. The adverse effects can be properly suppressed to induce stable operation. The method of the present invention performs Kalman filtering in units of five frames including the current frame to update the corrected cumulative mean of the current frame.
한편, 눈 개폐 여부를 판단하기 위해선 눈 개폐 임계값을 구할 필요가 있다. 새로운 프레임이 입력될 때마다 상대적으로 긴 소정의 직전 프레임 구간과 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값을 칼만 필터링을 수행하여 합산한 후, 프레임 수로 나눠 프레임 구간 평균을 구한다. 본 발명의 방법은 현 프레임을 포함해 70프레임 단위로 칼만 필터링과 평균 연산을 수행해 현 프레임의 프레임 구간 평균을 구한다.On the other hand, in order to determine whether the eyes open or close it is necessary to obtain the eye open and close threshold. Each time a new frame is input, a relatively long previous frame period and a corrected inner cumulative mean value of the current frame are summed by performing Kalman filtering, and the frame period average is obtained by dividing by the number of frames. The method of the present invention calculates the average frame interval of the current frame by performing Kalman filtering and averaging on the basis of 70 frames including the current frame.
이때, 프레임 구간 평균을 구할 시, 감은 눈으로 판단된 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값은 제외함으로써 눈을 뜬 상태의 프레임 구간 평균을 구할 수 있다. 이와 같이 구한 프레임 구간 평균은 다음 프레임이 입력될 때마다 프레임 구간을 중첩시켜 가면서 그 값을 갱신함으로써 안경의 착탈 여부나 인물의 변경 혹은 조명의 가변에 적응적으로 대응할 수 있다. In this case, when the average of the frame interval is obtained, the frame interval average of the open state may be obtained by excluding the corrected internal cumulative average value of the frame determined to be closed eyes. The frame section average obtained as described above can be adaptively responded to the detachment of glasses, the change of the person, or the change of the lighting by updating the value by overlapping the frame sections each time the next frame is input.
눈 개폐 임계값 은 식 (6)과 같이 이 프레임 구간 평균에 비례 계수 를 곱해 각 프레임 단위로 결정된다. 본 발명에서는 이 비례 계수로서 실험적으로 구한 0.8을 사용하고 있다. Eye open and close threshold Is proportional to the mean of this frame interval as Multiply by to determine each frame unit. In the present invention, 0.8 obtained experimentally is used as this proportional coefficient.
최종적으로, 식 (7)과 같이, 각 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값이 눈 개폐 임계값보다 크면 눈을 뜬 상태로 판단하고, 그렇지 않으면 눈을 감은 상태로 판단한다. Finally, as shown in equation (7), when the corrected cumulative mean value of each frame is larger than the eye open / close threshold value, it is determined that the eyes are opened, otherwise it is determined that the eyes are closed.
도 6은 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 보정한 내적 누적 평균을 이용해 눈 개폐 판단 여부를 나타낸 그래프이다.6 is a graph showing whether the eye is opened or closed by using an internal cumulative average corrected by the number of gradient vectors.
보정된 내적 누적 평균값이 눈 개폐 임계값보다 크면 눈을 뜬 상태로 판단하는데, 양호한 눈 개폐 판단 성능을 제공하고 있음을 확인할 수 있다.When the corrected inner cumulative mean value is larger than the eye open / close threshold value, it is determined that the eyes are opened, and it can be confirmed that the eye open / close judgment performance is provided.
<시청 현혹 검출><Viewing deception detection>
시청 현혹 검출 기능은 응시 판단 알고리즘의 허점을 분석하여 사람의 얼굴 사진이나 인형, 조형물 등을 이용해 마치 수강자가 강의 콘텐츠를 응시하는 것처럼 현혹해 허위로 온라인 강의 출석을 인정받는 것을 방지하기 위한 것이다. The deception function of viewing is to analyze the loopholes of the gaze determination algorithm and to prevent the attendees from being falsely admitted to the online lectures as if the learners are staring at the contents of the lecture using human photos, figurines, and sculptures.
도 7은 본 발명의 시스템의 시청 현혹 검출 실험 상황을 예시한 것이다. Figure 7 illustrates the situation of deception detection experiment of the system of the present invention.
실제 사람은 영상 콘텐츠를 시청할 경우, 눈 주변의 근육의 변화와 안구 운동에 의해 눈의 움직임이나 찌그러짐, 윙크, 눈 깜박거림 등이 발생한다. 이에 따라, 검출된 최종 눈 위치도 역시 미세하게 변동된다. 하지만, 사진이나 인형 등과 같이 사람의 얼굴의 특성을 가진 물체는 원칙적으로 눈의 움직임이 발생하지 않는다. When a real person watches a video content, eye movements, distortions, winks, and blinks are caused by changes in muscles and eye movements around the eyes. Accordingly, the detected final eye position also fluctuates slightly. However, in general, an object having a characteristic of a human face such as a photograph or a doll does not cause eye movement.
본 발명의 시스템에서는 일정 구간 이상의 연속 프레임들에서 얼굴 영역 혹은 눈 중심점이 변동되지 않을 경우, 수강자가 해당 강의 콘텐츠를 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단한다. In the system of the present invention, if a face region or an eye center point does not change in consecutive frames of a predetermined period or more, it is determined that a participant does not stare at the corresponding lecture content.
그러나 실제 시스템 구현 시, 움직임이 없는 인형이나 사진일지라도 주변 조도 변화나 카메라의 광전변환 노이즈 등에 기인해 촬영 영상에서 눈 중심점을 검출할 시, 미세한 거짓 떨림이 포함될 수 있다. However, when the actual system is implemented, even a doll or a picture without motion may include minute false vibration when detecting the eye center point in the captured image due to a change in ambient illumination or photoelectric conversion noise of the camera.
이를 억제하기 위해 이전 프레임과 현재 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 일정 기준치 이하이면 현재 프레임의 눈 중심점을 거짓 떨림으로 간주해 이전 프레임의 값으로 대체한다. To suppress this, if the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the previous frame and the current frame is less than a predetermined reference value, the eye center point of the current frame is regarded as false tremor and replaced with the value of the previous frame.
본 발명의 시스템은 눈 위치 떨림 방지책을 갖고 있는 것인데, 실험적으로 이 기준치는 2픽셀로 정하고 있다. 이 기준치를 너무 큰 값으로 선정하면 정상 시청을 시청 현혹 상태로 오판정하고, 그 반대의 경우엔 시청 현혹을 정상 시청으로 오인하는 비율이 급증한다.The system of the present invention has an eye position stabilization measure, which is experimentally set to 2 pixels. If the reference value is set to a too large value, the normal judgment is incorrectly judged to be a deceptive state of viewing, and vice versa.
다음으로, 연속된 프레임 간에서 거짓 떨림 현상이 제거된 눈 중심점의 수평 및 수직 좌표를 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행한 후, 현재 프레임과 이전 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 일정 기준치 이하이면 눈의 중심점이 변동되지 않은 것으로 판단해 안구 정지 횟수를 증가시킨다.Next, after performing Kalman filtering on the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the eye center point from which the false blur is eliminated between successive frames, the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the current frame and the previous frame is constant. If it is below the threshold, it is judged that the center point of the eye has not changed and the number of eye stops is increased.
소정 프레임 구간 동안에 상기 안구 정지 횟수가 일정 정지 횟수 이상이면 시청 현혹 상태로 판별하고 그렇지 않으면 정상 시청으로 판별하고, 상기 소정 프레임 구간마다 상기 안구 정지 횟수를 초기화시키면서 시청 현혹 여부를 지속적으로 감시한다.If the number of eyeball stops is equal to or greater than the predetermined number of stops during a predetermined frame period, it is determined as a viewing delusion state. Otherwise, it is determined to be normal viewing, and the watchdog is continuously monitored while initializing the number of eyeball stops for each predetermined frame period.
상기에서, 가령 일정 기준치는 3픽셀이고, 소정 프레임 구간은 30프레임이며, 일정 정지 횟수는 29회일 수 있다. For example, the predetermined reference value may be 3 pixels, the predetermined frame section may be 30 frames, and the number of predetermined stops may be 29 times.
따라서, 현재 프레임과 이전 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 3픽셀 이하이면 안구 정지 횟수 α값을 증가시킨다. 이 조건을 만족할 경우, 눈의 중심점이 변동되지 않은 것으로 판단한다.Therefore, when the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the current frame and the previous frame is 3 pixels or less, the value of the eye stop count α is increased. If this condition is satisfied, it is determined that the eye's center point does not change.
이때, 실제 사람이 화면을 응시하더라도 시선을 집중할 경우엔 일시적으로 눈의 중심점이 변하지 않는 경우가 종종 발생하기 때문에, 30프레임 구간 동안 α값이 29번 이상 증가하면 시청 현혹 상태로 판별하고 그렇지 않으면 정상 시청으로 판별한다. 30프레임 구간마다 α값을 초기화시켜 계속하여 시청 현혹 여부를 감시한다. At this time, even if a real person stares at the screen, the eye's center point often does not change temporarily when the eyes are focused, so if the α value increases more than 29 times in 30 frames, it is judged to be a deceptive state of viewing. We discriminate by city hall. The α value is initialized every 30 frames to continuously monitor whether or not viewing is deceptive.
수강자가 정상적으로 영상을 시청하는 경우엔 적색 경고등이 들어오지 않지만, 사진 혹은 인형 등의 가짜 수강자일 경우엔 적색 경고등을 표시함으로써 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되고 있음을 외부에 경고해 준다.If the attendees normally watch the video, the red warning light does not come in. However, if the student is a fake student such as a photograph or a doll, the red warning light is displayed to warn the outside that it is judged to be a deceptive state.
전체 프레임을 기준으로 할 때, 85% 이상의 구간에서 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되면 고의적 시청 현혹 의도로 최종 판단하고, 도 8처럼, 최종학습률을 0%로 처리하여 다시 강의를 시청할 수 있도록 유도한다. Based on the entire frame, if it is determined that the viewing is deceptive in the section of 85% or more, it is finally determined as the deliberate viewing deception intention, and as shown in FIG. 8, the final learning rate is treated as 0% to induce the viewer to watch the lecture again.
이러한 과정을 통해 실질적으로는 강의를 시청하지 않으면서도 시스템의 허점을 이용해 교묘하게 출석을 인정받는 시청 현혹자를 차단할 수 있다.Through this process, it is possible to block the deceptive viewers who are subtly recognized by using the system loophole without actually watching the lecture.
<눈 검출, 눈 개폐 판단 및 시선 현혹 검출의 시뮬레이션>Simulation of eye detection, eye open / closed judgment and gaze deception detection
성능 평가를 위해 Intel Core i7-7500U CPU, 8GB DDR4 RAM, Geforce 940MX(2GB) 환경에서 Microsoft Visual C++ 2013, OpenCV 2.4.9를 이용해 시뮬레이션을 수행하였다. For performance evaluation, the simulation was performed using Microsoft Visual C ++ 2013, OpenCV 2.4.9 in Intel Core i7-7500U CPU, 8GB DDR4 RAM, Geforce 940MX (2GB).
우선, 눈 검출용 시험 영상 시퀀스는 CMOS 웹캠을 통해 획득한 얼굴 영상들로, 약 25∼75㎝ 거리에서 정상 조도(약 400lux)의 실내조명 상태에서 촬영한 것이다. 안경 미착용 및 안경 착용 얼굴 영상의 각각 2,093장과 2,343장으로 구성된 640×480 크기의 총 4,436장이다. First, a test image sequence for eye detection is a face image obtained through a CMOS webcam, which is taken under normal illumination (about 400 lux) indoor lighting at a distance of about 25 to 75 cm. A total of 4,436 640 × 480 images consisted of 2,093 and 2,343 images of glasses without wearing and glasses wearing, respectively.
표 1은 본 발명의 방법과 기존의 방법들의 눈 검출 성능을 비교한 것이다. 시뮬레이션 결과에 따르면, 기존의 방법과 개선된 기존의 방법에 비해 우수한 재현율을 제공하면서도 개선된 기존의 방법과 유사한 연산 속도를 유지하는 장점이 있다. Table 1 compares the eye detection performance of the method of the present invention and the existing methods. According to the simulation results, it has the advantage of maintaining a similar computational speed as the improved conventional method while providing an excellent reproducibility compared to the conventional method and the improved conventional method.
구 분 Way
division
방법Conventional
Way
도 9는 본 발명의 방법을 적용한 눈 검출 결과를 예시한 것이다. 안경 착용 시와 미착용 시를 구분하지 않고 비교적 정확하게 좌우측의 동공을 검출하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 대부분의 눈 검출 방법에서 안경 착용을 검출 정확도를 저하시키는 주요한 원인이다. 본 발명의 방법은 동공 영역 레이블링 과정에서 안경테나 눈썹, 머리카락 등 비동공 영역이 자연스레 제거되는 장점이 있는데, 이것은 검출 정확도와 연산 속도를 동시에 제고시킨다. 전반적으로 본 발명의 방법은 낮은 연산량을 소요하면서 우수한 눈 검출 정확도를 제공하는 장점이 있다.9 illustrates an eye detection result to which the method of the present invention is applied. It can be seen that the pupils on the left and right sides are detected relatively accurately without distinguishing between wearing glasses and not wearing glasses. In most eye detection methods, wearing glasses is a major cause of poor detection accuracy. The method of the present invention has the advantage that the non-pupillary areas such as eyeglass frames, eyebrows and hair are naturally removed in the pupil area labeling process, which simultaneously improves the detection accuracy and the calculation speed. Overall, the method of the present invention has the advantage of providing excellent eye detection accuracy while requiring a low calculation amount.
한편, 눈 개폐 판단용 시험 영상 시퀀스는 눈 검출용과 같은 조건에서 촬영한 안경 미착용 및 안경 착용 얼굴 영상들로, 각각 4,534장과 5,375장으로 구성된 640×480 크기의 총 9,909장이다. On the other hand, the test image sequence for eye open / closed determination is 9,909 total of 640 × 480 sizes of 4,534 and 5,375 images of glasses-free and glasses-wearing face images taken under the same conditions as eye detection.
표 2는 본 발명의 방법과 기존의 방법의 눈 개폐 판단 성능을 비교한 것이고, 도 10은 본 발명의 눈 개폐 판단 방법을 이용한 판단 결과 영상을 나타낸 것이다. Table 2 compares the eye open / closed determination performance of the method of the present invention and the conventional method, and FIG. 10 shows an image of the determination result using the eye open / closed determination method of the present invention.
구 분 Way
division
방법Conventional
Way
방법Of the present invention
Way
(4,534장)Wearing glasses
(4,534)
(5,375장)Wearing glasses
(5,375)
표 2와 같이 본 발명의 눈 개폐 판단 방법을 적용해 눈 개폐 판단 성능을 측정하면, 안경 미착용 시엔 96.2%의 정확률(precision)과 96.3% 재현율(recall)로서 F1-Measure 값은 96.2%이었다. 또한, 안경 착용 시엔 97.1%의 정확률과 96.6 재현율인 바, F1-Measure 값은 96.8%이었다. When the eye open / closed judgment performance was measured by applying the eye open / closed judgment method of the present invention as shown in Table 2, the F 1 -Measure value was 96.2% as a precision and 96.3% recall when the glasses were not worn. In addition, when wearing glasses, the accuracy of 97.1% and 96.6 recall were F 1 -Measure value of 96.8%.
따라서, 안경 미착용 및 안경 착용 시, 종래의 눈 개폐 판단 방법에 비해 각각 3.7%p 및 2.0%p만큼 우수한 성능을 제공함을 확인할 수 있었다. 또한, 본 발명의 방법은 프레임당 처리시간 측면에서 기존의 방법과 유사한 성능을 제공함을 알 수 있었다.Thus, when not wearing glasses and wearing glasses, it was confirmed that they provide superior performance by 3.7% p and 2.0% p, respectively, compared to the conventional eye open / close determination method. In addition, the method of the present invention was found to provide performance similar to the conventional method in terms of processing time per frame.
표 3은 본 발명의 방법과 기존의 방법의 시청 현혹 검출 성능을 비교한 것으로, 본 발명의 방법은 99.40% 재현율(recall)과 98.82%의 정확률(precision)로서 F1-Measure값은 99.12%이었다.Table 3 compares the deceptive detection performance of the method of the present invention and the conventional method. The method of the present invention is 99.40% recall and 98.82% precision, with a F 1 -Measure value of 99.12%. .
구 분 Way
division
방법Conventional
Way
방법Of the present invention
Way
(5,110장)
+
실제 사람
(5,360장)Dazzle pictures
(5,110)
+
Real people
(5,360 photos)
재현율(%)
% Recall
85.11
85.11
99.40
99.40
본 발명의 시청 현혹 검출 방법은 F1-Measure 값에서 기존의 방법에 비해 7.48%p만큼 우수한 성능을 제공함을 확인할 수 있었고, 정확률이 기존의 방법보다 소폭 낮은 이유는 눈 중심점의 수평 및 수직 좌표를 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행할 경우에 칼만 필터의 특성상 변화를 억제시키는 경향이 있음으로 인해 정상 시청을 시청 현혹 상태로 오판정하는 비율을 소폭 증가시키기 때문이다.The deceptive detection method of the present invention was able to confirm that the F 1 -Measure value is superior to the conventional method by 7.48% p, the reason that the accuracy is slightly lower than the conventional method is because the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the eye center point This is because when the Kalman filtering is performed on the object, the change in the characteristics of the Kalman filter tends to be suppressed, thereby slightly increasing the rate of misjudged the normal viewing to the deceptive state.
이상에서 설명한 것처럼, 본 발명의 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법에서 채택하고 있는 시선 추적 기술은 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙 및 외곽에서 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 확장 혹은 수렴해 가면서 제한된 화소 수만큼만 양방향으로 동공 영역을 레이블링하고 해당 영역에서만 내적 누적 연산을 수행함으로써 검출 정확도와 연산 속도를 개선하였다. As described above, the gaze tracking technology adopted in the online lecture monitoring method of the present invention expands or converges in two concentric directions originating from the center and the outer portion of the eye search area, respectively, and the pupil area is bidirectionally limited by the limited number of pixels. The detection accuracy and the computation speed are improved by labeling and performing internal cumulative calculation only in the corresponding area.
또한, 눈 개폐 판단 방법의 시뮬레이션 결과로부터 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수가 많을수록 내적 누적 평균이 커짐에 따라 내적 누적 평균을 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 나눠 보정된 내적 누적 평균을 구하고 불특정 외난에 의한 성능 저하를 회피하기 위해 칼만 필터링을 수행해 눈 개폐 여부를 판단하는 방법의 우수성을 확인할 수도 있었다.In addition, as the number of gradient vectors increases as the number of gradient vectors increases from the simulation results of the eye open / close judgment method, the cumulative inner cumulative average is divided by the number of gradient vectors to obtain a corrected inner cumulative mean, and performance deteriorates due to unspecified external warming. In order to avoid the Kalman filtering was performed to determine the superiority of the method of determining whether the eyes open or closed.
시뮬레이션 결과에 따르면, 본 발명의 눈 검출 방법은 기존의 방법과 개선된 기존의 방법에 비해 우수한 정확도를 제공하면서도 안경 착용 시와 미착용 시 개선된 기존의 방법과 유사한 연산 속도를 유지하는 장점이 있다. According to the simulation results, the eye detection method of the present invention has an advantage of maintaining the operation speed similar to the conventional method improved when wearing glasses and non-wear while providing excellent accuracy compared to the existing method and the improved conventional method.
또한, 본 발명의 눈 검출 및 눈 개폐 판단 방법은 기존의 방법에 비해 카메라와 얼굴 간 거리 변화에 강인하고 저조도 영상에서도 상대적으로 높은 검출률을 제공할 뿐만 아니라 특히, 안경을 착용한 경우에도 상대적으로 양호한 성능을 제공하는 장점이 있었다. In addition, the eye detection and eye open and close determination method of the present invention is more robust to changes in the distance between the camera and the face than the conventional method, and provides a relatively high detection rate even in a low light image, and is particularly good even when wearing glasses. There was an advantage in providing performance.
이하, 단계 S24에서의 얼굴 인증 동작 과정에 대해 구체적으로 설명한다.Hereinafter, the face authentication operation process in step S24 will be described in detail.
도 11은 얼굴 인증 동작 과정을 나타낸 순서도이다.11 is a flowchart illustrating a face authentication operation process.
다수의 방향과 주파수 성분을 갖는 가버(Gabor) 커널을 생성한다(단계 S111).A Gabor kernel having a plurality of directions and frequency components is generated (step S111).
이어 갤러리(Gallery) 얼굴 영상을 대상으로 사전에 주요 얼굴 특징점을 추출한다(단계 S112).Subsequently, a main facial feature point is extracted in advance on the gallery face image (step S112).
가령, 오프라인으로 사전에 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 대해 D. Cristinacce와 T. Cootes가 제안한 CLM(Constrained Local Model)을 이용하여 눈, 코, 입, 턱 등의 주변에 존재하는 68개의 주요 얼굴 특징점(landmark)을 검출한다.For example, 68 major facial landmarks exist around the eyes, nose, mouth and chin using the CLM (Constrained Local Model) proposed by D. Cristinacce and T. Cootes for offline gallery facial images. Is detected.
사전에 오프라인으로 각 얼굴 특징점에서 가버 커널을 이용한 갤러리 특징 벡터를 추출 및 저장한다(단계 S113).The gallery feature vector using the Gabor kernel is extracted and stored at each facial feature point in advance offline (step S113).
가령, 검출한 얼굴 특징점을 중심으로 회전과 크기 측면의 기하학적 정규화를 수행한 상태에서 8개 방향과 5개 주파수로 이루어진 40차원 가버(Gabor) 특징 벡터를 추출해 저장한다. For example, a 40-dimensional Gabor feature vector consisting of eight directions and five frequencies is extracted and stored in the state of performing geometric normalization of rotation and magnitude in terms of the detected facial feature points.
이어, 온라인으로 추출한 프로브(Probe) 얼굴 영상의 가버 특징 벡터와 사전에 기 저장된 갤러리 특징 벡터 간의 유사도를 측정한다(단계 S114).Subsequently, the similarity between the Gabor feature vector of the Probe face image extracted online and the previously stored gallery feature vector is measured (step S114).
프로브 얼굴 영상과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물의 얼굴이 포함되어 있으면 정분류로 판정하고, 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정하여, 정분류된 경우에 한해 정분류 얼굴의 최근접 거리비(Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 구하고, 최근접 거리비(NNDR)가 인증 임계값보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정한다(단계 S116).If the gallery face image that is most similar to the probe face image contains the face of the same person as the probe face image, it is determined as a normal classification. Otherwise, it is determined as a misclassification. A ratio (Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio) is obtained, and when the nearest distance ratio NNDR is smaller than the authentication threshold value, it is determined that the face authentication succeeds, otherwise, it is determined to be unauthorized (step S116).
이하, 각 과정에 대해 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, each process is explained in full detail.
<CLM 기반의 주요 얼굴 특징점 검출><CLM-based Major Facial Feature Detection>
CLM(Constrained Local Model)은 얼굴 영역을 탐색한 후, 그 사람의 얼굴에서 눈, 코, 입과 같은 외관 요소들의 특징점이나 타인의 얼굴과의 차이점을 찾아내기 위해서 사용된다.Constrained Local Models (CLMs) are used to explore facial regions and to find differences in facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth, or from others.
CLM 모델 구축 및 탐색 과정의 개념을 간단하게 설명하면, 우선, 주어진 입력 영상에서 얼굴 영역을 탐색할 필요가 있는데, 이를 위해 Viola-Jones 알고리즘이 이용한다. Briefly explaining the concept of the CLM model building and searching process, first, it is necessary to search the face region in a given input image, which is used by the Viola-Jones algorithm.
이후 탐색된 얼굴 영역에서 얼굴의 외관 요소를 찾는 과정이 진행된다. 이때 외관 요소의 상대적인 배치 관계인 형상 제약(shape constraint) 개념이 적용된다. 형상 제약이란 눈이나 코, 입 등의 외관 요소들이 얼굴에서 특정한 부위에 존재하게 되고, 이 특정 부위를 얼마 이상 벗어날 수 없을 뿐만 아니라 다른 외관 요소들과 상대적인 배치 관계성을 준수해야 함을 의미한다. 예컨대, 눈은 얼굴의 특정 위치에서 어느 범위 이상 벗어날 수 없다거나, 코와 입은 눈 위에 위치할 수 없다거나 하는 등의 규약을 말한다. Subsequently, a process of searching for an appearance element of a face in the searched face area is performed. In this case, the concept of shape constraint, which is a relative arrangement of appearance elements, is applied. The shape constraints mean that the appearance elements such as eyes, nose, mouth, etc. are present in a certain part of the face, can not escape any more than this specific part, and must observe the relative placement relationship with other appearance elements. For example, the eye may refer to a protocol such that the eye cannot be moved beyond a certain range of the face, the nose and the mouth cannot be positioned above the eye, and the like.
눈, 코, 입, 눈썹 등의 독자적 얼굴 요소들 각각의 국부 패치(local patch)로 표현할 수 있는데, CLM 기반으로 주요 얼굴 특징점을 검출하기 위해선 이 패치와 관련된 2가지의 정보인 형상 모델(shape model)과 패치 모델(patch model)이 필요하다. 형상 모델은 각 패치의 위치(혹은 배치) 정보를 나타내고, 패치 모델은 각 패치의 외양(appearance, 무늬나 질감 등) 정보를 나타낸다.It can be expressed as a local patch of each of the unique facial elements such as eyes, nose, mouth, and eyebrows. In order to detect major facial features based on CLM, two types of information related to this patch are shape model. ) And a patch model. The shape model represents position (or placement) information of each patch, and the patch model represents appearance (appearance, pattern, texture, etc.) information of each patch.
당연한 것이지만 먼저, 훈련용 얼굴 데이터를 이용해 사전에 CLM 모델 구축(CLM Model-building)이 필요하다. CLM 모델 구축 과정을 통해 형상 모델과 패치 모델의 두 모델이 준비되면, 이후 새로운 입력 영상이 주어졌을 때, 기 구축된 CLM 모델을 이용해 각 주요 얼굴 특징점(landmark)의 위치를 탐색한다. 이때 찾고 싶은 각 주요 얼굴 특징점마다 확률적으로 가장 가능성이 높은 위치점 주변의 패치를 탐색함으로써 이 목적을 달성하는데, 이때 형상 제약(shape constraint)을 이용해 탐색 범위를 제한하고 또한 다른 특징점과의 상대적 배치 규약을 어기지 않도록 통제한다.Naturally, first, CLM Model-building needs to be done in advance using training face data. When two models of the shape model and the patch model are prepared through the CLM model construction process, when a new input image is given, the location of each major facial landmark is searched using the pre-built CLM model. This goal is achieved by searching for patches around the most probable location points for each major facial feature that you want to find, using shape constraints to limit the search range and also to place them relative to other feature points. Control not to break the protocol.
그것이 훈련 과정이든 실전 과정이든 CLM은 얼굴의 주요 얼굴 특징점을 찾기 전에 전처리로 얼굴의 회전, 크기, 평행 이동에 따른 변동 요인을 제거해야 한다. 이를 위해 프로크루스테스 분석(Procrustes Analysis)을 수행한다. 각 주요 얼굴 특징점의 패치가 어디에 있는지를 나타내는 형상 모델은 PCA(Principle Component Analysis)를 이용하여 구축한다. 이 과정에서 훈련용 얼굴 데이터로부터 주요 얼굴 특징점이 각각의 평균 형상 위치를 중심으로 어느 정도의 형상 편차(shape variation)를 갖는지를 PCA를 통해 학습한다. 이때 PCA는 편차의 유형(types of variations)은 고유벡터(eigen vectors)로 표현하고 대응하는 그들의 고유값(eigen value)은 그 편차의 정도를 값으로 나타낼 수 있음에 토대를 두고 있다.Whether it's a training course or a practice course, CLM needs to remove the variance factors of face rotation, size, and translation before preprocessing to find the main facial features of the face. Procrustes analysis is performed for this purpose. A shape model indicating where the patches of each major facial feature point are located is constructed using Principle Component Analysis (PCA). In this process, the PCA learns how much shape variation the main facial feature points have from each average shape position from the training face data. The PCA is based on the fact that the types of variations can be expressed as eigen vectors, and their corresponding eigen values can represent the degree of the deviation as a value.
한편, 패치 모델은 SVM(Support Vector Machine)을 이용해 구축한다. SVM은 초평면을 이용해 데이터들을 분류할 때 초평면과 각 데이터들 사이의 거리인 여백(margin)이 가장 큰 평면을 찾는 것이 핵심 발상이다. 예를 들어, 눈 패치와 코 패치가 있는 경우, 이 둘 사이를 나누는 여백이 가장 큰 초평면을 찾으면 된다. 즉, 각 패치가 올바른 패치인지 그렇지 않은 패치인지를 분류하기 위해 결정 경계가 필요한데, 이 결정 경계를 그리는 방법으로 SVM을 사용하는 것이다. 이것은 주어진 훈련 데이터 영상에서 각 SVM의 가중치를 찾는 과정이고 이러한 가중치를 이용해 패치들을 분류하다.The patch model, on the other hand, is built using SVM (Support Vector Machine). When SVM classifies data using hyperplanes, the key idea is to find the plane with the largest margin, the distance between each hyperplane and each data. For example, if you have an eye patch and a nose patch, you can find the hyperplane with the largest margin between the two. In other words, a decision boundary is needed to classify whether each patch is a valid patch or not, and using SVM as a way of drawing this decision boundary. This is the process of finding the weight of each SVM in a given training data image and using these weights to classify the patches.
일 예로, 임의의 패치에 코가 있는지 여부는 그 패치를 구성하는 각 화소 밝기값(혹은 컬러값)의 패턴으로 표현할 수 있는 바, SVM의 출력을 각 화소 밝기값의 선형 함수로 공식화하고 각 화소 밝기값의 적절한 가중치를 찾는 SVM 학습을 수행한다. 선형 SVM으로 패치 모델을 구축하는 과정은 주어진 훈련 영상들을 이용해 각 SVM의 가중치를 찾는 과정이다. 이러한 가중치를 찾은 후, 이 가중치를 이용해 입력 영상 내 제한된 국부 영역에서 소정 크기의 각 패치를 검사해 코가 담겨있는 최적의 패치를 탐색한다.For example, whether a patch has a nose can be expressed as a pattern of each pixel brightness value (or color value) constituting the patch. The output of the SVM is formulated as a linear function of each pixel brightness value and each pixel SVM training is performed to find the appropriate weights of brightness values. The process of building a patch model with linear SVM is to find the weight of each SVM using the given training images. After finding the weights, the weights are used to search for patches of a predetermined size in a limited local area of the input image to search for an optimal patch containing the nose.
앞선 일 예와 같이 CLM 모델을 구축한 후에 탐색이 가능한데, 탐색을 위해 초기 위치를 각 주요 특징점의 평균 형상 위치로 초기화하고 각 특징점에서 주위의 국부 영역을 탐색하는 템플릿 매칭을 수행한다. 탐색한 국부 영역에서 응답 특성을 조사하고 이 응답 특성이 가장 높은 값을 갖는 위치를 주요 얼굴 특징점으로 지정한다. 단, 이때 형상 제약(shape constraint)을 어기는 특징점을 제외하고 판단한다. 따라서 가장 높은 응답 특성을 갖는 특징점이 제약을 어긴다면 재탐색 과정이 필요한데, 이러한 재탐색 과정을 반복하다 보면 연산량이 폭증할 수 있다. 연산량의 경감을 위해 응답 특성을 2차 함수나 2차 가우스 함수로 모델링하고 이 함수를 최적화하여 각 특징점의 최적 위치를 고속으로 탐색할 수 있다. 이와 같은 방법으로 모든 주요 얼굴 특징점들의 위치를 탐색한다. As shown in the previous example, after the CLM model is constructed, the search is possible. For the search, the initial position is initialized to the average shape position of each major feature point, and template matching is performed to search the local area around each feature point. The response characteristics are examined in the searched local area and the position having the highest value is designated as the main facial feature point. At this time, it is determined by excluding the feature point that violates the shape constraint. Therefore, if a feature point with the highest response characteristic violates the constraint, a rescan process is required. If the rescan process is repeated, the amount of calculation may increase. In order to reduce the amount of computation, the response characteristics can be modeled as quadratic or quadratic Gaussian functions, and the function can be optimized to quickly find the optimal location of each feature point. In this way, the location of all major facial features is searched.
도 12는 CLM을 이용한 주요 얼굴 특징점의 추출 결과를 나타낸 것이다.12 shows extraction results of major facial feature points using CLM.
<가버 웨이블렛(Gabor Wavelets)>Gabor Wavelets
가버 함수는 하나의 신호를 가우시안 포락선(Gaussian envelope)을 가지는 삼각함수 파형을 취한다. 공간 영역과 공간 주파수 영역 양쪽에서 최적으로 국부화(localization)되는 필터이기 때문에 잡음이나 조명 변화에 강인한 특성을 갖는 것으로 알려져 있다. 선택된 simple cell의 방향성을 적용한 모델 수립을 위해 식(8)과 같이 2차원 Gabor 함수를 일반화하였다.The Gabor function takes a triangular waveform with a Gaussian envelope of one signal. Since it is a filter that is optimally localized in both the spatial domain and the spatial frequency domain, it is known to have characteristics that are robust against noise and light changes. To establish a model applying the orientation of the selected simple cell, the 2D Gabor function is generalized as shown in Equation (8).
각 는 가우시안 함수에 의해 포락된 벡터 에 의해 특성을 갖는 평면파이고, 는 가우시안 포락선의 표준편차이다. 이때 은 서로 다른 공간 주파수 대역이 대략적으로 동일한 에너지를 갖도록 조정한다. 번째 Gabor 커널은 로 주어지는 주파수와 방향을 갖는 특성파 벡터로 표현된다.bracket Is a vector enveloped by a Gaussian function Plane pie having characteristics by Is the standard deviation of the Gaussian envelope. At this time Is adjusted so that different spatial frequency bands have approximately the same energy. The first Gabor kernel It is expressed as a characteristic wave vector with frequency and direction given by.
여기서 와 는 Gabor 커널의 방향과 주파수의 인덱스이고 이고 이다. 그리고 는 주파수 영역에서 커널 사이의 공간 팩터(spacing factor)이다. 가우시안의 폭은 인데, 비례 계수 를 적절히 정하는 것이 매우 중요하다. here Wow Is the index of the direction and frequency of the Gabor kernel ego to be. And Is the spacing factor between kernels in the frequency domain. Gaussian width Is a proportional factor It is very important to set the appropriately.
식(8)에서 괄호 내 첫 번째 수식은 커널의 진동 부분을 결정하고 두 번째 수식은 커널의 DC(Direct Current)값을 보정한다. DC 응답(DC response)을 배제함으로써 Gabor Wavelets은 조명 변화에 둔감하게 된다. In Equation (8), the first equation in parentheses determines the oscillation part of the kernel, and the second equation corrects the kernel's DC (Direct Current) value. By excluding the DC response, Gabor Wavelets become insensitive to light changes.
식(10)과 같이 영상 에서 주어진 특징점 의 위치에 다중 방향 및 주파수의 Gabor 커널로 컨벌루션(convolution)을 수행하는데, 통상 를 가버 제트(Gabor jet)라고 한다. 여기서 는 위치에서의 영상 밝기값이다.Image as shown in equation (10) Feature points given by Convolution is performed with a Gabor kernel of multiple directions and frequencies at the position of Is called a Gabor jet. here Is Image brightness at the location.
본 발명에서는 , , 이고 5개의 다른 주파수 와 8개의 다른 방향 을 갖는 Gabor 커널을 사용한다. 5개의 주파수 성분 과 8개의 방향 성분 의 조합에 의해 로 인덱스되는 40개의 파형 벡터를 구한다.In the present invention , , And 5 different frequencies And 8 different directions Use a Gabor kernel with 5 frequency components And eight direction components By a combination of Obtain 40 waveform vectors indexed by.
가버 웨이블렛은 몇 개의 필터를 몇 개의 기준점에 적용할 것인지를 정해야 하는데, 영상의 모든 화소에 적용하면 완벽한 정보를 얻겠지만 부담스런 수준의 연산 부하와 정보 중복이 발생한다. 통상적으로 적정 간격의 사각형 격자나 얼굴의 주요 특징점에 대해서만 다중 방향 및 주파수의 가버 커널을 적용하는데, 본 발명에서는 잘 알려진 CLM(Constrained Local Models) 기반의 얼굴 특징점 추출을 통해 확보한 눈, 코, 입, 눈썹, 얼굴 윤곽 등을 대변하는 68개의 주요 얼굴 특징점마다 40차원의 가버 특징 벡터를 구한다. Gabor wavelets need to determine how many filters to apply to which reference points. Applying them to all the pixels in an image will give you complete information, but it will result in a heavy computational load and information duplication. In general, Gabor kernels of multiple directions and frequencies are applied only to the main features of rectangular grids or faces at appropriate intervals. In the present invention, eye, nose, and mouth obtained through the extraction of facial features based on well-known Constrained Local Models (CLM) 40-dimensional Gabor feature vectors are obtained for each of the 68 major facial feature points representing eyebrows, facial contours, and the like.
이러한 40차원의 가버 특징 벡터 각각을 가버 제트(Gabor jet)라고 부르는데, 번째 특징점의 Gabor 제트 을 40개의 복소 계수(complex coefficients)의 집합 를 이용하여 표현하면, 가 된다. Each of these 40-dimensional Gabor feature vectors is called a Gabor jet. Gabor jet at the first feature point Is a set of 40 complex coefficients If you express using Becomes
이때, 는 가버 커널의 인덱스()이고 은 각 특징점()의 인덱스를 의미한다. 가버 제트의 각 요소는 로 표현된다. 이때 는 허수(imaginary number)를 의미하는 기호이다.At this time, Is the index of the Gabor kernel. )ego Each feature point ( ) Index. Each element of the Gabor Jet It is expressed as At this time Is a symbol for imaginary number.
하나의 얼굴 영상에 대한 모든 주요 얼굴 특징점들의 집합으로 얼굴 특징 그래프를 구성한다. 프로브 얼굴 영상 및 번째 갤러리 얼굴 영상의 얼굴 특징 그래프에 대한 전체 가버 제트는 식(11)과 같이 각각 및 로 표현할 수 있다. A facial feature graph is composed of a set of all major facial feature points of one face image. Probe face imaging and The total Gabor jets for the facial feature graph of the first gallery face image are shown in Eq. (11), respectively. And Can be expressed as
<얼굴 인증><Face Recognition>
얼굴 인증을 위해선 대응되는 각 특정점들 간의 상호 상관도(cross correlation)를 이용해 개별 유사도를 구하고 모든 개별 유사도들을 가중 결합한 전체 유사도가 필요하다. For face authentication, it is necessary to obtain individual similarity by using cross correlation between corresponding specific points, and total similarity which is weighted combination of all individual similarities.
우선, 번째 Probe 얼굴 특징점과 갤러리 얼굴 특징점 간의 가버 제트 유사도 을 다음과 같이 정의한다.priority, Gabor Jet Similarity Between the First Probe Face Feature and the Gallery Face Feature Define as
다음으로 Probe 얼굴 특징 그래프와 번째 갤러리 얼굴 특징 그래프 간의 전체 가버 제트 유사도 를 식(13)과 같이 정의한다. 여기서 은 68개이고, 은 번째 특징점의 가중치로서 실험적으로 결정하였다.Next we have a Probe facial feature graph Total Gabor Jet Similarity Between Second Gallery Facial Feature Graphs Is defined as in Equation (13). here Is 68, silver It was determined experimentally as the weight of the first feature point.
얼굴 인증을 원하는 프로브 얼굴 영상과 모든 갤러리 얼굴 영상들 간의 전체 유사도들을 식(13)으로 구하고 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴이면 정분류로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정한다. The total similarity between the probe face image and all gallery face images for face authentication is determined by Equation (13), and if the gallery face with the highest similarity to the probe face is the same face as the probe face, it is classified as a correct classification. Determine.
더불어 본 발명의 방법은 얼굴 인증의 정확도를 높이기 위해 정분류된 경우에 한해 최근접 거리비(NNDR : Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 얼굴 인증 척도로 삼아 최종적인 얼굴 인증을 수행한다. 프로브 얼굴 영상의 얼굴 특징 그래프 와 가장 잘 정합된 갤러리 얼굴 영상의 얼굴 특징 그래프 간의 전체 가버 제트 유사도가 이고, 프로브 얼굴 특징 그래프 와 두 번째로 잘 정합된 갤러리 얼굴 특징 그래프 간의 전체 가버 제트 유사도가 이라고 가정할 때, 최근접 거리비(NNDR)는 다음과 같이 정의할 수 있다.In addition, the method of the present invention performs final face authentication by using the nearest nearest distance ratio (NNDR) as a face authentication measure only when it is classified in order to increase the accuracy of face authentication. Facial feature graph of probe face image Feature graph of gallery face images best matched with Overall Gabor Jet Similarity Between Probe face feature graph Second best matched gallery facial features graph with Overall Gabor Jet Similarity Between In this case, the nearest distance ratio NNDR can be defined as follows.
식(14)의 이 두 얼굴의 최근접 거리비가 인증 임계치()보다 작으면(), 프로브 얼굴의 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정한다. 본 발명에서는 인증 임계값()으로 0.95를 사용한다. The closest distance ratio of these two faces in equation (14) is Less than) ), It is determined that authentication of the probe face is successful, otherwise, it is determined as unauthorized. In the present invention, the authentication threshold ( 0.95 is used.
다양한 연구진의 실험 결과에 따르면 최근접 거리비(NNDR) 척도가 임계치 이하의 최근접 이웃(nearest neighbor)을 찾거나 고정된 임계값을 이용하는 척도보다 상대적으로 양호한 성능을 제공하는 것으로 발표되고 있다.Experiments with various researchers have shown that the NNDR scale provides relatively better performance than finding a nearest neighbor below the threshold or using a fixed threshold.
이상의 얼굴 인증 과정을 재차 간략히 설명하면, 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴인 정분류된 경우에 한해 최근접 거리비(NNDR)가 인증 임계값(0.95)보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정한다. The above face authentication process is briefly described again, when the closest distance ratio NNDR is smaller than the authentication threshold value (0.95) only when the gallery face having the most similarity to the probe face is classified as the same face as the probe face. It is determined that face authentication succeeds, otherwise it is determined not to be authenticated.
<시뮬레이션 결과 및 고찰>Simulation Results and Discussion
시스템의 성능 평가를 위해 Intel Core i7-7500U CPU, 8GB DDR4 RAM, Geforce 940MX(2GB) 환경에서 Microsoft Visual C++ 2015, OpenCV 3.0.0을 이용해 시뮬레이션을 수행하였다. To evaluate the performance of the system, simulations were performed using Microsoft Visual C ++ 2015 and OpenCV 3.0.0 in an Intel Core i7-7500U CPU, 8GB DDR4 RAM, and Geforce 940MX (2GB).
얼굴 인증 단계에서는 브라질 FEI 대학교에서 제작·공개한 FEI 데이터베이스를 토대로 얼굴 인증률을 평가하였다. In the face recognition stage, the face recognition rate was evaluated based on the FEI database produced and published by FEI University in Brazil.
도 13은 FEI Face Database의 1인당 14장씩 촬영한 얼굴 영상 세트를 예시한 것이다. FIG. 13 exemplifies a set of face images captured by 14 people in the FEI Face Database.
FEI Face 데이터베이스는 브라질 상파울로(So Paulo, Brazil)에 소재한 FEI 대학교(University Center of FEI(Faculty of Industrial Engineering))의 인공지능연구실(Artificial Intelligence Laboratory에서 2005년 6월~2006년 3월 사이에 200명(19세~40세의 남자 100명 및 여자 100명)의 브라질인을 대상으로 각 사람당 14장씩 촬영한 얼굴 데이터베이스로, 얼굴 인식 및 인증 관련 연구자들에게 널려 알려진 공개된 벤치마킹 데이터베이스이다. 남녀 혼합, 다양한 인종(백인, 흑인, 황인), 안경 착용 및 미착용, 정상 조도 및 저 조도 환경의 흰색 배경상에서 180도 회전하면서 왼쪽 및 오른쪽의 단계적 측면 얼굴과 정면 얼굴을 촬영한 640×480 크기의 상반신 컬러 얼굴로 구성되어 있다. 특히 각 사람당 4장의 정면 얼굴 영상은 정상 조도의 무표정 정면 얼굴(11번 영상) 및 미소진 정면 얼굴(12번 영상), 중간 조도의 정면 얼굴(13번 영상), 저 조도의 정면 얼굴(14번 영상)로 구성된다. 도 13은 FEI Face 데이터베이스의 2번 남자의 좌상부터 우하단 순으로 1번 영상~14번 얼굴 영상을 예시한 것이다.The FEI Face database is located in São Paulo, Brazil. o 200 people (19-40 years old) between June 2005 and March 2006 at the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at the University Center of Faculty of Industrial Engineering (FEI) in Paulo, Brazil. This is a database of 14 images taken for each person from 100 Brazilians and 100 females, and is an open benchmark database known to researchers involved in facial recognition and authentication. Yellow face), 640 × 480 upper torso color face with 180 degrees rotated to the left and right side face and front face on white background in normal and low light conditions. Four frontal face images per person include the normal faceless front face (image 11) and the unsharp front face (image 12), the front face with medium illumination (image 13), and the low It consists of a front face (image 14) Figure 13 illustrates
프로브 얼굴 영상(11번 영상 혹은 13번 영상)이 정상 조도 혹은 중간 조도일 때, 갤러리 얼굴 영상은 FEI Face Database 200명과 자체 촬영한 5명에 대해 1인당 6장씩 각각 총 1,230장을 사용하고, 프로브 얼굴 영상(14번 영상)이 저 조도일 때, FEI Face Database 137명과 자체 촬영한 5명에 대해 1인당 7장씩 총 994장을 사용하였다. 프로브 얼굴 영상의 조명 상태가 정상 조도에서 저조도로 가변되는 상황에서도 평균 98.72%의 양호한 얼굴 인증률을 제공함을 확인할 수 있었다. When the probe face image (image 11 or 13) is normal or medium illuminance, the gallery face image uses a total of 1,230 shots for each of 200 FEI Face Databases and 5 self shots. When the face image (image 14) was low, a total of 994 images were used, with 7 images per person for 137 FEI Face Databases and 5 self-images. In the situation where the illumination state of the probe face image varies from normal illumination to low illumination, it can be confirmed that the average face recognition rate is 98.72%.
영상수Face per person
Number of images
영상수Face per person
Number of images
영상수Face per person
Number of images
표 4는 본 발명에 적용되는 시스템의 평균 얼굴 인증률을 나타낸 것이고, 표 5~7은 프로브 얼굴 영상이 각각 정상 조도, 중간 조도 및 저 조도일 경우에 대한 얼굴 인증률을 제시한 것이다.Table 4 shows the average face authentication rate of the system applied to the present invention, Tables 5 to 7 shows the face authentication rate for the case where the probe face image is normal illumination, medium illumination and low illumination, respectively.
본 발명에서는 CLM(Constrained Local Models) 기반의 얼굴 특징점 추출을 통해 얼굴의 주요 성분을 추출하는 과정과 이렇게 추출된 특징점을 대상으로 가버 웨이블렛 변환을 통해 가버 특징 벡터를 생성한 후, 가버 특징 벡터 간의 상호 상관도와 최근접 거리비를 이용해 개인을 인증하는 방법을 제안하였다.In the present invention, after extracting the main components of the face through the extraction of facial feature points based on Constrained Local Models (CLM) and generating the Gabor feature vector through Gabor wavelet transformation on the extracted feature points, We proposed a method of authenticating individuals using the correlation and the nearest distance ratio.
시뮬레이션 결과에 따르면, 본 발명의 방법은 프로브 얼굴 영상의 조명 상태가 정상 조도에서 저조도로 가변되는 상황에서도 평균 98.72%의 양호한 얼굴 인증률을 제공함을 확인할 수 있었다. 특히 저조도의 프로브프로브 영상이 입력되는 상황에서 99.26%의 우수한 얼굴 인증률을 제공하는 장점이 있었다. 평균적으로, 98.72%의 얼굴 인증률은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템은 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템에 적용할 경우, 실용적인 수준에서 유용함을 확인할 수 있었다. According to the simulation results, it was confirmed that the method of the present invention provides a good face authentication rate of 98.72% on average even when the illumination state of the probe face image varies from normal illumination to low illumination. In particular, it has an advantage of providing excellent face recognition rate of 99.26% when a low light probe probe image is input. On average, 98.72% of the face recognition rates proved that the online lecture monitoring system is useful at the practical level when applied to the online lecture monitoring system.
본 발명의 얼굴 인증 방법은 온라인 강의 모니터링 분야 외에도 원격 심사나 검사, 의무 보수 교육, 출입 관리, 병상 환자 관리 등과 같이 원격지에서 수강자 혹은 심사위원이 온라인 콘텐츠를 취지에 맞게 정상적으로 시청 혹은 학습했는지 여부를 확인하거나 피감자가 원래 취지에 맞게 행동하는지를 모니터링하는 응용 분야에서 널리 용용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다. 물론, 전통적인 얼굴 인식이나 얼굴 인증 분야에 적용되더라도 양호한 결과를 제공할 것으로 예측된다.The face authentication method of the present invention checks whether a student or a reviewer has normally watched or learned online contents in a remote place such as remote screening or inspection, compulsory pay training, access management, and patient care in addition to online lecture monitoring. It is expected to be widely used in applications that monitor whether or not the subject behaves according to its original purpose. Of course, even if applied to the field of traditional face recognition or face authentication is expected to provide good results.
본 발명의 방법을 졸음 방지, 시선 제어, 온라인 강의 모니터링 등과 같은 시선 추적 응용 시스템에 접목할 경우, 안정된 시선 추적 기능을 제공할 수 있고, 또한 눈 개폐 판단을 활용하는 응용 분야에서도 유용하게 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.When the method of the present invention is applied to a gaze tracking application system such as drowsiness prevention, gaze control, online lecture monitoring, etc., it can provide a stable gaze tracking function and can also be usefully applied to an application that utilizes eye open / close judgment. It is expected to be.
이상에서 살펴본 바와 같이, 본 발명의 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법은 온라인 강의의 성실 시청 여부를 감시하고 시청 현혹자의 허위 출석을 방지하며 시청 현혹 상황이나 시선 이탈 혹은 복귀 여부에 따라 강의를 자동으로 재생하거나 정지함으로써 온라인 강의 시스템의 신뢰성과 학습효율성 및 사용자 편의성을 제고할 수 있다. As described above, the online lecture monitoring method of the present invention monitors whether the online lectures are faithfully watched, prevents the false attendance of the viewers, and automatically replays or stops the lectures according to the situation of viewing deception or gaze or return. It can improve the reliability, learning efficiency and user convenience of online lecture system.
특히, 수강자로 하여금 온라인 강의에 성실히 참여하도록 은연중에 유도하면서도 전체적인 학습 흐름을 방해하지 않는 것이 유용하다. In particular, it is useful to induce participants to participate faithfully in online lectures while not disturbing the overall learning flow.
또한, 온라인 강의 콘텐츠의 제작 측면에서는 모니터링으로 인한 추가적인 저작 시간과 비용이 발생하지 않는 것이 장점이다. In addition, in terms of producing online lecture contents, it is advantageous that no additional authoring time and cost are incurred due to monitoring.
본 발명의 방법이 적용되는 온라인 강의 모니터링 시스템은 온라인 강의 시스템 외에도 조달청 온라인 심사, 의무 보수 교육 등과 같이 원격지에서 수강자 혹은 심사위원이 온라인 콘텐츠를 취지에 맞게 정상적으로 시청 혹은 학습했는지 여부를 확인하기 위한 응용 분야에서 널리 사용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.The online lecture monitoring system to which the method of the present invention is applied is not only an online lecture system but also an application field for confirming whether a student or a reviewer has normally watched or learned online contents at a remote location such as a public procurement agency online examination and compulsory remuneration training. It is expected to be widely used in.
이상에서는 본 발명의 실시 예를 중심으로 설명하였지만, 당업자의 수준에서 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있음은 물론이다. 따라서, 본 발명의 권리범위는 상기한 실시 예에 한정되어 해석될 수 없으며, 이하에 기재되는 청구범위에 의해 해석되어야 한다.In the above description, the embodiment of the present invention has been described, but various changes can be made at the level of those skilled in the art. Therefore, the scope of the present invention should not be construed as being limited to the above embodiments, but should be construed by the claims described below.
Claims (17)
카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계;
강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠 화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계;
내적 누적 평균을 그레이디언트 벡터의 개수로 나눠 보정된 내적 누적 평균값을 구하고, 직전 프레임과 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값들을 입력받아 칼만 필터링(Kalman filtering)을 수행해 현 프레임의 보정된 내적 누적 평균값을 갱신하고 이렇게 갱신된 내적 누적 평균과 눈 개폐 임계값을 비교해 눈의 개폐 여부를 판단하는 단계; 및
실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.Operating the software on a computer and selecting and playing the lecture content by opening the file;
Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames;
Determining whether the learner stares at the screen;
If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner;
When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture content screen;
The inner cumulative mean is calculated by dividing the inner cumulative mean by the number of gradient vectors, and the Kalman filtering is performed by inputting the corrected inner cumulative mean values of the previous frame and the current frame and performing the Kalman filtering. Determining whether to open or close the eyes by comparing the updated internal cumulative average and the eye opening and closing threshold value; And
In real time, from the number of full screens played so far, the number of screens checked by eye tracking, the screen staring rate which is the ratio of the number of screens to the total number of screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens which are the ratio of the number of screens and the number of full screens On-line lecture monitoring method comprising the step of displaying the final learning rate that is the ratio of the subtracted number of screens and the total number of screens.
상기 얼굴 인증 단계는,
다수의 방향과 주파수 성분을 갖는 가버 커널을 생성하는 서브단계;
갤러리 얼굴 영상을 대상으로 사전에 주요 얼굴 특징점들을 추출하는 서브단계;
사전에 오프라인으로 각 얼굴 특징점에서 가버 커널을 이용한 갤러리 특징 벡터를 추출 및 저장하는 서브단계;
온라인으로 추출한 프로브 얼굴 영상의 가버 특징 벡터와 사전에 기 저장된 갤러리 특징 벡터 간의 유사도를 측정하는 서브단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴 영상과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물의 얼굴이 포함되어 있으면 정분류로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정하는 단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴인 정분류된 경우에 한해 정분류 얼굴의 최근접 거리비(Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 구하는 서브단계; 및
상기 최근접 거리비가 인증 임계값보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정하는 서브단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 1
The face authentication step,
Generating a Gabor kernel having a plurality of directions and frequency components;
A sub-step of extracting major facial feature points from a gallery face image in advance;
Extracting and storing a gallery feature vector using a Gabor kernel at each facial feature point in advance offline;
Measuring a similarity between the Gabor feature vector of the online extracted probe face image and a previously stored gallery feature vector;
Determining that the gallery face image having the highest similarity with the probe face image includes a face of the same person as the probe face, and determines a misclassification otherwise;
A substep of obtaining a nearest neighbor distance ratio only when the gallery face having the highest similarity to the probe face is classified as the same face as the probe face; And
And determining that the face authentication succeeds when the nearest distance ratio is smaller than the authentication threshold value, and otherwise, determines that the face authentication is successful.
상기 주요 얼굴 특징점은 CLM(Constrained Local Models)을 이용해 68개를 추출하고,
상기 가버 커널은 8개의 방향 성분과 4개의 주파수 성분을 이용해 40개가 생성되며,
상기 인증 임계값은 0.95인 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 1
The main facial features are extracted 68 using CLM (Constrained Local Models),
40 Gabor kernels are generated using eight direction components and four frequency components,
The authentication threshold is 0.95 online lecture monitoring method characterized in that.
상기 눈 개폐 임계값은, 직전 프레임들과 현 프레임의 갱신된 내적 누적 평균값을 소정 프레임 수만큼 누적한 후, 프레임 수로 나눈 구간 평균값을 이용해 구하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 1,
The eye opening / closing threshold value is obtained by accumulating the updated internal cumulative average value of the previous frames and the current frame by a predetermined number of frames, and then using the section average value divided by the number of frames.
상기 소정 프레임 수는 눈을 감은 프레임을 제외해 뜬 눈 상태로 판단된 70 프레임만으로 계수하고,
상기 눈 개폐 임계값은 상기 구간 평균값에 비례계수 0.8을 곱한 값을 이용하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 4,
The predetermined number of frames is counted as only 70 frames determined as the opened eye state except for the closed frames,
The eye opening and closing threshold value of the online lecture monitoring method, characterized in that for using the average value of the interval multiplied by a proportional coefficient 0.8.
카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계;
강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계; 및
실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하며,
상기 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계는,
이전 프레임과 현재 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 일정 기준치 이하이면 현재 프레임의 눈 중심점을 거짓 떨림으로 간주해 이전 프레임의 값으로 대체하는 서브단계;
연속된 프레임 간에서 상기 거짓 떨림 현상이 제거된 눈 중심점의 수평 및 수직 좌표를 대상으로 칼만 필터링을 수행한 후, 현재 프레임과 이전 프레임 간의 좌우 눈 중심점의 수직 및 수평 좌표의 차분합이 상기 일정 기준치 이하이면 눈의 중심점이 변동되지 않은 것으로 판단해 안구 정지 횟수를 증가하는 서브단계; 및
소정 프레임 구간 동안에 상기 안구 정지 횟수가 일정 정지 횟수 이상이면 시청 현혹 상태로 판별하고 그렇지 않으면 정상 시청으로 판별하고, 상기 소정 프레임 구간마다 상기 안구 정지 횟수를 초기화시키면서 시청 현혹 여부를 지속적으로 감시하는 서브단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.Operating the software on a computer and selecting and playing the lecture content by opening the file;
Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames;
Determining whether the learner stares at the screen;
If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner;
When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture contents screen; And
In real time, from the number of full screens played so far, the number of screens checked by eye tracking, the screen staring rate which is the ratio of the number of screens to the total number of screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens which are the ratio of the number of screens and the number of full screens And displaying the final learning rate, which is the ratio of the subtracted screen count to the total screen count.
Detecting the viewing deception,
A sub-step of substituting the eye center point of the current frame as the value of the previous frame if the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the previous frame and the current frame is equal to or less than a predetermined reference value;
After performing Kalman filtering on the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the eye center point from which the false tremor is removed between successive frames, the difference between the vertical and horizontal coordinates of the left and right eye center points between the current frame and the previous frame is the predetermined reference value. A sub-step of determining that the eye's center point is not changed to increase the number of eye stops; And
A sub-step of determining whether the eye stop is deceptive if the number of eye stops is equal to or greater than a predetermined stop number during a predetermined frame period; otherwise, judging from normal viewing; Online lecture monitoring method comprising a.
상기 얼굴 인증 단계는,
다수의 방향과 주파수 성분을 갖는 가버 커널을 생성하는 서브단계;
갤러리 얼굴 영상을 대상으로 사전에 주요 얼굴 특징점들을 추출하는 서브단계;
사전에 오프라인으로 각 얼굴 특징점에서 가버 커널을 이용한 갤러리 특징 벡터를 추출 및 저장하는 서브단계;
온라인으로 추출한 프로브 얼굴 영상의 가버 특징 벡터와 사전에 기 저장된 갤러리 특징 벡터 간의 유사도를 측정하는 서브단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴 영상과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물의 얼굴이 포함되어 있으면 정분류로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정하는 단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴인 정분류된 경우에 한해 정분류 얼굴의 최근접 거리비(Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 구하는 서브단계; 및
상기 최근접 거리비가 인증 임계값보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정하는 서브단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 6
The face authentication step,
Generating a Gabor kernel having a plurality of directions and frequency components;
A sub-step of extracting major facial feature points from a gallery face image in advance;
Extracting and storing a gallery feature vector using a Gabor kernel at each facial feature point in advance offline;
Measuring a similarity between the Gabor feature vector of the online extracted probe face image and a previously stored gallery feature vector;
Determining that the gallery face image having the highest similarity with the probe face image includes a face of the same person as the probe face, and determines a misclassification otherwise;
A substep of obtaining a nearest neighbor distance ratio only when the gallery face having the most similarity to the probe face is classified as the same face as the probe face; And
And determining that the face authentication succeeds when the nearest distance ratio is smaller than the authentication threshold value, and otherwise, determines that the face authentication is successful.
상기 주요 얼굴 특징점은 CLM(Constrained Local Models)을 이용해 68개를 추출하고,
상기 가버 커널은 8개의 방향 성분과 4개의 주파수 성분을 이용해 40개가 생성되며,
상기 인증 임계값은 0.95인 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 6
The main facial features are extracted 68 using CLM (Constrained Local Models),
40 Gabor kernels are generated using eight direction components and four frequency components,
The authentication threshold is 0.95 online lecture monitoring method characterized in that.
상기 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계는,
수강자가 정상적으로 영상을 시청하는 경우엔 적색 경고등이 들어오지 않지만, 시청 현혹 상태로 판별되면 적색 경고등을 표시함으로써 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되고 있음을 외부에 경고하는 서브단계;
전체 프레임 중 85% 이상의 구간에서 시청 현혹 상태로 판정되면 고의적 시청 현혹 의도로 최종 판단하고, 상기 최종학습률을 0%로 처리하는 서브단계를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 6,
Detecting the viewing deception,
A sub-step, in which the red warning light does not come in when the attendees normally watch the video, but the external warning that the red warning light is determined by displaying a red warning light when it is determined that the viewing state is deceptive;
If it is determined that the viewing dazzle state in more than 85% of the entire frame, the final judgment as the deliberate viewing deception intention, and further comprising a sub-step of processing the final learning rate to 0%.
상기 일정 기준치는 3 픽셀이고,
상기 소정 프레임 구간은 30 프레임이고,
상기 일정 정지 횟수는 29회인 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 6,
The predetermined reference value is 3 pixels,
The predetermined frame period is 30 frames,
The schedule number of stops online monitoring method characterized in that 29 times.
카메라를 통해 취득한 수강자의 입력 영상에서 얼굴을 검출하고 시선을 추적하여 프레임 간 안구 운동의 변화량을 조사해서 시청 현혹을 검출하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계;
상기 수강자가 화면을 응시하는 것으로 판단되면, 상기 수강자의 얼굴 인증을 통해 대리 수강이나 대리 출석을 방지하는 얼굴 인증 단계;
강의 콘텐츠가 재생되고 있는 상태에서, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되면 시청 현혹인지를 판단하여 응시화면수가 증가하고, 상기 수강자의 얼굴과 동공이 검출되지 않으면 화면을 응시하지 않는 것으로 판단해 비응시 화면수가 증가하고 강의 콘텐츠화면에 경고등을 표시하는 단계; 및
실시간으로, 지금까지 재생된 전체화면수, 시선 추적으로 확인한 응시화면수, 응시화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 화면응시율, 현혹화면수와 전체화면수의 비율인 시청현혹률 및 응시화면수에서 현혹화면수를 뺀 값과 전체화면수의 비율인 최종학습률을 표시하는 단계를 포함하며,
상기 화면을 응시하는지를 판단하는 단계는,
입력 영상에서 얼굴 영역을 검출하는 서브단계;
상기 검출된 얼굴 영역을 이용하여 좌측 및 우측 눈 탐색 영역을 지정하는 서브단계;
상기 지정된 각 눈 탐색 영역으로부터 동공 후보 영역을 검출하는 서브단계;
상기 검출된 동공 후보 영역 중에서 상기 각 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙과 외곽 각각 발원하는 두 개의 동심원 방향으로 수렴해가면서 양방향으로 제한된 화소수만큼만을 동공 영역으로 레이블링하는 서브단계;
수평 및 수직 미분 마스크를 이용해 에지 맵을 구하여 에지 여부를 판정하는 서브단계; 및
상기 레이블링된 동공 영역에서 내적 누적 연산을 수행하여 내적 누적값을 산출하여 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출하는 서브단계를 포함하며,
상기 동공 영역으로 레이블링하는 단계에서, 상기 눈 탐색 영역의 중앙에서부터 동심원 확산 방향으로 진행해 가면서 소정의 화소 면적 한도 내에서 동공 영역을 레이블링한 이후, 이렇게 레이블링된 동공 영역이 상기 눈 탐색 영역의 외곽에 접할 경우엔 상기 외곽으로부터 동심원 수축 방향으로 진행해 가면서 상기 레이블링된 동공 면적의 일정 비율 한도 내에서 외곽 인접 영역을 상기 레이블링된 동공 영역에서 제거해 최종 레이블링된 동공 영역으로 지정하고,
상기 내적 누적 연산을 수행하는 단계에서, 상기 최종 레이블링된 동공 영역에서만 정규 변위 벡터를 취해 상기 각 눈 탐색 영역 내 모든 그레이디언트 벡터와의 내적을 구한 후, 누적 연산을 수행하여 내적 누적값을 구하고, 각각의 상기 내적 누적값에 대응되는 역 밝기 가중치를 곱해 내적 누적값을 갱신한 후, 최대 내적 누적값의 위치를 좌우 눈의 중심으로 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.Operating the software on a computer and selecting and playing the lecture content by opening the file;
Detecting a face-to-face detection by detecting a face from an input image of a participant acquired through a camera, tracking eyeballs, and examining changes in eye movement between frames;
Determining whether the learner stares at the screen;
If it is determined that the learner gazes at the screen, a face authentication step of preventing the attendance or the attendance of the surrogate through the face authentication of the learner;
When the lecture content is being reproduced, if the face and pupil of the student are detected, it is determined whether or not the audience is deceived, and the number of screens is increased. If the face and pupil of the learner are not detected, the screen is determined not to stare. Increasing the number of screens and displaying a warning light on the lecture contents screen; And
In real time, from the total number of screens played so far, the number of screens checked by eye tracking, the screen staring rate which is the ratio of the number of screens to the total screens, the viewing dazzle rate and the number of screens, which is the ratio of the number of screens to the deception And displaying the final learning rate, which is the ratio of the subtracted screen count to the total screen count.
Determining whether to stare at the screen,
Detecting a face region in the input image;
Specifying a left and right eye search region using the detected face region;
Detecting a pupil candidate region from each of the designated eye searching regions;
Labeling the pupil area of the detected pupil candidate area as only the limited number of pixels in both directions while converging in two concentric directions originating from each of the center and the outside of the eye searching area;
A substep of determining an edge by obtaining an edge map using horizontal and vertical differential masks; And
A sub-step of performing an inner cumulative operation in the labeled pupil area to calculate an inner cumulative value and detecting the inner cumulative value as the center of the left and right eyes;
In the step of labeling the pupil area, the pupil area is labeled within a predetermined pixel area limit while proceeding from the center of the eye search area to the concentric diffusion direction, and the thus labeled pupil area may be in contact with the outside of the eye search area. In this case, while advancing in the concentric contraction direction from the outer region, an outer adjacent region is removed from the labeled pupil region within a predetermined ratio of the labeled pupil area, and designated as the final labeled pupil region,
In the step of performing the dot product accumulation operation, the dot product is obtained by taking a normal displacement vector only in the final labeled pupil area to obtain a dot product with all the gradient vectors in each eye search area, and then performs a cumulative operation to obtain the dot product cumulative value. And updating the inner cumulative value by multiplying inverse brightness weights corresponding to each of the inner cumulative values, and then detecting the position of the maximum inner cumulative value as the center of the left and right eyes.
상기 얼굴 인증 단계는,
다수의 방향과 주파수 성분을 갖는 가버 커널을 생성하는 서브단계;
갤러리 얼굴 영상을 대상으로 사전에 주요 얼굴 특징점들을 추출하는 서브단계;
사전에 오프라인으로 각 얼굴 특징점에서 가버 커널을 이용한 갤러리 특징 벡터를 추출 및 저장하는 서브단계;
온라인으로 추출한 프로브 얼굴 영상의 가버 특징 벡터와 사전에 기 저장된 갤러리 특징 벡터 간의 유사도를 측정하는 서브단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴 영상과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴 영상에 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물의 얼굴이 포함되어 있으면 정분류로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 오분류로 판정하는 단계;
상기 프로브 얼굴과 가장 유사도가 높은 갤러리 얼굴이 프로브 얼굴과 동일 인물 얼굴인 정분류된 경우에 한해 정분류 얼굴의 최근접 거리비(Nearest Neighbor Distance Ratio)를 구하는 서브단계; 및
상기 최근접 거리비가 인증 임계값보다 작으면 얼굴 인증이 성공한 것으로 판정하고 그렇지 않으면 불인증으로 판정하는 서브단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 11
The face authentication step,
Generating a Gabor kernel having a plurality of directions and frequency components;
A sub-step of extracting major facial feature points from a gallery face image in advance;
Extracting and storing a gallery feature vector using a Gabor kernel at each facial feature point in advance offline;
Measuring a similarity between the Gabor feature vector of the online extracted probe face image and a previously stored gallery feature vector;
Determining that the gallery face image having the highest similarity with the probe face image includes a face of the same person as the probe face, and determines a misclassification otherwise;
A substep of obtaining a nearest neighbor distance ratio only when the gallery face having the most similarity to the probe face is classified as the same face as the probe face; And
And determining that the face authentication succeeds when the nearest distance ratio is smaller than the authentication threshold value, and otherwise, determines that the face authentication is successful.
상기 주요 얼굴 특징점은 CLM(Constrained Local Models)을 이용해 68개를 추출하고,
상기 가버 커널은 8개의 방향 성분과 4개의 주파수 성분을 이용해 40개가 생성되며,
상기 인증 임계값은 0.95인 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 11
The main facial features are extracted 68 using CLM (Constrained Local Models),
40 Gabor kernels are generated using eight direction components and four frequency components,
The authentication threshold is 0.95 online lecture monitoring method characterized in that.
상기 수강자의 동공이 검출되는 경우와 검출되지 않는 경우 각각 다른 색으로 상기 입력 영상의 눈의 영역에 표시하여 눈의 개폐 여부를 판단하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 11,
And if the pupil of the participant is detected or not, it is displayed on the eye region of the input image in a different color to determine whether the eye is opened or closed.
상기 입력 영상으로부터 얼굴이 검출되지 않을 시, 강의 동영상을 멈추고, 얼굴이 검출될 경우, 그 시점부터 다시 강의를 재생시키는 것을 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 11,
If a face is not detected from the input image, the lecture video is stopped, and if a face is detected, the lecture is restarted from that point in time.
상기 얼굴 영역을 검출하는 단계는,
초기 얼굴 템플릿을 입력 영상의 좌상단 시작점에 중첩해 놓고 겹쳐진 부분과의 상호 상관도(cross correlation)를 구하는 서브단계;
상기 시작점에서부터 한 화소씩 옮겨가면서 상호 상관도가 가장 높은 위치를 얼굴 영역으로 검출하는 서브단계; 및
상호 상관도가 일정 값 이상이면 계속하여 템플릿 정합을 진행하고, 그렇지 않으면 얼굴 영역을 재검출하고 새로운 얼굴 템플릿으로 갱신해 템플릿 정합을 수행하는 서브단계로 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 11,
Detecting the face area,
A sub-step of superimposing an initial face template on an upper left start point of an input image and obtaining cross correlation with the overlapped portion;
A sub-step of detecting a position having the highest cross-correlation as a face region while moving by one pixel from the starting point; And
And if the cross-correlation is above a predetermined value, continue template matching, otherwise, the online lecture monitoring method comprises a sub-step of re-detecting a face region and updating the new face template to perform template matching.
상기 얼굴 영역이 검출되지 않으면 상호 상관도를 낮춰서 템플릿 정합을 진행하고, 상기 낮춘 상호 상관도에서도 얼굴 영역이 검출되지 않으면 영상에 얼굴 영역이 없다고 판별하는 것을 특징으로 하는 온라인 강의 모니터링 방법.In claim 16,
And if the face region is not detected, template matching is performed by lowering the cross correlation, and if the face region is not detected even in the lower cross correlation, it is determined that there is no face region in the image.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180087533A KR20200012355A (en) | 2018-07-27 | 2018-07-27 | Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180087533A KR20200012355A (en) | 2018-07-27 | 2018-07-27 | Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20200012355A true KR20200012355A (en) | 2020-02-05 |
Family
ID=69514583
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180087533A KR20200012355A (en) | 2018-07-27 | 2018-07-27 | Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20200012355A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111881830A (en) * | 2020-07-28 | 2020-11-03 | 安徽爱学堂教育科技有限公司 | Interactive prompting method based on attention concentration detection |
| CN112115847A (en) * | 2020-09-16 | 2020-12-22 | 深圳印像数据科技有限公司 | Method for judging face emotion joyfulness |
| KR102244630B1 (en) * | 2020-11-30 | 2021-04-27 | 라온화이트햇 주식회사 | Method, device and computer program for verifying of watching content |
| KR102335534B1 (en) * | 2021-02-15 | 2021-12-07 | 한국전자인증 주식회사 | Method and Appratus of Attendance Management and Concentration Analysis for Supporting Online Education Based on Artificial Intelligent |
| CN114386772A (en) * | 2021-12-17 | 2022-04-22 | 鸿富锦精密电子(郑州)有限公司 | Video learning evaluation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| KR20220051515A (en) | 2020-10-19 | 2022-04-26 | 주식회사 씨앤비랩 | An on-line sensing system for identifing examinees and students |
| KR20230043302A (en) * | 2021-09-23 | 2023-03-31 | 국민대학교산학협력단 | Non-face-to-face real-time learning management system using deep learning |
| CN118351479A (en) * | 2024-03-13 | 2024-07-16 | 上饶市云上中文信息技术有限公司 | Online reading state detection method and system for students |
-
2018
- 2018-07-27 KR KR1020180087533A patent/KR20200012355A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111881830A (en) * | 2020-07-28 | 2020-11-03 | 安徽爱学堂教育科技有限公司 | Interactive prompting method based on attention concentration detection |
| CN112115847A (en) * | 2020-09-16 | 2020-12-22 | 深圳印像数据科技有限公司 | Method for judging face emotion joyfulness |
| CN112115847B (en) * | 2020-09-16 | 2024-05-17 | 深圳印像数据科技有限公司 | Face emotion pleasure degree judging method |
| KR20220051515A (en) | 2020-10-19 | 2022-04-26 | 주식회사 씨앤비랩 | An on-line sensing system for identifing examinees and students |
| KR102244630B1 (en) * | 2020-11-30 | 2021-04-27 | 라온화이트햇 주식회사 | Method, device and computer program for verifying of watching content |
| KR102335534B1 (en) * | 2021-02-15 | 2021-12-07 | 한국전자인증 주식회사 | Method and Appratus of Attendance Management and Concentration Analysis for Supporting Online Education Based on Artificial Intelligent |
| KR20230043302A (en) * | 2021-09-23 | 2023-03-31 | 국민대학교산학협력단 | Non-face-to-face real-time learning management system using deep learning |
| CN114386772A (en) * | 2021-12-17 | 2022-04-22 | 鸿富锦精密电子(郑州)有限公司 | Video learning evaluation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN118351479A (en) * | 2024-03-13 | 2024-07-16 | 上饶市云上中文信息技术有限公司 | Online reading state detection method and system for students |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20200012355A (en) | Online lecture monitoring method using constrained local model and Gabor wavelets-based face verification process | |
| Indi et al. | Detection of malpractice in e-exams by head pose and gaze estimation | |
| CN109522815A (en) | A kind of focus appraisal procedure, device and electronic equipment | |
| Hu et al. | Research on abnormal behavior detection of online examination based on image information | |
| WO2016090376A1 (en) | Eye tracking via patterned contact lenses | |
| CN111008971B (en) | Aesthetic quality evaluation method of group photo image and real-time shooting guidance system | |
| CN105373767A (en) | Eye fatigue detection method for smart phones | |
| CN111507592A (en) | Evaluation method for active modification behaviors of prisoners | |
| KR101879229B1 (en) | Online lecture monitoring system and method using gaze tracking technology | |
| Guo et al. | Open-eye: An open platform to study human performance on identifying ai-synthesized faces | |
| Cimmino et al. | M2FRED: Mobile masked face REcognition through periocular dynamics analysis | |
| Cowie et al. | An intelligent system for facial emotion recognition | |
| Montazeri et al. | Automatic extraction of eye field from a gray intensity image using intensity filtering and hybrid projection function | |
| Hossain et al. | Automated online exam proctoring system using computer vision and hybrid ML classifier | |
| Travieso et al. | Using a discrete Hidden Markov Model Kernel for lip-based biometric identification | |
| CN117316440A (en) | Intelligent facial paralysis degree evaluation method based on machine learning facial feature calculation | |
| KR102038413B1 (en) | Online lecture monitoring method using face verification and gaze tracking technology | |
| Mittal et al. | GOTCHA: Real-time video deepfake detection via challenge-response | |
| Khan | Detection of emotions from video in non-controlled environment | |
| Huang et al. | Research on learning state based on students’ attitude and emotion in class learning | |
| Montazeri et al. | Automatically eye detection with different gray intensity image conditions | |
| Perdana et al. | Lie Detector with Eye Movement and Eye Blinks Analysis Based on Image Processing using Viola-Jones Algorithm | |
| CN112052721A (en) | Wink oscillogram generation method, device and equipment based on deep learning | |
| Bennett et al. | Looking at faces: autonomous perspective invariant facial gaze analysis | |
| Salam et al. | Integrating head pose to a 3D multi-texture approach for gaze detection |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |