KR20190122453A - A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re - Google Patents
A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20190122453A KR20190122453A KR1020180046262A KR20180046262A KR20190122453A KR 20190122453 A KR20190122453 A KR 20190122453A KR 1020180046262 A KR1020180046262 A KR 1020180046262A KR 20180046262 A KR20180046262 A KR 20180046262A KR 20190122453 A KR20190122453 A KR 20190122453A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- ginsenoside
- rhinovirus
- infection
- treatment
- present
- Prior art date
Links
- PWAOOJDMFUQOKB-WCZZMFLVSA-N ginsenoside Re Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O[C@@H]2[C@H]3C(C)(C)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]3(C)[C@@H]3[C@@]([C@@]4(CC[C@@H]([C@H]4[C@H](O)C3)[C@](C)(CCC=C(C)C)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O3)O)C)(C)C2)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O PWAOOJDMFUQOKB-WCZZMFLVSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 62
- AOGZLQUEBLOQCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N ginsenoside-Re Natural products CC1OC(OCC2OC(OC3CC4(C)C(CC(O)C5C(CCC45C)C(C)(CCC=C(C)C)OC6OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C6O)C7(C)CCC(O)C(C)(C)C37)C(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O AOGZLQUEBLOQCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 62
- 208000023504 respiratory system disease Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 45
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 19
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 title claims description 12
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 241000709661 Enterovirus Species 0.000 claims description 50
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims description 50
- 102000000591 Tight Junction Proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 41
- 108010002321 Tight Junction Proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 41
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 210000001578 tight junction Anatomy 0.000 claims description 11
- 206010057190 Respiratory tract infections Diseases 0.000 claims description 9
- 206010046306 Upper respiratory tract infection Diseases 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000013376 functional food Nutrition 0.000 claims description 8
- 201000008197 Laryngitis Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 201000007100 Pharyngitis Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000003612 virological effect Effects 0.000 claims 3
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 206010061494 Rhinovirus infection Diseases 0.000 abstract description 64
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 abstract description 9
- 239000003642 reactive oxygen metabolite Substances 0.000 description 45
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 30
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 30
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 30
- 210000002919 epithelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 28
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 28
- 102000004160 Phosphoric Monoester Hydrolases Human genes 0.000 description 26
- 108090000608 Phosphoric Monoester Hydrolases Proteins 0.000 description 26
- 102000004722 NADPH Oxidases Human genes 0.000 description 23
- 108010002998 NADPH Oxidases Proteins 0.000 description 23
- 229930182494 ginsenoside Natural products 0.000 description 22
- DCWXELXMIBXGTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphotyrosine Chemical compound OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(OP(O)(O)=O)C=C1 DCWXELXMIBXGTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 17
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 16
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 15
- 229910002091 carbon monoxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 description 10
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 10
- TXEWRVNOAJOINC-UHFFFAOYSA-N ginsenoside Rb2 Natural products CC(=CCCC(OC1OC(COC2OCC(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O)C3CCC4(C)C3C(O)CC5C6(C)CCC(OC7OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C7OC8OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C8O)C(C)(C)C6CCC45C)C TXEWRVNOAJOINC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 9
- -1 Alkoxy radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 238000012258 culturing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000001262 western blot Methods 0.000 description 7
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229940089161 ginsenoside Drugs 0.000 description 6
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229940080817 rotenone Drugs 0.000 description 6
- JUVIOZPCNVVQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N rotenone Natural products O1C2=C3CC(C(C)=C)OC3=CC=C2C(=O)C2C1COC1=C2C=C(OC)C(OC)=C1 JUVIOZPCNVVQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 241000208340 Araliaceae Species 0.000 description 5
- UFNDONGOJKNAES-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ginsenoside Rb1 Natural products CC(=CCCC(C)(OC1OC(COC2OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O)C3CCC4(C)C3C(O)CC5C6(C)CCC(OC7OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C7OC8OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C8O)C(C)(C)C6CC(O)C45C)C UFNDONGOJKNAES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-tyrosine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 235000005035 Panax pseudoginseng ssp. pseudoginseng Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 235000003140 Panax quinquefolius Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 229940122907 Phosphatase inhibitor Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- CNHRRMQBWQJRPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N chikusetsusaponin LM5 Natural products C1CC(C2(CC(O)C3C(C)(C)C(OC4C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O4)OC4C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O4)O)CCC3(C)C2CC2O)C)(C)C2C1C(C)(CCC=C(C)C)OC(C(C(O)C1O)O)OC1COC1OC(CO)C(O)C1O CNHRRMQBWQJRPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 235000008434 ginseng Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- GZYPWOGIYAIIPV-JBDTYSNRSA-N ginsenoside Rb1 Chemical compound C([C@H]1O[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O)O[C@@](C)(CCC=C(C)C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@]([C@@]3(CC[C@H]4C(C)(C)[C@@H](O[C@H]5[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O5)O[C@H]5[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O5)O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H]2O)C)(C)CC1)O[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O GZYPWOGIYAIIPV-JBDTYSNRSA-N 0.000 description 5
- JDCPEKQWFDWQLI-LUQKBWBOSA-N ginsenoside Rc Chemical compound C([C@H]1O[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)O)O[C@@](C)(CCC=C(C)C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@]([C@@]3(CC[C@H]4C(C)(C)[C@@H](O[C@H]5[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O5)O[C@H]5[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O5)O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3C[C@H]2O)C)(C)CC1)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O JDCPEKQWFDWQLI-LUQKBWBOSA-N 0.000 description 5
- SPFXZQZPHXUJSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ginsenoside-Rc Natural products CC(=CCCC(C)(OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1OC2OC(CO)C(O)C2O)C3CCC4(C)C3C(O)CC5C6(C)CCC(OC7OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C7OC8OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C8O)C(C)(C)C6CCC45C)C SPFXZQZPHXUJSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229930182490 saponin Natural products 0.000 description 5
- 150000007949 saponins Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 235000017709 saponins Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 102000009097 Phosphorylases Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010073135 Phosphorylases Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 4
- 210000000170 cell membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000026731 phosphorylation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006366 phosphorylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 208000020029 respiratory tract infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 4
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N salicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LPXPTNMVRIOKMN-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium nitrite Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]N=O LPXPTNMVRIOKMN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 4
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyrosine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical group [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OUUQCZGPVNCOIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Superoxide Chemical compound [O-][O] OUUQCZGPVNCOIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007844 bleaching agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000002889 endothelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000069 prophylactic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000001397 quillaja saponaria molina bark Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 3
- 210000002345 respiratory system Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N (+)-Biotin Chemical compound N1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)O)SC[C@@H]21 YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MIJYXULNPSFWEK-GTOFXWBISA-N 3beta-hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid Chemical compound C1C[C@H](O)C(C)(C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@]3(C)[C@]4(C)CC[C@@]5(C(O)=O)CCC(C)(C)C[C@H]5C4=CC[C@@H]3[C@]21C MIJYXULNPSFWEK-GTOFXWBISA-N 0.000 description 2
- NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylhydroxytoluene Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000000905 Cadherin Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108050007957 Cadherin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZKQDCIXGCQPQNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium hypochlorite Chemical compound [Ca+2].Cl[O-].Cl[O-] ZKQDCIXGCQPQNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N D-gluconic acid Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- JKLISIRFYWXLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epioleonolsaeure Natural products C1CC(O)C(C)(C)C2CCC3(C)C4(C)CCC5(C(O)=O)CCC(C)(C)CC5C4CCC3C21C JKLISIRFYWXLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZRALSGWEFCBTJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Guanidine Chemical compound NC(N)=N ZRALSGWEFCBTJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-lysine Chemical compound NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 2
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 2
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YBRJHZPWOMJYKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleanolic acid Natural products CC1(C)CC2C3=CCC4C5(C)CCC(O)C(C)(C)C5CCC4(C)C3(C)CCC2(C1)C(=O)O YBRJHZPWOMJYKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MIJYXULNPSFWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleanolinsaeure Natural products C1CC(O)C(C)(C)C2CCC3(C)C4(C)CCC5(C(O)=O)CCC(C)(C)CC5C4=CCC3C21C MIJYXULNPSFWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108010059712 Pronase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000003443 antiviral agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- OORMXZNMRWBSTK-LGFJJATJSA-N dammarane Chemical compound C1CCC(C)(C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@]3(C)[C@]4(C)CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@H]4CC[C@@H]3[C@]21C OORMXZNMRWBSTK-LGFJJATJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000015872 dietary supplement Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002526 effect on cardiovascular system Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000002409 epiglottis Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229930182470 glycoside Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000002338 glycosides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N lactic acid Chemical compound CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000000867 larynx Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011572 manganese Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007721 medicinal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000004379 membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 2
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanoic acid Natural products OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010755 mineral Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000003928 nasal cavity Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000005036 nerve Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229940100243 oleanolic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000003800 pharynx Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- HZLWUYJLOIAQFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N prosapogenin PS-A Natural products C12CC(C)(C)CCC2(C(O)=O)CCC(C2(CCC3C4(C)C)C)(C)C1=CCC2C3(C)CCC4OC1OCC(O)C(O)C1O HZLWUYJLOIAQFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000241 respiratory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229960004889 salicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000010288 sodium nitrite Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium sulfite Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])=O GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000013343 vitamin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011782 vitamin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940088594 vitamin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229930003231 vitamin Natural products 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VQVUBYASAICPFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (6'-acetyloxy-2',7'-dichloro-3-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-1,9'-xanthene]-3'-yl) acetate Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C21C1=CC(Cl)=C(OC(C)=O)C=C1OC1=C2C=C(Cl)C(OC(=O)C)=C1 VQVUBYASAICPFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CHHHXKFHOYLYRE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 2,4-Hexadienoic acid, potassium salt (1:1), (2E,4E)- Chemical compound [K+].CC=CC=CC([O-])=O CHHHXKFHOYLYRE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azaniumyl-2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound NCC(O)C(O)=O BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MRBKEAMVRSLQPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 MRBKEAMVRSLQPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MGWGWNFMUOTEHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-amine Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=CC(C=2N=C(N)SC=2)=C1 MGWGWNFMUOTEHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)aniline Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1 OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TWCMVXMQHSVIOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aglycone of yadanzioside D Natural products COC(=O)C12OCC34C(CC5C(=CC(O)C(O)C5(C)C3C(O)C1O)C)OC(=O)C(OC(=O)C)C24 TWCMVXMQHSVIOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000009027 Albumins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010088751 Albumins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- PLMKQQMDOMTZGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Astrantiagenin E-methylester Natural products CC12CCC(O)C(C)(CO)C1CCC1(C)C2CC=C2C3CC(C)(C)CCC3(C(=O)OC)CCC21C PLMKQQMDOMTZGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000282817 Bovidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282836 Camelus dromedarius Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 description 1
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000003883 Cystic fibrosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N D-gluconic acid Natural products OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SHZGCJCMOBCMKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N D-mannomethylose Natural products CC1OC(O)C(O)C(O)C1O SHZGCJCMOBCMKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicyclohexylamine Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC1CCCCC1 XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004278 EU approved seasoning Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000991587 Enterovirus C Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N L-Cysteine Chemical compound SC[C@H](N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P L-argininium(2+) Chemical compound NC(=[NH2+])NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- SHZGCJCMOBCMKK-JFNONXLTSA-N L-rhamnopyranose Chemical compound C[C@@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O SHZGCJCMOBCMKK-JFNONXLTSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PNNNRSAQSRJVSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N L-rhamnose Natural products CC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O PNNNRSAQSRJVSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N L-tryptophane Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-valine Chemical compound CC(C)[C@H](N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005913 Maltodextrin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002774 Maltodextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 1
- PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Manganese Chemical compound [Mn] PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CHJJGSNFBQVOTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-methyl-guanidine Natural products CNC(N)=N CHJJGSNFBQVOTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000008589 Obesity Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000003940 Occludin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000304 Occludin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010033078 Otitis media Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000004316 Oxidoreductases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000854 Oxidoreductases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ozone Chemical compound [O-][O+]=O CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001494479 Pecora Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920002230 Pectic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000045595 Phosphoprotein Phosphatases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108700019535 Phosphoprotein Phosphatases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000709664 Picornaviridae Species 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000035415 Reinfection Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010062106 Respiratory tract infection viral Diseases 0.000 description 1
- WINXNKPZLFISPD-UHFFFAOYSA-M Saccharin sodium Chemical compound [Na+].C1=CC=C2C(=O)[N-]S(=O)(=O)C2=C1 WINXNKPZLFISPD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000004288 Sodium dehydroacetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005708 Sodium hypochlorite Substances 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000269722 Thea sinensis Species 0.000 description 1
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tryptophan Natural products C1=CC=C2C(CC(N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Valine Natural products CC(C)C(N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000036142 Viral infection Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000783 alginic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960001126 alginic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000004781 alginic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001450 anions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000890 antigenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000022 bacteriostatic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- PARMADWNFXEEFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N bamethan sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O.CCCC[NH2+]CC(O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1.CCCC[NH2+]CC(O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 PARMADWNFXEEFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940092714 benzenesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013361 beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001164 bioregulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960002685 biotin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000020958 biotin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011616 biotin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010006451 bronchitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007975 buffered saline Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001720 carbohydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000014633 carbohydrates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000014171 carbonated beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonic acid Chemical compound OC(O)=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001734 carboxylic acid salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N choline Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CCO OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001231 choline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001684 chronic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cysteine Natural products SCC(N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000018417 cysteine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010012601 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 235000005911 diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000037213 diet Effects 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SWSQBOPZIKWTGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylaminoamidine Natural products CN(C)C(N)=N SWSQBOPZIKWTGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241001493065 dsRNA viruses Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M ethanesulfonate Chemical compound CCS([O-])(=O)=O CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000684 flow cytometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940014144 folate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-N folic acid Chemical compound C=1N=C2NC(N)=NC(=O)C2=NC=1CNC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019152 folic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011724 folic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013373 food additive Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002778 food additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011194 food seasoning agent Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000003599 food sweetener Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000019253 formic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001530 fumaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011087 fumaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000417 fungicide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000174 gluconic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012208 gluconic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000002791 glucosyl group Chemical group C1([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O1)CO)* 0.000 description 1
- 229930195712 glutamate Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 230000035876 healing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012676 herbal extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004009 herbicide Substances 0.000 description 1
- PFOARMALXZGCHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N homoegonol Natural products C1=C(OC)C(OC)=CC=C1C1=CC2=CC(CCCO)=CC(OC)=C2O1 PFOARMALXZGCHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940071870 hydroiodic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001969 hypertrophic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000987 immune system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000036039 immunity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000027866 inflammatory disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004692 intercellular junction Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004310 lactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014655 lactic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000002596 lactones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940035034 maltodextrin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940098779 methanesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 244000005700 microbiome Species 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000002438 mitochondrial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004877 mucosa Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000002850 nasal mucosa Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 201000009240 nasopharyngitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000005445 natural material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960003512 nicotinic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011664 nicotinic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JCXJVPUVTGWSNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen dioxide Inorganic materials O=[N]=O JCXJVPUVTGWSNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000957 no side effect Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000015097 nutrients Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000016709 nutrition Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000035764 nutrition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000020824 obesity Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000002927 oxygen compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007911 parenteral administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007170 pathology Effects 0.000 description 1
- LCLHHZYHLXDRQG-ZNKJPWOQSA-N pectic acid Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@@H]1OC1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O2)C(O)=O)O)[C@@H](C(O)=O)O1 LCLHHZYHLXDRQG-ZNKJPWOQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000001539 phagocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 102000013147 phosphatase activity proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108040007807 phosphatase activity proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010318 polygalacturonic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229940050271 potassium alum Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GNHOJBNSNUXZQA-UHFFFAOYSA-J potassium aluminium sulfate dodecahydrate Chemical compound O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Al+3].[K+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O.[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O GNHOJBNSNUXZQA-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 239000004302 potassium sorbate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010241 potassium sorbate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940069338 potassium sorbate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002203 pretreatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012744 reinforcing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000027756 respiratory electron transport chain Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010039083 rhinitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 201000009890 sinusitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WXMKPNITSTVMEF-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium benzoate Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WXMKPNITSTVMEF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000004299 sodium benzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010234 sodium benzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960003885 sodium benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019259 sodium dehydroacetate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940079839 sodium dehydroacetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SUKJFIGYRHOWBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium hypochlorite Chemical compound [Na+].Cl[O-] SUKJFIGYRHOWBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010265 sodium sulphite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- DSOWAKKSGYUMTF-GZOLSCHFSA-M sodium;(1e)-1-(6-methyl-2,4-dioxopyran-3-ylidene)ethanolate Chemical compound [Na+].C\C([O-])=C1/C(=O)OC(C)=CC1=O DSOWAKKSGYUMTF-GZOLSCHFSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008223 sterile water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004936 stimulating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005728 strengthening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003460 sulfonic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001356 surgical procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000946 synaptic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegermanium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ge] JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930182493 triterpene saponin Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 210000001944 turbinate Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 241000701161 unidentified adenovirus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000712461 unidentified influenza virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004474 valine Substances 0.000 description 1
- MWOOGOJBHIARFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanillin Chemical compound COC1=CC(C=O)=CC=C1O MWOOGOJBHIARFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000012141 vanillin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- FGQOOHJZONJGDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanillin Natural products COC1=CC(O)=CC(C=O)=C1 FGQOOHJZONJGDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009385 viral infection Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019155 vitamin A Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011719 vitamin A Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003722 vitamin derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7028—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages
- A61K31/7034—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin
- A61K31/704—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin attached to a condensed carbocyclic ring system, e.g. sennosides, thiocolchicosides, escin, daunorubicin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS, OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES A21D OR A23B-A23J; THEIR PREPARATION OR TREATMENT, e.g. COOKING, MODIFICATION OF NUTRITIVE QUALITIES, PHYSICAL TREATMENT; PRESERVATION OF FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS, IN GENERAL
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS, OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES A21D OR A23B-A23J; THEIR PREPARATION OR TREATMENT, e.g. COOKING, MODIFICATION OF NUTRITIVE QUALITIES, PHYSICAL TREATMENT; PRESERVATION OF FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS, IN GENERAL
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
- A23L33/125—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives containing carbohydrate syrups; containing sugars; containing sugar alcohols; containing starch hydrolysates
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
- A61P31/14—Antivirals for RNA viruses
- A61P31/16—Antivirals for RNA viruses for influenza or rhinoviruses
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23V—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES AND LACTIC OR PROPIONIC ACID BACTERIA USED IN FOODSTUFFS OR FOOD PREPARATION
- A23V2002/00—Food compositions, function of food ingredients or processes for food or foodstuffs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23V—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES AND LACTIC OR PROPIONIC ACID BACTERIA USED IN FOODSTUFFS OR FOOD PREPARATION
- A23V2200/00—Function of food ingredients
- A23V2200/30—Foods, ingredients or supplements having a functional effect on health
- A23V2200/314—Foods, ingredients or supplements having a functional effect on health having an effect on lung or respiratory system
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re의 호흡기 질환 예방 또는 치료용도에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는 진세노사이드 Re를 포함하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물; 상기 약학적 조성물을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 호흡기 질환의 치료 방법; 건강기능식품; 및 밀착연접 붕괴 억제용 조성물에 관한 것이다. 구체적으로는 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 호흡기 질환에 대한 진세노사이드 Re의 예방 및 치료 용도에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to the use of ginsenoside Re for preventing or treating respiratory diseases, and more particularly, to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating respiratory diseases, including ginsenoside Re; A method of treating a respiratory disease comprising administering the pharmaceutical composition; Health functional food; And a composition for inhibiting close splice collapse. Specifically, the present invention relates to the use of Ginsenoside Re for the prevention of respiratory diseases caused by rhinovirus infection.
호흡기 질환은 기체 교환에 관여하는 기관과 조직 그리고 호흡 신경 및 근육에 영향을 주는 병리적 상태를 포함하는 것으로 알려져 있다. 호흡기 질환은 그 종류가 다양하나 그 중 가장 흔하게 발병하는 것은 일상적으로 감기라고 부르는 상기도 감염이다. 호흡기 중 비강, 인두, 후두개 및 후두 부분의 감염을 의미하는 상기도 감염은 그 원인의 80%이상이 바이러스에 의한 감염이며 아데노바이러스, 인플루엔자 바이러스 등에 의한 감염도 존재하나 바이러스에 의한 감염 중 가장 큰 부분을 차지하는 것은 라이노바이러스에 의한 감염으로 알려져 있다. Respiratory diseases are known to include pathologies that affect organs and tissues involved in gas exchange and respiratory nerves and muscles. Respiratory diseases come in many varieties, the most common of which is the upper respiratory tract infections commonly called colds. Upper respiratory tract infections, which refer to infections of the nasal cavity, pharynx, epiglottis and larynx in the respiratory tract, are caused by viruses and more than 80% of the causes are caused by adenoviruses, influenza viruses, etc. It is known that infection is caused by rhinoviruses.
라이노바이러스(Rhinovirus)는 피코르나바이러스(Phcormaviridae)과에 속하는 바이러스로 RNA바이러스이며, 형태는 폴리오바이러스와 유사하며, 부비강염, 중이염, 낭성 섬유종, 기관지염 등을 수반한다. 상술한 바와 같이 바이러스성 호흡기 감염의 가장 큰 원인이기 때문에 라이노바이러스에 대한 문제는 세계적으로 관심을 가지고 있으며, 미국에서도 라이노바이러스 특이적인 항바이러스제를 개발하기 위한 연구가 활발하게 진행중이다.Rhinovirus (Rhinovirus) is a virus belonging to the family of Phcormaviridae, RNA virus, the form is similar to poliovirus, accompanied by sinusitis, otitis media, cystic fibrosis, bronchitis. As described above, the problem with rhinoviruses is of global interest because it is the largest cause of viral respiratory infections, and research to develop rhinovirus specific antiviral agents is actively underway in the United States.
계절의 변화가 뚜렷하여 환절기마다 감기 환자가 급증하는 한국 또한 상기도 감염에 대한 치료 방안이 시급한 상황이며, 이에 따라 많은 연구자들이 상기도 감염의 원인이 되는 라이노바이러스에 대해 연구하고 있으나, 현재 라이노바이러스에 따른 감염 기전은 명확하게 규명되지 않아 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 치료제의 개발이 용이치 않으며, 화학적인 방법으로 제조된 약제나, 항바이러스제에서 수많은 종류의 바이러스에 대한 약제는 있으나, 부작용이 없으면서 동시에 라이노바이러스에 특이적인 치료제는 알려진 바가 없다.In Korea, where there is a sharp change in seasonality and a sudden increase in cold patients in each season, there is an urgent need for treatment for upper respiratory tract infections. Therefore, many researchers are studying rhinoviruses that cause upper respiratory tract infections. The mechanism of infection is not clearly identified, so it is not easy to develop a therapeutic agent for rhinovirus infection, and there are drugs prepared by chemical methods or antiviral drugs for many kinds of viruses, but without side effects, rhino No specific treatment for viruses is known.
한편, 인삼 내에 포함된 사포닌이며, 인삼(Ginseng)의 배당체(Glycoside)라는 의미를 지닌 진세노사이드(Ginsenoside)는 아글리콘(aglycone)의 구조에 따라 프로토파낙사다이올계(Protopanaxadiol-type, PPD 타입) 진세노사이드, 프로토파낙사트라이올계(Protopanaxatriol-type, PPT 타입) 진세노사이드 및 올레아놀린산계 (oleanolic acid 타입) 진세노사이드의 세 가지로 분류될 수 있으며, 현재 진세노사이드는 약 180여종 이상의 진세노사이드들이 분리되었다고 알려져 있다.Meanwhile, ginsenoside, which is a saponin contained in ginseng and a glycoside of ginseng, is a Protopanaxadiol-type or PPD type according to the structure of aglycone. ) Ginsenosides, Protopanaxatriol-type (PPT type) Ginsenosides, and oleanolic acid type (oleanolic acid type) Ginsenosides can be classified into three categories. It is known that the above ginsenosides have been separated.
그 중, 진세노사이드 Re는 담마란(dammarane)계 사포닌 중 프로토파낙사트라이올계(Protopanaxatriol-type, PPT 타입) 진세노사이드로 면역시스템 강화 효과(Experimental parasitology 135.2, 2013: 234-239), 심혈관계 보호 효과(Cardiovascular therapeutics 30.4, 2012), 항산화 효과(European journal of pharmacology 550.1, 2006: 173-179), 당뇨병 및 비만 치료 효과(Biochimica et Biophysica Acta ( BBA )-Molecular Basis of Disease 1740.3, 2005: 319-325)에 대해서 이미 보고된 바 있으나, 진세노사이드 Re의 라이노바이러스 감염 억제 관련 효과에 대해서는 알려진 바가 없다.Among them, ginsenoside Re is a protopanaxatriol-type (PPT type) ginsenoside among dammarane-based saponins, and the immune system strengthening effect ( Experimental parasitology 135.2, 2013: 234-239), cardiovascular Cardiovascular therapeutics (30.4, 2012), antioxidant effects ( European journal of pharmacology 550.1, 2006: 173-179), diabetes and obesity treatment effects ( Biochimica et Biophysica Acta ( BBA ) -Molecular Basis of Disease 1740.3, 2005: 319 -325) has already been reported, but there is no known effect of ginsenoside Re on the inhibition of rhinovirus infection.
이러한 배경 하에, 본 발명자들은 라이노바이러스에 따른 호흡기 질환의 치료를 위해 예의 연구 노력한 결과, 라이노바이러스의 감염기전을 규명하였으며, 진세노사이드 Re가 상기 감염기전을 억제하는 것을 확인함으로써 진세노사이드 Re를 통한 호흡기 질환 관련 증상 개선 효과를 확인하여 본 발명을 완성하였다.Under these backgrounds, the present inventors have conducted extensive research efforts for the treatment of respiratory diseases according to rhinoviruses, and have identified the mechanism of infection of rhinoviruses and confirm that ginsenoside Re inhibits the infection mechanism. The present invention was completed by confirming the effect of improving symptoms related to respiratory disease.
본 발명의 하나의 목적은, 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.One object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of respiratory diseases containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
본 발명의 다른 하나의 목적은, 상기 약학적 조성물을 인간을 제외한 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for preventing or treating a respiratory disease, comprising administering the pharmaceutical composition to a subject other than a human.
본 발명의 또 다른 하나의 목적은, 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선용 건강기능식품을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention to provide a health functional food for the prevention or improvement of respiratory diseases containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
본 발명의 또 다른 하나의 목적은, 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 밀착연접(tight junction) 붕괴 억제용 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a composition for inhibiting tight junction breakdown containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
상기의 과제를 해결하기 위한 하나의 양태로서, 본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물을 제공한다.As one embodiment for solving the above problems, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of respiratory diseases containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
이하, 본 발명에서의 진세노사이드 Re를 함유하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물을 구체적으로 설명한다.Hereinafter, a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating a respiratory disease containing ginsenoside Re in the present invention will be described in detail.
본 발명에서의 용어, “진세노사이드 Re”는 담마란(dammarane)계 사포닌 중 프로토파낙사트라이올계(Protopanaxatriol-type, PPT 타입) 진세노사이드로, 하기 화학식 1에서 볼 수 있는 바와 같이, PPT 타입의 기본 탄소 골격에서, 6번 탄소에 글루코스와 람노스(Glc-Rha)가 결합되어 있고 20번 탄소에 한 개의 글루코스가 결합되어 있는 형태의 진세노사이드이다.As used herein, the term “ginsenoside Re” is a protopanaxatriol-type (PPT type) ginsenoside in a dammarane-based saponin, as shown in
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
상기 진세노사이드는 인삼에 있는 사포닌을 의미한다. 인삼 사포닌은 다른 식물에서 발견되는 사포닌과는 다른 특이한 화학구조인 트리테르펜사포닌(triterpene saponin)을 가지고 있으며, 약리효능도 특이하여 인삼(Ginseng) 배당체(Glycoside)란 의미로 진세노사이드라 불린다. Ginsenoside means saponin in ginseng. Ginseng saponins have triterpene saponin, a chemical structure that is different from those found in other plants, and because of its unique pharmacological effect, it is called ginsenoside as Ginseng glycoside.
본 발명에서의 용어, “호흡기 질환”은 기체 교환에 관여하는 기관과 조직 그리고 호흡 신경 및 근육에 영향을 주는 병리적 상태를 포함하는 것으로, 이에 한정된 것은 아니나, 구체적으로는 상기도 감염일 수 있고, 보다 구체적으로는 감기, 인두염, 후두염일 수 있다. As used herein, the term “respiratory disease” includes a pathological condition that affects organs and tissues involved in gas exchange and respiratory nerves and muscles, but is not limited thereto, and specifically may be an upper respiratory tract infection. More specifically, it may be a cold, pharyngitis, or laryngitis.
상기 상기도 감염은 바이러스가 호흡기 중 비강, 인두, 후두개 및 후두 부분을 포함한 상기도 점막에 감염되어 발생하는 염증성 질환을 통칭하는 용어이며 급격한 기온 변화, 감기, 열성질환, 과로 및 허약 체질 등의 원인으로 인해 바이러스를 통해 감염될 수 있고, 여기에서는 구체적으로 라이노바이러스에 의해 유발되는 바이러스성 감염이 주요 감염원일 수 있다.The upper respiratory tract infection is a general term for inflammatory diseases caused by infection of the upper respiratory tract mucosa, including the nasal cavity, pharynx, epiglottis and larynx in the respiratory tract, and causes rapid temperature changes, colds, recessive diseases, overwork and weakness. Can be infected through a virus, where a viral infection specifically caused by rhinoviruses may be the main source of infection.
본 발명에서의 용어, “라이노바이러스”는 피코르나바이러스과 라이노바이러스속에 포함된 바이러스를 의미하며, 현재 1(A, B), 2~113까지 100여종의 항원형이 알려져 있다. 감기 바이러스로 잘 알려져 있으며 겨울과 봄에 걸리기 쉽고 2 내지 5일의 잠복기를 가지며 일주일 정도 감기 증상이 지속된다. 치유 후에도 면역의 지속이 짧아 재감염을 일으키기 쉽다는 특징이 있다. 상기 라이노바이러스는, 이에 한정된 것은 아니나, 라이노바이러스 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20일 수 있으며, 보다 구체적으로 라이노바이러스 16일 수 있다.The term "rhinovirus" in the present invention refers to a virus included in the genus Picornaviruses and rhinoviruses, and is currently known as 1 (A, B), from 2 to 113, about 100 antigenic types. Known as the common cold virus, it is susceptible to winter and spring, has an incubation period of 2 to 5 days, and lasts about a week for cold symptoms. Even after healing, the immunity is short and easy to cause re-infection. The rhinoviruses include, but are not limited to,
본 발명자들은 상기 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 호흡기 질환을 치료하기 위해 연구 노력한 결과, 라이노바이러스의 감염 기전을 확인하였으며, 진세노사이드 Re가 상기 감염 기전을 억제하는 것을 확인하여 본 발명을 완성하였다.The present inventors have conducted research to treat respiratory diseases caused by rhinovirus infection, confirmed the mechanism of infection of rhinovirus, and confirmed that ginsenoside Re inhibits the infection mechanism, thereby completing the present invention.
본 발명에서는 라이노바이러스 감염 기전을 확인하기 위해 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시킨 후, 밀착연접(tight junction) 단백질 수준과 활성산소종(reactive oxygen species, ROS) 생성량을 확인하고 NADPH 산화효소(NADPH oxidase, NOX) 억제제를 사용하여 그 변화를 확인하였다.In the present invention, after infecting rhinoviruses to non-mucosal epithelial cells to confirm the rhinovirus infection mechanism, the level of tight junction protein and the amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the NADPH oxidase (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) inhibitors were used to confirm the change.
본 발명에서의 용어, “밀착연접(tight junction)”은 주로 상피세포와 내피세포에서 나타나는 세포간 연접장치의 일종으로 격벽 기능을 하여 상피세포 또는 내피세포의 시트를 구성하는 세포 사이를 물질이 누출하는 것을 방지할 수 있고, 울타리 기능을 하여 세포막의 지질에서 끈모양 울타리를 둘러 세포막을 구획하는 기능이며 상피세포나 내피세포의 극성을 유지하는 에 도움을 줄 수 있다.In the present invention, the term "tight junction" is a kind of intercellular junction that appears mainly in epithelial cells and endothelial cells, and functions as a septum to leak substances between cells constituting a sheet of epithelial cells or endothelial cells. It can be prevented, and acts as a hedge function to partition the cell membrane around the cord-shaped fence in the lipid of the cell membrane and can help maintain the polarity of epithelial or endothelial cells.
본 발명에서의 용어, “NADPH 산화효소(NADPH oxidase, NOX)”는 막-결합 효소 복합체(membrane-bound enzyme complex)로서 식세포의 세포막 등에 존재하여 초산화물(superoxide)을 생산하고 세균이나 곰팡이 등과 같은 미생물의 분해를 돕는 역할을 한다. NOX에 의해 생성된 초산화물은 과산화수소를 형성하고, 더 나아가 활성산소종을 형성할 수 있다.In the present invention, the term "NADPH oxidase (NOX)" is a membrane-bound enzyme complex (membrane-bound enzyme complex) is present in the cell membranes of phagocytes to produce superoxide, such as bacteria and fungi It helps to break down microorganisms. Superoxides produced by NOX can form hydrogen peroxide and, moreover, form reactive oxygen species.
본 발명에서의 용어, “활성산소종(reactive oxygen species, ROS)”은 보통으로 존재하는 기저상태의 삼중항산소(3O2)보다 반응성이 크고 활성이 풍부한 산소종을 의미한다. 일반적으로 삼중항산소의 단계적 환원으로부터 생성되는 슈퍼옥시드(O2-), 과산화수소(H2O2), 히드록시라디칼(OH) 그리고 일중항산소(1O2)를 활성산소종으로 정의하나, 알콕시라디칼(ROㆍ). 퍼옥시라디칼(ROOㆍ) 또는 오존(O3), 이산화질소(NO2) 등의 반응성이 높은 산소화합물도 활성산소종에 포함될 수 있다. 활성산소종은 산화력이 강해 주변의 세포막 또는 DNA에 산화작용을 일으키며, 이 과정에서 세포 구조가 손상당할 수 있고, 더 나아가 세포가 기능을 잃거나 변질될 수 있다.As used herein, the term “reactive oxygen species (ROS)” refers to an oxygen species that is more reactive and richer than the normal triplet oxygen ( 3 O 2 ). Generally, superoxide (O 2- ), hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ), hydroxy radical (OH) and singlet oxygen ( 1 O 2 ) generated from the stepwise reduction of triplet oxygen are defined as active oxygen species. , Alkoxy radicals (RO ·). Highly reactive oxygen compounds, such as peroxy radicals (ROO.) Or ozone (O 3 ), nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ), may also be included in the active oxygen species. Oxygen species are highly oxidative, causing oxidative action on surrounding cell membranes or DNA, which can damage cell structures and further cause cells to lose function or deteriorate.
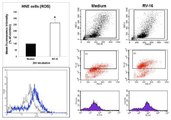
본 발명의 구체적인 일 실시예에서는, 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 밀착연접 단백질 수준 및 ROS 생성량을 확인한 결과, 정상군과 비교하여 라이노바이러스 감염군은 밀착연접 단백질이 감소하고 ROS 생성량이 증가하는 것을 확인하였다 (도 1 및 2).In a specific embodiment of the present invention, as a result of infecting rhinoviruses to non-mucosal epithelial cells and confirming the level of tight junction protein and ROS production, the rhinovirus infected group has a low level of tight junction protein and an increase in ROS production compared to the normal group. It was confirmed (FIGS. 1 and 2).
또한, 본 발명의 구체적인 일 실시예에서는, ROS를 억제할 수 있는 NOX 억제제인 DPI를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 ROS 생성량 및 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 확인한 결과, DPI 비처리 대조군은 밀착연접 단백질 수준이 감소하고 ROS 생성량이 증가한 반면, NOX 억제제 처리군은 단백질 수준이 증가하고 ROS 생성량이 감소한 것을 확인하였다 (도 3 및 4).In addition, in one specific embodiment of the present invention, as a result of infecting rhinovirus to non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with DPI, a NOX inhibitor capable of inhibiting ROS, and confirming the amount of ROS production and the junction protein level, the DPI untreated control was in close contact. While the level of synaptic protein was decreased and ROS production was increased, the NOX inhibitor treatment group was found to have increased protein levels and decreased ROS production (FIGS. 3 and 4).
본 발명의 구체적인 일 실시예에서는, 진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 배양한 후 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 측정한 결과, 진세노사이드 Re를 처리하지 않은 라이노바이러스 감염 대조군에서는 밀착연접 단백질 수준이 감소한 반면, 진세노사이드 Re 처리군에서는 밀착연접 단백질 수준이 증가한 것을 확인하였다 (도 8).In a specific embodiment of the present invention, after infecting and cultured rhinoviruses to non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with ginsenoside Re and measuring the level of tight junction protein, in the rhinovirus infection control group not treated with ginsenoside Re While the level of tight junction protein was reduced, it was confirmed that the level of tight junction protein was increased in the ginsenoside Re treatment group (FIG. 8).
본 발명의 일 실시예에서는, 진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 배양한 후 ROS의 생성량을 측정한 결과, 진세노사이드 Re를 처리하지 않은 라이노바이러스 감염 대조군에서는 ROS의 생성량이 증가한 반면, 진세노사이드 Re 처리군에서는 ROS의 생성량이 감소한 것을 확인하였다 (도 9).In one embodiment of the present invention, after inoculating rhinoviruses to non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with ginsenoside Re and culturing the amount of ROS produced, the ROS of the rhinovirus infection control group not treated with ginsenoside Re was measured. While the production amount was increased, it was confirmed that the production amount of ROS decreased in the ginsenoside Re treatment group (FIG. 9).
반면, 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1을 전처리한 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 배양한 후 밀착연접 단백질 수준 및 ROS 생성량을 측정한 결과, 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1을 처리하지 않은 라이노바이러스 감염 대조군에서 감소한 밀착연접 단백질 수준 및 증가한 ROS 생성량이 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1 처리군에서도 그 차이를 나타내지 않는 것을 확인하였다 (도 11 및 12).On the other hand, after infection and culture of non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with ginsenosides Rc and Rb1, and measuring the level of tight junction protein and ROS production, in the rhinovirus infection control group not treated with ginsenosides Rc and Rb1 Reduced tight junction protein levels and increased ROS production was confirmed to show no difference in the ginsenoside Rc and Rb1 treatment group (FIGS. 11 and 12).
이러한 결과는 진세노사이드 Re의 라이노바이러스 감염 억제 효과를 나타내며, 모든 진세노사이드가 라이노바이러스 감염 억제 효과를 나타내지 않음을 의미하는 것이다.These results indicate that ginsenoside Re has an inhibitory effect on rhinovirus infection, and that all ginsenosides do not exhibit rhinovirus infection inhibition effect.
본 발명에서 사용되는 용어, "예방"이란, 본 발명에 따른 진세노사이드 Re을 개체에 투여하여 호흡기 질환의 발병을 억제하거나 지연시키는 모든 행위를 의미할 수 있다.As used herein, the term "prevention" may mean any action that inhibits or delays the onset of respiratory disease by administering ginsenoside Re according to the present invention to a subject.
본 발명에서 사용되는 용어, "치료"란, 본 발명의 상기 조성물을 호흡기 질환 발병 의심 개체에 투여하여 호흡기 질환의 증세가 호전되도록 하거나 이롭게 되도록 하는 모든 행위를 의미할 수 있다.As used herein, the term "treatment" may mean any action that improves or benefits the symptoms of respiratory disease by administering the composition of the present invention to a subject suspected of developing a respiratory disease.
본 발명의 약학 조성물은 단일제제로도 사용할 수 있고, 공인된 호흡기 질환 치료 효과를 가진다고 알려진 약물을 추가로 포함하여 복합제제로 제조하여 사용할 수 있으며, 약제학적으로 허용되는 담체 또는 부형제를 이용하여 제제화함으로써 단위 용량 형태로 제조되거나 다용량 용기 내에 내입시켜 제조될 수 있다. The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may also be used as a single agent, and may be prepared and used as a complex preparation, further including a drug known to have a recognized respiratory disease treatment effect, and formulated using a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient unit. It may be prepared in a dosage form or incorporated into a multi-dose container.
본 발명에서 사용되는 용어, "약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체"란 생물체를 자극하지 않으면서, 주입되는 화합물의 생물학적 활성 및 특성을 저해하지 않는 담체 또는 희석제를 의미할 수 있다. 본 발명에 사용 가능한 상기 담체의 종류는 특별히 제한되지 아니하며 당해 기술 분야에서 통상적으로 사용되고 약학적으로 허용되는 담체라면 어느 것이든 사용할 수 있다. 상기 담체의 비제한적인 예로는, 식염수, 멸균수, 링거액, 완충 식염수, 알부민 주사 용액, 덱스트로즈 용액, 말토 덱스트린 용액, 글리세롤, 에탄올 등을 들 수 있다. 이들은 단독으로 사용되거나 2 종 이상을 혼합하여 사용될 수 있다. 상기 담체는 비자연적 담체 (non-naturally occuring carrier)를 포함할 수 있다.As used herein, the term "pharmaceutically acceptable carrier" may refer to a carrier or diluent that does not interfere with the biological activity and properties of the compound to be injected without stimulating the organism. The kind of the carrier usable in the present invention is not particularly limited, and any carrier can be used as long as it is a conventionally used and pharmaceutically acceptable carrier in the art. Non-limiting examples of the carrier include saline, sterile water, Ringer's solution, buffered saline, albumin injection solution, dextrose solution, maltodextrin solution, glycerol, ethanol and the like. These may be used alone or in combination of two or more thereof. The carrier may include a non-naturally occuring carrier.
또한, 필요한 경우 항산화제, 완충액 및/또는 정균제 등 다른 통상의 첨가제를 첨가하여 사용할 수 있으며, 희석제, 분산제, 계면 활성제, 결합제, 윤활제 등을 부가적으로 첨가하여 수용액, 현탁액, 유탁액 등과 같은 주사용 제형, 환약, 캡슐, 과립 또는 정제 등으로 제제화하여 사용할 수 있다.In addition, if necessary, other conventional additives such as antioxidants, buffers and / or bacteriostatic agents may be added and used, and diluents, dispersants, surfactants, binders, lubricants, and the like may be additionally added to provide a solution such as an aqueous solution, a suspension, an emulsion, or the like. It may be formulated into a use formulation, pills, capsules, granules or tablets.
또한, 본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 약제학적으로 유효한 양의 진세노사이드 Re를 포함할 수 있다. 본 발명에서 용어, "약제학적으로 유효한 양"은 의학적 치료에 적용 가능한 합리적인 수혜/위험 비율로 질환을 치료하기에 충분한 양을 의미하며, 일반적으로 0.001 내지 1000 mg/kg의 양, 바람직하게는 0.05 내지 200 mg/kg, 보다 바람직하게는 0.1 내지 100 mg/kg의 양을 일일 1회 내지 수회로 나누어 투여할 수 있다. 그러나 본 발명의 목적상, 특정 환자에 대한 구체적인 치료적 유효량은 달성하고자 하는 반응의 종류와 정도, 경우에 따라 다른 제제가 사용되는지의 여부를 비롯한 구체적 조성물, 환자의 연령, 체중, 일반 건강 상태, 성별 및 식이, 투여 시간, 투여 경로 및 조성물의 분비율, 치료기간, 구체적 조성물과 함께 사용되거나 동시 사용되는 약물을 비롯한 다양한 인자와 의약 분야에 잘 알려진 유사 인자에 따라 다르게 적용하는 것이 바람직하다. In addition, the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may include a pharmaceutically effective amount of ginsenosides Re. As used herein, the term “pharmaceutically effective amount” means an amount sufficient to treat a disease at a reasonable benefit / risk ratio applicable to medical treatment, generally in an amount of 0.001 to 1000 mg / kg, preferably 0.05 The amount of to 200 mg / kg, more preferably 0.1 to 100 mg / kg may be administered once to several times daily. However, for the purposes of the present invention, the specific therapeutically effective amount for a particular patient is determined by the specific composition, including the type and extent of the reaction to be achieved, whether or not other agents are used in some cases, the age, weight, general health of the patient, It is desirable to apply differently depending on various factors and similar factors well known in the medical field, including sex and diet, time of administration, route of administration and rate of composition, duration of treatment, drugs used with or co-specific with the specific composition.
본 발명의 약학적 조성물은 개별 치료제로 투여하거나 다른 치료제와 병용하여 투여될 수 있고 종래의 치료제와는 순차적 또는 동시에 투여할 수 있다. 그리고 단일 또는 다중 투여될 수 있다. 상기 요소를 모두 고려하여 부작용을 유발하지 않으면서 최소한의 양으로 최대 효과를 얻을 수 있는 양을 투여하는 것이 중요하며, 당업자에 의해 용이하게 결정될 수 있다.The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention may be administered as individual therapeutic agents or in combination with other therapeutic agents and may be administered sequentially or simultaneously with conventional therapeutic agents. And single or multiple administrations. In consideration of all the above factors, it is important to administer an amount that can achieve the maximum effect in a minimum amount without causing side effects, and can be easily determined by those skilled in the art.
본 발명에서의 용어, "투여"는 어떠한 적절한 방법으로 환자에게 본 발명의 약학적 조성물을 도입하는 것을 의미하며, 본 발명의 조성물의 투여 경로는 목적 조직에 도달할 수 있는 한 경구 또는 비경구의 다양한 경로를 통하여 투여될 수 있다.The term "administration" in the present invention means introducing the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention to a patient in any suitable manner, and the route of administration of the composition of the present invention may be varied orally or parenterally as long as the target tissue can be reached. It can be administered via the route.
본 발명에 따른 약학 조성물의 투여 방식은 특별히 제한되지 아니하며, 당해 기술 분야에서 통상적으로 사용하는 방식에 따를 수 있다. 상기 투여 방식의 비제한적인 예로, 조성물을 경구 투여 또는 비경구 투여 방식으로 투여할 수 있다. 본 발명에 따른 약학 조성물은 목적하는 투여 방식에 따라 다양한 제형으로 제작될 수 있다. The mode of administration of the pharmaceutical composition according to the present invention is not particularly limited, and may be in accordance with methods commonly used in the art. As a non-limiting example of the mode of administration, the composition may be administered by oral or parenteral administration. The pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention may be prepared in various formulations depending on the desired mode of administration.
본 발명의 조성물의 투여빈도는 특별히 이에 제한되지 않으나, 1일 1회 투여하거나 또는 용량을 분할하여 수회 투여할 수 있다.The frequency of administration of the composition of the present invention is not particularly limited, but may be administered once a day or several times in divided doses.
본 발명에서의 용어, '약학적으로 허용가능한 염'이란 투여되는 진세노사이드 Re의 생물학적 활성과 물성들을 손상시키지 않는 제형을 의미한다. 상기 약학적으로 허용가능한 염은, 약학적으로 허용되는 음이온을 함유하는 무독성 산부가염을 형성하는 산, 예를 들어, 염산, 황산, 질산, 인산, 브롬화수소산, 요드화수소산 등과 같은 무기산, 타타르산, 포름산, 시트르산, 아세트산, 트리클로로아세트산, 트리플로로아세트산, 글루콘산, 벤조산, 락트산, 푸마르산, 말레인산, 살리신산 등과 같은 유기 카본산, 메탄설폰산, 에탄술폰산, 벤젠설폰산, p-톨루엔설폰산 등과 같은 설폰산 등에 의해 형성된 산부가염이 포함된다. 예를 들어, 약학적으로 허용되는 카르복실산 염에는, 리튬, 나트륨, 칼륨, 칼슘, 마그네슘 등에 의해 형성된 금속염 또는 알칼리 토금속 염, 라이신, 아르지닌, 구아니딘 등의 아미노산 염, 디시클로헥실아민, N-메틸-D-글루카민, 트리스(히드록시메틸)메틸아민, 디에탄올아민, 콜린 및 트리에틸아민 등과 같은 유기염 등이 포함된다.As used herein, the term 'pharmaceutically acceptable salt' refers to a formulation that does not impair the biological activity and physical properties of the ginsenoside Re administered. The pharmaceutically acceptable salts are acids that form non-toxic acid addition salts containing pharmaceutically acceptable anions, such as inorganic acids, such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, and tartaric acid. Organic carbonic acid, such as formic acid, citric acid, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, gluconic acid, benzoic acid, lactic acid, fumaric acid, maleic acid, salicylic acid, methanesulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfate Acid addition salts formed by sulfonic acids and the like such as phonic acid and the like. For example, pharmaceutically acceptable carboxylic acid salts include metal salts or alkaline earth metal salts formed by lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, amino acid salts such as lysine, arginine, guanidine, dicyclohexylamine, N Organic salts such as -methyl-D-glucamine, tris (hydroxymethyl) methylamine, diethanolamine, choline and triethylamine and the like.
다른 하나의 양태로서, 본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re를 인간을 제외한 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료방법을 제공한다.In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for preventing or treating respiratory disease, comprising administering ginsenoside Re to a subject other than a human.
본 발명에서의 용어, “진세노사이드 Re”, “호흡기 질환”은 상기에서 설명한 바와 같다.The terms "ginsenoside Re" and "respiratory disease" in the present invention are as described above.
본 발명에서의 용어, "개체"란, 호흡기 질환이 발병되었거나 발병할 가능성이 있는 인간을 포함한 모든 동물을 의미할 수 있다. 상기 동물은 인간뿐만 아니라 이와 유사한 증상의 치료를 필요로 하는 소, 말, 양, 돼지, 염소, 낙타, 영양, 개, 고양이 등의 포유동물일 수 있으나, 이에 제한되지는 않는다.As used herein, the term "individual" may mean any animal, including a human, who has or is likely to develop a respiratory disease. The animal may be a mammal such as, but not limited to, a human, a cow, a horse, a sheep, a pig, a goat, a camel, a antelope, a dog, a cat, and the like, which require treatment of similar symptoms.
본 발명의 상기 예방 또는 치료 방법은 구체적으로, 호흡기 질환이 발병하였거나 발병할 위험이 있는 개체에 상기 조성물을 약학적으로 유효한 양으로 투여하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The prophylactic or therapeutic method of the present invention may specifically include administering the composition in a pharmaceutically effective amount to a subject having or at risk of developing a respiratory disease.
본 발명에서의 용어, "투여"는 어떠한 적절한 방법으로 환자에게 본 발명의 약학적 조성물을 도입하는 것을 의미하며, 본 발명의 조성물의 투여 경로는 목적 조직에 도달할 수 있는 한 경구 또는 비경구의 다양한 경로를 통하여 투여될 수 있다.The term "administration" in the present invention means introducing the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention to a patient in any suitable manner, and the route of administration of the composition of the present invention may be varied orally or parenterally as long as the target tissue can be reached. It can be administered via the route.
또 다른 하나의 양태로서, 본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선용 건강기능식품을 제공한다.As another aspect, the present invention provides a health functional food for the prevention or improvement of respiratory diseases containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
본 발명에서의 용어, “진세노사이드 Re”, “호흡기 질환”은 상기에서 설명한 바와 같다.The terms "ginsenoside Re" and "respiratory disease" in the present invention are as described above.
상기 진세노사이드 Re는 천연 물질로서 오랫동안 사용되어 안정성이 입증되었으므로, 상식할 수 있으면서도 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선을 도모할 수 있는 식품의 형태로 제조되어 섭취할 수 있다.Since ginsenoside Re has been used for a long time as a natural substance and has been proved to be stable, it can be prepared and consumed in the form of a food that can prevent or improve respiratory diseases while having common sense.
건강기능식품(functional food)이란, 특정보건용 식품(food for special health use, FoSHU)와 동일한 용어로, 영양 공급 외에도 생체조절기능이 효율적으로 나타나도록 가공된 의학, 의료효과가 높은 식품을 의미하는데, 상기 식품은 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선에 유용한 효과를 얻기 위하여 정제, 캡슐, 분말, 과립, 액상, 환 등의 다양한 형태로 제조될 수 있다.Functional food is the same term as food for special health use (FOSHU), and means foods that have high medical effects and medical effects that are processed so that their bioregulatory functions are efficiently displayed in addition to nutrition. In addition, the food may be prepared in various forms such as tablets, capsules, powders, granules, liquids, pills, etc. in order to obtain useful effects in preventing or improving respiratory diseases.
본 발명의 식품 조성물은 식품학적으로 허용가능한 담체를 추가로 포함하는 것일 수 있다.The food composition of the present invention may further comprise a food acceptable carrier.
본 발명의 진세노사이드 Re를 포함하는 조성물을 첨가할 수 있는 식품의 종류에는 별다른 제한이 없으며, 예를 들어 각종 음료, 껌, 차, 비타민 복합제, 건강보조 식품류 등이 있다. 상기 식품 조성물에는 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선 효과에 방해가 되지 않는 다른 성분을 추가할 수 있으며, 그 종류는 특별히 제한되지 않는다. 예를 들어, 통상의 식품과 같이 여러 가지 생약 추출물, 식품학적으로 허용가능한 식품보조첨가제 또는 천연 탄수화물 등을 추가 성분으로서 함유할 수 있다.There is no restriction | limiting in particular in the kind of food which can add the composition containing ginsenoside Re of this invention, For example, there are various drinks, a gum, tea, a vitamin complex, a dietary supplement, etc. The food composition may be added to other ingredients that do not interfere with the effect of preventing or improving respiratory diseases, the kind is not particularly limited. For example, various herbal extracts, food acceptable additives, natural carbohydrates, and the like may be contained as additional ingredients, such as conventional foods.
상기 식품보조첨가제는 각 제형의 건강기능식품을 제조하는데 첨가되는 것으로서 당업자가 적절히 선택하여 사용할 수 있다. 예를 들어 여러 가지 영양제, 비타민, 광물 (전해질), 합성 풍미제 및 천연 풍미제 등의 풍미제, 착색제 및 충진제, 펙트산 및 그의 염, 알긴산 및 그의 염, 유기산, 보호성 콜로이드 증점제, pH 조절제, 안정화제, 방부제, 글리세린, 알코올, 탄산음료에 사용되는 탄산화제 등이 포함되지만, 상기 예들에 의해 그 종류가 제한되는 것은 아니다.The food supplement additive is added to prepare the health functional food of each formulation can be used by those skilled in the art as appropriate. For example, various nutrients, vitamins, minerals (electrolytes), flavors such as synthetic and natural flavors, colorants and fillers, pectic acid and salts thereof, alginic acid and salts thereof, organic acids, protective colloidal thickeners, pH adjusters , Stabilizers, preservatives, glycerin, alcohols, carbonation agents used in the carbonated beverage, and the like, but the type is not limited by the above examples.
이때, 상기 식품에 포함되는 추출물의 함량은 특별히 이에 제한되지 않으나, 식품 조성물의 총 중량에 대하여 0.01 내지 100 중량%, 보다 바람직하게는 1 내지 80 중량%로 포함될 수 있다. At this time, the content of the extract included in the food is not particularly limited, but may be included in 0.01 to 100% by weight, more preferably 1 to 80% by weight relative to the total weight of the food composition.
식품이 음료인 경우에는 100㎖를 기준으로 1 내지 30g, 바람직하게는 3 내지 20g의 비율로 포함될 수 있다. 또한, 상기 조성물은 식품 조성물에 통상 사용되어 냄새, 맛, 시각 등을 향상시킬 수 있는 추가 성분을 포함할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 비타민 A, C, D, E, B1, B2, B6, B12, 니아신(niacin), 비오틴(biotin), 폴레이트(folate), 판토텐산(panthotenic acid) 등을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 아연(Zn), 철(Fe), 칼슘(Ca), 크롬(Cr), 마그네슘(Mg), 망간(Mn), 구리(Cu) 등의 미네랄을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 라이신, 트립토판, 시스테인, 발린 등의 아미노산을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 방부제(소르빈산 칼륨, 벤조산나트륨, 살리실산, 데히드로초산나트륨 등), 살균제(표백분과 고도 표백분, 차아염소산나트륨 등), 산화방지제(부틸히드록시아니졸(BHA), 부틸히드록시톨류엔(BHT) 등), 착색제(타르색소 등), 발색제(아질산 나트륨, 아초산 나트륨 등), 표백제(아황산나트륨), 조미료(MSG 글루타민산나트륨 등), 감미료(둘신, 사이클레메이트, 사카린, 나트륨 등), 향료(바닐린, 락톤류 등), 팽창제(명반, D-주석산수소칼륨 등), 강화제, 유화제, 증점제(호료), 피막제, 검기초제, 거품억제제, 용제, 개량제 등의 식품 첨가물(food additives)을 첨가할 수 있다. 상기 첨가물은 식품의 종류에 따라 선별되고 적절한 양으로 사용된다.When the food is a beverage, it may be included in a ratio of 1 to 30 g, preferably 3 to 20 g based on 100 ml. In addition, the composition may include additional ingredients that are commonly used in food compositions to improve the smell, taste, time and the like. For example, it may include vitamins A, C, D, E, B1, B2, B6, B12, niacin, biotin, folate, panthotenic acid, and the like. In addition, it may include minerals such as zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), chromium (Cr), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu). It may also contain amino acids such as lysine, tryptophan, cysteine, valine and the like. In addition, preservatives (potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, salicylic acid, sodium dehydroacetate, etc.), fungicides (bleaching powder and highly bleaching powder, sodium hypochlorite, etc.), antioxidants (butylhydroxyanisol (BHA), butylhydroxytoluene ( BHT), etc.), colorants (such as tar pigments), colorants (such as sodium nitrite, sodium nitrite), bleach (sodium sulfite), seasonings (such as MSG glutamate), sweeteners (ducin, cyclate, saccharin, sodium, etc.) Food additives such as flavors (vanillin, lactones, etc.), swelling agents (alum, potassium D-tartrate, etc.), reinforcing agents, emulsifiers, thickeners (pigments), coatings, gum herbicides, foam inhibitors, solvents, improvers, etc. ) Can be added. The additive is selected according to the type of food and used in an appropriate amount.
본 발명의 건강기능성 식품은 당업계에서 통상적으로 사용되는 방법에 의하여 제조가능하며, 상기 제조 시에는 당업계에서 통상적으로 첨가하는 원료 및 성분을 첨가하여 제조할 수 있다. 또한 일반 약품과는 달리 식품을 원료로 하여 약품의 장기 복용 시 발생할 수 있는 부작용 등이 없는 장점이 있고, 휴대성이 뛰어날 수 있다.The health functional food of the present invention can be prepared by a method commonly used in the art, and the preparation can be prepared by adding raw materials and ingredients commonly added in the art. In addition, unlike the general medicine has the advantage that there is no side effect that can occur when taking a long-term use of the drug with food as a raw material, can be excellent in portability.
또 다른 하나의 양태로서, 본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re를 유효성분으로 함유하는 밀착연접 붕괴 억제용 조성물을 제공한다.As another aspect, the present invention provides a composition for inhibiting close splice collapse, comprising ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
본 발명에서의 용어, “진세노사이드 Re”, “밀착연접”은 상기에서 설명한 바와 같다.The terms "ginsenoside Re" and "close contact" in the present invention are as described above.
본 발명에서의 용어, “붕괴 억제”는 단백질의 결합을 유지하여 분해를 억제하는 것을 의미할 수 있다.As used herein, the term “inhibition of disintegration” may mean inhibiting degradation by maintaining binding of a protein.
본 발명의 일 실시예에서는, 진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스를 감염시키고 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 측정한 결과, 대조군과 비교하여 밀착연접 단백질이 증가한 것을 확인하였다. 따라서, 본 발명은 진세노사이드 Re를 밀착연접 붕괴 억제용 조성물로 사용가능한 것을 시사할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the rhinoviruses were infected with non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with ginsenoside Re and the level of tight junction protein was measured. As a result, the tight junction protein was confirmed to be increased. Therefore, this invention can suggest that ginsenoside Re can be used as a composition for suppressing close splice collapse.
본 발명에 따른 조성물은 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 호흡기 질환의 증상들을 개선할 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명에 따른 조성물은 호흡기 질환의 예방 및 치료에 유용하게 사용될 수 있다.The composition according to the invention can ameliorate the symptoms of respiratory disease caused by rhinovirus infection. Therefore, the composition according to the present invention can be usefully used for the prevention and treatment of respiratory diseases.
도 1은 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스 감염 후 밀착연접 붕괴를 확인하기 위한 밀착연접 관련 단백질 측정 그래프이다; A. Occludion, B. ZO-1, C. Claudin, D. E-cadherin; RV 24~72h: 라이노바이러스 감염 후 배양 24~72시간.
도 2는 비점막 상피세포에 라이노바이러스 감염 후 ROS의 생성량을 확인하는 그래프이다; MEDIUM: 정상군, RV-16: 라이노바이러스 감염군.
도 3은 NOX 활성 억제제(DPI) 처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 ROS 생산량을 측정한 그래프이다; A. DPI 처리 후 ROS 생성량, B. 로테논 처리 후 ROS 생성량, C. DPI 처리 후 현미경을 이용한 ROS 생산량, MEDIUM: 정상군, RV-16: 라이노바이러스 감염군, DPI 25~50μM: DPI 25~50μM 처리군, Rotenone 15~30μM: 로테논 15~30μM 처리군.
도 4는 DPI 처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 측정한 그래프이다; A. ZO-1, B. E-cadherin, C. Occludin. D. Claudin; MEDIUM: 정상군, DPI 25~50μM: DPI 25~50μM 처리군, RV 72h: 라이노바이러스 감염 후 72시간 배양.
도 5는 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 및 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 확인한 그래프이다; A. 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 그래프, B. 인산화 타이로신 단백질 측정 그래프; Medium: 정상군, RV16(48h): 라이노바이러스 감염 후 48시간 배양, RV 24~72h: 라이노바이러스 감염 후 24~72시간 배양, p-tyrosine: 인산화 타이로신.
도 6은 DPI 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 및 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 나타낸 그래프이다; A. 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 그래프, B. 인산화 타이로신 단백질 측정 그래프; Medium: 정상군, DPI 25~50μM: DPI 25~50μM 처리군.
도 7은 인산 가수분해 효소 억제제(PAO) 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 및 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 나타낸 그래프이다; A. 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 그래프, B. 밀착연접 단백질 측정 그래프; PAO 1~500nM: PAO 1~500nM 처리군.
도 8은 진세노사이드 Re 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 나타낸 그래프이다; Re (50~100μg/ml): 진세노사이드 Re 50~100μg/ml 처리군.
도 9는 진세노사이드 Re 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 ROS 생성량을 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 10은 진세노사이드 Re 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 및 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 11은 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1 각각 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 밀착연접 단백질 수준을 나타낸 그래프이다; Rc (50~100μg/ml): 진세노사이드 Rc 50~100μg/ml 처리군, Rb1 (50~100μg/ml): 진세노사이드 Rb1 50~100μg/ml 처리군.
도 12는 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1 각각 전처리 후 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 ROS 생성량을 나타낸 그래프이다.1 is a graph of tight junction-related protein measurements to confirm tight junction collapse after rhinovirus infection in non-mucosal epithelial cells; A. Occludion, B. ZO-1, C. Claudin, D. E-cadherin; RV 24-72h: 24-72 hours of culture after rhinovirus infection.
Figure 2 is a graph confirming the amount of ROS generated after rhinovirus infection to non-mucosal epithelial cells; MEDIUM: normal group, RV-16: rhinovirus infected group.
Figure 3 is a graph measuring ROS production following rhinovirus infection after NOX activity inhibitor (DPI) treatment; A. ROS production after DPI treatment, B. ROS production after rotenone treatment, C. ROS production using microscope after DPI treatment, MEDIUM: normal group, RV-16: rhinovirus infection group, DPI 25-50μM: DPI 25 ~ 50 µM treatment group, Rotenone 15-30 µM: Rotenone 15-30 µM treatment group.
Figure 4 is a graph measuring tight junction protein levels following rhinovirus infection after DPI treatment; A. ZO-1, B. E-cadherin, C. Occludin. D. Claudin; MEDIUM: normal group, DPI 25-50 μM: DPI 25-50 μM treated group,
5 is a graph confirming the phosphatase activity and phosphorylated tyrosine protein level according to rhinovirus infection; A. phosphatase activity graph, B. phosphorylated tyrosine protein measurement graph; Medium: normal group, RV16 (48h): cultured 48 hours after rhinovirus infection, RV 24-72h: cultured 24-72 hours after rhinovirus infection, p-tyrosine: phosphorylated tyrosine.
6 is a graph showing phosphatase activity and phosphorylated tyrosine protein levels following rhinovirus infection after DPI pretreatment; A. phosphatase activity graph, B. phosphorylated tyrosine protein measurement graph; Medium: normal group, DPI 25-50 μM: DPI 25-50 μM treatment group.
7 is a graph showing phosphatase activity and tight junction protein levels following rhinovirus infection after phosphatase inhibitor (PAO) pretreatment; A. phosphatase activity graph, B. tightly coupled protein measurement graph; PAO 1-500 nM: PAO 1-500 nM treatment group.
Figure 8 is a graph showing the tight junction protein level following rhinovirus infection after ginsenoside Re pretreatment; Re (50-100 μg / ml): Ginsenoside Re 50-100 μg / ml treated group.
9 is a graph showing the amount of ROS produced by rhinovirus infection after ginsenoside Re pretreatment.
10 is a graph showing phosphatase activity and phosphorylated tyrosine protein levels following rhinovirus infection after ginsenoside Re pretreatment.
FIG. 11 is a graph showing tight junction protein levels following rhinovirus infection after pretreatment of ginsenosides Rc and Rb1, respectively; Rc (50-100 μg / ml): Ginsenoside Rc 50-100 μg / ml treated group, Rb1 (50-100 μg / ml): Ginsenoside Rb1 50-100 μg / ml treated group.
12 is a graph showing the amount of ROS produced by rhinovirus infection after pretreatment of ginsenosides Rc and Rb1, respectively.
이하, 본 발명을 실시예를 통하여 더욱 상세히 설명한다. 그러나 이들 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 것으로, 본 발명의 범위가 이들 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to Examples. However, these examples are for illustrating the present invention, and the scope of the present invention is not limited to these examples.
실시예Example 1. One. 비점막Nasal mucosa 상피세포 및 라이노바이러스의 준비 Preparation of Epithelial Cells and Rhinoviruses
비점막 상피세포에서 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 변화를 확인하기 위해 비점막 상피세포 및 라이노바이러스를 준비하였다. 비점막 상피세포의 경우, 하비갑개 수술을 시행하는 만성 비후성 비염환자로부터 하비갑개 (turbinate) 조직과 비용종 (nasal polyp) 조직을 얻은 뒤, 1% 프로나아제 (pronase)를 이용하여 비점막 상피세포를 분리하였다. 라이노바이러스의 경우, 헬라 세포 (HeLa cell)를 라이노바이러스 16 (RV-16)으로 감염시키고 세포병변효과 (CPE)가 형성될 때까지 33℃에서 7 내지 10일 동안 두고 바이러스 역가를 높이기 위해 농축하였다. 농축 후 50%의 헬라 세포를 감염시키기 위해 필요한 시료의 양 (50% tissue culture infection dose, TCID50)을 측정하였고 바이러스 역가는 Karber 공식을 이용하여 TCID50/ml로 나타내었다.Non-mucosal epithelial cells and rhinoviruses were prepared to identify changes in rhinovirus infection in non-mucosal epithelial cells. In the case of nasal mucosal epithelial cells, the nasal epithelial cells were obtained from chronic hypertrophic rhinitis patients who underwent inferior turbinate surgery, and then treated with 1% pronase using 1% pronase. Separated. For rhinoviruses, HeLa cells were infected with rhinovirus 16 (RV-16) and left at 33 ° C. for 7-10 days until cell lesion effect (CPE) was formed and concentrated to increase virus titer. . The amount of sample required to infect 50% HeLa cells after concentration (50% tissue culture infection dose, TCID 50 ) was measured and the virus titer was expressed as TCID 50 / ml using Karber's formula.
실험예Experimental Example 1. 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 변화 확인 1. Confirm changes due to rhinovirus infection
1-1. 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 밀착연접 단백질 변화 확인1-1. Confirmation of tight junction protein change by rhinovirus infection
라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 밀착연접 단백질의 변화를 확인하기 위해 라이노바이러스에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24 내지 72시간 동안 배양한 비점막 상피세포의 밀착연접 단백질을 추출하여 웨스턴 블롯을 수행하였다. In order to confirm the change in the tight junction protein caused by rhinovirus infection, Western blot was performed by extracting the tight junction protein of non-mucosal epithelial cells cultured for 24 to 72 hours at 37 ° C. and 5% CO 2. It was.
그 결과, 도 1에 나타낸 바와 같이, 라이노바이러스에 감염 후 시간이 경과함에 따라 밀착연접 단백질이 감소하는 것을 확인하였다. 이로부터, 라이노바이러스는 밀착연접 단백질을 해리시켜 밀착연접 붕괴를 일으키는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.As a result, as shown in Figure 1, it was confirmed that the tight junction protein decreases with time after infection with rhinovirus. From this, it was confirmed that the rhinovirus dissociated the tight junction protein to cause the tight junction collapse.
1-2. 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 1-2. Caused by rhinovirus infection 활성산소종Reactive oxygen species (( ROSROS ) 생산량 측정Output measurement
라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 ROS 생성량 증가를 확인하기 위해, BEGM 배지에 배양된 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시키고 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24시간 배양한 후 DCFDA 염료를 사용하여 유동세포계수법 및 현미경을 통해 ROS 생산량을 확인하였다.In order to confirm the increase in ROS production caused by rhinovirus infection, non-mucosal epithelial cells cultured in BEGM medium were infected with rhinovirus and incubated for 24 hours at 37 ° C. and 5% CO 2 , followed by flow cytometry and DCFDA dye. ROS production was confirmed through a microscope.
그 결과, 도 2에 나타낸 바와 같이, 24시간 배양 후 세포 내 ROS가 증가하여 라이노바이러스 감염이 ROS의 생산량을 증가시키는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.As a result, as shown in Figure 2, it was confirmed that the intracellular ROS increased after 24 hours of culture, rhinovirus infection increases the production of ROS.
실험예Experimental Example 2. 라이노바이러스 감염이 2. rhinovirus infection NADPHNADPH 산화효소( Oxidase ( NADPHNADPH oxidaseoxidase , , NOXNOX )에 미치는 영향 확인) Impact on
2-1. DPI 처리 후 2-1. After DPI processing ROSROS 생산량 변화 측정 Measure changes in production
NOX 억제제를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 ROS 생산이 억제될 수 잇는지 확인하기 위해, NOX 활성 억제제(DPI) 및 미토콘드리아 전자 전송 억제제인 로테논(rotenone)을 각각 비점막 상피세포에 전처리한 후 라이노바이러스를 감염시켜 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24시간 배양한 후 저해제에 따른 ROS 생성에 대한 차이를 확인하였다.After pretreatment of the NOX inhibitor, to determine whether ROS production by rhinovirus infection can be inhibited, the NOX activity inhibitor (DPI) and the mitochondrial electron transfer inhibitor rotenone (rotenone), respectively, were pretreated into the nasal mucosal epithelial cells, followed by rhino After infecting the virus and incubating at 37 ° C., 5% CO 2 for 24 hours, the difference in ROS production was determined.
그 결과, 도 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 저해제를 사용한 경우, 로테논 처리군은 바이러스 감염군과 차이가 없었으나, DPI 처리군은 라이노바이러스에 의해 증가한 ROS가 감소한 것을 확인하여 NOX의 활성이 ROS의 생성과 연관되어 있음을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Fig. 3, when the inhibitor was used, the rotenone treated group was not different from the virus infected group, but the DPI treated group confirmed that the ROS increased by the rhinovirus was decreased, indicating that NOX activity was increased by ROS. It was confirmed that it is associated with the production.
2-2. 2-2. NOXNOX 억제제 처리 후 밀착연접 단백질 변화 측정 Measurement of tight junction protein changes after inhibitor treatment
NOX의 억제제를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스에 의한 밀착연접 단백질의 감소를 억제할 수 있는지 확인하기 위해, 각각 농도별로 DPI를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포를 RV-16에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 72시간 동안 배양한 뒤 밀착연접 단백질을 추출하여 웨스턴 블롯을 수행하였다. After pretreatment of the inhibitor of NOX, to determine whether it is possible to suppress the decrease in the tight junction protein caused by rhinoviruses, 37 ° C., 5% CO after infecting RV-16 with non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with DPI for each concentration. After culturing for 72 hours at 2 conditions, the contact protein was extracted and Western blot was performed.
그 결과, 도 4에 나타낸 바와 같이, 라이노바이러스 감염시 감소되었던 밀착연접 단백질이 DPI 처리 후 증가하는 것을 확인하여 밀착연접의 붕괴는 NOX의 활성과 연관되어 있음을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 4, it was confirmed that the tight junction protein decreased during rhinovirus infection increased after DPI treatment, it was confirmed that the breakdown of the tight junction is associated with the activity of NOX.
실험예Experimental Example 3. 라이노바이러스 감염이 인산 가수분해효소 및 인산화 3. Rhinovirus Infection of Phosphorylase and Phosphorylation 타이로신Tyrosine 단백질에 미치는 영향 확인 Identify the impact on protein
3-1. 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 인산 가수분해효소 활성 및 인산화 3-1. Phosphorylase Activity and Phosphorylation by Rhinovirus Infection 타이로신Tyrosine 단백질 수준 측정 Protein level measurement
라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 인산 가수분해효소의 활성 및 인산화 타이로신의 단백질 수준을 측정하기 위해, BEGM 배지에 배양된 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시키고 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24 내지 72시간 동안 배양 후 인산 가수분해효소 활성 키트를 이용하여 인산 가수분해효소의 활성을 측정하였으며, 웨스턴 블롯을 이용하여 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 측정하였다.In order to determine the activity of phosphatase and protein level of phosphorylated tyrosine by rhinovirus infection, non-mucosal epithelial cells cultured in BEGM medium were infected with rhinovirus for 24 to 72 hours at 37 ° C., 5% CO 2 conditions. After incubation, the activity of phosphatase was measured using a phosphatase activity kit, and the phosphorylated tyrosine protein level was measured using a Western blot.
그 결과, 도 5에 나타낸 바와 같이, 라이노바이러스 감염시 인산 가수분해효소의 활성이 감소한 반면, 인산화 타이로신 단백질은 증가한 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in FIG. 5, the activity of phosphatase was decreased during rhinovirus infection, whereas the phosphorylated tyrosine protein was increased.
3-2. 3-2. NOXNOX 억제제 처리 후 인산 가수분해효소 활성 및 인산화 Phosphorylase Activity and Phosphorylation after Inhibitor Treatment 타이로신Tyrosine 단백질 수준 측정 Protein level measurement
NOX 억제제를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 변화한 인산 가수분해 활성 및 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수치에 영향을 주는지 확인하기 위해, 각각 농도별로 DPI를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 72시간 동안 배양한 뒤 인산 가수분해효소 활성 키트를 이용하여 인산 가수분해효소의 활성을 측정하였으며, 웨스턴 블롯을 이용하여 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 측정하였다.After pretreatment of NOX inhibitors, 37 ° C after infection of rhinovirus epithelial cells pre-treated with DPI at different concentrations to determine whether phosphatase activity and phosphorylated tyrosine protein levels changed by rhinovirus infection were affected. After culturing for 72 hours at 5% CO 2 condition, the activity of phosphatase was measured using a phosphatase activity kit, and the phosphorylated tyrosine protein level was measured using a Western blot.
그 결과, 도 6에 나타낸 바와 같이, NOX 억제제 처리군은 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 감소하였던 인산 가수분해효소 활성은 증가하였고, 증가하였던 인산화 타이로신 단백질은 감소한 것을 확인하여 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 인산 가수분해 효소 및 인산화 타이로신에 미치는 영향이 NOX 활성과 연관이 있음을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 6, the NOX inhibitor treatment group was confirmed that the phosphatase activity decreased by rhinovirus infection was increased, and that the increased phosphorylated tyrosine protein was decreased, the phosphatase according to rhinovirus infection And it was confirmed that the effect on phosphorylated tyrosine is associated with NOX activity.
3-3. 인산 가수분해효소 억제제 처리 후 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 및 밀착연접 단백질 변화 측정3-3. Measurement of phosphatase activity and changes in tight junction protein after phosphatase inhibitor treatment
인산 가수분해효소가 라이노바이러스 감염과 밀착연접 사이에 영향을 주는지 확인하기 위해, BEGM 배지에 배양된 비점막 상피세포에 인산 가수분해효소 저해제를 각 농도별로 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스에 감염시키고 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 48시간 동안 배양한 후, 인산 가수분해효소의 활성을 측정하고 밀착연접 단백질의 수준을 측정하였다.To determine whether phosphatase affects rhinovirus infection and tight junctions, pretreatment with phosphatase inhibitors at each concentration in non-mucosal epithelial cells cultured in BEGM medium, followed by infection with rhinovirus, After 48 hours of incubation at 5% CO 2 , the activity of phosphatase was measured and the level of tight junction protein was measured.
그 결과, 도 7에 나타낸 바와 같이, 인산 가수분해 효소의 활성은 감소하였으며, 밀착연접 단백질 수준도 감소한 것을 확인하여 라이노바이러스 감염에 따른 밀착연접 붕괴에 인산 가수분해 효소의 활성 또한 연관되어 있음을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 7, the activity of the phosphatase was decreased, confirming that the level of tight junction protein also decreased, confirming that the activity of phosphatase is also associated with the tight junction collapse due to rhinovirus infection. It was.
실험예 1 내지 3의 내용을 종합하면, 라이노바이러스 감염은 NOX의 활성을 유도하고 이는 ROS의 생성량을 증가시켜 인산 가수분해 효소의 활성을 감소시키며 인산화 타이로신 단백질을 증가시켜 최종적으로 밀착연접의 붕괴를 일으키는 것을 유추할 수 있었다.Incorporating the contents of Experimental Examples 1 to 3, rhinovirus infection induces NOX activity, which increases the amount of ROS produced, decreases the activity of phosphatase, increases phosphorylated tyrosine protein, and finally breaks the tight junction. I could infer what caused it.
실험예Experimental Example 4. 진세노사이드 Re에 따른 라이노바이러스 감염 증상 억제 효과 확인 4. Confirmation of ginsenoside Re according to the inhibitory effect of rhinovirus infection
4-1. 진세노사이드 Re 처리 후 밀착연접 단백질 변화 확인4-1. Changes in tight junction protein after ginsenoside Re treatment
진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스에 의한 밀착연접 단백질의 감소를 억제할 수 있는지 확인하기 위해, 각각 농도별로 진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 72시간 동안 배양한 뒤 밀착연접 단백질을 추출하여 웨스턴 블롯을 수행하였다. After pre-treatment with ginsenoside Re, to determine whether it is possible to suppress the decrease in the tight junction protein caused by rhinovirus, 37 ℃, After culturing for 72 hours at 5% CO 2 conditions, the contact protein was extracted and Western blot was performed.
그 결과, 도 8에 나타낸 바와 같이, 진세노사이드 Re 처리군은 라이노바이러스 감염시 감소되었던 밀착연접 단백질이 증가한 것을 확인하여 진세노사이드 Re가 라이노바이러스에 의한 밀착연접 붕괴를 억제한다는 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 8, the ginsenoside Re treatment group confirmed that the increase in the tight junction protein reduced during rhinovirus infection confirmed that the ginsenoside Re inhibits the tight junction collapse by the rhinovirus.
4-2. 진세노사이드 Re 처리 후 4-2. After Ginsenoside Re Treatment ROSROS 생성량 변화 확인 Confirmation of change in generation
진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 ROS 생산이 억제될 수 있는지 확인하기 위해, 진세노사이드 Re를 비점막 상피세포에 전처리한 후 라이노바이러스를 감염시켜 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24시간 동안 배양 후 ROS 생성량을 확인하였다.After pretreatment of ginsenoside Re, to determine whether ROS production by rhinovirus infection can be inhibited, pretreatment of ginsenoside Re to non-mucosal epithelial cells, followed by infection with rhinovirus at 37 ° C., 5% CO 2 conditions After culturing for 24 hours at ROS production was confirmed.
그 결과, 도 9에 나타낸 바와 같이, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 증가했던 ROS가 진세노사이드 Re 처리군에서는 감소하는 것을 확인하여 진세노사이드 Re가 라이노바이러스에 의한 ROS 생성량 증가를 억제한다는 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 9, it was confirmed that the ROS increased by rhinovirus infection decreased in the ginsenoside Re treatment group, confirming that ginsenoside Re inhibits the increase in ROS production by rhinoviruses.
4-3. 진세노사이드 Re 처리 후 인산 가수분해효소 활성 및 인산화 4-3. Phosphorylase Activity and Phosphorylation after Ginsenoside Re Treatment 타이로신Tyrosine 단백질 변화 확인 Identify protein changes
진세노사이드 Re를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 변화한 인산 가수분해 활성 및 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수치에 영향을 주는지 확인하기 위해, 각각 농도별로 진세노사이드Re를 전처리한 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 48 내지 72시간 동안 배양한 뒤 인산 가수분해효소 활성 키트를 이용하여 인산 가수분해효소의 활성을 측정하였으며, 웨스턴 블롯을 이용하여 인산화 타이로신 단백질 수준을 측정하였다.After pretreatment with ginsenoside Re, non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with ginsenoside Re for each concentration were examined for rhinoviruses to determine whether the phosphatase activity and phosphorylated tyrosine protein levels changed by rhinovirus infection. After infection, the cells were incubated for 48 to 72 hours at 37 ° C. and 5% CO 2 , and the phosphatase activity was measured using a phosphatase activity kit, and the phosphorylated tyrosine protein level was measured using a Western blot. It was.
그 결과, 도 10에 나타낸 바와 같이, 진세노사이드 Re 처리군은 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 감소하였던 인산 가수분해효소 활성은 증가하였고, 증가하였던 인산화 타이로신 단백질은 감소한 것을 확인하여 라이노바이러스에 의한 변화를 억제한 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 10, the ginsenoside Re treatment group was found to increase the phosphatase activity decreased by rhinovirus infection, increased phosphorylated tyrosine protein was reduced to suppress the change by rhinovirus It confirmed that it did.
실험예 4의 내용을 종합하면, 진세노사이드 Re의 처리로 인해, 라이노바이러스 감염 증상으로 나타났던 ROS 생성량 증가, 인산 가수분해 효소 활성 감소, 인산화 타이로신 단백질 증가 및 밀착연접 단백질 감소에 대해 개선 효과를 나타내어 진세노사이드 Re가 라이노바이러스 감염 증상 억제 효과를 갖는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이러한 내용은 진세노사이드 Re가 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 유발되는 호흡기 질환에 대한 예방 또는 치료효과를 가지는 것을 시사한다.According to the contents of Experimental Example 4, the treatment of ginsenoside Re improves ROS production, phosphatase activity, phosphorylated tyrosine protein, and tightly-coupled protein, which were shown as symptoms of rhinovirus infection. It was confirmed that ginsenoside Re has an inhibitory effect on rhinovirus infection symptoms. This suggests that ginsenoside Re has a prophylactic or therapeutic effect on respiratory diseases caused by rhinovirus infection.
비교예Comparative example 1. 다른 진세노사이드의 라이노바이러스 감염 증상 억제 효과 확인 1. Confirm the effect of inhibiting the symptoms of rhinovirus infection of other ginsenosides
1-1. 진세노사이드 1-1. Ginsenoside RcRc 및 And Rb1Rb1 처리 후 밀착연접 단백질 변화 확인 Confirmation of tight junction protein changes after treatment
진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1를 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 밀착연접 단백질 변화를 확인하기 위해, 각 농도별로 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1을 전처리한 비점막 상피세포를 라이노바이러스에 감염시킨 후 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 72시간 동안 배양한 뒤 밀착연접 단백질을 추출하여 웨스턴 블롯을 수행하였다.After pretreatment with ginsenosides Rc and Rb1, in order to confirm the change in the tight junction protein due to rhinovirus infection, non-mucosal epithelial cells pretreated with each ginsenoside Rc and Rb1 were infected with rhinovirus at 37 ° C., After culturing for 72 hours at 5% CO 2 conditions, the contact protein was extracted and Western blot was performed.
그 결과, 도 11에 나타낸 바와 같이, 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1의 처리군은 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 감소되었던 밀착연접 단백질의 변화가 없는 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 11, the treatment group of ginsenosides Rc and Rb1 confirmed that there is no change in the tight junction protein that was reduced by rhinovirus infection.
1-2. 진세노사이드 1-2. Ginsenoside RcRc 및 And Rb1Rb1 처리 후 After treatment ROSROS 생성량 변화 확인 Confirmation of change in generation
진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1을 전처리한 후, 라이노바이러스 감염에 의한 ROS 생산이 억제될 수 잇는지 확인하기 위해, 진세노사이드 Re를 비점막 상피세포에 전처리한 후 라이노바이러스를 감염시켜 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 24시간 동안 배양 후 ROS 생성량을 확인하였다.After pretreatment of ginsenosides Rc and Rb1, to determine whether ROS production by rhinovirus infection can be inhibited, pretreatment of ginsenoside Re into non-mucosal epithelial cells followed by infection of rhinoviruses at 37 ° C., 5% CO After culturing for 24 hours under 2 conditions, ROS production was confirmed.
그 결과, 도 12에 나타낸 바와 같이, 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1의 처리군은 라이노바이러스 감염에 의해 증가되었던 ROS 생성량의 변화가 없는 것을 확인하였다.As a result, as shown in Figure 12, the treatment group of ginsenosides Rc and Rb1 confirmed that there was no change in the amount of ROS production increased by rhinovirus infection.
이를 종합하면, 진세노사이드 Re는 라이노바이러스 감염 증상 억제 효과를 가져 감기, 인두염, 후두염과 같은 라이노바이러스에 의해 유발되는 호흡기 질환에 대한 예방 또는 치료효과를 가지는 반면, 진세노사이드 Rc 및 Rb1은 영향을 주지 않는 것으로 확인되어 진세노사이드 중에서도 진세노사이드 Re가 특이적으로 라이노바이러스에 의해 유발되는 호흡기 질환 예방 또는 치료용 약학적 조성물로 사용가능한 것을 확인할 수 있었다.Taken together, ginsenoside Re has the effect of suppressing rhinovirus infection symptoms and has a prophylactic or therapeutic effect against respiratory diseases caused by rhinoviruses such as colds, pharyngitis and laryngitis, whereas ginsenosides Rc and Rb1 have an effect. Ginsenoside Re was specifically found to be usable as a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of respiratory diseases caused by rhinoviruses.
이상의 설명으로부터, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 당업자는 본 발명이 그 기술적 사상이나 필수적 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 실시될 수 있다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 이와 관련하여, 이상에서 기술한 실시 예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적인 것이 아닌 것으로서 이해해야만 한다. 본 발명의 범위는 상기 상세한 설명보다는 후술하는 특허 청구범위의 의미 및 범위 그리고 그 등가 개념으로부터 도출되는 모든 변경 또는 변형된 형태가 본 발명의 범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 한다.From the above description, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the present invention can be implemented in other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features. In this regard, the embodiments described above are to be understood in all respects as illustrative and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention should be construed that all changes or modifications derived from the meaning and scope of the following claims and equivalent concepts rather than the detailed description are included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (8)
Pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of viral respiratory diseases caused by rhinoviruses comprising ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
상기 호흡기 질환은 감기, 인두염, 후두염을 포함하는 상기도 감염인 것인, 약학적 조성물.
The method of claim 1,
The respiratory disease is an upper respiratory tract infection, including colds, pharyngitis, laryngitis.
상기 진세노사이드 Re는 라이노바이러스에 의해 증가된 NOX의 활성을 억제하고 밀착연접의 붕괴를 억제하는 것인, 약학적 조성물.
The method of claim 1,
The ginsenoside Re is to inhibit the activity of NOX increased by rhinoviruses and inhibit the breakdown of the close junction, pharmaceutical composition.
A method for preventing or treating a viral respiratory disease caused by rhinoviruses, comprising administering the pharmaceutical composition of claim 1 to an individual other than a human.
상기 호흡기 질환은 감기, 인두염, 후두염을 포함하는 상기도 감염인 것인, 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 치료방법.
The method of claim 4, wherein
The respiratory disease is an upper respiratory tract infection including a cold, pharyngitis, laryngitis, method of preventing or treating respiratory disease.
Health functional food for the prevention or improvement of viral respiratory disease caused by rhinovirus containing ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
상기 호흡기 질환은 감기, 인두염, 후두염을 포함하는 상기도 감염인 것인, 호흡기 질환의 예방 또는 개선용 건강기능식품.
The method of claim 6,
The respiratory disease is an upper respiratory tract infection including a cold, pharyngitis, laryngitis, health functional foods for the prevention or improvement of respiratory diseases.
A tight junction decay suppression composition comprising ginsenoside Re as an active ingredient.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046262A KR20190122453A (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046262A KR20190122453A (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190122453A true KR20190122453A (en) | 2019-10-30 |
Family
ID=68462990
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046262A KR20190122453A (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20190122453A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021203038A1 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2021-10-07 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Delivery of ginsenosides to the respiratory system via electronic breath actuated droplet delivery device |
| US11285274B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for the systemic delivery of therapeutic agents to the pulmonary system using a droplet delivery device |
| US11285284B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for treatment of pulmonary lung diseases with improved therapeutic efficacy and improved dose efficiency |
| US11285283B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for generating and delivering droplets to the pulmonary system using a droplet delivery device |
| US11285285B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Systems and methods comprising a droplet delivery device and a breathing assist device for therapeutic treatment |
| US11458267B2 (en) | 2017-10-17 | 2022-10-04 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Nasal drug delivery apparatus and methods of use |
| US11529476B2 (en) | 2017-05-19 | 2022-12-20 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Dry powder delivery device and methods of use |
| US11738158B2 (en) | 2017-10-04 | 2023-08-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Electronic breath actuated in-line droplet delivery device and methods of use |
| US11771852B2 (en) | 2017-11-08 | 2023-10-03 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Electronic breath actuated in-line droplet delivery device with small volume ampoule and methods of use |
| US11793945B2 (en) | 2021-06-22 | 2023-10-24 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Droplet delivery device with push ejection |
-
2018
- 2018-04-20 KR KR1020180046262A patent/KR20190122453A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11285274B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for the systemic delivery of therapeutic agents to the pulmonary system using a droplet delivery device |
| US11285284B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for treatment of pulmonary lung diseases with improved therapeutic efficacy and improved dose efficiency |
| US11285283B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Methods for generating and delivering droplets to the pulmonary system using a droplet delivery device |
| US11285285B2 (en) | 2016-05-03 | 2022-03-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Systems and methods comprising a droplet delivery device and a breathing assist device for therapeutic treatment |
| US11529476B2 (en) | 2017-05-19 | 2022-12-20 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Dry powder delivery device and methods of use |
| US11738158B2 (en) | 2017-10-04 | 2023-08-29 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Electronic breath actuated in-line droplet delivery device and methods of use |
| US11458267B2 (en) | 2017-10-17 | 2022-10-04 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Nasal drug delivery apparatus and methods of use |
| US11771852B2 (en) | 2017-11-08 | 2023-10-03 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Electronic breath actuated in-line droplet delivery device with small volume ampoule and methods of use |
| WO2021203038A1 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2021-10-07 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Delivery of ginsenosides to the respiratory system via electronic breath actuated droplet delivery device |
| US11793945B2 (en) | 2021-06-22 | 2023-10-24 | Pneuma Respiratory, Inc. | Droplet delivery device with push ejection |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20190122453A (en) | A pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of respiratory disease comprising Ginsenoside Re | |
| US10960040B2 (en) | Composition for preventing and treating muscle diseases or improving muscular function, containing platycodon grandiflorum extract | |
| KR101078376B1 (en) | Composition for preventing and treating obesity comprising piperine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as an active ingredient | |
| US20100124537A1 (en) | Medical applications of alpha-ketoglutarate | |
| US20120251490A1 (en) | Compositions And Methods For Immunotherapy | |
| JPH03501126A (en) | Compositions that suppress the development of pathological craving for alcohol | |
| Shengyu et al. | Selenium alleviates heart remodeling through Sirt1/AKT/GSK-3β pathway | |
| Xia et al. | Lactobacillus plantarum AR113 attenuates liver injury in D-galactose-induced aging mice via the inhibition of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress | |
| JP6944221B2 (en) | Composition for prevention, amelioration or treatment of bone loss disease containing CHP (cyclo-hispro) | |
| EP3903589A2 (en) | Kimchi for preventing or treating helicobacter pylori-associated diseases | |
| WO2003082308A1 (en) | Drugs including anticancer agents and immunopotentiators and health foods and drinks | |
| KR20040074696A (en) | Scrophularia buergeriana extract with anti-aging activity and a composition containing the extract | |
| US20160113955A1 (en) | Compositions And Methods For Immunotherapy | |
| CN105853399B (en) | Application of the patchouli alcohol in the drug for preparing treatment chronic gastritis | |
| KR101762798B1 (en) | Antibacterial pharmaceutical composition against Salmonella spp. comprosong glue extract | |
| KR101823997B1 (en) | Beverage comprising extract of Korean Maca for improving erectile dysfunction | |
| KR20210003614A (en) | A composition for the improving, preventing and treating of influenza virus infection comprising polysaccharide fraction isolated from persimmon leaf | |
| US20240307348A1 (en) | Composition for preventing and treating muscle disease, improving muscle function or enhancing motor performance comprising hydrangenol or hydrangea extract as active ingredient | |
| RU2781828C1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition with adaptogenic activity | |
| KR102483814B1 (en) | Compositions for Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Effect Comprising Oil of Ulvoid green algae | |
| KR102115353B1 (en) | Composition comprising chp (cyclo-his pro) and pth for preventing, improving or treating of bone loss related disease | |
| KR102517569B1 (en) | A lactic acid bacterium from Dokdo shrimp and a composition comprising thereof | |
| KR101847479B1 (en) | Composition for prevention or treatment of trychophytia comprising Dalbergia odorifera extract | |
| KR102059452B1 (en) | Composition comprising the extract of Patriniae Radix for preventing and treating Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | |
| EP3964228A1 (en) | Composition for preventing or treating obesity, comprising phospholipase a2 as active ingredient |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |