KR20190093478A - Converter and its control apparatus - Google Patents
Converter and its control apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20190093478A KR20190093478A KR1020180026765A KR20180026765A KR20190093478A KR 20190093478 A KR20190093478 A KR 20190093478A KR 1020180026765 A KR1020180026765 A KR 1020180026765A KR 20180026765 A KR20180026765 A KR 20180026765A KR 20190093478 A KR20190093478 A KR 20190093478A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- current
- converter
- parallel operation
- voltage
- control
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 abstract 2
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 22
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1584—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1584—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel
- H02M3/1586—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel switched with a phase shift, i.e. interleaved
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02S—GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER BY CONVERSION OF INFRARED RADIATION, VISIBLE LIGHT OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT, e.g. USING PHOTOVOLTAIC [PV] MODULES
- H02S40/00—Components or accessories in combination with PV modules, not provided for in groups H02S10/00 - H02S30/00
- H02S40/30—Electrical components
-
- H02M2003/1586—
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/56—Power conversion systems, e.g. maximum power point trackers
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Dc-Dc Converters (AREA)
Abstract
Description
전 세계적으로 또는 국가적으로 무공해(無公害)의 전력생산에 대한 요구가 증대되고 있으며, 원자력 및 화력 발전을 대체하는 방안으로 태양광 발전에 대한 관심이 증대되고 있다. 본 발명은 태양전지에서 생산된 전력을 저전압-대전류의 직류(DC) 부하(Load)에 전달하기 위한 태양광 전력변환 장치에 관한 것이며, 대전류 방식에서 직류(DC) 부하(Load)의 전압 리플을 저감시키며, 효율을 개선시키기 위하여 3상 인터리브드(Interleaved) 방식의 컨버터 및 이의 제어장치에 관한 것이다.There is an increasing demand for pollution-free power generation globally or nationally, and interest in solar power is increasing as a way to replace nuclear and thermal power generation. BACKGROUND OF THE
최근 신재생 에너지에 대한 관심이 증대되며, 태양광 패널(Solar Panel)은 태양 빛을 전기적인 에너지로 변화시키는 기능을 수행하는 장치이다.Recently, interest in renewable energy is increasing, and a solar panel is a device that performs a function of converting sunlight into electrical energy.
도 1은 태양광 발전의 원리를 나타낸다. 태양광 패널(Solar Panel)이란 광전효과(光電效果)를 이용하여 태양 빛을 전기에너지로 변환시키는 반도체 소자를 나타낸다. 상기 광전효과(光電效果)는 금속과 반도체의 접촉면 또는 반도체의 p-n 전합에 태양 빛을 받으면, 반도체 중에 전자(電子)와 정공(正孔)이 형성된다. 상기 전자는 전면전극으로 이동하며, 상기 정공은 후면전극으로 이동하게 된다. 이를 통하여 상기 전면전극과 상기 후면전극은 전압 차가 생성되며, 전기부하로 상기 전자 및 전공은 이동하게 된다. 일반적으로 전류의 흐름은 정공의 이동방향으로 규정되어 있기 때문에, 전기적으로 후면전극을 (+)전압이 발생하며, 전면전극을 (-)전압이 발생하게 된다.1 shows the principle of solar power generation. Solar panel refers to a semiconductor device that converts sunlight into electrical energy using a photoelectric effect. In the photoelectric effect, electrons and holes are formed in the semiconductor when the solar light is applied to the contact surface of the metal and the semiconductor or the p-n junction of the semiconductor. The electrons move to the front electrode, and the holes move to the back electrode. As a result, a voltage difference is generated between the front electrode and the rear electrode, and the electrons and the electrons are moved by an electric load. In general, since the flow of current is defined in the direction of movement of holes, a positive voltage is generated on the rear electrode and a negative voltage is generated on the front electrode.
태양전지 또는 직류전원으로부터 전력을 변환시키는 방식에 대하여 기존에 다양한 발명이 진행되었다.Various inventions have been made in the related art for converting electric power from a solar cell or a direct current power source.
관련된 선행문헌으로는 대한민국 등록특허공보 제10-1304777호, 공고일 2013. 09. 05.(이하 [특허문헌1]이라함)에서는 넓은 입력전압 제어범위를 갖는 직류-직류 컨버터를 공개하였다. 상기 [특허문헌1]에서는 넓은 입력범위를 갖는 태양전지에서 발생된 전기에너지를 부하에 전달하기 위하여 인터리브드 플라이백 컨버터(Interleaved Flyback Converter)와 LLC 공진형 컨버터를 결합시켜 넓은 입력전압 범위에서 안정적인 출력 전압을 생성시키는 직류-직류 컨버터를 공개하였다.In related prior documents, Korean Patent Publication No. 10-1304777, Publication Date 2013. 09. 05. (hereinafter referred to as [Patent Document 1]) discloses a DC-DC converter having a wide input voltage control range. In [Patent Document 1], a stable output in a wide input voltage range by combining an interleaved flyback converter and an LLC resonant converter in order to transfer electrical energy generated from a solar cell having a wide input range to a load. A DC-DC converter for generating a voltage is disclosed.
또 다른 선행문헌으로는 대한민국 공개특허공보 제10-2018-0003122호, 공개일 2018.01.09.(이하 [특허문헌2]이라함)에서는 인터리브드 LLC 공진형 컨버터 및 그 제어방법을 제안하였다. 상기 [특허문허2]에서는 풀브리지 회로로 구성된 LLC 공진형 컨버터가 N개 병렬로 운전하며, 전력을 부하에 공급하는 공진형 컨버터 및 그 제어방식에 대하여 공개하였다.As another prior document, Korean Unexamined Patent Publication No. 10-2018-0003122, Publication No. 2018.01.09. (Hereinafter referred to as [Patent Document 2]) has proposed an interleaved LLC resonant converter and its control method. [Patent Document 2] discloses a resonant converter and a control method thereof in which an LLC resonant converter composed of a full bridge circuit is operated in N parallel and supplies power to a load.
하지만, 기존의 상기 [특허문헌1] 및 [특허문헌2]에서는 인터리브드 컨버터 방식을 제안하였지만, 태양전지에서 생성된 에너지를 저전압-대전류 방식에 최적화 되지 못하는 문제점이 있었다.However, although the existing [Patent Documents 1] and [Patent Documents 2] proposed the interleaved converter method, there was a problem in that energy generated in the solar cell was not optimized for the low voltage-high current method.
본 발명에서는 태양전지에서 생산된 전력을 저전압-대전류의 직류(DC) 부하(Load)에 전달하기 위한 컨버터 및 이의 제어장치를 제안하고자 한다. 저전압-대전류의 출력에 적합하기 위하여 3상 인터리브드 방식을 적용하였다. 더불어 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 안정적인 제어를 위하여 6개의 스위치로 구성되며, 단일 코어(Core)로 구성된 자기적인 결합(44)을 이용하여 안정적인 정류 공급을 수행하며, 새롭게 제안하는 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식을 이용하여 태양전지에서 생산된 전력을 저전압-대전류의 직류(DC) 부하(Load)에 가장 안정적으로 전력을 공급할 수 있는 장치를 제공하고자 한다.The present invention proposes a converter and a control device thereof for transferring the power produced in a solar cell to a direct current (DC) load of a low voltage-high current. Three-phase interleaved method is applied to suit low-voltage-current output. In addition, it is composed of six switches for stable control of three-phase interleaved solar converter, and performs stable rectification supply by using
본 발명에서는 저전압-대전류 방식에 적합한 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 및 이의 제어장치를 위하여, 첫째, 6개의 스위치로 구성된 3상 인터리브드 회로를 제안하였다. 3상 인터리브드 회로는 3개의 전원장치가 교번(交番)으로 동작하여 전력을 공급하며, 출력전류 리플을 최대한 저감시키는 장점을 지니고 있으며, 둘째, 단일 코어(Core)로 구성된 자기적인 결합(44)을 이용하기 때문에 회로에서 사용되는 인덕터(Inductor)의 수를 최소로 저감시키며, 셋째, 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식을 도입하여 가장 최적의 전류제어를 통하여 안정적인 전류제어가 가능한 저전압-대전류 방식에 적합한 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 및 이의 제어장치를 제공하는 것을 과제의 해결수단으로 한다.In the present invention, first, a three-phase interleaved circuit composed of six switches has been proposed for a three-phase interleaved solar converter and a control device thereof suitable for a low voltage-high current method. Three-phase interleaved circuits have the advantage that the three power supplies operate in alternating fashion to provide power and to minimize output current ripple. Second, magnetic coupling consisting of a single core (44). Since the number of inductors used in the circuit is reduced to a minimum, third, the average current and the maximum current variable control method are introduced, and the low voltage-high current method enables stable current control through the most optimal current control. It is a solution to the problem to provide a suitable three-phase interleaved solar converter and a control device thereof.
본 발명에서는 제안하는 저전압-대전류 방식에 적합한 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터를 통하여 첫째, 3상 인터리브드 회로는 3개의 전원장치가 교번(交番)으로 동작하여 전력을 공급하며, 출력전류 리플을 최대한 저감시키는 효과가 있으며, 둘째, 단일 코어(Core)로 구성된 자기적인 결합(44)을 이용하였기 때문에 코어(Core)의 수를 최소로 하는 효과가 있으며, 셋째, 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식을 도입하여 가장 최적의 전류제어를 통하여 안정적인 전류제어가 가능하며, 넷째, 정밀한 전류 및 전압제어기의 도입을 통하여 수십[A] 내지 수백[A]의 대전류 출력에서도 안정적인 출력이 가능하며, 다섯째, 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 필요한 경우, 즉 중부하[Heavy Load: 출력전류가 정격(政格) 전류의 50% 이상이 되는 부하]에서 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에 전류가 평균적으로 제어가 수행되며, 전체적으로 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에서 전류의 균형을 맞출 수 있으며, 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 요구되지 않는 경우, 즉 경부하[Light Load: 출력전류가 정격(政格) 전류의 50% 미만이 되는 부하]에서는 최대전류 모드로 동작하는 상승된 효과가 있다.In the present invention, the three-phase interleaved photovoltaic converter suitable for the low voltage-to-current method proposed by the present invention. First, three-phase interleaved circuit supplies power by alternating three power supplies and maximizes output current ripple. Secondly, since the
도 1은 태양광 발전 원리
도 2는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 개념도
도 3은 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 회로도
도 4는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 세부 회로도
도 5는 단일 코어를 이용한 자기적인 결합
도 6은 제1 전압제어기 형태
도 7은 제2 전압제어기 형태
도 8은 제3 전압제어기 형태
도 9는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류제어 방식
도 10은 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 최대전류제어 방식
도 11은 제안된 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식1 is the principle of photovoltaic power generation
2 is a conceptual diagram of a three-phase interleaved solar converter
3 is a three-phase interleaved solar converter circuit diagram
4 is a detailed circuit diagram of a three-phase interleaved solar converter.
5 is a magnetic coupling using a single core
6 is a first voltage controller form
7 is a second voltage controller form
8 is a third voltage controller form
9 is an average current control method of the three-phase interleaved solar converter
10 is the maximum current control method of the three-phase interleaved solar converter
11 is a variable control method of average current and maximum current of the proposed three-phase interleaved solar converter
본 발명을 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 2는 본 발명에서 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 개념도를 나타낸다.2 shows a conceptual diagram of a three-phase interleaved solar converter in the present invention.
상기 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 개념도(도 3)에서는 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)이 위치되어 있으며, 상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)은 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)이 모두 병렬로 연결되어 있으며, 상기 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)의 (+) 단자에서는 제1 내지 제5 역전압 방지 다이오드(21 내지 25)가 배치되어 있다.In the conceptual diagram of the three-phase interleaved solar converter (FIG. 3),
상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)의 출력은 입력 커패시터(27)에 의해서 평활되며, 인터리브드(Interleaved) 방식으로 제어되는 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)를 통하여 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전력을 전달한다. 주 제어부(70)는 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 전류 정보를 검출받으며, 상기 출력전압 검출부(58)로부터 출력 전압 정보를 검출받아서 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 스위치(S1,S2,S3)를 제어하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.The outputs of the
도 3은 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 회로도를 나타낸다.3 shows a circuit diagram of a three-phase interleaved solar converter.
상기 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 회로도(도 3)에서는 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)이 위치되어 있으며, 상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)은 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)이 모두 병렬로 연결되어 있으며, 상기 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)의 (+) 단자에서는 제1 내지 제5 역전압 방지 다이오드(21 내지 25)가 배치되어 있다.In the three-phase interleaved solar converter circuit diagram (FIG. 3),
상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)의 출력은 입력 커패시터(27)에 의해서 평활되며, 인터리브드(Interleaved) 방식으로 제어되는 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)를 통하여 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전력을 전달한다. 주 제어부(70)는 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 전류 정보를 검출받아서 주 제어부(70)의 전류 검출부(72)로 입력된다. 또한 상기 주 제어부(70)는 출력전압 검출부(58)로부터 출력 전압 정보를 검출받아서 제1,2 제어이득(Z1,Z2)(60,61)의 증폭을 통하고, 주 제어부(70)의 전압 검출부(73)로 입력된다.The outputs of the
상기 주 제어부(70)는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 제어기(도 3)를 통하여 주 스위치 구동부(71)에서 3상 인터리브드 전력변환 회로부(300)의 각 스위치를 제어하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.The
무엇보다 본 발명에서는 인덕터(코어)의 수를 최소화 하며, 출력 전류리플을 저감시키기 위하여 제1 내지 제3 인덕터(41 내지 43)는 하나의 코어에 자기적인 결합(44)을 하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다. 단일 코어(Core)로 구성된 자기적인 결합(44)을 이용하였기 때문에 코어(Core)의 수를 최소로 하는 상승된 효과가 있다.Above all, in the present invention, in order to minimize the number of inductors (cores) and to reduce output current ripple, the first to
도 4는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 세부 회로도를 나타낸다.4 shows a detailed circuit diagram of a three-phase interleaved solar converter.
상기 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 회로도(도 4)에서는 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)이 위치되어 있으며, 상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)은 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)이 모두 병렬로 연결되어 있으며, 상기 제1 내지 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)(11 내지 15)의 (+) 단자에서는 제1 내지 제5 역전압 방지 다이오드(21 내지 25)가 배치되어 있다.In the three-phase interleaved solar converter circuit diagram (FIG. 4),
상기 병렬로 연결된 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)의 출력은 입력 커패시터(27)에 의해서 평활되며, 인터리브드(Interleaved) 방식으로 제어되는 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)를 통하여 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전력을 전달한다. 주 제어부(70)는 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 전류 정보를 검출받아서 주 제어부(70)의 전류 검출부(72)로 입력된다. 또한 상기 주 제어부(70)는 출력전압 검출부(58)로부터 출력 전압 정보를 검출받아서 제1,2 제어이득(Z1,Z2)(60,61)의 증폭을 통하고, 주 제어부(70)의 전압 검출부(73)로 입력된다.The outputs of the
상기 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터 세부 회로도(도 4)에서 상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력인 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출정보는 전류 검출부(72)를 통하여 전류 제어부(220)을 통하여 기준 전류값(iref)과 비교된다. 상기 전류 제어부(220)에서 상기 제1 전류 비교기(221)는 제1 출력전류(io1)와 기준 전류값(iref)을 비교하며, 상기 제2 전류 비교기(222)는 제2 출력전류(io2)와 기준 전류값(iref)을 비교하며, 제3 전류 비교기(223)는 제3 출력전류(io1)와 기준 전류값(iref)을 비교한다. First to third outputs that are outputs of the first to
또한, 출력전압(Vo)를 제1,2 전압검출 저항(54,55)를 통하여 검출된 전압은 제1,2 제어이득(Z1,Z2)(60,61)의 증폭을 통하고, 주 제어부(70)의 전압 검출부(73)로 입력된다. 전압 제어부(210)는 출력제어를 위한 기준 전압(Vref1)과 비교하여 제1,2 제어이득(Z1,Z2)(60,61)의 증폭을 통하여 제어전압(Vc)을 출력된다.In addition, the voltage detected from the output voltage Vo through the first and second
게이트 신호 생성부(240)는 상기 전압 제어부(210)에서 출력된 제어전압(Vc) 및 제1 내지 제3 전류 비교기(221 내지 223)의 출력이 입력된다. 상기 게이트 신호 생성부(240)의 제1, 제3, 제5 제어 비교기는 전압 제어부(210)에서 출력된 제어전압(Vc)과 제1 내지 제3 전류 비교기(221 내지 223)의 출력과 비교한다.The
또한, 제2 제어 비교기는 제1 전류 비교기(221)의 출력과 제1 컨버터 기준 전류값(IrefA)을 비교하며, 상기 제4 제어 비교기는 제2 전류 비교기(222)의 출력과 제2 컨버터 기준 전류값(IrefB)을 비교하며, 상기 제6 제어 비교기는 제3 전류 비교기(223)의 출력과 제3 컨버터 기준 전류값(IrefC)을 비교한다.The second control comparator compares the output of the first
또한, 제1 제어 OR 게이트(247)는 제1 제어 비교기(241)의 출력과 제2 제어 비교기(242)의 출력을 OR 조건으로 출력하며, 제2 제어 OR 게이트(248)는 제3 제어 비교기(243)의 출력과 제4 제어 비교기(244)의 출력을 OR 조건으로 출력하며, 제3 제어 OR 게이트(249)는 제5 제어 비교기(245)의 출력과 제6 제어 비교기(246)의 출력을 OR 조건으로 출력함을 통하여 게이트 신호를 생성하게 됨을 기술적 특징으로 한다.In addition, the first control OR
제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 각 스위치 제어를 위하여 상기 게이트 신호 생성부(240)의 상기 제1 내지 제3 제어 OR 게이트(247 내지 249)의 출력은 RS 플립플롭(260)에서 제1 RS 플립플롭(261)은 제1 OR 게이트(247)의 출력과 제1 발진기 펄스(PH1)가 입력되어 상기 제1 RS 플립플롭(261)에서 게이트 신호가 출력되며, 제2 RS 플립플롭(262)은 제2 OR 게이트(248)의 출력과 제2 발진기 펄스(PH2)가 입력되어 상기 제2 RS 플립플롭(261)에서 게이트 신호가 출력되며, 제3 RS 플립플롭(263)은 제3 OR 게이트(249)의 출력과 제3 발진기 펄스(PH3)가 입력되어 상기 제3 RS 플립플롭(263)에서 게이트 신호가 출력된다. 또한, 상기 게이트 신호들은 게이트 구동부(270)를 통하여 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 각 스위치를 구동하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.In order to control each switch of the first to
또한, 과전압 및 과전류 보호부(230)에서는 과전압 및 과전류 보호 비교기(231)을 통하여 출력전압 또는 출력전류가 과전압 및 과전류 제어를 위한 기준 전압(Vref2) 이상인 경우 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 모든 스위치 오프(off)시키는 FAULT 신호를 생성시키므로 상기 저전압-대전류 방식에 적합한 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터를 보호하는 상승된 효과가 있다.In addition, the overvoltage and
도 5는 단일 코어를 이용한 자기적인 결합을 나타낸다.5 shows magnetic coupling using a single core.
단일 코어를 이용한 자기적인 결합(도 5)에서는 각각의 코어 레그(Lag)에 권선을 감으며, 제1 내지 제3 인덕터(41 내지 43)가 자기적인 결합(44)를 형성시키는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.In the magnetic coupling using a single core (FIG. 5), a winding is wound around each core leg, and the first to
도 6 내지 도 8은 제1 내지 제3 전압제어기 형태를 나타낸다.6 to 8 illustrate the first to third voltage controller types.
상기 제1 전압제어기(도 6)는 제1 제어이득(Z1)(60)은 제1 제어저항(R1)으로 구성되며, 제2 제어이득(Z2)(61)은 제11 제어저항(R11) 및 제11 제어 커패시터(C11)가 직렬로 연결되며 상기 제11 제어저항(R11) 및 제11 제어 커패시터(C11)와 병렬로 제12 제어 커패시터(C12)가 구성하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In the first voltage controller (FIG. 6), the first control gain (Z1) 60 is composed of the first control resistor (R1), and the second control gain (Z2) 61 is the eleventh control resistor (R11). And an eleventh control capacitor C11 is connected in series, and a twelfth control capacitor C12 is configured in parallel with the eleventh control resistor R11 and the eleventh control capacitor C11.
상기 제2 전압제어기(도 7)는 제1 제어이득(Z1)(60)은 제1 제어저항(R1) 및 제1 커패시터(C1)가 병렬로 연결되며, 상기 제1 제어저항(R1) 및 제1 커패시터(C1)와 직렬로 제2 제어저항(R2)로 구성되며, 제2 제어이득(Z2)(61)은 제11 제어저항(R11)과 제11 제어 커패시터(C11)가 직렬로 연결되어 구성되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In the second voltage controller (FIG. 7), a first control gain (Z1) 60 is connected to a first control resistor (R1) and a first capacitor (C1) in parallel, and the first control resistor (R1) and A second control resistor (R2) in series with the first capacitor (C1), the second control gain (Z2) 61 is connected to the eleventh control resistor (R11) and the eleventh control capacitor (C11) in series. It is characterized in that the configuration.
상기 제3 전압제어기(도 8)는 제1 제어이득(Z1)(60)은 제1 제어저항(R1)과 병렬로 제2 제어저항(R2) 및 제1 커패시터(C1)로 구성되며, 제2 제어이득(Z2)(61)은 제11 제어저항(R11)과 제11 제어 커패시터(C11)가 직렬로 연결되며, 상기 제11 제어저항(R11)과 제11 제어 커패시터(C11)와 병렬로 제12 제어 커패시터(C12)가 배치되어 구성되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In the third voltage controller (FIG. 8), the first control gain (Z1) 60 includes a second control resistor R2 and a first capacitor C1 in parallel with the first control resistor R1. The second control gain (Z2) 61 is connected to the eleventh control resistor (R11) and the eleventh control capacitor (C11) in series, in parallel with the eleventh control resistor (R11) and the eleventh control capacitor (C11). The twelfth control capacitor C12 is disposed and configured.
도 9는 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류제어 방식을 나타낸다.9 shows an average current control method of a three-phase interleaved solar converter.
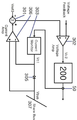
제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하고, 공유함을 통하여 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)을 형성하게 된다.First to third outputs of the first to
3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)의 출력은 전류센서(50)로부터 특정(特定) 컨버터의 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303)를 통하여 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하며, 상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 병렬운전 저항(304)를 배치하고, 상기 병렬운전 저항(304)의 양단저항의 전압을 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)를 센싱함을 통하여 그 오차를 검출하게 된다. 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)는 상기 공유버스 전압(Vbus)과 상기 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)의 오차를 검출하여 저감하는 방식이기 때문에 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류제어 방식이라고 한다.The output of the three-phase interleaved
또한 병렬운전 덧셈부(301)에서 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)와 병렬운전 기준전압(Vref3)의 오차를 출력하며, 병렬운전 전압 비교부(302)를 통하여 최종적으로 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)를 제어하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
도 10은 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 최대전류제어 방식을 나타낸다.10 shows the maximum current control method of the three-phase interleaved solar converter.
제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하고, 공유함을 통하여 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)을 형성하게 된다.First to third outputs of the first to
3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)의 출력은 전류센서(50)로부터 특정(特定) 컨버터의 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303)를 통하여 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하며, 상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 병렬운전 다이오드(305)를 배치하고, 상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)의 전압을 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)를 센싱함을 통하여 그 오차를 검출하게 된다. 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)는 상기 공유버스 전압(Vbus)과 상기 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)의 최대 오차를 항상 검출하여 저감하는 방식이며, 최대 전류 기준으로 제어되기 때문에 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 최대전류제어 방식이라고 한다.The output of the three-phase interleaved
또한 병렬운전 덧셈부(301)에서 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)와 병렬운전 기준전압(Vref3)의 오차를 출력하며, 병렬운전 전압 비교부(302)를 통하여 최종적으로 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)를 제어하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
도 11은 제안된 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식을 나타낸다.Figure 11 shows the average current and maximum current variable control scheme of the proposed three-phase interleaved solar converter.
제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 출력전류를 각각 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하고, 공유함을 통하여 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)을 형성하게 된다. First to third outputs of the first to
3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)의 출력은 전류센서(50)로부터 특정(特定) 컨버터의 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303)를 통하여 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하며, 상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 병렬운전 다이오드(305)를 배치하고, 상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)와 병렬운전 저항(304) 및 N형 트랜지스터(311)의 직렬회로가 병렬로 연결되어 있다.The output of the three-phase interleaved
무엇보다 제안된 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식(도 11)은 공유버스 전압(Vbus)을 제1,2 병렬운전 피드백 저항(314,315)에 의해서 검출하며, 레귤레이터(312)에 기준전압(Reference Voltage)에 입력된다. 상기 레귤레이터(312)는 TL431의 소자가 사용되며 2.5[V]의 기준전압에서 동작하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다. Above all, in the proposed three-phase interleaved solar converter, the average current and the maximum current variable control scheme (FIG. 11) detect the shared bus voltage Vbus by the first and second parallel
상기 레귤레이터(312)의 애노드(Anode)는 제어부 전원(Vcc)에 입력되며, 공유버스 전압(Vbus)이 기준전압 이상이면, 상기 레귤레이터(312)는 애노드(Anode)에서 캐소드(Cathode)로 도통하게 되며, 레귤레이터 연결저항(313)에 전압이 인가되며, N형 트랜지스터(311)이 도통(on)하게 되므로 상기 병렬운전 저항(304)가 도통하고 평균전류 모드로 동작하게 된다.The anode of the
따라서 상기 공유버스 전압(Vbus)이 기준전압(Reference Voltage) 이하이면, 최대전류 모드로 동작하고, 상기 공유버스 전압(Vbus)이 기준전압(Reference Voltage) 이상이면, 평균전류 모드로 동작하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.Therefore, when the shared bus voltage (Vbus) is less than the reference voltage (Reference Voltage), the operation in the maximum current mode, if the shared bus voltage (Vbus) is more than the reference voltage (Reference Voltage), operating in the average current mode It features.
즉, 경부하(Light Load)에서는 최대전류 모드로 동작하고, 중부하[Heavy Load: 출력전류가 정격(政格) 전류의 50% 이상이 되는 부하]에서는 평균전류 모드로 동작하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 하며, 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 필요한 경우, 즉 중부하(Heavy Load)에서 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에 전류가 평균적으로 제어가 수행되며, 전체적으로 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에서 전류의 균형을 맞출 수 있으며, 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 요구되지 않는 경우, 즉 경부하[Light Load: 출력전류가 정격(政格) 전류의 50% 미만이 되는 부하]에서는 최대전류 모드로 동작하는 것을 기술적 특징으로 한다.In other words, it operates in the maximum current mode at light loads and in the average current mode at heavy loads (heavy load: the load at which the output current is 50% or more of the rated current). In the case where a large amount of current is required in the direct current (DC)
상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305) 또는 병렬운전 저항(304)의 전압을 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)를 센싱함을 통하여 그 오차를 검출하게 된다. 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)는 상기 공유버스 전압(Vbus)과 상기 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)의 최대 오차 또는 평균 오차를 항상 검출하여 저감하는 방식이며, 최대 전류 기준 또는 평균 전류 기준으로 제어되기 때문에 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터의 평균전류 및 최대전류 가변제어 방식이라고 한다.The error is detected by sensing the voltage of the
또한 병렬운전 덧셈부(301)에서 상기 병렬운전 전류 비교부(306)와 병렬운전 기준전압(Vref3)의 오차를 출력하며, 병렬운전 전압 비교부(302)를 통하여 최종적으로 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터(200)를 제어하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
이를 통하여 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 필요한 경우, 즉 중부하(Heavy Load)에서 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에 전류가 평균적으로 제어가 수행되며, 전체적으로 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)에서 전류의 균형을 맞출 수 있으며, 직류(DC) 부하(59)에 전류가 많이 요구되지 않는 경우, 즉 경부하(Light Load)에서는 최대전류 모드로 동작하는 상승된 효과가 발생한다.Accordingly, when a large amount of current is required in the direct current (DC)
따라서 본 발명에서는 컨버터에 있어서, 태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)로부터 발생된 전압을 공급받아 전력을 변환시키는 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33); 상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53); 상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3) 정보를 공유하는 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307);Therefore, in the present invention, a converter comprising: first to
상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53) 중에서 특정(特定) 전류센서를 통하여 특정(特定) 컨버터의 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하는 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303); 상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 위치한 병렬운전 다이오드(305); 상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)와 병렬로 배치된 병렬운전 저항(304) 및 N형 트랜지스터(311)를 포함하는 컨버터를 제안하고자 한다.A parallel operation
또한, 컨버터의 제어장치에 있어서, 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53); 상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 위치한 병렬운전 다이오드(305); 상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)와 병렬로 배치된 병렬운전 저항(304) 및 N형 트랜지스터(311)를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨버터의 제어장치를 제안하고자 한다.In addition, the control device of the converter, comprising: first to third current sensors (51 to 53) for detecting first to third output currents (io1 to io3) of the first to third converters (31 to 33); A
본 발명은 이 분야의 통상의 지식을 가진자가 다양한 변형에 의하여 컨버터 및 이의 제어장치에 적용시킬 수 있으며, 기술적으로 용이하게 변형시키는 기술의 범주도 본 특허의 권리범위에 속하는 것으로 인정해야 할 것이다.The present invention can be applied to a converter and its control device by various modifications having ordinary skill in the art, it should be recognized that the scope of technology that can be easily modified technically falls within the scope of the patent.
11 : 제1 태양전지 셀(Cell)
12 : 제2 태양전지 셀(Cell)
13 : 제3 태양전지 셀(Cell)
14 : 제4 태양전지 셀(Cell)
15 : 제5 태양전지 셀(Cell)
21 : 제1 역전압 방지 다이오드
22 : 제2 역전압 방지 다이오드
23 : 제3 역전압 방지 다이오드
24 : 제4 역전압 방지 다이오드
25 : 제5 역전압 방지 다이오드
27 : 입력 커패시터
31 : 제1 컨버터
31-1 : 제1 컨버터의 상부 스위치
31-2 : 제1 컨버터의 하부 스위치
32 : 제2 컨버터
32-1 : 제2 컨버터의 상부 스위치
32-2 : 제2 컨버터의 하부 스위치
33 : 제3 컨버터
33-1 : 제3 컨버터의 상부 스위치
33-2 : 제3 컨버터의 하부 스위치
41 : 제1 인덕터
42 : 제2 인덕터
43 : 제3 인덕터
44 : 자기적인 결합
50 : 전류센서
51 : 제1 전류센서
52 : 제2 전류센서
53 : 제3 전류센서
54 : 제1 전압검출 저항
55 : 제2 전압검출 저항
57 : 출력 커패시터
58 : 출력전압 검출부
59 : 직류(DC) 부하
60 : 제1 제어이득(Z1)
61 : 제2 제어이득(Z2)
70 : 주 제어부
71 : 주 스위치 구동부
72 : 전류 검출부
73 : 전압 검출부
100 : 태양전지 셀(Cell)
200 : 3상 인터리브드 태양광 컨버터
201 : 제1 제어부 저항
202 : 제1 제어부 커패시터
203 : 제2 커패시터
204 : 제2 저항
205 : 제3 커패시터
206 : 제3 저항
207 : 제4 저항
208 : 제5 저항
209 : 제4 커패시터
210 : 전압 제어부
211 : 전압 비교기
220 : 전류 제어부
221 : 제1 전류 비교기
222 : 제2 전류 비교기
223 : 제3 전류 비교기
225 : 전류 덧셈기
230 : 과전압 및 과전류 보호부
231 : 과전압 및 과전류 보호 비교기
232 : 3.3[V] 기준전압 생성부
233 : 제1 과전압 보호부 저항
234 : 제2 과전압 보호부 저항
240 : 게이트 신호 생성부
241 : 제1 제어 비교기
242 : 제2 제어 비교기
243 : 제3 제어 비교기
244 : 제4 제어 비교기
245 : 제5 제어 비교기
246 : 제6 제어 비교기
247 : 제1 제어 OR 게이트
248 : 제2 제어 OR 게이트
249 : 제3 제어 OR 게이트
260 : RS 플립플롭
261 : 제1 RS 플립플롭
262 : 제2 RS 플립플롭
263 : 제3 RS 플립플롭
270 : 게이트 구동부
271 : 제1 컨버터의 게이트 구동부
271-1 : 제1 컨버터의 상부 게이트 버퍼(Buffer)
271-2 : 제1 컨버터의 하부 게이트 Not 게이트
272 : 제2 컨버터의 게이트 구동부
272-1 : 제2 컨버터의 상부 게이트 버퍼(Buffer)
272-2 : 제2 컨버터의 하부 게이트 Not 게이트
273 : 제3 컨버터의 게이트 구동부
273-1 : 제3 컨버터의 상부 게이트 버퍼(Buffer)
273-2 : 제3 컨버터의 하부 게이트 Not 게이트
280 : 발진부
282 : 발진기 저항
300 : 3상 인터리브드 전력변환 회로부
301 : 병렬운전 덧셈부
302 : 병렬운전 전압 비교부
303 : 병렬운전 전류 모니터부
304 : 병렬운전 저항
305 : 병렬운전 다이오드
306 : 병렬운전 전류 비교부
307 : 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)
311 : N형 트랜지스터
312 : 레귤레이터
313 : 레귤레이터 연결저항
314 : 제1 병렬운전 피드백 저항
315 : 제2 병렬운전 피드백 저항
A : 제1 컨버터의 상부 및 하부 스위치의 접점
B : 제2 컨버터의 상부 및 하부 스위치의 접점
C : 제3 컨버터의 상부 및 하부 스위치의 접점
C1 : 제1 제어 커패시터
C11 : 제11 제어 커패시터
C12 : 제12 제어 커패시터
FAULT : 스위치 오프(off)
io1 : 제1 출력전류
io2 : 제2 출력전류
io3 : 제3 출력전류
Iref : 기준 전류값
OSC : 오실레이터(발진기)
PH1 : 제1 발진기 펄스
PH2 : 제2 발진기 펄스
PH3 : 제3 발진기 펄스
R1 : 제1 제어저항
R2 : 제2 제어저항
R11 : 제11 제어저항
S1 : 제1 컨버터의 주 스위치(상부 및 하부스위치)
S2 : 제2 컨버터의 주 스위치(상부 및 하부스위치)
S3 : 제3 컨버터의 주 스위치(상부 및 하부스위치)
T : 직류(DC) 부하의 (+) 단자
Vc : 제어전압
Vcc : 제어부 전원
Vc1 : 제1 병렬운전 제어전압
Vc2 : 제2 병렬운전 제어전압
Vref1 ; 출력제어를 위한 기준 전압
Vref2 : 과전압 및 과전류 제어를 위한 기준 전압
Vref3 : 병렬운전 기준전압
IrefA : 제1 컨버터 기준 전류값
IrefB : 제2 컨버터 기준 전류값
IrefC : 제3 컨버터 기준 전류값
Z1 : 제1 제어이득
Z2 : 제2 제어이득11: first solar cell
12: second solar cell (Cell)
13: third solar cell (Cell)
14: fourth solar cell (Cell)
15: fifth solar cell
21: first reverse voltage prevention diode
22: second reverse voltage protection diode
23: third reverse voltage protection diode
24: fourth reverse voltage protection diode
25: fifth reverse voltage prevention diode
27: input capacitor
31: first converter
31-1: Upper switch of the first converter
31-2: lower switch of the first converter
32: second converter
32-1: upper switch of the second converter
32-2: lower switch of the second converter
33: third converter
33-1: upper switch of the third converter
33-2: lower switch of the third converter
41: first inductor
42: second inductor
43: third inductor
44: magnetic coupling
50: current sensor
51: first current sensor
52: second current sensor
53: third current sensor
54: first voltage detection resistor
55: second voltage detection resistor
57: output capacitor
58: output voltage detector
59: DC load
60: first control gain (Z1)
61: second control gain (Z2)
70: main control unit
71: main switch drive unit
72: current detector
73: voltage detector
100: solar cell
200: three-phase interleaved solar converter
201: first control unit resistor
202: first control capacitor
203: second capacitor
204: second resistance
205: third capacitor
206: third resistance
207: fourth resistor
208: fifth resistance
209: fourth capacitor
210: voltage control unit
211: voltage comparator
220: current controller
221: first current comparator
222: second current comparator
223: third current comparator
225: current adder
230: overvoltage and overcurrent protection unit
231: Overvoltage and Overcurrent Protection Comparators
232: 3.3 [V] reference voltage generator
233: first overvoltage protection resistor
234: resistance of the second overvoltage protection unit
240: gate signal generator
241: first control comparator
242: second control comparator
243: third control comparator
244 fourth control comparator
245: fifth control comparator
246: sixth control comparator
247: first control OR gate
248: second control OR gate
249: third control OR gate
260 RS flip flop
261: first RS flip-flop
262: second RS flip-flop
263: third RS flip-flop
270 gate driver
271: gate driver of the first converter
271-1: Upper gate buffer of the first converter
271-2: Lower gate Not gate of the first converter
272: gate driver of the second converter
272-1: Upper gate buffer of the second converter
272-2: Lower gate Not gate of the second converter
273: gate driver of the third converter
273-1: Upper gate buffer of the third converter
273-2: Lower gate Not gate of the third converter
280: oscillation unit
282: Oscillator Resistance
300: three-phase interleaved power conversion circuit
301: parallel operation adder
302: parallel operation voltage comparison unit
303: parallel operation current monitor
304: parallel operation resistance
305: parallel operation diode
306: parallel operation current comparison unit
307: shared bus line
311: N-type transistor
312: Regulator
313: regulator connection resistance
314: first parallel operation feedback resistor
315: second parallel operation feedback resistor
A: contacts of the upper and lower switches of the first converter
B: contacts of the upper and lower switches of the second converter
C: contacts of the upper and lower switches of the third converter
C1: first control capacitor
C11: eleventh control capacitor
C12: 12th control capacitor
FAULT: switch off
io1: first output current
io2: second output current
io3: third output current
Iref: reference current value
OSC: Oscillator
PH1: first oscillator pulse
PH2: second oscillator pulse
PH3: third oscillator pulse
R1: first control resistor
R2: second control resistor
R11: eleventh control resistor
S1: main switch (upper and lower switch) of the first converter
S2: main switch (upper and lower switch) of the second converter
S3: Main switch (upper and lower switch) of the third converter
T: (+) terminal of DC load
Vc: control voltage
Vcc: control unit power
Vc1: first parallel operation control voltage
Vc2: second parallel operation control voltage
Vref1; Reference voltage for output control
Vref2: reference voltage for overvoltage and overcurrent control
Vref3: Parallel operation reference voltage
IrefA: first converter reference current value
IrefB: Second converter reference current value
IrefC: third converter reference current value
Z1: First gain
Z2: Second control gain
Claims (3)
태양전지 셀(Cell)(100)로부터 발생된 전압을 공급받아 전력을 변환시키는 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33);
상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53);
상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3) 정보를 공유하는 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307);
상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53) 중에서 특정(特定) 전류센서를 통하여 특정(特定) 컨버터의 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하는 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303);
상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 위치한 병렬운전 다이오드(305);
상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)와 병렬로 배치된 병렬운전 저항(304) 및 N형 트랜지스터(311)를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨버터In the converter,
First to third converters 31 to 33 for converting electric power by receiving a voltage generated from the solar cell 100;
First to third current sensors 51 to 53 for detecting first to third output currents io1 to io3 of the first to third converters 31 to 33;
A shared voltage bus line (307) sharing the first to third output currents (io1 to io3) information from the first to third current sensors (51 to 53);
A parallel operation current monitor unit 303 for outputting a first parallel operation control voltage Vc1 of a specific converter through a specific current sensor among the first to third current sensors 51 to 53;
A parallel driving diode 305 positioned between the shared bus line 307 and the parallel operating current monitor 303;
A converter comprising a parallel operation resistor 304 and an N-type transistor 311 disposed in parallel with the parallel operation diode 305.
상기 제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)는 중부하(Heavy Load)에서 평균전류 모드로 동작하며, 경부하(Light Load)에서는 최대전류 모드로 동작하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨버터The method of claim 1,
The first to third converters 31 to 33 operate in an average current mode under heavy load, and operate in a maximum current mode under light load.
제1 내지 제3 컨버터(31 내지 33)의 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3)를 검출하는 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53);
상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53)로부터 상기 제1 내지 제3 출력전류(io1 내지 io3) 정보를 공유하는 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307);
상기 제1 내지 제3 전류센서(51 내지 53) 중에서 특정(特定) 전류센서를 통하여 특정(特定) 컨버터의 제1 병렬운전 제어전압(Vc1)을 출력하는 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303);
상기 공유전압 버스 라인(Share Bus)(307)과 상기 병렬운전 전류 모니터부(303) 사이에 위치한 병렬운전 다이오드(305);
상기 병렬운전 다이오드(305)와 병렬로 배치된 병렬운전 저항(304) 및 N형 트랜지스터(311)를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨버터의 제어장치In the control device of the converter,
First to third current sensors 51 to 53 for detecting first to third output currents io1 to io3 of the first to third converters 31 to 33;
A shared voltage bus line (307) sharing the first to third output currents (io1 to io3) information from the first to third current sensors (51 to 53);
A parallel operation current monitor unit 303 for outputting a first parallel operation control voltage Vc1 of a specific converter through a specific current sensor among the first to third current sensors 51 to 53;
A parallel driving diode 305 positioned between the shared bus line 307 and the parallel operating current monitor 303;
Control device of the converter comprising a parallel operation resistor 304 and the N-type transistor 311 disposed in parallel with the parallel operation diode 305
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180026765A KR102034726B1 (en) | 2018-03-07 | 2018-03-07 | Converting Apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180026765A KR102034726B1 (en) | 2018-03-07 | 2018-03-07 | Converting Apparatus |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180012837A Division KR101849901B1 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2018-02-01 | Three Phase Interleaved Solar Converter Suitable for Low-Voltage High-Current |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190093478A true KR20190093478A (en) | 2019-08-09 |
| KR102034726B1 KR102034726B1 (en) | 2019-10-21 |
Family
ID=67613594
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180026765A KR102034726B1 (en) | 2018-03-07 | 2018-03-07 | Converting Apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102034726B1 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6897636B2 (en) * | 2002-03-29 | 2005-05-24 | Intersil Americas Inc. | Method and circuit for scaling and balancing input and output currents in a multi-phase DC-DC converter using different input voltages |
| US20050225307A1 (en) * | 2004-04-12 | 2005-10-13 | Tetsuo Sato | Current sensing circuit for a multi-phase DC-DC converter |
| KR101304777B1 (en) | 2011-08-19 | 2013-09-05 | 전주대학교 산학협력단 | DC/DC converter with wide input voltage range |
| KR101500206B1 (en) | 2013-11-26 | 2015-03-06 | 현대자동차주식회사 | A two phase interleaved converter and the conrol method thereof |
| KR20180003122A (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2018-01-09 | 한국에너지기술연구원 | Interleaved llc resonant converter and control method thereof |
-
2018
- 2018-03-07 KR KR1020180026765A patent/KR102034726B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6897636B2 (en) * | 2002-03-29 | 2005-05-24 | Intersil Americas Inc. | Method and circuit for scaling and balancing input and output currents in a multi-phase DC-DC converter using different input voltages |
| US20050225307A1 (en) * | 2004-04-12 | 2005-10-13 | Tetsuo Sato | Current sensing circuit for a multi-phase DC-DC converter |
| US7466116B2 (en) * | 2004-04-12 | 2008-12-16 | Renesas Technology America, Inc. | Current sensing circuit for a multi-phase DC-DC converter |
| KR101304777B1 (en) | 2011-08-19 | 2013-09-05 | 전주대학교 산학협력단 | DC/DC converter with wide input voltage range |
| KR101500206B1 (en) | 2013-11-26 | 2015-03-06 | 현대자동차주식회사 | A two phase interleaved converter and the conrol method thereof |
| KR20180003122A (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2018-01-09 | 한국에너지기술연구원 | Interleaved llc resonant converter and control method thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Jieli Li et al. "Coupled Inductor Design Optimization for Fast-Response Low-Voltage DC-DC Converters". IEEE. (발표일 : 2012.03.) * |
| Texas Instruments Application Report (발표일 : 2014.07.) * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102034726B1 (en) | 2019-10-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20240222978A1 (en) | Maximizing Power in a Photovoltaic Distributed Power System | |
| DK2450770T3 (en) | Photovoltaic converter with maximum current limitation in discontinuous wiring current mode | |
| US8335090B2 (en) | Low cost high efficiency high power solar power conversion system circuit and solar power supply system | |
| US10615698B2 (en) | Resonant power converter and control method thereof | |
| US9318960B2 (en) | High efficiency and low loss AC-DC power supply circuit and control method | |
| CN102263508A (en) | Resonant-type conversion system and over-current protection method | |
| TW201228203A (en) | DC power conversion module, control method thereof, junction box and power harvesting system | |
| US11011992B2 (en) | Method and system for reducing the circulating current between multiple non-isolated modules operating in parallel | |
| US20140056044A1 (en) | Photovoltaic inverter and a control method thereof | |
| Ji et al. | High step-up Y-source coupled-inductor impedance network boost DC–DC converters with common ground and continuous input current | |
| KR20140003520A (en) | Relative efficiency measurement in a pulse width modulation system | |
| KR101208252B1 (en) | Apparatus and method of generating current command for tracking maximum power point in solar enery generating system | |
| EP4318911A1 (en) | Power conversion apparatus having multi-level structure | |
| JP2012065441A (en) | Power converter and photovoltaic power generation system | |
| US20110215778A1 (en) | Solar power converter with multiple outputs and conversion circuit thereof | |
| Honarjoo et al. | Analysis and implementation of a new single switch, high voltage gain DC-DC converter with a wide CCM operation range and reduced components voltage stress | |
| KR101849901B1 (en) | Three Phase Interleaved Solar Converter Suitable for Low-Voltage High-Current | |
| CN112532021B (en) | Input parallel output series multi-converter switching power supply | |
| KR102034726B1 (en) | Converting Apparatus | |
| US20240171059A1 (en) | Power conversion device having multi-level structure | |
| US20240056022A1 (en) | Power conversion device having multi-level structure | |
| Nirmala et al. | Investigations of DC-DC converter topologies for pv fed telecom applications | |
| KR102688932B1 (en) | Solar Power Generation System Capable of Accurately Calculating the Amount of Power Supplied to the Converter | |
| US20240170961A1 (en) | Power conversion device having multi-level structure | |
| JP6025663B2 (en) | Uninterruptible power system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |