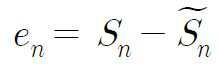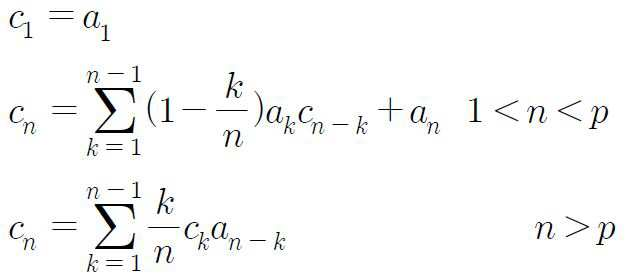KR20180073167A - Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons - Google Patents
Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20180073167A KR20180073167A KR1020160176716A KR20160176716A KR20180073167A KR 20180073167 A KR20180073167 A KR 20180073167A KR 1020160176716 A KR1020160176716 A KR 1020160176716A KR 20160176716 A KR20160176716 A KR 20160176716A KR 20180073167 A KR20180073167 A KR 20180073167A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- sound
- dangerous
- feature
- sounds
- risk
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01H—MEASUREMENT OF MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS OR ULTRASONIC, SONIC OR INFRASONIC WAVES
- G01H17/00—Measuring mechanical vibrations or ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves, not provided for in the preceding groups
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/16—Sound input; Sound output
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R1/00—Details of transducers, loudspeakers or microphones
- H04R1/10—Earpieces; Attachments therefor ; Earphones; Monophonic headphones
- H04R1/1083—Reduction of ambient noise
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R5/00—Stereophonic arrangements
- H04R5/033—Headphones for stereophonic communication
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 소리 인식에 관한 것으로서, 구체적으로는 일상에서의 다양한 소리를 인식하고 판별하는 방법 및 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to sound recognition, and more particularly, to a method and system for recognizing and recognizing various sounds in daily life.
고령화 사회로 인해 노인 인구가 늘어나고 헤드폰의 과다 사용 등으로 인한 난청인구가 증가하고 있으며, 청각장애인의 숫자 또한 통상 인구의 3% 정도까지 이를 정도로 점증하고 있다. 완전히 소리를 못듯거나 또는 소리를 잘 구별하지 못하는 청각장애인들은 소리를 듣고 상황을 판단하는 것이 어렵기 때문에 일상생활에 많은 어려움이 있을 뿐만 아니라 소리 정보를 이용하여 실내, 실외 환경에서의 위험한 상황을 인지할 수 없어 즉각적인 대처가 불가능하다. 따라서 청각장애인들이 위험에 처했을 때, 몸에 부착된 센서 또는 휴대용 기기를 통해 위험상황을 시각, 촉각 정보로 변환하여 전달할 필요가 있다.Due to the aging society, the elderly population is increasing and the number of hearing impaired people is increasing due to excessive use of headphones, and the number of hearing-impaired people is also increasing to about 3% of the normal population. Hearing-impaired people who are completely unable to hear or can not distinguish their sounds are hard to hear and understand the situation, so they have many difficulties in everyday life, and use sound information to detect dangerous situations in indoor and outdoor environments Immediate action is not possible. Therefore, when a person with hearing impairment is in danger, it is necessary to convert the dangerous situation into visual and tactile information through sensors attached to the body or handheld devices.
하지만, 일상생활의 다양한 소리를 높은 신뢰도로 파악하는 것이 가능해야 위험상황인지를 정확히 판별할 수 있는바, 이에 대한 실증적이고 구체적인 일상생활 소리 인식 방법 및 시스템이 필요하다.However, it is necessary to have an empirical and concrete daily life sound recognition method and system which can accurately identify the dangerous situation by being able to grasp various sounds of daily life with high reliability.
전술한 문제점을 해결하기 위하여, 본 발명은 실내 및 실외의 위험상황시 날 수 있는 소리를 정확히 파악하는 방법 및 시스템을 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다.In order to solve the above-described problems, it is an object of the present invention to provide a method and system for accurately grasping a sound that can be blown in a dangerous situation in indoor and outdoor.
또한, 파악된 소리로부터 상황을 파악하고 이를 시각 또는 촉각 등 청각 이외의 방식으로 경고하는 위험상황 대응 방법 및 시스템을 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다.It is also an object of the present invention to provide a dangerous situation countermeasure method and system that catches a situation from a detected sound and warns it in a manner other than auditory sense such as visual or tactile sense.
본 발명은, 위험상황시 발생하는 소리 데이터를 저장하는 데이터베이스와, 주변의 소리를 수집하는 소리수집부와, 상기 소리수집부에 의해 수집된 소리의 특징을 추출하는 특징추출부와, 상기 특징추출부로부터 입력받은 특징으로부터 인공신경망 패턴인식 알고리즘을 이용하여 위험소리를 검출하는 위험소리 검출엔진을 포함하는 위험상황 인식 시스템을 제공한다.The present invention relates to a sound processing apparatus, including a database for storing sound data generated in a dangerous situation, a sound collecting unit for collecting sound around the sound collecting unit, a feature extracting unit for extracting characteristics of sounds collected by the sound collecting unit, And a dangerous sound detection engine for detecting a dangerous sound by using an artificial neural network pattern recognition algorithm from characteristics input from the input unit.
이에 더하여 상기 위험소리 검출엔진의 검출 결과에 따라 소리 대체 알림 신호를 발생하는 경보부를 더 포함하는 것이 좋다.And a warning unit for generating a sound replacement notification signal according to the detection result of the dangerous sound detection engine.
데이터베이스는, 실내 및 실외 위험상황 DB, 혼잡잡음 DB, 상기 실내 및 실외 위험상황 DB와 상기 혼잡잡음 DB를 혼합한 시뮬레이션 DB를 포함하고, 상기 소리수집부가 수집한 소리를 축적해 나간다. The database includes an indoor and outdoor risk database, a congestion noise database, and a simulation DB that is a mixture of the indoor and outdoor risk database and the congestion noise database, and the sound collector collects the collected sounds.
위험상황 추출부는, LPCC 특징벡터를 이용하여 수집되는 소리의 특징을 추출하되, 소리의 크기와 종류에 따라 MFCC 특징벡터를 이용하여 소리의 특징을 추출하여 상황별 최적 소리 인식이 가능하도록 한다.The risk context extractor extracts features of the sound collected using the LPCC feature vector, and extracts features of the sound using the MFCC feature vector according to the size and type of the sound, thereby enabling optimum sound recognition in each situation.
위 데이터베이스는, 상기 소리수집부로부터 전달된 데이터와 저장데이터와의 대비를 통하여 위험상황 소리를 판별하는 대비판단부를 포함할 수 있다.The above-mentioned database may include a contrast judgment unit for discriminating a dangerous situation sound by comparing the data transmitted from the sound collection unit and the stored data.
또한, 본 발명은, 주변 상황의 소리를 수집하는 단계와, 상기 수집된 소리의 특징을 추출하는 단계와, 상기 특징을 인공신경망 알고리즘을 이용하여 소리를 분류하는 단계와, 상기 분류하는 단계의 결과를 토대로 위험상황 여부를 판단하는 단계를 포함하는 위험상황 인식 방법을 제공한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a sound processing method comprising the steps of: collecting sound of a surrounding situation; extracting characteristics of the collected sounds; classifying sounds using the artificial neural network algorithm; And a step of determining whether or not a risk situation is determined on the basis of the determination result.
상기 소리의 특징을 추출은 소리의 크기 및 패턴을 판별하는 단계와, 상기 판별 결과에 따라 특징벡터를 선택하는 단계를 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And extracting the feature of the sound, the step of discriminating the size and the pattern of the sound, and the step of selecting the feature vector according to the discrimination result.
본 발명에 따르면, 위험상황에서 발생할 수 있는 소리를 정확히 인식하여 위험상황 여부를 판단하고, 빠르게 대처할 수 있는 소리 대체 정보를 청각장애인들에게 전달해주어 위험상황에서 벗어날 수 있게 도와준다.According to the present invention, it is possible to accurately detect a sound that may occur in a dangerous situation, determine whether or not a dangerous situation exists, and transmit sound substitute information to a hearing-impaired person so that the user can escape from a dangerous situation.
도 1은 위험소리 검출 및 알림 시스템의 구조도.
도 2 내지 4은 특징벡터를 달리 하여 각 위험상황에 대한 인식률을 실험한 결과를 도시한 도면.1 is a structural diagram of a dangerous sound detection and notification system.
FIGS. 2 to 4 are diagrams showing the results of experimenting recognition rates for each dangerous situation by differentiating feature vectors. FIG.
청각장애인들을 위한 위험상황 감지 기술에 대한 연구에는 MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient) 특징벡터 기반의 GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model) 패턴인식 알고리즘을 이용하여 오토바이, 차 경적, 천둥, 대형자동차, 공사장, UBM(Universial Background Model), 총 6가지의 상황 인식을 위한 연구, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient(MFCC)를 기반의 Hidden Markov Model(HMM)을 사용한 연구, 음향 간의 스펙트럼 특징의 차이를 이용한 연구 등이 있다.A study on the risk detection technology for the hearing impaired people has been carried out using the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) feature vector-based GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model) pattern recognition algorithm to detect motorcycle, car horn, thunder, (HMCC) based on the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC), and the study of differences in the spectral characteristics of the sound.
본 발명에서는 인공신경망(ANN : Artificial Neural Network)을 이용하여 청각장애인을 위한 웨어러블 기기의 위험상황 검출 엔진을 설계한다. In the present invention, a risk detection engine for a wearable device for the hearing impaired is designed using an artificial neural network (ANN).
도 1은 본 발명에 따른 위험상황 인식 및 경보 시스템의 구조도이다.1 is a structural diagram of a dangerous situation recognition and alarm system according to the present invention.
도시된 바와 같이, 위험상황에 발생하는 소리를 저장한 데이터베이스(위험상황 소리 DB), 일상생활에서의 평상시 소리를 저장한 데이터베이스(환경잡음 DB), 상기 데이터베이스에 저장된 소리로부터 각 소리의 특징을 추출하는 제1 특징추출부(특징추출부), 위험소리와 환경잡음을 합성하는 결과를 저장하는 시뮬레이션 DB, 시뮬레이션 DB에 저장된 합성음으로부터 특징을 추출하는 제2 특징추출부(특징추출), 상기 제1 특징추출부 및 제2 특징추출부로부터 입력받은 특징으로부터 위험소리를 검출하는 위험소리 검출엔진 및 검출된 결과에 따라 소리 대체 알림 신호(시각적 신호, 촉각적 신호 등)를 발생하는 경보부(미도시)를 포함한다.As shown in the figure, a database (a dangerous situation sound DB) storing sounds generated in a dangerous situation, a database (ambient noise DB) storing everyday sounds in everyday life, a characteristic of each sound from the sounds stored in the database A second feature extracting unit (feature extracting unit) for extracting features from the synthesized sound stored in the simulation DB, a first feature extracting unit (feature extracting unit) (Not shown) for generating a sound substitution notification signal (visual signal, tactile signal, etc.) according to the detected result and a dangerous sound detection engine for detecting a dangerous sound from the features input from the feature extraction unit and the second feature extraction unit, .
위험상황 소리 DB는 실내 및 실외에 각각 일어날 수 있는 위험상황시 발생하는 소리에 대한 데이터베이스이고, 환경잡음 DB는 조용한 방, 번화가, 골목길, 차도 등 실내 및 실외의 일반적인 상황에서의 소리에 대한 데이터베이스이다.The Dangerous Situation DB is a database of sounds that occur during a dangerous situation that may occur in indoor or outdoor environments, and the environmental noise database is a database of sounds in general indoor and outdoor situations such as a quiet room, a busy street, an alleyway, .
기본적으로 데이터베이스는 특징점을 추출하는 모집단이 되는데, 본 발명에 따른 위험상황 인식 시스템이 동작하면서 지속적으로 각 경우의 소리를 수집하며 학습에 이용할 수 있다.Basically, the database serves as a population for extracting minutia points, and the dangerous situation recognition system according to the present invention can be continuously used to collect sounds of each case while being operated.
제1 특징추출부는 위험상황 소리 DB 및 환경잡음 DB에 저장된 소리로부터 각 소리의 특징을 추출하는 기능을 하며, LPB, LPCC, MFCC 등의 특징벡터를 이용하여 소리의 특징부를 추출한다.The first feature extraction unit extracts the feature of each sound from the sound stored in the dangerous situation sound DB and the environmental noise database, and extracts the feature of the sound using the feature vectors such as LPB, LPCC, and MFCC.
시뮬레이션 DB는 위험소리 검출 엔진을 학습시키기 위하여 위험소리와 환경잡음을 합성하는 결과를 저장하여 일상 생활에서의 환경 잡음하에서 위험소리가 발생하는 경우를 혼합한 소리 데이터를 저장한다. 제2 특징추출부는 시뮬레이션 DB에 저장된 합성음으로부터 특징을 추출한다.The simulation DB stores the result of synthesizing the dangerous sound and the environmental noise in order to learn the dangerous sound detection engine and stores the sound data in which the dangerous sound occurs under the environmental noise in daily life. The second feature extraction unit extracts features from the synthesized speech stored in the simulation DB.
위험소리 검출엔진은 ANN 분류기를 사용하여 패턴분류를 진행하고 이 결과에 따라서 판단부(Decision Block)에서 위험상황 여부를 최종 판단한다.The dangerous sound detection engine proceeds to pattern classification using the ANN classifier, and finally determines whether or not a dangerous situation exists in a decision block according to the result.
경보부는 위험소리 검출엔진의 판단 결과에 따라 시각적 신호, 진동 등의 촉각적 신호로 사용자에게 위험상황을 알린다.The alarm unit informs the user of the dangerous situation by a tactile signal such as a visual signal or vibration according to the judgment result of the dangerous sound detection engine.
또한, 소리 입력부(미도시)가 주변의 소리를 수집하여 제1 및/또는 제2 특징추출부로 전달함으로써 실제 일어나는 상황에 대한 판단을 위험소리 검출엔진이 수행하도록 한다.In addition, a sound input unit (not shown) collects surrounding sounds and transmits them to the first and / or second feature extracting unit, so that the dangerous sound detecting engine judges actual situations.
한편, 소리 입력부의 출력은 위험상황 소리 DB, 환경잡음 DB, 시뮬레이션 DB 중 어느 하나 이상에 전달되어 각 DB를 갱신하거나, 또는 DB에 저장된 저장데이터와의 대비를 통하여 위험상황 소리 DB 및/또는 시뮬레이션 DB에 포함된 대비판단부(미도시)가 위험소리인지 여부를 판단하는데 이용될 수 있다.On the other hand, the output of the sound input unit is transmitted to at least one of the dangerous situation sound database, the environmental noise database, and the simulation DB to update each DB, or to compare with the stored data stored in the DB, (Not shown) included in the DB may be used to determine whether or not the sound is a dangerous sound.
즉, 본 발명에서는 특징 추출부를 거쳐 위험소리 검출엔진이 위험상황을 판단하는 것을 기본으로 하되, 보조적으로 또는 이에 대체하여 대비판단부가 위험상황을 판단하도록 구성할 수 있다.That is, in the present invention, the dangerous sound detection engine determines the dangerous situation through the feature extraction unit. Alternatively, or in place of the dangerous sound detection engine, the contrast determination unit may determine the dangerous situation.
이상의 설명에서는 제1 및 제2 특징추출부의 출력이 위험소리 검출 엔진으로 입력되는 것으로 설명하였으나, 제1 특징추출부의 출력 또는 제2 특징추출부의 출력만이 위험소리 검출엔진으로 입력되도록 구성할 수 있음은 물론이다.In the above description, the outputs of the first and second feature extraction units are input to the dangerous sound detection engine. However, only the output of the first feature extraction unit or the output of the second feature extraction unit can be input to the dangerous sound detection engine Of course.
이하, 구체적으로 본 발명에 따라 주변의 소리로부터 위험상황을 파악하는 과정을 설명한다.Hereinafter, a process of grasping a dangerous situation from surrounding sounds according to the present invention will be described in detail.
위험상황 소리 DB는 대표적이고 가장 빈도가 높은 위험상황 소리를 저장한다. 구체적으로는 위험상황을 실내 위험상황, 실외 위험상황으로 나누고 실내 위험상황에는 물 끓는 소리, 화재경보, 초인종, 전화벨 소리를 저장하고 실외 위험상황에는 사이렌, 차 경적 소리 등 6종의 수집된 위험상황별 데이터를 저장한다.The dangerous situation sound database stores representative and most frequent dangerous situation sounds. Specifically, it divides the dangerous situation into an indoor risk situation and an outdoor dangerous situation. In the indoor risk situation, it stores the boiling sound, the fire alarm, the doorbell and the telephone sound. In the outdoor risk situation, Stores star data.
환경잡음 DB는 환경잡음을 조용한방, 골목길, 번화가, 차도 총 4가지로 정의하고 약 5분가량의 데이터를 저장한다. The environmental noise database defines environmental noise as 4 kinds of quiet one way, alley road, highway, and roadway, and stores about 5 minutes of data.
제1 및 제2 특징추출부는 신호처리 분야에서 가장 많이 쓰이는 특징벡터인 LPC, LPCC, MFCC를 사용하여 위험상황 검출 정확도를 비교 분석한다.The first and second feature extraction units compares and analyzes the accuracy of detecting a dangerous situation using LPC, LPCC, and MFCC, which are feature vectors most commonly used in the field of signal processing.
- 환경잡음 DB- Environmental noise DB
청각장애인들에게 위험상황이 발생할 수 있는 환경은 실내 환경과 실외 환경이 있으며, 두 가지 환경에서 발생할 수 있는 잡음이 다르기 때문에 실내 환경과 실외 환경은 별도의 수집이 필요하며, 따라서 본 발명의 환경잡음 DB는 실내 환경으로는 조용한 방으로 정의하였으며 실외 환경으로는 위험 상황이 발생할 수 있는 위치를 고려하여 한적한 골목길, 번화가, 차도 3가지로 정의하고 이들 소리를 저장한다.The indoor environment and the outdoor environment are different from each other because the environment in which the risk of hearing-impaired persons may occur is the indoor environment and the outdoor environment and the noise that can be generated in the two environments is different. Therefore, The DB is defined as a quiet room for the indoor environment. The outdoor environment is defined as three kinds of alleys, highways, and roads in consideration of the locations where dangerous situations may occur, and these sounds are stored.
총 4가지 환경잡음은 각각 5분가량 녹음되어 16kHz로 샘플링하여 저장된다.All four environmental noises are recorded for 5 minutes each and sampled at 16kHz.
- 위험상황 소리 DB- Risk situation sound DB
청각장애인들의 주변 환경에 따라 발생할 수 있는 위험상황 소리가 다르다. 실내 환경에서는 주전자 물 끓는 소리, 화재경보, 전화벨소리, 초인종 등이 있고, 실외 환경으로는 차 경적소리, 응급차량의 사이렌 소리 등이 있다. 따라서 본 발명에 따른 위험상황 소리 DB는 실내 환경에서 발생하는 위험 소리는 주전자 물 끓는 소리, 화재경보, 전화벨소리, 초인종 총 4가지로 정의하였고 실외 환경에서 발생하는 위험 소리는 차 경적소리, 응급차량의 사이렌 소리 총 2가지로 정의하여, 각 위험상황 소리 데이터는 모노채널로 30초 ~ 60초가량 녹음되고, 16kHz로 샘플링되어 저장된다.There are different sounds of dangerous situations that can occur depending on the surroundings of hearing-impaired people. In the indoor environment, there are boiling water of kettle, fire alarm, telephone ringtone, doorbell, etc. There are car horn sound and emergency siren sound in outdoor environment. Therefore, the dangerous situation sound DB according to the present invention defines four kinds of dangerous sounds generated in the indoor environment as boiling water, fire alarm, telephone ringing sound, and doorbell. In the outdoor environment, , And each dangerous situation sound data is recorded for 30 seconds to 60 seconds on a mono channel, and is sampled and stored at 16 kHz.
- 특징벡터- feature vector
제1 및 제2 특징추출부에 대해 상술한다.The first and second feature extracting units will be described in detail.
MFCC(Mel-Frequenct Cepstrum Coefficient)는 프레임 내의 음성 신호에 대하여 계산한 파워 스펙트럼을 청각기의 주파수 반응도를 모사한 Mel-scale 주파수 도메인에서 DCT(DiscreteCosine Transform)를 취한 값이다. The Mel-Frequent Cepstrum Coefficient (MFCC) is a value obtained by taking DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) in the Mel-scale frequency domain in which the power spectrum calculated for the voice signal in the frame is simulated with the frequency response of the hearing instrument.
LPC는 선형 결합에 의해 과거의 신호에서 현재의 신호[n]을 예측하는 방법으로 전극(All-pole) 모델을 사용하여 수학식 1과 같이 차분 방정식의 형태로 나타낼 수 있다. LPC is a method of predicting a current signal [n] in a past signal by linear combination, and can be represented in the form of a differential equation as shown in Equation (1) using an all-pole model.
여기서 Sn 은 입력신호, 은 예측신호, a i 는 선형예측계수이며, p는 예측계수의 차수이다. Where Sn is the input signal, A i is a linear prediction coefficient, and p is a degree of a prediction coefficient.
현재신호와 예측된 신호의 예측오차는 수학식 2와 같다. The prediction error of the current signal and the predicted signal is expressed by Equation (2).
수학식 3은 예측신호에 대한 mean square error(MSE) J이이다.Equation 3 is the mean square error (MSE) J for the prediction signal.
예측신호의 에러를 최소로 하는 선형예측계수를 찾기 위하여 수학식 3을 ai에 대해 편미분하면 p개의 선형 연립방정식 수학식 4를 얻을 수 있다.To find a linear prediction coefficient that minimizes the error of the prediction signal, the equation (3) can be partially differentiated with respect to a i to obtain p linear simultaneous equations (4).
수학식 4에서 E[s(n-i)s(n-j)]는 입력신호의 자기상관함수이기 때문에 수학식 4는 수학식 5와 같이 나타낼 수 있고, 선형예측계수는 수학식 5에서의 자기 상관 행렬의 역행렬을 이용하여 구할 수 있다. 자기상관함수의 역행렬을 구하는 것의 시간 복잡도 문제를 해결하기 위해 일반적으로 잘 알려져 있는 Levinson-Durvin 알고리즘을 사용한다.(4) can be expressed by Equation (5) because E [ s ( ni ) s ( nj )] in Equation 4 is an autocorrelation function of the input signal, and the linear prediction coefficient can be expressed by Equation Can be obtained by using an inverse matrix. The Levinson-Durvin algorithm, which is generally well known, is used to solve the time complexity problem of finding the inverse of the autocorrelation function.
? ? ? ?? ? ? ?
LPCC는 C(z)의 inverse z-transform으로 정의되고 다음 수학식 6과 같다.LPCC is defined as an inverse z-transform of C (z) and is expressed by Equation (6).
??? ?? ??? ??
전극(All-pore) z=z i 가 unit cycle 안에 있고, 게인값을 1로 주면 LPCC (cip(n))는 다음 수학식 7과 같이 정의된다.If the all-pore z = z i is in the unit cycle and the gain value is 1, the LPCC (c ip (n)) is defined by Equation (7).
LPCC는 recursive에 의해 선형예측계수로부터 구한다. recursive 과정은 다음 수학식 8과 같다.LPCC is obtained from linear prediction coefficients by recursive. The recursive procedure is shown in Equation (8).
? ? ? ? ? ?
- 분리도 비교- Separation degree comparison
본 발명에서 쓰이는 MFCC, LPC, LPCC 3가지의 특징벡터들의 성능을 확인하기 위하여 Bhattacharyya거리 측정을 이용하였다.The Bhattacharyya distance measurement was used to check the performance of the three feature vectors of MFCC, LPC and LPCC used in the present invention.
Bhattacharyya거리 측정은 오류율을 측정하여 거리를 계산하는 방법으로 각 클래스의 분포가 가우시안 형태를 가질 때 가장 좋은 평가기준이 된다. Bhattacharyya거리가 가장 큰 값이 나온 특징벡터가 클래스 간의 거리가 가장 멀리 떨어져있다는 의미로, 위험상황 검출에 가장 적합하다고 할 수 있다. 총 6가지의 위험상황 소리 실험데이터에서 각 15초가량의 소리를 윈도우 크기 150ms 단위로 특Bhattacharyya distance measurement is the method of calculating the distance by measuring the error rate, which is the best evaluation criterion when the distribution of each class has Gaussian form. Bhattacharyya The feature vector with the greatest distance is the most distant from the class, so it is most suitable for detecting the dangerous situation. A total of 6 hazardous situations sound data are stored in a window size of 150ms
징벡터를 추출하여 각 120개 씩 총 720개를 추출하였다. 이렇게 추출된 특징벡터들의 분리도를 Bhattacharyya거리를 구하여 비교하였다.Ging vectors were extracted and a total of 720 vectors were extracted for each 120 points. The Bhattacharyya distances were obtained by comparing the extracted feature vectors.
각각 6개의 위험상황 소리에서 LPC 특징벡터, LPCC 특징벡터, MFCC 특징벡터를 추출한 후에 각 클래스간의 거리를 Bhattacharyya거리를 비교 분석한 결과, LPC 특징벡터의 평균 분리도는 2.79로 나왔으며 MFCC 특징벡터의 평균분리도는 3.77로 나왔다. 가장 높게 나온 LPCC 특징벡터의 평균 분리도는 3.79로 나왔다. 이는 LPCC 특징벡터를 사용하였을 때, 평균적으로 각 위험상황 소리간의 거리가 가장 멀다는 의미로 통계적으로 LPCC 특징벡터가 각 위험상황의 특징을 잘 반영할 수 있는 특징벡터이므로, 본 발명의 특징추출부는 LPCC 특징벡터를 주된 특징벡터로 채택한다.After extracting LPC feature vectors, LPCC feature vectors, and MFCC feature vectors from six hazardous sounds, the average separation of LPC feature vectors was 2.79, and the average of MFCC feature vectors The separation was 3.77. The average separation of the highest LPCC feature vectors was 3.79. This means that when the LPCC feature vector is used, the LPCC feature vector is a feature vector that can accurately reflect the characteristics of each dangerous situation statistically, meaning that the distance between the sounds of the dangerous situations is the longest on average. The LPCC feature vector is adopted as the main feature vector.
- 위험 상황 인지- Risk awareness
위험소리 검출 엔진은 추출된 특징벡터를 이용하여 위험 상황을 인지하기 위해 ANN(Artifical Neural Network) 패턴인식 알고리즘을 사용한다. ANN 훈련을 통해 각 퍼셉트론간의 연결 강도를 의미하는 가중치 값을 조정하여 훈련하고 입력의 비선형 함수를 유추할 수 있도록 설계된 패턴 인식 알고리즘이다. The dangerous sound detection engine uses Artificial Neural Network (ANN) pattern recognition algorithm to recognize the dangerous situation using extracted feature vectors. It is a pattern recognition algorithm designed to adjust the weight value, which means the connection strength between each perceptron through ANN training, and to train the nonlinear function of input.
본 발명에서 사용되는 ANN 신경회로망은 웨어러블 기기의 컴퓨팅 환경을 고려하여 구조를 복잡하게 하지 않기 위해 그리고 특징벡터를 추출할 때 신호의 성질이 인코딩되기 때문에 input layer와 hidden layer 사이에 신호의 성질을 인코딩할 수 있는 전처리 과정이 들어가지 않는다. 이로 인해 신경회로망 내의 많은 양의 파라미터를 줄일 수 있다. Since the ANN neural network used in the present invention does not complicate the structure in consideration of the computing environment of the wearable device and the nature of the signal is encoded when extracting the feature vector, the characteristics of the signal are encoded between the input layer and the hidden layer There is no preprocessing that can be done. This can reduce large amounts of parameters in the neural network.
본 발명의 신경회로망 구조는 input layer와 hidden layer, output layer로 구성되고 임베디드 환경을 고려하여 hidden layer는 한 개의 층으로 복잡하지 않게 구성되며, input layer의 입력 뉴런의 개수는 추출한 특징벡터의 차수와 같이 10개로 정한다. hidden layer의 뉴런 개수는 6개로 여러 번 반복하여 실험적으로 결정하였다. 6개의 뉴런 중 하나의 뉴런은 bias 값을 갖는다. The neural network structure of the present invention is composed of an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer. In consideration of the embedded environment, the hidden layer is not complicated as one layer. The number of input neurons in the input layer is determined by the degree of the extracted feature vector We set it to ten together. The number of neurons in the hidden layer was determined experimentally by repeating several times. One of the six neurons has a bias value.
output layer는 6개의 뉴런으로 구성되어 있으며 각 뉴런은 6개의 위험상황에 대하여 각각의 클래스 점수를 출력하게 된다. 신경회로망내의 전체 뉴런의 계수는 학습과정에서 output layer의 출력의 에러에 따라 오차역전파법(Back-Propagation)을 사용하여 에러를 최소화하는 계수를 업데이트한다. The output layer consists of six neurons, each of which outputs a class score for each of the six hazardous situations. The coefficients of the whole neurons in the neural network update the coefficients minimizing the error using error back propagation according to the error of the output layer output during the learning process.
마지막으로, ANN 신경회로망에서 사용된 활성 함수는 α=1인 양극 시그모이드를 사용하고, 계수의 학습율은 p 0.6으로 정한다.Finally, the active function used in the ANN neural network is a bipolar sigmoid with α = 1, and the learning rate of the coefficient is set to p 0.6.
- 최적 구성- Optimum configuration
위험상황 인식을 위한 최적 구성을 이끌어 내기 위하여 전술한 구성을 이용하여 실내 환경, 실외 환경(사이렌, 차경적)의 각 경우에 소리의 크기를 5db, 10db, 15db, 20db로 하여 실험을 하였고, 그 결과를 도 2 내지 4에 도시하였다.Experiments were carried out to obtain the optimal configuration for the recognition of the dangerous situation by using the above-described configuration and setting the sound volume to 5 db, 10 db, 15 db, and 20 db in each case of the indoor environment and the outdoor environment (siren and car horn) The results are shown in Figs.
도 3의 실내 실험 결과는 전반적으로 LPCC 특징벡터를 이용할 경우가 양호하였으나, 실외 환경에 있어서는 사이렌과 차경적에 있어서 MFCC의 인식률이 차이가 크고, 차경적에 있어서도 MFCC는 5db일 경우 55.07%로 낮은 인식률을 보였지만 20dB 이상의 경우 가장 높은 100%의 정확도를 보이는 등 큰 인식률 변화를 보였다.3, the LPCC feature vectors were generally used. However, in the outdoor environment, the recognition rate of the MFCC was large in the siren and the vehicle horn, and the MFCC was 55.07% But the recognition rate of 20dB or more showed the highest 100% accuracy.
한편, 각 특징벡터 추출 방식의 복잡도를 고려할 때, LPC, LPCC에 비하여 MFCC가 제곱에 상당하는 복잡도를 보이므로, 기본적으로는 웨어러블 디바이스와 같은 임베디드 환경에서는 LPC, LPCC 특징벡터가 더 적합하다.On the other hand, considering the complexity of each feature vector extraction method, the MFCC has a complexity equivalent to the square of LPC and LPCC, and therefore, LPC and LPCC feature vectors are more suitable in an embedded environment such as wearable device.
따라서, 본 발명에서는 제1 및 제2 특징검출부를 구성함에 있어서, LPCC를 기본 특징벡터로 이용하되, 소리의 크기와 종류를 사전에 감지하여 MFCC가 높은 성능을 보이는 경우에 보조적으로 MFCC 특징벡터를 이용하여 특징을 추출하는 방식을 취한다.Therefore, in the present invention, the LPCC is used as a basic feature vector in constructing the first and second feature detectors, and when the MFCC is high in performance, the MFCC feature vector And extracts a feature using the extracted feature.
이상 몇몇 실시예를 통하여 본 발명의 구성을 상세히 설명하였으나, 이는 예시에 불과한 것으로서, 그 외의 다양한 변형과 변경 역시 본 발명의 기술적 사상에 포함됨은 물론이다. 본 발명의 목적 및 효과 역시 기술 상식을 고려한 합리적인 범주 내에서 본 명세서에 기재한 이외의 것을 포함함은 물론이다. 예컨대, ANN의 활성함수와 학습률의 변경은 본 발명의 기술적 사상의 범주에 그대로 포함된다.While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments. It is needless to say that the objects and effects of the present invention also include those other than those described herein within a reasonable range in consideration of the technical sense. For example, changes in the activation function and the learning rate of the ANN are included in the technical scope of the present invention.
따라서, 본 발명의 권리범위는 이하의 특허청구범위의 기재에 의하여 정하여져야 한다.Accordingly, the scope of the present invention should be determined by the description of the following claims.
Claims (7)
주변의 소리를 수집하는 소리수집부와,
상기 소리수집부에 의해 수집된 소리의 특징을 추출하는 특징추출부와,
상기 특징추출부로부터 입력받은 특징으로부터 인공신경망 패턴인식 알고리즘을 이용하여 위험소리를 검출하는 위험소리 검출엔진
을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 위험상황 인식 시스템.
A database for storing sound data generated in a dangerous situation,
A sound collecting unit for collecting sounds of the surroundings,
A feature extraction unit for extracting features of sounds collected by the sound collection unit;
A danger sound detection engine for detecting a danger sound using an artificial neural network pattern recognition algorithm from the features input from the feature extraction unit;
Wherein the risk identification system comprises:
상기 위험소리 검출엔진의 검출 결과에 따라 소리 대체 알림 신호를 발생하는 경보부를 더 포함하는 위험상황 인식 시스템.
The method according to claim 1,
And a warning unit for generating a sound replacement notification signal according to the detection result of the dangerous sound detection engine.
실내 및 실외 위험상황 DB, 혼잡잡음 DB, 상기 실내 및 실외 위험상황 DB와 상기 혼잡잡음 DB를 혼합한 시뮬레이션 DB를 포함하고,
상기 소리수집부가 수집한 소리를 축적해 나가는 것인 위험상황 인식 시스템.
The system according to claim 1,
An indoor and outdoor risk DB, a congestion noise DB, and a simulation DB in which the indoor and outdoor risk DB and the congestion noise DB are mixed,
Wherein the sound collector collects the collected sounds.
LPCC 특징벡터를 이용하여 수집되는 소리의 특징을 추출하되, 소리의 크기와 종류에 따라 MFCC 특징벡터를 이용하여 소리의 특징을 추출하는 것인 위험상황 인식 시스템.
The risk assessment system according to claim 1,
And extracts characteristics of the sound collected using the LPCC feature vector, and extracts features of the sound using the MFCC feature vector according to the size and type of the sound.
상기 소리수집부로부터 전달된 데이터와 저장데이터와의 대비를 통하여 위험상황 소리를 판별하는 대비판단부를 포함하는 것인 위험상황 인식 시스템.
4. The system according to claim 3,
And a contrast determination unit for determining a sound of a dangerous situation by comparing the data transmitted from the sound collecting unit and the stored data.
상기 수집된 소리의 특징을 추출하는 단계와,
상기 특징을 인공신경망 알고리즘을 이용하여 소리를 분류하는 단계와,
상기 분류하는 단계의 결과를 토대로 위험상황 여부를 판단하는 단계
를 포함하는 위험상황 인식 방법.
Collecting sound of a surrounding situation,
Extracting features of the collected sounds;
Classifying sounds using the artificial neural network algorithm,
Determining whether or not a risk situation exists based on a result of the classifying step
The method comprising the steps of:
소리의 크기 및 패턴을 판별하는 단계와,
상기 판별 결과에 따라 특징벡터를 선택하는 단계를 포함하는 것
인 위험상황 인식 방법.7. The method of claim 6, wherein extracting the feature of the sound comprises:
Determining a size and a pattern of the sound;
And selecting a feature vector according to the determination result
Risk identification method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160176716A KR20180073167A (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2016-12-22 | Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160176716A KR20180073167A (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2016-12-22 | Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180073167A true KR20180073167A (en) | 2018-07-02 |
Family
ID=62914414
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160176716A KR20180073167A (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2016-12-22 | Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20180073167A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102148378B1 (en) * | 2020-01-22 | 2020-08-26 | 강태욱 | Apparatus and method of notifying interested event using machine learning model |
| US12020560B2 (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2024-06-25 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Device and method of providing audiovisual content for the disabled |
-
2016
- 2016-12-22 KR KR1020160176716A patent/KR20180073167A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102148378B1 (en) * | 2020-01-22 | 2020-08-26 | 강태욱 | Apparatus and method of notifying interested event using machine learning model |
| US12020560B2 (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2024-06-25 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Device and method of providing audiovisual content for the disabled |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Litvak et al. | Fall detection of elderly through floor vibrations and sound | |
| CN109407504B (en) | Personal safety detection system and method based on smart watch | |
| TWI682368B (en) | Surveillance system and surveillance method using multi-dimensional sensor data | |
| Zigel et al. | A method for automatic fall detection of elderly people using floor vibrations and sound—Proof of concept on human mimicking doll falls | |
| CN106251874B (en) | A kind of voice gate inhibition and quiet environment monitoring method and system | |
| US20090018828A1 (en) | Automatic Speech Recognition System | |
| Schröder et al. | Automatic acoustic siren detection in traffic noise by part-based models | |
| Carmel et al. | Detection of alarm sounds in noisy environments | |
| WO2009113056A1 (en) | System for automatic fall detection for elderly people | |
| CN111223261B (en) | Composite intelligent production security system and security method thereof | |
| CN109036382A (en) | A kind of audio feature extraction methods based on KL divergence | |
| CN110364141A (en) | Elevator typical case's abnormal sound alarm method based on depth single classifier | |
| CN113674768B (en) | Acoustic-based help calling detection method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| US20070299671A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for analysing sound- converting sound into information | |
| JP2017062349A (en) | Detection device and control method for the same, and computer program | |
| Kim et al. | Hierarchical approach for abnormal acoustic event classification in an elevator | |
| EP2028651A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for detection of specific input signal contributions | |
| KR101736466B1 (en) | Apparatus and Method for context recognition based on acoustic information | |
| KR101250668B1 (en) | Method for recogning emergency speech using gmm | |
| Choi et al. | Selective background adaptation based abnormal acoustic event recognition for audio surveillance | |
| CN110797034A (en) | Automatic voice and video recognition intercom system for caring old people and patients | |
| KR20180073167A (en) | Method of dangerous sound detection for hearing impaired persons | |
| Klumpp et al. | Surgical mask detection with deep recurrent phonetic models. | |
| KR101741418B1 (en) | A method for recognizing sound based on acoustic feature extraction and probabillty model | |
| Yella et al. | Comparison of pattern recognition techniques for the classification of impact acoustic emissions |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |