KR20180059308A - Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid - Google Patents
Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20180059308A KR20180059308A KR1020160158729A KR20160158729A KR20180059308A KR 20180059308 A KR20180059308 A KR 20180059308A KR 1020160158729 A KR1020160158729 A KR 1020160158729A KR 20160158729 A KR20160158729 A KR 20160158729A KR 20180059308 A KR20180059308 A KR 20180059308A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- adhesion
- hyaluronic acid
- composition
- acid
- hyaluronidase inhibitor
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/04—Macromolecular materials
- A61L31/041—Mixtures of macromolecular compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/04—Macromolecular materials
- A61L31/06—Macromolecular materials obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/14—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- A61L31/16—Biologically active materials, e.g. therapeutic substances
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/40—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a specific therapeutic activity or mode of action
- A61L2300/41—Anti-inflammatory agents, e.g. NSAIDs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/40—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a specific therapeutic activity or mode of action
- A61L2300/42—Anti-thrombotic agents, anticoagulants, anti-platelet agents
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 히알루론산 및 폴리감마글루탐산을 포함하는 유착 방지 조성물에 대한 것이다.The present invention is directed to an anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic acid and polygamma glutamic acid.
유착(adhesion)이란 염증, 창상, 마찰, 수술 등에 의한 창상 등 상처의 치유 과정에서 섬유조직(fibrous tissue)이 과도하게 생성되거나, 혈액이 유출되어 응고하여 서로 분리되어 있어야 할 주변 장기 또는 조직이 서로 달라붙는 현상을 의미하는 것이다.Adhesion refers to the formation of fibrous tissue during wound healing, such as inflammation, wound healing, friction, and wound healing, or the surrounding organs or tissues to be separated from each other It is a phenomenon that sticks.
유착은 모든 종류의 수술 후에 발생할 수 있으며, 이로 인하여 심각한 임상적 후유증이 발생할 수 있다.Adhesion can occur after all types of surgery, which can lead to serious clinical sequelae.
이러한 유착방지를 위한 여러 방법 중 하나로 방벽(barrier)을 사용하여 조직의 상처가 치유되는 동안 계면활성제와 유사하게 물리적인 장벽을 형성하여 인접한 조직 사이에 유착이 형성되는 것을 막아주는 유착방지재에 대한 연구가 활발하게 진행되고 있다.One of the methods for preventing such adhesion is to use a barrier to form a physical barrier similar to a surfactant during the healing of tissue wounds and to prevent the formation of adhesion between adjacent tissues. Research is actively under way.
방벽용으로 사용되는 유착방지재는 형태상 크게 두 가지로 분류할 수 있는데, 첫째는 필름, 부직포, 스폰지형을 포함하는 막 형태의 방벽이며, 둘째는 겔 형을 포함한 용액형 방벽이다(한국등록특허 10-1624511호).The anti-adhesion material used for the barrier may be divided into two types, one of which is a membrane type barrier including a film, a nonwoven fabric, and a sponge type, and the other is a solution type barrier containing a gel type 10-1624511).
막 형태의 유착방지 재료로는 산화재생 셀룰로오스(Oxydized-regenerated cellulose), 익스팬디드 PTFE(Expanded polyterafluoroethylene, 이하 ePTFE), 개질된 히알루론산과 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스나트륨 및 화학적 가교제 등으로 구성된 필름 등이 있다.Film-like adhesion preventive materials include oxidized regenerated cellulose, Expanded polyterafluoroethylene (hereinafter abbreviated as ePTFE), modified hyaluronic acid, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and chemical crosslinking agents.
용액형 유착방지 재료로는 락테이트링거 용액, 덱스트란-70 용액, 헤파린 용액, 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스나트륨(Carboxymethyl cellulose) 용액, 히알루론산 용액, 콘드로이틴셀페이트(Chondroitin sulfate) 용액, 폴리에틸렌글리콜(Polyethylene glycol) 용액, 덱스트란-70 용액, 헤파린 용액 등아 있다. 이들은 복막의 치유가 일어나는 동안에 섬유소로 덮인 표면을 서로 뜨도록 부유시키는 것이 주된 기전으로, 조직들을 서로 분리시켜 유착을 억제할 목적으로 사용했던 제제들이다.Examples of the solution type adhesion preventive material include a lactate ringer solution, a dextran-70 solution, a heparin solution, a carboxymethyl cellulose solution, a hyaluronic acid solution, a chondroitin sulfate solution, a polyethylene glycol, Solution, dextran-70 solution, heparin solution and the like. These were the main mechanisms by which the fiber-covered surfaces were floated to each other during the peritoneal healing process, which were used to separate the tissues from each other and to inhibit adhesion.
그러나 이러한 용핵형 유착방지 재료들은 복강 내에서 흡수가 과하게 빨라 일어나 생체 내에서 오래 지속되지 못하여 효과적인 유착 방지가 어려운 문제가 있다. However, such a nucleus-type adhesion preventive material suffers from the fact that absorption in the abdominal cavity is excessively rapid, and it is not long-lasting in vivo, thereby making it difficult to effectively prevent adhesion.
본 발명자들의 목적은 생체 내 지속 시간이 긴 유착 방지 조성물을 제공하는 것이다.It is an object of the present invention to provide an anti-adhesion composition having a long duration in vivo.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위하여 본 발명은 히알루로니다아제 저해제 및 히알루론산을 포함하는 유착방지용 조성물을 제공한다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a hyaluronidase inhibitor and a composition for preventing adhesion comprising hyaluronic acid.
본 발명의 유착 방지 조성물은 생체 내 지속 시간이 증진되어 유착 방지 효능이 오래 지속되는 효과가 있다.The anti-adhesion composition of the present invention has an effect of enhancing the persistence time in vivo and prolonging the anti-adhesion effect.
도 1은 실시예 1 및 비교군 1 및 2의 유착 방지 효과를 보여준다.
도 2는 마우스에 실시예 1 및 비교군 1 및 2를 적용한 후 14일째 조직 내 유착 유무를 육안으로 관찰한 사진이다( (a): 대조군, (b): 실시예 1, (c): 비교군 1).
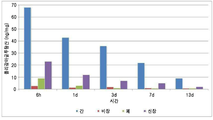
도 3은 폴리감마글루탐산의 생체 내 잔존량을 보여준다.
도 4는 히알루론산 및 폴리감마글루탐산의 비율에 따른 히알루론산의 생체 내 잔존 기간의 차이를 보여준다.Fig. 1 shows the effect of preventing adhesion of Example 1 and
FIG. 2 is a photograph showing the naked eye observation of adhesion of tissues on the 14th day after application of the Example 1 and
Fig. 3 shows the in vivo residual amount of polygamma glutamic acid.
FIG. 4 shows the difference in the survival period of hyaluronic acid in vivo according to the ratio of hyaluronic acid and polygamma glutamic acid.
본 발명은The present invention
히알루로니다아제 저해제 및 히알루론산을 포함하는 유착방지용 조성물에 대한 것이다.A hyaluronidase inhibitor, and hyaluronic acid.
또한 본 발명은Also,
히알루로니다아제 저해제 및 히알루론산을 혼합하는 단계를 포함하는 유착방지용 조성물의 제조 방법에 대한 것이다.A hyaluronidase inhibitor, and a hyaluronic acid, which comprises the step of mixing a hyaluronidase inhibitor and hyaluronic acid.
이하, 본 발명을 자세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
히알루로니다아제 저해제Hyaluronidase inhibitor
본 발명의 히알루로디아제 저해제는 히알루로니다아제에 의한 히알루론산 분해를 억제하는 효능을 갖는다. 이로써 본 발명의 히알루로디아제 저해제는 상처에 적용된 유착방지용 조성물이 체내에서 분해, 배출을 억제하여 히알루론산의 생체 내 잔존 기간을 증가시키고, 이로써 유착방지용 조성물의 지속 시간을 증진시킨다.The hyaluronidase inhibitor of the present invention has an effect of inhibiting hyaluronic acid degradation by hyaluronidase. As a result, the hyaluronidase inhibitor of the present invention increases the duration of the hyaluronic acid in vivo by inhibiting the decomposition and release of the anti-adhesion composition applied to the wound, thereby improving the duration of the antiadherent composition.
상기 히알루로디아제 저해제는 바람직하게는 폴리감마글루탐산(γ-PGA)이다. 상기 폴리감마글루탐산은 높은 점탄성과 접착력을 제공하여 수술 후 조직에서의 유착방지재의 지속력을 효과적으로 높여준다.The hyaluronidase inhibitor is preferably polygamma glutamic acid (γ-PGA). The polygamma glutamic acid provides high viscoelasticity and adhesive strength to effectively enhance the persistence of the anti-adhesion material in post-surgical tissue.
히알루론산Hyaluronic acid
본 발명의 히알루론산은 유착 방지용 조성물에 일반적으로 사용되는 히알루론산이면 되고 특별히 제한되지 않는다.The hyaluronic acid of the present invention is not particularly limited as long as it is hyaluronic acid generally used in the composition for preventing adhesion.
유착방지용 조성물Composition for preventing adhesion
본 발명은 히알루로니다아제 저해제 및 히알루론산을 포함하는 유착방지용 조성물에 대한 것이다. 상기 히알루론산 및 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 1: 0.005 내지 2.550의 중량비로 포함되며, 바람직하게는 상기 히알루론산 및 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 1: 0.01 내지 2.0의 중량비로 포함된다. 상기 범위를 유지함으로써, 유착방지용 조성물에 사용된 히알루론산의 생체 내 잔존 기간을 증가시키게 되어, 유착 효능을 증진시키게 된다.The present invention relates to a hyaluronidase inhibitor and a composition for preventing adhesion comprising hyaluronic acid. The hyaluronic acid and the hyaluronidase inhibitor are contained in a weight ratio of 1: 0.005 to 2.550, and preferably the hyaluronic acid and the hyaluronidase inhibitor are contained in a weight ratio of 1: 0.01 to 2.0. By maintaining the above range, the duration of the hyaluronic acid used in the anti-adhesion composition is increased in vivo, and the adhesion efficiency is enhanced.
본 발명의 유착방지용 조성물은 상처에 적용 시 10일 이상 히알루론산이 체내에 잔존하게 한다. 이로써 본 발명의 유착 방지의 지속 시간을 증진시킨다. The composition for preventing adhesion of the present invention causes hyaluronic acid to remain in the body for 10 days or more when applied to a wound. Thereby enhancing the duration of the adhesion prevention of the present invention.
본 발명의 유착방지용 조성물은 액상이다. 상기 액상은, 고상을 제외한 유동성이 있는 재질을 가리키며, 겔상을 포함한다.The composition for preventing adhesion of the present invention is a liquid. The liquid phase refers to a material having fluidity excluding a solid phase, and includes a gel phase.
본 발명의 유착방지용 조성물은 항염증제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 상기 항염증제은 디플루니살, 로나졸락, 로녹시캄, 록소프로펜, 메크로페남산, 메페남산, 멜록시캄, 모니플루메이트, 베노릴레이트, 브로멜라인, 살리실산이미다졸, 세라티오펩티다제, 세레콕시브, 술린닥, 시녹시캄, 아세메타신, 아세클로페낙, 아스피린, 알미노프로펜, 암페낙나트륨, 에몰파죤, 에토돌락, 염산벤지다민, 염산프로파세타몰, 옥사프로진, 이부프로펜, 이부프록삼, 인도메타신,잘토프로펜, 케토롤락, 케토프로펜, 나부메톤, 나프록센, 니메수리드, 덱사메타손, 덱시부프로펜, 디클로페낙, 피라지노부타존, 클로닉신, 탈니플루메이트, 테녹시캄, 톨메틴나트륨, 톨페남산, 티아프로펜산, 페노프로펜, 펜티아작, 펠루비프로펜, 프라노프로펜, 피록시캄, 프로제스토젠스, 플루르비프로펜, 플루페남산, 글루카메타신 및 프로글루메타신으로 구성되는 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나일 수 있다.The anti-adhesion composition of the present invention may further comprise an anti-inflammatory agent. Wherein the anti-inflammatory agent is at least one selected from the group consisting of dipyrinic acid, lorazolec, lanoxicam, loxoprofen, meclofenanic acid, mefenamic acid, meloxicam, monofluomate, benorylate, bromelain, salicylic acid imidazole, A prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, a prodrug, But are not limited to, ibuprofen, ibuproxam, indomethacin, zetofrofen, ketorolac, ketoprofen, nabumetone, naproxen, nimesulide, dexamethasone, dexibupropene, diclofenac, pyrazinobutarone, clonixin, , Tenoxycam, tolmetin sodium, tolpennamic acid, thiopropenoic acid, fenoprofen, fentiazac, felubiprofen, pranoprofen, piroxycam, progestogen, fluvifrophen, flufenamic acid , Glutamate, and proglumethasin It may be any one selected from the group.
또한 본 발명의 유착방지용 조성물은 항혈액응고제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 상기 항혈액응고제는 에녹사파린, 레피루딘, 헤파린, 저분자량 헤파린, 안크로드, 와파린 및 다나파로이드로 구성되는 군으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나일 수 있다.The anti-adhesion composition of the present invention may further comprise an anti-blood coagulant. The anti-coagulant may be any one selected from the group consisting of enoxaparin, reefuridine, heparin, low molecular weight heparin, anchor rod, warfarin, and dinapharoid.
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나, 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 것이며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다.Advantages and features of the present invention and methods of achieving them will become apparent with reference to the embodiments described in detail below. It should be understood, however, that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but is capable of many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, To fully disclose the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art, and the invention is only defined by the scope of the claims.
<재료 및 방법>≪ Materials and methods >
실험 동물로는 마우스(Balb/C)를 사용하였다. 이들 마우스들은 (주) 오리엔트바이오로부터 공급받았으며, 온도 20±3℃, 상대습도 40-70%, 환기횟수 13-18 /hr, 조명시간 12시간 (오전 7시-오후 7시), 조도 200-300 Lux의 조건으로서 시판사료와 음용수를 급여하여 순화 및 시험기간 동안 격리 사육하였다.A mouse (Balb / C) was used as an experimental animal. These mice were supplied from Orient Bio Co., Ltd., and the temperature was 20 ± 3 ° C, the relative humidity was 40-70%, the ventilation frequency was 13-18 / hr, the illumination time was 12 hours (7:00 am to 7:00 pm) As a condition of 300 Lux, commercially available feed and drinking water were fed and kept isolated during the purification and test period.
마우스 생체 내 투여된 실시예 1의 조성물의 정량 분석은, 실시예 2의 조성물 내 폴리감마글루탐산에 Gd를 부착하고, ICP-MS(Inductivity Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer, X-series, Thermo Elemental, 한국기초과학지원 연구원 환경과학연구부)를 이용하여 정량화하여 수행하였다.Quantitative analysis of the composition of Example 1 in which the mouse was administered in vivo was carried out by attaching Gd to polygamma glutamic acid in the composition of Example 2 and measuring the concentration of Gd by ICP-MS (Inductivity Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer, X-series, Thermo Elemental, Research Institute of Environmental Sciences).
폴리감마글루탐산은 바이오리더스사 제품 및 휴메딕스사 제품을 구입하여 사용하였고, 히알루론산은 신풍제약 제품 및 엘지생명과학 제품을 구입하여 사용하였다.Polygamma glutamic acid was purchased from Bio Reader and Humidix, and hyaluronic acid was purchased from Shinpung Pharmaceutical and LG Life Science.
<실시예 1>≪ Example 1 >
Bz-DTPA를 200㎎/㎖ 농도가 되도록 클로로포름에 용해하고, 450㎕를 분취하여 여기에 1㎖ TFA를 넣고 4℃에서 24시간 반응시켰다. 반응 후 TFA를 제거하고 1M 탄산수소나트륨 10㎖를 첨가하였다. PBS버퍼 용액에서 dialysis 시킨 후 입자의 동결을 위해 초저온 냉동기를 이용하여 -80℃의 온도에서 6시간 동안 동결 후 건조기에서 -80~ -85℃의 온도와 5 Pa의 압력을 유지하면서 48시간 이상 건조하였다. 건조된 물질을 100㎎/㎖ 농도로 준비하고, 100mM 아세트산 나트륨에 100mg/ml 농도의 히알루론산 용액 370㎕를 분취하여 준비된 용액과 혼합하여 약 30분간 반응시킨 후 건조하였다. 폴리감마글루탐산의 농도가 10 mg/ml인 용액 10ml에 EDC/NHS 반응시킨 후 히알루론산 용액 10ml를 본 발명의 혼합용액을 만들었다.Bz-DTPA was dissolved in chloroform so as to have a concentration of 200 mg / ml, 450 쨉 l of aliquots were taken, and 1 ml of TFA was added thereto, followed by reaction at 4 째 C for 24 hours. After the reaction, the TFA was removed and 10 ml of 1M sodium bicarbonate was added. After freezing at -80 ° C for 6 hours, the particles were frozen at -80 to -85 ° C and dried for more than 48 hours at a pressure of 5 Pa. Respectively. The dried material was prepared at a concentration of 100 mg / ml, and 370 μl of a 100 mg / ml hyaluronic acid solution was added to 100 mM sodium acetate, mixed with the prepared solution, reacted for about 30 minutes, and then dried. 10 ml of a solution having a concentration of polygamma glutamic acid of 10 mg / ml was subjected to EDC / NHS reaction, and 10 ml of a hyaluronic acid solution was added to prepare a mixed solution of the present invention.
<실시예 2>≪ Example 2 >
Bz-DTPA를 200 ㎎/㎖ 농도가 되도록 클로로포름에 용해하여 450 μl를 분취하여 1 ㎖ TFA를 넣고 4℃에서 24시간 반응시켰다. 반응 후 TFA를 제거하고 1M 탄산수소나트륨 10 ㎖를 첨가하였다. PBS 버퍼 용액에서 dialysis 시킨 후 입자의 동결을 위해 초저온 냉동기를 이용하여 -80 ℃의 온도에서 6 시간 동안 동결 후 동결 건조기에서 -80 ~ -85 ℃의 온도와 5 Pa의 압력을 유지하면서 48 시간 이상 건조하였다. 건조 된 물질을 100 ㎎/㎖ 농도가 되도록 준비 한 후 100 mM 아세트산 나트륨에 100 ㎎/㎖ 농도로 염화 가돌리늄을 용해한 용액 370 μl를 분취하여 준비된 용액에 넣고 약 30분간 반응시켰다. 반응 후 dialysis 및 건조를 수행하였다. 폴리감마글루탐산의 농도가 10 ㎎/㎖인 용액 10 ㎖에 EDC/NHS 반응시킨 후 건조 된 Bz-DTPA-Gd 110 ㎎을 첨가 하여 폴리감마글루탐산-Bz-DTPA-Gd 합성한다. 합성 된 물질을 0.22 ㎛ 인 멤브레인 필터로 필터하고 dialysis 후 건조하였다.Bz-DTPA was dissolved in chloroform to a concentration of 200 mg / ml, 450 μl aliquotted, and 1 ml of TFA was added and reacted at 4 ° C for 24 hours. After the reaction, TFA was removed and 10 ml of 1 M sodium bicarbonate was added. After dialysis in PBS buffer solution, the particles were frozen at -80 ° C for 6 hours using a cryocooler, and maintained at -80 to -85 ° C and pressure of 5 Pa for 48 hours or more And dried. The dried material was prepared to have a concentration of 100 mg / ml, and 370 μl of a solution of 100 mg / ml of sodium gadolinium chloride dissolved in 100 mM sodium acetate was added to the prepared solution, followed by reaction for about 30 minutes. After the reaction, dialysis and drying were performed. Bz-DTPA-Gd was synthesized by adding 110 mg of dried Bz-DTPA-Gd to 10 ml of a solution having a concentration of polygamma glutamic acid of 10 mg / ml, followed by EDC / NHS reaction. The synthesized material was filtered with a 0.22 ㎛ membrane filter, and then dialyzed and dried.
<비교군 1><
시판 유착방지제를 구입하여 사용하였다. 이는 sodium hyaluronate 100 중량부에 대하여, hydroxyethylstaarch 50 중량부, sodium chloride 85 중량부, sodium phosphate, dibasic 0.64 중량부 포함하고, 주입을 위한 정제수를 10000 중량부 포함하는 유착방지제이다.Commercial adhesion inhibitors were purchased and used. It is an anti-adhesion agent containing 50 parts by weight of hydroxyethylstarch, 85 parts by weight of sodium chloride, 0.64 part by weight of sodium phosphate and dibasic, and 10000 parts by weight of purified water for injection, relative to 100 parts by weight of sodium hyaluronate.
<비교군 2>≪
시판 유착방지제를 구입하여 사용하였다. 이는 poloxamer, 젤라틴 및 키토산을 포함하는 제품이다.Commercial adhesion inhibitors were purchased and used. It is a product containing poloxamer, gelatin and chitosan.
<실험예 1> γ-PGA의 히알루로니다아제 저해능 평가Experimental Example 1 Evaluation of hyaluronidase in γ-PGA
γ-PGA의 히알루로니다아제 저해능을 평가하였다. 먼저, PGA 농도가 0.002% 내지 0.008%가 되도록 400unit/㎖의 히알루로니다아제에 PGA 용액을 첨가한 후 0.4㎎/㎖의 히알루론산과 37℃에서 20분간 반응시킨 결과 IC50은 약 0.0025%로 나타났다. 반면, 0.008%의 γ-PGA 용액에서 거의 100%의 저해활성을 확인했다.The inhibition of hyaluronidase of γ-PGA was evaluated. First, the PGA solution was added to 400 units / ml of hyaluronidase so that the concentration of PGA was 0.002% to 0.008%, and the reaction was carried out at 37 ° C for 20 minutes with 0.4 mg / ml of hyaluronic acid. As a result, the IC50 was about 0.0025% . On the other hand, almost 100% inhibition activity was confirmed in the 0.008% γ-PGA solution.
<실험예 2><Experimental Example 2>
상기 실시예 1, 비교군 1 및 비교군 2에 대하여 겔 잔존 시간을 평가하였다. 먼저, 상기 조성물들을 1 ml 씩 앰플에 넣고, 상온의 밀실에 보관하면서 정기적으로 하루 한번씩 겔의 잔류 부피를 확인하여, 겔 잔존 시간을 측정하였다. 이 때, 앰플에 남은 겔이 육안으로 보이지 않을 때까지의 시간을 겔 잔존 시간으로 정하였다. The gel retention time was evaluated for Example 1,
그 결과, 실시예 1의 조성물이 비교군 1 및 2에 비하여 더 오래 남아 있는 것이 확인되었다. 그러므로 γ-PGA의 히알루로니다아제 저해능에 의하여, 겔의 분해가 억제되고 지속력이 증가되는 것으로 판단되었다(표 1).As a result, it was confirmed that the composition of Example 1 remained longer than
<실험예 3> 유착 방지 효능<Experimental Example 3> Anti-adhesion effect
동물 시험을 통하여 본 발명의 유착방지재 조성물의 유착 방지 효능을 평가하였다. The anti-adhesion effect of the anti-adhesion composition of the present invention was evaluated through animal tests.
먼저, 마우스를 개복하고, 1 x 1㎝ 크기의 장막 표면을 출혈이 일어날 정도로 손상을 가하였다. 그리고 손상 부위에 실시예 1, 비교군 1 및 비교군 2의 조성물들을 각각 1 ml씩 균일하게 도포한 후 피부층을 연속 봉합하였다. 그리고 대조군으로는 유착방지를 위한 시료를 아무 것도 처리하지 않은 군을 이용하였다.First, the mouse was opened and the surface of the membrane of 1 x 1 cm was damaged to such an extent that hemorrhage occurred. The compositions of Example 1, Comparative Example 1, and Comparative Example 2 were applied uniformly to each damaged area by 1 ml each, and then the skin layer was continuously sutured. As a control group, a sample in which no sample was treated for adhesion prevention was used.
수술 14일 경과 후, 조직의 유착 정도를 육안으로 평가하였다. 그리고, 유착 정도를 0 내지 3.5 사이의 숫자로 나타내었다. (0: 유착이 없음: 1: 손상 부위의 30% 정도로 유착이 이루어짐, 2: 손상 부위의 50% 정도로 유착이 이루어짐, 3: 손상부위의 70% 정도로 유착이 이루어짐). 그 결과, 실시예 1의 조성물은 비교군 1 및 2보다 유착 방지 효능이 우수한 것으로 나타났다(도 1 및 도 2, (a): 대조군, (b): 실시예 1, (c): 비교군 1).After 14 days of operation, the degree of adhesion of the tissue was visually evaluated. The degree of adhesion is represented by a number between 0 and 3.5. (0: no adhesion: 1: adhesion of about 30% of the damaged area, 2: adhesion of about 50% of the damaged area, and 3: adhesion of about 70% of the damaged area). As a result, the composition of Example 1 was superior to the
<실험예 4> 유착 형성 방지 후 생체 흡수 및 배출 시험<Experimental Example 4> Bioabsorption and release test after prevention of adhesion formation
실시예 2의 조성물을 근육주사 투여 방법을 이용하여 마우스에 투입하였다(시간 별로 3마리 씩 총 15마리 이용). 그리고 투입 후, 6시간, 1일, 3일, 7일, 14일이 경과한 후에 실시예 2의 조성물의 생체 내 장기 별 분포를 분석함으로써, 체내에서의 대사거동을 분석하였다. 이 때, 6시간, 1일, 3일, 7일, 14일이 경과한 후 마우스로부터 장기(간, 비장, 폐, 신장)를 적출하고, 이를 건조하여, ICP-MS를 이용하여 조성물에 사용된 폴리감마글루탐산의 분포를 분석하였다. The composition of Example 2 was injected into the mice using the intramuscular administration method (total of 15 mice per 3 mice per time). After 6 hours, 1 day, 3 days, 7 days, and 14 days after the injection, the metabolic behavior in the body was analyzed by analyzing the distribution of the composition of Example 2 in vivo organs. At this time, organs (liver, spleen, lung, kidney) were extracted from the mouse after 6 hours, 1 day, 3 days, 7 days and 14 days and were dried and used in the composition using ICP-MS The distribution of polygamma glutamic acid was analyzed.
근육주사 전 폴리감마글루탐산에 부착된 Gd의 농도를 ICP-MS를 이용하여 측정한 결과 약 24 %의 부착율을 확인하였다. 이를 기초로, 근육주사에 시간에 따른 각 장기에 분포하는 폴리가감마글루탐산의 양을 정량화 할 수 있었다.The concentration of Gd attached to poly-gamma glutamate before intramuscular injection was measured by ICP-MS and the adhesion rate was confirmed to be about 24%. Based on this, it was possible to quantify the amount of polygamma glutamic acid distributed in each organs over time in intramuscular injection.
그 결과, 마우스들에서 일반 중독 증상이 관찰되지 않았으며, 모든 장기들에서도 이상 소견은 발견되지 않았다. As a result, general poisoning symptoms were not observed in the mice, and no abnormality was found in all the organs.
한편, 근육주사를 통하여 마우스내에 도입된 폴리감마글루탐산은 초기에 대부분이 간에 축적되었으며, 2주 동안 관찰결과, 시간에 따라 간에 축적된 양이 점점 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 비장과 폐에서도 비슷한 경향이 관찰되었다(도 3).On the other hand, the polygamma glutamic acid introduced into the mouse through intramuscular injection accumulated in most of the liver in the early stage, and as a result of observation for 2 weeks, the accumulated amount of liver tended to decrease gradually with time. Similar trends were observed in the spleen and lung (FIG. 3).
그러므로 근육주사를 통하여 마우스에 도입된 폴리감마글루탐산이 시간에 따라, 신장을 통하여 배출되는 꾸준히 배출되는 것을 ICP-MS를 통하여 확인할 수 있었으며, 시간에 따라서 배출되는 양이 점점 감소되는 경향을 통하여, 체내의 간, 비장, 폐 등에 축적되었던 폴리감마글루탐산이 생체 내의 대사작용이나 분해에 의해 신장을 통하여 배출된다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이는 투여한 폴리감마글루탐산이 체내 대사 작용에 의하여 분해되거나 체외로 배출되는 것을 의미한다.Therefore, ICP-MS was able to confirm that the polygamma-glutamic acid introduced into the mouse through the intramuscular injection was continuously discharged from the kidney through the kidney, and the amount discharged was gradually decreased, It was confirmed that polygamma glutamic acid accumulated in liver, spleen, lung and the like was excreted through elongation by metabolism or decomposition in vivo. This means that the administered polygamma-glutamic acid is decomposed by metabolism in the body or excreted outside the body.
<실험예 5> 폴리감마글루탐산의 농도에 따른 히알루론산 잔존능 평가<Experimental Example 5> Evaluation of hyaluronic acid remaining ability according to the concentration of polygamma glutamic acid
유착 억제 조성물 내 폴리감마글루탐산와 히알루론산의 비율(중량%에 따른 중량비)에 따른 히알루론산의 잔존능을 평가하였다. 이 때, 생체(37 ℃) 모의 환경에 시료들을 도포하여 Hemo-Vac 흡입을 통한 시료의 잔존량을 평가하였다. 시료의 잔존량은 색소를 적용하여 흡광도 측정을 통하여 측정하였다(Elisa 흡광도 분석기).The residual ability of hyaluronic acid was evaluated according to the ratio of polygamma glutamic acid to hyaluronic acid (weight ratio by weight%) in the adhesion inhibition composition. At this time, samples were applied to a living body (37 ° C) simulated environment, and the amount of the sample remaining after hemo-vacuum inhalation was evaluated. The residual amount of the sample was measured by absorbance measurement using a dye (Elisa absorbance analyzer).
그 결과, 히알루론산 0.50 중량% 내지 1.00 중량%, 폴리감마글루탐산 0.01 내지 1 중량%에서 히알루론산이 특히 오래 유지되는 것이 확인되었다(도 4, HA:, 히알루론산, γ-PGA: 폴리감마글루탐산).As a result, it was confirmed that hyaluronic acid was kept particularly long in 0.50% by weight to 1.00% by weight of hyaluronic acid and 0.01 to 1% by weight of polygamma glutamic acid (Fig. 4, HA :, hyaluronic acid,? -PGA: polygamat glutamic acid) .
Claims (11)
A hyaluronidase inhibitor and hyaluronic acid.
상기 조성물은 액상인 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the composition is in a liquid phase.
상기 히알루론산 및 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 1: 0.005 내지 2.550의 중량비로 포함되는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the hyaluronic acid and the hyaluronidase inhibitor are contained in a weight ratio of 1: 0.005 to 2.550.
상기 히알루론산 및 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 1: 0.01 내지 2.0의 중량비로 포함되는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the hyaluronic acid and the hyaluronidase inhibitor are contained in a weight ratio of 1: 0.01 to 2.0.
상기 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 히알루론산의 생체 내 잔존 기간을 증가시키는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the hyaluronidase inhibitor increases the residence time of hyaluronic acid in vivo.
항염증제를 추가로 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
A composition for preventing adhesion, which further comprises an anti-inflammatory agent.
항혈액응고제를 추가로 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
A composition for preventing adhesion, which further comprises an anti-blood coagulant.
상기 히알루로니다아제 저해제는 폴리감마글루탐산인 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the hyaluronidase inhibitor is polygamma glutamic acid.
상처에 적용 시 10일 이상 히알루론산이 잔존하는 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
Characterized in that hyaluronic acid remains for 10 days or more when applied to a wound.
유착 방지의 지속 시간이 증진된 것을 특징으로 하는 유착방지용 조성물.
The method according to claim 1,
And the duration of the adhesion prevention is improved.
A method for producing an anti-adhesion composition comprising mixing a hyaluronidase inhibitor and hyaluronic acid.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160158729A KR102313490B1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160158729A KR102313490B1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180059308A true KR20180059308A (en) | 2018-06-04 |
| KR102313490B1 KR102313490B1 (en) | 2021-10-15 |
Family
ID=62628197
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160158729A KR102313490B1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2016-11-25 | Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102313490B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021178803A (en) * | 2020-05-15 | 2021-11-18 | 学校法人東京電機大学 | Adhesion preventive material and method for manufacturing adhesion preventive material |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100582120B1 (en) * | 2005-10-20 | 2006-05-22 | 주식회사 바이오리더스 | Hyaluronidase inhibitor containing poly-gamma-glutamic acid as an effective component |
| WO2009088118A1 (en) * | 2008-01-07 | 2009-07-16 | Bioleaders Corporation | Pharmaceutical composition for treating corneal wound comprising poly-gamma-glutamic acid |
| KR101005079B1 (en) * | 2008-10-23 | 2010-12-30 | 금오공과대학교 산학협력단 | Biodegradable Nanofiber sheet for Anti-adhesion Membrane and Process for Preparing the Same |
| KR20150030682A (en) * | 2015-02-04 | 2015-03-20 | (주)웰빙해피팜 | Hyaluronic acid (HA) inhibitory biomaterials containing anti-inflammatory and anti-blood clotting components |
-
2016
- 2016-11-25 KR KR1020160158729A patent/KR102313490B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100582120B1 (en) * | 2005-10-20 | 2006-05-22 | 주식회사 바이오리더스 | Hyaluronidase inhibitor containing poly-gamma-glutamic acid as an effective component |
| WO2009088118A1 (en) * | 2008-01-07 | 2009-07-16 | Bioleaders Corporation | Pharmaceutical composition for treating corneal wound comprising poly-gamma-glutamic acid |
| KR101005079B1 (en) * | 2008-10-23 | 2010-12-30 | 금오공과대학교 산학협력단 | Biodegradable Nanofiber sheet for Anti-adhesion Membrane and Process for Preparing the Same |
| KR20150030682A (en) * | 2015-02-04 | 2015-03-20 | (주)웰빙해피팜 | Hyaluronic acid (HA) inhibitory biomaterials containing anti-inflammatory and anti-blood clotting components |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021178803A (en) * | 2020-05-15 | 2021-11-18 | 学校法人東京電機大学 | Adhesion preventive material and method for manufacturing adhesion preventive material |
| JP7448944B2 (en) | 2020-05-15 | 2024-03-13 | 学校法人東京電機大学 | Anti-adhesion material and method for manufacturing the anti-adhesion material |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102313490B1 (en) | 2021-10-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Ohya et al. | The potential of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)(PNIPAM)-grafted hyaluronan and PNIPAM-grafted gelatin in the control of post-surgical tissue adhesions | |
| KR101841469B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing wound covering material using biopolymer and wound covering material using biopolymer manufactured by the same | |
| RU2635510C2 (en) | Procoagulant peptides, their derivatives and their application | |
| Ma et al. | Alginate/chondroitin sulfate based hybrid hydrogel with different molecular weight and its capacity to regulate chondrocytes activity | |
| Zhang et al. | A drug-loaded composite coating to improve osteogenic and antibacterial properties of Zn–1Mg porous scaffolds as biodegradable bone implants | |
| JP4280962B2 (en) | Sulfated hyaluronic acid and its sulfated derivatives covalently bonded to polyurethane and methods for their preparation | |
| US20210023259A1 (en) | Poly (ionic liquid) compositions and their use as tissue adhesives | |
| Ponsen et al. | A new hemostatic agent composed of Zn2+-enriched Ca2+ alginate activates vascular endothelial cells in vitro and promotes tissue repair in vivo | |
| US20100204174A1 (en) | Novel active ingredient in cicatrization and use thereof | |
| US20240058502A1 (en) | Medical device, and hydrogel, preparation method therefor, and application thereof | |
| WO2013121983A1 (en) | Biological tissue reinforcement material kit and biological tissue reinforcement material | |
| Bi et al. | A new class of β-carboline alkaloid-peptide conjugates with therapeutic efficacy in acute limb ischemia/reperfusion injury | |
| Cheng et al. | First‐Aid Hydrogel Wound Dressing with Reliable Hemostatic and Antibacterial Capability for Traumatic Injuries | |
| AU2014353199B2 (en) | Solutions for increasing the stability and shelf life of an organ and tissue preservation solution | |
| Meng et al. | Restrained MSUM crystallization via hydrogel composited membrane based platform for gout prevention and control | |
| KR20180059308A (en) | Anti-adhesion composition comprising hyaluronic aicd and poly-gamma-glutamate acid | |
| Liu et al. | Peptide/glycyrrhizic acid supramolecular polymer: An emerging medical adhesive for dural sealing and repairing | |
| Songkroh et al. | In situ forming chitosan-based hydrogel as a lung sealant for biological lung volume reduction | |
| Bim-Junior et al. | Biomimetic Growth of Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Stabilization of the Dentin Matrix and Control of Collagenolysis | |
| WO2020137903A1 (en) | Powder, wound-covering material, adhesion prevention material, hemostatic material, and production method for powder | |
| CN103550833A (en) | Medicine controlled-release film material and preparation method | |
| Wang et al. | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps‐Inhibiting and Fouling‐Resistant Polysulfoxides Potently Prevent Postoperative Adhesion, Tumor Recurrence, and Metastasis | |
| Yu et al. | A versatile modification strategy for functional non-glutaraldehyde cross-linked bioprosthetic heart valves with enhanced anticoagulant, anticalcification and endothelialization properties | |
| Ross et al. | Fibrillin containing elastic microfibrils support platelet adhesion under dynamic shear conditions | |
| EP3148553A1 (en) | Antithrombotic compounds, methods and uses thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| X701 | Decision to grant (after re-examination) |