KR20180027877A - Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof - Google Patents
Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20180027877A KR20180027877A KR1020160115090A KR20160115090A KR20180027877A KR 20180027877 A KR20180027877 A KR 20180027877A KR 1020160115090 A KR1020160115090 A KR 1020160115090A KR 20160115090 A KR20160115090 A KR 20160115090A KR 20180027877 A KR20180027877 A KR 20180027877A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- electrospinning
- solution
- air filter
- nanofiber layer
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D39/00—Filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D39/14—Other self-supporting filtering material ; Other filtering material
- B01D39/16—Other self-supporting filtering material ; Other filtering material of organic material, e.g. synthetic fibres
- B01D39/1607—Other self-supporting filtering material ; Other filtering material of organic material, e.g. synthetic fibres the material being fibrous
- B01D39/1623—Other self-supporting filtering material ; Other filtering material of organic material, e.g. synthetic fibres the material being fibrous of synthetic origin
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D39/00—Filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D39/02—Loose filtering material, e.g. loose fibres
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D46/00—Filters or filtering processes specially modified for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours
- B01D46/10—Particle separators, e.g. dust precipitators, using filter plates, sheets or pads having plane surfaces
- B01D46/12—Particle separators, e.g. dust precipitators, using filter plates, sheets or pads having plane surfaces in multiple arrangements
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/0007—Electro-spinning
- D01D5/0015—Electro-spinning characterised by the initial state of the material
- D01D5/003—Electro-spinning characterised by the initial state of the material the material being a polymer solution or dispersion
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/0007—Electro-spinning
- D01D5/0061—Electro-spinning characterised by the electro-spinning apparatus
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2239/00—Aspects relating to filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D2239/02—Types of fibres, filaments or particles, self-supporting or supported materials
- B01D2239/025—Types of fibres, filaments or particles, self-supporting or supported materials comprising nanofibres
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2239/00—Aspects relating to filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D2239/06—Filter cloth, e.g. knitted, woven non-woven; self-supported material
- B01D2239/0604—Arrangement of the fibres in the filtering material
- B01D2239/0631—Electro-spun
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2239/00—Aspects relating to filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D2239/06—Filter cloth, e.g. knitted, woven non-woven; self-supported material
- B01D2239/065—More than one layer present in the filtering material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2239/00—Aspects relating to filtering material for liquid or gaseous fluids
- B01D2239/10—Filtering material manufacturing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Filtering Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 다층 에어필터 및 이의 제조 방법에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는 필터의 여과 효율을 향상시키면서 나노 섬유층의 박리를 막을 수 있는 다층 에어필터 및 이의 제조 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a multilayered air filter and a method of manufacturing the same, and more particularly, to a multilayered air filter capable of preventing separation of a nanofiber layer while improving filter filtration efficiency and a method of manufacturing the same.
나노 섬유는 지름이 수십에서 수백 나노미터에 불과한 초극세실을 말하며, 이는 사람 머리카락의 약 1/1000~1/2000 직경 크기 수준으로 다공성을 가지며 전기 방사나 혼합 방사 방법 등에 의해 제조된다. 대부분의 나노 섬유는 전기 방사법을 이용하여 제조되며, 용액에 고전압을 인가하여 매우 작은 직경을 갖는 노즐에서 테일러콘을 형성하여 표면 장력보다 전기적인 힘이 더 강하면 대전된 입자가 반대편 극으로 방사되는 원리를 이용하여 만들어지고, 방사가 끝나면 용매는 증발하고 고분자의 섬유만 남게 된다.Nanofibers are microfibers with diameters ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers. They are porous with a size of about 1 / 1000-1 / 2000 diameter of human hair and are manufactured by electrospinning or mixed spinning. Most nanofibers are manufactured by electrospinning. When a high voltage is applied to a solution to form a Taylor cone in a nozzle having a very small diameter, the electric force is stronger than the surface tension, and the principle that the charged particles are radiated to the opposite pole When the spinning is finished, the solvent evaporates and only the fiber of the polymer is left.
이러한 나노 섬유는 여러 방면으로 활용되고 있다. 예를 들어, 부직포의 표면에 나노 섬유를 코팅하여 필터의 여과 효율과 수명을 증대시키고 있다. 그런데, 부직포의 표면에 나노 섬유만을 코팅할 경우, 나노 섬유층이 박리되는 문제가 발생할 수 있다.These nanofibers are used in many ways. For example, nanofibers are coated on the surface of a nonwoven fabric to increase filtration efficiency and lifetime of the filter. However, when only the nanofibers are coated on the surface of the nonwoven fabric, the nanofiber layer may peel off.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, 나노 섬유층의 위에 부직포 보호재를 덧대는 방법을 사용하고 있다. 그러나, 부직포 보호재는 나노 섬유층의 박리를 방지할 수 있으나, 필터 효율을 저감시키는 문제가 있다.In order to solve this problem, a method of applying a nonwoven fabric protective material on the nano fiber layer is used. However, the nonwoven fabric protective material can prevent peeling of the nano fiber layer, but has a problem of reducing the filter efficiency.
본 발명은 상기 문제점을 해결하기 위한 것으로, 불규칙한 나노 섬유층 위에 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 코팅함으로써, 필터의 여과 효율을 높이면서 나노 섬유층의 박리를 막을 수 있는 다층 에어필터 및 이의 제조 방법을 제공한다.Disclosure of Invention Technical Problem [8] The present invention provides a multilayered air filter capable of preventing separation of a nano fiber layer while improving filtration efficiency of a filter by coating microfibers aligned on irregular nanofiber layers, and a method of manufacturing the same.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제들은 이상에서 언급한 과제들로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 과제들은 아래의 기재로부터 당업자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The problems to be solved by the present invention are not limited to the above-mentioned problems, and other matters not mentioned can be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following description.
상기 과제를 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터는, 부직포 기재; 전기방사에 의해 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 부직포 기재의 일면에 형성되는 나노 섬유층; 및 전기방사에 의해 나란히 정렬되어 상기 나노 섬유층 상에 형성되는 마이크로 섬유층을 포함한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a multi-layer air filter comprising: a nonwoven fabric substrate; A nanofiber layer randomly arranged by electrospinning and formed on one surface of the nonwoven substrate; And a microfiber layer arranged side by side by electrospinning and formed on the nano fiber layer.
또한, 상기 부직포 기재는, 폴리프로필렌을 포함할 수 있다.In addition, the nonwoven substrate may include polypropylene.
또한, 상기 나노 섬유층은, 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리우레탄 용액을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성될 수 있다.The nanofiber layer is prepared by electrospinning a polyurethane solution having a concentration of 8 to 15% (W / W) at a voltage of 10 to 25 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm .
그리고, 상기 마이크로 섬유층은, 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리스티렌 용액을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성될 수 있다.The microfiber layer is formed by electrospinning a polystyrene solution having a concentration of 16 to 21% (W / W) at a voltage of 25 to 35 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm .
상기 과제를 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법은, 부직포 기재를 마련하는 단계; 상기 부직포 기재의 일면에 제1 방사용액을 전기방사하여 랜덤하게 배열되는 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계; 및 상기 나노 섬유층 상에 제2 방사용액을 전기방사하여 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of manufacturing a multilayered air filter, comprising: providing a nonwoven fabric substrate; Forming a nanofiber layer randomly arranged by electrospinning a first spinning solution on one surface of the nonwoven substrate; And electrospinning the second spinning solution on the nano fiber layer to form a microfiber layer arranged side by side.
또한, 상기 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계는, 클로로포름에 폴리우레탄을 교반시켜 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제1 방사용액을 만드는 단계; 상기 제1 방사용액을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하는 단계; 및 폴리우레탄으로 이루어진 나노 섬유가 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of forming the nanofiber layer may include stirring the polyurethane in chloroform to prepare the first spinning solution having a concentration of 8 to 15% (W / W); Electrospinning the first spinning solution at a voltage of 10 to 25 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a spinning distance of 1 to 20 cm; And nanofibers composed of polyurethane may be randomly arranged to form the nanofiber layer.
그리고, 상기 마이크로 섬유층을 형성하는 단계는, 클로로포름에 폴리스티렌을 교반시켜 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제2 방사용액을 만드는 단계; 상기 제2 방사용액을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하는 단계; 및 폴리스티렌으로 이루어진 마이크로 섬유가 나란히 정렬되어 상기 마이크로섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of forming the microfibre layer comprises stirring the polystyrene in chloroform to prepare the second spinous liquid having a concentration of 16 to 21% (W / W); Electrospinning the second spinning solution at a voltage of 25 to 35 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a spinning distance of 1 to 20 cm; And microfibers composed of polystyrene are aligned side by side to form the microfiber layer.
본 발명의 기타 구체적인 사항들은 상세한 설명 및 도면들에 포함되어 있다.Other specific details of the invention are included in the detailed description and drawings.
본 발명에 따르면 필터의 여과 효율을 유지하면서 나노 섬유층의 박리를 막을 수 있다.According to the present invention, peeling of the nano fiber layer can be prevented while maintaining the filtering efficiency of the filter.
또한, 양산형 전기 방사 시스템에 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 방사할 수 있는 구조를 추가하여 한 번의 공정으로 에어필터를 생산할 수 있다.In addition, it is possible to produce an air filter in a single process by adding a structure capable of radiating micro fibers aligned in the mass-production electrospinning system.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 단면도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터를 제조하기 위한 전기 방사의 개념을 도시한 도면이다.
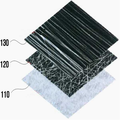
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 사시도이다.
도 4는 정렬된 마이크로 섬유의 SEM 사진을 도시한 도면이다.
도 5는 상면에 랜덤하게 배열된 나노 섬유층(좌) 및 나란히 정렬된 마이크로 섬유층(우)을 각각 배치하고 촬영한 사진을 도시한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법의 순서도이다.1 is a cross-sectional view of a multi-layer air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a view showing the concept of electrospinning for producing a multilayered air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a perspective view of a multi-layer air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a SEM photograph of aligned microfibers.
Fig. 5 is a photograph showing photographs in which a nanofiber layer (left) randomly arranged on the upper surface and a microfiber layer (right) aligned side by side are respectively disposed.
6 is a flowchart of a method of manufacturing a multilayered air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 것이며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다. 명세서 전체에 걸쳐 동일 참조 부호는 동일 구성 요소를 지칭한다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The advantages and features of the present invention, and the manner of achieving them, will be apparent from and elucidated with reference to the embodiments described hereinafter in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The present invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as being limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. Is provided to fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art, and the invention is only defined by the scope of the claims. Like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout the specification.
비록 제1, 제2 등이 다양한 소자, 구성요소 및/또는 섹션들을 서술하기 위해서 사용되나, 이들 소자, 구성요소 및/또는 섹션들은 이들 용어에 의해 제한되지 않음은 물론이다. 이들 용어들은 단지 하나의 소자, 구성요소 또는 섹션들을 다른 소자, 구성요소 또는 섹션들과 구별하기 위하여 사용하는 것이다. 따라서, 이하에서 언급되는 제1 소자, 제1 구성요소 또는 제1 섹션은 본 발명의 기술적 사상 내에서 제2 소자, 제2 구성요소 또는 제2 섹션일 수도 있음은 물론이다.Although the first, second, etc. are used to describe various elements, components and / or sections, it is needless to say that these elements, components and / or sections are not limited by these terms. These terms are only used to distinguish one element, element or section from another element, element or section. Therefore, it goes without saying that the first element, the first element or the first section mentioned below may be the second element, the second element or the second section within the technical spirit of the present invention.
본 명세서에서 사용된 용어는 실시예들을 설명하기 위한 것이며 본 발명을 제한하고자 하는 것은 아니다. 본 명세서에서, 단수형은 문구에서 특별히 언급하지 않는 한 복수형도 포함한다. 명세서에서 사용되는 "포함한다(comprises)" 및/또는 "이루어지다(made of)"는 언급된 구성요소, 단계, 동작 및/또는 소자는 하나 이상의 다른 구성요소, 단계, 동작 및/또는 소자의 존재 또는 추가를 배제하지 않는다. The terminology used herein is for the purpose of illustrating embodiments and is not intended to be limiting of the present invention. In the present specification, the singular form includes plural forms unless otherwise specified in the specification. As used herein, the terms "comprises" and / or "made of" means that a component, step, operation, and / or element may be embodied in one or more other components, steps, operations, and / And does not exclude the presence or addition thereof.
다른 정의가 없다면, 본 명세서에서 사용되는 모든 용어(기술 및 과학적 용어를 포함)는 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 공통적으로 이해될 수 있는 의미로 사용될 수 있을 것이다. 또 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 용어들은 명백하게 특별히 정의되어 있지 않는 한 이상적으로 또는 과도하게 해석되지 않는다. Unless defined otherwise, all terms (including technical and scientific terms) used herein may be used in a sense commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Also, commonly used predefined terms are not ideally or excessively interpreted unless explicitly defined otherwise.
이하, 본 발명에 대하여 첨부된 도면에 따라 보다 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 단면도이다. 또한, 도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터를 제조하기 위한 전기 방사의 개념을 도시한 도면이다. 그리고, 도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 사시도이다.1 is a cross-sectional view of a multi-layer air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention. 2 is a diagram showing the concept of electrospinning for producing a multilayered air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention. 3 is a perspective view of a multi-layer air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1 내지 도 3을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터(100)는 부직포 기재(110), 전기방사에 의해 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 부직포 기재(110)의 일면에 형성되는 나노 섬유층(120), 및 전기방사에 의해 나란히 정렬되어 상기 나노 섬유층(120) 상에 형성되는 마이크로 섬유층(130)을 포함한다.1 to 3, a
이에 따라, 다층 에어필터(100)는 불규칙적으로 배열된 나노 섬유와 규칙적으로 배열된 마이크로 섬유가 층을 이루어 배치되며, 마이크로 섬유층(130)이 나노 섬유층(120)을 보호할 수 있게 된다. 또한, 나노 섬유층(120)이 Surface Filtration 방식으로 미세 입자를 여과하고, 마이크로 섬유층(130)이 Depth Filtration 방식으로 미세 입자를 여과함으로써, 필터의 여과 효율을 높일 수 있다.Accordingly, the
부직포 기재(110)는 폴리프로필렌(PP)을 포함할 수 있다. 폴리프로필렌은 화학적으로 안정되고, 인장 강도가 매우 높고, 높은 여과 압력(약 2.5 kgf/㎠)에도 조직의 파괴 현상이 발생하지 않는다.
이러한 부직포 기재(110)는 효율적인 여과를 위하여 소정 두께를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 부직포 기재(110)의 두께는 1~5mm 정도일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다. 예를 들어, 부직포 기재(110)의 두께를 1mm 보다 얇게 하여 여과하는 물질이 흐르는 거리가 여과에 필요한 정도 이상으로 길어지는 것을 방지할 수 있으며, 부직포 기재(110)의 두께를 5mm보다 크게 할 수도 있다.The
또한, 부직포 기재(110)는 미세한 물질을 여과하기 위해 적당한 기공의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 부직포 기재(110)는 기공의 크기가 5㎛ 이하일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다. 부직포 기재(110)의 기공 크기가 5㎛ 보다 크게 되면, 부직포 기재(110)에서 차단하지 못하는 입자가 증가하여 부직포 기재(110)의 위에 코팅되는 나노 섬유층(120)의 기공이 막혀 필터의 수명이 짧아질 수 있다.In addition, the
나노 섬유층(120)은 폴리우레탄(PU)을 포함할 수 있다. 나노 섬유층(120)은 전기방사에 의해 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 부직포 기재(110)의 일면에 형성된다. 나노 섬유층(120)은 수십에서 수백 나노미터의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 나노 섬유층(120)의 나노 섬유는 50 내지 500nm의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 나노 섬유층(120)의 나노 섬유의 직경이 작을수록 기공 크기가 작아지며, 기공 크기 분포도 작아지고, 나노 섬유의 비 표면적이 증대되므로 초미세 입자를 필터링하는 효율이 증대된다.The
이러한 나노 섬유층(120)은 효율적인 여과를 위하여 소정 두께를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 나노 섬유층(120)의 두께는 0.001~1mm 정도일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다.The
또한, 나노 섬유층(120)은 미세한 물질을 여과하기 위해 적당한 기공의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 나노 섬유층(120)은 기공의 크기가 2㎛ 이하일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다.In addition, the
마이크로 섬유층(130)은 폴리스티렌(PS)을 포함할 수 있다. 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 전기방사에 의해 나란히 정렬되어 상기 나노 섬유층(120)의 일면에 형성된다. 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 수에서 수십 마이크로미터의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 마이크로 섬유층(130)의 마이크로 섬유는 1 내지 10㎛의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 마이크로 섬유층(130)의 마이크로 섬유의 직경이 작을수록 기공 크기가 작아지며, 기공 크기 분포도 작아지고, 마이크로 섬유의 비 표면적이 증대되므로 미세 입자를 필터링하는 효율이 증대된다. 바람직하게는, 마이크로 섬유의 직경은 1 내지 2㎛의 크기 정도일 수 있으며, 나노 섬유에 마이크로 섬유가 코팅됨으로써 필터의 여과 효율을 높임과 동시에 나노 섬유의 손상을 막을 수 있다.The
이러한 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 효율적인 여과를 위하여 소정 두께를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 마이크로 섬유층(130)의 두께는 0.01~2mm 정도일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다.The
또한, 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 미세한 물질을 여과하기 위해 적당한 기공의 크기를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 기공의 크기가 3㎛ 이하일 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되지 않음은 물론이다.In addition, the
상술한 나노 섬유층(120) 및 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 다른 방식으로 형성될 수도 있으나, 전기 방사 방식으로 형성되는 것이 바람직하다. 도 2에 도시한 바와 같이, 부직포 기재(110)를 롤러(21) 등을 이용하여 이송하면서 순차적으로 폴리우레탄 용액(12)을 방사하는 제1 노즐 블록(22), 폴리스티렌 용액(13)을 방사하는 제2 노즐 블록(22)을 배치하여 부직포 기재(110)에 랜덤하게 배열되는 나노 섬유층(120)을 형성한 후 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유층(130)을 순차적으로 형성함으로써, 마이크로 섬유층(130)이 나노 섬유층(120)을 보호하고, 나노 섬유층(120) 및 마이크로 섬유층(130)의 이중 구조로 다층 에어 필터(100)의 여과 효율을 높일 수 있다. 이때, 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 제작할 수 있는 블록 및 콜렉터를 양산형 전기방사 시스템에 추가하여 한 번의 공정으로 다층 에어필터(100)를 생산할 수 있다.The
구체적으로, 나노 섬유층(120)은 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리우레탄 용액(12)을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성될 수 있다. 일반적으로, 랜덤하게 배열되는 나노 섬유는 이러한 방사 조건이 아니더라도 가능하며, 다른 방사 조건으로 변경 가능하다.Specifically, the
또한, 마이크로 섬유층(130)은 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리스티렌 용액(13)을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성될 수 있다. 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유는 이러한 방사 조건하에서만 형성되었으며, 상기 마이크로 섬유의 방사 조건을 벗어나면 섬유가 규칙적으로 배열되지 않음을 확인하였다. 섬유 직경의 차이는 전압의 세기, 방사용액의 농도, 방사 거리 등에 영향을 받으나, 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유를 형성하기 위해서는 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리스티렌 용액(13)을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여야 한다.The
도 4는 정렬된 마이크로 섬유의 SEM 사진을 도시한 도면이다. 또한, 도 5는 상면에 랜덤하게 배열된 나노 섬유층(좌) 및 나란히 정렬된 마이크로 섬유층(우)을 각각 배치하고 촬영한 사진을 도시한 도면이다.4 is a SEM photograph of aligned microfibers. 5 is a photograph showing a nanofiber layer (left) randomly arranged on the upper surface and a microfiber layer (right) aligned side by side, respectively, and photographed.
도 4에 도시한 나란히 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 얻기 위해, 폴리스티렌(Polystyrene)을 클로로포름(Chloroform)에 20%(W/W)으로 12시간 동안 200rpm으로 교반을 시켜 폴리스티렌 용액을 준비하였다. 그런 후에, 준비한 용액을 고점도와 고전압으로 전기방사를 진행하여 도 4에 도시한 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 생산하였다. 전기 방사를 하기 위하여 실린지에 준비된 용액을 넣고 1.0mL/hr의 유량으로 용출하고 콜렉터와 용액이 용출되는 팁과의 거리를 10cm로 설정하고 콜렉터의 회전수는 1000rpm으로 설정하고 방사 용액에 인가하는 전압은 30kV로 하였다.Polystyrene was stirred in chloroform at 20% (W / W) for 12 hours at 200 rpm in order to obtain the microfibers aligned side by side as shown in Fig. 4 to prepare a polystyrene solution. Thereafter, the prepared solution was subjected to electrospinning at a high viscosity and a high voltage to produce aligned microfibers as shown in Fig. The solution prepared in the syringe was eluted at a flow rate of 1.0 mL / hr. The distance between the collector and the tip from which the solution was eluted was set to 10 cm, the number of rotations of the collector was set to 1000 rpm, Was set at 30 kV.
도 5를 참조하면, 랜덤하게 배열된 나노 섬유층(좌) 및 나란히 정렬된 마이크로 섬유층(우)에 의해 좌측 부분은 불투명하게 보이고, 우측 부분은 투명하게 보임을 알 수 있다. 랜덤하게 배열된 나노 섬유 위에 나란히 정렬된 마이크로 섬유를 위치시킴으로써, 필터의 여과 효율이 향상되고, 나노 섬유를 마이크로 섬유가 보호한다.Referring to FIG. 5, it can be seen that the left portion appears opaque and the right portion looks transparent by the randomly arranged nanofiber layer (left) and the aligned microfiber layer (right). Placing microfibers arranged side by side on randomly arranged nanofibers improves the filtration efficiency of the filter and protects the nanofibers with microfibers.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법의 순서도이다.6 is a flowchart of a method of manufacturing a multilayered air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법은 부직포 기재를 마련하며(S110), 상기 부직포 기재의 일면에 제1 방사용액을 전기방사하여 랜덤하게 배열되는 나노 섬유층을 형성하고(S120), 상기 나노 섬유층 상에 제2 방사용액을 전기방사하여 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유층을 형성한다(S130).Referring to FIG. 6, a method for manufacturing a multilayered air filter according to an embodiment of the present invention includes providing a nonwoven fabric substrate (S110), electrospinning a first spinning solution on one surface of the nonwoven fabric substrate, (S120), and a second spinning solution is electrospun on the nano fiber layer to form a microfiber layer aligned in parallel (S130).
여기에서, 상기 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 경우(S120), 클로로포름에 폴리우레탄을 교반시켜 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제1 방사용액을 만드며, 상기 제1 방사용액을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하고, 폴리우레탄으로 이루어진 나노 섬유가 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 나노 섬유층을 형성한다.When the nanofiber layer is formed (S120), polyurethane is stirred in chloroform to make the first spinning solution having a concentration of 8 to 15% (W / W) 25 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm, and the nanofibers made of polyurethane are randomly arranged to form the nanofiber layer.
또한, 상기 마이크로 섬유층을 형성하는 경우(S120), 클로로포름에 폴리스티렌을 교반시켜 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제2 방사용액을 만드며, 상기 제2 방사용액을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하고, 폴리스티렌으로 이루어진 마이크로 섬유가 나란히 정렬되어 상기 마이크로섬유층을 형성한다.When the microfibre layer is formed (S120), polystyrene is stirred in chloroform to make the second spinning solution having a concentration of 16 to 21% (W / W), and the second spinning solution has a voltage of 25 to 35 kV , A solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm, and the microfibers composed of polystyrene are aligned side by side to form the microfiber layer.
이렇게 제조된 다층 에어필터는 다양한 산업 분야에 사용될 수 있으며, 부직포의 표면에 나노 섬유를 코팅하여 PM 2.5이하의 미세 입자 제거에 사용할 수 있고, 마이크로 섬유를 나노 섬유의 보호재로 이용하여 필터의 효율을 유지, 향상시키고, 나노 섬유의 박리를 막을 수 있다.The multi-layered air filter thus manufactured can be used in various industrial fields. It can be used to remove fine particles of not more than PM 2.5 by coating the surface of the nonwoven fabric with nanofibers. By using the microfibers as a protective material of nanofibers, Maintain, improve, and prevent peeling of the nanofibers.
이상 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예를 설명하였지만, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명이 그 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 실시될 수 있다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다.While the present invention has been described in connection with what is presently considered to be practical exemplary embodiments, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but, on the contrary, You will understand. It is therefore to be understood that the above-described embodiments are illustrative in all aspects and not restrictive.
100: 다층 에어필터
110: 부직포 기재
120: 나노 섬유층
130: 마이크로 섬유층100: Multilayer air filter
110: nonwoven fabric substrate 120: nano fiber layer
130: micro fiber layer
Claims (7)
전기방사에 의해 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 부직포 기재의 일면에 형성되는 나노 섬유층; 및
전기방사에 의해 나란히 정렬되어 상기 나노 섬유층 상에 형성되는 마이크로 섬유층을 포함하는, 다층 에어필터.Nonwoven fabric substrate;
A nanofiber layer randomly arranged by electrospinning and formed on one surface of the nonwoven substrate; And
And a microfiber layer arranged side by side by electrospinning and formed on the nano fiber layer.
상기 부직포 기재는, 폴리프로필렌을 포함하는, 다층 에어필터.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the nonwoven substrate comprises polypropylene.
상기 나노 섬유층은, 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리우레탄 용액을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성되는, 다층 에어필터.The method according to claim 1,
The nanofiber layer is formed by electrospinning a polyurethane solution having a concentration of 8 to 15% (W / W) at a voltage of 10 to 25 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm , Multilayer air filter.
상기 마이크로 섬유층은, 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 폴리스티렌 용액을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하여 형성되는, 다층 에어필터.The method according to claim 1,
The microfiber layer is formed by electrospinning a polystyrene solution having a concentration of 16 to 21% (W / W) at a voltage of 25 to 35 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr and a radiation distance of 1 to 20 cm. Multilayer air filter.
상기 부직포 기재의 일면에 제1 방사용액을 전기방사하여 랜덤하게 배열되는 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 나노 섬유층 상에 제2 방사용액을 전기방사하여 나란히 정렬되는 마이크로 섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함하는, 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법.Providing a nonwoven substrate;
Forming a nanofiber layer randomly arranged by electrospinning a first spinning solution on one surface of the nonwoven substrate; And
And a step of electrospinning the second spinning solution on the nano fiber layer to form a microfiber layer arranged side by side.
상기 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계는,
클로로포름에 폴리우레탄을 교반시켜 8~15 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제1 방사용액을 만드는 단계;
상기 제1 방사용액을 전압 10~25 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하는 단계; 및
폴리우레탄으로 이루어진 나노 섬유가 랜덤하게 배열되어 상기 나노 섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함하는, 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법.6. The method of claim 5,
The forming of the nanofiber layer comprises:
Stirring the polyurethane in chloroform to make the first spinning solution having a concentration of 8 to 15% (W / W);
Electrospinning the first spinning solution at a voltage of 10 to 25 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a spinning distance of 1 to 20 cm; And
Wherein the nanofibers of the polyurethane are randomly arranged to form the nanofiber layer.
상기 마이크로 섬유층을 형성하는 단계는,
클로로포름에 폴리스티렌을 교반시켜 16~21 %(W/W) 농도의 상기 제2 방사용액을 만드는 단계;
상기 제2 방사용액을 전압 25~35 kV, 용액 토출 속도 0.1~10 ml/hr, 방사거리 1~20 cm의 조건으로 전기 방사하는 단계; 및
폴리스티렌으로 이루어진 마이크로 섬유가 나란히 정렬되어 상기 마이크로섬유층을 형성하는 단계를 포함하는, 다층 에어필터의 제조 방법.6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein forming the microfiber layer comprises:
Stirring the polystyrene in chloroform to make the second spinning solution having a concentration of 16 to 21% (W / W);
Electrospinning the second spinning solution at a voltage of 25 to 35 kV, a solution discharge rate of 0.1 to 10 ml / hr, and a spinning distance of 1 to 20 cm; And
Wherein the microfibers constituted by polystyrene are aligned side by side to form the microfiber layer.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160115090A KR20180027877A (en) | 2016-09-07 | 2016-09-07 | Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160115090A KR20180027877A (en) | 2016-09-07 | 2016-09-07 | Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180027877A true KR20180027877A (en) | 2018-03-15 |
Family
ID=61659918
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160115090A KR20180027877A (en) | 2016-09-07 | 2016-09-07 | Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20180027877A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210121413A (en) * | 2020-03-30 | 2021-10-08 | 주식회사 김일두연구소 | Electrospinning alignment apparatus |
-
2016
- 2016-09-07 KR KR1020160115090A patent/KR20180027877A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210121413A (en) * | 2020-03-30 | 2021-10-08 | 주식회사 김일두연구소 | Electrospinning alignment apparatus |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102313590B1 (en) | Dustproof net for fine dust filtering | |
| US20110064928A1 (en) | Nonwoven material | |
| JP6593170B2 (en) | Fiber laminate including ultrafine fibers and filter comprising the same | |
| JP6172924B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of nonwoven fabric substrate for air filter or mask | |
| JP2011508665A5 (en) | ||
| KR101668395B1 (en) | Filter with Nano Fiber and Manufacturing Thereof | |
| JP2015045114A (en) | Fiber sheet and fiber product using the same | |
| KR20120029409A (en) | Fabric material composite construction for use as a filter means | |
| KR102139711B1 (en) | Nanofibrous Membrane and Method for Preparing Thereof | |
| JP2009006272A (en) | Filter medium and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101739845B1 (en) | Cartridge filter using composition adiabatic fiber yarn and the manufacture method thereof | |
| JP2011089226A (en) | Multilayer fiber structure | |
| CN111455566B (en) | Composite nanofiber membrane and preparation method thereof | |
| WO2019058292A1 (en) | Nano-fiber based filter media and methods of preparation thereof | |
| EP3523122B1 (en) | Method for depositing a layer of polymeric nanofibers prepared by electrostatic spinning of a polymer solution or melt on electrically nonconductive materials, and a multilayer composite thus prepared containing at least one layer of polymeric nanofibers | |
| KR20200090897A (en) | Systems and methods for forming self-adhesive fibrous media | |
| JP6675853B2 (en) | Optical sheet using extra-fine meltblown nonwoven fabric | |
| US20160194796A1 (en) | Melt Electrospun Fibers Containing Micro and Nanolayers and Method of Manufacturing | |
| CN113597369B (en) | Multilayer interlaced film and method of making same | |
| KR20180027877A (en) | Multi layer air filter and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR102157444B1 (en) | Multy-Layer Structure Filter Medium For High-Performance Air Cleaning Filter | |
| KR102153213B1 (en) | Multi centrifugal spinning disk for production of multi component nanofiber and fabrication of single layer complex nanofilter | |
| KR20100023155A (en) | Filter for removing a white corpuscle and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101386424B1 (en) | Filter for removing a white corpuscle and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101386391B1 (en) | Filter for removing a white corpuscle and method of manufacturing the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |