KR20170075366A - Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element - Google Patents
Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170075366A KR20170075366A KR1020150184929A KR20150184929A KR20170075366A KR 20170075366 A KR20170075366 A KR 20170075366A KR 1020150184929 A KR1020150184929 A KR 1020150184929A KR 20150184929 A KR20150184929 A KR 20150184929A KR 20170075366 A KR20170075366 A KR 20170075366A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- thermoelectric element
- temperature
- heat
- thermoelectric
- temperature sensor
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B1/00—Details of electric heating devices
- H05B1/02—Automatic switching arrangements specially adapted to apparatus ; Control of heating devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01K—MEASURING TEMPERATURE; MEASURING QUANTITY OF HEAT; THERMALLY-SENSITIVE ELEMENTS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01K13/00—Thermometers specially adapted for specific purposes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05D—SYSTEMS FOR CONTROLLING OR REGULATING NON-ELECTRIC VARIABLES
- G05D23/00—Control of temperature
- G05D23/19—Control of temperature characterised by the use of electric means
-
- H01L35/30—
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B3/00—Ohmic-resistance heating
- H05B3/40—Heating elements having the shape of rods or tubes
- H05B3/54—Heating elements having the shape of rods or tubes flexible
- H05B3/56—Heating cables
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Cooling Or The Like Of Semiconductors Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에 관한 것으로서, 보다 구체적으로는 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도가 외부 온도와 비슷하도록 열전소자의 흡열면에 인가되는 전원을 조절함으로써, 불필요하게 낭비되는 에너지 없이 열전소자의 구동 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에 관한 것이다.BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention [0001] The present invention relates to a thermoelectric-element driving method and a thermoelectric-element driving apparatus, and more particularly to a thermoelement driving method and a thermoelement driving apparatus which are unnecessarily wasted by adjusting a power source applied to a heat-absorbing surface of a thermoelectric element so that a temperature of a heat- And more particularly, to a thermoelectric element driving method and a thermoelectric element driving apparatus capable of improving driving performance of a thermoelectric element without energy.
Description
본 발명은 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에 관한 것으로서, 보다 구체적으로는 난방 모드(mode)로 작동되는 열전소자의 효율을 높을 수 있는 구동방법 및 구동장치에 관한 것이다.BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a thermoelectric device driving method and a thermoelectric device driving apparatus, and more particularly, to a driving method and a driving apparatus capable of increasing the efficiency of a thermoelectric device operating in a heating mode.
열전소자는 열 에너지(energy)를 전기 에너지로, 전기 에너지를 열 에너지로 직접 변환하는데 사용되는 소자로 에너지 절감이라는 시대적 요구에 가장 잘 부응하는 소재이자 기술이다. A thermoelectric element is a material and technology that most closely meets the demand for energy saving as a device used to directly convert energy from electric energy to electric energy into thermal energy.
이러한 열전소자는 자동차, 우주항공, 반도체, 바이오(bio), 광학, 컴퓨터(computer), 발전, 가전제품 등 산업 전반에서 광범위하게 활용되고 있으며, 선진국들은 연구소와 기업을 중심으로 이러한 열전소자의 효율을 증진시키기 위한 연구를 진행하고 있으며, 국내에서도 연구소와 대학을 중심으로 집중적인 연구가 수행되고 있다.These thermoelectric devices are widely used in industries such as automobiles, aerospace, semiconductor, bio, optical, computer, power generation, household appliances and the like. And research has been conducted intensively in Korea, centering on research institutes and universities.
또한, 열전소자는 인가되는 전류의 방향에 따라 냉각소자로도 활용도 가능하고, 발열소자로도 활용이 가능하다. 즉, 열전소자는 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 면의 열에너지를 발열작용이 이루어지는 면으로 전달하는 히팅 펌프(heating pump)라 볼 수 있다. In addition, the thermoelectric element can be used as a cooling element or a heating element depending on the direction of the applied current. That is, the thermoelectric element can be regarded as a heating pump that transfers heat energy of a surface on which an endothermic action is performed to a surface on which a heat generating action is performed.
그러나, 이러한 열전소자를 발열소자로 사용하는 경우, 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 면의 온도는 계속적으로 하강함으로써 열 공급이 중단되고 발열 작용이 이루어지는 면을 통한 열 에너지 생성의 효율이 낮아지는 문제점이 있는데, 이러한 문제점은 열전소자를 온수 매트(matt) 또는 보일러(boiler) 장치에서의 열 공급 장치로 사용할 때 더욱 두드러진다.However, when such a thermoelectric element is used as a heat generating element, the temperature of the surface on which the endothermic action is performed is continuously lowered, so that the heat supply is interrupted and the efficiency of generating heat energy through the surface where heat is generated is lowered. The problem is more pronounced when thermoelectric elements are used as a heat supply in hot water mats or boiler devices.
전술한 배경기술은 발명자가 본 발명의 도출을 위해 보유하고 있었거나, 본 발명의 도출 과정에서 습득한 기술 정보로서, 반드시 본 발명의 출원 전에 일반 공중에게 공개된 공지기술이라 할 수는 없다.The above-described background technology is technical information that the inventor holds for the derivation of the present invention or acquired in the process of deriving the present invention, and can not necessarily be a known technology disclosed to the general public prior to the filing of the present invention.
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위해 안출된 것으로, 발열소자로 작동되는 열전소자의 열 에너지 생성 효율을 더욱 향상시킬 수 있는 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치를 제공하고자 한다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been devised to solve the problems as described above, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a thermoelectric device driving method and a thermoelectric device driving device capable of further improving thermal energy generating efficiency of a thermoelectric device operated by a heat generating element.
또한, 열전소자의 흡열면인 반작용면에 서리 등이 발생하는 것을 방지할 수 있는 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치를 제공하고자 한다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a thermoelectric element driving method and a thermoelectric element driving apparatus capable of preventing frost from occurring on a reaction surface which is a heat absorbing surface of a thermoelectric element.
상기한 목적을 달성하기 위해, 본 발명에서는 열전소자의 반작용면에 위치한 제1 온도 센서(sensor)가 온도를 측정하는 단계; 상기 열전소자의 반작용면으로부터 이격되어 설치된 제2 온도 센서가 외부 온도를 측정하는 단계; 제어 모듈(module)이 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도와 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도를 비교하는 단계; 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도 이하인 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동을 지시하는 단계;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.In order to accomplish the above object, the present invention provides a method for measuring a temperature of a thermoelectric device, comprising: measuring a temperature of a first temperature sensor located on a reaction surface of a thermoelectric device; Measuring an external temperature by a second temperature sensor installed apart from a reaction surface of the thermoelectric element; Comparing a temperature measured by the first temperature sensor with an external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor by the control module; And when the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor is equal to or lower than the external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, the control module instructs the operation of the heating device on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric device A method of driving a thermoelectric element is provided.
또한, 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도 보다 낮은 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동을 지시하는 단계 이후에, 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도를 초과하는 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동의 중지를 지시하는 단계;를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.In addition, when the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor is lower than the external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, after the control module instructs the operation of the heating device on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element, And when the temperature measured by the temperature sensor exceeds the external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, the control module instructs stop of operation of the heating device on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element The present invention also provides a method of driving a thermoelectric element.
또한, 상기 열전소자의 반작용면에서는 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.The present invention also provides a method of driving a thermoelectric device, wherein an endothermic action is performed at a reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
또한, 상기 가열 장치는 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 열 교환기 사이에 구비되는 열선인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.Further, the present invention provides a method of driving a thermoelectric device, wherein the heating device is a heat line provided between heat exchangers on a reaction surface of the thermoelectric device.
또한, 상기 가열 장치는 상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 이격되어 열을 인가하는 히터(heater)인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.Further, the present invention provides a method of driving a thermoelectric device, wherein the heating device is a heater for applying heat to the reaction surface of the thermoelectric device.
또한, 상기 가열 장치는 상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 이격되어 외부 공기를 인가하는 팬(fan)인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.In addition, the heating device is a fan that is spaced apart from the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element to apply external air.
또한, 상기 열전소자의 작용면에서는 발열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법을 제공한다.The present invention also provides a method of driving a thermoelectric device, wherein a heat generating action is performed on the action surface of the thermoelectric device.
또한, 본 발명은 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도를 측정하는 제1 온도 센서; 상기 열전소자의 반작용면으로부터 이격되어 외부 온도를 측정하는 제2 온도 센서; 상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 열을 인가하는 가열 장치; 상기 열전소자의 동작과 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도와 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 온도를 비교하여 상기 가열 장치의 작동 여부를 결정하는 제어부;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치를 제공한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a temperature sensor comprising: a first temperature sensor for measuring a temperature of a reaction surface of a thermoelectric element; A second temperature sensor spaced apart from the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element to measure an external temperature; A heating device for applying heat to the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element; And a control unit for comparing the operation of the thermoelectric element and the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor and the temperature measured by the second temperature sensor to determine whether the heating apparatus is operated or not, Lt; / RTI >
또한, 상기 가열 장치는 열선, 히터 또는 팬 중에서 어느 하나로 선택되는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치를 제공한다.Also, the present invention provides a thermoelectric device driving apparatus, wherein the heating device is selected from a heat wire, a heater, or a fan.
또한, 상기 열전소자의 반작용면에서는 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치를 제공한다.The present invention also provides a thermoelectric device driving apparatus characterized in that an endothermic function is provided on a reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
또한, 상기 열전소자의 작용면에서는 발열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치를 제공한다.Further, there is provided a thermoelectric-element driving apparatus characterized in that a heat-generating function is performed on the action surface of the thermoelectric element.
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에 의하면 다음과 같은 효과가 있다.The thermoelectric element driving method and the thermoelectric element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention have the following effects.
첫째, 발열장치로 동작하는 열전소자의 구동 성능이 향상되는 효과가 있다. First, there is an effect that the driving performance of a thermoelectric element that operates as a heating device is improved.
둘째, 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도가 외부 온도와 비슷하도록 열전소자의 흡열면에 인가되는 전원을 조절함으로써, 불필요하게 낭비되는 에너지 없이 열전소자의 구동 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 효과가 있다.Secondly, by adjusting the power applied to the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element so that the temperature of the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element is similar to the external temperature, the driving performance of the thermoelectric element can be improved without unnecessary waste of energy.
셋째, 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도를 외부 온도와 비슷하게 유지함으로써, 열전소자의 흡열면에 서리 등이 발생하는 현상을 방지할 수 있는 효과가 있다. 따라서, 열전소자의 흡열면에 서리가 발생하여 물이 응축되어 전자 부품에 악영향을 미치는 것을 방지할 수 있는 효과가 있다.Third, by keeping the temperature of the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element close to the external temperature, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of frost on the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element. Therefore, there is an effect that frost is generated on the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element to prevent water from being condensed and adversely affecting the electronic parts.
도면 1도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에서 사용되는 열전소자의 모습을 개략적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도면 2도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치가 사용되는 난방장치의 내부구성을 개략적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
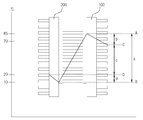
도면 3도는 열전소자의 작용면인 발열 블럭(100)이 공기상에 노출되었을 때, 열전소자의 흡열면으로부터 발열면까지의 온도 변화를 그래프(graph)로 보여주는 도면이다.
도면 4도는 열전소자의 작용면인 발열 블럭에 물과 같은 열 매체가 접촉하였을 때, 열전소자의 흡열면으로부터 발열면까지의 온도 변화를 보여주는 그래프이다.
도면 5도는 도면 4도와 같이 열전소자의 발열 블럭에 열 매체가 접촉하고 있는 상태에서, 열전소자에 공급되는 전원의 양을 증가시켰을 때의 온도 변화의 모습을 보여주는 도면이다.
도면 6도는 흡열면에 온도를 인가하여 열전소자의 작용면의 온도를 향상시킴으로써, 열전소자의 작용면의 온도를 올리는 방법을 보여주는 도면이다.
도면 7도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법을 보여주는 순서도이다.FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing a thermoelectric element driving method and a thermoelectric element used in a thermoelectric element driving apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a schematic view illustrating an internal configuration of a heating device in which a thermoelectric-element driving method and a thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention are used.
3 is a graph showing a change in temperature from the heat absorption surface to the heat generation surface of the thermoelectric element when the
4 is a graph showing a change in temperature from a heat absorbing surface to a heat generating surface of a thermoelectric element when a heat medium such as water is brought into contact with a heat generating block serving as an acting surface of the thermoelectric element.
5 is a view showing a state of a temperature change when the amount of power supplied to the thermoelectric element is increased in a state in which the heating medium is in contact with the heat generating block of the thermoelectric element as in FIG.
6 is a view showing a method of raising the temperature of the action surface of the thermoelectric element by applying a temperature to the heat absorbing surface to improve the temperature of the action surface of the thermoelectric element.
7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of driving a thermoelectric device according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
이하, 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예들에 대해 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들은 도면에 예시하고 본문에 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 개시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. While the invention is susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific embodiments thereof are shown by way of example in the drawings and are herein described in detail. It should be understood, however, that the invention is not intended to be limited to the particular forms disclosed, but includes all modifications, equivalents, and alternatives falling within the spirit and scope of the invention.
도면 1도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에서 사용되는 열전소자의 모습을 개략적으로 보여주는 도면이다.FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing a thermoelectric element driving method and a thermoelectric element used in a thermoelectric element driving apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
열전소자는 p형 반도체(10), n형 반도체(20), 전기전도판(40), 세라믹(ceramic)판(30)을 포함하여 구성될 수 있다.The thermoelectric element may include a p-
이러한 열전소자의 n형 반도체(20)에 (+), p형 반도체(10)에 (-)전압을 걸어 전류를 n형에서 p형으로 흘리면, 펠티에(peltier) 효과에 의해 pn 접합에서 열이 흡수되고 각 단자 전극에서는 열이 발생한다. 이때 각 단자 전극과 pn 접합면 부위에 전기전도판(40)과 세라믹판(30)을 부착함으로써, p형 반도체(10)와 n형 반도체(20)에서 발생한 에너지를 외부로 전달할 수 있다. 다시 정리하면, 열전소자는 흡열면에서 열에너지를 흡수하여 발열면으로 열을 전달하는 히팅 펌프의 역할을 수행할 수 있다.When a current flows from n-type to p-type by applying (+) voltage to the n-
이하, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치의 설명에서는 발열면은 열 매체와의 에너지 교환을 통하여 난방 장치로 사용되는 점에서 작용면으로, 흡열면은 작용면과 반대의 현상이 일어나는 점에서 반작용면으로 하여 설명토록 하겠다.In the following description of the thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the heat-generating surface is an action surface in that it is used as a heating device through energy exchange with a heat medium, I will explain it as a reaction side in that the opposite phenomenon occurs.
도면 2도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치가 사용되는 난방장치의 내부구성을 개략적으로 보여주는 도면이다.FIG. 2 is a schematic view illustrating an internal configuration of a heating device in which a thermoelectric-element driving method and a thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention are used.
앞서 살펴본 열전소자의 흡열면과 발열면에는 각각 열 교환기가 구비될 수 있다. 작용면인 발열면에 구비되는 열교환기는 발열 블럭(block)(100)으로 지칭될 수 있으며, 반작용면인 흡열면에 구비되는 열교환기는 흡열 블력(200)으로 지칭될 수 있다.The heat absorbing surface and the heat generating surface of the thermoelectric element can be provided with a heat exchanger, respectively. The heat exchanger provided on the heat generating surface, which is the acting surface, may be referred to as a
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치의 발열 블럭(100)은 열 매체 공급 탱크(700) 내에 구비될 수 있으며, 열 매체 공급 탱크(700) 내의 열 매체에 열 에너지를 공급하는 역할을 수행할 수 있다. 그리고, 열 매체 공급 탱크(700) 내의 열 매체로서는 물이 선택될 수 있으나, 반드시 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The
흡열 블럭(200)에서는 외부로부터 열을 흡수하는 흡열 작용이 발생하며, 앞서 살펴보았듯이, 열전 소자는 흡열 면의 열 에너지를 흡수하여 발열 면으로 공급하는 히팅 펌프의 역할을 수행하므로 흡열 블럭(200)으로는 열 에너지가 계속적으로 공급되어야 발열 면인 작용면에서 열매체로 열 에너지를 공급할 수 있다.In the
그러나, 열전소자에 전원 공급기(50)을 통하여 계속적으로 전기를 인가하다보면, 반작용면인 흡열면이 온도가 주위 온도보다 낮아져서 서리가 발생하는 현상이 생기면서 작용면인 발열면으로 공급되는 열 에너지가 급격하게 줄어드는 현상이 발생하게 된다. 따라서, 열전 소자의 성능이 급격하게 저하되는 현상이 발생하게 된다.However, when electricity is continuously applied to the thermoelectric element through the
이를 방지하기 위해서는 열전소자의 흡열면에 열에너지를 공급함으로써, 열전소자가 계속적으로 히팅 펌프의 역할을 지속하도록 하면 되는데, 이를 위하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 반작용면에 열 에너지를 공급하는 가열 장치를 구비할 수 있다. 그리고, 이러한 가열 장치는 히터(300), 팬(400) 또는 열전소자의 반작용면에 구비되는 흡열 블럭(200)에 구비되는 열선(600) 중 어느 하나 이상의 조합을 포함하여 구비될 수 있다. 즉, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 흡열 블럭(200)의 온도가 낮아지는 경우, 히터(300), 팬(400), 열선(600) 등을 포함하여 흡열 블럭(200)에 열을 공급하여 열전소자의 작용면인 발열면에서 계속적으로 열을 외부로 방출할 수 있도록 한다.In order to prevent this, the thermal energy is supplied to the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element so that the thermoelectric element continues to serve as the heating pump. To this end, the thermoelectric element driving method and the thermoelectric element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention And a heating device for supplying thermal energy to the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element. The heating device may include a combination of any one or more of the
또한, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도를 측정하는 제1 온도 센서(sensor)(미도시)와 열전소자의 반작용면에서 이격되어 외부 온도를 측정하는 제2 온도 센서(500)를 추가로 더 구비할 수 있다. 그리고, 이를 통하여 히터(300), 팬(fan)(400) 또는 열선(600) 등의 가열장치를 통하여 흡열 블럭(200)에 인가된 열 에너지로 인한 온도가 외부 온도와 비슷하도록 제어할 수 있다. The thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention may further include a first temperature sensor (not shown) for measuring the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element and a second temperature sensor And a
다시 말하면, 가열 장치로 흡열 블럭(200)에 무작정 열 에너지를 공급하는 것이 아니라, 외부 온도와 비슷한 온도까지만 흡열 블럭(200)의 온도가 상승하도록 열 에너지를 공급할 수 있다. 보다 구체적으로는 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 제2 온도 센서(500)가 측정한 온도보다 약 1도 정도 낮게 되도록 가열 장치를 구동할 수 있다. 이는 공급된 열에너지가 다시 외부로 빼앗기는 것을 방지하기 위해서이며, 이를 통하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 효율을 더욱 향상시킬 수 있다.In other words, the heat energy can be supplied to the
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치에서 열전 소자의 흡열면의 온도를 외부 온도와 비슷하게 유지토록 하는 이유는 이하 도면 3 내지 도면 6도를 바탕으로 설명토록 한다.The reason why the temperature of the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element in the thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention is maintained to be similar to the external temperature will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 6.
도면 3도 내지 도면 6도는 열전소자의 작동 개념을 온도 측면에서 간략히 설명하기 위하여 사용되는 도면이다.FIGS. 3 to 6 are views for explaining the operation concept of the thermoelectric element in brief from the viewpoint of temperature.
먼저, 도면 3도는 열전소자의 작용면인 발열 블럭(100)이 공기상에 노출되었을 때, 열전소자의 흡열면으로부터 발열면까지의 온도 변화를 그래프(graph)로 보여주는 도면이다.First, FIG. 3 is a graph showing a change in temperature from a heat absorption surface to a heat generation surface of a thermoelectric element when the
이상적인 열전소자의 작용면과 반작용면의 온도 차이는 섭씨 약 60 내지 85도이다. 따라서, 열전소자의 작용면을 섭씨 약 85도까지 상승시키게 되면, 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도는 섭씨 약 10도 정도까지 하강하게 된다. 이는 반작용면의 열 에너지를 흡수하여 작용면으로 전달함으로써 일어난다.The temperature difference between the working surface of the ideal thermoelectric element and the reaction surface is about 60 to 85 degrees Celsius. Accordingly, when the working surface of the thermoelectric element is raised to about 85 degrees Celsius, the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element is lowered to about 10 degrees Celsius. This occurs by absorbing the thermal energy of the reaction surface and transferring it to the working surface.
열전소자의 흡열 블럭(200)과 발열 블럭(100)은 각각 열 저항을 가지고 있다. 따라서, 열전소자의 발열 블럭(100)로부터 방출되는 최종 온도는 발열 블럭(100)의 열저항만큼 떨어진 정도의 온도가 대기 중으로 발산하게 되고 이 경우에는 섭씨 약 70도 정도의 온도가 대기 중으로 전달되게 된다. 그리고, 열전소자의 흡열 블럭(200)도 역시 10도 정도의 저항의 열 저항을 가지고 있으며, 최종적으로 흡열 블럭의 외부로는 약 20도의 온도가 측정되게 된다.The
결과적으로, 열전소자의 발열 블럭(100)의 바깥쪽 온도(C)와 열전소자의 흡열 블럭(200)의 바깥쪽 온도(D)의 차이가 냉각 시스템의 온도차(c)로서 측정되게 되고, 열전소자의 작용면 온도(A)와 열전소자의 흡열면 온도(B)의 차이가 열전소자의 온도차(a)로서 측정되게 된다. 또한, 발열 블럭(100)에 의한 열저항에 의한 온도차(b)는 A - C로, 흡열 블럭(200)에 의한 열저항에 의한 온도차(d)는 D - B로 측정되게 된다.As a result, the difference between the temperature (C) outside the heat generating block (100) of the thermoelectric element and the temperature (D) outside the heat absorbing block (200) of the thermoelectric element is measured as the temperature difference (c) The difference between the working surface temperature (A) of the element and the heat-absorbing surface temperature (B) of the thermoelectric element is measured as the temperature difference (a) of the thermoelectric element. The temperature difference b due to the heat resistance by the
도면 4도는 열전소자의 작용면인 발열 블럭에 물과 같은 열 매체가 접촉하였을 때, 열전소자의 흡열면으로부터 발열면까지의 온도 변화를 보여주는 그래프이다.4 is a graph showing a change in temperature from a heat absorbing surface to a heat generating surface of a thermoelectric element when a heat medium such as water is brought into contact with a heat generating block serving as an acting surface of the thermoelectric element.
열전소자의 발열 블럭(100)이 열 매체 공급 탱크(tank)(700) 내의 물과 같은 열 매체와 직접적으로 접촉하게 되면, 물은 공기보다 열 용량이 더 크기 때문에, 발열 블럭(100)의 열 에너지는 도면 3도의 경우보다 더 빨리 물과 같은 열 매체로 이동하게 된다. 즉, 열전소자의 열 에너지를 훨씬 빨리 열 매체로 빼앗기게 된다. 일 예로, 열 매체와 접촉하는 발열 블럭(100)의 외면의 온도는 섭씨 약 50도까지 떨어지게 되면, 이로 인하여 열전소자의 작용면의 온도는 섭씨 약 60도까지 떨어지게 된다. 그러므로, 동일한 전원 인가시, 열전소자의 작용면과 반작용면 사이의 온도 그래프는 동일한 기울기를 가지므로, 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도는 섭씨 약 -10 도까지 떨어지게 된다. 즉, 히팅 펌프 역할을 하는 열전소자가 열전소자의 흡열면으로부터 더 많은 에너지를 흡수하여 공급하므로, 흡열면의 온도가 낮아져서 영하로 떨어지게 되고 흡열 블럭(200)의 외부 온도는 열저항에 의하여 약 섭씨 0도가 되게 된다. When the
이로 인하여, 열전소자의 흡열 블럭(200)의 외부에는 서리와 같은 물방울이 맺히게 되는 현상이 발생하게 되고, 서리와 같은 물방울이 맺히면 열전소자의 발열 효율은 더 떨어질 뿐만 아니라, 물방울이 흘러내림으로써 전자부품에 합선 등을 일으키거나 심지어는 화재를 일으킬 수도 있다.As a result, a phenomenon that frost-like droplets are formed on the outside of the
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 이러한 서리 등을 방지함으로써 전자부품에 합선 등이 일어나는 것을 방지할 수 있는 효과가 있다.The thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention have such an effect that it is possible to prevent short-circuiting or the like from occurring in the electronic component by preventing such frost.
도면 5도는 도면 4도와 같이 열전소자의 발열 블럭에 열 매체가 접촉하고 있는 상태에서, 열전소자에 공급되는 전원의 양을 증가시켰을 때의 온도 변화의 모습을 보여주는 도면이다.5 is a view showing a state of a temperature change when the amount of power supplied to the thermoelectric element is increased in a state in which the heating medium is in contact with the heat generating block of the thermoelectric element as in FIG.
앞서 살펴 보았듯이, 열전소자의 발열 블럭(100)의 외부 온도는 열 매체의 온도 교환으로 인하여 섭씨 50도까지 떨어졌다. As previously noted, the outside temperature of the
물과 같은 열 매체의 온도를 올리기 위하여 열전소자에 인가되는 전원의 양을 증가시켜서 열전소자의 발열 블럭(100)과 열 매체가 접촉하는 부분의 온도를 섭씨 70도까지 증가시키면, 열전소자의 작용면의 온도는 약 섭씨 85도까지 올라가게 된다. If the temperature of the portion where the
그러나, 열전소자에 더 많은 전기 에너지를 인가한 결과, 열전소자의 흡열면과 발열면을 잇는 온도 그래프의 기울기가 더 크게 증가하므로, 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도는 더 낮아져서 섭씨 - 20 도까지 내려가게 되고, 흡열 블럭(200)의 외부 온도는 섭씨 - 10 도까지 떨어져서, 흡열 블럭(200)에 생기는 서리는 더 증가하게 된다. However, as a result of applying more electric energy to the thermoelectric element, the slope of the temperature graph connecting the heat-absorbing surface and the heat-generating surface of the thermoelectric element is further increased, so that the temperature of the heat-absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element is lowered down to -20 ° C And the temperature of the outside of the
따라서, 열전소자가 열 매체에 공급하는 열 용량을 증가시키고자, 열전소자에 인가되는 전류의 양만을 증가시키는 것은 결과적으로 열 매체의 온도를 목적하는 온도까지는 향상시킬 수는 있으나, 열 효율을 희생하면서 달성한 결과이다.Thus, increasing the amount of current applied to the thermoelectric element in order to increase the heat capacity supplied by the thermoelectric element to the thermal medium results in the improvement of the temperature of the thermal medium to the desired temperature, .
도면 6도는 흡열면에 온도를 인가하여 열전소자의 작용면의 온도를 향상시킴으로써, 열전소자의 작용면의 온도를 올리는 방법을 보여주는 도면이다.6 is a view showing a method of raising the temperature of the action surface of the thermoelectric element by applying a temperature to the heat absorbing surface to improve the temperature of the action surface of the thermoelectric element.
열전소자의 작용면의 온도를 향상시키는 방법으로써 열전소자를 구동하는 전류의 양을 증가시킬 수도 있으나, 이러한 방법은 앞서 살펴보았듯이 열전소자의 에너지 효율을 저해시키는 문제점이 있다.Although it is possible to increase the amount of current for driving the thermoelectric element as a method for improving the temperature of the surface of the thermoelectric element, this method has a problem that the energy efficiency of the thermoelectric element is inhibited as described above.
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 흡열면인 반작용면에 열 에너지를 공급함으로써 발열면의 온도를 목적하는 온도까지 올릴 수 있다. 즉, 도면 3도와 같이 열전소자의 발열면이 대기중에 노출되어 있다가 물과 같은 열 매체에 접촉하게 되면 도면 4도와 같이 발열면과 흡열면의 온도가 모두 떨어지게 된다. 이 상태에서, 도면 5도와 같이 열전소자에 인가되는 전류의 양을 증가시켜서 발열면의 온도를 목적하는 온도까지 증가시키면 흡열면은 온도가 더 떨어지게 되나, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자에 추가 전류를 인가하는 방식 대신에 열전소자의 흡열면에 가열 장치를 이용하여 열 에너지를 공급함으로써, 열전소자의 발열면의 온도를 상승시킨다. 예를 들어, 도면 4도에서 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도는 섭씨 - 10도까지 떨어졌으므로, 도면 3도와 같은 상태가 되도록 하기 위하여, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 흡열면인 반작용면에 히터(300), 팬(400) 또는 열선(600) 등의 가열장치를 이용하여 약 20도 정도의 온도를 가열할 수 있다. 그 결과, 히팅 펌프 역할을 하는 열전소자의 반작용면에 계속적으로 열이 인가되는 바, 열전소자의 작용면의 온도가 섭씨 85도까지 상승하게 되고, 열 매체의 온도도 75도가 되어 목적하는 온도까지 열 매체의 온도를 상승시킬 수 있다. 그리고, 이는 열전소자의 구동을 위하여 필요한 전류를 더 공급한 것이 아니라, 동일한 전류 인가하에 열전소자의 반작용면에 열 에너지를 더 인가함으로써 달성한 효과로서, 열전소자의 구동 성능을 향상시키면서 달성된 효과이다. 즉, 열전소자의 작용면의 발열량은 흡열량과 소비전력의 합이 되는데, 흡열량을 늘림으로써 열전소자의 효율을 향상시킨 것이다.The thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention can increase the temperature of the heat-generating surface to a desired temperature by supplying thermal energy to the reaction surface, which is a heat-absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element. That is, when the heating surface of the thermoelectric element is exposed to the atmosphere as shown in FIG. 3 and then comes into contact with the heating medium such as water, the temperature of the heating surface and the temperature of the heat absorbing surface are both lowered as shown in FIG. In this state, if the amount of current applied to the thermoelectric element is increased to increase the temperature of the heat-generating surface to the target temperature as shown in FIG. 5, the temperature of the endothermic surface becomes lower. However, in the thermoelectric element driving according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention The method and the thermoelectric element drive apparatus increase the temperature of the heat generating surface of the thermoelectric element by supplying thermal energy to the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element by using a heating device instead of a method of applying an additional current to the thermoelectric element. For example, since the temperature of the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element is lowered to -10 degrees centigrade in FIG. 4, in order to achieve the state shown in FIG. 3, the thermoelectric element driving method and the thermoelectric element driving method according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention The apparatus can heat a temperature of about 20 degrees by using a heating device such as a
또한, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법 및 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도가 외부 온도와 동일 또는 이보다 약 1도 정도 낮도록 열 에너지를 공급함으로써, 열전소자의 흡열면에 필요 이상의 열이 공급되어 이러한 열이 다시 외부로 방출되어서 열 손실이 일어나는 것을 방지할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 흡열면에 결로 현상이 발생하는 것을 방지할 수 있으므로 안전성 향상도 도모할 수 있는 효과가 있다.Further, the thermoelectric-element driving method and the thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention supply heat energy such that the temperature of the heat-absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element is equal to or lower than the external temperature by about 1 degree, It is possible to prevent heat loss from occurring due to excessive heat being supplied to the surface of the heat dissipating unit and to prevent the occurrence of condensation on the heat absorbing surface, have.
도면 7도는 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법을 보여주는 순서도이다.7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of driving a thermoelectric device according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법은 먼저, 열전소자 반작용면의 온도를 측정하는 과정을 거칠 수 있다.(S7-1) In the method of driving a thermoelectric device according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the temperature of the thermoelectric element reaction surface may be measured (S7-1)
흡열면인 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도를 측정하고 난 이후에는, 열전소자 외부의 온도를 측정하는 과정을 거칠 수 있다.(S7-2) 이 단계에서, 열전소자의 외부란 열전소자로부터 일정거리 이격된 위치를 지칭하는 것으로서 열전소자의 흡열면의 온도 흡수에 따른 영향이 미치지 않는 위치를 지칭하는 것일 수 있으며, 대기 중의 온도가 측정되는 것일 수 있다.After the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element as the heat absorbing surface is measured, the temperature outside the thermoelectric element may be measured. (S7-2) In this step, the outside of the thermoelectric element is a distance Refers to a position at which the temperature is not measured, and may refer to a position where the temperature is not measured by the temperature absorption of the heat absorbing surface of the thermoelectric element.
다음으로, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동방법은 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도가 외부 온도보다 더 높은지 여부를 판단하는 과정을 거칠 수 있다.(S7-3) Next, in the method of driving a thermoelectric device according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention, it can be determined whether the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric device is higher than the external temperature (S7-3)
만일, 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도가 외부 온도보다 더 높으면 열전소자로 인가되는 전원 공급을 오프하는 과정을 거칠 수 있다.(S7-4) 하지만, 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도가 외부 온도보다 높지 않은 경우에는 열전소자로의 전원 공급이 온되는 과정을 거칠 수 있다.(S7-5) 그리고, 이러한 과정은 계속적으로 반복될 수 있다.If the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element is higher than the external temperature, the power supply applied to the thermoelectric element may be turned off (S7-4). However, if the temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element is higher than the external temperature The power supply to the thermoelectric element can be turned on (S7-5). This process can be repeated continuously.
이러한 방법을 실현하기 위하여, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 따른 열전소자 구동장치는 열전소자의 반작용면의 온도를 측정하는 제1 온도 센서, 열전소자의 반작용면으로부터 이격되어 외부 온도를 측정하는 제2 온도 센서, 열전소자의 반작용면에 열을 인가하는 가열 장치, 열전소자의 동작과 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도와 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 온도를 비교하여 가열 장치의 작동여부를 결정하는 제어부를 포함하여 구성될 수 있다. 여기서, 가열 장치는 히터(300), 팬(400) 또는 열선(600) 등을 포함하여 구성될 수 있다.In order to realize such a method, a thermoelectric-element driving apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention includes a first temperature sensor for measuring a temperature of a reaction surface of a thermoelectric element, a second temperature sensor for measuring an external temperature, A controller for determining the operation of the heating device by comparing the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor and the temperature measured by the second temperature sensor by comparing the operation of the thermoelectric element and the temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, As shown in FIG. Here, the heating device may include a
상술한 바와 같이, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예들을 참조하여 설명하였지만 해당 기술 분야의 숙련된 당업자라면 하기의 특허 청구의 범위에 기재된 본 발명의 사상 및 영역으로부터 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 본 발명을 다양하게 수정 및 변경시킬 수 있음을 이해할 수 있을 것이다.Although the preferred embodiments of the present invention have been disclosed for illustrative purposes, those skilled in the art will appreciate that various modifications, additions and substitutions are possible, without departing from the scope and spirit of the invention as disclosed in the accompanying claims. And changes may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention.
10 : p형 반도체
20 : n형 반도체
30 : 세라믹판
40 : 전기전도판
50 : 전원 공급기
100 : 발열 블럭
200 : 흡열 블럭
300 : 히터
400 : 팬
500 : 제2 온도 센서
600 : 열선10: p-type semiconductor
20: n type semiconductor
30: Ceramic plate
40: Electrically conductive plate
50: Power supply
100: Heat block
200: heat absorption block
300: heater
400: Fan
500: second temperature sensor
600: Heat line
Claims (11)
상기 열전소자의 반작용면으로부터 이격되어 설치된 제2 온도 센서가 외부 온도를 측정하는 단계;
제어 모듈(module)이 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도와 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도를 비교하는 단계;
상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도 이하인 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동을 지시하는 단계;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
Measuring a temperature of a first temperature sensor located on a reaction surface of the thermoelectric element;
Measuring an external temperature by a second temperature sensor installed apart from a reaction surface of the thermoelectric element;
Comparing a temperature measured by the first temperature sensor with an external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor by the control module;
And when the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor is equal to or lower than the external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, the control module instructs the operation of the heating device on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric device A method of driving a thermoelectric device.
상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도 보다 낮은 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동을 지시하는 단계 이후에,
상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도가 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 외부 온도를 초과하는 경우, 상기 제어모듈이 상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 가열 장치의 작동의 중지를 지시하는 단계;를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
After the step of instructing the operation of the heating device of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element by the control module when the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor is lower than the temperature measured by the second temperature sensor,
And when the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor exceeds the external temperature measured by the second temperature sensor, the control module instructs to stop the operation of the heating device on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element And the thermoelectric element is driven.
상기 열전소자의 반작용면에서는 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein an endothermic action is performed on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
상기 가열 장치는
상기 열전소자의 반작용면의 열 교환기 사이에 구비되는 열선인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The heating device
And a heat line provided between the heat exchangers on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
상기 가열 장치는
상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 이격되어 열을 인가하는 히터(heater)인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The heating device
Wherein the heater is a heater which is spaced apart from the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element and applies heat.
상기 가열 장치는
상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 이격되어 외부 공기를 인가하는 팬(fan)인 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The heating device
And a fan for applying external air to the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
상기 열전소자의 작용면에서는 발열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein a heat generating action is performed on the action surface of the thermoelectric element.
상기 열전소자의 반작용면으로부터 이격되어 외부 온도를 측정하는 제2 온도 센서;
상기 열전소자의 반작용면에 열을 인가하는 가열 장치;
상기 열전소자의 동작과 상기 제1 온도 센서가 측정한 온도와 상기 제2 온도 센서가 측정한 온도를 비교하여 상기 가열 장치의 작동 여부를 결정하는 제어부;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치.
A first temperature sensor for measuring a temperature of the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element;
A second temperature sensor spaced apart from the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element to measure an external temperature;
A heating device for applying heat to the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element;
And a control unit for comparing the operation of the thermoelectric element with the temperature measured by the first temperature sensor and the temperature measured by the second temperature sensor to determine whether the heating apparatus is operated or not, .
상기 가열 장치는 열선, 히터 또는 팬 중에서 어느 하나로 선택되는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치.
9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the heating device is selected from a heat wire, a heater, and a fan.
상기 열전소자의 반작용면에서는 흡열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치.
9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein an endothermic action is performed on the reaction surface of the thermoelectric element.
상기 열전소자의 작용면에서는 발열 작용이 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 열전소자 구동장치.
9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein a heat generating action is performed on the action surface of the thermoelectric element.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150184929A KR20170075366A (en) | 2015-12-23 | 2015-12-23 | Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150184929A KR20170075366A (en) | 2015-12-23 | 2015-12-23 | Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170075366A true KR20170075366A (en) | 2017-07-03 |
Family
ID=59357881
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150184929A KR20170075366A (en) | 2015-12-23 | 2015-12-23 | Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20170075366A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20200113310A (en) * | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-07 | 목포대학교산학협력단 | Led street lamp and system using thermo electric element |
| KR20210041866A (en) * | 2019-10-08 | 2021-04-16 | 고정찬 | Heating and Cooling Supply System for Sleeping Bag |
-
2015
- 2015-12-23 KR KR1020150184929A patent/KR20170075366A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20200113310A (en) * | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-07 | 목포대학교산학협력단 | Led street lamp and system using thermo electric element |
| KR20210041866A (en) * | 2019-10-08 | 2021-04-16 | 고정찬 | Heating and Cooling Supply System for Sleeping Bag |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102034337B1 (en) | Thermoelectric-based thermal management of electrical devices | |
| CN102082133B (en) | Temperature-controlled radiator | |
| US8963048B2 (en) | Heating assembly, heating device, and auxiliary cooling module for a battery | |
| CN201398013Y (en) | Laser module with temperature control device | |
| CN101470449B (en) | Cooling control system and cooling control method | |
| CN104035459A (en) | Frequency converter and method for controlling temperature of frequency converter | |
| CN105407684B (en) | Locomotive electric cad system cabinet cooling device and locomotive electric cad system cabinet | |
| CN114284521A (en) | Fuel cell waste heat recovery system and vehicle | |
| KR20170075366A (en) | Driving method of thermoelectric element and driving apparatus of thermoelectric element | |
| KR101753152B1 (en) | A thermoelectric generator having heat exchanger using molten metal | |
| CN201498512U (en) | semiconductor refrigeration radiator | |
| CN200941653Y (en) | Thermal controller of CCD camera | |
| JP2008128833A (en) | High and low-temperature test device | |
| KR101684327B1 (en) | Complex Specifics Testing Apparatus for Thermoelectric Element | |
| JP2015148355A (en) | Waste-heat recovery unit and waste-heat utilization system | |
| TW201809697A (en) | Temperature control device for press-bonding unit of electronic component and testing device using the same capable of keeping the temperature difference between primary and secondary effect surfaces of a cooling chip within a better range | |
| CN216528872U (en) | Power device, frequency conversion system and air conditioning equipment | |
| KR101558053B1 (en) | heat exchanger | |
| JP2013143792A (en) | Electric power generation system | |
| JP2019204809A (en) | Thermoelectric conversion device | |
| KR101684129B1 (en) | Method for controlling electric water pump | |
| CN107831810A (en) | Semiconductor automatic thermostatic device | |
| KR101679954B1 (en) | Thermoelectric generator | |
| CN114171473A (en) | Power device, control method thereof, frequency conversion system and air conditioning equipment | |
| CN201638139U (en) | PC chip cooling device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |