KR20170049255A - Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same - Google Patents
Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170049255A KR20170049255A KR1020150150424A KR20150150424A KR20170049255A KR 20170049255 A KR20170049255 A KR 20170049255A KR 1020150150424 A KR1020150150424 A KR 1020150150424A KR 20150150424 A KR20150150424 A KR 20150150424A KR 20170049255 A KR20170049255 A KR 20170049255A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- group
- carbon atoms
- hydrazine
- resin
- formula
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/04—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent
- C08J9/06—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent by a chemical blowing agent
- C08J9/10—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent by a chemical blowing agent developing nitrogen, the blowing agent being a compound containing a nitrogen-to-nitrogen bond
- C08J9/104—Hydrazines; Hydrazides; Semicarbazides; Semicarbazones; Hydrazones; Derivatives thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/20—Compounding polymers with additives, e.g. colouring
- C08J3/22—Compounding polymers with additives, e.g. colouring using masterbatch techniques
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/04—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent
- C08J9/06—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent by a chemical blowing agent
- C08J9/10—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof using blowing gases generated by a previously added blowing agent by a chemical blowing agent developing nitrogen, the blowing agent being a compound containing a nitrogen-to-nitrogen bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L101/00—Compositions of unspecified macromolecular compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2203/00—Foams characterized by the expanding agent
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Porous Articles, And Recovery And Treatment Of Waste Products (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 가열분해 화합물 및 이를 이용한 가스 발생 방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는, 열분해되어 질소 가스를 발생시킴으로써, 수지를 발포시킬 수 있는 가열분해 화합물 및 이를 이용한 가스 발생 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a heat decomposition compound and a gas generating method using the same, and more particularly, to a heat decomposition compound capable of foaming a resin by pyrolysis to generate nitrogen gas and a gas generating method using the same.
발포제는 수지에 배합되어 다공성 발포체를 제조하기 위한 수지 첨가제이다. 폴리에틸렌, 폴리프로필렌, 에틸렌-비닐아세테이트 공중합체(EVA), 폴리염화비닐, 스티렌-부타디엔 고무, 아크릴로니트릴-부타디엔 고무 등의 열가소성 수지, 고무 등에 대한 발포제로서, 아조디카본아미드(azodicarbonamide: ADCA), p,p'-옥시비스(벤젠술포닐히드라지드)(p,p'-oxybis(benzenesulfonyl hydrazide)), 디니트로소 펜타메틸렌테트라민(dinitroso pentamethylene tetramine: DPT), p-톨루엔술포닐 히드라지드(ptoluenesulfonylhydrazide), 벤젠술포닐 히드라지드(benzenesulfonyl hydrazide), 5-페닐 테트라졸 (5-phenyl tetrazole) 등의 다양한 유기 화합물 발포제가 알려져 있다(대한민국 특허 10-1518698, 일본 특개 2001-139928, 일본 특허 3872961, 미국 특허 4885316 등 참조). The blowing agent is a resin additive for blending with a resin to prepare a porous foam. Azodicarbonamide (ADCA) is used as a foaming agent for thermoplastic resins such as polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), polyvinyl chloride, styrene-butadiene rubber, acrylonitrile- , p, p'-oxybis (benzenesulfonyl hydrazide), dinitroso pentamethylene tetramine (DPT), p-toluenesulfonyl hydrazide a variety of organic compound blowing agents such as ptoluenesulfonylhydrazide, benzenesulfonyl hydrazide and 5-phenyl tetrazole are known (Korean Patent No. 10-1518698, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-139928, Japanese Patent No. 3872961 , U. S. Patent No. 4885316, etc.).
상기 발포제 중, 아조디카본아마이드(ADCA)는 가열에 의한 질소 가스의 발생이 빠르고, 분해 생성물이 불연성이며, 독성이 적어, 범용적으로 사용되고 있다. 그러나, 아조디카본아미드를 사용하여 발포체를 제조하는 경우, 아조디카본아미드가 완전히 분해되지 않아 황색의 잔유물이 잔류하여, 발포체의 백색도가 저하되는 단점이 있다. 또한, 하기 반응식 1에 나타낸 바와 같이, 아조디카본아미드가 열분해될 때, 생식 독성을 일으킬 수 있는 포름아미드 (formamide), 암모니아(ammonia), 일산화탄소 등의 유해 성분이 발생하기도 한다. Among the above blowing agents, azodicarbonamide (ADCA) is a general-purpose product because nitrogen gas is rapidly generated by heating, decomposition products are incombustible, and toxicity is low. However, when a foam is produced using azodicarbonamide, the azodicarbonamide is not completely decomposed and yellowish remnants remain, and the whiteness of the foam is lowered. Further, as shown in Reaction Scheme 1 below, harmful components such as formamide, ammonia, and carbon monoxide which may cause reproductive toxicity may be generated when azodicarbonamide is pyrolyzed.
[반응식 1][Reaction Scheme 1]
따라서, 본 발명의 목적은, 포름아미드, 암모니아 등의 유해 성분을 발생시키지 않으며, 열분해되어 주로 질소 가스를 발생시킬 수 있는 가열분해 화합물 및 이를 이용한 가스 발생 방법을 제공하는 것이다. 본 발명의 다른 목적은, 친환경적이고, 유해물질 규제를 회피할 수 있을 뿐 만 아니라, 기존의 ADCA 이상의 발포 성능을 가지는 가열분해 화합물 및 이를 이용한 가스 발생 방법을 제공하는 것이다.Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a heat decomposition compound which does not generate harmful components such as formamide and ammonia and which is pyrolyzed to generate mainly nitrogen gas, and a gas generating method using the same. It is another object of the present invention to provide a heat decomposition compound which is eco-friendly, which can avoid regulation of harmful substances, and which has a foaming capability higher than that of the conventional ADCA, and a gas generating method using the same.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위하여, 본 발명은 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 발포제를 제공한다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a foaming agent represented by the following general formula (1).
[화학식 1][Chemical Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서, X는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 알킬기, 탄소수 4 내지 10의 아릴기, 탄소수 3 내지 10의 헤테로고리기 또는 3족, 4족 또는 5족 원자이고, R은 단일 결합 또는 이중 결합이며, D는 히드라진 포함 기(group including hydrazine moiety)이고, n는 3 내지 6의 정수이다.X is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, a heterocyclic group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, or a Group 3, 4, or 5 group atom, and R is a single bond or a double bond , D is a hydrazine containing group (group including hydrazine moiety), and n is an integer of 3 to 6.
본 발명에 따른 발포제는, 포름아미드, 암모니아 등의 유해 성분을 발생시키지 않으며, 열분해되어 주로 질소 가스를 발생시키므로, 친환경적이고, 유해물질 규제를 회피할 수 있을 뿐 만 아니라, 기존의 ADCA 이상의 발포 성능을 가진다. The foaming agent according to the present invention does not generate harmful components such as formamide and ammonia and is pyrolyzed to generate mainly nitrogen gas. Therefore, it is eco-friendly and can avoid the regulation of harmful substances, .
도 1 및 2는, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 발포제를 이용하여, 각각 폴리프로필렌(PP) 및 에틸렌-비닐아세테이트 공중합체(EVA)를 발포시켜 얻은 발포체의 내부 기공 형태를 보여주는 전자 현미경 사진.1 and 2 are electron micrographs showing the internal pore shape of a foam obtained by foaming a polypropylene (PP) and an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), respectively, using a blowing agent according to an embodiment of the present invention.
이하, 본 발명을 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
본 발명에 따른 가열분해 화합물은 하기 화학식 1로 표시된다.The heat decomposition compound according to the present invention is represented by the following general formula (1).
[화학식 1][Chemical Formula 1]
상기 화학식 1에서, X는 탄소수 1 내지 10(구체적으로는 탄소수 1 내지 6)의 알킬(alky)기, 탄소수 4 내지 10(구체적으로는 탄소수 5 내지 8)의 아릴(aryl)기, 탄소수 3 내지 10(구체적으로는 탄소수 5 내지 8)의 헤테로고리기, 알루미늄(Al) 등의 3족, 실리콘(Si) 등의 4족 또는 질소(N) 등의 5족 원자이고, R은 단일 결합 또는 이중 결합이며, D는 히드라진 포함 기(group including hydrazine moiety)이고, n는 3 내지 6의 정수이다. 필요에 따라, 상기 D는 인접한 기 간에 탄소수 2 내지 5의 알킬기를 포함하는 알루미늄을 중심으로 결합될 수 있다.X is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms (specifically 1 to 6 carbon atoms), an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms (specifically 5 to 8 carbon atoms), an aryl group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, A heterocyclic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms (specifically 5 to 8 carbon atoms), a Group 3 element such as aluminum (Al), a Group 4 element such as silicon (Si) or nitrogen (N) D is a hydrazine containing group, and n is an integer of 3 to 6. If necessary, D may be bonded to an aluminum containing an alkyl group having 2 to 5 carbon atoms in the adjacent groups.
상기 X의 구체적인 예로는 탄소 원자(메틸기), 페닐기, 1,3,5-트리아진 (triazine)기 등의 헤테로아릴기 등을 예시할 수 있다. 상기 히드라진 포함 기(D)는, 가열에 의해 질소로 변환될 수 있는 히드라진 부분(hydrazine moiety), 즉 -N-N-기를 포함하는 기로서, 히드라진기(-NHNH2), 니트로아민기(-NHNO2), -N-N-기를 포함하는 헤테로고리기 등을 예시할 수 있고, 상기 히드라진 부분을 포함하는 헤테로고리기로는 테트라졸(tetrazole)기, 테트라졸아민(tetrazole amine)기 등을 예시할 수 있다. Specific examples of X include a heteroaryl group such as a carbon atom (methyl group), a phenyl group, and a 1,3,5-triazine group. The hydrazine containing group (D) is a group containing a hydrazine moiety, i.e., -NN- group, which can be converted into nitrogen by heating, and includes a hydrazine group (-NHNH 2 ), a nitroamine group (-NHNO 2 And a -NH- group. Examples of the heterocyclic group containing the hydrazine moiety include a tetrazole group, a tetrazole amine group and the like.
또한, 필요에 따라, 상기 히드라진 포함 기(D)는 히드라진 부분에 치환되는 치환기로서, 카보닐기(-CO- 또는 -COR1, 여기서, R1은 탄소수 1 내지 10의 탄화수소기를 나타낸다), 아미드기(-CONH2), 헤테로 원자를 포함하거나 포함하지 않는 탄소수 1 내지 20(구체적으로는 탄소수 1 내지 10)의 탄화수소기, 아민기, 이들의 조합 등의 치환기를 더욱 포함할 수 있다.In addition, if necessary, the hydrazine containing group (D) may be substituted with a carbonyl group (-CO- or -COR 1 , wherein R 1 represents a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms), an amide group (-CONH 2 ), a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms (specifically having 1 to 10 carbon atoms) with or without a hetero atom, an amine group, and combinations thereof.
예를 들면, 상기 히드라진 포함 기(D)는 세미디카바자이드기, 벤조하이드라지드기, 하이드라진카보닐기 등과 같이 히드라진 부분과 그에 치환되는 하나 이상의 치환기를 포함한다. 상기 헤테로 원자를 포함하거나 포함하지 않는 탄소수 1 내지 20의 탄화수소기는 선형, 가지형, 고리형의 탄화수소기로써, 탄소수 1 내지 10의 가지형(iso or branched) 또는 선형의 알킬기, 탄소수 2 내지 10의 알케닐기(알릴기 등), 탄소수 2 내지 10의 알키닐기, 탄소수 5 내지 10의 시클로알킬기, 시클로알케닐기 또는 시클로알키닐기, 탄소수 4 내지 10의 아릴기, 1 내지 5개의 헤테로 원자를 포함하거나 포함하지 않는 탄소수 4 내지 10의 헤테로아릴기 또는 헤테로시클릭기, 이들의 조합 등일 수 있다. For example, the hydrazine containing group (D) includes a hydrazine moiety such as a semydicarbazide group, a benzohydrazide group, a hydrazinecarbonyl group and the like and at least one substituent substituted therewith. The hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, which may or may not contain a hetero atom, is a linear, branched, or cyclic hydrocarbon group, and may be an iso or branched alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms or a linear alkyl group having 2 to 10 carbon atoms An alkenyl group having 2 to 10 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 10 carbon atoms, a cycloalkenyl group or a cycloalkynyl group, an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 1 to 5 heteroatoms A heteroaryl group or a heterocyclic group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, and combinations thereof.
일예로, X는 알킬기(예를 들면, 하기 화학식 1d, 1p, 1q 및 1r), 아릴기 (예를 들어, 페닐 구조, 하기 화학식 1b, 1h), 헤테로고리기(예를 들면, 하기 화학식 1i) 또는 5족 화합물(예를 들어, 실리콘, 하기 화학식 1s)일 수 있다. For example, X may be an alkyl group (for example, the following formulas 1d, 1p, 1q and 1r), an aryl group (for example, a phenyl structure, the following formula 1b and 1h), a heterocyclic group ) Or a Group 5 compound (for example, silicon, the following Formula 1s).
본 발명에 따른 발포제는 발포제의 구조 안정성 및 발포 성능이 우수하고, 필요에 따라, 고온 또는 저온 발포제로서 유용하게 이용될 수 있으며, 분해시 질소 가스를 발생시킬 수 있고, 분해 온도를 제어할 수 있다.The foaming agent according to the present invention is excellent in the structural stability and foaming performance of the foaming agent, and can be usefully used as a high-temperature or low-temperature foaming agent when necessary, can generate nitrogen gas upon decomposition, and can control the decomposition temperature .
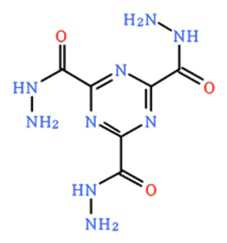
본 발명에 따른 발포제의 구체적인 예로는 하기 화학식으로 표시되는 화합물을 예시할 수 있다.Specific examples of the blowing agent according to the present invention include compounds represented by the following formulas.
(화학식 1a), (화학식 1b), (Formula 1a), (1b),
(화학식 1c), (화학식 1d), (Formula 1c), (1d),
(화학식 1e), (화학식 1f), (1e), (1f),
(화학식 1g), (화학식 1h), (Formula 1g), (1h),
(화학식 1i), (화학식 1j), (1i), (1j),
(화학식 1k), (화학식 1l), (Ik), (Formula l),
(화학식 1m), (화학식 1n), (1m), (1n),
(화학식 1o), (화학식 1p), (Io), (Formula 1p),
(화학식 1q), (화학식 1r), (Formula 1q), (1R),
(화학식 1s) (화학식 1t) (Formula 1s) (Formula 1t)
본 발명의 발포제는, 3개 이상의 질소-질소 기능성 기를 스타-형상(Star- shape)으로 포함하고 있어, 보다 많은 질소 가스를 생성할 수 있으며, 범용적으로 사용되는 ADCA 발포제와 비교하여, 동등 이상의 발포 성능을 가지면서도, 열분해시 포름아미드(formamide), 암모니아(ammonia) 가스의 발생이 적은 장점이 있다. 예를 들면, 화학식 1d로 표시되는 발포제의 열분해 메커니즘은 하기 반응식 2와 같다.The foaming agent of the present invention contains three or more nitrogen-nitrogen functional groups in a star-shape, and can produce more nitrogen gas. Compared to the ADCA foaming agent used in general use, It is advantageous in that it has low foaming performance and less generation of formamide and ammonia gas during thermal decomposition. For example, the pyrolysis mechanism of the blowing agent represented by the formula (1d) is as shown in the following reaction formula (2).
[반응식 2][Reaction Scheme 2]
본 발명에 따른 발포제는, 기존 ADCA 발포제와 비교하여, 가스 발생량이 통상 약 25~40 % 더 많으므로, 경제적일 뿐만 아니라, 일산화탄소의 발생량이 적으므로, 생식 독성물질로서 REACH 규제 등록 물질로 등재된 포름아미드의 발생량도 적은 장점이 있다.The foaming agent according to the present invention is not only economical but also generates a small amount of carbon monoxide because the amount of generated gas is usually about 25 to 40% larger than that of the conventional ADCA foaming agent. Therefore, There is also a small amount of formamide generated.
본 발명에 따른 발포제는, 통상의 다양한 유기 합성법으로 제조될 수 있으며, 구체적으로는, 하기 실시예에 나타낸 바와 같이, (i) 구아니딘(Guanidine)과 히드라진 또는 그 유도체를 반응시키거나(실시예 1, 5, 6), (ii) 3개의 반응성 할로겐을 포함하는 화합물을 히드라진 또는 그 유도체와 반응시키거나(실시예 2, 3), (iii) 3개의 시아노기(-CN)와 NaN3를 반응시키는(실시예 7) 방법 등으로 제조될 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명에 따른 발포제는 원-폿(one-pot) 반응으로 합성될 수 있으므로, 합성이 용이하고 경제적이다. The foaming agent according to the present invention can be produced by a variety of conventional organic synthesis methods, and specifically, as shown in the following examples, (i) by reacting guanidine with hydrazine or a derivative thereof, (Ii) reacting a compound containing three reactive halogens with hydrazine or a derivative thereof (Examples 2 and 3), (iii) reacting three cyano groups (-CN) with NaN 3 (Example 7) or the like. Therefore, the foaming agent according to the present invention can be synthesized by a one-pot reaction, so that the synthesis is easy and economical.
본 발명에 따른 수지의 발포 방법은, 본 발명의 발포제와 발포 대상 수지를 혼합하고, 가열하는 단계를 포함한다. 상기 발포제와 발포 대상 수지의 혼합에는 교반기 또는 프레스 롤(press roll) 등의 통상적인 수지 혼합 수단이 사용될 수 있고, 상기 가열에는 압출기, 프레스 몰드(press mold), 열풍 순환식 오븐 등의 통상적인 수지 가열 수단이 사용될 수 있다. 상기 수지 혼합 수단 및 수지 가열 수단의 운전 조건은 발포 대상 수지의 종류, 발포제, 첨가제의 종류 및 상태에 따라 적절하게 운전될 수 있으며, 대표적인 운전 조건들로는 상기 발포제가 파우더(powder)의 형태로 사용되는 경우와 마스터 배치(master batch, 여기서 마스터 배치란, 수지에 발포제를 고농도, 예를 들면, 10 내지 55 중량%로 농축하여 분산시켜 놓은 것을 의미한다.)의 형태로 사용되는 경우로 나눌 수 있는데, 상기 마스터 배치는 90 내지 120 ℃의 온도를 가지는 수지 혼합 수단에서 10 내지 30 분 동안 혼합되고, 90 내지 250 ℃의 온도를 가지는 수지 가열 수단에서 가열되어 제조될 수 있다. 상기 발포 대상 수지와 발포제(파우더의 형태 또는 마스터 배치의 형태 등)는 25 내지 120 ℃의 온도를 가지는 수지 혼합 수단에서 1 내지 30 분 동안 혼합되고, 150 내지 250 ℃(구체적으로 170 내지 230 ℃)의 온도, 100 내지 160 kg/cm2(구체적으로 100 내지 150 kg/cm2)의 압력을 가지는 수지 가열 수단에서 20 초 내지 30 분 동안 가열되어 발포된다. 상기 발포제의 사용량도 발포 대상 수지의 종류, 발포제의 종류, 희망하는 발포도 등에 따라 달라질 수 있으나, 예를 들면, 파우더 형태의 발포제는 발포 대상 수지 100 중량부에 대하여, 1 내지 40 중량부(구체적으로는 1 내지 20 중량부, 더욱 구체적으로는 1.5 내지 10 중량부, 더욱 구체적으로는 2 내지 6 중량부)가 사용될 수 있고, 마스터 배치 형태의 발포제는 발포 대상 수지 100 중량부에 대하여, 10 내지 80 중량부(구체적으로는 20 내지 70 중량부, 더욱 구체적으로는 30 내지 55 중량부)가 사용될 수 있다.The method for foaming a resin according to the present invention includes a step of mixing and heating the foaming agent of the present invention with a resin to be foamed. The foaming agent may be mixed with the resin to be foamed by a conventional resin mixing means such as a stirrer or a press roll. The heating may be carried out using a conventional resin such as an extruder, a press mold or a hot air circulating oven Heating means can be used. The operation conditions of the resin mixing means and the resin heating means can be appropriately operated according to the kind of the resin to be foamed, the type of the foaming agent, the kind of the additive, and the state. Typical operating conditions include the use of the foaming agent in the form of powder And master batch (master batch means that the foaming agent is concentrated and dispersed in the resin at a high concentration, for example, 10 to 55% by weight) The masterbatch may be prepared by mixing in a resin mixing means having a temperature of 90 to 120 캜 for 10 to 30 minutes and heating in a resin heating means having a temperature of 90 to 250 캜. The foamable resin and the foaming agent (in the form of a powder or a master batch) are mixed in a resin mixing means having a temperature of 25 to 120 캜 for 1 to 30 minutes and then heated at 150 to 250 캜 (specifically 170 to 230 캜) And a resin heating means having a pressure of 100 to 160 kg / cm 2 (specifically, 100 to 150 kg / cm 2 ) for 20 seconds to 30 minutes. The amount of the blowing agent to be used may vary depending on the type of the resin to be foamed, the type of the blowing agent, the desired degree of foaming, etc. For example, the powdered blowing agent may be used in an amount of 1 to 40 parts by weight 1 to 20 parts by weight, more specifically, 1.5 to 10 parts by weight, and more specifically 2 to 6 parts by weight) of the blowing agent in the form of a master batch may be used in an amount of 10 to 100 parts by weight, 80 parts by weight (specifically, 20 to 70 parts by weight, more specifically 30 to 55 parts by weight) may be used.
본 발명의 발포제가 사용되는 발포 대상 수지로는, 폴리에틸렌(PE), 폴리프로필렌(PP), 폴리염화비닐(PVC), 폴리카보네이트(PC), 폴리스티렌(PS), 폴리아미드, 아세탈, 스티렌부타디엔 고무(SBR), 에틸렌-비닐아세테이트 공중합체(Ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer: EVA), 에틸렌프로필렌 고무(monomer rubber: EPDM), 열가소성 탄성체(Thermoplastic Elastomer: TPE), 열가소성 폴리우레탄(thermoplastic polyurethane: TPU), 열가소성 고무(Thermoplastic rubber: TPR), ABS 수지(acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer), 고무(rubber), 에폭시(epoxy) 수지, 아크릴 수지 등의 각종 합성 또는 천연 수지가 사용될 수 있다. 또한, 상기 발포 공정에서, 칼슘 카보네이트(Calcium carbonate), 산화 아연(Zinc Oxide), 스테아릭산(Stearic acid), 디시클로헥실 프탈레이트(Dicyclohexyl phthalate) 등의 각종 첨가제를 사용할 수 있다.Examples of the resin to be foamed in which the foaming agent of the present invention is used include polyethylene, polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polycarbonate (PC), polystyrene (PS), polyamide, acetal, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), an ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), an ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM), a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), a thermoplastic rubber Various synthetic or natural resins such as thermoplastic rubber (TPR), ABS resin (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer), rubber, epoxy resin and acrylic resin may be used. In the foaming step, various additives such as calcium carbonate, zinc oxide, stearic acid, and dicyclohexyl phthalate may be used.
본 발명에 따른 발포제는 차량용 시트, 타이어 및 루프텍 커버, 가니쉬 커버장치, 웨더 스트립(weather strip), 공조 장치용 에어덕트 등의 엔지니어링 플라스틱(engineering plastic), 차량용 내/외장재 등의 차량용 제품, 에어컨, TV, PC(개인용 컴퓨터) 등의 가전기기 케이스, 샷시, 스펀지, 우레탄 등의 발포 성형 제품 건축 내장재, 벽지, 바닥재, 인조피혁, 운동화, 슬리퍼 등의 신발류(footwear) 제품, 유아 및 어린이용 매트, 장난감 등의 유아용 제품, 합성 목재, 액세사리 장신구 또는 기타 플라스틱 용기 등에 유용하게 이용될 수 있다.The blowing agent according to the present invention can be applied to engineering plastics such as vehicle seat, tire and roof tec cover, garnish cover device, weather strip, air duct for air conditioner, automobile products such as interior / , Footwear products such as wallpaper, flooring, artificial leather, sneakers and slippers, infant and children's mats, household appliances such as TVs, PCs (personal computers), foam molding products such as sashes, sponges, , Children's products such as toys, synthetic wood, accessory ornaments, and other plastic containers.
이하, 실시예를 통하여 본 발명을 더욱 상세히 설명한다. 하기 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 것으로서, 본 발명의 범위가 이들 실시예에 의해 한정되는 것은 아니다. Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail by way of examples. The following examples are provided to illustrate the present invention, and the scope of the present invention is not limited by these examples.
[실시예 1] 화학식 1d로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 1] Production of blowing agent represented by the formula (1d)
하기 반응식 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 구아니딘 하이드로클로라이드 19.1g (0.2 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) 및 용매로서 디옥산(Dioxane) 100 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 히드라진 모노하이드레이트 (hydrazine monohydrate) 80% 40.0g (0.8 mol)을 상온에서 천천히 적가한 다음, 2시간 동안 환류(reflux) 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 디옥산(Dioxane) 및 에탄올(EtOH)로 세척하여, 화학식 1d로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 82%, DT: 224℃, GV: 300ml/g, NMR : δ 4.50 (2H, NH2), δ 8.60 (1H, NH)).19.1 g (0.2 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) of guanidine hydrochloride and 100 mL of dioxane as a solvent were placed in a flask and stirred, as shown in the following Reaction Scheme 3. To the flask, 40.0 g (0.8 mol) of 80% hydrazine monohydrate was slowly added dropwise at room temperature, and the mixture was refluxed and stirred for 2 hours. Finally, the reaction mixture was washed with dioxane and ethanol (EtOH) at room temperature to synthesize a white compound represented by the formula 1d (yield: 82%, DT: 224 ° C, GV: 300 ml / 4.50 (2H, NH 2),? 8.60 (1H, NH)).
[반응식 3][Reaction Scheme 3]
[실시예 1-1] 화학식 1p로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 1-1] Preparation of blowing agent represented by the formula 1p
하기 반응식 4에 나타낸 바와 같이, 구아니딘 나이트레이트 24.4g (0.2 mol, Guanidine nitrate) 및 용매로서 에탄올(Ethanol) 100 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 히드라진 모노하이드레이트 (hydrazine monohydrate) 80% 40.0g (0.8 mol)을 상온에서 천천히 적가한 다음, 2시간 동안 환류(reflux) 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 에탄올(EtOH)로 세척하여, 화학식 1p로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 80%, DT: 214℃, GV: 300ml/g, NMR : δ 4.46 (2H, NH2), δ 8.56 (1H, NH)).As shown in Reaction Scheme 4, 24.4 g (0.2 mol, guanidine nitrate) of guanidine nitrate and 100 mL of ethanol as a solvent were placed in a flask and stirred. To the flask, 40.0 g (0.8 mol) of 80% hydrazine monohydrate was slowly added dropwise at room temperature, and the mixture was refluxed and stirred for 2 hours. (Yield: 80%, DT: 214 캜, GV: 300 ml / g, NMR: δ 4.46 (2H, NH 2 ) ,? 8.56 (1H, NH).
[반응식 4][Reaction Scheme 4]
[실시예 2] 화학식 1b로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 2] Production of foaming agent represented by the formula (1b)
하기 반응식 5에 나타낸 바와 같이, 트리클로로벤젠 30.0 g (0.165 mol, Trichloro benzene) 및 물(H2O) 150 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 히드라진 모노하이드레이트 (hydrazine monohydrate) 80% 46.5g (0.74 mol)을 상온에서 천천히 적가한 다음, 2시간 동안 환류 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 물(H2O)로 세척하여, 화학식 1b로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 74%, DT: 300℃, GV: 160ml/g, NMR :δ 5.21 (2H, NH2), δ 7.37 (1H, Ph), 7.67 (2H, Ph), δ 9.67 (1H, NH)).30.0 g (0.165 mol, Trichloro benzene) of trichlorobenzene and 150 mL of water (H 2 O) were placed in a flask and stirred as shown in Reaction Scheme 5 below. To the flask, 46.5 g (0.74 mol) of 80% hydrazine monohydrate was slowly added dropwise at room temperature and then refluxed and stirred for 2 hours. Finally, at room temperature, water (H 2 O) with three to synthesize white compound represented by the general formula 1b (yield: 74%, DT: 300 ℃ , GV: 160ml / g, NMR: δ 5.21 (2H, NH 2 ) ,? 7.37 (1H, Ph), 7.67 (2H, Ph) ,? 9.67 (1H, NH).
[반응식 5] [Reaction Scheme 5]
[실시예 3] 화학식 1c로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 3] Preparation of blowing agent represented by the formula (1c)
하기 반응식 6에 나타낸 바와 같이, 시아누릭 클로라이드 18.4 g (0.1 mol, Cyanuric chloride) 및 물(H2O) 276 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 히드라진 모노하이드레이트 (hydrazine monohydrate) 60% 31.25g (0.5 mol)을 천천히 적가한 다음, 2시간 동안 환류 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 물(H2O)로 세척하여, 화학식 1c로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 91%, DT: 270℃, GV: 220ml/g, NMR :δ 4.64 (1H, NH), δ 8.81 (2H, NH2)).18.4 g (0.1 mol, Cyanuric chloride) of cyanuric chloride and 276 mL of water (H 2 O) were placed in a flask and stirred as shown in Scheme 6 below. To the flask, 31.25 g (0.5 mol) of 60% hydrazine monohydrate was slowly added dropwise, and the mixture was refluxed and stirred for 2 hours. Finally, at room temperature, washed with water (H 2 O), was synthesized in the white compound of formula 1c (yield: 91%, DT: 270 ℃ , GV: 220ml / g, NMR: δ 4.64 (1H, NH), 8 8.81 (2H, NH 2 ).
[반응식 6] [Reaction Scheme 6]
[실시예 4] 화학식 1m로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 4] Production of blowing agent represented by the formula (1m)
하기 반응식 7에 나타낸 바와 같이, 실시예 1에서 합성한 화학식 1d로 표시되는 화합물 20.0g (0.21 mol), 아세트산 63.0 g (1.05 mol, acetic acid) 및 물(H2O) 200 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, NaOCN 61.2 g (0.942 mol)을 천천히 실온에서 적가한 다음, 75 ℃에서 하룻밤(overnight) 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 물(H2O) 및 에탄올(EtOH)로 세척하여, 화학식 1m로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 88%, DT: 295℃, GV: 166ml/g, NMR :δ 7.22 (1H, NH), δ 8.87 (1H, NH), δ 9.99 (2H, NH2)).20.0 g (0.21 mol) of the compound represented by the formula (1d) synthesized in Example 1, 63.0 g (1.05 mol, acetic acid) of acetic acid and 200 mL of water (H 2 O) were placed in a flask Lt; / RTI > To the flask was slowly added 61.2 g (0.942 mol) of NaOCN dropwise at room temperature and then stirred overnight at 75 ° C. Finally, at room temperature, water (H 2 O) and ethanol and washed with (EtOH), was synthesized in the white compound of formula 1m (yield: 88%, DT: 295 ℃ , GV: 166ml / g, NMR: ? 7.22 (1H, NH) ,? 8.87 (1H, NH) ,? 9.99 (2H, NH2).
[반응식 7] [Reaction Scheme 7]
[실시예 5] 화학식 1n로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 5] Preparation of a blowing agent represented by the formula (1n)
하기 반응식 8에 나타낸 바와 같이, 구아니딘 하이드로클로라이드 5.0 g (0.05 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) 및 용매로서 디옥산(Dioxane) 100 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 테트라졸 아민 15.6g (0.18 mol, tetrazole amine)을 실온에서 적가한 다음, 2시간 동안 환류 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 디옥산(Dioxane) 및 에탄올(EtOH)로 세척하여, 화학식 1n로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 51%, DT: 280℃, GV: 80ml/g, NMR :δ 6.45 (1H, NH), δ 14.35 (1H, NH)).5.0 g (0.05 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) of guanidine hydrochloride and 100 mL of dioxane as a solvent were added to a flask and stirred, as shown in the following reaction formula (8). To the flask, 15.6 g (0.18 mol, tetrazole amine) of tetrazole amine was added dropwise at room temperature, and the mixture was refluxed and stirred for 2 hours. Finally, at room temperature, washed with dioxane (Dioxane) and ethanol (EtOH), was synthesized in the white compound of formula 1n (yield: 51%, DT: 280 ℃ , GV: 80ml / g, NMR: δ 6.45 (1H, NH), 8 14.35 (1H, NH)).
[반응식 8] [Reaction Scheme 8]
[실시예 6] 화학식 1o로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 6] Production of blowing agent represented by formula (Io)
하기 반응식 9에 나타낸 바와 같이, 구아니딘 하이드로클로라이드 20.0 g (0.2 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) 및 용매로서 디옥산(Dioxane) 200 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에, 벤조산 하이드라지드 100.0 g (0.73 mol, benzoic acid hydrazide)을 적가한 다음, 하룻밤(overnight) 동안 환류 및 교반하였다. 끝으로, 실온에서, 디옥산(Dioxane)으로 세척하여, 화학식 1o로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 77%, DT : 110℃,GV: 100ml/g NMR :δ 6.99 (1H, NH), 7.33 (5H, ph), δ 11.13 (1H, NH)).As shown in Reaction Scheme 9, 20.0 g (0.2 mol, Guanidine hydrochloride) of guanidine hydrochloride and 200 mL of dioxane as a solvent were placed in a flask and stirred. To the flask, 100.0 g (0.73 mol, benzoic acid hydrazide) of benzoic acid hydrazide was added dropwise, and the mixture was refluxed and stirred overnight. (Yield: 77%, DT: 110 캜, GV: 100 ml / g NMR: δ 6.99 (1H, NH). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, and then washed with dioxane at room temperature. , 7.33 (5H, pH), 8 11.13 (1H, NH)).
[반응식 9] [Reaction Scheme 9]
[실시예 7] 화학식 1k로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 7] Production of blowing agent represented by the formula (1k)
하기 반응식 10에 나타낸 바와 같이, 포타슘 트리시아노메타이드 1.29 g (10 mmol, Potassium tricyanomethide), NaN3 2.2 g (33 mmol), ZnBr2 6.76 g (30 mmol) 및 용매로서 물(H2O) 50 mL를 플라스크에 넣고, 하룻밤(overnight) 동안 환류 및 교반하였다. 반응물을 실온에서 물로 세척하여 갈색 화합물을 얻고, 이를 4N HCl에 첨가하여 18 시간 동안 교반하였다. 반응물을 여과(filter)하여 얻은 고체 화합물을 다시 1M NaOH 25 mL에 용해시킨 후, 여과하였다. 여과물(filterate)를 4N HCl로 중화시킨 후, 물로 세척하여, 화학식 1k로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 46%, DT : 310℃,GV: 84ml/g NMR : δ 7.01 (1H, CH), δ 12.01 (1H, NH)). As shown in following Reaction Scheme 10, potassium Tricia furnace methide 1.29 g (10 mmol, Potassium tricyanomethide ), NaN 3 2.2 g (33 mmol), ZnBr 2 6.76 g (30 mmol) and water (H 2 O) 50 as a solvent mL was placed in a flask and refluxed and stirred overnight. The reaction was washed with water at room temperature to give a brown compound which was added to 4N HCl and stirred for 18 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the resulting solid compound was dissolved again in 25 mL of 1 M NaOH and filtered. Filtered and neutralized with water (filterate) in 4N HCl, washed, it was synthesized white compound represented by formula 1k (yield: water: 46%, DT: 310 ℃ , GV: 84ml / g NMR: δ 7.01 (1H, CH), [ delta] 12.01 (1H, NH)).
[반응식 10][Reaction Scheme 10]
[실시예 8] 화학식 1s로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 8] Preparation of blowing agent represented by the formula 1s
하기 반응식 11에 나타낸 바와 같이, 실리콘 테트라클로라이드 16.9 g (0.1 mol, Silicon tetrachloride) 및 용매로서 헥산(Hexane) 200 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 0℃ 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에 100% 하이드라진 용액 15.6g (0.4 mol, Hydrazine Hydrate 100%)을 ℃에서 적가한 다음, 하룻밤 동안 0℃~20℃ 교반하였다. 끝으로, -5℃ 에서 헥산(Hexane) 용액 하에 재결정을 작업을 하면, 화학식 1s로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 65%).16.9 g (0.1 mol, Silicon tetrachloride) of silicon tetrachloride and 200 mL of hexane (Hexane) as a solvent were placed in a flask and stirred at 0 ° C, as shown in Scheme 11 below. 15.6 g of a 100% hydrazine solution (0.4 mol, Hydrazine Hydrate 100%) was added dropwise to the flask at 0 占 폚 and the mixture was stirred overnight at 0 占 폚 to 20 占 폚. Finally, recrystallization was carried out in hexane at -5 ° C to synthesize a white compound represented by the formula (1s) (yield: 65%).
[반응식 11][Reaction Scheme 11]
[실시예 9] 화학식 1t로 표시되는 발포제의 제조 [Example 9] Preparation of blowing agent represented by the formula (1t)
하기 반응식 12에 나타낸 바와 같이, 트리메틸알루미늄 7.21 g (0.1 mol,Trimethylaluminium) 및 용매로서 헥산(Hexane) 200 mL를 플라스크에 넣고 0℃ 교반하였다. 상기 플라스크에 100% 하이드라진 용액 7.5g (0.15 mol, Hydrazine Hydrate 100%)을 ℃에서 적가한 다음, 30분 동안 0℃~20℃ 교반하였다. 끝으로, -30℃ 에서 헥산(Hexane) 용액 하에 재결정을 작업을 하면, 화학식 1t로 표시되는 흰색 화합물을 합성하였다(수율: 85%, mp: 105℃).7.21 g (0.1 mol, trimethylaluminium) of trimethylaluminum and 200 mL of hexane (Hexane) as a solvent were placed in a flask and stirred at 0 ° C, as shown in Scheme 12 below. 7.5 g (0.15 mol, Hydrazine Hydrate 100%) of 100% hydrazine solution was added dropwise to the flask at 0 ° C, and the mixture was stirred at 0 ° C to 20 ° C for 30 minutes. Finally, recrystallization was carried out at -30 ° C in a hexane solution to synthesize a white compound represented by the formula 1t (yield: 85%, mp: 105 ° C).
[반응식 12] [Reaction Scheme 12]
[[ 실험예Experimental Example 1] 발포제의 분해온도 1] Decomposition temperature of foaming agent
실시예 1 내지 7과 비교예로서 아조디카본아미드(ADCA) 각각 500 mg을 가열하여 분해시키면서, 분해온도(DT: Decomposition temperature) 및 가스부피 (GV: gas volume)를 측정하였으며, 그 결과를 하기 표 1에 나타내었다. The decomposition temperature (DT) and the gas volume (GV) were measured while 500 mg of each of the azodicarbonamide (ADCA) was heated and decomposed as Examples 1 to 7 and Comparative Example. Table 1 shows the results.
유해가스 XHigh temperature process application O
Hazardous gas X
유해가스 XHigh temperature process application O
Hazardous gas X
유해가스 XHigh temperature process application O
Hazardous gas X
유해가스 XHigh temperature process application O
Hazardous gas X
유해가스 XHigh temperature process application O
Hazardous gas X
도 1 및 2는 본 발명의 실시예 1에 따른 발포제를 이용하여, 각각 폴리프로필렌(PP) 및 에틸렌-비닐아세테이트 공중합체(EVA)를 발포시켜 얻은 발포체의 내부 기공 형태를 보여주는 전자 현미경 사진이다. 도 1, 2 및 표 1에 나타낸 바와 같이, 본 발명에 따른 발포제는, 범용적으로 사용되는 아조디카본아미드(ADCA)와 비교하여, 분해온도 및 가스부피가 유사하거나 우수하고, 균일한 기공을 가지며, 유해가스가 발생하지 않는 발포체를 형성할 수 있다.1 and 2 are electron micrographs showing the internal pore shape of a foam obtained by foaming a polypropylene (PP) and an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), respectively, using the foaming agent according to Example 1 of the present invention. As shown in Figs. 1 and 2 and Table 1, the foaming agent according to the present invention has a decomposition temperature and a gas volume similar or superior to those of azodicarbonamide (ADCA) used in general use, and has uniform pores And it is possible to form a foam which does not generate noxious gas.
[실험예 2] PVC sol에 대한 유해가스 분석[Experimental Example 2] Analysis of noxious gas against PVC sol
상기 실시예 1 에서 합성한 화학식 1d로 표시되는 발포제 3.5 phr와 발포 대상 수지(Resin)로서 PVC sol 100 gr을 3000 rpm의 속도로 설정된 기계식 교반기(mechanical stirrer)에서 2분간 혼합하였다. 상기 혼합 sol 100 gr을 코팅(coating)지에 붓고, 1.1 mm의 바-코터(Bar-coater)를 이용하여 도포시킨 후, 열풍 순환식 오븐에 넣어 PVC foam을 제조하였고, 제조된 PVC 폼의 발포배율 및 유해 가스인 포름아미드 농도를 측정하여 그 결과를 하기 표 2에 나타내었다. 이 때, 상기 열풍 순환식 오븐의 온도는 230 ℃였고, 발포 시간은 1 분 14 초였다. 또한, 하기 표 2의 포름아미드의 농도는 환경유해물질 분석(SGS)을 통하여 한국 생산 기술 연구원에서 검사하였다. N.D.(Not detected)는 포름아미드의 농도가 측정할 수 없을 만큼 소량 발생했거나, 발생하지 않은 것을 의미한다.3.5 phr of the foaming agent represented by the formula 1d synthesized in Example 1 and 100 gr of PVC sol as a resin to be foamed were mixed for 2 minutes on a mechanical stirrer set at a speed of 3000 rpm. 100 g of the mixed sol was poured into a coating paper and coated with 1.1 mm of a bar-coater, and then put into a hot air circulating oven to prepare a PVC foam. The foaming magnification And the concentration of noxious gas formamide were measured. The results are shown in Table 2 below. At this time, the temperature of the hot air circulating oven was 230 DEG C and the foaming time was 1 minute and 14 seconds. In addition, the concentration of formamide in Table 2 below was examined by the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KIT) through the Environmental Hazardous Substance Analysis (SGS). N.D. (Not detected) means that the concentration of formamide has occurred in such a small amount that it can not be measured or has not occurred.
(화학식 1d)Example 1
(1d)
상기 표 2에 나타낸 바와 같이, 범용적으로 사용되는 아조디카본아미드(ADCA)는 포름아미드가 다량 발생하는 반면, 본 발명에 따른 발포제는 포름아미드가 측정할 수 없을만큼 소량 발생했거나, 발생하지 않는다는 것을 알 수 있다.As shown in Table 2, a large amount of formamide was generated in the azodicarbonamide (ADCA) used in general use, while the foaming agent according to the present invention had a small amount of formamide that could not be measured, .
[실험예 3] 발포제의 분해시 발생되는 가스 성분 분석 [Experimental Example 3] Analysis of gas components generated upon decomposition of blowing agent
Pyrolizer는 Eco-cup LF 를 사용하여 시료(실시예 1에서 합성한 화학식 1d로 표시되는 발포제와 비교예로써의 아조디카본아미드(ADCA))를 미량 계량(weighing)하고, 전처리 없이 바로(direct) 측정하였다. 상기 시료는 250 ℃의 온도를 가지는 가열로(Furnance)에서 1 분간 처리한 뒤, 분해 가스를 담아 가스크로마토그래프 질량분석계(gas chromatograph/mass spectrophotometer, 이하, GC-MS)로 관찰하였다. 발포제의 가스 분석에 이용한 GC-MS 분석 기기는 (Agilent社 7890)을 이용하였고, GC-MS의 컬럼(Column)은 Ultra Alloy-5 (30 m * 0.25 mm *0.25 ㎛)를 이용하였다. 흐름 속도(Flow rate)는 1 ml/min으로 하였고, 30 분간 관찰 하였으며, 그 결과를 하기 표 3에 나타내었다.Pyrolizer was used to weigh a sample (the foaming agent represented by the formula 1d synthesized in Example 1 and the azodicarbonamide (ADCA) as a comparative example) by using Eco-cup LF, Respectively. The sample was treated in a furnace having a temperature of 250 ° C for 1 minute and then analyzed with a gas chromatograph / mass spectrophotometer (GC-MS) containing a decomposition gas. GC-MS analysis equipment (Agilent 7890) was used for the gas analysis of the blowing agent, and Ultra Alloy-5 (30 m * 0.25 mm * 0.25 ㎛) was used for the GC-MS column. The flow rate was 1 ml / min and observed for 30 minutes. The results are shown in Table 3 below.
상기 표 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 범용적으로 사용되는 아조디카본아미드(ACDA)의 경우, 포름아미드, 암모니아 등의 유해가스가 다량 발생하는 반면, 본 발명에 따른 발포제는 발생되는 기체의 대부분이 인체에 무해한 질소 기체로써, 포름아미드가 발생하지 않고, 암모니아 등의 유해 물질 발생량이 적은 장점이 있다.As shown in Table 3, in the case of azodicarbonamide (ACDA) which is generally used, a large amount of noxious gases such as formamide and ammonia are generated. On the other hand, in the blowing agent according to the present invention, Which is harmless to nitrogen, does not generate formaldehyde, and has an advantage in that the amount of harmful substances such as ammonia is reduced.
Claims (9)
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서, X는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 알킬기, 탄소수 4 내지 10의 아릴기, 탄소수 3 내지 10의 헤테로고리기 또는 3족, 4족 또는 5족 원자이고, R은 단일 결합 또는 이중 결합이며, D는 히드라진 포함 기(group including hydrazine moiety)이고, n는 3 내지 6의 정수이다.A blowing agent represented by the following formula (1).
[Chemical Formula 1]
X is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, a heterocyclic group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, or a Group 3, 4, or 5 group atom, and R is a single bond or a double bond , D is a hydrazine containing group (group including hydrazine moiety), and n is an integer of 3 to 6.
하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 발포제 10 내지 80 중량부를 포함하는 마스터 배치.
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서, X는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 알킬기, 탄소수 4 내지 10의 아릴기, 탄소수 3 내지 10의 헤테로고리기 또는 3족, 4족 또는 5족 원자이고, R은 단일 결합 또는 이중 결합이며, D는 히드라진 포함 기(group including hydrazine moiety)이고, n는 3 내지 6의 정수이다.100 parts by weight of a resin; And
A master batch comprising 10 to 80 parts by weight of a blowing agent represented by the following formula (1).
[Chemical Formula 1]
X is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, a heterocyclic group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, or a Group 3, 4, or 5 group atom, and R is a single bond or a double bond , D is a hydrazine containing group (group including hydrazine moiety), and n is an integer of 3 to 6.
[화학식 1]
상기 화학식 1에서, X는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 알킬기, 탄소수 4 내지 10의 아릴기, 탄소수 3 내지 10의 헤테로고리기 또는 3족, 4족 또는 5족 원자이고, R은 단일 결합 또는 이중 결합이며, D는 히드라진 포함 기(group including hydrazine moiety)이고, n는 3 내지 6의 정수이다.A foamed foamed article using the foaming agent represented by the following formula (1).
[Chemical Formula 1]
X is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 4 to 10 carbon atoms, a heterocyclic group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, or a Group 3, 4, or 5 group atom, and R is a single bond or a double bond , D is a hydrazine containing group (group including hydrazine moiety), and n is an integer of 3 to 6.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150150424A KR20170049255A (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2015-10-28 | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same |
| TW105135114A TW201730258A (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2016-10-28 | Heat-decomposable compound and method for foaming resin using the same |
| CN201680063727.1A CN108350207B (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2016-10-28 | Thermally decomposable compound and method for foaming resin using same |
| PCT/KR2016/012247 WO2017074099A1 (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2016-10-28 | Thermally decomposable compound and method for foaming resin using same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150150424A KR20170049255A (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2015-10-28 | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170049255A true KR20170049255A (en) | 2017-05-10 |
Family
ID=58631792
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150150424A KR20170049255A (en) | 2015-10-28 | 2015-10-28 | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20170049255A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN108350207B (en) |
| TW (1) | TW201730258A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2017074099A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018110842A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | 주식회사 동진쎄미켐 | Foaming agent composition containing triaminoguanidine salt compound |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107188826A (en) * | 2017-06-07 | 2017-09-22 | 重庆锦杉科技有限公司 | A kind of method for preparing hydrazinobenzene hydrochloride salt |
| CN112409771A (en) * | 2020-10-27 | 2021-02-26 | 上海锦湖日丽塑料有限公司 | Lightweight foaming PC/ABS composition for automobile and preparation method thereof |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4351911A (en) * | 1973-07-02 | 1982-09-28 | General Electric Company | Foamable polyester composition |
| US5329000A (en) * | 1991-10-31 | 1994-07-12 | Becton, Dickinson And Company | Purification of DNA with silicon tetrahydrazide |
| JPH05254977A (en) * | 1992-03-11 | 1993-10-05 | Nippon Kayaku Co Ltd | Gas generating agent |
| CZ20033101A3 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2004-03-17 | Nippon Kayaku Kabushiki-Kaisha | Gas-generating mixture |
| US7396938B1 (en) * | 2005-05-27 | 2008-07-08 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Process for making multifunctional tetrazole polyols to produce tetrazole based polymers |
| CN102985507B (en) * | 2010-07-09 | 2015-11-25 | 美国圣戈班性能塑料公司 | Foam seal pad |
| KR20130077669A (en) * | 2011-12-29 | 2013-07-09 | 도레이첨단소재 주식회사 | Foamed plastic film for light diffusing and light diffusing film using the same |
| EP3381975A1 (en) * | 2011-12-29 | 2018-10-03 | CertainTeed Corporation | Foam, composition, and method |
| KR101951068B1 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2019-02-21 | 다우 글로벌 테크놀로지스 엘엘씨 | Foamable compositions, foams and articles thereof |
| CN103483264A (en) * | 2012-06-12 | 2014-01-01 | 北京理工大学 | Energetic ion salts of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe and preparation method thereof |
| CN103059009A (en) * | 2013-01-24 | 2013-04-24 | 北京理工大学 | 4-nitro-3-(5-tetrazole) furoxan energetic ionic salt and preparation method thereof |
| CN104744185B (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2017-11-17 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | A kind of gas generant composition and preparation method thereof |
-
2015
- 2015-10-28 KR KR1020150150424A patent/KR20170049255A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2016
- 2016-10-28 CN CN201680063727.1A patent/CN108350207B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-10-28 WO PCT/KR2016/012247 patent/WO2017074099A1/en active Application Filing
- 2016-10-28 TW TW105135114A patent/TW201730258A/en unknown
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018110842A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | 주식회사 동진쎄미켐 | Foaming agent composition containing triaminoguanidine salt compound |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2017074099A1 (en) | 2017-05-04 |
| CN108350207B (en) | 2021-09-10 |
| TW201730258A (en) | 2017-09-01 |
| CN108350207A (en) | 2018-07-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Coste et al. | From gas release to foam synthesis, the second breath of blowing agents | |
| KR20170049255A (en) | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same | |
| KR101327439B1 (en) | Modified blowing agent surface-treated with metallic siloxylated compound and polymer resin composition including the same | |
| Quinn | Chemical blowing agents: providing production, economic and physical improvements to a wide range of polymers | |
| KR20150125612A (en) | Foaming agent composition and method for foaming using the same | |
| JP2012082420A (en) | Foamable rubber composition | |
| KR101873019B1 (en) | Foaming agent composition and foamable polymer composition comprising the same | |
| KR20170049245A (en) | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same | |
| US3925270A (en) | Polymeric composition comprising sulfonyl carbazates as blowing agents | |
| TW201120003A (en) | Bi-or tricyclic sterically hindered alkoxyamines and process for their preparation | |
| US4885316A (en) | Substituted 5-amidotetrazoles as blowing agents in the production of cellular thermoplastic or rubber materials | |
| KR20170049263A (en) | Heat-decomposed compound and method for gasification using the same | |
| CA2016535A1 (en) | Dialkyl dicarbonates as blowing agents for polymers | |
| US4263165A (en) | Blowing agent combination comprising azodicarbonamide, zinc oxide and a benzenethiol sulphonic acid derivative | |
| CN108484919A (en) | A kind of phosphorous macromolecular fire retardant and preparation method thereof | |
| KR20200066064A (en) | Foaming agent and foam formed using the same | |
| GB1561278A (en) | Carbohydrazides as blowing agents | |
| US4012432A (en) | Sulfonyl carbazates as blowing agents | |
| US4135049A (en) | Sulfonyl carbazates as blowing agents | |
| US4921965A (en) | Method of producing alkyl substituted 5-amidotetrazoles | |
| Nedel'ko et al. | Synthesis and thermal decomposition of ditetrazol-5-ylamine | |
| US5051206A (en) | Blowing agent composition | |
| KR20160060919A (en) | Azo compound foaming agent, method for preparing the same and method of foaming using the same | |
| CN106661422B (en) | The manufacturing method of the foaming body of gas-forming agent and the use gas-forming agent | |
| KR102374731B1 (en) | A azo-based foaming agent, method for preparing the same and method for foaming resin using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |