KR102693771B1 - Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof - Google Patents
Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102693771B1 KR102693771B1 KR1020160169538A KR20160169538A KR102693771B1 KR 102693771 B1 KR102693771 B1 KR 102693771B1 KR 1020160169538 A KR1020160169538 A KR 1020160169538A KR 20160169538 A KR20160169538 A KR 20160169538A KR 102693771 B1 KR102693771 B1 KR 102693771B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- phosphor
- fluorescent
- layer
- layers
- plate
- Prior art date
Links
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 151
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 12
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 6
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 229910052593 corundum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 claims 3
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 229910001845 yogo sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- RUDFQVOCFDJEEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N yttrium(III) oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Y+3].[Y+3] RUDFQVOCFDJEEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 19
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 13
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 4
- BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Orthosilicate Chemical compound [O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002223 garnet Substances 0.000 description 3
- -1 germano silicate Chemical compound 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propane Chemical compound CCC ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc monoxide Chemical compound [Zn]=O XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GEIAQOFPUVMAGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ZrO Inorganic materials [Zr]=O GEIAQOFPUVMAGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000000149 argon plasma sintering Methods 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- TZCXTZWJZNENPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L barium sulfate Chemical compound [Ba+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O TZCXTZWJZNENPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920003207 poly(ethylene-2,6-naphthalate) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011112 polyethylene naphthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910019655 synthetic inorganic crystalline material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl urethane Chemical compound CCOC(N)=O JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000877 Melamine resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphide Chemical compound [S-2] UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 1
- HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-acetylene Natural products C#C HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- JNDMLEXHDPKVFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminum;oxygen(2-);yttrium(3+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Y+3] JNDMLEXHDPKVFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000003763 carbonization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012159 carrier gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- KPUWHANPEXNPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N disiloxane Chemical class [SiH3]O[SiH3] KPUWHANPEXNPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002534 ethynyl group Chemical group [H]C#C* 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000001307 helium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052734 helium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N helium atom Chemical compound [He] SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000395 magnesium oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium oxide Inorganic materials [Mg]=O CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[Mg+2] AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N melamine Chemical compound NC1=NC(N)=NC(N)=N1 JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010445 mica Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052618 mica group Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001294 propane Substances 0.000 description 1
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011342 resin composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;oxocalcium;hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+].[Ca]=O HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004408 titanium dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012780 transparent material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910019901 yttrium aluminum garnet Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011787 zinc oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/48—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor body packages
- H01L33/50—Wavelength conversion elements
- H01L33/505—Wavelength conversion elements characterised by the shape, e.g. plate or foil
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/08—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing inorganic luminescent materials
- C09K11/0838—Aluminates; Silicates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/08—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing inorganic luminescent materials
- C09K11/77—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing inorganic luminescent materials containing rare earth metals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/08—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing inorganic luminescent materials
- C09K11/77—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing inorganic luminescent materials containing rare earth metals
- C09K11/7706—Aluminates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/44—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the coatings, e.g. passivation layer or anti-reflective coating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/48—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor body packages
- H01L33/50—Wavelength conversion elements
- H01L33/501—Wavelength conversion elements characterised by the materials, e.g. binder
- H01L33/502—Wavelength conversion materials
- H01L33/504—Elements with two or more wavelength conversion materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12041—LED
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2933/00—Details relating to devices covered by the group H01L33/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2933/0008—Processes
- H01L2933/0033—Processes relating to semiconductor body packages
- H01L2933/0041—Processes relating to semiconductor body packages relating to wavelength conversion elements
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Luminescent Compositions (AREA)
Abstract
실시 예는, 기판; 상기 기판 상에 배치되는 제 1 형광체층 및 상기 제 1 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제 2 형광체층을 포함하는 복수의 형광체층; 상기 제 1 형광체층과 상기 제 2 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층;을 포함하는 형광체 플레이트를 개시한다.The embodiment discloses a phosphor plate including: a substrate; a plurality of phosphor layers including a first phosphor layer disposed on the substrate and a second phosphor layer disposed on the first phosphor layer; a first boundary layer disposed between the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer and including pores;
Description
실시 예는 형광체 플레이트 및 이를 제조하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a phosphor plate and a method for manufacturing the same.
형광체 플레이트는 형광체 분말을 포함하며, LED(Light Emitting Diode) 또는 LD(Laser Diode) 등의 광원으로부터 출력된 빛을 색 변환 시킬 수 있다.The phosphor plate contains phosphor powder and can convert the color of light output from a light source such as an LED (Light Emitting Diode) or LD (Laser Diode).
하지만, 광원으로부터 출력된 빛은 중심부의 파워가 높아 형광체 플레이트를 통과하면서 가장자리에 노란색 원이 보이는 이른바 '옐로우 링(Yellow Ring)' 현상이 나타날 수 있다.However, the light emitted from the light source has high power at the center, so when it passes through the phosphor plate, a yellow circle can appear at the edge, which is called the 'yellow ring' phenomenon.
형광체 플레이트는 광원으로부터 출력된 빛을 넓게 확산시키기 어려운 한계가 존재할 수 있다. Phosphor plates may have limitations in widely dispersing the light emitted from a light source.
또한, 일반적으로, 형광체 플레이트를 접착제, 바인더 등을 이용하여 투명 부재와 결합시켜 탄화가 발생하는 문제가 존재할 수 있다. In addition, there may be a problem of carbonization when combining a fluorescent plate with a transparent member using an adhesive, binder, etc. in general.
뿐만 아니라, 신뢰성이 떨어지는 문제점도 존재할 수 있다.In addition, there may be issues with reliability.
실시 예는 형광체 플레이트 및 이를 제조하는 방법, 형광체 플레이트를 포함하는 광 디바이스를 제공한다.The embodiments provide a phosphor plate and a method for manufacturing the same, and an optical device including the phosphor plate.
또한, 광 확산 효율이 우수한 형광체 플레이트를 제공한다.In addition, a phosphor plate having excellent light diffusion efficiency is provided.
또한, 신뢰성이 향상된 형광체 플레이트를 제공한다.Additionally, a phosphor plate with improved reliability is provided.
또한, 내부에서 광 산란이 큰 형광체 플레이트를 제공한다.Additionally, it provides a phosphor plate with large light scattering inside.
본 발명의 일 실시 예에 따른 형광체 플레이트는 기판; 상기 기판 상에 배치되는 제 1 형광체층 및 상기 제 1 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제 2 형광체층을 포함하는 복수의 형광체층; 및 상기 제 1 형광체층과 상기 제 2 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층;을 포함한다.According to one embodiment of the present invention, a phosphor plate includes: a substrate; a plurality of phosphor layers including a first phosphor layer disposed on the substrate and a second phosphor layer disposed on the first phosphor layer; and a first boundary layer disposed between the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer and including pores.
상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율은 상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율과 상이할 수 있다.The refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers may be different from the refractive index of the first boundary layer.
상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율은 상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율의 0.5배 내지 0.6배일 수 있다.The refractive index of the first boundary layer may be 0.5 to 0.6 times the refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers.
상기 제1 경계층은 기공이 형성될 수 있다.The above first boundary layer may have pores formed.
상기 복수의 형광체층은, YAG, LuAg 및 LuYAG 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The above plurality of phosphor layers may include at least one of YAG, LuAg, and LuYAG.
상기 복수의 형광체층은 확산제를 포함할 수 있다.The above plurality of phosphor layers may include a diffuser.
상기 확산제는, Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 및 Y2O3, SiO2 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The above-mentioned dispersants are Al 2 O 3 , TiO 2 , ZrO 2 and may include at least one of Y 2 O 3 , SiO 2 .
상기 복수의 형광체층 각각의 두께는 50㎛ 내지 150㎛일 수 있다.The thickness of each of the plurality of fluorescent layers may be 50 ㎛ to 150 ㎛.
상기 복수의 형광체층의 표면 러프니스는 0.23㎛ 내지 0.27㎛일 수 있다.The surface roughness of the above plurality of fluorescent layers may be 0.23 ㎛ to 0.27 ㎛.
상기 복수의 형광체층은 상기 제2 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제3 형광체층을 더 포함하고, 상기 제2 형광체층과 상기 제3 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제2 경계층을 더 포함할 수 있다.The above plurality of phosphor layers may further include a third phosphor layer disposed on the second phosphor layer, and may further include a second boundary layer disposed between the second phosphor layer and the third phosphor layer and including pores.
본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 광 디바이스는 광원; 상기 광원으로부터 출사된 광이 조사되는 기판, 상기 기판 상에 배치되는 제 1 형광체층 및 상기 제 1 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제 2 형광체층을 포함하는 복수의 형광체층; 및 상기 제 1 형광체층과 상기 제 2 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층;을 포함하는 형광체 플레이트;를 포함한다.An optical device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a phosphor plate including a light source; a substrate on which light emitted from the light source is irradiated; a plurality of phosphor layers including a first phosphor layer disposed on the substrate and a second phosphor layer disposed on the first phosphor layer; and a first boundary layer disposed between the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer and including pores.
상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율은 상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율의 0.5배 내지 0.6배일 수 있다.The refractive index of the first boundary layer may be 0.5 to 0.6 times the refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers.
상기 제1 경계층은 기공이 형성될 수 있다.The above first boundary layer may have pores formed.
상기 광원은 레이저 및 발광다이오드(light emitting diode, led) 중 적어도 하나일 수 있다.The light source may be at least one of a laser and a light emitting diode (LED).
상기 복수의 형광체층은 상기 제2 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제3 형광체층을 더 포함하고, 상기 제2 형광체층과 상기 제3 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제2 경계층을 더 포함할 수 있다.The above plurality of phosphor layers may further include a third phosphor layer disposed on the second phosphor layer, and may further include a second boundary layer disposed between the second phosphor layer and the third phosphor layer and including pores.
본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트 제조 방법은 기판 상에 형광체를 분사하는 단계; 및 상기 형광체를 복수회 분사하여 복수의 형광체층을 형성하는 단계;를 포함하고, 상기 복수의 형광체층 사이에 기공을 포함하는 경계층이 배치된다.A method for manufacturing a phosphor plate according to one embodiment of the present invention includes the steps of spraying a phosphor onto a substrate; and the steps of spraying the phosphor multiple times to form a plurality of phosphor layers; wherein a boundary layer including pores is arranged between the plurality of phosphor layers.
상기 형광체는 저온 용사(Cold spray) 코팅, 열 용사(Thermal spray) (Thermal Spray)코팅 및 플라즈마(Plasma) 코팅중 적어도 하나에 의해 상기 기판 상에 분사할 수 있다.The above-mentioned phosphor can be sprayed onto the substrate by at least one of cold spray coating, thermal spray coating, and plasma coating.
실시 예에 따르면, 표면이 거칠기가 큰 형광체 플레이트를 구현할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, a phosphor plate having a large surface roughness can be implemented.
또한, 광 확산 효율이 우수한 형광체 플레이트를 제작할 수 있다.In addition, a fluorescent plate with excellent light diffusion efficiency can be manufactured.
또한, 신뢰성이 향상된 형광체 플레이트를 제작할 수 있다.In addition, it is possible to manufacture a phosphor plate with improved reliability.
또한, 광이 넓게 확산되도록 함으로써 광효율을 높임과 동시에 '옐로우 링' 현상이 발생하는 것도 방지할 수 있다.In addition, by allowing the light to spread widely, the light efficiency can be increased while also preventing the occurrence of the 'yellow ring' phenomenon.
또한, 내부에서 광 산란이 큰 형광체 플레이트를 제작할 수 있다.Additionally, it is possible to manufacture a phosphor plate with large internal light scattering.
본 발명의 다양하면서도 유익한 장점과 효과는 상술한 내용에 한정되지 않으며, 본 발명의 구체적인 실시형태를 설명하는 과정에서 보다 쉽게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The various advantageous and beneficial effects of the present invention are not limited to the above-described contents, and will be more easily understood in the course of explaining specific embodiments of the present invention.
도 1은 종래의 형광체 플레이트에서 발생하는 옐로우 링 현상을 나타낸 도면이고,
도 2는 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 단면도이고,
도 3은 제1 실시예에 다른 형광체 플레이트의 단면확대도이고,
도 4는 도 3에서 A부분으로 경계층의 광 확산을 설명하는 도면이고,
도 5는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 표면을 도시한 도면이고,
도 6은 종래의 형광체 플레이트의 표면 러프니스를 도시한 도면이고,
도 7은 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 표면 러프니스를 도시한 도면이고,
도 8은 본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 단면도이고,
도 9는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각을 나타낸 도면이고,
도 10은 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각을 나타낸 도면이고,
도 11은 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트 제조 방법의 순서도이고,
도 12는 저온 용사(Cold spray) 코팅 장치의 개요를 나타내는 모식도이고,
도 13은 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 장치의 개요를 나타내는 모식도이고,
도 14 및 도 15는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트를 다양한 광 디바이스에 적용한 예를 도시한 도면이다.Figure 1 is a drawing showing the yellow ring phenomenon that occurs in a conventional fluorescent plate.
Figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 3 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of another fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
Figure 4 is a drawing explaining the light diffusion in the boundary layer in part A of Figure 3.
FIG. 5 is a drawing illustrating the surface of a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
Figure 6 is a drawing showing the surface roughness of a conventional fluorescent plate.
Fig. 7 is a drawing showing the surface roughness of a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
Fig. 8 is a cross-sectional view of a fluorescent plate according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 9 is a drawing showing the orientation angle of the fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
Fig. 10 is a drawing showing the orientation angle of a fluorescent plate according to the second embodiment.
Figure 11 is a flow chart of a method for manufacturing a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
Figure 12 is a schematic diagram showing an outline of a cold spray coating device.
Figure 13 is a schematic diagram showing an outline of a thermal spray coating device.
FIG. 14 and FIG. 15 are drawings showing examples of applying the fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment to various optical devices.
본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 실시예를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 설명하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 실시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. The present invention can have various modifications and various embodiments, and specific embodiments are illustrated and described in the drawings. However, this is not intended to limit the present invention to specific embodiments, but should be understood to include all modifications, equivalents, or substitutes included in the spirit and technical scope of the present invention.
제2, 제1 등과 같이 서수를 포함하는 용어는 다양한 구성요소들을 설명하는데 사용될 수 있지만, 상기 구성요소들은 상기 용어들에 의해 한정되지는 않는다. 상기 용어들은 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소로부터 구별하는 목적으로만 사용된다. 예를 들어, 본 발명의 권리 범위를 벗어나지 않으면서 제2 구성요소는 제1 구성요소로 명명될 수 있고, 유사하게 제1 구성요소도 제2 구성요소로 명명될 수 있다. 및/또는 이라는 용어는 복수의 관련된 기재된 항목들의 조합 또는 복수의 관련된 기재된 항목들 중의 어느 항목을 포함한다. Terms including ordinal numbers such as second, first, etc. may be used to describe various components, but the components are not limited by the terms. The terms are only used to distinguish one component from another. For example, without departing from the scope of the present invention, the second component may be referred to as the first component, and similarly, the first component may also be referred to as the second component. The term and/or includes any combination of a plurality of related described items or any item among a plurality of related described items.
어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "연결되어" 있다거나 "접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. 반면에, 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "직접 연결되어" 있다거나 "직접 접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 할 것이다. When it is said that a component is "connected" or "connected" to another component, it should be understood that it may be directly connected or connected to that other component, but that there may be other components in between. On the other hand, when it is said that a component is "directly connected" or "directly connected" to another component, it should be understood that there are no other components in between.
본 출원에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 본 출원에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 명세서상에 기재된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The terminology used in this application is only used to describe specific embodiments and is not intended to limit the present invention. The singular expression includes the plural expression unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. In this application, it should be understood that the terms "comprises" or "has" and the like are intended to specify the presence of a feature, number, step, operation, component, part or combination thereof described in the specification, but do not exclude in advance the possibility of the presence or addition of one or more other features, numbers, steps, operations, components, parts or combinations thereof.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가지고 있다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥 상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가지는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.Unless otherwise defined, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Terms defined in commonly used dictionaries, such as those defined in common dictionaries, should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the meaning they have in the context of the relevant art, and shall not be interpreted in an idealized or overly formal sense, unless expressly defined in this application.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 실시예를 상세히 설명하되, 도면 부호에 관계없이 동일하거나 대응하는 구성 요소는 동일한 참조 번호를 부여하고 이에 대한 중복되는 설명은 생략하기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments will be described in detail with reference to the attached drawings. Regardless of the drawing symbols, identical or corresponding components are given the same reference numerals and redundant descriptions thereof will be omitted.
도 1은 종래의 형광체 플레이트에서 발생하는 옐로우 링 현상을 나타낸 도면이다. 도 1을 참조하면, 종래의 경우, 형광체 플레이트(100A)를 통과한 광의 가장자리에 노란색 원이 보이는 이른바 '옐로우 링(Yellow Ring)' 현상(Y)이 나타날 수 있다. 이러한 '옐로우 링' 현상(Y)은 형광체 플레이트(100A)를 통과하는 광이 충분히 확산되지 않는 경우에 발생할 수 있다.Fig. 1 is a drawing showing a yellow ring phenomenon that occurs in a conventional fluorescent plate. Referring to Fig. 1, in a conventional case, a so-called 'yellow ring' phenomenon (Y) may appear, in which a yellow circle is visible at the edge of light passing through a fluorescent plate (100A). This 'yellow ring' phenomenon (Y) may occur when light passing through a fluorescent plate (100A) is not sufficiently diffused.
도 2는 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)의 단면도이다.FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 기판(110), 기판(110) 상에 배치되는 복수의 형광체층(120), 복수의 형광체층(120) 사이에 배치되는 경계층(130)을 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2, a fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment may include a substrate (110), a plurality of fluorescent layers (120) disposed on the substrate (110), and a boundary layer (130) disposed between the plurality of fluorescent layers (120).
기판(110)은 플렉서블 기판일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 플렉서블(flexible) 디스플레이 장치를 구현하기 위하여, 기판(110)은 유리나 폴리이미드(PI, Polyimide)를 포함할 수 있다.The substrate (110) may be a flexible substrate. For example, in order to implement a flexible display device, the substrate (110) may include glass or polyimide (PI).
예시적으로, 기판(110)은 예를 들어, 소다라임 실리카, 보론 실리케이트, 알루미나 실리케이트, 알칼리게르마노 실리케이트을 포함할 수 있다.For example, the substrate (110) may include, for example, soda lime silica, boron silicate, alumina silicate, or alkali germano silicate.
또한, 기판(110)은 절연성이 있고, 유연성 있는 재질이면, 예를 들어 PEN(Polyethylene Naphthalate), PET(Polyethylene Terephthalate) 등 어느 것이라도 사용될 수 있다.Additionally, the substrate (110) may be made of any insulating and flexible material, such as PEN (Polyethylene Naphthalate) or PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate).
또한, 기판(110)은 투명한 재질 또는 불투명한 재질 어느 것이나 될 수 있다. 기판(110)의 두께(d1)는 400㎛ 내지 500㎛일 수 있다.Additionally, the substrate (110) may be made of either a transparent material or an opaque material. The thickness (d1) of the substrate (110) may be 400 μm to 500 μm.
복수의 형광체층(120)은 기판(110) 상에 배치될 수 있다. 복수의 형광체층(120)은 형광체를 포함할 수 있다. 형광체층(120)은 형광체 분말이 경화된 형태일 수 있으나, 이에 한정되지 않는다.A plurality of phosphor layers (120) may be arranged on a substrate (110). The plurality of phosphor layers (120) may include a phosphor. The phosphor layer (120) may be in the form of a hardened phosphor powder, but is not limited thereto.
형광체는 경화성 수지 및 형광 수지 조성물 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 형광체는 파장 변환 기능을 수행할 수 있다. 예컨대, 형광체는 청색 광을 황색 광으로 변환할 수 있는 황색 형광체, 청색 광을 적색 광으로 변환할 수 있는 적색 형광체 등일 수 있다.The phosphor may include at least one of a curable resin and a fluorescent resin composition. The phosphor may perform a wavelength conversion function. For example, the phosphor may be a yellow phosphor capable of converting blue light into yellow light, a red phosphor capable of converting blue light into red light, or the like.
형광체는 이트륨-알루미늄-가넷(Y3Al5O12: Ce(YAG): Ce), 테르븀-알루미늄-가넷(Tb3Al3O12: Ce(TAG: Ce)), 루테늄-알루미늄-가넷(Lutetium aluminium garnet; LuAG)계를 포함하는 가넷계 등의 가넷형 결정 구조를 갖는 가넷형 형광체를 포함할 수 있다.The phosphor may include a garnet-type phosphor having a garnet-type crystal structure, such as a garnet system including yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Y 3 Al 5 O 12 : Ce(YAG: Ce), terbium-aluminum-garnet (Tb 3 Al 3 O 12 : Ce(TAG: Ce)), and ruthenium-aluminum-garnet (LuAG) systems.
또한, 형광체는 황화물(sulfide)계 또는 규산염(silicate)계 형광체를 포함할 수 있다.Additionally, the phosphor may include a sulfide-based or silicate-based phosphor.
형광체는 평균입경이 0.1㎛ 내지 0.5㎛일 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The fluorescent material may have an average particle diameter of 0.1 ㎛ to 0.5 ㎛, but is not limited thereto.
형광체층(120)은 복수 개일 수 있다. 예시적으로, 형광체층(120)은 제1 형광체층(120a), 제2 형광체층(120b), 제3 형광체층(120c) 및 제4 형광체층(120d)를 포함할 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. There may be multiple fluorescent layers (120). For example, the fluorescent layer (120) may include a first fluorescent layer (120a), a second fluorescent layer (120b), a third fluorescent layer (120c), and a fourth fluorescent layer (120d), but is not limited thereto.
각각의 형광체층(120a, 120b, 120c, 120d) 두께(d2)는 50㎛ 내지 150㎛일 수 있다. 그리고 형광체층(120) 전체의 두께는 200㎛ 내지 600㎛일 수 있다. 여기서, 두께는 Y축 방향의 길이일 수 있다. The thickness (d2) of each phosphor layer (120a, 120b, 120c, 120d) may be 50 µm to 150 µm. And the thickness of the entire phosphor layer (120) may be 200 µm to 600 µm. Here, the thickness may be the length in the Y-axis direction.
또한, 각각의 형광체층(120a, 120b, 120c, 120d) 두께(d2)는 동일할 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 각각의 형광체(120a, 120b, 120c, 120d)는 상이하게 형성될 수도 있다.In addition, the thickness (d2) of each fluorescent layer (120a, 120b, 120c, 120d) may be the same. However, this is not limited to the present invention, and each fluorescent layer (120a, 120b, 120c, 120d) may be formed differently.
경계층(130)은 복수의 형광체층(120) 사이에 배치될 수 있다. 경계층(130)도 복수 개일 수 있다. 예시적으로, 경계층(130)은 제1 경계층(130a), 제2 경계층(130b) 및 제3 경계층(130c)를 포함할 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The boundary layer (130) may be arranged between a plurality of fluorescent layers (120). There may also be a plurality of boundary layers (130). For example, the boundary layer (130) may include a first boundary layer (130a), a second boundary layer (130b), and a third boundary layer (130c), but is not limited thereto.
또한, 제1 형광체층 (120a)과 제2 형광체층 (120b) 사이에 제1 경계층 (130a)이 배치될 수 있다. 경계층(130)은 기공을 포함할 수 있다. 기공은 형광체 플레이트(100A)를 제작하는 과정에서 소성 및 접착하지 않고, 반복하여 형광체층을 코팅함에 따라 생성될 수 있다.Additionally, a first boundary layer (130a) may be arranged between the first phosphor layer (120a) and the second phosphor layer (120b). The boundary layer (130) may include pores. The pores may be created by repeatedly coating the phosphor layers without firing and bonding during the process of manufacturing the phosphor plate (100A).
도 3은 제1 실시예에 다른 형광체 플레이트의 단면확대도이고, 도 4는 도 3에서 A부분으로 경계층의 광 확산을 설명하는 도면이다.FIG. 3 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a fluorescent plate according to another embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 4 is a drawing explaining light diffusion in a boundary layer in part A of FIG. 3.
도 3 및 도 4를 참조하면, 형광체층(120)은 복수 개이고, 인접한 형광체층(120) 사이에 경계층(130)이 배치될 수 있다. Referring to FIGS. 3 and 4, there are multiple fluorescent layers (120), and a boundary layer (130) can be placed between adjacent fluorescent layers (120).
경계층(130)은 기판(110)에 반복된 형광체 코팅 방법을 적용함에 의하여 인접한 형광체층(120) 사이에 배치될 수 있다. 형광체 코팅 방법은 저온 용사(Cold spray) 코팅, 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 및 플라즈마(Plasma) 코팅 중 적어도 하나가 이용될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The boundary layer (130) can be placed between adjacent phosphor layers (120) by applying a repeated phosphor coating method to the substrate (110). The phosphor coating method may use at least one of cold spray coating, thermal spray coating, and plasma coating, but is not limited thereto.
반복된 코팅 작업이 수행됨으로써, 경계층(130)은 불규칙적인 요철구조로 이루어질 수 있다. 이러한 구성에 의하여, 광 확산이 향상될 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. By performing repeated coating operations, the boundary layer (130) can be formed into an irregular rough structure. By this configuration, light diffusion can be improved. However, the present invention is not limited thereto.
제1 형광체층 (120a)와 제2 형광체층 (120b) 사이에 제1 경계층(130a)가 배치될 수 있다. 그리고 제1 경계층(130a)은 복수의 기공을 포함할 수 있다.A first boundary layer (130a) may be placed between the first fluorescent layer (120a) and the second fluorescent layer (120b). And the first boundary layer (130a) may include a plurality of pores.
예시적으로, 광원으로부터 방출된 여기광은 제1 형광체층(120a)을 통과하고, 제1 경계층(130a)으로 확산될 수 있다.For example, the excited light emitted from the light source can pass through the first fluorescent layer (120a) and diffuse into the first boundary layer (130a).
이 때, 상기 여기광은 제1 경계층(130a)의 기공으로 인해 산란이 증폭될 수 있다. 이로써, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 광 확산이 크게 향상 시킬 수 있다. 또한, 추가적으로 옐로우 링 현상을 방지할 수 있다.At this time, the above-mentioned light can be amplified in scattering due to the pores of the first boundary layer (130a). Accordingly, the fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment can greatly improve light diffusion. In addition, the yellow ring phenomenon can be additionally prevented.
도 5는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 표면을 도시한 도면이다. 도 5를 참조하면, 복수의 형광체층(120) 상부의 표면은 거칠 수 있다.FIG. 5 is a drawing illustrating a surface of a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment. Referring to FIG. 5, the surface of the upper portion of a plurality of fluorescent layers (120) may be rough.
형광체 플레이트(100A) 제조 시, 형광체층(120)은 저온 용사(Cold spray) 코팅, 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 및 플라즈마(Plasma) 코팅 중 적어도 하나로 형성되므로, 형광체층(120)이 소결 등에 의해 형성되는 경우보다 표면 거칠기(Roughness)가 클 수 있다. When manufacturing a phosphor plate (100A), the phosphor layer (120) is formed by at least one of cold spray coating, thermal spray coating, and plasma coating, so the surface roughness may be greater than when the phosphor layer (120) is formed by sintering or the like.
형광체 플레이트(100A)의 표면은 물결 형상, 요철 형상일 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The surface of the fluorescent plate (100A) may have a wavy shape or an uneven shape, but is not limited thereto.
이러한 구성에 의하여, 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 통과하는 광을 크게 산란시킬 수 있다.By this configuration, the fluorescent plate (100A) can greatly scatter the light passing through it.
도 6은 종래의 형광체 플레이트의 표면 러프니스를 도시한 도면이고, 도 7은 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 표면 러프니스를 도시한 도면이다.FIG. 6 is a drawing illustrating the surface roughness of a conventional fluorescent plate, and FIG. 7 is a drawing illustrating the surface roughness of a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment.
도 6을 참조하면, 소결에 의해 형광체층(120)이 형성되는 경우에 형광체층 표면 러프니스는 0.03㎛ 내지 0.4㎛일 수 있다. 또한, 소결에 의해 형성된 형광체층 표면 러프니스의 평균은 0.035㎛일 수 있다.Referring to Fig. 6, when a phosphor layer (120) is formed by sintering, the surface roughness of the phosphor layer may be 0.03 µm to 0.4 µm. Additionally, the average surface roughness of the phosphor layer formed by sintering may be 0.035 µm.
도 7을 참조하면, 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)의 표면 러프니스는 0.23㎛ 내지 0.27㎛일 수 있다. 또한, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)의 표면 러프니스의 평균은 0.25㎛일 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 소결체의 크기 등에 따라 다양하게 적용될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 7, the surface roughness of the fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment of the present invention may be 0.23 ㎛ to 0.27 ㎛. In addition, the average surface roughness of the fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment may be 0.25 ㎛. However, it is not limited thereto, and may be applied in various ways depending on the size of the sintered body, etc.
이러한 구성에 의하면, 소결에 의해 형성된 형광체층(120) 표면은 평탄하여 광이 통과하면서 산란이 적게 발생할 수 있다. 이로써, 광은 직진하는 경향을 크게 가질 수 있다.According to this configuration, the surface of the fluorescent layer (120) formed by sintering is flat, so that less scattering can occur when light passes through it. Accordingly, the light can have a strong tendency to travel in a straight line.
반면에, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 표면 거칠기가 크므로 광이 형광체 플레이트(100A)의 표면에서 다양한 방향으로 산란될 수 있다. 이로써, 제1 실시예의 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 광을 크게 확산시킬 수 있다.On the other hand, since the fluorescent plate (100A) according to the first embodiment has a large surface roughness, light can be scattered in various directions on the surface of the fluorescent plate (100A). Accordingly, the fluorescent plate (100A) of the first embodiment can greatly diffuse light.
복수의 형광체층(120)의 굴절율은 경계층(130)의 굴절율과 상이할 수 있다. 경계층(130)의 굴절율은 형광체층(120)의 굴절율의 0.5배 내지 0.6배일 수 있다.The refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers (120) may be different from the refractive index of the boundary layer (130). The refractive index of the boundary layer (130) may be 0.5 to 0.6 times the refractive index of the fluorescent layer (120).
예시적으로, 형광체층(120)의 굴절율은 1.8이고, 기공을 포함하는 경계층(130)의 굴절율은 1.0일 수 있다. 이러한 구성에 의하면, 형광체층(120)과 경계층(130) 사이의 굴절율 차이에 의해 광은 크게 산란할 수 있다.For example, the refractive index of the fluorescent layer (120) may be 1.8, and the refractive index of the boundary layer (130) including pores may be 1.0. With this configuration, light may be significantly scattered due to the difference in refractive index between the fluorescent layer (120) and the boundary layer (130).
제1 형광체층(120a)을 통과한 광은 제1 형광체층(120a)의 굴절율과 상이한 제1 경계층(130a)에서 다양한 방향으로 산란할 수 있다.Light passing through the first fluorescent layer (120a) can be scattered in various directions in the first boundary layer (130a) which has a different refractive index than that of the first fluorescent layer (120a).
또한, 제1 경계층(130a)에서 산란한 광은 제1 경계층(130a)의 굴절율과 상이한 제2 형광체층(120b)에서 다시 산란할 수 있다. 이로써, 실시예의 형광체 플레이트(100A) 내에서 광은 경계층(130)의 수에 따라 반복적으로 산란할 수 있다. 이에, 실시예의 형광체 플레이트(100A)는 광의 확산효율을 향상시킬 수 있다.In addition, light scattered in the first boundary layer (130a) can be scattered again in the second phosphor layer (120b) having a different refractive index than that of the first boundary layer (130a). Accordingly, light can be scattered repeatedly according to the number of boundary layers (130) in the phosphor plate (100A) of the embodiment. Accordingly, the phosphor plate (100A) of the embodiment can improve the light diffusion efficiency.
도 8은 본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 단면도이다.Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view of a fluorescent plate according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100B)는 기판(110), 기판(110) 상에 배치되고 형광체와 확산제를 포함하는 복수의 형광체층(120), 복수의 형광체층(120) 사이에 배치되는 경계층(130)을 포함할 수 있다.A phosphor plate (100B) according to the second embodiment may include a substrate (110), a plurality of phosphor layers (120) disposed on the substrate (110) and including a phosphor and a diffuser, and a boundary layer (130) disposed between the plurality of phosphor layers (120).
기판(110), 형광체, 경계층(130)에 대한 내용은 상기 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100A)에서 설명한 내용이 동일하게 적용될 수 있다.The contents of the substrate (110), the fluorescent substance, and the boundary layer (130) can be applied identically to the contents described in the fluorescent substance plate (100A) according to the first embodiment.
제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트(100B)의 형광체층(120)은 형광체와 확산제를 포함할 수 있다.The phosphor layer (120) of the phosphor plate (100B) according to the second embodiment may include a phosphor and a diffuser.
확산제는 광분포도를 개선할 수 있다. 그리고 확산제는 Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 및 Y2O3, SiO2 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.Diffusers can improve the light distribution. And the diffusers are Al 2 O 3 , TiO 2 , ZrO 2 and may include at least one of Y 2 O 3 , SiO 2 .
또한, 확산제는 광확산제로, 유기계 광확산제 또는 무기계 광확산제를 포함할 수 있다. 유기계 광확산제는 아크릴계 입자, 실록산계 입자, 우레탄계 입자, 멜라민계 입자, 폴리카보네이트계 입자, 스티렌계 입자 등을 포함할 수 있으나, 반드시 이에 제한되는 것은 아니다.In addition, the diffuser is a light diffuser, and may include an organic light diffuser or an inorganic light diffuser. The organic light diffuser may include, but is not necessarily limited to, acrylic particles, siloxane particles, urethane particles, melamine particles, polycarbonate particles, styrene particles, etc.
상기 무기계 광확산제는 탄산칼슘, 황산바륨, 이산화티탄, 수산화알루미늄, 실리카, 유리, 활석, 운모, 화이트카본, 산화마그네슘, 산화아연 등을 포함할 수 있으나, 반드시 이에 제한되는 것은 아니다. The above inorganic light diffusing agent may include, but is not necessarily limited to, calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, titanium dioxide, aluminum hydroxide, silica, glass, talc, mica, white carbon, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, etc.
광확산제는 우수한 광확산 효과를 확보할 수 있는 동시에 내스크래치성을 향상시킬 수 있다.A light diffusing agent can secure excellent light diffusion effects while improving scratch resistance.
확산제는 형광체에 대비하여 10wt% 내지 30wt% 중량부일 수 있다. 확산제는 형광체 대비 10wt% 중량부 이하로 포함되는 경우에는 충분한 반광 효과를 확보하기 어려우며, 30wt% 중량부를 초과하여 포함되는 경우에는 분산성을 충분히 확보할 수 없다.The amount of the diffuser may be 10 wt% to 30 wt% by weight relative to the fluorescent substance. If the amount of the diffuser is less than 10 wt% by weight relative to the fluorescent substance, it is difficult to secure a sufficient reflection effect, and if the amount of the diffuser is more than 30 wt% by weight, it is difficult to secure sufficient dispersibility.
확산제의 평균 입경은 0.1㎛ 내지 0.5㎛일 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The average particle size of the dispersant may be 0.1 ㎛ to 0.5 ㎛, but is not limited thereto.
또한, 확산제는 형광체층(120) 내에서 층을 형성할 수 있다. 이 때, 확산제를 포함하는 층은 5㎛ 내지 10㎛의 두께를 가질 수 있다. 그리고 형광체를 포함하는 층은 80㎛ 내지 90㎛의 두께를 가질 수 있다. 다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In addition, the diffuser can form a layer within the fluorescent layer (120). At this time, the layer including the diffuser can have a thickness of 5 μm to 10 μm. And the layer including the fluorescent substance can have a thickness of 80 μm to 90 μm. However, the present invention is not limited thereto.
확산제는 광의 휘도 분포를 균일하게 하는 역할과 더불어 일부 광의 경로를 변경할 수 있다. In addition to uniformly distributing the brightness of light, a diffuser can also change the path of some light.
이로써, 확산제는 형광체 플레이트(100A)를 통과하는 광의 양을 증가시킬 수 있다. 또한, 확산제는 형광체 플레이트(100A)를 통과하는 광의 확산을 더욱 향상시킬 수 있다. Thereby, the diffuser can increase the amount of light passing through the fluorescent plate (100A). In addition, the diffuser can further improve the diffusion of light passing through the fluorescent plate (100A).
도 9는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각을 나타낸 도면이고, 도 10은 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각을 나타낸 도면이다.FIG. 9 is a drawing showing the orientation angle of a phosphor plate according to the first embodiment, and FIG. 10 is a drawing showing the orientation angle of a phosphor plate according to the second embodiment.
도 9 및 도 10을 참조하면, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각은 122°일 수 있다. 그리고 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트의 지향각은 143°일 수 있다. 여기서, 지향각은 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광의 지향각으로 정의한다.Referring to FIGS. 9 and 10, the beam angle of the phosphor plate according to the first embodiment may be 122°. And the beam angle of the phosphor plate according to the second embodiment may be 143°. Here, the beam angle is defined as the beam angle of light passing through the phosphor plate.
제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광이 발광하는 면적보다 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광이 발광하는 면적이 더 클 수 있다. (도 9 및 도 10에 도시된 각 영역(S1, S2)은 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광의 발광 영역이다)The area where light passes through the phosphor plate according to the second embodiment is emitted may be larger than the area where light passes through the phosphor plate according to the first embodiment. (Each area (S1, S2) illustrated in FIGS. 9 and 10 is an area where light passes through the phosphor plate is emitted.)
확산제는 형광체 플레이트를 통과하는 광 확산을 향상시켜 지향각을 개선시킬 수 있다.A diffuser can improve the beam spread by enhancing the light diffusion through the phosphor plate, thereby improving the beam angle.
도 11은 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트 제조 방법의 순서도이다. 도 11을 참조하면, 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트 제조 방법은 형광체를 분사하는 단계(S210), 복수의 형광체층을 형성하는 단계(S220)을 포함할 수 있다.Fig. 11 is a flowchart of a method for manufacturing a phosphor plate according to the first embodiment. Referring to Fig. 11, a method for manufacturing a phosphor plate according to the first embodiment may include a step of spraying a phosphor (S210) and a step of forming a plurality of phosphor layers (S220).
형광체를 분사하는 방법으로는 저온 용사(Cold spray) 코팅, 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 및 플라즈마(Plasma) 코팅 중 적어도 하나가 이용될 수 있다.As a method for spraying the phosphor, at least one of cold spray coating, thermal spray coating, and plasma coating can be used.
저온 용사 코팅 장치의 개요를 나타내는 모식도인 도 12를 참조하면, 저온 용사 코팅 장치(300)는 압축 가스를 가열하는 가스 가열기(301), 형광체 및 확산제 중 적어도 하나의 분말을 수용하여 스프레이건(303)에 공급하는 분말 공급 장치(302), 가열된 압축 가스 및 공급된 재료 분말을 기판(110)에 분사하는 가스 노즐(304), 가스 가열기(301) 및 분말 공급 장치(302)에 대한 압축 가스의 공급량을 각각 조절하는 밸브(305, 306)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 12, which is a schematic diagram showing an outline of a low-temperature spray coating device, a low-temperature spray coating device (300) may include a gas heater (301) that heats compressed gas, a powder supply device (302) that receives powder of at least one of a fluorescent substance and a dispersant and supplies it to a spray gun (303), a gas nozzle (304) that sprays the heated compressed gas and the supplied material powder onto a substrate (110), and valves (305, 306) that control the supply amount of compressed gas to the gas heater (301) and the powder supply device (302), respectively.
압축 가스로는, 헬륨, 질소, 공기 등이 사용될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 가스 가열기(301)에 공급된 압축 가스는 예를 들어, 형광체 및 확산제 중 어느 하나의 분말의 융점보다 낮은 범위의 온도로 가열된 후에 스프레이건(303)로 공급될 수 있다. As the compressed gas, helium, nitrogen, air, etc. can be used, but are not limited thereto. The compressed gas supplied to the gas heater (301) can be supplied to the spray gun (303) after being heated to a temperature lower than the melting point of the powder of either the fluorescent substance or the diffusion agent, for example.
분말 공급 장치(302)에 공급된 압축 가스는 분말 공급 장치(302) 내의 재료 분말을 스프레이건(303)에 소정의 토출량이 되도록 공급될 수 있다.The compressed gas supplied to the powder supply device (302) can be supplied so that the material powder in the powder supply device (302) is discharged to the spray gun (303) at a predetermined amount.
압축 가스의 가스 압력은, 1MPa 내지 5MPa 일 수 있으나, 이에 한정되지 않는다. The gas pressure of the compressed gas may be, but is not limited to, 1 MPa to 5 MPa.
스프레이건(303)에 공급된 형광체 및 확산제 중 어느 하나의 분말은 압축 가스에 의해 가속되고, 기판(110) 상에 고속으로 충돌되어 피막을 형성할 수 있다. 이러한 피막으로 형광체층이 형성될 수 있다.Powder of either a fluorescent substance or a diffusion agent supplied to the spray gun (303) can be accelerated by compressed gas and collide at high speed on the substrate (110) to form a film. A fluorescent substance layer can be formed with this film.
형광체 및 확산제 중 어느 하나의 분말을 기판(110)를 향하여 고상상태에서 충돌시켜 형광체층을 형성할 수 있는 장치라면, 도 12에 나타내는 저온 용사 코팅 장치(300)에 한정되는 것은 아니다.Any device capable of forming a phosphor layer by colliding powder of either a phosphor or a diffuser in a solid state toward a substrate (110) is not limited to the low-temperature spray coating device (300) shown in FIG. 12.
도 13은 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 장치의 개요를 나타내는 모식도이다. 도 13을 참조하면, 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 장치(400)는 챔버(401)와 노즐(402)을 포함할 수 있다.Fig. 13 is a schematic diagram showing an outline of a thermal spray coating device. Referring to Fig. 13, a thermal spray coating device (400) may include a chamber (401) and a nozzle (402).
열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 장치(400)는 분말이 분사되는 노즐 (402)과 분말이 주입되는 챔버(401)를 포함한다. 예시적으로, 챔버(401)는 연소를 통해 노즐로 압력을 제공할 수 있다. 챔버는 아세틸렌, 수소, 프로판 또는 프로필렌과 같은 연료 및 산소와 같은 캐리어 가스 혼합물(mixture ofcarrier gas)을 포함할 수 있다. 이 혼합물은 점화되어 고압을 발생시키고 챔버(401) 내에 압력을 생성할 수 있다. A thermal spray coating device (400) includes a nozzle (402) into which powder is sprayed and a chamber (401) into which powder is injected. For example, the chamber (401) can provide pressure to the nozzle through combustion. The chamber can contain a mixture of a fuel such as acetylene, hydrogen, propane or propylene and a carrier gas such as oxygen. The mixture can be ignited to generate high pressure and create pressure within the chamber (401).
형광체 및 확산제 중 어느 하나의 분말(20)은 챔버(401)로 제공될 수 있다. 예시적으로, 연소를 통한 고온열원으로부터 분말은 용융할 수 있고, 고속으로 기판(110) 상면을 향해 분사할 수 있다. 분말은 기판(110) 상면에 충돌할 수 있다. 이로써, 기판(110) 상에 형광체 층이 형성될 수 있다.A powder (20) of either a fluorescent substance or a diffuser may be provided to the chamber (401). For example, the powder may be melted from a high-temperature heat source through combustion and may be sprayed at a high speed toward the upper surface of the substrate (110). The powder may collide with the upper surface of the substrate (110). As a result, a fluorescent substance layer may be formed on the substrate (110).
다만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 열 용사(Thermal spray) 코팅 방법들로는 분말 플레임 스프레이, 플라즈마 스프레이, 및 고속 산소 연료 스프레이(HVOF) 등 다양한 방법이 적용될 수 있다.However, it is not limited thereto, and various methods can be applied as thermal spray coating methods, such as powder flame spray, plasma spray, and high velocity oxygen fuel spray (HVOF).
이러한 분말의 분사를 반복하면, 복수의 형광체층을 형성할 수 있다(S220).By repeating the spraying of this powder, multiple fluorescent layers can be formed (S220).
도 14 및 도 15는 제1 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트를 다양한 광 디바이스에 적용한 예를 도시한 도면이다.FIG. 14 and FIG. 15 are drawings showing examples of applying the fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment to various optical devices.
광 디바이스는 형광체 플레이트, 형광체 플레이트에 광을 조사하는 광원을 포함할 수 있다. 여기서, 형광체 플레이트는 상기 설명한 제1 실시예 및 제2 실시예의 형광체 플레이트 중 어느 하나가 적용될 수 있다.The optical device may include a phosphor plate and a light source that irradiates light to the phosphor plate. Here, the phosphor plate may be any one of the phosphor plates of the first embodiment and the second embodiment described above.
도 14를 참조하면, 형광체 플레이트는 레이저 모듈에 이용될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 14, a phosphor plate can be used in a laser module.
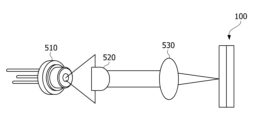
레이저 모듈은 광원, 시준기, 집광기 및 형광체 플레이트를 포함할 수 있다. 광원은 레이저다이오드(Laser Diode, LD) (510)일 수 있다. The laser module may include a light source, a collimator, a condenser, and a phosphor plate. The light source may be a laser diode (LD) (510).
시준기(520)는 레이저 다이오드로부터 출사한 광을 평행광선으로 변화시킬 수 있다. 시준기(520)는 콜리메이터(Collimator)일 수 있다.The collimator (520) can change the light emitted from the laser diode into parallel light. The collimator (520) can be a collimator.
렌즈부(530)는 시준기를 통과한 광을 집광시킬 수 있다.The lens unit (530) can focus light passing through the collimator.
렌즈부(530)를 통과한 광은 형광체 플레이트의 일부로 집중 조사될 수 있다. 그리고 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광은 외부로 확산될 수 있다. 예시적으로, 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광은 백색일 수 있다.Light passing through the lens unit (530) can be focused on a portion of the fluorescent plate. And light passing through the fluorescent plate can be diffused to the outside. For example, light passing through the fluorescent plate can be white.
도 15를 참조하면, 형광체 플레이트는 조명 장치에 적용될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 15, the phosphor plate can be applied to a lighting device.
조명 장치는 광을 출사하는 광원, 상기 광이 조사되는 형광체 플레이트(100)를 포함할 수 있다. 형광체 플레이트(100)는 상기 제1 실시예 및 제2 실시예에 따른 형광체 플레이트가 적용될 수 있다.The lighting device may include a light source that emits light and a fluorescent plate (100) on which the light is irradiated. The fluorescent plate (100) may be a fluorescent plate according to the first embodiment and the second embodiment.
광은 광을 출사하고, 예를 들어, LED 칩(610)일 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The light emits light and may be, for example, but is not limited to, an LED chip (610).
형광체 플레이트는 광이 출사하는 방향에 배치될 수 있다. LED 칩으로부터 출사된 광은 형광체 플레이트로 조사되고, 형광체 플레이트를 통과한 광은 외부로 확산될 수 있다.The phosphor plate can be placed in the direction in which light is emitted. Light emitted from the LED chip is irradiated to the phosphor plate, and light passing through the phosphor plate can be diffused to the outside.
이와 같이, 형광체 플레이트는 레이저 모듈에 적용될 수 있다. 뿐만 아니라, 형광체 플레이트는 LED 패키지, 차량용 헤드 램프 등을 포함하는 조명 장치 등 다양한 광 디바이스에 적용될 수 있다.In this way, the phosphor plate can be applied to a laser module. In addition, the phosphor plate can be applied to various optical devices such as lighting devices including LED packages, vehicle headlamps, etc.
이상에서 설명한 본 발명 실시 예는 상술한 실시 예 및 첨부된 도면에 한정되는 것이 아니고, 실시 예의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경이 가능하다는 것이 본 발명 실시 예가 속하는 기술분야에서 종래의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어 명백할 것이다.The embodiments of the present invention described above are not limited to the above-described embodiments and the attached drawings, and it will be apparent to a person having prior knowledge in the technical field to which the embodiments of the present invention belong that various substitutions, modifications, and changes are possible within a scope that does not depart from the technical spirit of the embodiments.
100, 100A, 100B: 형광체 플레이트
110: 기판
120: 형광체층
121: 형광체
122: 확산제
130: 경계층100, 100A, 100B: Phosphor Plate
110: Substrate
120: Phosphor layer
121: Phosphor
122: Diffuser
130: Boundary layer
Claims (17)
상기 기판 상에 배치되는 제1 형광체층 및 상기 제1 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제2 형광체층을 포함하는 복수의 형광체층; 및
상기 제1 형광체층과 상기 제2 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층;을 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율은 상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율과 상이하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은, YAG, LuAg 및 LuYAG 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은 확산제를 포함하고,
상기 확산제는,
Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 및 Y2O3, SiO2 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고, 형광체에 대비하여 10wt% 내지 30wt% 중량부인 형광체 플레이트.
substrate;
A plurality of phosphor layers including a first phosphor layer disposed on the substrate and a second phosphor layer disposed on the first phosphor layer; and
A first boundary layer is disposed between the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer and includes pores;
The refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers is different from the refractive index of the first boundary layer,
The above plurality of phosphor layers include at least one of YAG, LuAg and LuYAG,
The above plurality of fluorescent layers include a diffuser,
The above-mentioned dispersant is,
A phosphor plate comprising at least one of Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2, and Y2O3, SiO2, and having a weight portion of 10 wt% to 30 wt% relative to the phosphor.
상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율은 상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율의 0.5배 내지 0.6배인 형광체 플레이트.
In the first paragraph,
A phosphor plate wherein the refractive index of the first boundary layer is 0.5 to 0.6 times the refractive index of the plurality of phosphor layers.
상기 복수의 형광체층 각각의 두께는 50㎛ 내지 150㎛이고,
상기 복수의 형광체층의 표면 러프니스는 0.23㎛ 내지 0.27㎛인 형광체 플레이트.
In the first paragraph,
The thickness of each of the above multiple fluorescent layers is 50 ㎛ to 150 ㎛,
A phosphor plate having a surface roughness of the plurality of phosphor layers of 0.23 ㎛ to 0.27 ㎛.
상기 복수의 형광체층은 상기 제2 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제3 형광체층을 더 포함하고,
상기 제2 형광체층과 상기 제3 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제2 경계층을 더 포함하는 형광체 플레이트.
In the first paragraph,
The above plurality of fluorescent layers further include a third fluorescent layer disposed on the second fluorescent layer,
A phosphor plate further comprising a second boundary layer disposed between the second phosphor layer and the third phosphor layer and including pores.
상기 광원으로부터 출사된 광이 조사되는 기판;
상기 기판 상에 배치되는 제1 형광체층 및 상기 제1 형광체층 상에 배치되는 제2 형광체층을 포함하는 복수의 형광체층; 및
상기 제1 형광체층과 상기 제2 형광체층 사이에 배치되고 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층;을 포함하는 형광체 플레이트;를 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율은 상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율과 상이하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은, YAG, LuAg 및 LuYAG 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은 확산제를 포함하고,
상기 확산제는,
Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 및 Y2O3, SiO2 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고, 형광체에 대비하여 10wt% 내지 30wt% 중량부인 광 디바이스.
light source;
A substrate on which light emitted from the light source is irradiated;
A plurality of phosphor layers including a first phosphor layer disposed on the substrate and a second phosphor layer disposed on the first phosphor layer; and
A phosphor plate including a first boundary layer disposed between the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer and including pores;
The refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers is different from the refractive index of the first boundary layer,
The above plurality of phosphor layers include at least one of YAG, LuAg and LuYAG,
The above plurality of fluorescent layers include a diffuser,
The above-mentioned dispersant is,
An optical device comprising at least one of Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2, and Y2O3, SiO2, and having a weight portion of 10 wt% to 30 wt% relative to a phosphor.
상기 형광체를 복수회 분사하여 복수의 형광체층을 형성하는 단계;를 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층 사이에 기공을 포함하는 제1 경계층이 배치되고,
상기 복수의 형광체층의 굴절율은 상기 제1 경계층의 굴절율과 상이하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은, YAG, LuAg 및 LuYAG 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고,
상기 복수의 형광체층은 확산제를 포함하고,
상기 확산제는,
Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 및 Y2O3, SiO2 중 적어도 하나를 포함하고, 형광체에 대비하여 10wt% 내지 30wt% 중량부인 형광체 플레이트 제조 방법.a step of spraying a fluorescent substance onto a substrate; and
A step of forming multiple fluorescent layers by spraying the fluorescent substance multiple times;
A first boundary layer including pores is disposed between the plurality of fluorescent layers,
The refractive index of the plurality of fluorescent layers is different from the refractive index of the first boundary layer,
The above plurality of phosphor layers include at least one of YAG, LuAg and LuYAG,
The above plurality of fluorescent layers include a diffuser,
The above-mentioned dispersant is,
A method for manufacturing a phosphor plate comprising at least one of Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2 and Y2O3, SiO2, and having a weight portion of 10 wt% to 30 wt% relative to the phosphor.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160169538A KR102693771B1 (en) | 2016-12-13 | 2016-12-13 | Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160169538A KR102693771B1 (en) | 2016-12-13 | 2016-12-13 | Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180068012A KR20180068012A (en) | 2018-06-21 |
| KR102693771B1 true KR102693771B1 (en) | 2024-08-13 |
Family
ID=62806667
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160169538A KR102693771B1 (en) | 2016-12-13 | 2016-12-13 | Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102693771B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102121249B1 (en) * | 2018-07-04 | 2020-06-10 | 한국광기술원 | Phosphor Plate and Method for Manufacturing Thereof |
| US20240145640A1 (en) * | 2021-03-22 | 2024-05-02 | Denka Company Limited | Phosphor plate and light emitting device |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009158637A (en) * | 2007-12-26 | 2009-07-16 | Kyocera Corp | Light-emitting device |
| JP2013526007A (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2013-06-20 | 日東電工株式会社 | Garnet phosphor ceramic sheet for light emitting devices |
| JP2014530449A (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-11-17 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Light emitting device |
| JP2015151305A (en) * | 2014-02-14 | 2015-08-24 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Optical component and method for manufacturing the same |
| KR101640197B1 (en) * | 2012-05-25 | 2016-07-15 | 오스람 옵토 세미컨덕터스 게엠베하 | Method for producing optoelectronic components and device for producing optoelectronic components |
| KR101657876B1 (en) * | 2014-03-03 | 2016-09-30 | 쿠어스택 가부시키가이샤 | Sintered compact for wavelength conversion |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090039375A1 (en) * | 2007-08-07 | 2009-02-12 | Cree, Inc. | Semiconductor light emitting devices with separated wavelength conversion materials and methods of forming the same |
-
2016
- 2016-12-13 KR KR1020160169538A patent/KR102693771B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009158637A (en) * | 2007-12-26 | 2009-07-16 | Kyocera Corp | Light-emitting device |
| JP2013526007A (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2013-06-20 | 日東電工株式会社 | Garnet phosphor ceramic sheet for light emitting devices |
| JP2014530449A (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-11-17 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Light emitting device |
| KR101640197B1 (en) * | 2012-05-25 | 2016-07-15 | 오스람 옵토 세미컨덕터스 게엠베하 | Method for producing optoelectronic components and device for producing optoelectronic components |
| JP2015151305A (en) * | 2014-02-14 | 2015-08-24 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Optical component and method for manufacturing the same |
| KR101657876B1 (en) * | 2014-03-03 | 2016-09-30 | 쿠어스택 가부시키가이샤 | Sintered compact for wavelength conversion |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20180068012A (en) | 2018-06-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5782246B2 (en) | Optical film and method for producing the same | |
| US9291315B2 (en) | Lighting device | |
| TW201546519A (en) | Solid-state light emitting devices and signage with photoluminescence wavelength conversion | |
| CN102980136A (en) | Direct type backlight module and light source diffusion structure thereof | |
| RU2586268C2 (en) | Light-emitting diode assembly, including light-scattering layer | |
| EP2791574B1 (en) | Optical arrangement with diffractive optics | |
| JP6162537B2 (en) | LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE, LIGHTING DEVICE, AND VEHICLE LIGHT | |
| US20200243726A1 (en) | Wavelength conversion member and light emitting device | |
| TWI717329B (en) | Lighting apparatus | |
| KR102693771B1 (en) | Phosphor plate and method of manufacturing thereof | |
| US11320099B2 (en) | Wavelength conversion member and production method therefor | |
| KR102362017B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of wavelength conversion member | |
| US20180003356A1 (en) | Lighting apparatus and vehicle headlight comprising lighting apparatus | |
| JP2015038978A (en) | Wavelength conversion member | |
| JP2015065142A (en) | Solid lighting device, and wavelength conversion member | |
| US10788190B2 (en) | Light source unit | |
| KR101592581B1 (en) | Optical film and method for fabricating the same | |
| US8471281B2 (en) | Side emitting device with hybrid top reflector | |
| KR102157688B1 (en) | Lighting device | |
| EP3495857B1 (en) | Wavelength conversion member and production method therefor | |
| KR101600945B1 (en) | Optical film and method for fabricating the same | |
| KR101742680B1 (en) | Optical film and method for fabricating the same | |
| EP3495721B1 (en) | Wavelength conversion member and production method therefor | |
| KR101558598B1 (en) | Optical film and method for fabricating the same | |
| US20210091274A1 (en) | Wavelength conversion member and light emitting device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |