KR102258055B1 - Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment - Google Patents
Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102258055B1 KR102258055B1 KR1020190105189A KR20190105189A KR102258055B1 KR 102258055 B1 KR102258055 B1 KR 102258055B1 KR 1020190105189 A KR1020190105189 A KR 1020190105189A KR 20190105189 A KR20190105189 A KR 20190105189A KR 102258055 B1 KR102258055 B1 KR 102258055B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- unit
- temperature
- laser beam
- emissivity
- laser
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/70483—Information management; Active and passive control; Testing; Wafer monitoring, e.g. pattern monitoring
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/70008—Production of exposure light, i.e. light sources
- G03F7/70025—Production of exposure light, i.e. light sources by lasers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/708—Construction of apparatus, e.g. environment aspects, hygiene aspects or materials
- G03F7/70858—Environment aspects, e.g. pressure of beam-path gas, temperature
- G03F7/70883—Environment aspects, e.g. pressure of beam-path gas, temperature of optical system
- G03F7/70891—Temperature
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67005—Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67011—Apparatus for manufacture or treatment
- H01L21/67098—Apparatus for thermal treatment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67005—Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67242—Apparatus for monitoring, sorting or marking
- H01L21/67248—Temperature monitoring
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S3/00—Lasers, i.e. devices using stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation in the infrared, visible or ultraviolet wave range
- H01S3/0007—Applications not otherwise provided for
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Atmospheric Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Radiation Pyrometers (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 레이저를 이용하는 열처리 공정 시에 반응부에서의 온도측정 및 피가공물의 물성에 따른 온도보정을 위한 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템에 관한 것으로, 더욱 자세하게는 더욱 정밀한 온도측정이 가능하며, 이때 방사율을 측정하기 위한 별도의 모니터링장비가 공정용 레이저빔의 이동과 독립되어 작동함으로써, 레이저 가공공정에 속도를 저하하지 않고 빠른 공정을 유지할 수 있는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment for temperature measurement in a reaction part during a heat treatment process using a laser and temperature correction according to the physical properties of a workpiece, and in more detail, a more precise temperature measurement is possible. It relates to a temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment capable of maintaining a fast process without slowing down the laser processing process by operating a separate monitoring device for measuring the emissivity independently from the movement of the laser beam for the process.
Description
본 발명은, 레이저를 이용하는 열처리 공정 시에, 반응부에서의 온도측정 및 피가공물의 물성에 따른 온도보정을 위한 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment for temperature measurement in a reaction part and temperature correction according to physical properties of a workpiece during a heat treatment process using a laser.
반도체 제조공정 중의 하나인 반도체 포토공정에서, 감광막(Photo-resist) 도포 전 감광막의 접착력을 증진시키고, 도포 후 감광막내의 솔벤트, 폴리머, 센시타이저 등의 성분을 안정화하여 임계선폭(Critical Dimesion)의 조정을 용이하기 하기 위하여, 웨이퍼 표면을 가열한 후 냉각하여 재료 표면을 변형시키는 열처리 공정(어닐링, Annealing)을 통하여, 웨이퍼에 불순물 이온을 주입한 후 활성화 하거나, 실리콘을 재결정화하는 공정을 수행하게 된다.In the semiconductor photo process, which is one of the semiconductor manufacturing processes, the adhesion of the photoresist film is improved before the photo-resist is applied, and the components such as solvent, polymer, and sensitizer in the photo-resist film are stabilized after application. For ease of adjustment, through a heat treatment process (annealing) in which the surface of the wafer is heated and then cooled to deform the material surface, impurity ions are implanted into the wafer and then activated, or silicon is recrystallized. do.
이때, 상기 어닐링 공정에서는, 웨이퍼 전체온도 균일화 및 온도제어 정밀도가 임계선폭 형성에 결정적인 역할을 하기 때문에, 목표온도의 정밀도 및 균일성이 무엇보다도 중요하며, 현재 반도체 어닐링 기술은 퍼니스(furnace), 급속열처리(RTP, Rapid Thermal Process) 방식이 주류를 이루고 있었으나, 반도체 웨이퍼 두께가 점점 얇아짐에 따라, 기존의 어닐링 공정은 웨이퍼 전체에 열이 퍼져 주변 소자 및 회로에 손상을 주게 된다는 한계가 발생하였고, 한국 공개특허공보 제10-2004-0031276호(레이저 어닐링 장비 및 이를 이용한 실리콘 결정화 방법, 2004.04.13. 공개)에서 개시하고 있는 바와 같은 수 나노 급 차세대 반도체 공정 및 플렉시블 디스플레이, 저온롤리실리콘 LCD 등과 같은 공정에서 웨이퍼 전체를 가열하지 않고 특정 부분만 선택적으로 처리하는 레이저 어닐링 기술이 도입되었다.At this time, in the annealing process, since uniformization of the overall temperature of the wafer and precision of temperature control play a decisive role in forming the critical line width, the accuracy and uniformity of the target temperature is of paramount importance. The heat treatment (RTP, Rapid Thermal Process) method was the mainstream, but as the thickness of the semiconductor wafer became thinner, the existing annealing process had a limitation in that heat spread over the entire wafer, causing damage to peripheral devices and circuits. As disclosed in Korean Patent Laid-Open Publication No. 10-2004-0031276 (laser annealing equipment and silicon crystallization method using the same, published on April 13, 2004), the next-generation semiconductor process and flexible display of several nano-levels, such as a flexible display, low-temperature silicon LCD, etc. In the process, a laser annealing technology has been introduced that selectively processes a specific portion of the wafer without heating the entire wafer.
그러나, 기존에는 웨이퍼 상 레이저 빔의 움직임을 x,y축 상으로 이동하는 스테이지(stage)를 이용하여 제어하였으며, 이때 레이저 빔 자체는 고정된 곳을 가리키므로, 온도 모니터링을 위한 계측기를 고정된 한 곳만을 가리키도록 설치되면 되었으나. 최근에 들어 공정 시간을 단축시키기 위해 고정된 스테이지에 레이저빔이 조사되는 방향이 이동하도록 구성되는 스캐너를 이용하여 레이저빔의 움직임을 제어하는 기술이 관심을 받고 있으며, 이때 스캐너 방식에서는 레이저 빔 자체가 움직이기 때문에 온도 모니터링을 위한 계측 장치도 빔의 움직임을 동반하며 반응부를 추적해야 하는 문제에 직면하게 되었다.However, in the past, the movement of the laser beam on the wafer was controlled by using a stage that moves on the x and y axes.At this time, the laser beam itself points to a fixed place, so the instrument for temperature monitoring is fixed. It had to be installed to point to only one place. Recently, in order to shorten the process time, the technology of controlling the movement of the laser beam by using a scanner configured to move the direction in which the laser beam is irradiated to a fixed stage is attracting attention. In this case, the laser beam itself is Because it is moving, the measuring device for temperature monitoring is accompanied by the movement of the beam and faced the problem of tracking the reaction part.
본 발명은 상기한 문제점을 해결하고자 안출된 것으로, 레이저빔이 이동하는 스캐너방식의 레이저 어닐링 장비에서, 레이저빔의 이동을 병행 가능한 온도 모니터링 시스템을 제공한다.The present invention has been conceived to solve the above problems, and provides a temperature monitoring system capable of concurrently moving a laser beam in a scanner-type laser annealing equipment in which a laser beam moves.
또한, 본 발명은 피가공물의 방사율에 따른 온도를 보정함으로써, 더욱 정밀한 온도측정이 가능한 모니터링 시스템을 제공한다.In addition, the present invention provides a monitoring system capable of more precise temperature measurement by correcting the temperature according to the emissivity of the object to be processed.
상기한 과제를 해결하기 위한, 본 발명은 제1파장을 갖는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 사출하는 고정된 제1레이저발진기(110);
상기 고정된 레이저발진기(110)로부터 인가받은 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 편향시키기 위한 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122) 및 상기 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122)를 통해 반사 및 굴절되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 초점을 모으기 위한 스캐닝렌즈(123, Scanning lens)를 포함하되, 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사된 반응부(S)에서 발산되는 광신호(R1)을 수집하여, 반응부(S)의 이동을 병행하지 않고 광신호(R1)를 수집가능한 스캐너부(120); 및 상기 레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 진행하는 빛의 경로상에 구비되어, 상기 제1파장을 갖는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)만을 투과시키는 제1광학필터(210) 및 상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 반사된 광신호(R1)의 세기를 검출하는 제1포토센서(270)가 구비된 검출부(200);를 포함하고, 상기 검출부(200)는 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 구비되는 제1광학필터(210)를 통해, 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면에 조사되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사된 반응부(S)의 발열에 의해 발산되는 광신호(R1)의 세기를 측정함으로써, 상기 스캐너부(120)의 가변미러(121, 122)의 동작을 간섭하지 않으면서, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 온도를 검출하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In order to solve the above problems, the present invention is a fixed
Reflected and refracted through a pair of
또한, 본 발명은 상기 제1포토센서(270)로부터 검출된 광신호(R1)의 세기에 따른 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 산출하는 온도산출부(310)가 구비된 모니터링부(300)를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the present invention is a monitoring provided with a
또한, 상기 온도산출부는 하기의 식을 통해 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 산출하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the temperature calculation unit is characterized in that it calculates the process temperature (T) in the reaction unit (S) through the following equation.
{ 여기에서,{ From here,
I : 제1포토센서에서 감지된 광신호(R1)의 세기I: intensity of the optical signal R1 detected by the first photosensor
h : plank 상수, c : 빛의 속도, v : 빛의 주파수, : 볼츠만상수,h: plank constant, c: speed of light, v: frequency of light, : Boltzmann constant,
T : 반응부의 온도 }T: temperature of the reaction part}
또한, 상기 검출부(200)는, 서로 다른 파장의 광신호(R1)를 검출하는 복수의 제1포토센서(270) 및 상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 인가된 광신호(R1)를 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(270)로 각기 분열시키는 빔스플리터(240)를 더 포함하며, 상기 온도산출부(310)는 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(270)로부터 측정된 광신호(R1)에 따른 온도들의 평균값을 공정온도(T)로 정의하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
또한, 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면상에 임의의 한 지점(P)에 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)을 사출하는 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 반사된 반사광(R2)의 세기를 검출하는 제2포토센서(420)가 구비된 방사율측정부(400);를 더 포함하되, 상기 모니터링부(300)는 상기 방사율측정부(400)로부터 검출된 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기로부터 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)을 산출하는 방사율산출부(320)를 더 포함하고, 상기 온도산출부(310)는 산출된 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)에 따라 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, a
또한, 상기 방사율산출부는 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)과 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 피가공물에 같은 지점(S, P)을 지나는 순간 반사된 모니터링 레이저빔(L2)의 반사광(R2)의 세기에 따른 방사율(E)을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the emissivity calculation unit of the reflected light (R2) of the monitoring laser beam (L2) reflected the moment the processing laser beam (L1) and the monitoring laser beam (L2) pass the same point (S, P) to the workpiece. It is characterized by calculating the emissivity (E) according to the intensity.
또한, 상기 모니터링부(300)는 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 최초 조사되는 상기 피가공물(1)의 최선단(P_edge)에서의 방사율(E)을 산출하여, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
또한, 상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)가 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면과 평행하는 어느 한 평면상에서 이동 가능하도록 구성되는 구동부(430)를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
또한, 상기 구동부(430)는 상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)를 상기 피가공물(1)의 중심을 지나는 어느 일직선상을 따라 이동하도록 작동되되, 상기 방사율측정부(400)는 상기 제2레이저발진기(410)로부터 조사되는 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)과 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사되는 반응부(S)가 일치되는 적어도 둘 이상의 지점(P)을 측정하고, 상기 방사율산출부(320)는 측정된 각각의 지점(P)에서 검출된 빛의 세기의 최소값(min)을 선정하여, 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)을 결정하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
또한, 상기 모니터링부(300)는, 공정이 종료된 어느 하나의 피가공물(1)에 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T1)를 저장하는 메모리부(330) 및 공정을 시작하는 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)로부터 측정된 공정온도(T2)와 상기 메모리부(330)에 저장된 공정온도(T1) 프로파일을 비교하여, 상기 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)의 공정에서의 이상신호를 판단하는 불량판단부(340)를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the
상기한 구성에 따른 본 발명은, 고정된 레이저발진기로부터 사출되는 레이저빔(L1)을 편향시켜 피가공물의 표면에 조사되는 반응부를 이동시키는 스캐너 타입 레이저 어닐링 장비에, 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사되는 반응부(S)로부터 발산되는 광신호(R1)의 세기를 검출하여 온도를 산출함으로써, 반응부의 이동을 병행하지 않아, 레이저 어닐링 장비의 공정 속도의 저하를 방지함과 동시에 실시간 온도 모니터링이 가능한 장점이 있다.The present invention according to the above configuration is a scanner type laser annealing equipment that deflects the laser beam L1 emitted from the fixed laser oscillator to move the reaction part irradiated to the surface of the workpiece, and the laser beam L1 for the process is By detecting the intensity of the light signal (R1) emitted from the irradiated reaction part (S) and calculating the temperature, the movement of the reaction part is not parallel, preventing a decrease in the process speed of the laser annealing equipment and simultaneously monitoring the temperature in real time. There are possible advantages.
또한, 본 발명은 피가공물의 방사율(E)을 측정하여 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정함으로써, 더욱 정밀한 온도측정이 가능하며, 이때 방사율을 측정하기 위한 별도의 모니터링장비가 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 이동과 독립되어 작동함으로써, 레이저 가공공정에 속도를 저하하지 않고 빠른 공정을 유지할 수 있는 장점이 있다.In addition, in the present invention, by measuring the emissivity (E) of the workpiece and correcting the process temperature (T) in the reaction unit (S), a more precise temperature measurement is possible, and at this time, a separate monitoring device for measuring the emissivity is provided. By operating independently of the movement of the process laser beam L1, there is an advantage of maintaining a fast process without reducing the speed of the laser processing process.
도 1은 본 발명의 일실시에에 따른 모니터링 시스템을 도시한 구성도.
도 2는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 모니터링부의 작동을 도시한 예시도.
도 3 은 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 공정순서를 도시한 예시도.
도 4는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 공정순서에 따른 방사율측정부의 작동을 설명하기 위한 예시도.1 is a block diagram showing a monitoring system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 2 is an exemplary view showing the operation of the monitoring unit according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is an exemplary diagram showing a process sequence of the process laser beam L1.
Figure 4 is an exemplary view for explaining the operation of the emissivity measuring unit according to the process sequence of the laser beam (L1) for processing.
본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 실시예를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세한 설명을 하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 실시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. In the present invention, various modifications may be made and various embodiments may be provided, and specific embodiments are illustrated in the drawings and will be described in detail. However, this is not intended to limit the present invention to a specific embodiment, it should be understood to include all changes, equivalents, and substitutes included in the spirit and scope of the present invention.
어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 “연결되어” 있다거나 “접속되어” 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. When a component is referred to as being “connected” or “connected” to another component, it is understood that it may be directly connected or connected to the other component, but other components may exist in the middle. It should be.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가지고 있다. Unless otherwise defined, all terms used herein including technical or scientific terms have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention belongs.
일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가지는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다. Terms such as those defined in a commonly used dictionary should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the meaning in the context of the related technology, and should not be interpreted as an ideal or excessively formal meaning unless explicitly defined in the present application. Does not.
이하, 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 첨부된 도면을 사용하여 더욱 구체적으로 설명한다.Hereinafter, the technical idea of the present invention will be described in more detail using the accompanying drawings.
첨부된 도면은 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 더욱 구체적으로 설명하기 위하여 도시한 일예에 불과하므로 본 발명의 기술적 사상이 첨부된 도면의 형태에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The accompanying drawings are only an example illustrated to describe the technical idea of the present invention in more detail, so the technical idea of the present invention is not limited to the form of the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 일실시에에 따른 모니터링 시스템을 도시한 구성도로서, 도 1을 참조하면, 상기 모니터링 시스템(1000)은, 레이저어닐링장비(100), 검출부(200) 및 모니터링부(300)를 포함하여 구성될 수 있으며, 상기 레이저어닐링장비(100)는 피가공물(1)의 표면상에 공정용레이저빔(L1)을 조사하여, 상기 피가공물(1) 표면에서의 열처리를 수행하기 위한 구성으로서, 더욱 자세하게는 제1파장을 갖는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 사출하는 고정된 제1레이저발진기(110)와, 상기 고정된 제1레이저발진기(110)로부터 인가받은 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 편향시키기 위한 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122) 및 상기 가변미러(121, 122)를 통해 반사 및 굴절되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 초점을 모으기 위한 스캐닝렌즈(123, Scanning lens)를 포함하는 스캐너부(120)를 포함하여 구성될 수 있으며, 상기 스캐너부(120)는 반응부(S)의 이동을 병행하지 않고 광신호(R1)를 수집이 가능하여 레이저 어닐링 장비의 공정 속도의 저하를 방지함과 동시에 실시간 온도 모니터링이 가능한 장점이 있다.1 is a configuration diagram showing a monitoring system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, the
여기에서, 상기 가변미러(121, 122)는 인가되는 레이저빔을 반사시키기 위한 반사경(mirror)를 회전시키기 위한 스텝모터가 설치되어, 반사경의 각도를 미세조정함으로써, 인가되는 레이저빔이 편향(偏向)되도록 반사시키게 된다. 이때, 상기 가변미러(121, 122)는 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면으로 조사되는 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 2차원(x,y축) 평면상에서 이동시키기 위하여 한 쌍으로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하며, 이때 소정거리 이격된 두 개의 가변미러(121, 122)의 각도 변화(모터의 회전)시에, 상기 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122) 사이의 거리가 미세하게 변화하게 되고, 이에 따라 상기 피가공물(1)에 조사되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 굴절에 따른 상면만곡 수차(Pinchusion distortion)가 발생함에 따라서, 조사되는 반응부(SPOT)의 중심으로 초점이 모아지지 않아, 원하는 지름의 반응부(SPOT)를 형성할 수 없어, 이에 따른 에너지 밀도가 저하되어 정밀 가공을 할 수 없는 문제가 발생하게 된다. 이때, 상기 스캐닝렌즈(123)는 평면을 이루는 상기 피가공물의 표면에 초점을 모으기 위한 다양한 스캐닝렌즈로 이루어질 수 있으나, 갈바노미터(galvaometer or galvo)로 이루어지는 상기 가변미러(121, 122)의 정밀한 제어를 위하여, 상기 스캐닝렌즈(123)는 초점거리와 굴절각도의 곱이 렌즈와 피가공물(1)과의 거리를 이루는 F-theta lens로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하다. 또한, 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)는 특정 파장에서 이들을 얻을 수 있는 원소가 첨가되어 있는 광섬유를 이득 매질로 사용하여 공진기를 구성한 광섬유 레이저로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하나, 이때 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)를 상술한 구성으로 한정하는 것은 아니며, 본 발명의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 조사하기 위한 다양한 방식으로 구성될 수 있다.Here, the variable mirrors 121 and 122 are provided with a step motor for rotating a reflector for reflecting the applied laser beam, and by finely adjusting the angle of the reflector, the applied laser beam is deflected. ) To be reflected. At this time, the variable mirrors 121 and 122 are preferably made of a pair to move the process laser beam L1 irradiated to the surface of the
< 본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템의 공정온도(T) 검출 방법 ><Process temperature (T) detection method of the temperature monitoring system of the present invention>
본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템(1000)은, 스캐너 타입의 상기 레이저 어닐링 장비(100)에서 고속으로 미세하게 변화하는 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122)의 동작에 독립되어, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 온도를 검출하기 위한 것을 주된 목적으로 하며, 바람직하게는 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 진행하는 빛의 경로 상에 구비되어, 상기 제1파장을 갖는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)만을 투과시키는 제1광학필터(210) 및 상기 제1광학필터로부터 반사된 반사광의 광신호(R1)의 세기를 검출하는 제1포토센서(270)를 포함하는 검출부(200)를 더 포함하여 구성될 수 있다. 여기에서, 상기 제1광학필터(210)는 특정 파장을 갖는 빛은 투과시키며, 이외의 파장을 갖는 빛은 반사하는 다이크로익 미러(Dichroic mirror)로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하며, 이때 상기 제1광학필터(210)는 본 발명의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 박막필터, 간섭필터 또는 이색 반사 미러 등의 다양한 광학필터(optical Filter) 등으로 변형 실시 가능할 것이다.The
즉, 상기 검출부(200)는 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 구비되는 제1광학필터(210)를 통해, 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면에 조사되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사된 반응부(S)의 발열에 의해 발산되는 광신호(R1)의 세기를 측정함으로써, 상기 스캐너부(120)의 가변미러(121, 122)의 동작을 간섭하지 않으면서, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 온도를 검출할 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템(1000)은 상기 제1포토센서(270)로부터 검출된 상기 광신호(R1)의 세기에 따른 반응부(S)의 온도(T)를 산출하는 온도산출부(310)를 포함하는 모니터링부(300)를 더 포함하여 이루어지며, 이때 상기 온도산출부(310)는 하기의 식 1을 통해 상기 공정온도(T)를 산출한다.That is, the
식 1 : Equation 1:
{여기에서, I : 제1포토센서에서 감지된 광신호(R1)의 세기, h : plank 상수, c : 빛의 속도, v : 빛의 주파수, : 볼츠만상수, T : 반응부의 온도 이다.}{Here, I: intensity of the optical signal (R1) detected by the first photosensor, h: plank constant, c: speed of light, v: frequency of light, : Boltzmann constant, T: It is the temperature of the reaction part.}
여기에서, 상기 검출부(200)는 상기 제1포토센서(270)에 특정 파장의 신호만을 투과시키는 제2광학필터(260)을 더 포함하여 구성될 수 있으며, 일반적으로 상기 공정온도(T)는 1000 ~ 2000℃의 범위에서 이루어짐에 따라서, 상기 제2광학필터(260)에서 투과되는 파장(λ)은 복사량이 높은 적외선 파장(1㎛ < λ < 2㎛)을 갖는 것이 바람직하다. Here, the
또한, 본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템(1000)은 상기 검출부(200)에서의 공정온도(T)에 정밀도를 더욱 향상시키기 위하여, 상기 검출부(200)는 서로 다른 파장의 광신호(R1)를 검출하는 복수의 제1포토센서(271, 272) 및 상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 인가된 광신호(R1)를 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(271, 272)로 각기 분열시키는 빔스플리터(240)를 더 포함하며, 상기 온도산출부(310)는 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(271, 272)로부터 측정된 광신호(R1)에 따른 온도들의 평균값을 공정온도(T)로 정의함으로써, 하나의 반응부(S)에서 발산된 하나의 광신호(R1)의 각기 다른 파장에서의 빛의 세기에 따른 온도를 산출하고, 산출된 복수의 온도들에 평균값을 산정함으로써, 산출된 공정온도(T)의 정밀도를 더욱 향상 시킬 수 있다.In addition, the
더욱 자세하게는, 상기 검출부(200)는 상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 발산된 광신호(R1)를 집광하는 제1집광렌즈(220)와, 상기 제1집광렌즈(220)로부터 전달받은 광신호(R1)가 발산하지 않고 평행하게 전파되도록 하는 빔익스팬더(230, beam expander), 상기 빔익스팬더(210)를 통과한 광신호(R1)를 인가받아 각기 동일한 세기를 갖는 복수로 분열시키는 빔스플리터(240, beam splitter)와, 상기 빔스플리터(240)를 지나 각기 분열된 광신호(R1)를 집광하는 제2집광렌즈(250), 상기 제2집광렌즈(250)를 투과한 광신호(R1)에서 특정 파장의 광신호(R1)만을 투과 하는 제2광학필터(260) 및 상기 제2광학필터(260)로부터 인가받은 광신호(R1)의 세기를 검출하는 복수의 제1포토센서(271, 272)로 이루어지며, 이때 검출하는 파장의 개수 즉, 상기 제1포토센서(270)의 개수는 본 발명의 요지에 벗어남이 없이 본 발명의 규격 및 요구하는 정밀도에 따라 다양하게 변형실시 될 수 있을 것이다.In more detail, the
< 피가공물의 방사율(E)에 따른 공정온도(T)의 보정 ><Correction of the process temperature (T) according to the emissivity (E) of the workpiece>
전술한 바와 같이, 본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템(1000)은, 피공정물(1)의 반응부(S)에서의 방사열에 따른 공정온도(T)를 검출하는 비접촉식 검출법을 갖는 것을 특징으로 하며, 이때 상기 피공정물(1)이 1의 방사율(E, Emissivity)을 갖는 Black Body(이론적으로, 모든 파장의 빛을 완벽하게 흡수하는 물체)로 이루어진다면, 상기 반응부(S)에서 방출되는 광신호(R1)의 세기를 이용하여 산출된 온도를 반응부(S)의 실제온도로 정의할 수 있으나, 자연계 대부분의 경우에는 실제 방사율(E)이 1 미만의 값을 가짐으로써, 보다 정확한 공정온도(T)를 산출하기 위해서는, 상기 피공정물(1)의 정확한 방사율(E) 값을 실시간으로 계측하여, 상기 공정온도(T)를 보정하여야 한다.As described above, the
이때, 상기 방사율(E)은 키르히로프 법칙(Kirchoff's law)에 따른 하기의 식 2에 관계식을 갖는다.At this time, the emissivity (E) has a relational expression in Equation 2 below according to Kirchoff's law.
식 2 : Equation 2:
{여기에서, E : 방사율(Emissivity), r : 반사율(Reflectivity) 및 t : 투과율(Transmissivity) 이다.}{Here, E: Emissivity, r: Reflectivity, and t: Transmissivity.}
즉, 상기 식 2에 따른 방사율(E)을 산출하기 위해서는 상기 피공정물(1)에서의 반사율(r) 및 투과율(t)을 측정하여야 하며, 일반적으로 반도체 공정에 사용되는 실리콘 웨이퍼(Si Wafer)의 경우, 히터를 이용하여 웨이퍼에 전체면적을 가열하게 되고, 이때 900℃ 이상의 고온에서는 실리콘의 광학적 흡수율(absorption coefficient)이 매우 높아져, 투과되는 빛을 정확히 측정하기 어렵기 때문에, 특정 두께 이상의 웨이퍼들의 경우, 상기 식 2의 투과율(t)은 0으로 특정하여 계산하는 것이 바람직하다.That is, in order to calculate the emissivity (E) according to Equation 2, the reflectance (r) and transmittance (t) of the workpiece (1) must be measured. ), the entire area of the wafer is heated by using a heater. At this time, the optical absorption coefficient of silicon becomes very high at a high temperature of 900°C or higher, making it difficult to accurately measure the transmitted light. Therefore, wafers with a specific thickness or more In the case of, it is preferable to calculate the transmittance (t) of Equation 2 by specifying 0.
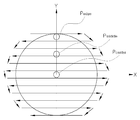
도 2는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 모니터링부의 작동을 도시한 예시도이고, 도 3은 일반적인 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 공정순서를 도시한 예시도로서, 도 1 내지 도 3을 참조하면, 본 발명의 온도 모니터링 시스템(1000)은 상기 피가공물(1)에 표면상의 임의의 한 지점(P)에 제2파장을 갖는 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)을 사출하는 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 반사된 반사광(R2)의 세기를 검출하는 제2포토센서(420)를 포함하는 방사율측정부(400)를 더 포함하여 구성될 수 있다. 이때 상기 모니터링부(300)는 상기 방사율측정부(400)로부터 검출된 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기로부터 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)을 산출하는 방사율산출부(320)를 더 포함하고, 상기 온도산출부(310)는 상기 방사율산출부(320)에서 산출된 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)에 따라 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정한다. 여기에서, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)은 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)과 상이한 파장을 이루는 것이 바람직하며, 더욱 바람직하게는 600 ~ 700 nm 파장을 이용할 수 있다. 즉, 반사된 모니터링용 레이저빔(R2)이 향하는 곳에 상기 제2포토센서(420)를 위치시키고, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 반사된 반사광(R2)의 세기를 측정할 수 있다. 이때, 상기 방사율산출부(320)은 측정된 값을 상기 공정용레이저빔(L1)의 입사 전, 상기 모니터링 레이저빔(L2)의 반사광(R2)의 세기와 비교하여 반사율(R)을 산출 할 수 있다. 더욱 자세하게는, 도 2의 (b)에 도시된 바와 같이, 입사된 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 간섭에 의해 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 반사되는 세기(R2)가 감소하게 되고, 이때, 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기가 최소가 되는 지점(min)에서의 빔의 세기와 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)에 따른 반사광(R2)의 세기가 일정한 지점을 비교하여 상기 피가공물(1)의 반사율(r)을 산출할 수 있으며, 이때 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기가 최소(min)가 되는 시점은 상기 반응부(S)가 가열된 온도의 최고점이 되는 시점으로, 상기 피가공물(1)의 반사율(r)값은 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 입사되기 전의 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기 대비 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기가 최소가 된 시점에서의 반사광(R2)의 세기의 비율에 대응된다.2 is an exemplary diagram showing the operation of a monitoring unit according to an embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 3 is an exemplary diagram showing a process sequence of a general process laser beam L1, referring to FIGS. 1 to 3 , The
더하여, 상기 피가공물(1)이 투명하거나, 특정 두께 이하로 매우 얇게 이루어질 경우, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 투과되는 위치에서 투과광을 검출하는 별도의 포토센서(미도시)를 구비하여, 측정된 투과율(T) 값을 고려하여 상기 식 2에 따른 방사율(E)값을 구하는 것이 바람직할 것이다.In addition, when the
이때, 상기 방사율산출부(320)는 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)과 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 피가공물(1)에 같은 지점(S, P)을 지나는 순간 반사된 모니터링 레이저빔(L2)의 반사광(R2)의 세기에 따른 방사율(E)을 산출하는 것이 바람직하며, 더욱 바람직하게는 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 최초 조사되는 상기 피가공물(1)의 최선단(P_edge)에서의 방사율(E)을 산출함으로써, 공정이 시작된 피가공물(1)에 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 최초 조사되는 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정할 수 있다.At this time, the
더하여, 상기 방사율측정부(400)는 상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)가 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면과 평행하는 어느 한 평면(xy)상에서 이동 가능하도록 구성되는 구동부(430)를 더 포함하여, 어느 하나의 피가공물(1)의 공정을 진행하는 동안, 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 이동에 대응하여 상기 반응부(S)에서의 방사율(E)을 실시간으로 검출할 수 있다. 즉 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사되는 반응부(S)의 위치정보와 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 조사되는 지점(P)의 위치정보는 연동되어, 상기 방사율측정부(400)의 이동을 제어하는 것이 바람직하다. 다만, 상기 방사율측정부(400)의 구동부(430)를 이동 가능한 스테이지 혹은 겐트리(Gantry)시스템을 이용할 경우에는 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 편향속도에 대응하기 어렵다는 한계가 발생하게 된다.In addition, the
즉, 본 발명의 구동부(430)는 상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)를 상기 피가공물(1)의 중심(Center)을 지나는 어느 일직선상을 따라 이동하도록 작동되되, 상기 제2레이저발진기(410)로부터 조사되는 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)과 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사되는 반응부(S)가 일치되는 적어도 둘 이상의 지점(P)을 측정하고,상기 방사율산출부(320)는 측정된 각각의 지점(P)에서 검출된 빛의 세기의 최소값(min)을 선정하여 상기 피가공물의 방사율(E)을 결정함으로써, 상기 구동부(430)의 이동속도의 한계를 극복할 수 있다. 더욱 자세하게는, 도 4에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)은 피가공물(1)의 최선단의 모서리(P_edge)를 조사하도록 위치하고(a), 이후 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 상기 최선단의 모서리(P_edge)를 지날 경우, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)는 피가공물(1)의 중심방향으로 소정거리 이동하여 대기한다(b).{여기에서, 상기 모니터리용 레이저빔(L2)이 이동하는 거리는 피가공물(1)의 산포도를 고려하여 적절하게 산정되는 것이 바람직하며, 본 발명에서는 최선단의 모서리(P_edge), 중심점(P_center) 및 중간 지점(P_middle)을 포함하여 설명하기로 한다.} 이때, 상기 최선단의 모서리(P_edge)부터 중간 지점(P_middle)까지 진행하는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 공정온도(T)는 상기 최선단의 모서리(P_edge)에서 산출된 방사율(E)을 이용하여 보정하며, 이후 상기 중간 지점(P_middle)에서 재 측정된 반사율(r_middle)의 최저점(min_middle)이 기존에 측정된 반사율(r_edge)의 최저점(min_edge) 보다 적을 시에는, 상기 재 측정된 반사율(r_middle)에 따른 방사율(E)을 이용하여, 측정된 공정온도(T)를 보정한다. 이후 (c)-(d)의 과정에서는 전술한 (a)-(b)에 일련의 과정을 반복하며, 이때, 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 피가공물(1)의 중심점(P_center)을 지난 후, 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)은 상기 최선단의 모서리(P_edge) 위치로 이동하여, 다음 공정에 시작되는 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)의 측정을 위해 대기한다.That is, the driving
즉, 재 갱신되는 반사율(r)의 최저점(min)에 따른 오차율은 상기 피가공물의 산포도에 오차율에 기인되며, 이때, 상기 피가공물(1)의 산포도의 오차율에 대비하여, 반사율(r)에 임계치 이상의 차이가 발생할 경우, 해당 피가공물(1)의 레이저 열처리 공정 상의 불량으로 판단 할 수 있다.That is, the error rate according to the lowest point (min) of the re-updated reflectance (r) is due to the error rate in the scattering diagram of the workpiece, and in this case, compared to the error rate in the scattering diagram of the
이에 따라, 본 발명의 모니터링부(300)는 공정이 종료된 어느 하나의 피가공물(1)에 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T1)를 저장하는 메모리부(330) 및 공정을 시작하는 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)로부터 측정된 공정온도(T2)와 상기 메모리부(330)에 저장된 공정온도(T1) 프로파일을 비교하여, 상기 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)의 공정에서의 이상신호를 판단하는 불량판단부(340)를 더 포함하여, 보정된 온도 프로파일 중 이상점이 있을 경우 다음 웨이퍼의 공정을 중지하도록 레이저 어닐링 장비(100)를 제어하는 것이 바람직하다.Accordingly, the
본 발명은 상기한 실시예에 한정되지 아니하며, 적용범위가 다양함은 물론이고, 청구범위에서 청구하는 본 발명의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 다양한 변형 실시가 가능한 것은 물론이다.The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and of course, various modifications can be made without departing from the gist of the present invention as claimed in the claims.
1000 : 모니터링 시스템
100 : 레이어 어닐링 장비
110 : 제1레이저발진기 120 : 스캐너부
121, 122 : 가변미러 123 : 스캐닝렌즈
200 : 검출부
210 : 제1광학필터
220 : 제1집광렌즈 230 : 빔익스펜더
240 : 빔스플리터 250, 251, 252 : 제2집광렌즈
260, 261, 262 : 제2광학필터 270, 271, 272 : 제1포토센서
300 : 모니터링부
310 : 온도산출부 320 : 방사율산출부
330 : 메모리부 340 : 불량판단부
400 : 방사율 측정부
410 : 제2레이저발진기 420 : 제2포토센서
430 : 구동부
1 : 웨이퍼 S : 반응부
L1 : 공정용 레이저빔 R1 : 반응부에서 발산되는 광신호
L2 : 모니터링용 레이저빔 R2 : 모니터링용 레이저빔의 반사광
P : 모니터링 지점
P_e : Edge P_m : middle
P_c : Center1000: monitoring system
100: layer annealing equipment
110: first laser oscillator 120: scanner unit
121, 122: variable mirror 123: scanning lens
200: detection unit
210: first optical filter
220: first condensing lens 230: beam expander
240:
260, 261, 262: second
300: monitoring unit
310: temperature calculation unit 320: emissivity calculation unit
330: memory unit 340: defect determination unit
400: emissivity measuring unit
410: second laser oscillator 420: second photo sensor
430: drive unit
1: wafer S: reaction part
L1: Process laser beam R1: Optical signal emitted from the reaction section
L2: Monitoring laser beam R2: Reflected light of monitoring laser beam
P: monitoring point
P_e: Edge P_m: middle
P_c: Center
Claims (10)
상기 고정된 레이저발진기(110)로부터 인가받은 공정용 레이저빔(L1)을 편향시키기 위한 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122) 및 상기 한 쌍의 가변미러(121, 122)를 통해 반사 및 굴절되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)의 초점을 모으기 위한 스캐닝렌즈(123, Scanning lens)를 포함하되, 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사된 반응부(S)에서 발산되는 광신호(R1)을 수집하여, 반응부(S)의 이동을 병행하지 않고 광신호(R1)를 수집가능한 스캐너부(120); 및
상기 레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 진행하는 빛의 경로상에 구비되어, 상기 제1파장을 갖는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)만을 투과시키는 제1광학필터(210) 및 상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 반사된 광신호(R1)의 세기를 검출하는 제1포토센서(270)가 구비된 검출부(200);를 포함하고,
상기 검출부(200)는 상기 제1레이저발진기(110)와 스캐너부(120) 사이에 구비되는 제1광학필터(210)를 통해, 피가공물(1)의 표면에 조사되는 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사된 반응부(S)의 발열에 의해 발산되는 광신호(R1)의 세기를 측정함으로써, 상기 스캐너부(120)의 가변미러(121, 122)의 동작을 간섭하지 않으면서, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 온도를 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
A fixed first laser oscillator 110 for emitting a process laser beam L1 having a first wavelength;
Reflected and refracted through a pair of variable mirrors 121 and 122 for deflecting the process laser beam L1 applied from the fixed laser oscillator 110 and the pair of variable mirrors 121 and 122 Includes a scanning lens 123 (Scanning lens) for focusing the process laser beam L1, but collects the optical signal R1 emitted from the reaction part S irradiated with the process laser beam L1 Thus, the scanner unit 120 capable of collecting the optical signal (R1) without parallel movement of the reaction unit (S); And
The first optical filter 210 and the first optical filter 210 are provided on the path of light traveling between the laser oscillator 110 and the scanner unit 120 and transmit only the process laser beam L1 having the first wavelength. Including; a detection unit 200 provided with a first photosensor 270 for detecting the intensity of the optical signal (R1) reflected from the 1 optical filter 210,
The detection unit 200 is a process laser beam (L1) irradiated to the surface of the workpiece 1 through a first optical filter 210 provided between the first laser oscillator 110 and the scanner unit 120. ), by measuring the intensity of the optical signal R1 emitted by the heat generated by the irradiated reaction unit S, without interfering with the operation of the variable mirrors 121 and 122 of the scanner unit 120, the reaction The temperature monitoring system of the laser annealing equipment, characterized in that detecting the temperature in the part (S).
상기 제1포토센서(270)로부터 검출된 광신호(R1)의 세기에 따른 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 산출하는 온도산출부(310)가 구비된 모니터링부(300);를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 1,
A monitoring unit 300 including a temperature calculation unit 310 for calculating a process temperature T in the reaction unit S according to the intensity of the optical signal R1 detected from the first photosensor 270; Temperature monitoring system of the laser annealing equipment, characterized in that it further comprises.
상기 온도산출부(310)는 하기의 식을 통해 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
{ 여기에서,
I : 제1포토센서에서 감지된 광신호(R1)의 세기
h : plank 상수, c : 빛의 속도, v : 빛의 주파수, : 볼츠만상수,
T : 반응부의 온도 }
The method of claim 2,
The temperature calculation unit 310 is a temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment, characterized in that to calculate the process temperature (T) in the reaction unit (S) through the following equation.
{ From here,
I: intensity of the optical signal R1 detected by the first photosensor
h: plank constant, c: speed of light, v: frequency of light, : Boltzmann constant,
T: temperature of the reaction part}
상기 검출부(200)는,
서로 다른 파장의 광신호(R1)를 검출하는 복수의 제1포토센서(270), 및
상기 제1광학필터(210)로부터 인가된 광신호(R1)를 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(270)로 각기 분열시키는 빔스플리터(240)를 더 포함하며,
상기 온도산출부(310)는 상기 복수의 제1포토센서(270)로부터 측정된 광신호(R1)에 따른 온도들의 평균값을 공정온도(T)로 정의하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 2,
The detection unit 200,
A plurality of first photosensors 270 for detecting optical signals R1 of different wavelengths, and
Further comprising a beam splitter 240 for dividing the optical signal R1 applied from the first optical filter 210 by the plurality of first photosensors 270, respectively,
The temperature calculator 310 monitors the temperature of the laser annealing equipment, characterized in that the average value of the temperatures according to the optical signal R1 measured from the plurality of first photosensors 270 is defined as the process temperature T. system.
상기 피가공물(1)의 표면상에 임의의 한 지점(P)에 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)을 사출하는 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 상기 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 반사된 반사광(R2)의 세기를 검출하는 제2포토센서(420)가 구비된 방사율측정부(400);를 더 포함하되,
상기 모니터링부(300)는,
상기 방사율측정부(400)로부터 검출된 상기 반사광(R2)의 세기로부터 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)을 산출하는 방사율산출부(320)를 더 포함하고,
상기 온도산출부(310)는 산출된 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)에 따라 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 2,
A second laser oscillator 410 for emitting a monitoring laser beam L2 to an arbitrary point P on the surface of the workpiece 1 and the reflected light R2 from which the monitoring laser beam L2 is reflected. Including further; ), the emissivity measuring unit 400 provided with a second photosensor 420 for detecting the intensity of the,
The monitoring unit 300,
Further comprising an emissivity calculating unit 320 for calculating the emissivity E of the workpiece 1 from the intensity of the reflected light R2 detected by the emissivity measuring unit 400,
The temperature calculation unit 310 is a temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment, characterized in that correcting the process temperature (T) in the reaction unit (S) according to the calculated emissivity (E) of the workpiece (1) .
상기 방사율산출부(320)는,
상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)과 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)이 피가공물(1)에 같은 지점(S, P)을 지나는 순간 반사된 모니터링 레이저빔(L2)의 반사광(R2)의 세기에 따른 방사율(E)을 산출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 5,
The emissivity calculation unit 320,
According to the intensity of the reflected light R2 of the monitoring laser beam L2 that is reflected at the moment when the process laser beam L1 and the monitoring laser beam L2 pass the same point S, P on the workpiece 1 Temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment, characterized in that calculating the emissivity (E).
상기 모니터링부(300)는,
상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 최초 조사되는 상기 피가공물(1)의 최선단(P_edge)에서의 방사율(E)을 산출하여, 상기 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T)를 보정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 6,
The monitoring unit 300,
Compensating the process temperature (T) in the reaction unit (S) by calculating the emissivity (E) at the leading edge (P_edge) of the workpiece (1) to which the process laser beam (L1) is first irradiated. Temperature monitoring system of the laser annealing equipment, characterized in that.
상기 방사율측정부(400)는,
상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)가 상기 피가공물(1)의 표면과 평행하는 어느 한 평면상에서 이동 가능하도록 구성되는 구동부(430);를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 5,
The emissivity measurement unit 400,
The second laser oscillator 410 and the second photosensor 420 are configured to move on any one plane parallel to the surface of the workpiece (1); a driving unit (430); characterized in that it further comprises a. Temperature monitoring system for laser annealing equipment.
상기 구동부(430)는,
상기 제2레이저발진기(410) 및 제2포토센서(420)를 상기 피가공물(1)의 중심을 지나는 어느 일직선상을 따라 이동하도록 작동되되,
상기 방사율측정부(400)는,
상기 제2레이저발진기(410)로부터 조사되는 모니터링용 레이저빔(L2)과 상기 공정용 레이저빔(L1)이 조사되는 반응부(S)가 일치되는 적어도 둘 이상의 지점(P)을 측정하고,
상기 방사율산출부(320)는,
측정된 각각의 지점(P)에서 검출된 빛의 세기의 최소값(min)을 선정하여, 상기 피가공물(1)의 방사율(E)을 결정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method of claim 8,
The driving unit 430,
Operated to move the second laser oscillator 410 and the second photosensor 420 along a certain straight line passing through the center of the workpiece (1),
The emissivity measurement unit 400,
At least two points P at which the monitoring laser beam L2 irradiated from the second laser oscillator 410 and the reaction unit S irradiated with the process laser beam L1 coincide are measured,
The emissivity calculation unit 320,
A temperature monitoring system of a laser annealing equipment, characterized in that for determining the emissivity (E) of the workpiece (1) by selecting a minimum value (min) of the intensity of light detected at each measured point (P).
상기 모니터링부(300)는,
공정이 종료된 어느 하나의 피가공물(1)에 반응부(S)에서의 공정온도(T1)를 저장하는 메모리부(330), 및
공정을 시작하는 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)로부터 측정된 공정온도(T2)와 상기 메모리부(330)에 저장된 공정온도(T1) 프로파일을 비교하여, 상기 다른 하나의 피가공물(1)의 공정에서의 이상신호를 판단하는 불량판단부(340)를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 레이저 어닐링 장비의 온도 모니터링 시스템.
The method according to any one of claims 2 to 9,
The monitoring unit 300,
A memory unit 330 for storing the process temperature T1 in the reaction unit S in any one of the workpieces 1 at which the process has been completed, and
The process temperature (T2) measured from the other work piece (1) starting the process is compared with the process temperature (T1) profile stored in the memory unit 330, and the process of the other work piece (1) Temperature monitoring system of the laser annealing equipment, characterized in that it further comprises a defect determination unit 340 for determining an abnormal signal in the.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190105189A KR102258055B1 (en) | 2019-08-27 | 2019-08-27 | Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190105189A KR102258055B1 (en) | 2019-08-27 | 2019-08-27 | Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20210025319A KR20210025319A (en) | 2021-03-09 |
| KR102258055B1 true KR102258055B1 (en) | 2021-05-27 |
Family
ID=75179715
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190105189A KR102258055B1 (en) | 2019-08-27 | 2019-08-27 | Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102258055B1 (en) |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013092502A (en) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-16 | Jfe Steel Corp | Temperature measuring apparatus and emissivity measuring device |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20040031276A (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-13 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | laser annealing apparatus and method for crystallizing the using |
| US6747245B2 (en) * | 2002-11-06 | 2004-06-08 | Ultratech Stepper, Inc. | Laser scanning apparatus and methods for thermal processing |
| SG10201503482QA (en) * | 2012-06-11 | 2015-06-29 | Ultratech Inc | Laser annealing systems and methods with ultra-short dwell times |
| US10083843B2 (en) * | 2014-12-17 | 2018-09-25 | Ultratech, Inc. | Laser annealing systems and methods with ultra-short dwell times |
-
2019
- 2019-08-27 KR KR1020190105189A patent/KR102258055B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013092502A (en) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-16 | Jfe Steel Corp | Temperature measuring apparatus and emissivity measuring device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20210025319A (en) | 2021-03-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6284629B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining the focal position of a high energy beam | |
| CN111670345B (en) | Method and device for detecting the focal position of a laser beam | |
| JP2008119716A (en) | Laser beam machining apparatus, and focus maintaining method therein | |
| US8399808B2 (en) | Systems and methods for forming a time-averaged line image | |
| JP5459944B2 (en) | Surface shape measuring device, stress measuring device, surface shape measuring method and stress measuring method | |
| US20180283957A1 (en) | Apparatus and method to measure temperature of 3d semiconductor structures via laser diffraction | |
| TWI483296B (en) | Systems and methods for forming a time-averaged line image | |
| KR20130114131A (en) | Method for operating a projection exposure tool and control apparatus | |
| JP7308286B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining focal position of laser beam | |
| KR20160127461A (en) | Laser apparatus and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR102258055B1 (en) | Temperature monitoring system of laser annealing equipment | |
| US11878367B2 (en) | Optical device and article manufacturing method | |
| JP7308439B2 (en) | LASER PROCESSING DEVICE AND OPTICAL ADJUSTMENT METHOD | |
| JP7262081B2 (en) | LASER PROCESSING DEVICE AND OPTICAL ADJUSTMENT METHOD | |
| KR20130088916A (en) | Thickness measuring method using laser interferometer | |
| JP6727724B2 (en) | Wafer position measuring device and wafer position measuring method | |
| JP3386278B2 (en) | Measurement method and apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP4225121B2 (en) | Laser annealing method and apparatus | |
| JP2018081232A (en) | Optical lens and laser processing apparatus | |
| US20060285107A1 (en) | Method for sensing and controlling radiation incident on substrate | |
| US8093540B2 (en) | Method of focus and automatic focusing apparatus and detecting module thereof | |
| US20230011199A1 (en) | Process monitor and process monitoring method | |
| US20240219699A1 (en) | High-performance euv microscope device with free-form illumination system structure | |
| JP4419427B2 (en) | Method for controlling focal position of reticle inspection apparatus | |
| JPH11104873A (en) | Laser beam machining device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |