KR101897632B1 - Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same - Google Patents
Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101897632B1 KR101897632B1 KR1020170008015A KR20170008015A KR101897632B1 KR 101897632 B1 KR101897632 B1 KR 101897632B1 KR 1020170008015 A KR1020170008015 A KR 1020170008015A KR 20170008015 A KR20170008015 A KR 20170008015A KR 101897632 B1 KR101897632 B1 KR 101897632B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- compound
- organic
- light emitting
- group
- Prior art date
Links
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract 7
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 title claims description 13
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 94
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 28
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002346 layers by function Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 85
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 23
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 19
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 12
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 10
- 239000012153 distilled water Substances 0.000 description 10
- IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[4-(n-naphthalen-1-ylanilino)phenyl]phenyl]-n-phenylnaphthalen-1-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC=1)C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)C=C1 IBHBKWKFFTZAHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 10
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 8
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 7
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical group CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 6
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- NFHFRUOZVGFOOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium;triphenylphosphane Chemical compound [Pd].C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 NFHFRUOZVGFOOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000010898 silica gel chromatography Methods 0.000 description 5
- 125000004642 (C1-C12) alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229940093499 ethyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 235000019439 ethyl acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000006749 (C6-C60) aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000003983 fluorenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3CC12)* 0.000 description 3
- -1 heptylphenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 229940078552 o-xylene Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 125000004400 (C1-C12) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000000923 (C1-C30) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000006761 (C6-C60) arylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MEKOFIRRDATTAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,5,8-tetramethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol Chemical compound C1CC(C)(C)OC2=C1C(C)=C(O)C=C2C MEKOFIRRDATTAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OZAIFHULBGXAKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-cyanopropan-2-yldiazenyl)-2-methylpropanenitrile Chemical compound N#CC(C)(C)N=NC(C)(C)C#N OZAIFHULBGXAKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UJOBWOGCFQCDNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9H-carbazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=C1 UJOBWOGCFQCDNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YZCKVEUIGOORGS-OUBTZVSYSA-N Deuterium Chemical compound [2H] YZCKVEUIGOORGS-OUBTZVSYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ozone Chemical compound [O-][O+]=O CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 125000002252 acyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004305 biphenyl Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000006267 biphenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- ILAHWRKJUDSMFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N boron tribromide Chemical compound BrB(Br)Br ILAHWRKJUDSMFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940125904 compound 1 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052805 deuterium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- TXCDCPKCNAJMEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzofuran Chemical group C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 TXCDCPKCNAJMEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000004051 hexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 2
- CCERQOYLJJULMD-UHFFFAOYSA-M magnesium;carbanide;chloride Chemical compound [CH3-].[Mg+2].[Cl-] CCERQOYLJJULMD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940098779 methanesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 150000002825 nitriles Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001181 organosilyl group Chemical group [SiH3]* 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000000843 phenylene group Chemical group C1(=C(C=CC=C1)*)* 0.000 description 2
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000003003 spiro group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000859 sublimation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008022 sublimation Effects 0.000 description 2
- CAYQIZIAYYNFCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-chlorophenyl)boronic acid Chemical compound OB(O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 CAYQIZIAYYNFCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006750 (C7-C60) arylalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ICPSWZFVWAPUKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-spirobi[fluorene] Chemical group C1=CC=C2C=C3C4(C=5C(C6=CC=CC=C6C=5)=CC=C4)C=CC=C3C2=C1 ICPSWZFVWAPUKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-Diphenylbenzene Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IBXMKLPFLZYRQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-one;palladium Chemical compound [Pd].[Pd].C=1C=CC=CC=1C=CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 IBXMKLPFLZYRQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HULDTYWPYADGGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(2-bromo-3-methoxyphenyl)ethanone Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C(C)=O)=C1Br HULDTYWPYADGGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YOUSWNMOPSGTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(2-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl)ethanone Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(Br)C(C(C)=O)=C1 YOUSWNMOPSGTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzofuran Chemical group C1=CC=C2OC=CC2=C1 IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FCEHBMOGCRZNNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzothiophene Chemical group C1=CC=C2SC=CC2=C1 FCEHBMOGCRZNNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- FIPWRIJSWJWJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl carbitol 6-propylpiperonyl ether Chemical compound C1=C(CCC)C(COCCOCCOCCCC)=CC2=C1OCO2 FIPWRIJSWJWJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003860 C1-C20 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 0 CC1(*)c(c(-c2ccccc2)cc(-c2ccccc2)c2)c2-c2c(C)cccc12 Chemical compound CC1(*)c(c(-c2ccccc2)cc(-c2ccccc2)c2)c2-c2c(C)cccc12 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical group [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005103 alkyl silyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000304 alkynyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004984 aromatic diamines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000000319 biphenyl-4-yl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1C1=C([H])C([H])=C([*])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002529 biphenylenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C12)* 0.000 description 1
- IPWKHHSGDUIRAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(pinacolato)diboron Chemical compound O1C(C)(C)C(C)(C)OB1B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 IPWKHHSGDUIRAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000609 carbazolyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000392 cycloalkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- UZVGSSNIUNSOFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzofuran-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound O1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=C1C=CC=C2C(=O)O UZVGSSNIUNSOFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012467 final product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005283 ground state Effects 0.000 description 1
- MILUBEOXRNEUHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium(3+) Chemical class [Ir+3] MILUBEOXRNEUHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005647 linker group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004020 luminiscence type Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- YTIFDAAZLZVHIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphtho[1,2-g][1]benzofuran Chemical group C1=CC=C2C3=CC=C4C=COC4=C3C=CC2=C1 YTIFDAAZLZVHIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AICOOMRHRUFYCM-ZRRPKQBOSA-N oxazine, 1 Chemical compound C([C@@H]1[C@H](C(C[C@]2(C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)N(C)C)[C@H](O)C[C@]21C)=O)CC1=CC2)C[C@H]1[C@@]1(C)[C@H]2N=C(C(C)C)OC1 AICOOMRHRUFYCM-ZRRPKQBOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIBWKRNGBLPSSY-UHFFFAOYSA-L palladium(II) chloride Chemical compound Cl[Pd]Cl PIBWKRNGBLPSSY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- UQPUONNXJVWHRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium;triphenylphosphane Chemical compound [Pd].C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 UQPUONNXJVWHRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001792 phenanthrenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylbenzene Natural products C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- IEQIEDJGQAUEQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phthalocyanine Chemical compound N1C(N=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C(N=C3C4=CC=CC=C4C(=N4)N3)=N2)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1N=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C4=N1 IEQIEDJGQAUEQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960005235 piperonyl butoxide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 1
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003760 tallow Substances 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005580 triphenylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C211/00—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton
- C07C211/43—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton
- C07C211/57—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems of the carbon skeleton
- C07C211/61—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems of the carbon skeleton with at least one of the condensed ring systems formed by three or more rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C211/00—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton
- C07C211/43—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton
- C07C211/57—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems of the carbon skeleton
- C07C211/60—Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems of the carbon skeleton containing a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring forming part of at least one of the condensed ring systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/06—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing organic luminescent materials
-
- H01L51/006—
-
- H01L51/5012—
-
- H01L51/5056—
-
- H01L51/5088—
-
- H01L51/5096—
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/11—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/14—Carrier transporting layers
- H10K50/15—Hole transporting layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/17—Carrier injection layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/18—Carrier blocking layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/631—Amine compounds having at least two aryl rest on at least one amine-nitrogen atom, e.g. triphenylamine
- H10K85/633—Amine compounds having at least two aryl rest on at least one amine-nitrogen atom, e.g. triphenylamine comprising polycyclic condensed aromatic hydrocarbons as substituents on the nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2603/00—Systems containing at least three condensed rings
- C07C2603/02—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems
- C07C2603/04—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings
- C07C2603/06—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members
- C07C2603/10—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members containing five-membered rings
- C07C2603/12—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members containing five-membered rings only one five-membered ring
- C07C2603/18—Fluorenes; Hydrogenated fluorenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1003—Carbocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1011—Condensed systems
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
하기 화학식 a로 표시되는 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 유기화합물이 제공된다.
<화학식 a>
상기 식에서, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R, n, Ar, X 및 L은 전술하여 정의된 바와 같다.There is provided a diarylfluoreneamine derivative organic compound represented by the following formula (a).
<Formula a>
Wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R, n, Ar , X and L are as defined above.
Description
디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물 및 이를 포함하는 유기 전계 발광 소자에 관한 것이다.
Diarylfluoreneamine derivative compounds and organic electroluminescent devices comprising the same.
전계 발광 소자(electroluminescence device: EL device)는 자체 발광형 표시 소자로서 응답 속도가 빠르고, 시야각이 넓다는 장점을 가지고 있다. 1987년 이스트만 코닥(Eastman Kodak)사는 발광층 재료로서 저분자 방향족 디아민과 알루미늄 착물을 이용한 유기EL 소자를 처음으로 개발하였다[Appl. Phys. Lett. 51, 913, 1987].An electroluminescence device (EL device) is a self-emissive type display device having a high response speed and a wide viewing angle. In 1987, Eastman Kodak Company first developed an organic EL device using a low molecular aromatic diamine and an aluminum complex as a light emitting layer material [Appl. Phys. Lett. 51, 913, 1987].
유기 전계 발광 소자에서 발광 효율을 결정하는 가장 중요한 요인은 발광 재료인데, 발광 재료 중 인광 재료는 이론적으로 형광 재료 대비 4배까지 발광 효율을 개선시킬 수 있다. 현재까지 이리듐(III)착물 계열과 카바졸 계열의 재료들이 인광 발광 재료로 널리 알려져 있으며, 최근 새로운 인광 재료들이 연구되고 있다.The most important factor for determining the luminous efficiency in an organic electroluminescent device is a luminescent material. The phosphorescent material of the luminescent material can theoretically improve the luminous efficiency up to 4 times as compared with the fluorescent material. Until now, iridium (III) complexes and carbazole-based materials have been widely known as phosphorescent materials, and new phosphorescent materials are being studied in recent years.
유기 전계 발광 현상의 원리는, 음극과 양극 사이에 유기 박막층이 있을 때 두 전극 사이에 전압을 걸어주면 음극과 양극으로부터 각각 전자와 정공이 유기 박막층으로 주입된다. 유기 박막층으로 주입된 전자와 정공은 재결합하여 엑시톤 (exciton)을 형성하고, 이 엑시톤이 다시 바닥 상태로 떨어지면서 빛이 나게 된다. 이러한 원리를 이용하는 유기 전계 발광 소자는 일반적으로 음극과 양극 및 그 사이에 위치한 유기 박막층, 예컨대 정공주입층, 정공수송층, 발광층, 전자수송층을 포함하는 유기 박막층으로 구성될 수 있다.The principle of organic electroluminescent phenomenon is that when a voltage is applied between two electrodes when an organic thin film layer exists between a cathode and an anode, electrons and holes are injected into the organic thin film layer from the cathode and the anode, respectively. Electrons and holes injected into the organic thin film layer are recombined to form an exciton, and the exciton falls back to the ground state to emit light. An organic electroluminescent device using this principle can be generally constituted of an organic thin film layer including a cathode, an anode and an organic thin film layer disposed therebetween, for example, a hole injecting layer, a hole transporting layer, a light emitting layer, and an electron transporting layer.
유기 전계 발광 소자에서 사용되는 재료로는 순수 유기물 또는 유기물과 금속이 착물을 이루는 착화합물이 대부분을 차지하고 있으며, 용도에 따라 정공주입 재료, 정공수송 재료, 발광 재료, 전자수송 재료, 전자주입 재료 등으로 구분될 수 있다. 여기서, 정공주입 재료나 정공수송 재료로는 p-타입의 성질을 가지는 유기 재료, 즉 쉽게 산화가 되고 산화시에 전기화학적으로 안정한 상태를 가지는 유기물이 주로 사용되고 있다. 한편, 전자주입 재료나 전자수송 재료로는 n-타입 성질을 가지는 유기 재료, 즉 쉽게 환원이 되고 환원시에 전기화학적으로 안정한 상태를 가지는 유기물이 주로 사용되고 있다. 발광층 재료로는 p-타입 성질과 n-타입 성질을 동시에 가진 재료, 즉 산화와 환원 상태에서 모두 안정한 형태를 갖는 재료가 바람직하며, 엑시톤이 형성되었을 때 이를 빛으로 전환하는 발광 효율이 높은 재료가 바람직하다. 따라서, 당 기술 분야에서는 상기와 같은 요건을 갖춘 새로운 유기 재료의 개발이 요구되고 있다.
Most of materials used in organic electroluminescent devices are pure organic materials or complexes in which an organic material and a metal form a complex with each other. Depending on the application, a hole injecting material, a hole transporting material, a light emitting material, an electron transporting material, Can be distinguished. As the hole injecting material and the hole transporting material, an organic material having a p-type property, that is, an organic material which is easily oxidized and electrochemically stable at the time of oxidation, is mainly used. On the other hand, as an electron injecting material and an electron transporting material, an organic material having an n-type property, that is, an organic material which is easily reduced and electrochemically stable at the time of reduction is mainly used. As the light emitting layer material, a material having both a p-type property and an n-type property, that is, a material having both a stable state in oxidation and in a reduced state is preferable, and a material having a high luminous efficiency for converting an exciton into light desirable. Accordingly, there is a need in the art to develop new organic materials having the above-described requirements.
본 발명의 일 구현예는 적절한 에너지 준위, 전기화학적 안정성 및 열적 안정성을 가지는 신규한 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 제공한다.One embodiment of the present invention provides novel diarylfluoreneamine derivative compounds having appropriate energy levels, electrochemical stability, and thermal stability.
본 발명의 또 다른 구현예는 상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 포함하는 유기 전계 발광 소자를 제공한다.
Another embodiment of the present invention provides an organic electroluminescent device comprising the diarylfluorenamine derivative compound.
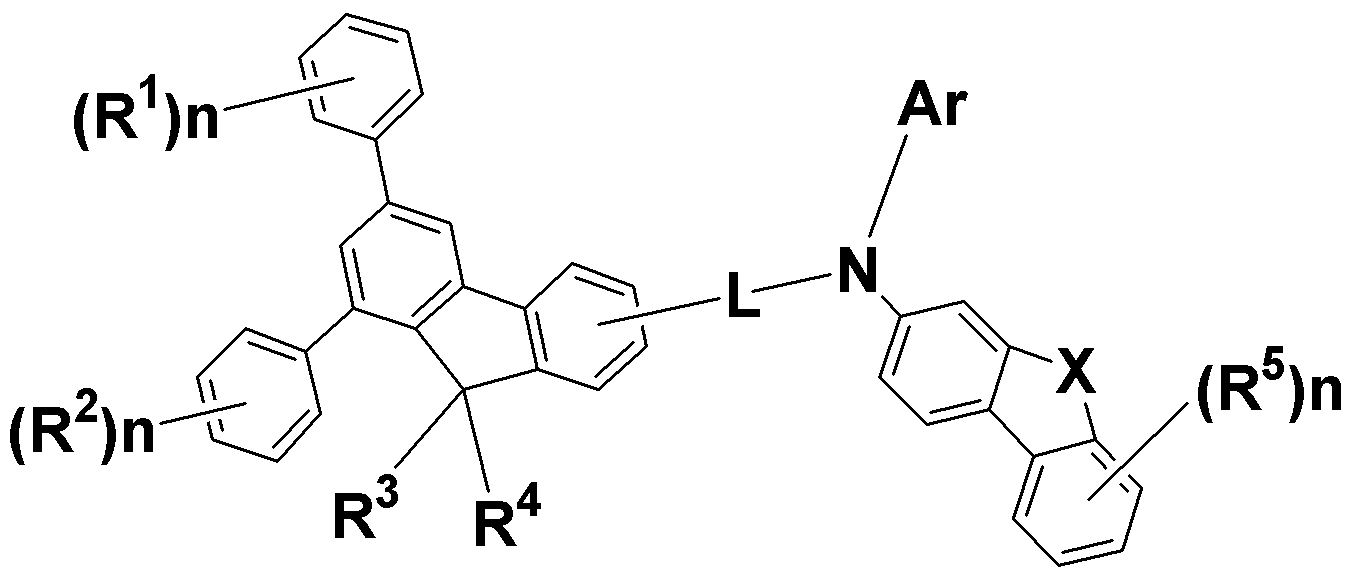
본 발명의 일 구현예에서, 하기 화학식 a로 표시되는 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 제공한다.In one embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a diarylfluoreneamine derivative compound represented by the following formula (a).
<화학식 a><Formula a>
상기 식에서, In this formula,
R1 내지 R5는, 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 중수소, 할로겐, C1~C12의 알콕시, 아미노, 니트릴, C2~C12의 아실, C3~C12의 실릴, 또는, 치환 또는 비치환된 C6~C60의 아릴기이고, 상기 R1 내지 R5는 서로 인접한 기와 연결되어 5원환 내지 6원환을 형성하면서 C5~C30의 축합고리를 형성할 수 있고, 상기 R1 내지 R5가 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1~C30의 알킬기, C1~C12의 알콕시기 또는 C6~C30의 아릴기이고,R 1 to R 5 each independently represent hydrogen, deuterium, halogen, C 1 to
n 은 서로 동일하거나 서로 상이한 0 내지 4의 정수이고,n is an integer of 0 to 4, which are the same as or different from each other,
L 은 단일결합이거나, 치환 또는 비치환된 C6~C60의 아릴렌 및 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 하나이고, 상기 L이 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1~C12의 알킬기, C1~C12의 알콕시기 또는 C6~C30의 아릴기이고,L is a single bond, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C60 arylene, or a combination thereof, and when L is substituted, the substituent may be a C1-C12 alkyl group, a C1-C12 alkoxy group Or a C6 to C30 aryl group,
X 는 O, S 또는 C(R)2 기이고, 상기 R은, 각각 독립적으로, C1~C6의 알킬 또는 C6~C60의 아릴기이고, 상기 두 개의 R은 서로 연결되어 스파이로 구조를 형성할 수 있고,X is an O, S or C (R) 2 group, each R is independently C1 to C6 alkyl or C6 to C60 aryl group, and the two Rs are connected to each other to form a spiro structure Can,
Ar 은 치환 또는 비치환된 C6-C60의 아릴기, 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 C3-C60의 헤테로아릴기이고, 상기 Ar 이 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1-C30의 알킬기, C6-C30의 아릴기 또는 C5~C30의 헤테로 아릴기이다.
Ar is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C60 aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted C3-C60 heteroaryl group, and when the Ar is substituted, the substituent is a C1-C30 alkyl group, a C6-C30 aryl group Or a C5-C30 heteroaryl group.
본 발명의 다른 구현예에서, 음극과 양극 사이에 적어도 하나의 유기 박막층이 협지되어 있는 유기 전계 발광 소자에 있어서, 상기 유기 박막층은 적어도 하나의 발광층을 포함하는 다층 구조이고, 상기 발광층 또는 상기 발광층 이외의 상기 유기 박막층 내의 적어도 하나의 층이 상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 단독 또는 2종 이상의 혼합물을 포함하는 유기 전계 발광 소자를 제공한다.
In another embodiment of the present invention, at least one organic thin film layer is sandwiched between a cathode and an anode, wherein the organic thin film layer has a multilayer structure including at least one light emitting layer, and the light emitting layer or the light emitting layer Wherein at least one layer in the organic thin film layer comprises the diarylfluorene amine derivative compound alone or a mixture of two or more thereof.
상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물은 유기 전계 발광 소자에서 사용 가능한 물질에 요구되는 조건, 예컨대 적절한 에너지 준위, 전기화학적 안정성 및 열적 안정성 등을 모두 우수하게 만족시킬 수 있으며, 치환기에 따라 유기 전계 발광 소자에서 요구되는 다양한 역할을 할 수 있다.
The diarylfluorene amine derivative compound can satisfactorily satisfy conditions required for a material usable in an organic electroluminescent device, for example, an appropriate energy level, an electrochemical stability, and a thermal stability, and the organic electroluminescent device Can play a variety of roles as required by < RTI ID = 0.0 >
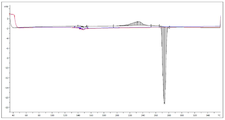
도 1 은 화합물 6의 1H-NMR 측정 결과이다.
도 2 는 화합물 6의 DSC 측정 결과이다.Fig. 1 shows the 1H-NMR measurement results of Compound 6. Fig.
2 shows the results of DSC measurement of Compound 6.
이하, 본 발명의 구현예를 상세히 설명하기로 한다. 다만, 이는 예시로서 제시되는 것으로, 이에 의해 본 발명이 제한되지는 않으며 본 발명은 후술할 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다. Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail. However, the present invention is not limited thereto, and the present invention is only defined by the scope of the following claims.
본 명세서에서 "치환"된 경우는 별도의 정의가 없는 한, C1-C50의 알킬기, C3-C50의 시클로알킬기, C2-C50의 알케닐기, C3-C50의 시클로알케닐기, C2-C50의 알키닐기, C5-C50의 시클로알키닐기, 시아노기, C1-C20의 알콕시기, C3-C50의 알킬실릴기, C6-C60의 아릴기 및 C7-C60의 아릴알킬기 및 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 치환기로 치환된 경우를 포함한다.Unless defined otherwise, the term "substituted" in the present specification means a C1-C50 alkyl group, a C3-C50 cycloalkyl group, a C2-C50 alkenyl group, a C3-C50 cycloalkenyl group, a C2-C50 alkynyl group , A C5-C50 cycloalkynyl group, a cyano group, a C1-C20 alkoxy group, a C3-C50 alkylsilyl group, a C6-C60 aryl group and a C7-C60 arylalkyl group, . ≪ / RTI >
본 명세서에서 "이들의 조합"이란 별도의 정의가 없는 한, 둘 이상의 치환기가 연결기로 결합되어 있거나, 둘 이상의 치환기가 축합하여 결합되어 있는 것을 의미한다. In the present specification, the term "combination thereof" means that two or more substituents are bonded to each other via a linking group or two or more substituents are condensed and bonded.
본 명세서에서 "헤테로"란 별도의 정의가 없는 한, 하나의 화합물 또는 치환기 내에 헤테로 원자를 포함함을 의미하고, 상기 헤테로 원자는 N, O, S, P 및 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 하나일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 하나의 화합물 또는 치환기 내에 헤테로 원자를 1 내지 3 포함하고, 나머지는 탄소인 경우를 의미할 수 있다.
"Hetero" as used herein, unless otherwise defined, means containing a heteroatom in one compound or substituent, wherein the heteroatom is selected from the group consisting of N, O, S, P, Lt; / RTI > For example, it may mean one to three heteroatoms in the one compound or substituent, and the remainder is carbon.
본 발명의 일 구현예에서, 신규한 하기 화학식 a로 표시되는 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 제공한다.In one embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a novel diarylfluorenamine derivative compound represented by the following formula (a).
<화학식 a><Formula a>
R1 내지 R5는, 각각 독립적으로, 수소, 중수소, 할로겐, C1~C12의 알콕시, 아미노, 니트릴, C2~C12의 아실, C3~C12의 실릴, 또는, 치환 또는 비치환된 C6~C60의 아릴기이고, 상기 R1 내지 R5는 서로 인접한 기와 연결되어 5원환 내지 6원환을 형성하면서 C5~C30의 축합고리를 형성할 수 있고, 상기 R1 내지 R5가 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1~C30의 알킬기, C1~C12의 알콕시기 또는 C6~C30의 아릴기이고,R 1 to R 5 each independently represent hydrogen, deuterium, halogen, C 1 to
n 은 서로 동일하거나 서로 상이한 0 내지 4의 정수이고,n is an integer of 0 to 4, which are the same as or different from each other,
L 은 단일결합이거나, 치환 또는 비치환된 C6~C60의 아릴렌 및 이들의 조합으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 하나이고, 상기 L이 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1~C12의 알킬기, C1~C12의 알콕시기 또는 C6~C30의 아릴기이고,L is a single bond, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C60 arylene, or a combination thereof, and when L is substituted, the substituent may be a C1-C12 alkyl group, a C1-C12 alkoxy group Or a C6 to C30 aryl group,
X 는 O, S 또는 C(R)2 기이고, 상기 R은, 각각 독립적으로, C1~C6의 알킬 또는 C6~C60의 아릴기이고, 상기 두 개의 R은 서로 연결되어 스파이로 구조를 형성할 수 있고,X is an O, S or C (R) 2 group, each R is independently C1 to C6 alkyl or C6 to C60 aryl group, and the two Rs are connected to each other to form a spiro structure Can,
Ar 은 치환 또는 비치환된 C6-C60의 아릴기, 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 C3-C60의 헤테로아릴기이고, 상기 Ar 이 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1-C30의 알킬기, C6-C30의 아릴기 또는 C5~C30의 헤테로 아릴기이다.
Ar is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C60 aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted C3-C60 heteroaryl group, and when the Ar is substituted, the substituent is a C1-C30 alkyl group, a C6-C30 aryl group Or a C5-C30 heteroaryl group.
구체적으로, 치환 또는 비치환된 페닐렌기, 치환 또는 비치환된 비페닐렌기, 치환 또는 비치환된 나프탈렌기 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오렌기이고, 상기 L이 치환된 경우의 치환기는 C1-C12의 알킬기, C1-C12의 알콕시기 또는 C6-C30의 아릴기이다.Specifically, a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene group, a substituted or unsubstituted biphenylene group, a substituted or unsubstituted naphthalene group or a substituted or unsubstituted fluorene group, and when L is substituted, the substituent is C1-C12 An alkyl group of C1-C12, an alkoxy group of C1-C12 or an aryl group of C6-C30.
더욱 구체적으로, Ar은 페닐기, 중수소페닐기, 나프틸기, 비페닐기, 페난트렌기, 플루오렌기, 스파이로플루오렌기, 벤조티오펜기, 벤조퓨란기, 디벤조퓨란기, 디벤조티오펜기, 나프토벤조퓨란기, 터페닐기, 카바졸기 또는 트리페닐렌기일 수 있다.
More specifically, Ar represents a phenyl group, a heptylphenyl group, a naphthyl group, a biphenyl group, a phenanthrene group, a fluorene group, a spirobifluorene group, a benzothiophene group, a benzofuran group, a dibenzofurane group, , A naphthobenzofuran group, a terphenyl group, a carbazole group or a triphenylene group.
구체적으로, 상기 L 이 페닐렌기인 경우 치환 위치는 1,4 치환 이거나 1,2 치환일 수 있다.
Specifically, when L is a phenylene group, the substitution position may be 1,4-substituted or 1,2-substituted.
일 구현예에서, 상기 화학식 a는 하기 화학식 b 내지 화학식 c로 표시될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the formula (a) may be represented by the following formulas (b) to (c).
<화학식 b><Formula b>
<화학식 c><Formula c>
상기 화학식 b 또는 c 에서,In the above formula (b) or (c)
R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R, n, Ar, X, L는, 상기 화학식 a 에서 정의된 바와 같다.
R 1, R 2, R 3, R 4, R 5, R 6, n, Ar , X and L are as defined in Formula a above.
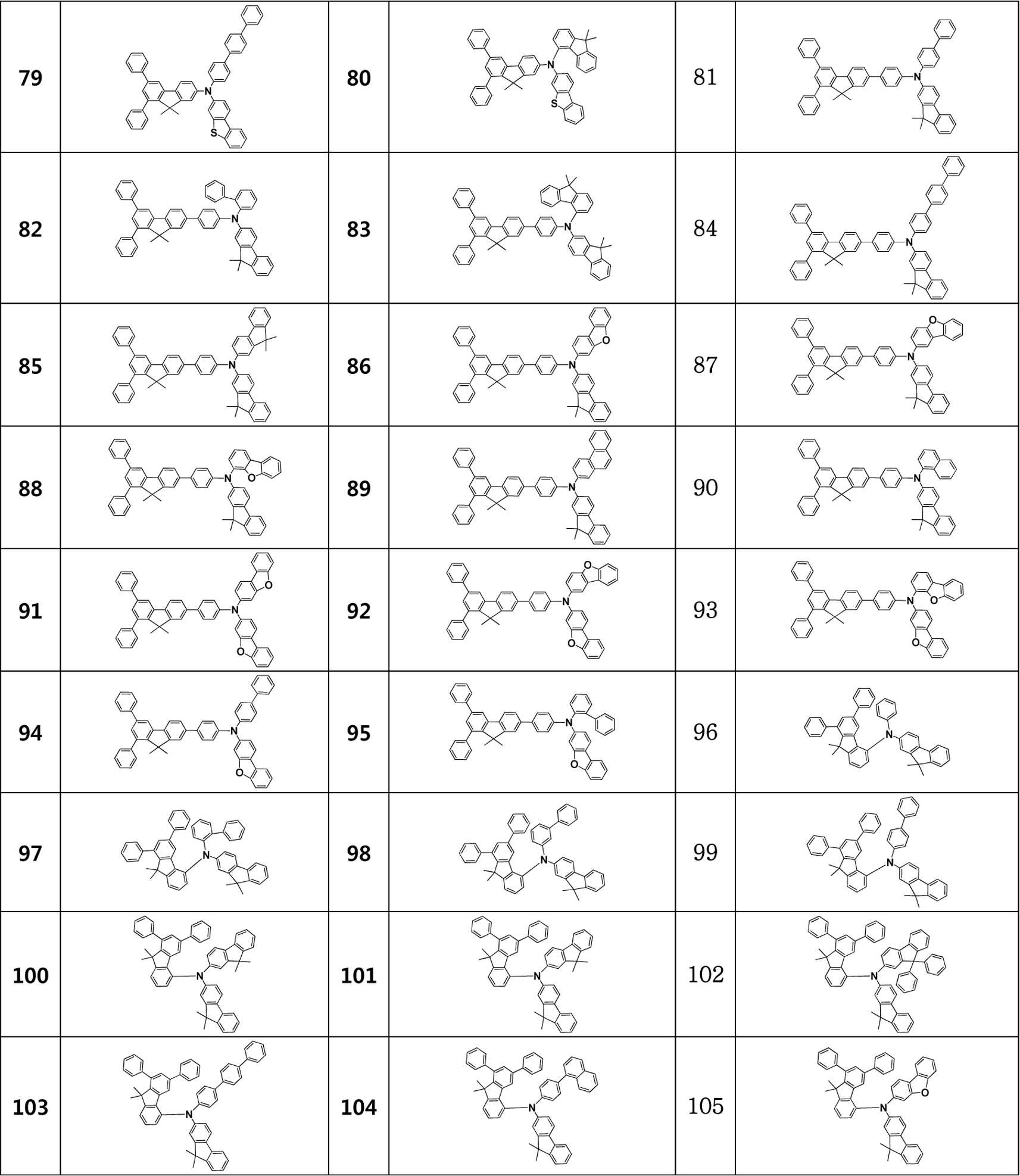
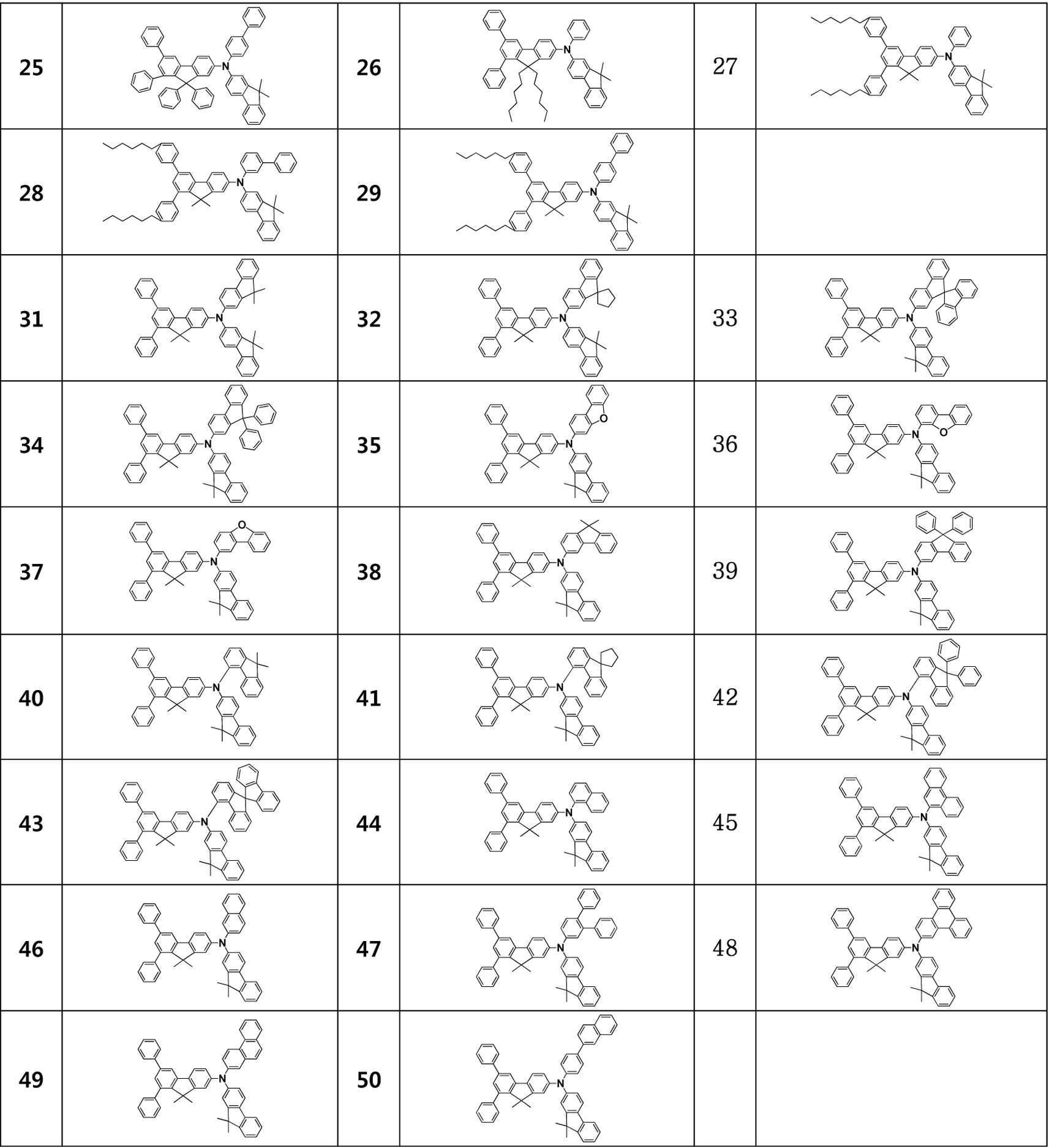
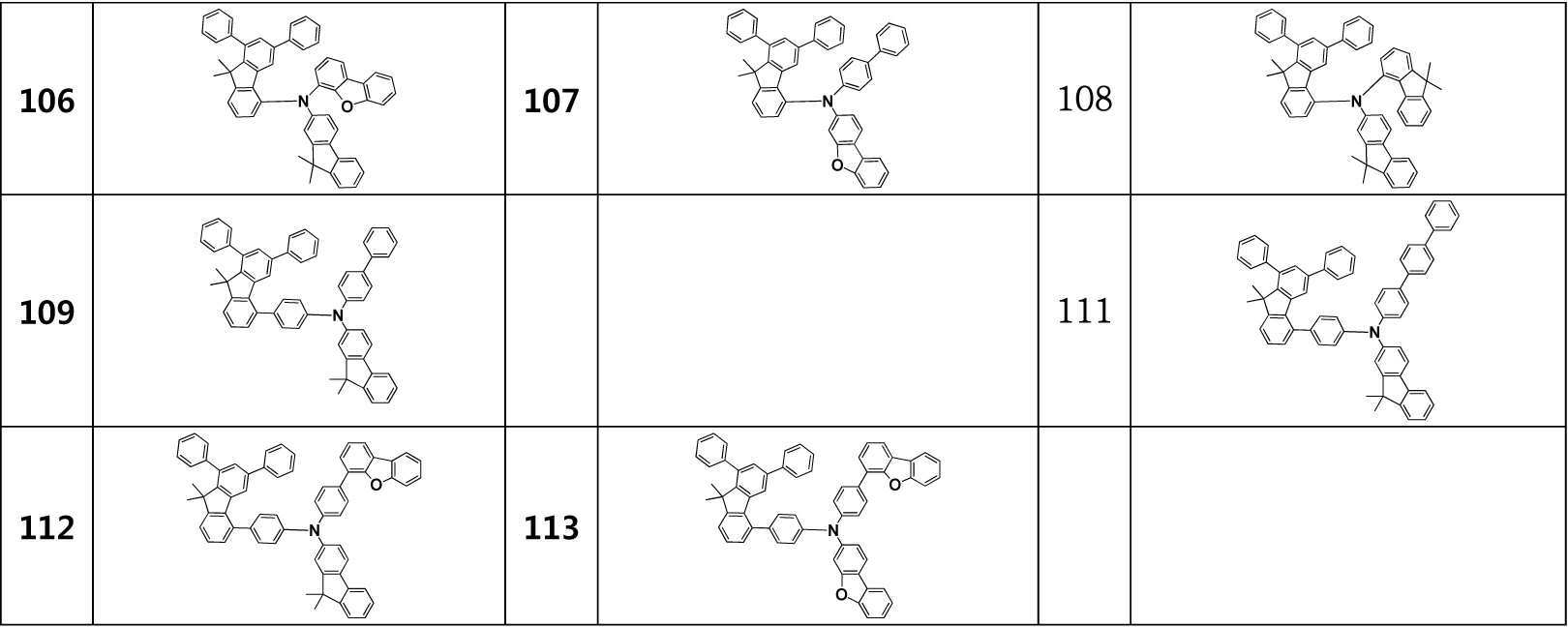
예를 들어, 상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물은 하기 표 1에 기재된 1 내지 113 중의 어느 하나의 화합물일 수 있다.
For example, the diarylfluoreneamine derivative compound may be any one of compounds 1 to 113 described in Table 1 below.
상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물은 유기 전계 발광 소자용 재료로 사용되는 경우, 유기 전계 발광 소자에서 사용 가능한 물질에 요구되는 조건, 예컨대 적절한 에너지 준위, 전기화학적 안정성 및 열적 안정성 등을 모두 우수하게 만족시킬 수 있으며, 치환기에 따라 유기 전계 발광 소자에서 요구되는 다양한 역할을 할 수 있다.
When the diarylfluorene amine derivative compound is used as a material for an organic electroluminescent device, it is preferable that the diarylfluorene amine derivative compound satisfies conditions required for a material usable in an organic electroluminescent device, such as appropriate energy level, electrochemical stability and thermal stability Depending on the substituent, it can play various roles required in the organic electroluminescent device.
본 발명의 또 다른 구현예에서, 음극과 양극 사이에 적어도 하나의 유기 박막층이 협지되어 있는 유기 전계 발광 소자에 있어서, 상기 유기 박막층은 적어도 하나의 발광층을 포함하는 다층 구조이고, 상기 발광층 또는 상기 발광층 이외의 상기 유기 박막층 내의 적어도 하나의 층이 상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 단독 또는 2종 이상의 혼합물을 포함하는 유기 전계 발광 소자를 제공한다.In another embodiment of the present invention, at least one organic thin film layer is sandwiched between a cathode and an anode, wherein the organic thin film layer has a multilayer structure including at least one light emitting layer, and the light emitting layer or the light emitting layer At least one layer in the organic thin film layer contains the diarylfluorene amine derivative compound alone or a mixture of two or more thereof.
상기 유기 전계 발광 소자의 유기 박막층에 포함되는 상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물은 상기 화학식 a로 표시되는 화합물이고, 그에 대한 상세한 설명은 전술한 바와 같다.The diarylfluorene amine derivative compound contained in the organic thin film layer of the organic electroluminescent device is a compound represented by the above formula (a), and a detailed description thereof is as described above.
일 구현예에서, 상기 유기 박막층은 필요한 용도에 따라서 적절히 정공수송층, 정공주입층, 정공차단층, 전자수송층, 전자주입층 및 전자차단층으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 하나 이상을 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the organic thin film layer may suitably include at least one selected from the group consisting of a hole transporting layer, a hole injecting layer, a hole blocking layer, an electron transporting layer, an electron injecting layer and an electron blocking layer.
다른 구현예에서, 상기 유기 박막층은 양극과 발광층 사이에 개재되며, 정공주입층, 정공수송층, 정공주입 기능 및 정공수송 기능을 동시에 갖는 기능층, 버퍼층 및 전자차단층 중 적어도 하나를 포함한 정공 수송 영역을 포함할 수 있다.In another embodiment, the organic thin film layer is disposed between the anode and the light emitting layer and includes a hole transporting layer, a hole transporting layer, a hole transporting region including at least one of a functional layer having both a hole injecting function and a hole transporting function, . ≪ / RTI >
상기 정공 수송 영역은 p-도펀트를 더 포함할 수 있다. The hole transporting region may further include a p-dopant.
상기 정공주입층, 정공수송층, 기능층, 버퍼층, 전자차단층, 발광층 정공차단층 전자수송층, 전자주입층 등은, 각각, 공지된 물질을 사용하여 형성되거나, 상기 화학식 a로 표시되는 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 화합물을 1종 이상 포함할 수 있다.
The hole injection layer, the hole transport layer, the functional layer, the buffer layer, the electron blocking layer, the hole blocking layer of the light emitting layer, and the electron injection layer may be formed using known materials, And one or more kinds of an organic amine derivative compound.
상기 유기 박막층에 관한 상세한 설명은 전술한 바와 같다.
A detailed description of the organic thin film layer is as described above.
이하 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예를 기재한다. 그러한 하기한 실시예는 본 발명의 일 실시예일뿐 본 발명이 하기한 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니다.
Hereinafter, examples and comparative examples of the present invention will be described. The following embodiments are only examples of the present invention, and the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
(( 실시예Example ))
이하에서, 반응예 및 비교예를 구체적으로 예시하지만, 본 발명이 하기의 반응예 및 실시예로 한정되는 것은 아니다. 이하의 반응예에서 중간체 화합물은 최종 생성물의 번호에 일련번호를 추가하는 방식으로 표기한다. 예를 들어, 화합물 1은 화합물 [1] 로 상기 화합물의 중간체 화합물은 [1-1] 등으로 표기한다. 본 명세서에서 화합물의 번호는 상기 표 1에 기재된 화학식의 번호로서 표기한다. 예를 들어, 표 1에서 1로 표시된 화합물은 화합물 1로 표기한다.
Hereinafter, the reaction examples and the comparative examples are specifically exemplified, but the present invention is not limited to the following reaction examples and examples. In the following reaction examples, the intermediate compounds are indicated by adding the serial number to the final product number. For example, Compound 1 is represented by the compound [1], and the intermediate compound of the above compound is represented by [1-1] or the like. In the present specification, the numbers of the compounds are represented by the numbers of the formulas shown in Table 1 above. For example, compounds designated 1 in Table 1 are designated Compound 1.
[반응식 1][Reaction Scheme 1]
중간체 화합물 [6-1]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-1]
질소분위기하에 2L 반응플라스크에 1-브로모-3,5-디페닐 65g (210.22mmol), 비스(피나콜라토)디보론 64.1g (252.26mmol), 포타슘아세테이트 61.9g (630.66mmol), (1,1'-비스(디페닐포스피노)페로센) 팔라듐(Ⅱ) 디클로라이드 7.7g (10.51mmol) 그리고 1,4-디옥산 650ml를 가하고 온도를 올려준다. 3시간 환류 반응 후 반응액을 celite로 여과하고 디클로로메탄, 증류수로 추출한 다음 유기층은 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 감압 농축한다. 실리카겔 크로마토그라프로 분리정제 후, 디클로메탄과 메탄올로 재결정하여 흰색 고체 중간체 화합물 [6-1] 68.3g (91%)을 제조하였다.
To a 2 L reaction flask under nitrogen was added 65 g (210.22 mmol) of 1-bromo-3,5-diphenyl, 64.1 g (252.26 mmol) of bis (pinacolato) diboron, 61.9 g (630.66 mmol) 7.7 g (10.51 mmol) of palladium (II) dichloride, 650 ml of 1,4-dioxane, and the temperature is raised. After refluxing for 3 hours, the reaction mixture is filtered through celite and extracted with dichloromethane and distilled water. The organic layer is treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The product was purified by silica gel chromatography and then recrystallized from dichloromethane and methanol to obtain 68.3 g (91%) of a white solid intermediate compound [6-1] .
중간체 화합물 [6-2]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-2]
질소분위기에서 2L 반응플라스크에 1-(2-브로모-5-메폭시페닐)에타논 41.6g (181.77mmol), 화합물 [6-1] 68g (190.86mmol) 그리고 1,4-다이옥산 410ml를 투입하고 온도를 올려준다. 60℃에서 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0) 4.2g (3.64mmol)과 증류수에 녹인 포타슘카보네이트 75.4g (545.33mmol)을 넣어준 후 밤샘 환류 교반한다. 반응이 종료되면 실온까지 냉각한 다음 에틸아세테이트, 증류수로 추출하고, 유기층은 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 여과한다. 여과액은 감압 농축하고, 실리카겔 크로마토그라프로 분리정제하여, 투명한 오일 상태의 중간체 화합물 [6-2] 64.7g (94%)을 제조하였다.
In a nitrogen atmosphere, 41.6 g (181.77 mmol) of 1- (2-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl) ethanone, 68 g (190.86 mmol) of the compound [6-1] and 410 ml of 1,4- And raise the temperature. 4.24 g (3.64 mmol) of tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) and 75.4 g (545.33 mmol) of potassium carbonate dissolved in distilled water were added at 60 ° C, followed by stirring at reflux overnight. When the reaction is completed, the reaction mixture is cooled to room temperature, and extracted with ethyl acetate and distilled water. The organic layer is treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by silica gel chromatography to obtain 64.7 g (94%) of intermediate compound [6-2] in a clear oil state.
중간체 화합물 [6-3]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-3]
질소분위기하에 2L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-2] 64.7g (170.86mmol)과 테트라하이드로퓨란 650ml을 투입하고, 0℃에서 메틸마그네슘클로라이드(3.0M in THF) 256ml (768.88mmol)를 천천히 적가하고 상온에서 밤샘 교반한다. 반응 종료 후 증류수 1.5L에 반응물을 천천히 적가한다. 에탈아세테이트, 증류수로 추출하여 유기층을 얻고 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 감압 농축한다. 실리카겔 크로마토그라프로 분리 정제하여 흰색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [6-3] 53.9g (80%)을 제조하였다.
64.7 g (170.86 mmol) of the compound [6-2] and 650 ml of tetrahydrofuran were placed in a 2 L reaction flask under a nitrogen atmosphere, and 256 ml (768.88 mmol) of methylmagnesium chloride (3.0 M in THF) Lt; / RTI > After completion of the reaction, slowly drop the reaction mixture into 1.5 L of distilled water. The mixture is extracted with ethylacetate and distilled water to obtain an organic layer, which is treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel chromatography to obtain 53.9 g (80%) of intermediate compound [6-3] as a white solid.
중간체 화합물 [6-4]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-4]
질소분위기하에 2L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-3] 53.9g (136.66mmol)과 디클로로메탄 540ml를 투입한다. 0℃에서 메탄설폰산 22.2ml (341.65mmol)을 천천히 적가하고 2시간 교반한다. 반응 종료 후 디클로로메탄, 염화나트륨 수용액으로 추출하여 유기층을 얻고 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 감압 농축한다. 실리카겔 크로마토그라프로 분리 정제하고, 톨루엔으로 재결정하여 흰색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [6-4] 42.2g (82%)을 제조하였다.
53.9 g (136.66 mmol) of the compound [6-3] and 540 ml of dichloromethane are introduced into a 2 L reaction flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. Methanesulfonic acid (22.2 ml, 341.65 mmol) was slowly added dropwise at 0 ° C and stirred for 2 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was extracted with dichloromethane and an aqueous solution of sodium chloride to obtain an organic layer, which was treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel chromatography and recrystallized with toluene to obtain 42.2 g (82%) of an intermediate compound [6-4] as a white solid.
중간체 화합물 [6-5]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-5]
질소분위기하에 1L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-4] 42g (111.55mmol)과 디클로로메탄 400ml을 투입한다. 0℃에서 보론 트리브로마이드 18.3ml (189.64mmol)을 천천히 적가하고 상온에서 2시간 교반 후 반응을 종결한다. 소듐비카보네이트 수용액에 반응물을 천천히 적가하고, 디클로로메탄, 증류수로 추출한다. 유기층은 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 여과하고 감압 농축한다. 디클로메탄과 헥산으로 재결정하여 미색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [6-5] 38g (94%)을 제조하였다.
42 g (111.55 mmol) of the compound [6-4] and 400 ml of dichloromethane are introduced into a 1 L reaction flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. 18.3 ml (189.64 mmol) of boron tribromide was slowly added dropwise at 0 ° C, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and the reaction was terminated. The reaction mixture is slowly added dropwise to an aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate and extracted with dichloromethane and distilled water. The organic layer was treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and then concentrated under reduced pressure. Recrystallization from dichloromethane and hexane gave 38 g (94%) of an off-white solid intermediate compound [6-5] .
중간체 화합물 [6-6]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [6-6]
질소분위기하에 1L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-5] 38g (104.86mmol)과 디클로로메탄 390ml를 투입한다. 0℃에서 피리딘 17.1ml (209.71mmol)을 천천히 적가 후 무수 트리플루오로메탄술폰 25.8ml (157.29mmol)을 천천히 적가한다. 상온에서 2시간 반응 후 증류수 300ml를 천천히 가하고 추출한다. 유기층은 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 silica 여과하고 감압 농축한다. 디클로메탄과 헥산으로 재결정하여 흰색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [6-6] 44g (85%)을 제조하였다.
38 g (104.86 mmol) of the compound [6-5] and 390 ml of dichloromethane are introduced into a 1 L reaction flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. 17.1 ml (209.71 mmol) of pyridine is slowly added dropwise at 0 ° C, and then 25.8 ml (157.29 mmol) of anhydrous trifluoromethanesulfone is slowly added dropwise. After reacting at room temperature for 2 hours, 300 ml of distilled water is slowly added and extracted. The organic layer is subjected to anhydrous magnesium sulfate treatment and silica filtration and concentration under reduced pressure. Recrystallization from dichloromethane and hexane gave 44 g (85%) of intermediate compound [6-6] as white solid.
화합물 [6]의 제조Preparation of compound [6]
질소분위기하에 1L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-6] 44g (88.98mmol), N-([1,1'-바이페닐]-4-일)-9,9-디메틸-9H-플루오렌-2-아민 30.6g (84.53mmol), 소듐터트부톡사이드 12.8g (133.46mmol), 트리스(디벤질리덴아세톤)디팔라듐(0) 2.4g (2.67mmol), 4,5-비스(디페닐포스피노)-9,9-디메틸잔텐 3.1g (5.34mmol), o-자일렌 440ml을 투입하고 3시간 환류 교반한다. 반응 종료 후 에틸아세테이트, 증류수로 추출 및 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 여과하고 감압 농축한다. 실리카겔 크로마토그라프로 분리 정제하고, 톨루엔으로 재결정하여 흰색 고체의 목적화합물 [6] 33.3g (53%)을 제조하였다.
(88.98 mmol) of compound [6-6], N - ([1,1'-biphenyl] -4- yl) -9,9- (Diphenylphosphino) - (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) diphenylphosphonium chloride, 30.6g (84.53mmol) of amine, 12.8g (133.46mmol) of sodium tallow butoxide, 2.4g 3.1 g (5.34 mmol) of 9,9-dimethylzane and 440 ml of o-xylene were charged and refluxed and stirred for 3 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate, distilled water, and anhydrous magnesium sulfate, followed by filtration and concentration under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel chromatography, and recrystallized from toluene to obtain 33.3 g (53%) of the target compound [6] as a white solid.
[반응식 2][Reaction Scheme 2]
중간체 화합물 [88-1]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [88-1]
질소분위기하에 2L 반응플라스크에 화합물 [6-6] 25g (50.55mmol), (4-클로로페닐)보론산 9.5g (60.66mmol), 1,4-다이옥산 250ml를 가하고 온도를 올려준다. 60℃에서 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0) 1.2g (1.01mmol)을 넣고 증류수에 녹인 포타슘카보네이트 10.5g (75.83mmol)을 넣어준 후 5시간 환류 교반한다. 반응 종료 후 에틸아세테이트, 증류수로 추출, 무수황산 마그네슘 처리 후 감압 농축한다. 실리카겔 크로마토그라프 분리 정제하여 흰색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [88-1] 16.6g (72%)을 제조하였다.
25.5 g (50.55 mmol) of the compound [6-6], 9.5 g (60.66 mmol) of (4-chlorophenyl) boronic acid and 250 ml of 1,4-dioxane were added to a 2 L reaction flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. 1.2 g (1.01 mmol) of tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) was added at 60 ° C, 10.5 g (75.83 mmol) of potassium carbonate dissolved in distilled water was added, and the mixture was refluxed with stirring for 5 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and distilled water, treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and then concentrated under reduced pressure. The silica gel chromatograph was separated and purified to obtain 16.6 g (72%) of intermediate compound [88-1] as a white solid.
화합물 [88]의 제조Preparation of compound [88]
화합물 [6]과 동일한 합성 방법으로 화합물 [88-1] 16.6g (36.40mmol), N-(9,9-디메틸-9H-플루오렌-2-일)디벤조[b,d]퓨란-4-아민 12.9g (34.57mmol), 소듐터트부톡사이드 5.2g (54.59mmol), 트리스(디벤질리덴아세톤)디팔라듐(0) 1.0g (1.09mmol), 4,5-비스(디페닐포스피노)-9,9-디메틸잔텐 1.3g (2.18mmol), o-자일렌 170ml을 사용하여 흰색 고체의 목적화합물 [88] 13.9g (48%)을 제조하였다.
(36.40 mmol) of the compound [88-1], N- (9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl) dibenzo [b, (Dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), 1.0 g (1.09 mmol) of 4,5-bis (diphenylphosphino) -amine, 12.9 g (34.57 mmol) 13.9 g (48%) of the target compound [88] as a white solid were prepared by using 1.3 g (2.18 mmol) of 2,2-dimethyl-9,9-dimethylzantane and 170 ml of o-xylene.
[반응식 3][Reaction Scheme 3]
중간체 화합물 [108-1]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [108-1]
중간체 화합물 [6-2]와 동일한 합성 방법으로 1-(2-브로모-3-메톡시페닐)에타논 13.5g (58.94mmol), 화합물 [6-1] 20g (56.14mmol), 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0) 1.4g (1.18mmol), 포타슘카보네이트 16.3g (117.88mmol), 1,4-다이옥산 200ml을 사용하여 투명한 오일 상태의 중간체 화합물 [108-1] 19.8g (89%)을 제조하였다.
(58.94 mmol) of 1- (2-bromo-3-methoxyphenyl) ethanone, 20 g (56.14 mmol) of compound [6-1], tetrakis (89% ) of Intermediate Compound [108-1] in a clear oil state was obtained by using 1.4 g (1.18 mmol) of triphenylphosphine palladium (0), 16.3 g (117.88 mmol) of potassium carbonate and 200 ml of 1,4- ).
중간체 화합물 [108-2]의 제조Preparation of intermediate compound [108-2]
상기 반응식 1과 동일한 합성 방법으로 화합물 [108-1] 19.8g (52.45mmol), 메틸마그네슘클로라이드(3.0M in THF) 78.7ml (236.05mmol), 메탄설폰산 7.8ml (119.60mmol), 보론 트리브로마이드 5.6ml (57.61mmol), 무수 트리플루오로메탄술폰 7.6ml (46.26mmol)을 사용하여 흰색 고체의 중간체 화합물 [108-2] 12.7g 을 제조하였다.
(52.45 mmol) of the compound [108-1], 78.7 ml (236.05 mmol) of methylmagnesium chloride (3.0 M in THF), 7.8 ml (119.60 mmol) of methanesulfonic acid, 12.7 g of an intermediate compound [108-2] as a white solid was prepared using 5.6 ml (57.61 mmol) of anhydrous trifluoromethanesulfone and 7.6 ml (46.26 mmol) of anhydrous trifluoromethanesulfone.
화합물 [108]의 제조Preparation of compound [108]
화합물 [6]과 동일한 합성 방법으로 화합물 [108-5] 12.7g (25.60mmol), N-(9,9-디메틸-9H-플루오렌-4-일)-9,9-디메틸-9H-플루오렌-2-아민 10.8g (26.88mmol), 소듐터트부톡사이드 3.7g (38.40mmol), 트리스(디벤질리덴아세톤)디팔라듐(0) 0.7g (0.77mmol), 4,5-비스(디페닐포스피노)-9,9-디메틸잔텐 0.9g (1.54mmol), o-자일렌 130ml을 사용하여 흰색 고체의 목적화합물 [108] 9.7g (51%)을 제조하였다.
12.7 g (25.60 mmol) of the compound [108-5], N- (9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-4-yl) -9,9-dimethyl- (Dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), 0.7 g (0.77 mmol) of 4,5-bis (diphenyl) (51%) of the target compound [108] as a white solid were prepared by using 0.9 g (1.54 mmol) of o-xylene and 0.9 g of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile.
상기 반응식 1 내지 3의 제조 방법에 따라 화합물 1 내지 화합물 113 및 비교예 화합물로서 하기 구조식의 화합물 114를 제조하였고 그 결과를 하기의 표 2에 나타내었다.
According to the production methods of the above Reaction Schemes 1 to 3, Compound 1 to Compound 113 and Compound 114 of the following structural formula were prepared as Comparative Examples and the results are shown in Table 2 below.
Q-Q-
TOFTOF
(M+)(M +) <
비교예Comparative Example
화합물 compound
<α-NPD> <화학식 d>< alpha -NPD > < EMI ID =
<화학식 e> <화학식 114><Formula e> <Formula 114>
비교예Comparative Example 1 One
하기 화학식 f로 표시되는 화합물 f를 형광 청색 호스트로 사용하고, 하기 화학식 g로 표시되는 화합물 g를 형광 청색 도판트로 사용하고, 2-TNATA(4,4’,4”-tris(N-naphthalen-2-yl)-N-phenylamino)-triphenylamine)을 정공주입층 물질로 사용하고, α-NPD(N,N’-di(naphthalene-1-yl)-N,N’-diphenylbenzidine)을 정공수송층 물질로 사용하여 다음과 같은 구조를 갖는 유기발광소자를 제작하였다: ITO/2-TNATA(60 nm)/α-NPD(30 nm)/ 화합물f + 화합물 g(30 nm)/Alq3(25 nm)/Liq(1 nm)/ Al(100 nm).(4,4 ', 4 " -tris (N-naphthalen-2-yl) phthalocyanine), using compound f represented by the following formula f as a fluorescent blue host and using compound g represented by the following formula g as a fluorescent blue dopant: 2-yl) -N-phenylamino) -triphenylamine was used as a hole injection layer material and α-NPD (N, N'-di (naphthalene- (30 nm) / compound f + compound g (30 nm) / Alq 3 (25 nm) was used as an organic light emitting device having the following structure: ITO / 2-TNATA / Liq (1 nM) / Al (100 nM).
애노드는 코닝(Corning)사의 15Ω/cm2 (1000Å) ITO 유리 기판을 25 mm x 25 mm x 0.7 mm크기로 잘라서 아세톤 이소프로필 알콜과 순수한 물 속에서 각 15분 동안 초음파 세정한 후, 30분 동안 UV 오존 세정하여 사용하였다. 상기 기판 상부에 2-TNATA를 진공 증착하여 60 nm 두께의 정공주입층을 형성하였다. 상기 정공주입층 상부에, α-NPD를 진공 증착하여 30 nm 두께의 정공수송층을 형성하였다. 상기 정공수송층 상부에 화학식 f로 표시되는 화합물 및 화학식 g로 표시되는 화합물(도핑율: 4wt%)를 진공 증착하여 30 nm두께의 발광층을 형성하였다. 이후, 상기 발광층 상부에 Alq3 화합물을 25 nm의 두께로 진공증착하여 전자수송층을 형성하였다. 상기 전자수송층 상부에 Liq 1 nm(전자주입층)과 Al 100 nm(캐소드)를 순차적으로 진공증착하여, 표 3에 표시된 바와 같은 유기발광소자를 제조하였다. 이를 비교샘플 1이라고 한다.
The anode was prepared by cutting Corning's 15 Ω / cm 2 (1000 Å) ITO glass substrate to a size of 25 mm × 25 mm × 0.7 mm, ultrasonically cleaning it in acetone isopropyl alcohol and pure water for 15 minutes each, UV ozone cleaning was used. 2-TNATA was vacuum deposited on the substrate to form a 60 nm thick hole injection layer. On top of the hole injection layer, α-NPD was vacuum deposited to form a hole transport layer having a thickness of 30 nm. A compound represented by Formula f and a compound represented by Formula g (doping ratio: 4 wt%) were vacuum-deposited on the hole transport layer to form a light emitting layer having a thickness of 30 nm. Then, an Alq 3 compound was vacuum deposited on the light emitting layer to a thickness of 25 nm to form an electron transporting layer. Liq 1 nm (electron injecting layer) and
<화학식 f> <화학식 g> <Formula f> <Formula g>
비교예Comparative Example 2 ~ 4 2 to 4
정공 수송층으로 사용되는 α-NPD 대신 상기 화합물 d, e, 114 를 정공 수송층으로 각각 이용한 것을 제외하고는 상기 비교예 1과 동일한 방법으로 유기발광소자를 제조하여 표 3에 나타내었다. 이를 각각 비교예 2 내지 4 이라고 한다.
An organic light emitting device was prepared in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 except that the above-mentioned compounds d, e, and 114 were used as a hole transport layer instead of? -NPD used as a hole transport layer. These are referred to as Comparative Examples 2 to 4, respectively.
비교예Comparative Example 5 5
상기 비교예 1 중, 정공 수송층 α-NPD와 발광층(화학식 f + 화학식 g -도핑율:4%) 사이에 화학식 d로 표시되는 화합물 d 를 전자차단 화합물로 사용하여, 다음과 같은 구조를 갖는 유기발광소자를 제작하였다: ITO/2-TNATA(60 nm)/α-NPD(30 nm)/ 화합물 d(10nm)/ 화합물 f + 화합물 g(30 nm)/Alq3(25 nm)/Liq(1 nm)/ Al(100 nm).In Comparative Example 1, using a compound d represented by the formula (d) as an electron-blocking compound between the hole transport layer α-NPD and the light emitting layer (formula f + g - doping rate: 4%), A light emitting device was prepared: ITO / 2-TNATA (60 nm) /? -NPD (30 nm) / compound d (10 nm) / compound f + compound g (30 nm) / Alq 3 nm) / Al (100 nm).
애노드는 코닝(Corning)사의 15Ω/cm2 (1000Å) ITO 유리 기판을 25 mm x 25 mm x 0.7 mm크기로 잘라서 아세톤 이소프로필 알콜과 순수한 물 속에서 각 15분 동안 초음파 세정한 후, 30분 동안 UV 오존 세정하여 사용하였다. 상기 기판 상부에 2-TNATA를 진공 증착하여 60 nm 두께의 정공주입층을 형성하였다. 상기 정공주입층 상부에, α-NPD를 진공 증착하여 30 nm 두께의 정공수송층을 형성하였다. 상기 정공수송층 상부에 화합물 d를 10nm 두께로 증착하여 전자차단층을 형성하였다. 화학식 f로 표시되는 화합물f 및 화학식 g로 표시되는 화합물 g(도핑율: 4wt%)를 진공 증착하여 30 nm두께의 발광층을 형성하였다. 이후, 상기 발광층 상부에 Alq3 화합물을 25 nm의 두께로 진공증착하여 전자수송층을 형성하였다. 상기 전자수송층 상부에 Liq 1 nm(전자주입층)과 Al 100 nm(캐소드)를 순차적으로 진공증착하여, 표 3에 표시된 바와 같은 유기발광소자를 제조하였다. 이를 비교예 5 라고 한다.
The anode was prepared by cutting Corning's 15 Ω / cm 2 (1000 Å) ITO glass substrate to a size of 25 mm × 25 mm × 0.7 mm, ultrasonically cleaning it in acetone isopropyl alcohol and pure water for 15 minutes each, UV ozone cleaning was used. 2-TNATA was vacuum deposited on the substrate to form a 60 nm thick hole injection layer. On top of the hole injection layer, α-NPD was vacuum deposited to form a hole transport layer having a thickness of 30 nm. Compound d was deposited on the hole transport layer to a thickness of 10 nm to form an electron blocking layer. A compound f represented by the formula f and a compound g represented by the formula g (g doping ratio: 4 wt%) were vacuum deposited to form a light emitting layer with a thickness of 30 nm. Then, an Alq 3 compound was vacuum deposited on the light emitting layer to a thickness of 25 nm to form an electron transporting layer. Liq 1 nm (electron injecting layer) and
실시예Example 1 ~ 8 1 to 8
정공 수송층으로 사용되는 α-NPD 대신 상기 표1에 개시된 화합물 6, 7, 13, 31, 62, 78, 81, 88 들을 승화 정제 과정을 거쳐 정공 수송층으로 각각 이용한 것을 제외하고는 상기 비교예 1과 동일한 방법으로 유기발광소자를 제조하여 표 3에 나타내었다. 이를 각각 실시예 1 내지 8 이라고 한다.
Except that the compounds 6, 7, 13, 31, 62, 78, 81, and 88 shown in Table 1 were used as a hole transport layer through sublimation purification, respectively, instead of? -NPD used as a hole transport layer. An organic light emitting device was fabricated in the same manner as in Table 3. These are referred to as Examples 1 to 8, respectively.
실시예Example 9 ~ 11 9-11
비교예 4 중, 전자 차단층으로 사용되는 화학식 d 대신 상기 표1에 개시된 화합물 98, 108, 112 들을 승화 정제 과정을 거쳐 전자 차단층으로 각각 이용한 것을 제외하고는 상기 비교예 4와 동일한 방법으로 유기발광소자를 제조하여 표 3에 나타내었다. 이를 각각 실시예 9 내지 11 이라고 한다.
In the same manner as in Comparative Example 4, except that Compound 98, 108, and 112 shown in Table 1 were used as an electron blocking layer through a sublimation purification process in place of Compound d used as an electron blocking layer in Comparative Example 4, A light emitting device was prepared and shown in Table 3. These are referred to as Examples 9 to 11, respectively.
평가예Evaluation example 1: One: 비교예Comparative Example 1~5 및 1 to 5 and 실시예Example 1~11의 발광 특성 및 수명 평가 Evaluation of luminescence characteristics and life span of 1 to 11
비교예 1~5 및 실시예 1~11 에 대하여, Keithley sourcemeter “2400”, KONIKA MINOLTA “CS-2000”을 이용하여 발광휘도, 발광효율을 평가하였다. Light emission luminance and luminous efficiency were evaluated using Keithley source meter "2400" and KONIKA MINOLTA "CS-2000" for Comparative Examples 1 to 5 and Examples 1 to 11.
맥사이언스사의 M6000S 수명측정장치를 이용하여 초기휘도 (L0) 1000 nit를 기준으로 휘도 (L)가 97%에 도달하는 시간(LT97)을 각각 측정하여, 그 결과를 하기 표 3 에 나타내었다.
The time (LT97) at which the luminance (L) reached 97% on the basis of the initial luminance (L 0 ) of 1000 nits was measured using a M6000S lifetime measuring device of Mac Science Inc., and the results are shown in Table 3 below.
화합물
No.Hole transportation
compound
No.
화합물
No.Electronic blocking
compound
No.
OP. VVoltage
OP. V
[cd/m2]Luminance
[cd / m 2 ]
[cd/A]efficiency
[cd / A]
[LT97]life span
[LT97]
상기 표 3 에 보여지는 바와 같이 실시예 1 내지 11 은 비교예 1 내지 5 에 비하여 저전압 구동 및 향상된 발광 특성을 나타내었다.
As shown in Table 3, Examples 1 to 11 exhibited low voltage driving and improved luminescent characteristics as compared with Comparative Examples 1 to 5.
상기 표 3에 보여지는 바와 같이 실시예 1 내지 11 은 비교예 1 내지 5 에 비하여 향상된 수명 특성을 나타내었다. 특히 플루오렌의 1, 3위치에 아릴기 치환되면서 플로렌, 디벤조퓨란 또는 디벤조티오펜 아민 유도체의 상기 화합물들이 우수한 성능과 수명을 나타내었다.
As shown in Table 3, Examples 1 to 11 exhibited improved life characteristics compared to Comparative Examples 1 to 5. Particularly, these compounds of fluorene, dibenzofurane or dibenzothiophenamine derivatives exhibit excellent performance and life span, with aryl groups substituted at the 1 and 3 positions of fluorene.
이상에서 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예들에 대하여 상세하게 설명하였지만 본 발명의 권리 범위는 이에 한정되는 것은 아니고 다음의 청구 범위에서 정의하고 있는 본 발명의 기본 개념을 이용한 당업자의 여러 변형 및 개량 형태 또한 본 발명의 권리 범위에 속하는 것이다.
While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments, And falls within the scope of the invention.
Claims (10)
Gt; 1-7, 9-14, 19-21, 23-29, 31-50, 52-56, 58-66, 69-77, 79-81, 83-94, 96, 98-109 and 111-113 Wherein the organic compound is a diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compound.
상기 디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 유기화합물은 유기전기발광소자용 재료 중 정공주입층, 정공수송층, 전자차단층, 발광층, 정공차단층, 전자수송층 또는 전자주입층의 물질로 사용되는
디아릴플루오렌 아민 유도체 유기화합물.
The method according to claim 1,
The diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compound is used as a material for a hole injecting layer, a hole transporting layer, an electron blocking layer, a light emitting layer, a hole blocking layer, an electron transporting layer, or an electron injecting layer in a material for an organic EL device
Diarylfluorene amine derivatives Organic compounds.
At least one organic thin film layer sandwiched between a cathode and an anode, wherein the organic thin film layer has a multi-layer structure including at least one light emitting layer, and at least one organic thin film layer in the organic thin film layer other than the light emitting layer or the light emitting layer Wherein the layer comprises the diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compound according to claim 1 alone or a mixture of two or more thereof.
상기 유기 박막층은 양극과 발광층 사이에 개재되며, 정공주입층, 정공수송층, 정공주입 기능 및 정공수송 기능을 동시에 갖는 기능층, 버퍼층 및 전자차단층 중 적어도 하나를 포함한 정공 수송 영역을 포함하는
유기 전계 발광 소자.
9. The method of claim 8,
The organic thin film layer includes a hole transporting region interposed between the anode and the light emitting layer and including at least one of a hole injecting layer, a hole transporting layer, a functional layer having both a hole injecting function and a hole transporting function, a buffer layer,
Organic electroluminescent device.
상기 정공 수송 영역은 p-도펀트를 더 포함하는
유기 전계 발광 소자.10. The method of claim 9,
Wherein the hole transport region further comprises a p-dopant
Organic electroluminescent device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170008015A KR101897632B1 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2017-01-17 | Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170008015A KR101897632B1 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2017-01-17 | Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180084423A KR20180084423A (en) | 2018-07-25 |
| KR101897632B1 true KR101897632B1 (en) | 2018-10-29 |
Family
ID=63058840
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170008015A KR101897632B1 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2017-01-17 | Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101897632B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20240109280A (en) * | 2017-12-15 | 2024-07-10 | 메르크 파텐트 게엠베하 | Substituted aromatic amines for use in organic electroluminescent devices |
| CN110903276A (en) * | 2018-09-17 | 2020-03-24 | 北京鼎材科技有限公司 | Organic compound and organic electroluminescent device |
| CN109293516B (en) * | 2018-11-03 | 2022-01-14 | 长春海谱润斯科技股份有限公司 | Triarylamine compound and organic light-emitting device thereof |
| CN109651173B (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2022-02-15 | 武汉天马微电子有限公司 | Compound, display panel and display device |
| KR20210068642A (en) | 2019-11-29 | 2021-06-10 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Amine compound and light emitting device comprising the same |
| JP2021131254A (en) | 2020-02-18 | 2021-09-09 | アズビル株式会社 | Light detection system, discharge probability calculating method, and received light quantity measuring method |
| CN113328042A (en) * | 2020-02-28 | 2021-08-31 | 固安鼎材科技有限公司 | Organic electroluminescent element and preparation method thereof |
| CN113451518A (en) * | 2020-03-27 | 2021-09-28 | 合肥鼎材科技有限公司 | Organic electroluminescent device |
| CN116554039B (en) * | 2023-07-10 | 2023-09-19 | 吉林奥来德光电材料股份有限公司 | Organic light-emitting auxiliary material and preparation method and application thereof |
-
2017
- 2017-01-17 KR KR1020170008015A patent/KR101897632B1/en active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20180084423A (en) | 2018-07-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101897632B1 (en) | Diarylfluorene amine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR102081739B1 (en) | 2,3 substituted naphthylamine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR101910498B1 (en) | The novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR101404299B1 (en) | Light-emitting device material and light-emitting device | |
| JP5618753B2 (en) | Organic light emitting device | |
| KR102201104B1 (en) | organic light-emitting diode with High efficiency and long lifetime | |
| JP2020084189A (en) | Indolocarbazole derivatives and organic light-emitting elements using the same | |
| KR102144446B1 (en) | Organic Compound for organic light emitting diode and an organic light emitting diode including the same with long life | |
| KR102001425B1 (en) | Dibenzofuranyl trazine derivative organic compounds and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR20150033082A (en) | Compound for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent device comprising the same | |
| KR20120009761A (en) | Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same | |
| JP2012082187A (en) | New condensed polycyclic compound, and organic light-emitting element having the same | |
| KR20170081718A (en) | Amine derivatives, material for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent device using the same | |
| KR102714696B1 (en) | Fluorine-substituted polycyclic aromatic compounds | |
| KR20180069423A (en) | Spirofluorenexanthenyl derivatives and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR20170039020A (en) | Organic electroluminescent compound and organic electroluminescent device | |
| KR102503217B1 (en) | Organic Compound for organic light emitting diode and an organic light emitting diode including the same with long life | |
| CN113039189B (en) | Heterocyclic compound and organic light-emitting device comprising same | |
| KR101492527B1 (en) | Organic light-emitting diode including aryl substituted antracene derivatives | |
| KR20140125061A (en) | An organoelectro luminescent compound and an organoelectroluminescent device using the same | |
| KR20150051662A (en) | Compound for organic electronic element, organic electronic element using the same, and an electronic device thereof | |
| KR20160029962A (en) | Compound for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent device comprising the same | |
| KR20150072768A (en) | Compound for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent device comprising the same | |
| KR101764908B1 (en) | 2-phenanthrene carbazole derivative compound and organic electroluminescent device including the same | |
| KR101764907B1 (en) | 2-phenanthrene carbazole derivative compound and organic electroluminescent device including the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| N231 | Notification of change of applicant | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |