KR101892076B1 - Integrated circuit with different voltage domain circuits - Google Patents
Integrated circuit with different voltage domain circuits Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101892076B1 KR101892076B1 KR1020130028313A KR20130028313A KR101892076B1 KR 101892076 B1 KR101892076 B1 KR 101892076B1 KR 1020130028313 A KR1020130028313 A KR 1020130028313A KR 20130028313 A KR20130028313 A KR 20130028313A KR 101892076 B1 KR101892076 B1 KR 101892076B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- power supply
- supply voltage
- signal
- level
- circuit
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C7/00—Arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C7/10—Input/output [I/O] data interface arrangements, e.g. I/O data control circuits, I/O data buffers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C5/00—Details of stores covered by group G11C11/00
- G11C5/14—Power supply arrangements, e.g. power down, chip selection or deselection, layout of wirings or power grids, or multiple supply levels
- G11C5/147—Voltage reference generators, voltage or current regulators; Internally lowered supply levels; Compensation for voltage drops
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C7/00—Arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C7/22—Read-write [R-W] timing or clocking circuits; Read-write [R-W] control signal generators or management
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C8/00—Arrangements for selecting an address in a digital store
- G11C8/10—Decoders
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Logic Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 서로 다른 전압 도메인으로 구동되는 회로들을 포함하는 집적 회로에 대하여 개시된다. 집적 회로는 제1 전원 전압으로 구동되는 제1 회로 영역와, 제1 전원 전압 보다 높은 제2 전원 전압으로 구동되는 제2 회로 영역을 포함한다. 제2 회로 영역에서, 제1 회로 영역과 인터페이스되고 제1 회로 영역으로부터 적어도 하나의 신호를 수신하는 인터페이스 회로는, 제2 회로 영역의 출력 신호에 응답하여 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 전원이 공급되고, 적어도 하나의 신호를 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 레벨 시프팅한다. 제1 전원 전압은 제1 전압 도메인에 해당하고, 제2 전원 전압은 제2 전압 도메인에 해당한다.The present invention is directed to an integrated circuit including circuits driven into different voltage domains. The integrated circuit includes a first circuit region driven by a first power supply voltage and a second circuit region driven by a second power supply voltage higher than the first power supply voltage. In the second circuit region, the interface circuit interfaced with the first circuit region and receiving at least one signal from the first circuit region is powered by a second power supply voltage level in response to an output signal of the second circuit region, And level-shifts at least one signal to a second power supply voltage level. The first power supply voltage corresponds to the first voltage domain and the second power supply voltage corresponds to the second voltage domain.
Description
본 발명은 집적 회로에 관한 것으로, 특히 서로 다른 전압 도메인들로 구동되는 회로들을 포함하는 집적 회로에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to integrated circuits, and more particularly to integrated circuits including circuits driven with different voltage domains.
집적 회로에서의 전력 소비는 집적 회로로 인가되는 전원 전압과 관련된다. 집적 회로에서 소비되는 전력은 접지 전압에 대한 전원 전압의 크기에 좌우된다. 일반적으로 전원 전압 레벨을 낮춤으로써 전력 소모를 줄일 수 있다. 그러나, 전원 전압 레벨을 줄이는 데에는 한계가 있다. 예컨대, 집적 회로에 포함되는 SRAM과 같은 메모리 장치의 탄탄한 동작(robustness)과 관련해서, 전원 전압이 특정 전압 레벨 이하로 감소하면, 메모리 장치의 독출 및/또는 기입 동작 성능이 저하될 수 있다. 따라서, 전력 소비를 줄이기 위하여 집적 회로의 전원 전압 레벨을 메모리 장치의 동작 전압 레벨 보다 낮게 설정하더라도, 메모리 장치의 성능을 보장할 수 있는 집적 회로가 필요하다.The power consumption in the integrated circuit is related to the power supply voltage applied to the integrated circuit. The power consumed in the integrated circuit depends on the magnitude of the supply voltage relative to the ground voltage. Generally, power consumption can be reduced by lowering the power supply voltage level. However, there is a limit to reducing the power supply voltage level. For example, with respect to the robustness of a memory device such as an SRAM included in an integrated circuit, if the power supply voltage is reduced below a certain voltage level, the performance of the memory device's reading and / or writing operations may be degraded. Therefore, even if the power supply voltage level of the integrated circuit is set to be lower than the operation voltage level of the memory device in order to reduce power consumption, an integrated circuit capable of ensuring the performance of the memory device is needed.
본 발명이 이루고자 하는 기술적 과제는 서로 다른 전압 도메인들로 구동되는 회로들을 포함하는 집적 회로를 제공하는 데 있다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide an integrated circuit including circuits driven with different voltage domains.
본 발명의 일면에 따른 집적 회로는, 제1 전원 전압으로 구동되는 제1 회로 영역과, 제1 전원 전압과 다른 제2 전원 전압으로 구동되고 제1 회로 영역으로부터 수신되는 적어도 하나의 신호를 수신하는 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 제2 회로 영역을 구비한다. 인터페이스 회로는 제2 회로 영역의 출력 신호에 응답하여 상기 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 전원이 공급되고, 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 레벨 시프팅된 제2 회로 영역의 출력 신호를 발생한다.An integrated circuit according to an aspect of the present invention includes a first circuit region driven by a first power supply voltage and a second circuit region driven by a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage and receiving at least one signal received from the first circuit region And a second circuit area including an interface circuit. The interface circuit is powered to the second power supply voltage level in response to an output signal of the second circuit region and generates an output signal of a second circuit region level shifted to a second power supply voltage level.
본 발명의 다른 면에 따른 제1 및 제2 전압 도메인들 사이에 연결되는 인터페이스 회로는, 제1 전원 전압과 다른 제2 전원 전압에 연결되고 제2 전원 전압 레벨의 출력 신호에 의해 제어되는 제1 피모스 트랜지스터, 제1 트랜지스터와 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고 제1 전원 전압 레벨의 입력 신호에 의해 제어되는 제2 피모스 트랜지스터, 제2 전원 전압에 연결되고 클럭 신호에 의해 제어되는 제3 피모스 트랜지스터, 제1 노드와 접지 전압 사이에 직렬 연결되고 입력 신호와 클럭 신호에 각각 제어되는 제1 및 제2 엔모스 트랜지스터, 그리고 제1 노드에 연결되고 제1 노드의 신호에 따라 출력 신호를 출력하는 인버터를 포함한다. 제1 전원 전압은 제1 전압 도메인에 해당하고, 제2 전원 전압은 제2 전압 도메인에 해당한다.An interface circuit connected between the first and second voltage domains according to another aspect of the present invention includes a first power supply voltage and a second power supply voltage that are connected to a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage, A second PMOS transistor connected between the first transistor and the first node and controlled by an input signal of a first power supply voltage level, a third PMOS transistor connected to the second power supply voltage and controlled by a clock signal, A first and a second NMOS transistor serially connected between a first node and a ground voltage and controlled by an input signal and a clock signal, respectively, and a second NMOS transistor connected to the first node and outputting an output signal according to a signal of the first node Inverter. The first power supply voltage corresponds to the first voltage domain and the second power supply voltage corresponds to the second voltage domain.
본 발명의 다른 면에 따른 집적 회로는, 제1 전원 전압으로 구동되는 적어도 하나의 로직 회로와, 제1 전원 전압과 다른 제2 전원 전압으로 구동되고, 로직 회로와 인터페이스되는 하나 이상의 회로들을 포함하는 적어도 하나의 메모리 회로를 포함한다. 하나 이상의 회로들 각각은 자신의 출력 신호에 응답하여 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 전원이 공급되고, 로직 회로에서 수신되는 제1 전원 전압 레벨의 적어도 하나의 신호를 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 레벨 시프팅한다.An integrated circuit according to another aspect of the present invention includes at least one logic circuit driven by a first power supply voltage and one or more circuits driven by a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage and interfaced with a logic circuit And at least one memory circuit. Each of the one or more circuits is powered to a second power supply voltage level in response to its output signal and level shifts at least one signal of a first power supply voltage level received at the logic circuit to a second power supply voltage level .
본 발명의 다른 면에 따른 방법은, 제1 전원 전압으로 제1 회로 영역을 구동하는 단계, 제1 전원 전압과 다른 제2 전원 전압으로 제2 회로 영역을 구동하는 단계, 제1 회로 영역에서 제1 전원 전압 레벨을 갖는 적어도 하나의 신호를 발생하는 단계, 그리고 제2 회로 영역에서 적어도 하나의 신호에 응답하여 적어도 하나의 신호를 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 레벨 시프팅하고 출력 신호를 발생하는 단계를 포함한다. 제2 회로 영역은 출력 신호에 응답하여 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 전원이 공급된다.A method according to another aspect of the present invention includes the steps of driving a first circuit region with a first power supply voltage, driving a second circuit region with a second power supply voltage different from the first power supply voltage, Generating at least one signal having one power supply voltage level and shifting at least one signal to a second power supply voltage level in response to at least one signal in a second circuit region and generating an output signal, . The second circuit region is powered by a second power supply voltage level in response to the output signal.
상술한 본 발명의 집적 회로에 의하면, 제1 회로 영역과 인터페이스되는 제2 회로 영역의 인터페이스 회로는 제2 회로 영역의 출력 신호에 의해 전원이 공급된다. 제2 회로 영역은 제1 회로 영역에서 출력되는 제1 전원 전압 레벨의 신호를 제2 전원 전압 레벨로 레벨 시프팅시킨다. 제1 회로 영역의 제1 전원 전압은, 인터페이스 회로에 의하여 제 1 전원 전압의 레벨을 충분히 낮춤에 따라, 집적 회로는 전력 소비를 줄일 수 있다.According to the above-described integrated circuit of the present invention, the interface circuit of the second circuit region, which is interfaced with the first circuit region, is supplied with power by the output signal of the second circuit region. The second circuit region level-shifts the signal of the first power supply voltage level outputted from the first circuit region to the second power supply voltage level. As the first power supply voltage of the first circuit region sufficiently lowers the level of the first power supply voltage by the interface circuit, the power consumption of the integrated circuit can be reduced.
도 1은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 집적 회로를 설명하는 블락 다이어그램이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 로직 회로들과 메모리 회로들의 인터페이스를 설명하는 도면이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 클럭 신호 발생 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 도 2의 인터페이스 회로를 설명하는 회로 다이어그램이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 집적 회로에 포함되는 메모리 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 도 5의 제3 인터페이스 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 도 5의 동작 방법을 설명하는 플로우챠트이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 시스템의 제1 예를 설명하는 도면이다.
도 9는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 시스템의 제2 예를 설명하는 도면이다.1 is a block diagram illustrating an integrated circuit in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
2 is a diagram illustrating the interface of logic circuits and memory circuits in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
3 is a diagram illustrating a clock signal generation circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
Figure 4 is a circuit diagram illustrating the interface circuit of Figure 2 in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
5 is a diagram illustrating a memory circuit included in an integrated circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
Figure 6 is a diagram illustrating the third interface circuit of Figure 5 in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
Figure 7 is a flow chart illustrating the method of operation of Figure 5 in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
8 is a diagram illustrating a first example of a system including an interface circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
9 is a diagram illustrating a second example of a system including an interface circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
이하, 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 대해 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명의 실시예는 당 업계에서 평균적인 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 보다 완전하게 설명하기 위하여 제공되는 것이다. 본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 개시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 각 도면을 설명하면서 유사한 참조부호를 유사한 구성요소에 대해 사용한다. 첨부된 도면에 있어서, 구조물들의 치수는 본 발명의 명확성을 기하기 위하여 실제보다 확대하거나 축소하여 도시한 것이다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. Embodiments of the present invention are provided to more fully describe the present invention to those skilled in the art. The present invention is capable of various modifications and various forms, and specific embodiments are illustrated and described in detail in the drawings. It should be understood, however, that the invention is not intended to be limited to the particular forms disclosed, but includes all modifications, equivalents, and alternatives falling within the spirit and scope of the invention. Like reference numerals are used for similar elements in describing each drawing. In the accompanying drawings, the dimensions of the structures are enlarged or reduced from the actual dimensions for the sake of clarity of the present invention.
본 출원에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 본 출원에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 명세서 상에 기재된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성 요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to be limiting of the invention. The singular expressions include plural expressions unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. In this application, the terms "comprises", "having", and the like are used to specify that a feature, a number, a step, an operation, an element, a part or a combination thereof is described in the specification, But do not preclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, components, parts, or combinations thereof.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 갖는다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가지는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.Unless otherwise defined, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Terms such as those defined in commonly used dictionaries are to be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the contextual meaning of the related art and are to be interpreted as either ideal or overly formal in the sense of the present application Do not.
집적 회로 ??에 포함되는 트랜지스터들의 수가 증가하고, 집적 회로의 동작 주파수가 높아짐에 따라, 집적 회로에 의해 소비되는 전력 크기가 증가되고 있다. 전력 소비가 관리되지 않는다면, 집적 회로의 열적 요건을 만족하는데 너무 많은 돈이 들거나 집적 회로를 실현할 수 없을 수도 있다. 집적 회로의 열적 요건이란, 동작 중인 집적 회로를 적절히 냉각시켜 집적 회로를 열적 한계 내에서 유지되도록 하는 부품들(components)을 제공하는 것을 말한다. 아울러, 밧데리 전력 장치와 같은 어플리케이션들에서, 집적 회로의 소비 전력 관리는 적절한 밧데리 수명을 제공하는 데에도 중요한 요소가 된다.As the number of transistors in an integrated circuit increases and the operating frequency of the integrated circuit increases, the amount of power consumed by the integrated circuit is increasing. If power consumption is not managed, it may be too costly to meet the thermal requirements of the integrated circuit, or the integrated circuit may not be realized. The thermal requirement of an integrated circuit is to provide components that allow the integrated circuit in operation to cool properly to keep the integrated circuit within thermal limits. In addition, in applications such as battery power devices, power management of integrated circuits is also an important factor in providing adequate battery life.
집적 회로의 전력 소비는 집적 회로로 제공되는 전원 전압과 관련된다. 집적 회로에서 소비되는 전력은 접지 전압에 대한 전원 전압의 크기에 좌우된다. 일반적으로 전원 전압 레벨을 낮춤으로써 전력 소모를 줄일 수 있다.The power consumption of the integrated circuit is related to the supply voltage supplied to the integrated circuit. The power consumed in the integrated circuit depends on the magnitude of the supply voltage relative to the ground voltage. Generally, power consumption can be reduced by lowering the power supply voltage level.
도 1은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 집적 회로를 설명하는 블락 다이어그램이다.1 is a block diagram illustrating an integrated circuit in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 집적 회로(10)는 다수개의 로직 회로들(12)과 다수개의 메모리 회로들(14)을 포함한다. 로직 회로들(12)은 메모리 회로들(14)과 연결된다. 로직 회로들(12)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)에 의해 구동되는 제1 회로 영역(11)에 포함되고, 메모리 회로들(14)은 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)에 의해 구동되는 제2 회로 영역(13)에 포함된다. 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)는 집적 회로(10) 외부에서 제공될 수 있다. 또한, 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)는 집적 회로(10) 내부의 전압 발생부에서 제공될 수 있다. 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)보다 높게 설정될 수 있다. 집적 회로(10)는 하나의 반도체 기판에 집적화된 로직 회로들(12)과 메모리 회로들(14)로 구성될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1, an
로직 회로들(12)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 접지 전압(VSS)으로 각각 바이너리 1과 바이너리 0의 로직 상태를 나타낼 수 있다. 로직 회로들(12)은 동작 동안 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)에서 접지 전압(VSS)으로, 또는 접지 전압(VSS)에서 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 완전히 천이하는 로직 신호로 평가될 수 있다(evaluate). 로직 회로들(12)의 소비 전력은 접지 전압(VSS)에 대한 제1 전압 전압(VDDL)의 상대적인 전압 크기에 달려 있다. 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)을 낮춤으로써 로직 회로들(12)의 소비 전력을 낮출 수 있다. 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)은 로직 회로들(12)의 동작이 제대로 발휘될 수 있을 정도의 전압 레벨로까지 낮출 수 있다.The
로직 회로들(12)은 집적 회로(10)가 설계된 목적에 따른 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 로직 회로들(12)은 동작 동안 다양한 데이터 값들을 발생하고 메모리 회로들(14)에 저장할 수 있다. 또한, 로직 회로들(12)은 메모리 회로들(14)로부터 다양한 데이터 값들을 읽어올 수 있다. 메모리 회로들(14)은, 예컨대 캐시들, 레지스터 등으로 사용되는 메모리를 포함할 수 있다. 메모리 회로들(14)은 독출/기입 가능한 유형의 메모리로 구현될 수 있다.The
로직 회로들(12)은 메모리 회로들(14)을 억세스하기 위하여 다양한 제어 신호들(CTL)을 발생할 수 있다. 제어 신호들(CTL)에는 메모리 회로들(14) 내 억세스되는 메모리 위치를 나타내는 어드레스 신호, 독출 동작을 지시하는 독출 인에이블 신호, 기입 동작을 지시하는 기입 인에이블 신호를 포함할 수 있다. 독출 동작에서는 메모리 회로들(14)이 로직 회로들(12)로 데이터를 출력한다. 기입 동작에서는 로직 회로들(12)이 저장을 위한 데이터를 메모리 회로들(14)로 제공한다. 로직 회로들(12)에서 제공되는 제어 신호들(CTL)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 접지 전압(VSS)으로 동작하는 신호들이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 로직 회로들과 메모리 회로들의 인터페이스를 설명하는 도면이다.2 is a diagram illustrating the interface of logic circuits and memory circuits in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 로직 회로(12a)는 도 1의 로직 회로들(12) 중의 하나일 수 있다. 메모리 회로(14a)는 도 1의 메모리 회로들(14) 중 하나일 수 있다. 로직 회로(12a)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되는 도메인으로 설명되고, 메모리 회로(14a)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되는 도메인으로 설명될 수 있다. 즉, 로직 회로(12a)와 메모리 회로(14a)는 서로 다른 전압 도메인들로 구동되는 회로들이다.2, the
로직 회로(12a)는 다수개의 인버터들(21, 22, 23)을 포함할 수 있다. 제1 내지 제3 인버터들(21, 22, 23)에는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)이 공급된다. 제1 인버터(21)는 제1 클럭 신호들(CLK, CLKB)에 응답하여 입력 신호(IN)를 수신하고 출력 신호(OUT1)를 출력한다. 예컨대, 제1 인버터(21)는 제1 클럭 신호(CLK)의 하강 에지에 응답하여 입력 신호(IN)를 반전시키는 클럭드 인버터(clocked inverter)이다. 제2 및 제3 인버터들(22, 23)은 서로 교차 연결되어 래치(24)를 구성한다. 제1 인버터(21)의 출력은 래치(24)에 연결된다.The
래치(24)는 수신된 제1 인버터(21)의 출력 신호(OUT1)를 반전시키고 래치하여 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)를 출력한다. 제2 인버터(22)는 제1 인버터(21)의 출력 신호(OUT1)를 수신하고 반전시켜 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)를 출력한다. 제3 인버터(23)는 제1 클럭 신호들(CLK, CLKB)에 응답하여 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)를 수신하고, 제3 인버터(23)의 출력은 제2 인버터(22)의 입력으로 제공된다. 예컨대, 제3 인버터(23)는 제1 클럭 신호(CLK)의 로직 하이 레벨에 응답하여 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)를 반전시키는 클럭드 트라이 스테이트(tri-state) 인버터이다.The
로직 회로(12a)에서, 입력 신호(IN), 제1 클럭 신호들(CLK, CLKB), 출력 신호(OUT1) 그리고 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 접지 전압 사이로 동작하는 신호들이다. 로직 회로(12a)는 입력 신호(IN)와 동일한 로직 레벨을 갖는 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)를 발생한다. 제어 신호(CTL1)는 도 1의 제어 신호들(CTL)중 하나일 수 있다.In the
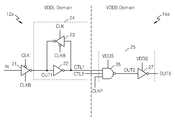
메모리 회로(14a)는 인터페이스 회로(25)를 통해 로직 회로(12a)와 연결된다. 인터페이스 회로(25)는 클럭드 게이트(clocked gate, 26)와 제4인버터(27)를 포함할 수 있다. 클럭드 게이트(26)와 제4 인버터(27)에는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 공급된다. 클럭드 게이트(26)는 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)과 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)를 입력하는 낸드 게이트로 구성될 수 있다. 다양한 실시예들에 따라, 클럭드 게이트(26)는 낸드 게이트 대신에 다른 논리 게이트로 구현될 수 있다.The
제1 제어 신호(CTL1)은 로직 회로(12a)로부터 제공된다. 이와 유사하게, 제2 제어 신호(CTL2)도 로직 회로(12a)로부터 제공될 수 있다. 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)과 접지 전압(VSS) 레벨로 동작하는 신호들이다. The first control signal CTL1 is provided from the
제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 도메인에서 제공되는 신호일 수 있다. 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)과 접지 전압(VSS) 레벨로 동작하는 신호이다. 클럭드 게이트(26)는 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)과 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)를 입력하고 제2 출력 신호(OUT2)를 출력한다. 제2 출력 신호(OUT2)는 제4 인버터(27)로 제공되고, 제4 인버터(27)는 제3 출력 신호(OUT3)를 출력한다.The second clock signal CLKP may be a signal provided in the second power supply voltage VDDS domain. The second clock signal CLKP is a signal that operates at the second power supply voltage VDDS and the ground voltage VSS level. The clocked
도 3은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 클럭 신호 발생 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating a clock signal generation circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
도 3을 참조하면, 클럭 신호 발생 회로(15)는 외부 클럭 신호(CLK_EXT)를 수신하여 제1 클럭 신호(CLK, CLKB)와 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)를 발생할 수 있다. 클럭 신호 발생 회로(15)는 외부 클럭 신호(CLK_EXT)를 수신하는 클럭 수신부(16)와, 클럭 수신부(16)의 출력에 연결되는 직렬 연결된 제1 및 제2 인버터들(17, 18)을 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3, the clock
클럭 수신부(16)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되고, 외부 클럭 신호(CLK_EXT)를 수신하고 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)를 발생할 수 있다. 클럭 수신부(16)는 차동 크로스-커플드 래치(differential cross-coupled latch) 타입의 클럭 발생부를 포함할 수 있다. 클럭 발생부(16)은 기능상 레벨 시프터(level shifter)와 버퍼(buffer) 기능을 할 수 있다. 외부 클럭 신호(CLK_EXT)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 또는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨을 가질 수 있다. 제2 내부 클럭 신호(CLKP)는 제1 인버터(17)로 입력되고, 제1 인버터(17)는 반전된 제1 클럭 신호(CLKB)를 발생할 수 있다. 반전된 제1 클럭 신호(CLKB)는 제2 인버터(18)로 입력되고, 제2 인버터(18)는 제1 클럭 신호(CLK)를 발생할 수 있다. 제1 및 제2 인버터들(17, 18)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되어, 제1 클럭 신호들(CLK, CLKB)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨을 갖는다.The
클럭 신호 발생 회로(15)는 외부 클럭 신호(CLK_EXT)를 수신하고, 서로 동기되는 제1 클럭 신호(CLK)와 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)를 발생할 수 있다. 이 때, 제1 클럭 신호(CLK)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨을 갖고, 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)을 갖는다.The clock
도 4는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 도 2의 인터페이스 회로(25)를 설명하는 회로 다이어그램이다.Figure 4 is a circuit diagram illustrating the
도 4를 참조하면, 인터페이스 회로(25)는 클럭드 게이트(26)와 인버터(27)를 포함한다. 클럭드 게이트(26)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되고, 제1 내지 제3 회로부(31-33)를 포함한다. 제1 회로부(31)는 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 전원이 공급되고 다수개의 피모스 트랜지스터들(P2, P3, P4)을 포함한다. P4 피모스 트랜지스터는 그 소스에 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 연결되고, 그 게이트에 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)가 연결된다. P3 피모스 트랜지스터는 그 게이트에 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)가 연결되고, 그 소스에 P4 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인이 연결된다. P2 피모스 트랜지스터는 그 게이트에 제2 제어 신호(CTL2)가 연결되고, 그 소스에 P4 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인이 연결된다. P2 및 P3 피모스 트랜지스터들의 드레인들은 서로 연결되고 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)에 연결된다.Referring to FIG. 4, the
제2 회로부(32)는 그 소스에 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 연결되고, 그 게이트에 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)가 연결되고, 그 드레인에 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)가 연결된다. 제3 회로부(33)는 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)와 접지 전압(VSS) 사이에 직렬 연결되는 엔모스 트랜지스터들(N1-N3)을 포함한다. N3 엔모스 트랜지스터는 그 드레인에 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)가 연결되고, 그 게이트에 제1 제어 신호(CTL1)가 연결된다. N2 엔모스 트랜지스터는 그 드레인에 N3 엔모스 트랜지스터의 소스가 연결되고, 그 게이트에 제2 제어 신호(CTL2)가 연결된다. N1 엔모스 트랜지스터는 그 드레인에 N2 엔모스 트랜지스터의 소스가 연결되고, 그 게이트에 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)가 연결되고, 그 소스에 접지 전압(VSS)이 연결된다.The
인버터(27)는 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)에 연결되고 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동된다. 인버터(27)는 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)의 로직 레벨을 반전시켜 출력 신호(OUT3)를 출력한다. 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)는 제1 회로부(31)로 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 전원을 공급하는 신호로 작용한다. 즉, 로직 로우 레벨의 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)에 의해 P4 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴온되어 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 제1 회로부(31)의 전원으로 동작한다.The
인터페이스 회로(25)는 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)가 로직 로우 레벨일 때 프리차아지 모드(precharge mode)로 동작한다. P1 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴온되어 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 되고, 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)는 로직 로우 레벨로 발생된다.The
제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)가 로직 하이레벨일 때, 인터페이스 회로(25)는 이벨류에이션 모드(evaluation mode)로 동작한다. 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2) 중 어느 하나가 로직 로우 레벨이면, 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)는 여전히 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)을 유지한다. 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2) 모두 로직 하이 레벨이면, N1 내지 N3 엔모스 트랜지스터가 턴온되어 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)는 디스차아징(discharging)을 시작한다. 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)가 접지 전압(VSS) 레벨로 디스차아징되고, 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)는 로직 하이 레벨이 된다. 로직 하이 레벨의 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)가 제1 회로부(31)로 피이드백되어, P4 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴오프된다. 클럭드 게이트(26)의 출력 신호(OUT2)는 궁극적으로 완전히 접지 전압(VSS)로 디스차아징된다. 이벨류에이션 모드 동안 P1 피모스 트랜지스터를 완전히 턴-오프시키기 위하여, 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)는 제2 전원 전압 레벨(VDDS)로 제공된다.When the second clock signal CLKP is at a logic high level, the
도 4에서, 제1 회로부(31)는 인버터(27)의 출력 신호(OUT3)에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 전원이 공급되고, 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)에 응답하는 위크 키퍼 디바이스(weak keeper device)라 칭할 수 있다. 제2 회로부(32)는 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)에 응답하는 스트롱 프리차이지 디바이스(strong precharge device)라 칭하고, 제3 회로부(33)는 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)과 제2 클럭 신호(CLKP)에 응답하는 스트롱 이벨류에이션 디바이스(strong evaluation device)라 칭할 수 있다.4, the
인터페이스 회로(25)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)를 입력하여 그 출력(OUT3)을 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨 시프팅시킨다. 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들(CTL1, CTL2)들이 어드레스 신호들인 경우, 인터페이스 회로(25)는 어드레싱 디코딩 동작과 레벨 쉬프팅 동작을 동시에 수행한다. 이에 따라, 인터페이스 회로(25)는 어드레싱 디코딩 시간과 레벨 시프팅 시간을 숨길 수 있기 때문에, 일종의 제로-지연 레벨 시프터(zero-delay level shifter)라고 칭할 수 있다. 또한, 인터페이스 회로(25)는 앞단의 마스터 래치(Master latch)와 연결된 슬레이브 래치(slave latch)의 형태를 같기 때문에 마스터-슬래이브 래치(master-slave latch) 형태의 기능의 한 부분을 담당하므로 추가적인 회로 감소의 효과가 있다.The
도 5는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 집적 회로에 포함되는 메모리 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.5 is a diagram illustrating a memory circuit included in an integrated circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
도 5를 참조하면, 로직 회로(12b)는 도 1의 로직 회로들(12) 중의 하나일 수 있다. 메모리 회로(14b)는 도 1의 메모리 회로들(14) 중 하나일 수 있다. 메모리 회로(14b)는 로직 회로(12b)와 연결되고, 로직 회로(12b)에서 출력되는 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)를 수신한다. 로직 회로(12b)는, 도 2에서 설명한 바와 같이, 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 도메인에서 동작하고, 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨과 접지 전압(VSS) 레벨로 동작하는 신호들이다.Referring to Fig. 5, the
메모리 회로(14b)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 도메인에서 동작하고, 어드레스 디코더(41), 제어 신호 발생부(42), 워드라인 드라이버(43) 그리고 메모리 어레이(45)를 포함한다. 어드레스 디코더(41)는 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)를 입력하는 다수개의 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b)을 포함한다. 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b)은 클럭드 게이트들(26a, 26b)과 인버터들(27a, 27b)을 포함한다. 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b)은 각각은 도 3에서 설명된 인터페이스 회로(25)와 동일하게 구성될 수 있다.The
인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b)은 로직 회로(12b)와 메모리 회로(14b) 사이에 연결된다. 제1 인터페이스 회로(25a)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 도메인으로 동작하고, 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)를 입력하고, 어드레스 래치 신호(ADR_LAT)를 출력한다. 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨로 제공되고, 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 제공된다. 제1 인터페이스 회로(25a)는 제1 인터페이스 회로(25a)의 출력인 어드레스 래치 신호(ADR_LAT)에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 전원이 공급된다. 마찬가지로, 제2 인터페이스 회로(25b)도 제2 인터페이스 회로(25b)의 출력에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 전원이 공급된다.The
제어 신호 발생부(42)는 독출 인에이블 신호와 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)를 입력하는 제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)를 포함한다. 제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)는 도 6와 같이 구성될 수 있다.The control
도 6은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 도 5의 제3 인터페이스 회로를 설명하는 도면이다.Figure 6 is a diagram illustrating the third interface circuit of Figure 5 in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
도 6을 참조하면, 제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되고, 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)와 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)를 입력하고 독출 신호(READ)를 출력한다. 제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)는 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)와 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)를 입력하는 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)와, 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력을 입력하고 독출 신호(READ)를 출력하는 인버터(27c)를 포함한다. 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)는 피모스 트랜지스터들(P11, P21, P41)과 엔모스 트랜지스터들(N11, N21)을 포함한다.6, the
P41, P21 피모스 트랜지스터들은 직렬 연결된다. P41 피모스 트랜지스터는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)에 연결되고, 독출 신호(READ)에 게이팅되어 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)을 P21 피모스 트랜지스터로 공급한다. P21 피모스 트랜지스터는 그 게이트에 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)가 연결된다. P11 피모스 트랜지스터는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)에 연결되고, 그 게이트에 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)가 연결된다. P11, P21 피모스 트랜지스터들의 드레인들은 서로 연결되어 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력이 된다. N21, N11 엔모스 트랜지스터들은 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력과 접지 전압(VSS) 사이에 직렬 연결된다. N21 엔모스 트랜지스터의 게이트에 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)가 연결되고, N11 엔모스 트랜지스터의 게이트에 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)가 연결된다.P41 and P21 PMOS transistors are connected in series. The P41 PMOS transistor is connected to the second power supply voltage VDDS and is gated to the read signal READ to supply the second power supply voltage VDDS to the P21 PMOS transistor. A read enable signal RDEN is connected to the gate of the PMOS transistor P21. The P11 PMOS transistor is connected to the second power supply voltage VDDS, and the internal clock signal CLK_INT is connected to the gate thereof. The drains of the P11 and P21 PMOS transistors are connected to each other and become the output of the 2-input clocked
인버터(27c)는 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력을 입력하고 독출 신호(READ)를 출력한다. 독출 신호(READ)는 P21 피모스 트랜지스터로 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)을 공급하는 전원 공급 신호로 작용한다. 즉, 로직 로우 레벨의 독출 신호(READ)에 의해 P41 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴온되어 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 P21 피모스 트랜지스터로 공급된다.The
제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)는 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)가 로직 로우 레벨일 때 P11 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴온되어 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력은 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)이 되고, 독출 신호(READ)는 로직 로우 레벨로 발생된다. 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)가 로직 하이레벨일 때, 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)가 로직 로우 레벨이면, 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력은 여전히 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)을 유지한다. 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)가 로직 하이 레벨이면, N11 및 N21 엔모스 트랜지스터들이 턴온되어 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력은 접지 전압(VSS) 레벨로 디스차아징되고, 독출 신호(READ)는 로직 하이 레벨이 된다. 로직 하이 레벨의 독출 신호(READ)가 P41 피모스 트랜지스터의 게이트로 피이드백되어, P41 피모스 트랜지스터가 턴오프된다. 2-입력 클럭드 게이트(26c)의 출력은 궁극적으로 완전히 접지 전압(VSS)로 디스차아징된다. P11 피모스 트랜지스터를 완전히 턴-오프시키기 위하여, 내부 클럭 신호(CLK_INT)는 제2 전원 전압 레벨(VDDS)로 제공된다.When the internal clock signal CLK_INT is at a logic low level, the
도 5로 돌아가서, 메모리 회로(14b) 내 제어 신호 발생부(42)의 제3 인터페이스 회로(25c)에서 출력되는 독출 신호(READ)는 센싱 인에이블 신호(SAEN)를 발생하는 지연 로직부(46)로 제공된다. 지연 로직부(46)는 독출 신호(READ)를 수신하고 메모리 어레이(45)의 메모리 셀 데이터를 센싱하는 데 충분한 지연 후 센싱 인에이블 신호(SAEN)를 발생한다.5, the read signal READ output from the
워드라인 드라이버(43)는 어드레스 디코더(41)에서 출력되는 어드레스 래치 신호(ADR-LAT)를 수신하고 워드라인(WL)을 구동한다. 메모리 어레이(45)는 메모리 셀들(47), 비트라인 선택부들(48) 그리고 센스 앰프부들(49)을 포함한다. 하나의 메모리 셀(47)은 T1, T2 엔모스 트랜지스터들을 통하여 비트라인쌍(BL, BLB)에 연결되는 크로스-커플드 인버터들(47A, 47B)로 구성되는 전형적인 CMOS SRAM 셀을 포함한다. T1, T2 엔모스 트랜지스터들의 게이트들은 워드라인(WL)에 연결된다. 워드라인(WL)이 로직 하이 레벨로 인에이블되면, T1, T2 엔모스 트랜지스터들은 인버터들(47A, 47B)과 비트라인쌍(BL, BLB) 사이에 도통 경로를 제공한다.The
비트라인 선택부(48)는 비트라인 선택 신호(CS)에 응답하여 비트라인들(BL, BLB)을 센스 앰프부(49)와 연결시킨다. 센스 앰프부(49)는 센싱 인에이블 신호(SAEN)에 응답하여 비트라인쌍(BL, BLB)의 전압 레벨을 감지 증폭하고 차동 신호쌍을 출력한다.The bit
본 실시예에서, 로직 회로(12b)에 제공되는 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨로 동작하는 신호들이다. 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2)과 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN)를 수신하는 메모리 회로(14b)의 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b, 25c)은 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 어드레스 래치 신호(ADR-LAT)와 독출 신호(READ)를 발생한다. 즉, 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b, 25c) 각각은 그 출력인 어드레스 래치 신호(ADR-LAT)와 독출 신호(READ)에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 전원이 공급되고, 어드레스 입력 신호(ADR1 및 ADR2)와 독출 신호(READ)를 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨-시프팅시킨다.In the present embodiment, the address signals ADR1 and ADR2 and the read enable signal RDEN provided to the
로직 회로(12b)를 구동하는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨은, 인터페이스 회로에 의하여 제 1 전원 전압의 레벨을 충분히 낮춤에 따라, 집적 회로는 전력 소비를 줄일 수 있다.The first power supply voltage VDDL level driving the
도 7은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예들에 따른 도 5의 동작 방법을 설명하는 플로우챠트이다.Figure 7 is a flow chart illustrating the method of operation of Figure 5 in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention.
도 7을 참조하면, 로직 회로(12b)는 메모리 회로(14b)를 제어하는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호들을 발생한다(61), 제어 신호들은 메모리 회로(14b)를 독출 및 기입하는 어드레스 신호들(ADR1, ADR2), 독출 인에이블 신호(RDEN) 등을 포함한다. 메모리 회로(14b)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호들을 수신하고, 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨 시프팅한다(62). 메모리 회로(14b)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨 시프트된 제어 신호들에 응답하여 고출 및 기입 동작을 수행한다(63).7, the
도 8은 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 시스템의 제1 예를 설명하는 도면이다.8 is a diagram illustrating a first example of a system including an interface circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
도 8을 참조하면, 시스템(70)은 무선 네트워크 통신 기능을 구비한 모바일 단말기로서, 휴대 전화기, 모바일 PC, 개인 휴대 단말기 등 다양한 형태의 장치로 구현될 수 있다. 모바일 단말기 시스템(70)은 발신자 및 착신자 상호 간 통화를 가능하게 하는 통화 기능을 수행한다. 모바일 단말기 시스템(70)에 의해 수행되는 통화는 음성 통화뿐 아니라 영상 및 음성을 주고 받으면서 통화를 가능하게 하는 영상 통화를 포함한다.Referring to FIG. 8, the
모바일 단말기 시스템(70)이 수행하는 통신 방식은, 예컨대 W-CDMA(Wideband Code Division Multiple Access), EDGE(Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution), LTE(Long Term Evolution), WiMAX(Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) 등일 수 있다. 무선 네트워크는 모바일 단말기 시스템(70) 각각과 무선 통신 신호를 주고 받기 위한 기지국(Base station Transmission System), 복수의 기지국을 제어 및 관리하는 기지국 제어기(Base Station Controller), 그리고 기지국 제어기를 통해 모바일 단말기 시스템(70) 간의 호 연결(call switching)을 수행하는 교환기를 포함할 수 있다.The communication system that the
모바일 단말기 시스템(70)은 카메라부(71), 음성 입력부(72), 무선 통신부(73), 디스플레이부(74), 음성 출력부(75), 사용자 입력부(76), 그리고 제어부(78)를 포함한다.The
카메라부(71)는 촬영을 수행하여 영상을 생성한다. 카메라부(71)는 광을 입사하는 적어도 하나의 렌즈를 포함하는 광학부와, 렌즈를 통해 입사된 광을 전기적 데이터로 변환하여 영상을 생성하는 이미지 센서를 포함할 수 있다. 카메라부(71)의 이미지 센서는 센서 인터페이스를 통해 이미지 프로세싱 유닛에 의해 동작되는 로우-베이어(RAW-Bayer) 및/또는 CMOS 타입일 수 있다. 카메라부(71)의 이미지 센서는 이미지 센서에 의해 검출된 광을 전기 신호로 변환하도록 구성된 다수의 광 검출기를 포함할 수 있다. 이미지 센서는 이미지 센서에 의해 캡처된 광을 필터링하여 컬러 정보를 캡쳐하는 컬러 필터 어레이를 더 포함할 수 있다.The
음성 입력부(72)는, 예컨대, 마이크로 폰과 같은 음성 센서를 포함하여, 음성 통화에 필요한 음성을 입력한다.The
무선 통신부(73)는 무선 네트워크에 연결되어 소정의 무선 통신 방식으로 상대방 단말기와의 통신을 수행한다. 무선 통신부(73)는, 통화시, 제어부(78)의 제어에 따라 카메라부(71)에 의해 생성된 영상 및/또는 음성 입력부(72)에 의해 입력된 음성을 포함하는 영상 통화 데이터를 상대방 단말기에 전송하고, 상대방 단말기로부터 영상 및/또는 음성을 포함하는 영상 통화 데이터를 수신한다.The
디스플레이부(74)는 화면을 표시하며, LCD 등과 같은 디스플레이 디바이스를 포함할 수 있다. 디스플레이부(74)는 카메라부(71)에 의해 생성된 영상을 제어부(78)의 제어에 의해 디스플레이할 수 있다. The
음성 출력부(75)는 음성을 출력하며, 내부 스피커 등과 같은 음성 출력 디바이스를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 음성 출력부(75)는 이어폰, 헤드셋, 외부 스피커 등과 같은 외부 음성 출력 디바이스와의 연결을 위한 커넥터를 더 포함하고, 연결된 외부 음성 출력 디바이스에 음성을 출력할 수 있다. 음성 출력부(75)는 음성 통화 또는 영상 통화시, 제어부(78)의 제어에 따라 상대방 단말기로부터의 음성을 출력할 수 있다.The
사용자 입력부(76)는 모바일 단말기 시스템(70)의 조작을 위한 사용자의 입력을 수신한다. 사용자 입력부(76)는, 숫자, 문자 등의 입력을 위한 복수의 키를 구비하는 키패드를 포함할 수 있다. 키패드는 터치 패드의 형태로 구현될 수 있다. 사용자 입력부(76)는 사용자 입력으로서 디스플레이부(74) 상의 사용자의 모션 또는 제스쳐를 감지하는 감지 센서를 더 포함할 수 있다. 사용자 입력부(76)의 감지 센서는, 예컨대 LCD와 같은 디스플레이부(74)의 패널 형태의 디스플레이 디바이스에 중첩되도록 마련되는 이른바 터치 스크린으로 구현될 수 있다.The
제어부(78)는 모바일 단말기 시스템(70)의 전반적인 제어를 수행한다. 제어부(78)는 사용자 입력부(76)를 통한 사용자의 입력에 의해 통화 기능이 선택되면, 입력된 전화 번호를 참조하여 무선 통신부(73)를 통해 상대방 단말기에 대한 호 연결을 요청한다. 제어부(78)는 호 연결이 이루어지면, 카메라부(71)에 의해 생성된 영상 및/또는 음성 입력부(72)에 의해 입력된 음성을 포함하는 통화 데이터를 무선 통신부(73)를 통해 상대방 단말기에 전송하고, 무선 통신부(73)를 통해 상대방 단말기로부터 수신되는 통화 데이터에 포함된 영상 및/또는 음성이 디스플레이(74) 및/또는 음성 출력부(75)에 출력되도록 제어를 수행한다.The
제어부(78)는 카메라부(71)의 이미지 센서에 의해 캡쳐된 이미지 데이터를 이미지 프로세싱 파이프 라인을 통해 다수의 이미지 프로세싱 동작을 수행한다. 프로세싱된 결과 이미지는 디스플레이부(74)에 표시될 수 있다. 프로세싱되는 이미지 데이터의 해상도와 프레임 레이트가 높아짐에 따라, 이에 부합하는 이미지 신호 프로세싱 시스템이 요구된다.The
제어부(78)는 프로세싱되는 데이터를 저장하기 위하여 소정의 메모리 영역을 포함할 수 있다. 제어부(78) 내 메모리 영역은 도 5와 같은 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b, 25c)를 포함하는 SRAM으로 구현될 수 있다.The
모바일 단말기 시스템(70)에서, 카메라부(71), 음성 입력부(72), 무선 통신부(73), 디스플레이부(74), 음성 출력부(75), 사용자 입력부(76) 그리고 제어부(78) 각각은, 예컨대 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 또는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 보다 높은 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되는, 즉, 서로 다른 전압 도메인들로 구동될 수 있다. 모바일 단말기 시스템(70)의 제어부(78)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되고, 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되는 카메라부(71), 음성 입력부(72), 무선 통신부(73), 디스플레이부(74), 음성 출력부(75), 그리고 사용자 입력부(76)로 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 제공할 수 있다. 또한, 제어부(78)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되고, 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되는 카메라부(71), 음성 입력부(72), 무선 통신부(73), 디스플레이부(74), 음성 출력부(75), 그리고 사용자 입력부(76)로부터 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 수신할 수 있다.In the
모바일 단말기 시스템(70)의 카메라부(71), 음성 입력부(72), 무선 통신부(73), 디스플레이부(74), 음성 출력부(75), 사용자 입력부(76) 그리고 제어부(78) 각각은, 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 수신하고 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 출력 신호로 레벨 시프팅하는 인터페이스 회로(IF)를 포함할 수 있다. 인터페이스 회로(IF)는 그 출력에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 전원이 공급되고, 클럭 신호에 응답하여 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 입력하고 그 출력을 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨 시프팅시킨다.The
도 9는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 시스템의 제2 예를 설명하는 도면이다.9 is a diagram illustrating a second example of a system including an interface circuit according to various embodiments of the present invention.
도 9를 참조하면, 시스템(80)은 도 7의 제어부(78)에 포함되는 이미지 프로세싱 시스템일 수 있다. 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 CPU (81), ISP (82), 이미지 코덱부(83), 제1 및 제2 메모리 콘트롤러들(84, 85), 이미지 입출력부(86), 그리고 인터페이스부(87)를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 그 내부에 존재하는 메모리 영역(102)을 제어하는 제3 메모리 콘트롤러(101)를 더 포함할 수 있다. 메모리 영역(102)은 도 5와 같은 인터페이스 회로들(25a, 25b, 25c)를 포함하는 SRAM 또는 DRAM으로 구현될 수 있다Referring to Fig. 9, the
ISP (Image Signal Processor, 82)는 베이어(Bayer) 프로세싱 유닛, RGB 프로세싱 유닛, 크기조정/회전/아핀-변환(Scaling/Rotating/Affine-Transform) 프로세싱 유닛 등을 포함할 수 있다. ISP (82)은 각 유닛의 프로세싱을 제어하기 위하여, 예컨대, 이미지의 크기, 색의 깊이, 데드 픽셀 보상(Dead Pixel Alive), 렌즈 셰이딩 보상(Lens Shading Compensation), 적합 컬러 보간(Adaptive Color Interpolation), 컬러 보정(Color Correction), 감마 제어(Gamma Control), 색상/게인 제어(hue/Gain Control), 영상 효과(Image Effect), 자동 노출(Auto Exposure), 자동 화이트 밸런스(Auto White Balance) 등을 제어할 수 있다. ISP (82)에서 프로세싱된 이미지 데이터는 버스(88)를 통하여 이미지 코덱부(83)로 전송될 수 있다.The ISP (Image Signal Processor) 82 may include a Bayer processing unit, an RGB processing unit, a Scaling / Rotating / Affine-Transform processing unit, and the like.
이미지 코덱부(83)는 이미지 데이터를 전송 및 저장에 용이한 형태로 이미지 인코딩 및 디코딩을 수행할 수 있다. 이미지 코덱부(83)는 JPEG 코덱부(JPEG CODEC)로 구성되어 고해상도의 JPEG 이미지를 생성할 수 있다. JPEG (Joint Photographic Expert Group)는 이미지 데이터가 블록 단위로 압축되고, 디코딩하고자 하는 위치의 블록 데이터 압축 스트림을 파일의 처음부터 스캐닝해가면서 해당 위치를 찾아 복원하여 재생한다.The
JPEG 압축의 최소 사양인 베이스라인 JPEG는, 이미지 데이터를 RGB에서 YIQ로 변환하고 각 컬러 성분(Y,I,G)의 이미지를 8x8 블록 단위의 매크로 블록으로 나눈 다음, DCT (Discrete Cosign Transform) 변환하고, 그 결과 값인 DCT 계수를 양자화(quantization) 테이블을 사용하여 계수마다 상이한 스텝 크기로 선형 양자화하여 시각적으로 중요한 부분과 덜 중요한 부분으로 분리하고, 중요한 부분은 살리고 덜 중요한 부분은 손실시켜 데이터 양을 줄인다. 8x8 블록 데이터는 최소 부호화 단위로서, 최소 블록 단위가 변경되면 블록 데이터의 크기도 변경될 수 있다.Baseline JPEG, which is the minimum specification of JPEG compression, converts image data from RGB to YIQ, divides the image of each color component (Y, I, G) into macroblocks of 8x8 block units, performs DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) And the resulting DCT coefficients are linearly quantized with different step sizes for each coefficient using a quantization table to separate the visually significant portions into less important portions and to save the important portions and lose the less important portions Reduce. The 8x8 block data is the minimum encoding unit. If the minimum block unit is changed, the size of the block data can be changed.
매크로 블록 단위로 블록화되어 양자화된 DCT 계수는 하나의 DC 성분(직류)과 63개의 AC 성분(교류)으로 나타나며, DC 성분은 인접한 신호 간의 상관 관계를 고려하여 인접한 이전 블록과의 차분 신호를 부호화 (DPCM: Differential Pulse Code Modulation)하고, AC 성분은 블록마다 지그재그 스캔에 의해 일렬로 나열한 후 부호화(Run-Length Coding)한다.The DCT coefficients that are blocked and quantized in macroblock units are represented by one DC component (DC) and 63 AC components (AC), and the DC component is encoded by considering the correlation between adjacent signals DPCM (Differential Pulse Code Modulation), and AC components are arranged in a line by zigzag scan for each block and then subjected to run-length coding.
JPEG 압축 방식에 의해 압축된 JPEG 이미지는 다수의 매크로 블록 단위로 경계를 이루게 되며, 각각의 매크로 블록은 하나의 DC 성분과 블록의 끝을 나타내는 EOB 코드로 구성하게 된다. JPEG 이미지를 구성하는 각 매크로 블록은 상호 종속적인 DC 값을 갖는다.A JPEG image compressed by the JPEG compression method is bounded by a plurality of macroblock units, and each macro block is composed of one DC component and an EOB code indicating the end of the block. Each macroblock that constitutes a JPEG image has a DC value that is mutually dependent.
ISP (82)은 JPEG 이미지 데이터의 노이즈를 개선하기 위하여 이미지를 보정한다. ISP (82)는 8x8 블록 데이터의 DC/AC 계수를 조정할 수 있다. ISP (82)는 블록 데이터에서 DC/AC 임계값(DC/AC Threshold value)에 따라 이미지 영역(Image area)을 분리한 다음, DC/AC 계수를 조정하거나 제어하여 노이즈를 감소시킨다(Noise reduction). ISP (82)는 AC 계수를 조정하여 블록성 잡음을 감소시킨다(Blocky effect reduction). 또한, ISP (82)는 DC/AC 계수를 조정하여 휘도 강화(Brightness enhancement)를 블록 데이터에 적용할 수 있다.The
CPU (81)는 상술한 이미지 데이터를 프로세싱하는 방법을 구현하는데 필요한 하드웨어, 소프트웨어, 및/또는 펌웨어를 포함하는 마이크로 프로세서이다. CPU (81)는 이미지 데이터를 프로세싱하는 것과 관련된 일련의 복잡한 프로세스를 핸들링함에 있어서 VPU (Video Processing Unit) 이라고도 할 수 있는 GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)을 포함할 수 있다.The
CPU (81)는 다양한 전자 게임 및 다른 어플리케이션에서 관심을 끄는 그래픽 이미지의 조작 및 렌더링(rendering) 처리할 수 있다. CPU (81)는, 소프트웨어 어플리케이션과 같은, 호스트로부터 명령어 및 이미지 데이터를 수신할 수 있다. 명령어는 이미지 데이터를 변경하여 렌더링된 이미지를 발생시키는데 필요한 계산 및 동작을 특정하는데 사용된다.The
CPU (81)는 카메라 기능, 멀티미디어 데이터 재생 등의 부가 프로세스 기능을 제어할 수 있다. CPU (81)는 이미지 데이터를 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)의 크기에 맞도록 축소, 확대 또는 크로핑(cropping)하며, 디스플레이부(74)에서 표시되는 이미지 데이터의 색상 규격에 맞도록 변환할 수 있다.The
CPU (81)에 의해 처리될 명령어들 또는 이미지 데이터는 메모리 장치(91)에 저장될 수 있다. 메모리 장치(91)는 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80) 외부에 존재하는 외장형 메모리 장치일 수 있다. 이미지 프로세싱 시스템 (80)는 제1 메모리 콘트롤러(84)를 통하여 메모리 장치(91)를 제어할 수 있다. 메모리 장치(91)는 SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)과 같은 휘발성 메모리일 수 있다. 제1 메모리 콘트롤러(84)는 SDRAM의 동작을 제어하는 SDRAM 콘트롤러일 수 있다. 메모리 장치(91)는 기본 입출력 시스템(BIOS), 운영 체계, 다양한 프로그램들, 어플리케이션들, 또는 사용자 인터페이스 기능의 펌-웨어를 저장할 수 있다.The instructions or image data to be processed by the
메모리 장치(91)는 카메라부(611, 도 8)의 이미지 센서로부터 수신되는 원본 이미지 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 메모리 장치(91)에 저장된 원본 이미지 데이터는 ISP (82)로 제공될 수 있다.The
메모리 장치(91)는 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)의 동작 동안에 버퍼링 또는 캐싱을 위해 사용될 수 있다. 예컨대, 메모리 장치(91)는 이미지 데이터가 디스플레이부(614, 도 8)로 출력될 때 이를 버퍼링하기 위한 하나 이상의 프레임 버퍼를 포함할 수 있다. 즉, 메모리 장치(91)는 이미지 데이터의 프로세싱 이전에, 이미지 데이터의 프로세싱 동안에, 그리고 이미지 데이터의 프로세싱 이후에 그 데이터를 저장할 수 있다.The
메모리 장치(91)에 더하여, 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 이미지 데이터 및/또는 명령어들의 영구 저장을 위해 비휘발성 저장 장치(92)와 접속될 수 있다. 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 제2 메모리 콘트롤러(85)를 통해 비휘발성 저장 장치(92)와 연결된다. 비휘발성 저장 장치(92)는 제2 메모리 콘트롤러(85)에 의해 제어된다. 비휘발성 저장 장치(92)는 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80) 외부에 존재하는 외장형 저장 장치일 수 있다.In addition to the
비휘발성 저장 장치(92)는 플래쉬 메모리, 하드 드라이브, 또는 임의의 다른 광, 자기 및/또는 고상 저장 매체들, 또는 이들의 일부 조합들을 포함할 수 있다. 제2 메모리 콘트롤러(85)는 플래쉬 메모리를 제어하는 플래쉬 메모리 콘트롤러일 수 있다. 도8에는 비휘발성 메모리 장치(92)가 단일 장치로 도시되어 있지만, 비휘발성 저장 장치(92)는 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)과 관련하여 동작하는 전술한 저장 장치들 중 하나 이상의 저장 장치들의 조합을 포함할 수 있다.
비휘발성 저장 장치(92)는 펌웨어, 데이터 파일들, 이미지 데이터, 소프트웨어 프로그램들 및 어플리케이션들, 무선 접속 정보, 개인 정보, 사용자 선호들 및 임의의 다른 적절한 데이터를 저장하는 데 사용될 수 있다. 비휘발성 저장 장치(92) 및/또는 메모리 장치(91)에 저장된 이미지 데이터는 디스플레이 상에 출력되기 전에 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)에 의해 처리될 수 있다.
이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)을 통하여, 메모리 장치(91)에는 카메라부(71, 도 7)의 이미지 센서를 통해 캡쳐된 원본 이미지 데이터를 저장하기도 하지만, 컴퓨터 등과 같은 전자 장치에 저장된 이미지 데이터를 저장할 수도 있다. 메모리 장치(91)는 메모리 장치(91)에 저장된 원본 이미지 데이터 또는 JPEG 이미지 데이터를 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)로 전달하여 디스플레이할 수 있다. 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)는 이미지 데이터를 디스플레이하거나 메뉴 및 명령을 사용자 인터페이스의 일부로서 디스플레이할 수 있다.Through the
카메라부(71, 도 7), 컴퓨터, 및/또는 디스플레이부(74, 도 7) 등과 같은 멀티미디어는, 카메라 기능, 멀티미디어 파일 재생, 3D 그래픽 등과 같은 부가 기능을 수행하기 위하여 멀티미디어 프로세서(Multimedia Processor; MMP) 또는 어플리케이션 프로세서(Application Processor; AP)에 의해 제어될 수 있다. MMP에 의해 수행되는 카메라 기능의 동작 모드는 프리뷰(Preview) 모드와 멀티미디어 동작 모드로 구분될 수 있다. 프리뷰 모드는 카메라 촬영 이전에 미리 보기를 위한 것이고, 멀티미디어 동작 모드는 카메라 촬영 명령 입력에 의한 촬영 동작 수행 모드이다.The multimedia such as the camera unit 71 (FIG. 7), the computer and / or the display unit 74 (FIG. 7) may be a multimedia processor, MMP) or an application processor (AP). The operation mode of the camera function performed by the MMP can be divided into a preview mode and a multimedia operation mode. The preview mode is for previewing before camera shooting, and the multimedia operation mode is a shooting operation performing mode by inputting camera shooting command.
이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 이미지 데이터에 관한 프론트-엔드 프로세서로 칭할 수 있고, MMP 및/또는 AP는 후속 프로세서에 해당하므로 백-엔드 프로세서(93)로 칭할 수 있다. 백-엔드 프로세서(93)는 카메라부(71, 도 7), 컴퓨터, 및/또는 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)와 연결될 수 있다. 이미지 프로세싱 시스템(80)은 이미지 입출력부(86)를 통해 메모리 장치(91)에 저장된 이미지 데이터를 백-엔드 프로세서(93)로 전송한다.The
이미지 입출력부(86)는 카메라부(71, 도 7)의 이미지 센서로부터 출력되는 원시 이미지 데이터를 백-엔드 프로세서(93)로 전송할 수 있다. 이미지 입출력부(86)는 백-엔드 프로세서(93)와 연결되는 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)의 크기에 맞도록 조정된 이미지 데이터를 전송할 수 있다. 또한, 이미지 입출력부(86)는 디스플레이부(74, 도 7)에서 표시되는 이미지 데이터의 색상 규격에 맞도록 변환된 이미지 데이터를 출력할 수 있다. 이미지 입출력부(86)와 벡-엔드 프로세서(93) 사이에는 이미지 데이터 교환을 수행하는 인터페이스부(87)가 연결될 수 있다.The image input /
인터페이스부(87)은 이미지 데이터 전송 단위인 프레임을 전송하는 MIPI 및/또는 병렬 인터페이스를 포함할 수 있다. 프레임은 실질적인 이미지 정보 이외에 주소와 필수적인 프로토콜 제어 정보를 포함할 수 있다. 프레임은 비트 단위로 전송되며, 데이터의 앞 뒤에 헤드 필드와 트레일러 필드를 포함할 수 있다. 병렬 인터페이스는 이미지 데이터가 낮은 해상도와 낮은 프레임 레이트를 갖는 경우에 사용된다. 고속 직렬 인터페이스인 MIPI는 해상도와 프레임 레이트가 높은 이미지 데이터를 전송할 때 사용된다.The
제어부(78) 내 CPU(81), ISP (82), 이미지 코덱부(83), 제1 및 제2 메모리 콘트롤러들(84, 85), 이미지 입출력부(86), 그리고 인터페이스부(87) 각각은, 예컨대 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 또는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 보다 높은 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되는, 서로 다른 전압 도메인으로 구동될 수 있다. CPU (81)는 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되고, 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되는 ISP (82), 이미지 코덱부(83), 제1 및 제2 메모리 콘트롤러들(84, 85) 그리고 이미지 입출력부(86)로 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제1 제어 신호를 제공할 수 있다. 또한, CPU (81)는 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 구동되고, 제1 전원 전압(VDDL)으로 구동되는 ISP (82), 이미지 코덱부(83), 제1 및 제2 메모리 콘트롤러들(84, 85) 그리고 이미지 입출력부(86)로 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 제어 신호를 수신할 수 있다.The
CPU(81), ISP (82), 이미지 코덱부(83), 제1 및 제2 메모리 콘트롤러들(84, 85) 그리고 이미지 입출력부(86) 각각은 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 수신하고 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨의 출력 신호로 레벨 시프팅하는 인터페이스 회로(IF)를 포함할 수 있다. 인터페이스 회로(IF)는 그 출력에 의해 제2 전원 전압(VDDS)으로 전원이 공급되고, 클럭 신호에 응답하여 제1 전원 전압(VDDL) 레벨의 제어 신호를 입력하고 그 출력을 제2 전원 전압(VDDS) 레벨로 레벨 시프팅시킨다.The
본 발명은 도면에 도시된 실시예를 참고로 설명되었으나 이는 예시적인 것에 불과하며, 본 기술 분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이로부터 다양한 변형 및 균등한 다른 실시예가 가능하다는 점을 이해할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명의 진정한 기술적 보호 범위는 첨부된 특허청구범위의 기술적 사상에 의하여 정해져야 할 것이다.While the present invention has been described with reference to exemplary embodiments, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments, but, on the contrary, is intended to cover various modifications and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit and scope of the appended claims. Accordingly, the true scope of the present invention should be determined by the technical idea of the appended claims.
Claims (20)
상기 제1 전원 전압 레벨과 다른 제2 전원 전압 레벨을 갖는 제2 전원 전압으로 구동되고, 상기 제1 회로 영역으로부터 제1 및 제2 제어 신호들을 수신하는 인터페이스 회로를 포함하는 제2 회로 영역을 포함하고,
상기 인터페이스 회로는,
상기 제2 전원 전압에 그 소스가 연결되고, 상기 인터페이스 회로의 출력 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제1 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인과 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 상기 제1 제어 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제2 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인과 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 상기 제2 제어 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제3 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제2 전원 전압과 상기 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 클럭 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제4 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 노드와 접지 전압 사이에 직렬 연결되고, 상기 제1 제어 신호, 상기 제2 제어 신호 그리고 상기 클럭 신호에 그 게이트 각각이 연결되는 제1 내지 제3 엔모스 트랜지스터들; 및
상기 제1 노드에 연결되고, 상기 제1 노드의 신호에 따라 상기 출력 신호를 출력하는 인버터를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.A first circuit region driven by a first power supply voltage having a first power supply voltage level; And
And a second circuit region including an interface circuit driven by a second power supply voltage having a second power supply voltage level different from the first power supply voltage level and receiving first and second control signals from the first circuit region and,
The interface circuit comprising:
A first PMOS transistor whose source is connected to the second power supply voltage and whose gate is connected to an output signal of the interface circuit;
A second PMOS transistor which is connected between a drain of the first PMOS transistor and a first node and whose gate is connected to the first control signal;
A third PMOS transistor connected between a drain of the first PMOS transistor and a first node, and having a gate connected to the second control signal;
A fourth PMOS transistor connected between the second power supply voltage and the first node and having a gate connected to the clock signal;
First to third NMOS transistors serially connected between the first node and a ground voltage and each having its gate connected to the first control signal, the second control signal and the clock signal; And
And an inverter coupled to the first node for outputting the output signal according to a signal of the first node.
상기 제1 전원 전압 레벨은 상기 제2 전원 전압 레벨 보다 낮게 설정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the first power supply voltage level is set to be lower than the second power supply voltage level.
상기 클럭 신호는 상기 제2 전원 전압 레벨과 상기 접지 전압의 레벨로 동작하는 신호인 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the clock signal is a signal that operates at a level of the second power supply voltage level and the ground voltage.
상기 제1 전원 전압 레벨과 다른 제2 전원 전압 레벨을 갖는 제2 전원 전압으로 구동되고, 상기 로직 회로로부터 제1 및 제2 어드레스 신호들을 수신하여 어드레스 래치 신호를 출력하는 어드레스 디코더를 포함하는 메모리 영역을 포함하고,
상기 어드레스 디코더는,
상기 제2 전원 전압에 그 소스가 연결되고, 상기 어드레스 래치 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제1 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인과 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 상기 제1 어드레스 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제2 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 피모스 트랜지스터의 드레인과 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 상기 제2 어드레스 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제3 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제2 전원 전압과 상기 제1 노드 사이에 연결되고, 클럭 신호에 그 게이트가 연결되는 제4 피모스 트랜지스터;
상기 제1 노드와 접지 전압 사이에 직렬 연결되고, 상기 제1 어드레스 신호, 상기 제2 어드레스 신호 그리고 상기 클럭 신호에 그 게이트 각각이 연결되는 제1 내지 제3 엔모스 트랜지스터들; 및
상기 제1 노드에 연결되고, 상기 제1 노드의 신호에 따라 상기 어드레스 래치 신호를 출력하는 인버터를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.A logic circuit driven by a first power supply voltage having a first power supply voltage level; And
And an address decoder driven by a second power supply voltage having a second power supply voltage level different from the first power supply voltage level and receiving first and second address signals from the logic circuit and outputting an address latch signal, / RTI >
Wherein the address decoder comprises:
A first PMOS transistor whose source is connected to the second power supply voltage and whose gate is connected to the address latch signal;
A second PMOS transistor connected between a drain and a first node of the first PMOS transistor and having a gate connected to the first address signal;
A third PMOS transistor connected between a drain of the first PMOS transistor and a first node, and having a gate connected to the second address signal;
A fourth PMOS transistor connected between the second power supply voltage and the first node and having a gate connected to the clock signal;
First to third NMOS transistors serially connected between the first node and a ground voltage, the first to third NMOS transistors being connected to the first address signal, the second address signal and the clock signal, respectively; And
And an inverter coupled to the first node for outputting the address latch signal in accordance with a signal of the first node.
상기 제1 전원 전압 레벨은 상기 제2 전원 전압 레벨 보다 낮게 설정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.19. The method of claim 18,
Wherein the first power supply voltage level is set to be lower than the second power supply voltage level.
상기 클럭 신호는 상기 제2 전원 전압 레벨과 상기 접지 전압의 레벨로 동작하는 신호인 것을 특징으로 하는 집적 회로.19. The method of claim 18,
Wherein the clock signal is a signal that operates at a level of the second power supply voltage level and the ground voltage.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW102144205A TWI614765B (en) | 2012-12-07 | 2013-12-03 | Integrated circuit including circuits driven in different voltage domains |
| US14/100,114 US9325314B2 (en) | 2012-12-07 | 2013-12-09 | Integrated circuit including circuits driven in different voltage domains |
| CN201310664282.0A CN103871458B (en) | 2012-12-07 | 2013-12-09 | Integrated circuit and its data processing method, decoder, memory |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201261734621P | 2012-12-07 | 2012-12-07 | |
| US61/734,621 | 2012-12-07 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20140074156A KR20140074156A (en) | 2014-06-17 |
| KR101892076B1 true KR101892076B1 (en) | 2018-08-27 |
Family
ID=51127450
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020130028313A KR101892076B1 (en) | 2012-12-07 | 2013-03-15 | Integrated circuit with different voltage domain circuits |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101892076B1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI614765B (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100329062A1 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-30 | Campbell Brian J | Leakage and NBTI Reduction Technique for Memory |
| US20120294095A1 (en) * | 2011-05-16 | 2012-11-22 | Shinye Shiu | Dynamic Level Shifter |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7355905B2 (en) * | 2005-07-01 | 2008-04-08 | P.A. Semi, Inc. | Integrated circuit with separate supply voltage for memory that is different from logic circuit supply voltage |
| WO2007104335A1 (en) * | 2006-03-16 | 2007-09-20 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | A wordline driver for a non-volatile memory device, a non-volatile memory device and method |
| US8164971B2 (en) * | 2009-06-02 | 2012-04-24 | Mediatek Inc. | Dual power rail word line driver and dual power rail word line driver array |
-
2013
- 2013-03-15 KR KR1020130028313A patent/KR101892076B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2013-12-03 TW TW102144205A patent/TWI614765B/en active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100329062A1 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-30 | Campbell Brian J | Leakage and NBTI Reduction Technique for Memory |
| US20120294095A1 (en) * | 2011-05-16 | 2012-11-22 | Shinye Shiu | Dynamic Level Shifter |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20140074156A (en) | 2014-06-17 |
| TW201432713A (en) | 2014-08-16 |
| TWI614765B (en) | 2018-02-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9325314B2 (en) | Integrated circuit including circuits driven in different voltage domains | |
| US10319115B2 (en) | Image compression device | |
| US9391635B2 (en) | Block scanner and run-level encoder from AC to DC values | |
| TWI524176B (en) | Method and apparatus for display power management | |
| TWI387314B (en) | Image processing apparatus and method thereof | |
| US20130201360A1 (en) | Method of changing an operation mode of a camera image sensor | |
| US20090135256A1 (en) | Sata camera system | |
| NL2012213B1 (en) | Power gating circuits using schmitt trigger circuits, semiconductor integrated circuits and systems including power gating circuits. | |
| US8798386B2 (en) | Method and system for processing image data on a per tile basis in an image sensor pipeline | |
| KR20130087119A (en) | Display drive ic | |
| US20090102850A1 (en) | Error Diffusion for Display Frame Buffer Power Saving | |
| KR101892076B1 (en) | Integrated circuit with different voltage domain circuits | |
| KR20230113786A (en) | Image processing method, device and electronic device | |
| US8548275B2 (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| TWI819455B (en) | System and method for processing video | |
| CN109102770B (en) | Low-power-consumption low-bandwidth display panel driving chip for high-performance calculation | |
| US20170094190A1 (en) | Processing display of digital camera readout with minimal latency | |
| US20140125821A1 (en) | Signal processing circuit, imaging apparatus and program | |
| KR20160067577A (en) | An image processor, a method of operating the image processor, and an application processor including the image processor | |
| US10659725B2 (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| CN118939589A (en) | Display card switching method and related equipment | |
| TWI451749B (en) | Image processing device | |
| CN113891078A (en) | Image processing apparatus and method | |
| KR20140126841A (en) | Memory apparatus and Image signal processing system | |
| KR19980022997A (en) | Discrete Cosine Transformation Block Designator for Digital Image |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |