KR101477848B1 - Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same - Google Patents
Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101477848B1 KR101477848B1 KR1020110145110A KR20110145110A KR101477848B1 KR 101477848 B1 KR101477848 B1 KR 101477848B1 KR 1020110145110 A KR1020110145110 A KR 1020110145110A KR 20110145110 A KR20110145110 A KR 20110145110A KR 101477848 B1 KR101477848 B1 KR 101477848B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- active layer
- formula
- polyamide active
- porous support
- reverse osmosis
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/76—Macromolecular material not specifically provided for in a single one of groups B01D71/08 - B01D71/74
- B01D71/80—Block polymers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D61/00—Processes of separation using semi-permeable membranes, e.g. dialysis, osmosis or ultrafiltration; Apparatus, accessories or auxiliary operations specially adapted therefor
- B01D61/02—Reverse osmosis; Hyperfiltration ; Nanofiltration
- B01D61/025—Reverse osmosis; Hyperfiltration
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D67/00—Processes specially adapted for manufacturing semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus
- B01D67/0002—Organic membrane manufacture
- B01D67/0006—Organic membrane manufacture by chemical reactions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D69/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by their form, structure or properties; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D69/10—Supported membranes; Membrane supports
- B01D69/107—Organic support material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D71/00—Semi-permeable membranes for separation processes or apparatus characterised by the material; Manufacturing processes specially adapted therefor
- B01D71/06—Organic material
- B01D71/56—Polyamides, e.g. polyester-amides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2321/00—Details relating to membrane cleaning, regeneration, sterilization or to the prevention of fouling
- B01D2321/281—Details relating to membrane cleaning, regeneration, sterilization or to the prevention of fouling by applying a special coating to the membrane or to any module element
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2323/00—Details relating to membrane preparation
- B01D2323/02—Hydrophilization
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2325/00—Details relating to properties of membranes
- B01D2325/04—Characteristic thickness
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Separation Using Semi-Permeable Membranes (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 다공성 지지체; 상기 다공성 지지체 상에 형성되는 폴리아미드 활성층; 및 상기 폴리아미드 활성층 상에 형성되는 초친수층을 포함하며, 상기 초친수층은 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 물질을 포함하는 역삼투막 및 그 제조 방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a porous support; A polyamide active layer formed on the porous support; And a super hydrophilic layer formed on the polyamide active layer, wherein the super hydrophilic layer comprises a material represented by the following formula (1) and a method for producing the same.
Description
본 발명은 역삼투막에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는 초친수층을 포함하여 내오염 성능이 우수한 역삼투막에 관한 것이다.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a reverse osmosis membrane, and more particularly, to a reverse osmosis membrane including a super hydrophilic layer and having excellent resistance to contamination.
반투과성막으로 격리된 두 용액 사이에서 용매가 용질의 농도가 낮은 용액에서 높은 용액 쪽으로 분리막을 통과하여 이동하는 현상을 삼투 현상이라 하며, 이때 용매의 이동으로 용질의 농도가 높은 용액 측에 작용하는 압력을 삼투압이라고 한다. 그런데 삼투압보다 높은 외부 압력을 걸어주면 용매는 용질의 농도가 낮은 용액 쪽으로 이동하게 되는데, 이 현상을 역삼투라고 한다. 역삼투 원리를 이용하여 압력 구배를 구동력으로 해서 반투과성 막을 통해 각종 염이나 유기 물질을 분리해낼 수 있다. 이러한 역삼투 현상을 이용한 역삼투 분리막은 분자 수준의 물질을 분리하고, 염수 또는 해수에서 염을 제거하여 가정용 및 건축용, 산업용 용수를 공급하는데 사용되고 있다.
The phenomenon that the solvent moves between the two solutions separated by the semi-permeable membrane through the membrane from the solution with a low solute concentration to the solution with a high solute concentration is called osmotic phenomenon. The pressure acting on the solution side Is called osmotic pressure. However, when an external pressure higher than osmotic pressure is applied, the solvent moves toward the solution having a low solute concentration. This phenomenon is called reverse osmosis. By using the reverse osmosis principle, it is possible to separate various salts or organic substances through the semipermeable membrane using the pressure gradient as a driving force. Reverse osmosis membranes using this reverse osmosis membrane are used for separating molecular-level substances and removing salts from brine or sea water to supply domestic, architectural and industrial water.
이러한 역삼투 분리막의 대표적인 예로는, 폴리아미드계 역삼투 분리막을 들 수 있으며, 폴리아미드계 역삼투 분리막은 미세 다공층 지지체 상에 폴리아미드 활성층을 형성하는 방법으로 제조되고 있으며, 보다 구체적으로는, 부직포 위에 폴리설폰층을 형성하여 미세 다공성 지지체를 형성하고, 이 미세 다공성 지지체를 m-페닐렌 디아민(m-Phenylene Diamine, mPD) 수용액에 침지시켜 mPD층을 형성하고, 이를 다시 트리메조일클로라이드(TriMesoyl Chloride, TMC) 유기 용매에 침지시켜 mPD층을 TMC와 접촉시켜 계면 중합시킴으로써 폴리아미드층을 형성하는 방법으로 제조되고 있다.
A typical example of such a reverse osmosis separator is a polyamide reverse osmosis separator. The polyamide reverse osmosis separator is manufactured by forming a polyamide active layer on a microporous layer support. More specifically, A polysulfone layer is formed on the nonwoven fabric to form a microporous support. The microporous support is immersed in an aqueous solution of m-Phenylene Diamine (mPD) to form an mPD layer, which is then reacted with trimethoyl chloride TriMesoyl Chloride (TMC)) in an organic solvent to form a polyamide layer by interfacial polymerization of the mPD layer in contact with TMC.
한편, 최근에는 역삼투막의 성능을 개선하기 위해 폴리아미드층 상에 내구성이나 내오염성을 향상시키기 위해 폴리아미드 활성층 표면에 비닐 모노머를 그라프트 공중합하거나(미국공개특허 20090308804), 폴리아미드 활성층에 TiO2 와 같은 무기입자를 도입하는 방법(미국등록특허 6551536) 등이 제안되었다. 그러나, 상기 기술들의 경우, 그 효과가 미미하거나, 여러층의 코팅층을 형성하여야 하기 때문에 역삼투막의 두께가 두꺼워지고, 그로 인해 정수 기능이 저하될 수 있으며, 제조 공정이 복잡하다는 문제점이 있다.
On the other hand, with recent TiO 2 to a polyamide active layer a vinyl monomer graft-copolymerized, or (U.S. Patent 20,090,308,804), a polyamide active layer on the surface to enhance the durability and stain resistance to the polyamide layers to improve the performance of the reverse osmosis membrane, And a method of introducing the same inorganic particles (USP 6551536). However, in the case of the above techniques, the effect is insignificant or the coating layer of several layers must be formed, so that the thickness of the reverse osmosis membrane becomes thick, thereby deteriorating the water purification function, and the manufacturing process is complicated.
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 것으로, 염제거율, 투과 유량과 같은 정수 성능을 저하시키지 않으면서도 우수한 내오염성을 가지며, 박형으로 구현할 수 있는 역삼투막을 제공하고자 한다.
Disclosure of Invention Technical Problem [8] Accordingly, the present invention has been made keeping in mind the above problems occurring in the prior art, and an object of the present invention is to provide a reverse osmosis membrane having excellent stain resistance without reducing detergency such as salt removal rate and permeation flow rate.
일 측면에서, 본 발명은 다공성 지지체; 상기 다공성 지지체 상에 형성되는 폴리아미드 활성층; 및 상기 폴리아미드 활성층 상에 형성되는 초친수층을 포함하며, 상기 초친수층은 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 물질을 포함하는 역삼투막을 제공한다.
In one aspect, the present invention provides a porous support comprising: a porous support; A polyamide active layer formed on the porous support; And a super hydrophilic layer formed on the polyamide active layer, wherein the super hydrophilic layer comprises a material represented by the following formula (1).
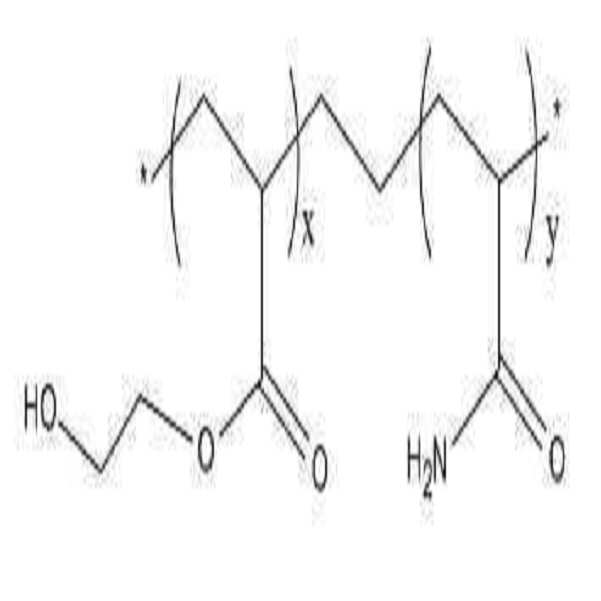
[화학식 1][Chemical Formula 1]
상기 [화학식 1]에서, x는 70 내지 95인 정수이고, y는 5 내지 30인 정수이다.
Wherein x is an integer of 70 to 95 and y is an integer of 5 to 30.
이때, 상기 초친수층의 두께는 1 내지 10nm 정도인 것이 바람직하다.
At this time, the thickness of the super hydrophilic layer is preferably about 1 to 10 nm.
다른 측면에서 본 발명은 폴리아미드 활성층이 형성된 다공성 지지체를 상기 화학식 1의 초친수성 물질이 함유된 수용액으로 처리하는 단계를 포함하는 역삼투막 제조 방법을 제공한다.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for preparing a reverse osmosis membrane, which comprises treating a porous support having a polyamide active layer formed thereon with an aqueous solution containing the superhydrophilic substance of Formula 1.
이때, 상기 수용액은 화학식 1로 표시되는 초친수성 물질을 0.0001 중량% 내지 10 중량%의 함량으로 포함하는 것이 바람직하며, 상기 처리는 침지법에 의해 수행될 수 있다.
At this time, it is preferable that the aqueous solution contains 0.0001 wt% to 10 wt% of the superhydrophilic substance represented by the formula (1), and the treatment may be performed by a dipping method.
한편, 상기 화학식 1의 초친수성 물질은 2-히드록시에틸 아크릴레이트와 아크릴아민을 70 : 30 ~ 95 : 5 의 당량비로 혼합한 후 반응시켜 제조될 수 있으며, 이때, 상기 반응은 45 내지 80℃에서 1 내지 6시간동안 수행되는 것이 바람직하다.
Meanwhile, the superhydrophilic substance of Formula 1 may be prepared by mixing 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and acrylamine in an equivalent ratio of 70:30 to 95: 5, and then reacting, For 1 to 6 hours.
본 발명의 초친수층을 포함하는 역삼투막은 정수 성능을 저하시키지 않으면서도 종래의 역삼투막에 비해 우수한 내오염성을 갖는다.
The reverse osmosis membrane containing the super hydrophilic layer of the present invention has excellent stain resistance compared to the conventional reverse osmosis membrane without deteriorating water purification performance.
이하, 본 발명을 보다 구체적으로 설명한다.
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically.
본 발명자들은 정수 성능을 저하시키지 않으면서도 내오염성이 우수한 역삼투막을 개발하기 위해, 연구를 거듭한 결과, 폴리아미드 활성층 상에 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 초친수성 물질을 포함하는 초친수층을 형성함으로써, 상기와 같은 목적을 달성할 수 있음을 알아내고, 본 발명을 완성하였다.
As a result of repeated studies to develop a reverse osmosis membrane having excellent stain resistance without deteriorating water purification performance, the present inventors have found that by forming an super hydrophilic layer containing a super hydrophilic substance represented by the following Chemical Formula 1 on a polyamide active layer, The present invention has been accomplished on the basis of these findings.
본 발명의 역삼투막은 (1) 다공성 지지체 (2)폴리아미드 활성층 및 (3) 초친수층을 포함한다.
The reverse osmosis membrane of the present invention comprises (1) a porous support, (2) a polyamide active layer, and (3) an super hydrophilic layer.
상기 (1)다공성 지지체로는, 부직포 상에 고분자 재료의 코팅층이 형성된 것을 사용할 수 있으며, 상기 고분자 재료로는, 예를 들면, 폴리설폰, 폴리에테르설폰, 폴리카보네이트, 폴리에틸렌옥사이드, 폴리이미드, 폴리에테르이미드, 폴리에테르에테르케톤, 폴리프로필렌, 폴리메틸펜텐, 폴리메틸클로라이드 및 폴리비닐리젠플루오라이드 등이 사용될 수 있으나, 반드시 이들로 제한되는 것은 아니다. 이 중에서도 특히 폴리설폰이 바람직하다.
The porous support may be a porous support having a coating layer of a polymeric material formed on a nonwoven fabric. Examples of the polymeric material include polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polycarbonate, polyethylene oxide, polyimide, poly An ether imide, a polyether ether ketone, a polypropylene, a polymethylpentene, a polymethyl chloride, and a polyvinylidene fluoride, but is not limited thereto. Of these, polysulfone is particularly preferable.
한편, 상기 (2) 폴리아미드 활성층은 아민 화합물과 아실 할라이드 화합물의 계면 중합체 의해 형성될 수 있으며, 이때 상기 아민 화합물은, 이로써 제한되는 것은 아니나, 예를 들면, m-페닐렌디아민, p-페닐렌디아민, 1,3,6-벤젠트리아민, 4-클로로-1,3-페닐렌디아민, 6-클로로-1,3-페닐렌디아민, 3-클로로-1,4-페닐렌 디아민 또는 이들의 혼합물인 것이 바람직하다. 또한, 상기 아실 할라이드 화합물은, 이로써 제한 되는 것은 아니나, 예를 들면, 트리메조일클로라이드, 이소프탈로일클로라이드, 테레프탈로일클로라이드 또는 이들의 혼합물인 것이 바람직하다.
On the other hand, (2) the polyamide active layer may be formed by an interface polymer of an amine compound and an acyl halide compound, wherein the amine compound includes, but is not limited to, m-phenylenediamine, p-phenyl 1,3-phenylenediamine, 3-chloro-1, 4-phenylenediamine, 3-chloro-1,3-phenylenediamine, . ≪ / RTI > In addition, the acyl halide compound is not limited thereto, but is preferably, for example, trimethoyl chloride, isophthaloyl chloride, terephthaloyl chloride, or a mixture thereof.
다음으로, 상기 (3) 초친수층은 하기 [화학식 1]로 표시되는 물질을 포함하는 것을 그 특징으로 한다.
Next, the (3) super hydrophilic layer comprises a material represented by the following formula (1).
[화학식 1][Chemical Formula 1]
상기 [화학식 1]에서, x는 70 ~ 95인 정수이며, y는 5~30인 정수일 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 x는 85~95인 정수, y는 5~15인 정수, 가장 바람직하게는 x는 85~90인 정수이고, y는 10~15인 정수이다.
X is an integer of 70 to 95, y is an integer of 5 to 30, preferably x is an integer of 85 to 95, y is an integer of 5 to 15, and most preferably x Is an integer of 85 to 90, and y is an integer of 10 to 15.
한편, 상기 [화학식 1]로 표시되는 물질은 다량의 하이드록실 및 아민 그룹을 갖는 초친수성 물질로, 상기 물질이 폴리아미드 활성층 위에 코팅이 되면 보통 소수성을 가지는 먼지 등의 오염 물질이 잘 달라 붙지 않기 때문에 역삼투막의 내오염성을 향상시키는 역할을 한다
On the other hand, the substance represented by the above formula (1) is a super hydrophilic substance having a large amount of hydroxyl and amine groups, and when the above substance is coated on the polyamide active layer, contaminants such as dust, Therefore, it has a role of improving the stain resistance of the reverse osmosis membrane
상기 [화학식 1]로 표시되는 물질은 2-히드록시에틸 아크릴레이트와 아크릴아미드를 70 : 30 ~ 95 : 5의 당량비로 혼합한 후 반응시켜 제조될 수 있다. 이때 상기 반응은 45 내지 80℃에서 1 내지 6시간동안 수행되는 것이 바람직하다.
The material represented by Formula 1 may be prepared by mixing 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and acrylamide in an equivalent ratio of 70:30 to 95: 5 and then reacting. At this time, the reaction is preferably carried out at 45 to 80 ° C for 1 to 6 hours.
한편, 상기 [화학식 1]로 표시되는 물질을 포함하는 상기 초친수층은 그 두께가 1 ~ 10nm 정도인 것이 바람직하다. 초친수성층의 두께가 상기 범위 내일 때, 내오염성과 정수 성능이 모두 양호하게 나타나기 때문이다.
On the other hand, it is preferable that the thickness of the super-hydrophilic layer including the substance represented by Formula 1 is about 1 to 10 nm. When the thickness of the super-hydrophilic layer is within the above-mentioned range, both the contamination resistance and the water purifying performance are good.
다음으로 본 발명의 역삼투막의 제조 방법에 대해 설명한다.
Next, a method for producing a reverse osmosis membrane of the present invention will be described.
본 발명의 역삼투막은 폴리아미드 활성층이 형성된 다공성 지지체를 상기 [화학식 1]의 초친수성 물질이 함유된 수용액으로 처리하는 단계를 포함하여 제조될 수 있다.
The reverse osmosis membrane of the present invention can be produced by treating a porous support having a polyamide active layer formed thereon with an aqueous solution containing the superhydrophilic substance of Formula 1.
이때, 상기 다공성 지지체 상에 폴리아미드 활성층을 형성하는 방법은 특별히 제한되지 않으며, 당해 기술 분야에 잘 알려진 역삼투막 제조 방법에 의해 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 다공성 지지체를 m-페닐렌 디아민(m-Phenylene Diamine, mPD) 수용액에 침지하여 mPD층을 형성하고, 이를 다시 트리메조일클로라이드(TriMesoyl Chloride, TMC) 유기 용매에 침지하여 mPD층을 TMC와 접촉시켜 계면 중합시킴으로써 폴리아미드 활성층을 형성할 수 있다. 또한, 침지법 대신 스프레이 또는 코팅 등의 방법을 통해 폴리아미드 활성층을 형성할 수도 있다.
At this time, the method of forming the polyamide active layer on the porous support is not particularly limited and may be performed by a reverse osmosis membrane manufacturing method well known in the art. For example, the porous support is immersed in an aqueous solution of m-Phenylene Diamine (mPD) to form an mPD layer, which is then immersed in an organic solvent of TriMesoyl Chloride (TMC) The polyamide active layer can be formed by interfacial polymerization by contacting with TMC. Alternatively, the polyamide active layer may be formed by a method such as spraying or coating instead of the dipping method.
한편, 폴리아미드 활성층이 형성된 다공성 지지체를 상기 [화학식 1]의 초친수성 물질이 함유된 수용액으로 처리하는 단계는, 예를 들면, 상기 폴리아미드 활성층이 형성된 다공성 지지체를 상기 [화학식 1]의 초친수성 물질이 함유된 수용액에 침지시키는 방법으로 수행될 수 있다. 이때, 상기 수용액은 초친수성 물질을 0.0001 내지 10 중량%, 바람직하게는 0.0001 내지 5 중량%, 가장 바람직하게는 0.0001 내지 1 중량%의 함량으로 포함하는 것이 바람직하다. 초친수성 물질의 농도가 0.0001 중량% 보다 작아지면 폴리아미드 활성층 위에 전체적으로 코팅이 되지 않으며, 10 중량% 보다 커지면 초친수성 물질을 코팅한 두께가 두꺼워져서 역삼투막의 성능 저하에 영향을 미칠 수 있기 때문이다.
On the other hand, the step of treating the porous support on which the polyamide active layer is formed with an aqueous solution containing the superhydrophilic substance of the above formula (1) can be carried out, for example, by mixing the porous support on which the polyamide active layer is formed with the superhydrophilic Or by immersing it in an aqueous solution containing the substance. At this time, the aqueous solution preferably contains the superhydrophilic substance in an amount of 0.0001 to 10% by weight, preferably 0.0001 to 5% by weight, and most preferably 0.0001 to 1% by weight. If the concentration of the superhydrophilic substance is less than 0.0001 wt%, the coating may not be entirely coated on the polyamide active layer. If the concentration of the superhydrophilic substance is greater than 10 wt%, the coated thickness of the superhydrophilic substance may be increased, which may affect the performance of the reverse osmosis membrane.
또한, 상기 침지 시간은 2 내지 3시간 정도인 것이 바람직하다. 침지 시간이 짧아지면 초친수성 물질이 폴리아미드 활성층에 잘 붙지 않으며 시간이 길어지면 초친수성 물질들 사이에 반응을 해서 물질들 사이에 집합을 이루어 역삼투막 성능 저하에 영향을 미치기 때문이다.
The immersion time is preferably about 2 to 3 hours. When the immersion time is short, the super hydrophilic material does not adhere well to the polyamide active layer. If the immersion time is prolonged, it reacts between the super hydrophilic materials and aggregates them to affect the performance of the reverse osmosis membrane.
상기 침지 처리를 통해 폴리아미드 활성층 상에 초친수층이 코팅되면, 초친수층과 폴리아미드 활성층의 밀착성을 향상시키기 위해 약 50 내지 60℃에서 약 30 내지 40분 동안 건조시키는 단계를 수행하는 것이 바람직하다.
When the super hydrophilic layer is coated on the polyamide active layer through the immersion treatment, it is preferable to perform the step of drying at about 50 to 60 ° C for about 30 to 40 minutes in order to improve the adhesion between the super hydrophilic layer and the polyamide active layer Do.
한편, 본 발명에서 사용되는 상기 [화학식 1]로 표시되는 물질은 2-히드록시에틸 아크릴레이트와 아크릴아미드를 70 : 30 ~ 95 : 5의 당량비로 혼합한 후 반응시켜 제조될 수 있다. 이때 상기 반응은 45 내지 80℃에서 1 내지 6시간동안 수행되는 것이 바람직하다.
Meanwhile, the substance represented by the formula 1 used in the present invention can be prepared by mixing 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and acrylamide in an equivalent ratio of 70:30 to 95: 5 and then reacting. At this time, the reaction is preferably carried out at 45 to 80 ° C for 1 to 6 hours.
상기와 같은 방법으로 제조된 본 발명의 역삼투막은 표면에 초친수층이 형성되어 있기 때문에 유기물에 대한 방오성이 매우 강하며, 초기 염베거율 및 초기 투과유량과 같은 정수 기능에 있어서도 종래의 역삼투막과 동등하거나 그 이상의 성능을 갖는 것으로 나타났다.
Since the reverse osmosis membrane of the present invention produced by the above-described method has a superfine hydrophilic layer formed on its surface, the antifouling property against organic substances is very strong, and even in the purification function such as initial salt wager ratio and initial permeation flow rate, Or more.
이하, 구체적인 실시예를 통해 본 발명을 더 자세히 설명한다.
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to specific examples.
제조예Manufacturing example
1 - 폴리아미드 활성층이 형성된 다공성 지지체 제조 Preparation of Porous Support with 1-Polyamide Active Layer
DMF(N,N-디메틸포름아미드) 용액에 18중량%의 폴리술폰 고형분을 넣고 80℃에서 12시간 이상 녹여 균일한 액상이 얻었다. 이 용액을 폴리에스테르 재질의 95 ~ 100㎛ 두께의 부직포 위에 45 ~ 50㎛ 두께로 캐스팅하여 다공성 폴리술폰 지지체를 형성하였다. 18% by weight of polysulfone solid was added to DMF (N, N-dimethylformamide) solution and dissolved at 80 DEG C for 12 hours or more to obtain a uniform liquid phase. This solution was cast on a nonwoven fabric having a thickness of 95 to 100 mu m made of polyester to a thickness of 45 to 50 mu m to form a porous polysulfone support.
상기 방법으로 제조된 다공성 폴리술폰 지지체를 2중량%의 메타페닐렌디아민을 포함하는 수용액에 2분 동안 담갔다 꺼낸 후, 지지체 상의 과잉의 수용액을 25psi 롤러를 이용하여 제거하고, 상온에서 1분간 건조하였다. The porous polysulfone support prepared in the above manner was immersed in an aqueous solution containing 2% by weight of m-phenylenediamine for 2 minutes, and then the excess aqueous solution on the support was removed using a 25 psi roller and dried at room temperature for 1 minute .
그런 다음, 상기 지지체를 ISOL-C(SK Chem)용매를 사용한 0.1중량%의 트리메조일클로라이드 유기 용액에 1분간 담갔다가 꺼내고, 60℃ 오븐에서 10분간 건조하였다. 그런 다음, 0.2중량% 탄산나트륨 수용액에서 상온에서 2시간 이상 수세한 후, 증류수로 수세하여 200nm 두께의 폴리아미드 활성층을 갖는 다공성 지지체를 제조하였다.
Then, the support was immersed in 0.1 wt% organic solution of trimesoyl chloride using ISOL-C (SK Chem) solvent for 1 minute, and then taken out and dried in an oven at 60 ° C for 10 minutes. Thereafter, the membrane was rinsed with 0.2 wt% sodium carbonate aqueous solution at room temperature for 2 hours or more, and then washed with distilled water to prepare a porous support having a polyamide active layer with a thickness of 200 nm.
제조예Manufacturing example
2 - 화학식 1의 2 -
초친수성Super hydrophilic
물질의 제조 Manufacture of materials
2-히드록시에틸 아크릴레이트와 아크릴아미드를 9 : 1의 당량비로 수용액 상에 넣고 60℃에서 3시간 동안 반응시켜 화학식 1의 물질을 얻었다.
2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and acrylamide were placed in an aqueous solution at an equivalent ratio of 9: 1 and reacted at 60 占 폚 for 3 hours to obtain the compound of formula (1).
실시예Example 1 One
제조예 1에 의해 제조된 폴리아미드 활성층을 갖는 다공성 지지체를 증류수로 세척한 후, 제조예 2에 의해 제조된 화학식 1의 물질을 0.0001-10 중량%의 함량으로 함유하는 수용액에 2 내지 3시간 동안 침지시킨 후, 60℃ 오븐에서 30 내지 40분간 건조시켜 초친수층을 형성하였다.
The porous support having the polyamide active layer prepared in Preparation Example 1 was washed with distilled water and then immersed in an aqueous solution containing 0.0001-10% by weight of the substance of the formula (1) prepared in Preparation Example 2 for 2 to 3 hours And then dried in an oven at 60 DEG C for 30 to 40 minutes to form an super hydrophilic layer.
실시예Example 2 2
수용액 내의 화학식 1의 물질의 함량을 0.001 중량%로 한 점 외에는 실시예 1과 동일한 방법으로 초친수층을 형성하였다.
A super hydrophilic layer was formed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the content of the substance of Chemical Formula 1 in the aqueous solution was changed to 0.001% by weight.
실시예Example 3 3
수용액 내의 화학식 1의 물질의 함량을 0.01 중량%로 한 점 외에는 실시예 1과 동일한 방법으로 초친수층을 형성하였다.
The superfine hydrophilic layer was formed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the content of the substance of Chemical Formula 1 in the aqueous solution was changed to 0.01 wt%.
실시예Example 4 4
수용액 내의 화학식 1의 물질의 함량을 0.1 중량%로 한 점 외에는 실시예 1과 동일한 방법으로 초친수층을 형성하였다.
A super-hydrophilic layer was formed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the content of the compound of Formula 1 in the aqueous solution was 0.1 wt%.
실시예Example 5 5
수용액 내의 화학식 1의 물질의 함량을 1 중량%로 한 점 외에는 실시예 1과 동일한 방법으로 초친수층을 형성하였다.
A super-hydrophilic layer was formed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the content of the substance of Chemical Formula 1 in the aqueous solution was 1 wt%.
실시예Example 6 6
수용액 내의 화학식 1의 물질의 함량을 10 중량%로 한 점 외에는 실시예 1과 동일한 방법으로 초친수층을 형성하였다.
A super hydrophilic layer was formed in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the content of the substance of Chemical Formula 1 in the aqueous solution was changed to 10 wt%.
비교예Comparative Example
비교를 위해 제조예 1에 의해 제조된 폴리아미드 활성층을 갖는 다공성 지지체를 증류수로 세척한 후, 어떠한 표면처리도 하지 않은 상태로 그대로 사용하였다.
For comparison, the porous support having the polyamide active layer prepared in Production Example 1 was washed with distilled water and used without any surface treatment.
실험예Experimental Example 1 - 정수 성능 평가 1 - integer performance evaluation
상기 실시예 1 ~ 6 및 비교예에 의해 제조된 역삼투막의 초기 염 배제율 및 초기 투과 유량을 측정하였다. 초기 염배제율과 초기 투과 유량은 25℃에서 32,000ppm의 염화나트륨 수용액을 1400mL/min의 유량으로 공급하면서 측정하였다. 막 평가에 사용한 역삼투막 셀 장치는 평판형 투과셀과 고압펌프, 저장조 및 냉각 장치를 구비하였으며, 평판형 투과 셀의 구조는 크로스-플로우(cross-flow) 방식으로 유효 투과면적은 140cm2이다. 세척한 역삼투막을 투과셀에 설치한 다음, 평가 장비의 안정화를 위하여 3차 증류수를 이용하여 1시간 정도 충분히 예비 운전을 실시하였다. 그런 다음, 32,000ppm의 염화나트륨 수용액으로 교체하여 압력과 투과 유량이 정상 상태에 이를 때까지 1시간 정도 장비 운전을 실시한 후, 10분간 투과되는 물의 양을 측정하여 유량을 계산하고, 전도도 미터(Conductivity Meter)를 사용하여 투과 전후 염 농도를 분석하여 염배제율을 계산하였다. 측정 결과는 하기 [표 1]에 나타내었다.
The initial salt rejection rate and the initial permeate flow rate of the reverse osmosis membrane prepared in Examples 1 to 6 and Comparative Examples were measured. The initial salt rejection rate and the initial permeate flow rate were measured while supplying 32,000 ppm aqueous sodium chloride solution at 25 ° C at a flow rate of 1400 mL / min. The reverse osmosis membrane cell device used for the evaluation of the membrane was equipped with a plate-type permeation cell, a high-pressure pump, a reservoir and a cooling device. The structure of the plate-type permeation cell was a cross-flow type with an effective permeate area of 140 cm 2 . After the washed reverse osmosis membrane was installed in the permeation cell, the preliminary operation was performed for about 1 hour using third distilled water for stabilization of the evaluation equipment. Then, the apparatus was operated for about 1 hour until the pressure and permeate flow rate reached a steady state by replacing with 32,000 ppm sodium chloride aqueous solution. Then, the flow rate was calculated by measuring the amount of water permeated for 10 minutes, and the conductivity was measured with a Conductivity Meter ) Was used to calculate the salt rejection rate by analyzing the salt concentration before and after permeation. The measurement results are shown in Table 1 below.
실험예Experimental Example 2 - 내오염성 평가 2 - Evaluation of stain resistance
실시예4 및 비교예에 의해 제조된 역삼투막의 내오염성을 평가하였다. 내오염성 평가는 32,000ppm의 NaCl 수용액과 100ppm의 카제인 혼합 수용액을 사용하여 측정하였다. 초기 염 배제율 및 유량을 평가한 후, 100ppm의 카제인 수용액을 평가기 탱크에 투입하고, 즉시 염배제율과 유량의 변화를 측정하였다. 그런 다음 2시간 후에 염배제율과 유량의 변화를 측정하였다. 카제인은 pH 11 이상의 수용액에 녹여 사용하였다. 측정 결과는 [표 2]에 나타내었다.
The stain resistance of the reverse osmosis membrane prepared in Example 4 and Comparative Example was evaluated. The stain resistance evaluation was carried out using a 32,000 ppm aqueous NaCl solution and a 100 ppm casein mixed aqueous solution. After the initial salt rejection rate and the flow rate were evaluated, a casein aqueous solution of 100 ppm was put into the evaluator tank, and the change in the salt rejection rate and the flow rate was immediately measured. Then, changes in salt excretion rate and flow rate were measured after 2 hours. Casein was dissolved in an aqueous solution having a pH of 11 or more. The measurement results are shown in Table 2.
Claims (11)
상기 다공성 지지체 상에 형성되는 폴리아미드 활성층; 및
상기 폴리아미드 활성층 상에 형성되는 초친수층을 포함하며,
상기 초친수층은 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 물질을 포함하는 역삼투막.
[화학식 1]
상기 [화학식 1]에서, x는 70 ~ 95인 정수이고, y는 5 ~ 30인 정수임.
A porous support;
A polyamide active layer formed on the porous support; And
And an ultra-hydrophilic layer formed on the polyamide active layer,
Wherein the super hydrophilic layer comprises a material represented by the following formula (1).
[Chemical Formula 1]
Wherein x is an integer of 70 to 95 and y is an integer of 5 to 30.
상기 초친수층은 그 두께가 1 ~ 10nm 인 역삼투막.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the super hydrophilic layer has a thickness of 1 to 10 nm.
상기 다공성 지지체는 부직포 상에 폴리설폰, 폴리에테르설폰, 폴리카보네이트, 폴리에틸렌옥사이드, 폴리이미드, 폴리에테르이미드, 폴리에테르에테르케톤, 폴리프로필렌, 폴리메틸펜텐, 폴리메틸클로라이드 및 폴리비닐리덴 플루오라이드로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상을 코팅하여 형성된 것인 역삼투막.
The method according to claim 1,
The porous support may be formed on a nonwoven fabric by using a polymeric material selected from the group consisting of polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polycarbonate, polyethylene oxide, polyimide, polyetherimide, polyetheretherketone, polypropylene, polymethylpentene, polymethylchloride and polyvinylidene fluoride Wherein the coating layer is formed by coating at least one selected from the group consisting of the following.
상기 폴리아미드 활성층은 아민 화합물과 아실 할라이드 화합물의 계면 중합체 의해 형성되는 것인 역삼투막.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the polyamide active layer is formed by an interface polymer of an amine compound and an acyl halide compound.
상기 아민 화합물은 m-페닐렌디아민, p-페닐렌디아민, 1,3,6-벤젠트리아민, 4-클로로-1,3-페닐렌디아민, 6-클로로-1,3-페닐렌디아민, 3-클로로-1,4-페닐렌 디아민 및 이들의 혼합물로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 역삼투막.
5. The method of claim 4,
The amine compound may be at least one selected from the group consisting of m-phenylenediamine, p-phenylenediamine, 1,3,6-benzenetriamine, 4-chloro-1,3-phenylenediamine, 6- 3-chloro-1,4-phenylenediamine, and mixtures thereof.
상기 아실 할라이드 화합물은 트리메조일클로라이드, 이소탈로일클로라이트 및 테레프탈로일클로라이드로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상인 역삼투막.
5. The method of claim 4,
Wherein the acyl halide compound is at least one selected from the group consisting of trimesoyl chloride, isotaryl chlorite, and terephthaloyl chloride.
[화학식 1]
상기 [화학식 1]에서, x는 70~95인 정수이고, y는 5~30인 정수임.
Treating the porous support on which the polyamide active layer is formed with an aqueous solution containing the superhydrophilic substance of Formula 1 below.
[Chemical Formula 1]
Wherein x is an integer of 70 to 95 and y is an integer of 5 to 30.
상기 수용액은 화학식 1로 표시되는 초친수성 물질을 0.0001 중량% 내지 10 중량%의 함량으로 포함하는 역삼투막 제조 방법.
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein the aqueous solution comprises 0.0001 wt% to 10 wt% of the superhydrophilic substance represented by the formula (1).
상기 처리는 침지법에 의해 수행되는 역삼투막 제조 방법.
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein the treatment is performed by a dipping method.
상기 화학식 1의 초친수성 물질은 2-히드록시에틸 아크릴레이트와 아크릴아미드를 70 : 30 ~ 95 : 5의 당량비로 혼합한 후 반응시켜 제조된 것인 역삼투막 제조 방법.
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein the superhydrophilic substance of Formula 1 is prepared by mixing 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and acrylamide in an equivalent ratio of 70:30 to 95: 5 and then reacting.
상기 반응은 45 내지 80℃에서 1 내지 6 시간동안 수행되는 역삼투막 제조 방법.
11. The method of claim 10,
Wherein the reaction is carried out at 45 to 80 DEG C for 1 to 6 hours.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110145110A KR101477848B1 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2011-12-28 | Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110145110A KR101477848B1 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2011-12-28 | Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130076498A KR20130076498A (en) | 2013-07-08 |
| KR101477848B1 true KR101477848B1 (en) | 2014-12-31 |
Family
ID=48990077
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110145110A KR101477848B1 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2011-12-28 | Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101477848B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017052256A1 (en) * | 2015-09-23 | 2017-03-30 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Water treatment membrane and method for manufacturing same |
| KR102085402B1 (en) * | 2016-05-18 | 2020-03-05 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Method for manufacturing water-treatment membrane, water-treatment membrane manufactured by thereof, and water treatment module comprising membrane |
| WO2017200313A1 (en) * | 2016-05-18 | 2017-11-23 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Method for manufacturing water treatment separator, water treatment separator manufactured using same, and water treatment module comprising water treatment separator |
| TWI652106B (en) * | 2017-04-19 | 2019-03-01 | 南韓商Lg化學股份有限公司 | Water treatment membrane and preparation method thereof |
| CN109337110B (en) * | 2018-08-28 | 2021-07-30 | 广东联城住工装备信息科技有限公司 | Waterproof breathable film and preparation method thereof |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001327840A (en) * | 2000-05-25 | 2001-11-27 | Toray Ind Inc | Composite semipermeable membrane and its manufacturing method |
| KR20080075765A (en) * | 2007-02-13 | 2008-08-19 | 웅진케미칼 주식회사 | Selective membrane having a high fouling resistance |
| KR20110115856A (en) * | 2010-04-16 | 2011-10-24 | 한국과학기술연구원 | The method of preparation for hydrophilic water filtration membrane having improved antifouling and hydrophilic water filtration membrane according to the method |
-
2011
- 2011-12-28 KR KR1020110145110A patent/KR101477848B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001327840A (en) * | 2000-05-25 | 2001-11-27 | Toray Ind Inc | Composite semipermeable membrane and its manufacturing method |
| KR20080075765A (en) * | 2007-02-13 | 2008-08-19 | 웅진케미칼 주식회사 | Selective membrane having a high fouling resistance |
| KR20110115856A (en) * | 2010-04-16 | 2011-10-24 | 한국과학기술연구원 | The method of preparation for hydrophilic water filtration membrane having improved antifouling and hydrophilic water filtration membrane according to the method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20130076498A (en) | 2013-07-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101432218B1 (en) | Reveres osmosis membrane having properties of high salt rejection and high flux and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101517686B1 (en) | Polyamide-based water-treatment membrane having an excellent antifouling property and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101546244B1 (en) | Water treatment membrane having a high chlorine resistance and a high permeability and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101733264B1 (en) | Polyamide water-treatment membranes having properties of high salt rejection and high flux and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101494541B1 (en) | Polyamide water-treatment membranes having an excellent antifouling property and manufacturing method thereof | |
| EP2857088B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing a reverse osmosis membrane | |
| EP2859938B1 (en) | Highly permeable carbodiimide comprising reverse osmosis membrane and method for preparing same | |
| KR101114668B1 (en) | Manufacturing method for polyamide-based reverse osmosis membrane and polyamide-based reverse osmosis membrane manufactured thereby | |
| EP2857085A1 (en) | Polyamide-based reverse osmosis membrane having excellent initial permeate flow rate and method for manufacturing same | |
| KR101477848B1 (en) | Reverse osmosis membrane having ultra hydrophilic layer and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP6642860B2 (en) | Water treatment separation membrane and method for producing the same | |
| KR101659122B1 (en) | Polyamide water-treatment membranes having properies of high salt rejection and high flux and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101230843B1 (en) | Fouling resistance polyamide reverse osmosis membrane and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR102041657B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing water-treatment membrane, water-treatment membrane manufactured by thereof, and water treatment module comprising membrane | |
| KR100813893B1 (en) | Method of manufacturing reverse osmosis composite membrane | |
| KR20190055664A (en) | A polyamide composite membrane having improved salt and boron rejection and method for preparation thereof | |
| KR102288033B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing water-treatment membrane and water-treatment membrane manufactured thereby | |
| KR101825632B1 (en) | Preparation Method of High Flux Polyamide composite Membrane | |
| KR20210136676A (en) | Excellent removing nitrate polyamide reverse osmosis membrane, Method of manufacturing the same and Membrane module comprising the same | |
| KR101474062B1 (en) | Reverse osmosis membrane and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101520150B1 (en) | Reverse osmosis membrane with high flux and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20030022915A (en) | Producing method of composite polyamide reverse osmosis membrane | |
| US20140034569A1 (en) | Reverse osmosis membrane having high initial permeate flux | |
| KR20150009802A (en) | Reverse osmosis membrane and method for manufacturing the same | |
| KR20220013744A (en) | Method for manufacturing water treatment membrane, water treatment membrane, and water treatment module |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20170919 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20181016 Year of fee payment: 5 |