KR100922900B1 - Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network - Google Patents
Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100922900B1 KR100922900B1 KR1020070133345A KR20070133345A KR100922900B1 KR 100922900 B1 KR100922900 B1 KR 100922900B1 KR 1020070133345 A KR1020070133345 A KR 1020070133345A KR 20070133345 A KR20070133345 A KR 20070133345A KR 100922900 B1 KR100922900 B1 KR 100922900B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- terminal
- information
- data
- receiving
- tunnel header
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/02—Buffering or recovering information during reselection ; Modification of the traffic flow during hand-off
- H04W36/023—Buffering or recovering information during reselection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/10—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/02—Processing of mobility data, e.g. registration information at HLR [Home Location Register] or VLR [Visitor Location Register]; Transfer of mobility data, e.g. between HLR, VLR or external networks
- H04W8/08—Mobility data transfer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/18—Processing of user or subscriber data, e.g. subscribed services, user preferences or user profiles; Transfer of user or subscriber data
- H04W8/186—Processing of subscriber group data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 핸드 오버 제어가 분산된 이동성 제어 구조에서의 데이터 전송 방법에 관한 것으로, 데이터 전송 요청을 수신하여, 상기 단말이 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹을 파악하고, 상기 단말이 속한 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 포워딩 정보를 이용하여 전송할 데이터에 터널 헤더를 추가하는 단계; 및 상기 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 상기 수신 단말이 속하는 네트워크 접속 장치를 포함하는 적어도 하나의 네트워크 접속 장치로 전송하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 데이터 전송 방법에 의해 버퍼링 현상을 없애고 지연시간을 줄일 수 있어, 데이터 전송을 더 신속하게 할 수 있는 효과가 있다. The present invention relates to a data transmission method in a mobility control structure in which handover control is distributed, and receives a data transmission request to determine a home address group to which the terminal belongs, and forwarding information on the home address group to which the terminal belongs. Adding a tunnel header to data to be transmitted using; And transmitting the data to which the tunnel header is added to at least one network access device including a network access device to which the receiving terminal belongs, thereby eliminating buffering and reducing delay time by the data transmission method. It is possible to make the data transfer more quickly.
모바일IP, 이동성제어, 홈어드레스 Mobile IP, Mobility Control, Home Address
Description
본 발명은 네트워크 내의 이동성 제어에 관한 것으로, 특히 핸드 오버 제어가 분산된 이동성 제어 구조에서의 데이터 전송 방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to mobility control in a network, and more particularly, to a data transmission method in a mobility control structure in which handover control is distributed.
본 발명은 정보통신부 및 정보통신연구진흥원의 IT성장동력기술개발사업의 일환으로 수행한 연구로부터 도출된 것이다. [과제관리번호 : 2006-S-058-02, ALL-IP 기반 통합 네트워크 서비스 제어 기술 개발]The present invention is derived from research conducted as part of the IT growth engine technology development project of the Ministry of Information and Communication and the Ministry of Information and Communication Research. [Task Management Number: 2006-S-058-02, Development of Integrated Network Service Control Technology based on ALL-IP]
최근 이동 통신 망뿐만 아니라 IEEE 802.11이나 무선 LAN 망, 블루투스 망과 그 관련 기술이 급격히 발전함에 따라, 무선 인터넷의 이용이 확대되고 있다. 이에 따라 모바일 인터넷 프로토콜(Mobile IP) 기술이 차세대 기술 중의 하나로 각광을 받고 있다.In recent years, as well as the mobile communication network, IEEE 802.11, wireless LAN network, Bluetooth network and related technologies are rapidly developed, the use of the wireless Internet is expanding. Accordingly, Mobile Internet Protocol (Mobile IP) technology is in the spotlight as one of the next generation technologies.
모바일IP는 IP 어드레스를 갖는 단말이 이동시에도 연결을 항상 보장하기 위해 필요한 기술이다. 모바일 IP에서는 이원화된 어드레스 체계를 통해 이동성을 지원한다. 즉, 모바일 IP는 홈 어드레스(Home Address)와 COA(Care of address)라는 두가지 어드레스 체계를 가진다. Mobile IP is a technology necessary to always ensure a connection even when a terminal having an IP address moves. Mobile IP supports mobility through a dual address system. That is, mobile IP has two address systems, a home address and a care of address.
홈 어드레스는 한번 설정된 세션은 그 설정시간 동안 같은 IP어드레스를 유지해야 한다는 점을 충족시키기 위해 변하지 않는 어드레스다. 그리고 COA는 단말이 이동했을 때 이동한 지역까지 라우팅하기 위해 단말의 이동에 따라 가변되는 어드레스이다. 따라서 COA는 단말이 이동해 라우팅 지역이 변하는 것에 따라 가변 되면서 지속적인 인터넷 서비스를 보장해준다. The home address is an address that does not change to satisfy that once a session is established, it must maintain the same IP address for that set time. The COA is an address that varies according to the movement of the terminal to route to the moved region when the terminal moves. Therefore, the COA guarantees continuous internet service as the terminal moves and changes as the routing area changes.
한편, 이 같은 모바일 IP 기술은 삼각 라우팅 문제, 긴 대기 시간, 병목현상과 같은 문제가 있다. 이런 문제점을 개선하기 위해서 이동성 제어에 필요한 기능 즉, 위치 관리(Location management)와 핸드오버 관리(Handover management)를 분산시키는 이동성 제어 구조가 제안된 바 있다. 그러나, 이러한 분산 구조에 내재된 특성으로 인해 추가적인 제어신호가 필요하기 때문에 이로 인한 버퍼링 현상 및 지연 시간(Latency time) 발생 현상이 나타나게 된다.On the other hand, such mobile IP technology has problems such as triangular routing problem, long waiting time and bottleneck. In order to solve this problem, a mobility control structure has been proposed that distributes functions necessary for mobility control, that is, location management and handover management. However, due to the inherent characteristics of such a distributed structure, an additional control signal is required, resulting in a buffering phenomenon and a latency time.
본 발명은 상술한 문제점을 해결하기 위해 도출된 것으로, 핸드오버 제어가 분산된 이동성 제어 구조에서 발생되는 버퍼링 현상과 대기시간을 감소시키는 것을 목적으로 한다. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve the above-mentioned problem, and an object thereof is to reduce the buffering phenomenon and the waiting time generated in the distributed mobility control structure.
추가적으로, 분산형 네트워크에서 데이터 전송에 따른 비효율성을 개선하는 것을 목적으로 한다.In addition, it aims to improve the inefficiency of data transmission in a distributed network.
또한, 라우터에서 유지되는 이동 단말로의 데이터 전달을 위한 포워딩 엔트리의 수를 줄이는 것을 목적으로 한다. It is also an object to reduce the number of forwarding entries for data transfer to a mobile terminal maintained at a router.
상술한 기술적 과제는 수신되는 데이터 전송 요청을 수신하여, 상기 단말이 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹을 파악하고, 상기 단말이 속한 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 포워딩 정보를 이용하여 전송할 데이터에 터널 헤더를 추가하는 단계; 및 상기 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 상기 수신 단말이 속하는 네트워크 접속 장치를 포함하는 적어도 하나의 네트워크 접속 장치로 전송하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 데이터 전송 방법에 의해 달성된다. The above technical problem may include receiving a received data transmission request, identifying a home address group to which the terminal belongs, and adding a tunnel header to data to be transmitted using forwarding information for the home address group to which the terminal belongs; And transmitting the data to which the tunnel header is added to at least one network access device including a network access device to which the receiving terminal belongs.
본 발명에 따르면, 핸드오버 제어와 이동성 제어가 분산된 형태의 네트워크에서 발생되는 버퍼링 현상과 지연시간을 줄일 수 있어, 데이터 전송을 더 신속하게 할 수 있는 효과가 있다. According to the present invention, the buffering phenomenon and the delay time generated in the network in which the handover control and the mobility control are distributed can be reduced, so that data transmission can be made faster.
또한, 송신 측 라우터 기능의 분산 수행을 제공할 수 있어 데이터 전송시 발생할 수 있는 병목 현상을 없앨 수 있으며, 네트워크 자원 운용의 효율성을 높일 수 있다. In addition, it is possible to provide a distributed execution of the router function of the transmitting side can eliminate the bottleneck that can occur during data transmission, and can increase the efficiency of network resource management.
뿐만 아니라 데이터 전달을 위한 포워딩 엔트리 수를 감소시켜 네트워크 자원을 절약할 수 있다. In addition, network resources can be saved by reducing the number of forwarding entries for data transfer.
전술한, 그리고 추가적인 본 발명의 양상들은 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 설명되는 바람직한 실시예들을 통해 더욱 명확해질 것이다. 이하에서는 본 발명을 이러한 실시예들을 통해 당업자가 용이하게 이해하고 재현할 수 있도록 상세히 설명하기로 한다.The foregoing and further aspects of the present invention will become more apparent through the preferred embodiments described with reference to the accompanying drawings. Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail so that those skilled in the art can easily understand and reproduce the present invention through these embodiments.
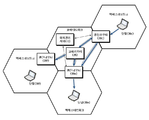
도 1 은 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 따른 이동성 제어 구조 네트워크의 예시도이다. 1 is an exemplary diagram of a mobility control architecture network according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
도 1 에 도시된 바와 같이 코어 네트워크를 중심으로 다수의 이종 액세스 네트워크들(액세스 네트워크a, 액세스 네트워크b,...) 이 연결된다. 코어 네트워크에는 위치 관리 서버(10)가 포함되고, 액세스 네트워크에는 각 액세스 네트워크 종류에 따라 유무선 모뎀, 기지국 등과 단말들이 포함된다. 또한, 액세스 네트워크와 코어 네트워크 사이에는 네트워크 접속 장치 즉, 라우터(20a, 20b,...)가 존재한다. As shown in FIG. 1, a plurality of heterogeneous access networks (access network a, access network b, ...) are connected around the core network. The core network includes a location management server 10, and the access network includes a wired / wireless modem, a base station, and terminals according to each type of access network. In addition, there are network connection devices, that is, routers 20a, 20b, ..., between the access network and the core network.
단말은 고정 단말 혹은 이동 단말일 수 있고, 본 실시예에 있어서 이동 단말의 경우 접속 액세스 망에서 사용하는 로컬(Local) IP 주소가 아닌 이동 단말에 할 당되는 홈 어드레스(Home address) IP를 사용한다. The terminal may be a fixed terminal or a mobile terminal. In the present embodiment, the mobile terminal uses a home address IP assigned to the mobile terminal instead of a local IP address used in the access network. .
이동 후에도 단말은 이동한 액세스 네트워크에서 사용하는 IP 주소를 사용하지 않기 때문에 단말 간 데이터 전달을 위해 위치 관리 서버(10)는 현재 이동 단말이 접속된 라우터의 정보를 유지한다. 현재 이동 단말이 접속된 라우터의 정보는 단말 간 데이터 전달 시 송신 단말이 접속된 라우터와 수신 단말이 접속된 라우터 간에 IP 터널을 생성하기 위해 사용된다. Since the terminal does not use the IP address used in the moved access network even after the movement, the location management server 10 maintains information of the router to which the mobile terminal is currently connected for data transfer between terminals. The information on the router to which the mobile terminal is currently connected is used to create an IP tunnel between the router to which the transmitting terminal is connected and the router to which the receiving terminal is connected during data transfer between the terminals.
그러나 라우터로부터 위치 관리 서버(10)로 질의가 발생하지 않는 경우, 즉, 임의의 단말로부터 다른 이동 단말로 데이터 송신시 발생하지 않은 경우에는, 위치 관리 서버에 유지되는 이동 단말이 접속된 라우터의 정보는 임의의 라우터로 전달되지 않는다. However, when a query does not occur from the router to the location management server 10, that is, when the data is not transmitted from one terminal to another mobile terminal, the information of the router to which the mobile terminal maintained in the location management server is connected. Is not forwarded to any router.
도 1 에 도시된 이동성 제어 구조 네트워크에서의 데이터 흐름을 살펴보면, 먼저 송신 단말(30c)은 전송할 데이터를 인접한 라우터(20c)로 전달한다. 이때 송신 단말(30c)이 이동 단말인 경우에, 송신 데이터의 목적지 주소는 수신 단말(30e)의 홈 어드레스이다. 데이터를 수신한 라우터(20c)는 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 보유한 경우에 수신 단말(30e)이 접속된 라우터(20e)와 IP 터널(t)을 생성한다. 생성된 터널(t)을 통해 터널 헤더가 추가(encap)된 데이터(Tunnelled data)를 전달한다. 반면, 송신 단말(30c)과 인접한 라우터(20c)가 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리를 보유하고 있지 않은 경우에는 위치 관리 서버(10)에 수신 단말(30e)이 접속된 라우터의 정보를 질의한다. 그리고 질의에 대한 응답으로 획득되는 정보에 기초하여 IP 터널(t)을 생성한다. 그리고 생성된 터널을 통해 생성된 IP 터널에 대한 터널 헤더가 추가(encap)된 데이터(Tunnelled data)를 전달할 수 있다.Referring to the data flow in the mobility control architecture network shown in FIG. 1, the transmitting terminal 30c first transmits data to be transmitted to an adjacent router 20c. At this time, when the transmitting terminal 30c is a mobile terminal, the destination address of the transmission data is the home address of the receiving terminal 30e. The router 20c receiving the data generates an IP tunnel t with the
이때 포워딩 엔트리(forwarding entry)는 일 예로 목적지 IPv6 주소, 프리픽스(Prefix) 길이, 스위칭과 서비스 품질(Qos)설정 관련 정보 등과 같은 데이터 포워딩을 위해 필요한 정보들을 포함한다. In this case, the forwarding entry includes information necessary for data forwarding, such as a destination IPv6 address, a prefix length, information related to switching and quality of service (Qos) configuration, and the like.
이하, 도 2를 참조하여 송신 단말(30c) 측 라우터(20c)에 포워딩 엔트리가 존재하지 않는 경우에 데이터 전송 과정을 보다 상세히 설명한다. Hereinafter, referring to FIG. 2, a data transmission process will be described in more detail when a forwarding entry does not exist in the router 20c of the transmitting terminal 30c.
도 2 는 본 발명의 바람직한 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 시스템 구조도이다. 2 is a structural diagram of a data transmission system according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
위치 관리 서버(10)는 단말이 접속된 라우터 정보뿐 아니라 단말이 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹(Home Address Group)에 속하는 단말들이 접속된 라우터 정보를 갖고 있다. 여기서 홈 어드레스 그룹은 사업자의 정책에 의해 구성될 수 있고, 일 예로는 IP 서브넷(subnet)일 수 있다. 이 정보는 적어도 하나의 다른 라우터들로 전달된다. 이하, 액세스 네트워크와 코어 네트워크 간 연계를 위한 라우터를 종단 라우터(20c, 20e, 20f), 종단 라우터 간 연계를 위해 코어 네트워크에 존재하는 라우터를 코어 라우터(25)라 한다. The location management server 10 has not only router information to which a terminal is connected, but also router information to which terminals belonging to a home address group to which the terminal belongs are connected. In this case, the home address group may be configured by a policy of an operator, and may be, for example, an IP subnet. This information is passed to at least one other router. Hereinafter, routers for linkage between the access network and the core network are referred to as
구체적으로 이동 단말이 최초로 접속하거나 핸드 오버로 인해 접속된 라우터가 변경된 경우에 이동 단말이 접속 가능한 모든 라우터들과 홈 어드레스 그룹 방식을 지원하는 코어 라우터로 전달된다. 전달된 정보들은 이 후에 홈 어드레스 그룹에 속하는 단말들에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 생성을 위해 사용된다.Specifically, when a mobile terminal is initially connected or a connected router is changed due to a handover, the mobile terminal is delivered to all the routers to which the mobile terminal is accessible and the core router supporting the home address group method. The conveyed information is then used for generating forwarding entries for terminals belonging to the home address group.
여기서 이동 단말이 접속 가능한 라우터는, 향후 단말이 이동하여 핸드 오버등을 수행함으로써 접속할 수 있는 주변에 존재할 수 있는 액세스 네트워크들의 종단 라우터(20c, 20e, 20f)일 수 있다. Here, the router to which the mobile terminal can be connected may be
도 2를 참조하여 데이터 전달 방식을 보다 구체적으로 설명하면, 송신 단말(30c)은 데이터를 인접한 라우터 즉, 자신이 등록된 종단 라우터(20c)로 전달한다. 이때, 수신 단말(30e)이 이동 단말인 경우에 송신 데이터의 목적지 주소는 수신 단말(30e)의 홈 어드레스이다. 2, the transmitting terminal 30c transmits data to an adjacent router, that is, an end router 20c in which it is registered. At this time, when the receiving terminal 30e is a mobile terminal, the destination address of the transmission data is the home address of the receiving terminal 30e.
송신 단말(30c)로부터 데이터를 수신한 종단 라우터(20c,edge router)는 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 보유하고 있는 경우에는 전술한 바와 같이 수신 단말(30e)이 접속한 종단 라우터(20e)와 IP 터널을 생성할 수 있다. 그리고 생성된 IP 터널을 통해 터널 헤더가 추가(encap)된 데이터(Tunnelled data)를 전달한다. The edge router 20c, which has received data from the transmitting terminal 30c, holds the forwarding entry information for the receiving terminal 30e, as described above. 20e) and create an IP tunnel. Then, the tunnel header is added (Tunnelled data) through the generated IP tunnel.
반면, 송신 단말(30c)로부터 데이터를 수신한 송신 단말 측 종단 라우터(20c)는 포워딩 엔트리가 존재하지 않는 경우에 위치 관리 서버(10)로 수신 단말(30c)이 접속된 라우터의 정보를 질의한다. 그리고, 수신 단말(30c)이 접속된 종단 라우터(20e)의 정보를 획득할 수 있다. 그런데 위치 관리 서버(10)로 수신 단말(30c)이 접속된 라우터 정보를 질의하고 응답을 수신하는 동안 데이터 전송의 지연 시간이 발생된다. On the other hand, the transmitting terminal side terminating router 20c which has received data from the transmitting terminal 30c queries the location management server 10 for information on the router to which the receiving terminal 30c is connected when there is no forwarding entry. . And, it is possible to obtain information of the terminating
따라서 본 발명의 특징적인 양상에 따르면, 송신 단말 측 종단 라우터(20c)가 위치 관리 서버(10)로 수신 라우터 정보를 질의함과 동시에, 수신 단말과 동일 한 홈 어드레스 그룹에 속하는 라우터 정보를 파악한다. 그리고, 그 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 알 수 있다. 즉, 수신 단말이 접속된 종단 라우터(20c)를 정확히 파악하지 못하더라도, 해당 수신 단말이 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹의 포워딩 엔트리 정보는 알 수 있다. Therefore, according to a characteristic aspect of the present invention, the transmitting terminal side end router 20c queries the location management server 10 for the receiving router information, and simultaneously grasps the router information belonging to the same home address group as the receiving terminal. . Then, the forwarding entry information for the home address group can be known. That is, even if the receiving terminal does not know the terminal router 20c to which it is connected, the forwarding entry information of the home address group to which the receiving terminal belongs may be known.
그리고, 위치 관리 서버(10)로 수신 라우터의 정보를 질의함과 동시에 그 정보에 따라 IP 또는 IP 상위 계층에 대한 데이터 전송 터널을 생성하고, 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터(Tunnelled data)를 전달한다. Then, while querying the location management server 10 for information on the receiving router, it generates a data transmission tunnel for the IP or the IP upper layer according to the information, and transmits the tunneled data with the tunnel header added thereto.
송신 단말 측 종단 라우터(20c)는 터널링 시에 데이터에 코어 네트워크 접속 장치의 주소 정보를 포함하는 제 1 터널 헤더와, 상기 적어도 하나의 목적지 주소가 포함되는 멀티캐스트 전송 주소가 포함되는 제 2 터널 헤더를 추가한다. 즉, 더블 터널링 데이터를 생성한다.The transmitting terminal side terminating router 20c includes a first tunnel header including address information of a core network connection device in data at the time of tunneling, and a second tunnel header including a multicast transmission address including the at least one destination address. Add That is, double tunneling data is generated.
그리고 수신 단말(30e)이 포함된 홈 어드레스 그룹에 속하는 단말들(30e, 30f)이 속한 종단 라우터(20e, 20f)들로 데이터를 전송한다.The data is transmitted to the
코어 네트워크에 코어 라우터(25, core network)가 존재하는 경우, 코어 라우터(25)는 제 1 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 수신하여 제 1 터널 헤더를 제거한다. 그리고 제 2 터널 헤더의 적어도 하나의 목적지 주소를 파악한다. 제 2 터널 헤더의 멀티캐스트 주소를 파악하여, 데이터를 전송할 목적지 주소의 수만큼 데이터를 복제한다. 그리고 복제된 데이터들 각각에 대해서 수신 종단 라우터(20e, 20f)의 주소 정보를 포함하는 터널 헤더와 수신 단말의 주소 정보를 포함하는 터널 헤더를 추가한다. 즉, 두 개의 터널 헤더를 포함한 데이터를 수신한 코어 라우터 는 다시 복제된 데이터들에 대해서 두 개의 터널 헤더를 포함시켜 전송한다. When the
그리고 복제된 데이터들을 홈 어드레스 그룹에 속하는 종단 라우터들(20e, 20f)로 포워딩한다. 이때 각각의 데이터는 수신 종단 라우터(20e, 20f)까지 유니캐스트 방식으로 전달된다.The replicated data is then forwarded to the
즉, 이 같은 양상에 따라 송신 라우터(20c)에서는 위치 관리 서버(10)로부터 수신 단말(30e)이 속한 종단 라우터(20e) 정보를 획득하기 이전에는 수신 단말(30e)이 속한 홈 어드레스 그룹의 종단 라우터들(20e, 20f)로 데이터들을 전송한다. 송신 단말이 속한 종단 라우터(20c)는 자체적으로 송신 단말이 속한 홈 어드레스 그룹 정보를 보유하고 있기 때문에, 홈 어드레스 그룹에 속하는 단말(30e,30f)들이 속하는 종단 라우터들(20e,20f)의 정보를 신속하게 파악할 수 있다. That is, according to this aspect, in the transmitting router 20c, the terminal of the home address group to which the receiving terminal 30e belongs before obtaining information from the location management server 10 to the terminating
두 개의 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 수신한 수신 단의 종단 라우터(20e)는 자신을 목적지 주소로 설정한 터널 헤더를 제거하고, 데이터에 지정된 목적지 주소를 갖는 터널 헤더를 파악하여 그 수신 단말(30e)이 접속되어 있는 경우에 그 단말로 데이터를 전달한다. 반면, 지정된 목적지 주소를 갖는 수신 단말(30e)이 접속되지 않는 종단 라우터(20f)는 데이터를 전달하지 않는다. The terminating
이에 따라 송신 라우터(20c)가 위치 관리 서버(10)로부터 수신 단말(30e)이 속한 네트워크 접속 장치(20e)의 정보를 파악하는 동안에도 수신 단말(30e)로 데이터를 전송하는 것이 가능하여 정확한 위치 파악을 위해 발생되는 지연시간을 없앨 수 있다. Accordingly, while the transmitting router 20c grasps the information of the
이 후에, 송신 단말(30c)이 접속된 라우터(20c)에서 위치 관리 서버(10)로 질의한 결과를 수신한 경우에, 수신 정보에 기초하여 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리를 추가한다. 이 후에 송신 단말(30c)로부터 수신한 데이터는 추가한 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리를 이용할 수 있다. 이 후에 송신 단말(30c)이 접속된 라우터(20c)가 수신 단말(30e)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 보유하고 있는 경우와 동일하게 데이터를 전달할 수 있다. After that, when the transmitting terminal 30c receives the query result from the connected router 20c to the location management server 10, the forwarding entry for the receiving terminal 30e is added based on the received information. Thereafter, the data received from the transmitting terminal 30c can use the forwarding entry for the additional receiving terminal 30e. Thereafter, the router 20c to which the transmitting terminal 30c is connected can transfer data in the same manner as when the router 20c holds the forwarding entry information for the receiving terminal 30e.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다. 3 is a flowchart illustrating a data transmission method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
먼저, 도 3 을 참조하여 단말의 등록 과정을 설명한다. First, a registration process of a terminal will be described with reference to FIG. 3.
전원을 새로 인가한 경우, 혹은 단말이 이동하여 위치가 변경됨에 따라 핸드 오버를 수행한 경우에 단말(30-2)은 인접한 종단 라우터(20-2)에 등록한다(S300). 그러면 단말(30-2)로부터 등록 요청을 받은 종단 라우터(20-2)는 단말(30-2)의 위치 정보를 업데이트하기 위해 이를 위치 관리 서버(10)로 이를 전송한다(S310). When the power is newly applied or when the terminal is moved and the handover is performed as the location is changed, the terminal 30-2 registers with the adjacent end router 20-2 (S300). Then, the end router 20-2 receiving the registration request from the terminal 30-2 transmits it to the location management server 10 to update the location information of the terminal 30-2 (S310).
그리고, 위치 관리 서버(10)는 수신되는 정보에 따라 새로 등록된 단말(30-2)에 대한 위치 정보를 업데이트 한다(S312). The location management server 10 updates location information on the newly registered terminal 30-2 according to the received information (S312).
도 4는 단말의 홈 어드레스에 대한 위치 정보 테이블이고, 도 5는 단말의 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 위치 정보 테이블이다. 4 is a location information table for a home address of a terminal, and FIG. 5 is a location information table for a home address group of a terminal.
도 4에 도시된 바와 같이 위치 관리 서버(10)는 단말들의 홈 어드레스와 각각의 단말이 연결된 종단 라우터의 IP 어드레스를 관리한다. 또한, 도 5에 도시된 바와 같이 위치 관리 서버(10)는 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 종단 라우터 혹은 코어 라우터의 IP 어드레스를 관리한다. As shown in FIG. 4, the location management server 10 manages home addresses of terminals and IP addresses of end routers to which respective terminals are connected. In addition, as shown in FIG. 5, the location management server 10 manages an IP address of an end router or a core router for a home address group.
즉, 위치 관리 서버(10)는 종단 라우터(20-2)로부터 새로 등록한 단말 정보를 수신하면, 그 새로 등록된 단말(30-2)이 접속된 종단 라우터(20-2)의 정보와, 그 단말에 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹이 접속된 라우터의 정보를 갱신한다. That is, when the location management server 10 receives the newly registered terminal information from the terminal router 20-2, the location management server 10 receives the information of the terminal router 20-2 to which the newly registered terminal 30-2 is connected, and The information on the router to which the home address group belonging to the terminal is connected is updated.
또한 단말이 접속 가능한 모든 종단 라우터들과, 코어 라우터(25)로 전달한다(S314, S316). 그리고, 갱신된 정보를 수신한 종단 라우터(20-1)들은 전달된 정보를 바탕으로 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 포워딩 엔트리를 갱신한다(S320).In addition, all terminal routers that can be connected to the terminal, and delivers to the core router 25 (S314, S316). The terminal routers 20-1 receiving the updated information update the forwarding entry for the home address group based on the transmitted information (S320).
이에 따라 새로 단말(30-2)이 종단 라우터(20-2)에 등록되는 경우에, 위치 관리 서버(10), 코어 라우터(25) 및 다른 종단 라우터들에서 단말(30-2)의 위치 변경에 따른 정보의 업데이트를 수행할 수 있다. Accordingly, when the terminal 30-2 is newly registered with the terminating router 20-2, the location change of the terminal 30-2 at the location management server 10, the
이하에서는 도 3 을 참조하여 코어 네트워크에 코어 라우터가 존재하는 경우의 데이터 전송 방법에 대해 상세히 설명한다. Hereinafter, a data transmission method in the case where a core router exists in the core network will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 3.
먼저, 송신 단말(30-1)은 인접한 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)로 데이터를 전송한다(S330). First, the transmitting terminal 30-1 transmits data to an adjacent transmitting end router 20-1 (S330).
이때 송신 단말(30-1)이 이동 단말인 경우에 송신 데이터의 목적지 주소는 수신 단말(30-2)의 홈 어드레스이다. 데이터를 수신한 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 수신 단말(30-2)에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 파악한다. At this time, when the transmitting terminal 30-1 is a mobile terminal, the destination address of the transmission data is the home address of the receiving terminal 30-2. The transmitting end router 20-1 receiving the data grasps the forwarding entry information for the receiving terminal 30-2.
도 6은 데이터 목적지 주소에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보 테이블이다. 6 is a forwarding entry information table for a data destination address.
즉, 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 도 6에 도시된 바와 같이 각각이 목적지 주소에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보 테이블을 보유한다. 전술한 바와 같이 포워딩 엔트리 정보는 일 예로 목적지 IPv6 주소, 프리픽스(Prefix) 길이, 스위칭과 서비스 품 질(Qos)설정 관련 정보 등과 같은 데이터 포워딩을 위해 필요한 정보들을 포함할 수 있다. That is, the transmitting end routers 20-1 each hold a forwarding entry information table for the destination address, as shown in FIG. As described above, the forwarding entry information may include, for example, information necessary for data forwarding such as a destination IPv6 address, a prefix length, information related to switching and quality of service (Qos) configuration, and the like.
또한, 도 7은 데이터 목적지 주소에 대한 터널링 정보 테이블이다. 7 is a tunneling information table for a data destination address.
송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 도 7에 도시된 바와 같이, 터널링 생성에 필요한 터널링 정보 테이블을 보유한다. 파악되는 포워딩 엔트리 정보에 기초하여 터널링 정보 테이블에 따라 목적지 주소 즉, 수신 종단 라우터(20-2)와 IP 터널을 형성할 수 있다(S340). 이때 더블 터널 목적 IP주소(Double Tunnel Destination IP Address)는 코어 네트워크의 코어 라우터와 터널 생성을 위한 터널 목적 IP로 제 1 터널 헤더로 추가되고, 홈 어드레스 그룹 기능이 구현되는 코어 라우터에서 수신 종단 라우터까지 터널 형성을 위한 제 2 목적 주소는 제 2 터널 헤더로 포함된다. 이 같이 터널링 정보 테이블에 기초하여 더블 터널링 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 그리고, 생성된 IP 터널을 통해 전달될 수 있도록 한다. The transmission termination router 20-1 holds the tunneling information table necessary for generating tunneling, as shown in FIG. An IP tunnel may be formed with the destination address, that is, the receiving end router 20-2, according to the tunneling information table based on the forwarding entry information that is identified (S340). In this case, the double tunnel destination IP address is added as the first tunnel header as the core router of the core network and the tunnel destination IP for creating the tunnel, and is from the core router to the destination end router in which the home address group function is implemented. The second destination address for tunnel formation is included in the second tunnel header. As such, the double tunneling data may be generated based on the tunneling information table. Then, it can be delivered through the generated IP tunnel.
이때, 더블 터널링이 형성된 데이터의 경우 코어 망에 존재하는 코어 라우터(25)를 경유한다. 즉, 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 코어 라우터(25)로 전송한다(S345). In this case, the data in which the double tunneling is formed is via the
그러면 코어 라우터(25)는 자신이 목적지로 설정된 제 1 터널 헤더를 제거하고, 제 2 터널 헤더에 추가된 멀티캐스트 주소 정보를 파악한다. 그리고 멀티캐스트 주소 정보에 기초하여 전송해야할 목적지 수만큼 데이터를 복제한다(S350).The
도 8은 코어 라우터가 데이터 복제에 참조하기 위한 포워드 정보 테이블이다. 8 is a forward information table for the core router to refer to data replication.
즉, 코어 라우터(25)는 기 저장된 포워드 정보 테이블에 기초하여 전송될 테이터의 목적지 주소에 따라 데이터를 복제할 수 있다. 그리고, 역시 포워드 정보 테이블에 기초하여 다음에 전송될 종단 라우터 주소로 전송한다(S360). That is, the
전송 데이터를 수신한 수신 종단 라우터(20-2)는 수신되는 터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터의 터널 헤더를 제거한다(S370). 그리고 데이터의 목적지 주소를 파악하여 그 목적지 주소에 따른 단말이 접속해 있는 경우에 그 수신 단말(30-2)로 터널 헤더를 제거한 데이터를 전송한다(S380). The receiving end router 20-2 receiving the transmission data removes the tunnel header of the data to which the received tunnel header is added (S370). When the destination address of the data is identified, and the terminal corresponding to the destination address is connected, the data in which the tunnel header is removed is transmitted to the receiving terminal 30-2 (S380).
도 9는 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다. 9 is a flowchart illustrating a data transmission method according to another embodiment of the present invention.
먼저, 도 9를 참조하여 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)에서 송신 단말(30-1)에 대한 정보를 보유하고 있지 않은 경우 데이터 전송 방법을 설명한다. First, with reference to FIG. 9, a data transmission method will be described when the transmission termination router 20-1 does not hold information on the transmission terminal 30-1.
송신 단말(30-1)이 인접한 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)로 전송 데이터를 전송한다(S900). 이때 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 수신 단말(30-2)이 접속한 종단 라우터에 대한 정보가 없는 경우에는, 위치 관리 서버(10)로 수신 단말(30-2)에 대한 위치 정보를 요청한다(S910). 그러면 위치 관리 서버(10)는 수신 단말(30-2)이 접속된 수신 종단 라우터(20-2) 정보를 제공할 수 있다(S915). 그리고, 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 위치 관리 서버(10)로부터 수신되는 수신 단말(30-2)의 위치 정보에 따라 기 저장된 홈 어드레스 그룹의 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 업데이트 한다(S920). 그리고, 전송 데이터에 대한 포워딩 엔트리에 기초하여 터널을 설정하고, 데이터에 터널 헤더를 추가한다(S930). 이에 따라 추 후에 해당 수신 단말(30-2)로 전송되 는 데이터들은 전술한 경우, 즉 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)가 포워딩 엔트리를 보유한 경우와 동일하게 신속한 데이터 전송 처리를 수행할 수 있다. The transmitting terminal 30-1 transmits the transmission data to the adjacent transmitting end router 20-1 (S900). At this time, when there is no information on the terminating router connected to the receiving terminal 30-2, the transmitting terminating router 20-1 requests the location management server 10 for the position information on the receiving terminal 30-2. (S910). Then, the location management server 10 may provide the reception terminal router 20-2 to which the reception terminal 30-2 is connected (S915). The transmission end router 20-1 updates the forwarding entry information of the pre-stored home address group according to the location information of the reception terminal 30-2 received from the location management server 10 (S920). Then, a tunnel is established based on a forwarding entry for transmission data, and a tunnel header is added to the data (S930). Accordingly, data transmitted later to the corresponding reception terminal 30-2 may perform a fast data transmission process in the same manner as described above, that is, when the transmission termination router 20-1 holds the forwarding entry.
이때 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 수신한 수신 단말 정보를 등록 시에 다른 종단 라우터 혹은 코어 라우터로 전송하는 것과 동일하게, 다른 라우터들로 전송하는 것이 바람직하다. In this case, it is preferable that the transmitting end router 20-1 transmit the received receiving terminal information to other routers in the same way as it transmits to the other end router or the core router at the time of registration.
본 발명의 특징적 양상에 따라 송신 종단 라우터(20-1)는 위치 관리 서버(10)로 위치 정보 요청을 전송함(S910)과 동시에 목적 단말이 속하는 홈 어드레스 그룹의 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 파악한다. 그리고, 그 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보를 찾아서, IP 혹은 IP 상위 계층에 대한 IP 터널을 생성한다(S940). 그리고, 그 홈 어드레스 그룹들 즉, 적어도 하나의 종단 라우터들로 데이터를 전송한다. According to a characteristic aspect of the present invention, the transmitting end router 20-1 transmits the location information request to the location management server 10 (S910) and simultaneously identifies forwarding entry information of the home address group to which the target terminal belongs. Then, the forwarding entry information about the home address group is found, and an IP tunnel for an IP or an IP upper layer is generated (S940). Then, data is transmitted to the home address groups, that is, at least one end routers.
터널 헤더가 추가된 데이터를 수신한 종단 라우터들은 터널 헤더를 제거한다(S950). 그리고, 수신되는 데이터에 포함된 목적지 주소에 따라 해당 수신 단말이 자신에게 접속된 단말인지 여부를 판단할 수 있다. 판단 결과 수신 단말이 접속되어있는 경우에는, 그 단말로 데이터를 전송한다(S960).End routers receiving the data to which the tunnel header has been added remove the tunnel header (S950). Then, it may be determined whether the corresponding receiving terminal is a terminal connected to the self according to the destination address included in the received data. If it is determined that the receiving terminal is connected, data is transmitted to the terminal (S960).
한편, 전술한 데이터 전송 방법 및 단말의 위치 관리 방법은 컴퓨터 프로그램으로 작성 가능하다. 또한, 상기 프로그램은 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 정보 저장 매체(computer readable media)에 저장되고, 컴퓨터에 의해 읽혀지고 실행됨으로써 구현될 수 있다. 상기 저장매체는 자기 기록매체, 광 기록 매체 등을 포함한다. On the other hand, the above-described data transmission method and the location management method of the terminal can be created by a computer program. The program may also be embodied by being stored in a computer readable media and being read and executed by a computer. The storage medium includes a magnetic recording medium, an optical recording medium and the like.
이제까지 본 발명에 대해 바람직한 실시예들을 중심으로 살펴보았다. 본 발 명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명이 본 발명의 본질적인 특성에 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 변형된 형태로 구현될 수 있음을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 개시된 실시예들은 한정적인 관점이 아니라 설명적인 관점에서 고려되어야 한다. 본 발명의 범위는 특허청구범위에 나타나 있으며, 그와 동등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 차이점은 본 발명에 포함된 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다. So far I looked at the preferred embodiments of the present invention. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the present invention can be implemented in a modified form without departing from the essential features of the present invention. Therefore, the disclosed embodiments should be considered in descriptive sense only and not for purposes of limitation. The scope of the present invention is shown in the claims, and all differences within the scope equivalent thereto should be construed as being included in the present invention.
도 1은 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 따른 이동성 제어 구조 네트워크의 예시도,1 is an exemplary diagram of a mobility control architecture network according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
도 2는 본 발명의 바람직한 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 시스템 구성도,2 is a block diagram of a data transmission system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 방법을 도시한 흐름도,3 is a flowchart illustrating a data transmission method according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 4는 단말의 홈 어드레스에 대한 위치 정보 테이블, 4 is a location information table for a home address of a terminal;
도 5는 단말의 홈 어드레스 그룹에 대한 위치 정보 테이블,5 is a location information table for a home address group of a terminal;
도 6은 데이터 목적지 주소에 대한 포워딩 엔트리 정보 테이블,6 is a forwarding entry information table for a data destination address;
도 7은 데이터 목적지 주소에 대한 터널링 정보 테이블,7 is a tunneling information table for a data destination address,
도 8은 코어 라우터가 데이터 복제에 참조하기 위한 포워드 정보 테이블,8 is a forward information table for the core router to refer to data replication;
도 9는 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따른 데이터 전송 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다. 9 is a flowchart illustrating a data transmission method according to another embodiment of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070133345A KR100922900B1 (en) | 2007-12-18 | 2007-12-18 | Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070133345A KR100922900B1 (en) | 2007-12-18 | 2007-12-18 | Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20090065835A KR20090065835A (en) | 2009-06-23 |
| KR100922900B1 true KR100922900B1 (en) | 2009-10-20 |
Family
ID=40994036
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070133345A KR100922900B1 (en) | 2007-12-18 | 2007-12-18 | Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100922900B1 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6721297B2 (en) | 2001-11-19 | 2004-04-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for providing IP mobility for mobile networks |
| KR20040039486A (en) * | 2001-10-02 | 2004-05-10 | 가부시키가이샤 엔티티 도코모 | Mobility control system, mobile node used in the system, mobility control method, mobility control program, and mobility control node |
| KR20060026311A (en) * | 2004-09-20 | 2006-03-23 | 주식회사 케이티 | Handover method in portable internet using explicit multi-casting scheme |
| KR20060084749A (en) * | 2005-01-20 | 2006-07-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for handover using multi-cast in mobile network system |
-
2007
- 2007-12-18 KR KR1020070133345A patent/KR100922900B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20040039486A (en) * | 2001-10-02 | 2004-05-10 | 가부시키가이샤 엔티티 도코모 | Mobility control system, mobile node used in the system, mobility control method, mobility control program, and mobility control node |
| US6721297B2 (en) | 2001-11-19 | 2004-04-13 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for providing IP mobility for mobile networks |
| KR20060026311A (en) * | 2004-09-20 | 2006-03-23 | 주식회사 케이티 | Handover method in portable internet using explicit multi-casting scheme |
| KR20060084749A (en) * | 2005-01-20 | 2006-07-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for handover using multi-cast in mobile network system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20090065835A (en) | 2009-06-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9769072B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for scalable content routing and mobility in named data networks | |
| US8837511B2 (en) | Seamless mobility schemes in names-data networking using multi-path routing and content caching | |
| US9686194B2 (en) | Adaptive multi-interface use for content networking | |
| CN105791457B (en) | A kind of data processing method and device | |
| JP3768406B2 (en) | Information distribution control method and system in mobile communication network, and information storage method in communication node in mobile communication network | |
| EP3340681B1 (en) | Seamless mobility schemes in named-data networking using multi-path routing and content caching | |
| US9008084B2 (en) | Method of IPv6 at data center network with VM mobility using graceful address migration | |
| CN102907072A (en) | Enabling ipv6 mobility with nat64 | |
| CA2422715A1 (en) | Methods and apparatus for supporting mobility within a radio access network | |
| JP2014504095A (en) | Method and system for efficient homeless MPLS micromobility | |
| WO2013007130A1 (en) | Location/id separation protocol motion node, motion control method and motion node | |
| US20120002600A1 (en) | System for data communications, router, and method for data transmission and mobility management | |
| JP3806094B2 (en) | Router device, network address management system, network address management method, and network address management program | |
| JP2003060685A (en) | Mobile communication system, home agent, correspondent node, mobile terminal, mobile communication method, program and recording medium | |
| KR101852104B1 (en) | SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING INTER-DOMAIN HANDOVER IN PROXY MOBILE IPv6 BASED ON SOFTWARE-DEFINED NETWORK AND METHOD THEREOF | |
| KR100922900B1 (en) | Method for transmitting Data in Distributed Network | |
| KR102437289B1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Defining Path of a Packet in Information-Centric Networking for Data Producer Mobility | |
| KR20160002154A (en) | Method for generate contents name and routing method based on contents name using sdn networkd, apparatus using the same | |
| US9763135B1 (en) | Load balancing with mobile resources | |
| KR101967379B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for managing mobile node of sdn controller | |
| JP2003348148A (en) | Ip multicast control method and ip multicast control system employing the same | |
| US20130163561A1 (en) | Fast handover method using l2/l3 combination | |
| KR20110071442A (en) | Wireless network method and system with distributed location management function | |
| Hou et al. | A Novel Mobility and Multihoming Support Scheme for Locator/Identifier Separation Networks | |
| WO2013026295A1 (en) | System and method for node communication between proxy mobile ip domains |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20121011 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20130923 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20140926 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20150925 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20170927 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20181001 Year of fee payment: 10 |