KR100697792B1 - Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium - Google Patents
Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100697792B1 KR100697792B1 KR1020060027853A KR20060027853A KR100697792B1 KR 100697792 B1 KR100697792 B1 KR 100697792B1 KR 1020060027853 A KR1020060027853 A KR 1020060027853A KR 20060027853 A KR20060027853 A KR 20060027853A KR 100697792 B1 KR100697792 B1 KR 100697792B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- correction
- information
- storage unit
- error
- unit
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B1/00—Details of transmission systems, not covered by a single one of groups H04B3/00 - H04B13/00; Details of transmission systems not characterised by the medium used for transmission
- H04B1/38—Transceivers, i.e. devices in which transmitter and receiver form a structural unit and in which at least one part is used for functions of transmitting and receiving
- H04B1/40—Circuits
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R16/00—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for
- B60R16/02—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for electric constitutive elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q1/00—Details of, or arrangements associated with, antennas
- H01Q1/27—Adaptation for use in or on movable bodies
- H01Q1/32—Adaptation for use in or on road or rail vehicles
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q3/00—Arrangements for changing or varying the orientation or the shape of the directional pattern of the waves radiated from an antenna or antenna system
- H01Q3/01—Arrangements for changing or varying the orientation or the shape of the directional pattern of the waves radiated from an antenna or antenna system varying the shape of the antenna or antenna system
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Techniques For Improving Reliability Of Storages (AREA)
- Read Only Memory (AREA)
Abstract
Description
도 1은 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치의 구성을 도시하는 블록도이다.1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of a storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
도 2는 4-값 기억 소자들로 형성된 기억 유닛의 등가 회로의 예를 도시한다.2 shows an example of an equivalent circuit of a memory unit formed of four-value memory elements.
도 3은 기억 소자들의 방전을 도시한다.3 shows the discharge of the memory elements.
도 4는 기억 소자들의 전하 분포의 일 예를 도시한다.4 shows an example of the charge distribution of the memory elements.
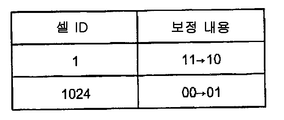
도 5는 보정 이력 기억 유닛의 예시적인 데이터 구조를 도시한다.5 shows an exemplary data structure of the correction history storage unit.
도 6은 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.6 is a flowchart of a storage medium reproducing operation according to the first embodiment.
도 7은 본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.7 is a flowchart of a storage medium reproducing operation according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
도 8은 본 발명의 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매채 재생 장치의 구성을 도시하는 블록도이다.Fig. 8 is a block diagram showing the construction of a storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
도 9는 보정 이력 기억 유닛의 예시적인 데이터 구조를 도시한다.9 shows an exemplary data structure of the correction history storage unit.
도 10은 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.10 is a flowchart of a storage medium reproducing operation according to the third embodiment.
도 11은 본 발명의 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치의 구조를 도시하 는 블록도이다.11 is a block diagram showing the structure of a storage medium reproducing apparatus according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
도 11은 본 발명의 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치의 구조를 도시하는 블록도이다.Fig. 11 is a block diagram showing the structure of the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention.
도 12는 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.12 is a flowchart of a storage medium reproducing operation according to the fourth embodiment.
본 발명은 기억 매체 재생 장치, 기억 매채 재생 방법, 및 기억 매체로부터 정보를 판독하기 위한 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a storage medium reproducing apparatus, a storage medium reproducing method, and a computer readable medium for reading information from a storage medium.
최근, 전하량에 따라 정보를 기억하기 위한 플래시 메모리와 같은 반도체 메모리가 널리 사용되었다. 또한, 복수 비트의 정보를 기억하기 위하여, 복수의 임계값들이 전하량에 대하여 설정되는 다-값(multi-value) 메모리 기술이 개발되었다.Recently, semiconductor memories such as flash memories for storing information in accordance with the amount of charge have been widely used. In addition, in order to store a plurality of bits of information, a multi-value memory technology has been developed in which a plurality of threshold values are set for the amount of charge.
이러한 반도체 메모리에서, 시간에 따라 전하가 방출된다. 그러므로, 방출된 전하량이 임계값을 넘으면, 정보 판독시 에러가 발생된다. 특히, 협한 간격에서의 임계값들을 갖는 다-값 메모리에서, 에러 발생의 확률이 높다.In such semiconductor memories, charge is released over time. Therefore, if the amount of discharged charges exceeds a threshold, an error occurs in reading information. In particular, in multi-value memories with thresholds at narrow intervals, the probability of error occurrence is high.
한편, 기억된 정보의 신뢰성을 유지하기 위하여, 에러 보정 코드가 메모리 셀 그룹들에 할당되고, 각 메모리 셀 그룹은 특정 수의 메모리 소자들을 포함하며, 정보에서의 에러는, 예컨대 일본 특개평 제H11-154394호에 개시된 방법에 따라 에러 보정 코드들을 사용하여 보정된다.On the other hand, in order to maintain the reliability of the stored information, an error correction code is assigned to the memory cell groups, each memory cell group includes a certain number of memory elements, and errors in the information are, for example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. H11. Correction using error correction codes according to the method disclosed in -154394.
그러나, 방전으로 인하여 임계값을 초과하는 전하량을 갖는 메모리 소자는 판독시에 에러를 일정하게 발생시킨다. 그러므로, 종래의 에러 보정 방법에 따르면, 동일한 에러 보정 동작이 판독이 수행될 때 마다 수행되어야 하여, 각 보정 동작시 많은 계산량이 발생된다.However, memory elements having a charge amount exceeding a threshold value due to discharge consistently generate an error upon reading. Therefore, according to the conventional error correction method, the same error correction operation must be performed each time reading is performed, so that a large amount of calculation is generated in each correction operation.
방전으로 인하여 에러가 일정하게 발생하는 메모리 소자 외에, 새롭게 에러를 생성하는 메모리 소자가 있을 수도 있다. 이러한 다수의 메모리 소자들의 에러를 보정하기 위하여, 다수의 보정 코드가 필요하다. 이는 각 보정 동작에서 심지어 더 많은 계산량을 유발시킨다.In addition to a memory device in which an error occurs constantly due to discharge, there may be a memory device that newly generates an error. In order to correct errors of such a plurality of memory elements, a plurality of correction codes are required. This causes even more computation in each correction operation.
본 발명의 일 태양에 따르면, 기억 매체 재생 장치는 기억 유닛, 보정 이력 기억 유닛, 보정 이력 실행 유닛, 및 보정 유닛을 포함한다. 기억 유닛은, 전하량이 미리 설정된 전하량 임계값보다 큰 지의 여부에 따라 정보를 기억하는 복수의 정보 기억 유닛과, 상기 복수의 정보 기억 유닛에 기억된 정보에 대한 에러 보정 코드들을 기억하는 보정 코드 기억 유닛을 포함한다. 보정 이력 기억 유닛은, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정 동작이 정보 기억 유닛들 간에 수행되는 정보 기억 유닛을 식별하기 위한 식별 정보와, 상기 보정의 내용을 포함하는 보정 이력을 기억한다. 보정 이력 실행 유닛은, 정보가 식별 정보에 의하여 식별된 정보 기억 유닛으로부터 판독될 때 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억된 보정의 내용에 따라 정보를 보정한다. 보정 유닛은 보정된 정보에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 동작을 수 행하고, 보정 이력 기억 유닛에, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정된 정보 기억 유닛의 보정의 내용과 식별 정보를 포함하는 보정 이력을 등록한다.According to one aspect of the present invention, the storage medium reproducing apparatus includes a storage unit, a correction history storage unit, a correction history execution unit, and a correction unit. The storage unit includes a plurality of information storage units for storing information depending on whether the charge amount is greater than a preset charge amount threshold value, and a correction code storage unit for storing error correction codes for information stored in the plurality of information storage units. It includes. The correction history storage unit stores identification information for identifying an information storage unit in which a correction operation using an error correction code is performed between the information storage units, and a correction history including the contents of the correction. The correction history execution unit corrects the information according to the contents of the correction stored in the correction history storage unit when the information is read out from the information storage unit identified by the identification information. The correction unit performs a correction operation using the error correction code on the corrected information, and registers a correction history including the contents of the correction of the information storage unit corrected using the error correction code and identification information in the correction history storage unit. do.
본 발명의 다른 태양에 따르면, 기억 매체 재생 방법은, 전하량이 미리 결정된 전하량 임계값보다 큰 지의 여부에 따라 정보를 각각 기억하는 복수의 정보 기억 유닛들 간에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정된 정보 기억 유닛을 식별하는 식별 정보와 보정 내용을 포함하는 보정 이력을 기억하는 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억된 보정 내용에 따라 식별 정보에 의하여 식별된 정보 기억 유닛으로부터 판독된 정보를 보정하는 단계; 및 상기 보정된 정보에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 동작을 실행하여, 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 에러 보정을 사용하여 보정된 정보 기억 유닛의 식별 정보와 보정 내용을 포함하는 보정 이력을 등록하는 단계를 포함한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, a storage medium reproducing method comprises: an information storage unit corrected using an error correction code among a plurality of information storage units, each of which stores information depending on whether the amount of charge is greater than a predetermined charge amount threshold; Correcting the information read from the information storage unit identified by the identification information according to the correction contents stored in the correction history storage unit which stores the correction history including the identification information and the correction contents identifying the identification information; And performing a correction operation on the corrected information by using an error correction code, and registering a correction history including identification information and correction contents of the information storage unit corrected by using error correction in the correction history storage unit. do.
본 발명의 또다른 태양에 따른 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체는 컴퓨터가 본 발명에 따른 기억 매체 재생 방법을 수행하도록 한다.A computer readable medium according to another aspect of the present invention allows a computer to perform the storage medium reproducing method according to the present invention.
본 발명에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치, 기억 매체 재생 방법, 및 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체의 예시적인 실시예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 이하에 상세히 설명한다.Exemplary embodiments of a storage medium reproducing apparatus, a storage medium reproducing method, and a computer readable medium according to the present invention are described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치는 기억 유닛에 과거의 에러 보정 코드를 이용하여 보정 이력을 기억하고, 정보 판독시에 보정 이력을 참조하여 보정 동작을 수행한다. 기억 매체 재생 장치는 또한 이력을 참조하여 수행된 보정 결과에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 동작을 수행한다.The storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the first embodiment stores a correction history in the storage unit using past error correction codes, and performs a correction operation with reference to the correction history when reading information. The storage medium reproducing apparatus also performs a correction operation by using an error correction code in the correction result performed by referring to the history.
도 1은 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)의 구성을 도시하는 블록도이다. 도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)는 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn), 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn), 제어 유닛(101), 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102), 및 보정 유닛(103)을 포함한다.1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the storage
기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 정보를 기억하는 기억 소자들이며, 전하량에 대하여 미리 결정된 임계값에 관한 전하량에서의 차이를 사용한다. 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 플래시 메모리 또는 DRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memories)와 같은, 일반적으로 사용되는 반도체 메모리로 형성될 수도 있다. 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 또한 하나의 임계값을 유지하고 0과 1로 구성된 2진 정보를 기억하는 2진 기억 소자들로 형성될 수도 있다. 또는, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 상이한 임계값들을 유지하는 다-값 기억 소자들로 형성될 수도 있다. 다음에, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)이 4-값 기억 소자들로 형성된 구성을 설명한다.The memory units M1 to Mn are memory elements that store information, and use a difference in the amount of charge with respect to a threshold value predetermined for the amount of charge. The storage units M1 to Mn may be formed of a commonly used semiconductor memory, such as flash memory or DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memories). The memory units M1 to Mn may also be formed of binary memory elements which maintain one threshold and store binary information consisting of zeros and ones. Alternatively, the memory units M1 to Mn may be formed of multi-value memory elements that hold different threshold values. Next, a configuration in which the memory units M1 to Mn are formed of four-value memory elements will be described.
기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)과 보정 코드 기억 유닛들(EC1 내지 ECn)을 각각 포함한다. 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)은 기억 유닛들이며, 이 기억 유닛들 각각은 4-값 기억 소자들인 메모리 셀들을 포함한다. 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)에 기억될 정보는 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에 실제로 기억된다.The memory units M1 to Mn include memory cell groups MC1 to MCn and correction code memory units EC1 to ECn, respectively. The memory cell groups MC1 to MCn are memory units, each of which includes memory cells that are four-value memory elements. Information to be stored in the storage units M1 to Mn is actually stored in the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn.
보정 코드 기억 유닛들(EC1 내지 ECn)은 기억 유닛들이고, 상기 기억 유닛들 각각은 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)과 같이, 4-값 기억 소자들인 메모리 셀들을 포함한다. 기억될 정보 대신, 보정 코드 기억 유닛들(EC1 내지 ECn)은 기억될 정보에 대응하는 에러 보정 코드들을 기억한다. 보정 코드 기억 유닛들(EC1 내지 ECn)의 각각을 구성하는 메모리 셀들의 수는 1에 한정되지 않으나, 보정의 최대수 에까지 이르를 수도 있다.The correction code storage units EC1 to ECn are storage units, and each of the storage units includes memory cells that are four-value memory elements, such as the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn. Instead of the information to be stored, the correction code storage units EC1 to ECn store error correction codes corresponding to the information to be stored. The number of memory cells constituting each of the correction code storage units EC1 to ECn is not limited to 1, but may reach the maximum number of corrections.
도 2는 4-값 기억 소자들을 포함하는 기억 유닛의 등가 회로의 예를 도시한다. 도 2에 도시된 등가 회로는 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)의 기억 유닛(이하, 기억 유닛(Mn)이라 칭함)이다.2 shows an example of an equivalent circuit of a storage unit including four-value memory elements. The equivalent circuit shown in FIG. 2 is a storage unit (hereinafter, referred to as a storage unit Mn) of the storage units M1 to Mn.
도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 유닛(Mn)은 기억 소자들(셀0 내지 셀i)을 포함하고, 기억 소자들 각각에 전하를 축적하도록 설계된다. 축적된 전하는 비교기에 의하여 3개의 임계값들과 비교되어, 비트(B0) 및 비트(B1)의 2-비트 정보가 출력될 수 있다. 따라서, 4-값 정보(01, 00, 10, 11)가 기억될 수 있다.As shown in Fig. 2, the memory unit Mn includes memory elements (
기억 소자들(셀0 내지 셀i)의 일부는 도 11에 도시된 메모리 셀 그룹들(MCn)을 구성하고, 기억 소자들의 나머지는 보정 코드 기억 유닛들(ECn)을 구성한다.Some of the memory elements (
도 3은 기억 소자들로부터의 방전을 도시한다. 도 3에 도시된 그래프에서, 기록의 개시점은 0으로 나타내며, 횡축은 경과된 시간을 나타내고, 종축은 출력 전압을 나타낸다. 플래시 메모리 또는 DRAM과 같은 반도체 메모리는, 전력 공급이 차단되어도 기억된 내용을 유지할 수 있다. 그러나, 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 소자들에 축적된 전하들은, 오랜 기간이 경과한 후 방전되어, 출력 전압이 감소한다.3 shows discharges from the memory elements. In the graph shown in Fig. 3, the starting point of recording is represented by 0, the horizontal axis represents elapsed time, and the vertical axis represents output voltage. A semiconductor memory such as a flash memory or a DRAM can retain the stored contents even when power supply is cut off. However, as shown in Fig. 3, the charges accumulated in the memory elements are discharged after a long period of time, so that the output voltage decreases.
도 4는 기억 소자들에서의 전하 분포의 예를 도시한다. 도 4의 좌측은 기록 동작 직후 관찰된 전하 분포를 도시한다. 도 4의 우측은 특정 기간이 경과한 후 관찰된 전하 분포를 도시한다. 전하량에 대한 임계값들은 Eth0 내지 Eth2로 나타낸다.4 shows an example of the charge distribution in the memory elements. The left side of Fig. 4 shows the charge distribution observed immediately after the write operation. 4 shows the distribution of charges observed after a certain period of time. Thresholds for the amount of charge are represented by Eth0 to Eth2.
도 4에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 소자들에 축적된 전하들은 시간에 따라 방전되며, 전하 분포는 임계값에 접근한다. 그 결과, 정보 판독 시에 유발될 에러의 확률은 더 높아진다.As shown in Fig. 4, the charges accumulated in the memory elements are discharged over time, and the charge distribution approaches a threshold. As a result, the probability of an error to be caused when reading information becomes higher.
보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)은 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 유닛(103)에 의하여 보정된 내용의 이력을 기억하는 기억 유닛들이다. 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)은 FeRAM(Ferroelectric Random Access Memories) 또는 SRAM(Static Random Access Memories)와 같은, 리프레시 동작을 요구하지 않는 기억 소자들로 형성된다.The correction history storage units EL1 to ELn are storage units that store a history of the content corrected by the
보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELn)은, 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)이 보정 이력을 참조하여 정보를 보정할 때 참조된다. 제1 실시예에서, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)을 각각 포함한다.The correction history storage unit ELn is referred to when the correction
도 5는 보정 기억 유닛(EL1 내지 ELn)의 예시적인 데이터 구조를 도시한다. 도 5에 도시된 데이터 구조는 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)의 보정 이력 기억 유닛(이하, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELn)으로 칭함)의 데이터 구조이다.5 shows an exemplary data structure of the correction storage units EL1 to ELn. The data structure shown in Fig. 5 is the data structure of the correction history storage units (hereinafter referred to as the correction history storage unit ELn) of the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn.
도 5에 도시된 바와 같이, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELn)은 메모리 셀 그룹(MCn)에 포함된 메모리 셀들 중 에러 보정 코드로 보정된 메모리 셀의 셀 ID를 기억한다. 셀 ID는 보정의 내용과 연관하여 기억된다. 예컨대, “11”이 “10”으로 보정되면, “11 -> 10”의 정보가 기억된다.As shown in FIG. 5, the correction history storage unit ELn stores a cell ID of a memory cell corrected by an error correction code among memory cells included in the memory cell group MCn. The cell ID is stored in association with the content of the correction. For example, when "11" is corrected to "10", information of "11-> 10" is stored.
보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에 기억된 보정 이력들은, 새로운 정보가 대응하는 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)에 기록될 때마다 지워진다. 이것은, 새로운 정보가 기록될때, 충분한 전하가 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에 축적되기 때문이다.The correction histories stored in the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn are erased each time new information is recorded in the corresponding storage units M1 to Mn. This is because sufficient charge is accumulated in the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn when new information is written.
제어 유닛(101)은 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)에 관한 정보 판독 커맨드와 같은 명령을 수신한다. 명령에 따라, 제어 유닛(101)은, 정보가 판독될 기억 유닛을 선택하여, 보정 동작을 제어한다.The
보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)은, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)로부터 판독된 정보에 관하여, 대응하는 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에 기억된 보정 이력을 참조한다. 다음, 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)은 보정 이력에 포함된 보정 내용과 동일한 보정 동작을 수행한다.The correction
예컨대, 기억 유닛(Mn)의 정보가 판독되고, “셀 ID = 1" 및 ”보정 내용 = 11 -> 10“의 보정 이력이 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELn)에 기억되면, 정보 ”11“에서 ”10“으로의 변화 동작이 기억 유닛(Mn)에 셀 ID "1"을 갖는 셀에 수행된다.For example, when the information of the storage unit Mn is read out and the correction history of "Cell ID = 1" and "Calibration contents = 11-> 10" is stored in the correction history storage unit ELn, the information "11" to "" is stored. The change operation to 10 " is performed on the cell having the cell ID " 1 " in the storage unit Mn.
보정 유닛(103)은 보정 이력의 보정 내용에 따라 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)에 의하여 보정된 정보에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 동작을 수행한다. 에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정 동작은, BCH(Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem) 코드 디코딩 또는 RS(Reed-Solomon) 코드 디코딩과 같은, 즉시 디코딩을 가능하게 하는 종래의 에러 보정 기술에 의하여 수행된다.The
보정 유닛(103)은 또한 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에서 에러 보정 동작의 내용을 기억한다. 보다 구체적으로는, 에러를 갖는 메모리 셀의 셀 ID는 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL1 내지 ELn)에 보정 전후의 정보를 포함하는 보정 내용과 연관하여 기억된다.The
다음, 제1 실시예에 따른 상기 구조를 갖는 기록 매체 재생 장치(100)에 의하여 수행될 기록 매체 재생 동작을 설명한다. 도 6은 본 발명에 따른 전체 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.Next, a recording medium reproducing operation to be performed by the recording
첫째, 제어 유닛(101)은 재생되도록 지정된 정보를 기억하는 기억 유닛으로부터 정보를 판독한다(단계 S601). 여기서, 정보는 메모리 유닛(Mk)(k는 정수)으로부터 판독된다.First, the
보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)은 기억 유닛(Mk)에 대응하는 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)으로부터 과거 보정의 내용을 포함하고, 보정의 획득된 내용에 따라 판독된 정보에 보정 동작을 수행한다(단계 S602).The correction
도 5에 도시된 보정 이력은, 예컨대 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 기억되고, 정보 “11”는 단계 S601에서 메모리 기억 유닛(Mk)의 메모리 셀 그룹(MCk)에 포함된 메모리 셀들 중에서 “1”의 셀 ID를 갖는 메모리 셀로부터 판독된다. 이 경우, “1”의 셀 ID에 대응하는 보정 이력은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 존재하고, 보정 콘텐츠는 정보 “11” 내지 “10”로의 변화를 나타낸다. 그러므로, 정보 “11”은 보정 내용에 따라 “10”으로 변한다.The correction history shown in FIG. 5 is stored in, for example, the correction history storage unit ELk, and information “11” is “1” among the memory cells included in the memory cell group MCk of the memory storage unit Mk in step S601. Is read from a memory cell having a cell ID of " In this case, the correction history corresponding to the cell ID of "1" exists in the correction history storage unit ELk, and the correction content indicates a change from information "11" to "10". Therefore, the information "11" changes to "10" according to the correction.
에러를 발생시킨 셀을 식별하고, 보정될 값을 식별하는 계산이 에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 종래의 에러 보정 동작에서 요구되어도, 이러한 계산은 제1 실시예의 방법에서 필수적인 것은 아니다. 그러므로, 각 보정 동작에서의 일 부하가 감소될 수 있다.This calculation is not essential to the method of the first embodiment, although a calculation for identifying the cell which caused the error and identifying the value to be corrected is required in the conventional error correction operation using the error correction code. Therefore, the work load in each correction operation can be reduced.
다음, 보정 유닛(103)은, 에러가 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)에 의하여 보정된 정보에 존재하는 지의 여부를 결정한다(단계 S603). 에러가 존재하면(단계 S603에서 “YES"), 보정 유닛(103)은, 에러가 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 형성될 수 있는지의 여부를 판정한다(단계 S604). 보다 구체적으로는, 상술된 에러 보정 기술을 사용하여, 보정이 행해질 수 있는 지의 여부는, 에러 비트의 수가 보정가능한 비트수를 초과하는 지의 여부에 따라 결정된다.Next, the
보정이 행해질 수 있다고 판정되면(단계 S604에서 “YES"), 보정 유닛(103)은 에러 위치와 에러 벡터를 계산하고, 정보를 보정한다(단계 S605). 에러 위치는 메모리 셀들 중에서 생성된 에러를 갖는 메모리 셀을 나타내는 정보이며, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)의 셀 ID와 동일하다. 에러 벡터는 에러 정보를 보정 정보로 변환하는 방법을 나타내는 정보이며, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 기억된 보정 내용과 동일하다.If it is determined that correction can be made (YES in step S604), the
다음, 보정 유닛(103)은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 보정 이력으로서, 계산된 셀 ID와 보정 내용을 등록한다(단계 S606). 단계 S605에서 계산된 보정 이력은 현재 정보 판독 동작에서 새롭게 생성된 에러의 보정 이력이다. 이러한 방식으로, 새롭게 생성된 에러의 보정 이력 만이 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 부가적으로 등록되어, 보정 이력이 이후 판독 동작에서 참조될 수 있다.Next, the
보정 이력이 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 등록된 후(단계 S606), 또는 에러가 보정 이력 실행 유닛(102)에 의하여 보정된 정보에 존재하지 않는 것으로 판정된 후(단계 S603에서 “NO"), 보정 유닛(103)은 보정된 정보를 출력하거나, 정상 판독후 판독된 정보가 실행된다(단계 S607). 여기서, 기억 매체 재생 동작이 종료된다.After the correction history is registered in the correction history storage unit ELk (step S606) or after it is determined that an error does not exist in the information corrected by the correction history execution unit 102 ("NO" in step S603) The
에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정이 행해지지 않은 것으로 판정되면(단계 S604에서 “NO"), 제어 유닛(101)은, 에러가 생성되었다는 취지로의 출력을 형성한다(단계 S608). 여기서, 기억 매체 재생 동작이 종료한다.If it is determined that the correction using the error correction code has not been performed ("NO" in step S604), the
상술된 바와 같이, 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 에러 보정은 기억 유닛에 기억된 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 에러 보정의 이력을 참조하여 행해질 수 있다. 따라서, 계산 일 부하는 각 보정 동작에서 감소될 수 있다. 또한, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정이 새롭게 생성된 에러에만 행해질 때, 보정에 요구되는 보정 코드의 수가 감소될 수 있다.As described above, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the first embodiment, error correction can be performed with reference to the history of error correction using the error correction code stored in the storage unit. Thus, the calculation load can be reduced in each correction operation. Also, when the correction using the error correction code is performed only on newly generated errors, the number of correction codes required for the correction can be reduced.
제1 실시예에서, 노이즈에 의하여 유발된 에러와 같은, 방전 이외의 인자들로 인하여 생성된 에러들도 보정 이력으로서 기억된다. 그러므로, 노이즈가 제거되고, 판독이 적절하게 수행되어도, 보정 이력 실행 방법에 의하여 보정이 행해진다. 그 결과, 의도하지 않은 보정이 행해질 수도 있다.In the first embodiment, errors generated due to factors other than discharge, such as an error caused by noise, are also stored as the correction history. Therefore, even if noise is removed and reading is appropriately performed, correction is performed by the correction history execution method. As a result, unintended correction may be made.
제2 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치는, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정될 에러가 방전에 의하여 유발되었던 것이라고 간주될 때만 기억 유닛에 에러 보정의 내용을 기억시킴으로써 이 문제점을 제거한다.The storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the second embodiment eliminates this problem by storing the contents of the error correction in the storage unit only when the error to be corrected using the error correction code is considered to have been caused by the discharge.
제2 실시예는, 보정 유닛(103)에 의하여 수행될 동작에서 제1 실시예와 상이하다. 구성과 기능의 다른 태양들은 도 1의 블록도에 도시된 제1 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)의 것들과 동일하여, 그 설명은 여기서 다시 하지 않는다.The second embodiment is different from the first embodiment in the operation to be performed by the
다음, 제2 실시예에 따라 기록 매체 재생 장치에 의하여 수행될 기억 매체 재생 동작을 설명한다. 도 7은 제2 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.Next, a storage medium reproducing operation to be performed by the recording medium reproducing apparatus according to the second embodiment will be described. 7 is a flowchart of a storage medium reproducing operation according to the second embodiment.
단계 S701 내지 단계 S705의 정보 판독 처리 및 정보 보정 처리는 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)에서 수행될 단계 S601 내지 단계 S605의 처리와 동일하므로, 그 설명은 여기서 반복하지 않는다.Since the information reading processing and the information correcting processing of steps S701 to S705 are the same as the processing of steps S601 to S605 to be performed in the storage
에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 정보를 보정한 후(단계 S705), 보정 유닛(103)은, 보정된 에러가 시간에 따라 유발되는 지의 여부를 판정한다(단계 S706). "시간에 따라 유발된 에러“는 도 3에 도시된 바와 같은 기억 소자들의 방전에 의하여 생성된 에러이다.After correcting the information using the error correction code (step S705), the
보다 구체적으로는, 보정 유닛(103)은, 정보에서의 에러가 도 4에 도시된 바와 같은 방전으로 인하여 임계값들(Eth0 내지 Eth2)을 초과하는 지의 여부를 판정한다. 예컨대, 정보 “01”는 “00”으로서 잘못 판독되고, 방전으로 인하여 도 4에 도시된 임계값(Eth2)을 초과하는 에러로서 간주될 수 있다. 따라서, 보정 유닛(103)은 에러가 시간에 따라 유발되는 것을 결정한다.More specifically, the
시간에 따라 유발될 수 있는 에러는 “01 -> 00”, “00 -> 10” 및 “10 -> 11”를 포함한다. 긴 기간이 경과되면, 에러는 2개의 임계값들을 초과할 수도 있으며, 따라서 “01 -> 10”, “01 -> 11” 및 “00 -> 11”를 포함할 수도 있다.Errors that can be triggered over time include "01-> 00", "00-> 10" and "10-> 11". If a long period has elapsed, the error may exceed two thresholds, and thus may include “01-> 10”, “01-> 11” and “00-> 11”.
에러가 시간에 따라 유발되었던 것이 아닌 것으로 판정되면(단계 S706에서 “NO"), 보정 이력은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL1 내지 ELn)에 등록되지 않으나, 보정 된 정보가 출력된다(단계 S708).If it is determined that the error was not caused by time (“NO” in step S706), the correction history is not registered in the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn, but the corrected information is output (step S708).
에러가 시간에 따라 유발되었던 것으로 판정되면(단계 S706에서 “YES"), 보정 이력은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL1 내지 ELn)에 등록되며(단계 S707), 보정된 정보가 출력된다(단계 S708).If it is determined that the error has been caused by time ("YES" in step S706), the correction history is registered in the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn (step S707), and the corrected information is output (step S708).
제1 실시예에서와 같이, 보정이 단계 S704에서 불가능한 것이라고 판정되면, 에러 메시지가 출력된다(단계 S709).As in the first embodiment, if it is determined that correction is impossible in step S704, an error message is output (step S709).
상술된 바와 같이, 제2 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정된 에러가 방전으로 인하여 유발된 에러로서 간주될 수 있을 때만, 에러 보정의 내용이 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억되어, 에러 보정의 내용이 이후의 보정 동작에 참조될 수 있다. 따라서, 불필요한 보정 동작이 최소 가능한 회수로 제한될 수 있다.As described above, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the second embodiment, the contents of the error correction are written to the correction history storage unit only when the error corrected using the error correction code can be regarded as an error caused by the discharge. The contents of the error correction can be referred to later correction operation. Thus, unnecessary correction operations can be limited to the minimum possible number of times.
본 발명의 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치는 단일 기억 유닛에 복수의 기억 유닛들의 보정 이력들을 기억한다.The storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the third embodiment of the present invention stores correction histories of a plurality of storage units in a single storage unit.
도 8은 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(800)의 구조를 도시하는 블록도이다. 도 8에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 매체 재생 장치(800)는 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn), 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL), 제어 유닛(101), 보정 이력 실행 유닛(802), 및 보정 유닛(803)을 포함한다.8 is a block diagram showing the structure of the storage
제3 실시예는, 보정 이력 실행 유닛(802)과 보정 유닛(803)에 의하여 수행될 동작과 단지 하나의 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)에서 제1 실시예와 상이하다. 제3 실시예의 구성과 기능의 다른 태양은 도 1의 블록도에 도시된 제1 실시예의 기억 매 체 재생 장치(100)의 것들과 동일하므로, 그 설명은 여기서 반복하지 않는다.The third embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the operation to be performed by the correction
제1 실시예의 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL1 내지 ELn)과 같이, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)은 에러 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정 유닛(803)에 의하여 보정된 내용의 이력을 기억한다. 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)은 FeRAM과 SRAM과 같은, 리프레시 동작을 요하지 않는 기억 소자들로 형성된다.Like the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn in the first embodiment, the correction history storage unit EL stores a history of the content corrected by the
보정 이력 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)이 제1 실시예에서 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)을 위하여 제공되어도, 단지 하나의 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)이 제3 실시예에서 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)을 위하여 제공된다.Although correction history units EL1 to ELn are provided for the storage units M1 to Mn in the first embodiment, only one correction history storage unit EL is used to store the storage units M1 to Mn in the third embodiment. Mn).
도 9는 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)의 데이터 구조의 예를 도시한다. 도 9에 도시된 바와 같이, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)은 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn) 중에서 세브젝트 기억 유닛을 식별하는 기억 유닛 ID와, 상기 기억 유닛 ID에 의하여 식별된 기억 유닛에서의 메모리 셀 그룹(MCn)에 포함된 메모리 셀들 중에서 에러 보정 코드로 보정된 메모리 셀을 식별하는 셀 ID와, 보정 내용을 기억한다. 여기서, 기억 유닛 ID, 셀 ID, 및 보정 내용이 서로 연관된다.9 shows an example of the data structure of the correction history storage unit EL. As shown in Fig. 9, the correction history storage unit EL includes a storage unit ID for identifying a subject storage unit among the storage units M1 to Mn, and a memory in the storage unit identified by the storage unit ID. Among the memory cells included in the cell group MCn, a cell ID for identifying a memory cell corrected by an error correction code and the correction contents are stored. Here, the storage unit ID, the cell ID, and the correction contents are associated with each other.
기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)이 개입되면, 각 기억 유닛으로의 큰 기억 영역의 할당은 기억 영역에서 큰 미사용 영역으로 이르게 할 수도 있으며, 이것은 에러를 자주 생성시키는 기억 유닛들의 수가 제한되기 때문이다. 제3 실시예에서, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)을 공유하여, 기억 영역의 사용 효율성을 향상시킨다.If the storage units M1 to Mn are involved, the allocation of a large storage area to each storage unit may lead to a large unused area in the storage area, because the number of storage units that frequently generate errors is limited. In the third embodiment, the storage units M1 to Mn share the correction history storage unit EL, thereby improving the use efficiency of the storage area.
보정 이력 기억 유닛의 수는 하나에 제한되지 않으나, 복수의 보정 이력 기 억 유닛들을 채용할 수 있다. 이러한 경우에서, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)이 그룹들로 구분되며, 하나의 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)이 그룹들 각각에 대하여 제공되어, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)이 각 그룹에서 기억 유닛들 간에 공유될 수 있다.The number of correction history storage units is not limited to one, but a plurality of correction history storage units may be employed. In this case, the storage units M1 to Mn are divided into groups, and one correction history storage unit EL is provided for each of the groups, so that the correction history storage unit EL is stored in each group. Can be shared between them.
보정 이력 실행 유닛(802)은, 정보가 판독되었던 기억 유닛(기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn) 중 하나)의 기억 유닛 ID에 대응하는 보정 이력에 대한 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)을 검색한다. 보정 이력이 찾아지면, 보정 동작이 보정 이력의 내용에 따라 수행된다.The correction
제3 실시예에서, 모든 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)의 보정 이력들은, 제1 실시예의 경우와는 달리, 단일 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)에 기억된다. 그러므로, 정보가 판독되었던 기억 유닛의 기억 유닛 ID와 연관된 보정 이력이 검색된다. 보정 이력이 찾아지면, 보정 동작이 획득된 보정 이력에 포함된 보정 내용에 따라 수행된다.In the third embodiment, correction histories of all the storage units M1 to Mn are stored in the single correction history storage unit EL, unlike in the case of the first embodiment. Therefore, the correction history associated with the storage unit ID of the storage unit from which the information was read is retrieved. If a correction history is found, a correction operation is performed according to the correction contents included in the obtained correction history.
제1 실시예의 보정 유닛(103)과 같이, 보정 유닛(803)은 보정 이력의 보정 내용에 따라 보정 이력 실행 유닛(802)에 의하여 보정된 정보에 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정 동작을 수행한다. 제3 실시예의 보정 유닛(803)은, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)에서 모든 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn)에 에러 보정 동작의 내용을 기억하는 점에서 제1 실시예의 보정 유닛(103)과는 상이하다.Like the
다음, 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(800)에 의하여 수행될 기억 매체 재생 동작을 설명한다. 도 10은 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.Next, a storage medium reproducing operation to be performed by the storage
단계 S1001에서 정보 판독 동작은 제1 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)에 수행될 단계 S601의 것과 동일하며, 따라서 단계 S1001의 설명을 반복하지 않는다.The information reading operation in step S1001 is the same as that of step S601 to be performed in the storage
정보 판독 동작(단계 S1001) 이후, 보정 이력 실행 유닛(802)은, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)으로부터, 정보가 판독되었던 기억 유닛(Mk)의 과거 보정의 내용을 획득한 후, 과거 보정의 내용에 따라 보정 동작을 수행한다(단계 S1002). 보다 구체적으로는, 정보가 판독되었던 기억 유닛(Mk)의 기억 유닛 ID에 대응하는 보정 이력이 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)으로부터 검색된다. 보정 이력이 찾아지면, 보정 동작이 검색된 보정 이력의 보정 내용에 따라 수행된다.After the information reading operation (step S1001), the correction
에러 보정 코드를 사용한 보정 동작과 단계 S1003 내지 단계 S1008의 정보 출력 동작은 제1 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)에서 수행될 단계 S603 내지 단계 S608의 것과 동일하며, 따라서 그 설명을 여기서 반복하지 않는다.The correction operation using the error correction code and the information output operation of steps S1003 to S1008 are the same as those of steps S603 to S608 to be performed in the storage
상술된 바와 같이, 제3 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 복수의 기억 유닛들의 보정 이력들이 단일 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억된다. 따라서, 보정 이력들을 기억하기 위하여 요구되는 기억 소자들의 수가 감소될 수 있어, 기억 영역의 사용 효율성이 증가될 수 있다.As described above, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the third embodiment, correction histories of a plurality of storage units are stored in a single correction history storage unit. Thus, the number of memory elements required for storing the correction histories can be reduced, so that the use efficiency of the storage area can be increased.
제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치는, 에러량이 미리 결정된 임계값을 초과한다면, 기억 소자들에 리프레시 동작을 수행한다.The storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the fourth embodiment performs a refresh operation on the storage elements if the error amount exceeds a predetermined threshold.
도 11은 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(1100)의 구성을 도시하는 블록도이다. 도 11에 도시된 바와 같이, 기억 매체 재생 장치(1100)는, 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn), 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn), 제어 유닛(101), 보정 이 력 실행 유닛(102), 보정 유닛(103), 및 리프레시 제어 유닛(1104)을 포함한다.11 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the storage
제4 실시예는, 리프레시 제어 유닛(1104)이 추가된다는 점에 제1 실시예와 상이하다. 제4 실시예의 구성 및 기능의 다른 태양은 도 1의 블록도에 도시된 제1 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)의 것과 동일하므로, 그 설명은 여기서 반복하지 않는다.The fourth embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that the
에러 생성의 정도를 나타내는 에러 생성량이 미리 결정된 임계값을 초과하면, 리프레시 제어 유닛(1104)가 리프레시 동작을 수행하여, 기억 소자들의 전하량을 정규 값에 유지한다. 예컨대, 에러 생성량이 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에 기록된 보정 이력들의 수이면, 보정 이력들의 수가 미리 결정된 임계값을 초과할 때 리프레시 동작이 수행된다.When the error generation amount indicating the degree of error generation exceeds the predetermined threshold value, the
메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)의 기억 소자들의 방전이 실질적으로 동일한 속도로 진행하면, 다수의 보정 이력들을 갖는 메모리 셀 그룹은 최종 기록 동작 이후 경과된 긴 기간을 가지며, 전하량이 임계값을 초과하면 정보 판독 동작시 에러를 생성시키는 많은 기억 소자들을 포함하는 경향이 있다(도 4에 도시된 Eth1 내지 Eth2). 그러므로, 기억된 보정 이력들 수가 미리 결정된 값을 초과하면, 리프레시 동작이 수행된다.If the discharge of the memory elements of the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn proceeds at substantially the same rate, the memory cell group having a plurality of correction histories has a long period elapsed since the last write operation, and the charge amount exceeds the threshold value. There is a tendency to include many memory elements which generate errors in the information read operation (Eth1 to Eth2 shown in Fig. 4). Therefore, when the number of stored correction histories exceeds a predetermined value, the refresh operation is performed.
메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)의 기억 소자들에서의 기록 정보의 타이밍은, 정보를 기록하는 동작과 대응하는 에러 보정 코드들을 부가하는 동작의 성질의 관점에서 크게 가변하지 않는다. 따라서, 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)의 기억 소자들에서의 기록 동작은 동시에 수행되는 것으로 간주될 수 있다. 따라서, 보정 이력들의 수는 상술된 바와 같이, 에러 생성량에 대한 판단 기준으로서 사용될 수 있다.The timing of the write information in the memory elements of the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn does not vary greatly in terms of the nature of the operation of writing the information and adding the error correction codes corresponding to the information. Therefore, the write operation in the memory elements of the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn can be considered to be performed at the same time. Thus, the number of correction histories can be used as a criterion for the error generation amount, as described above.
에러 생성량에 대한 기준은 보정 이력의 수에 제한되지 않으나, 에러 생성에 대한 정도를 나타내는 한 임의의 정보 형태일 수도 있다.The criterion for the error generation amount is not limited to the number of correction histories, but may be in any form of information as long as the degree of error generation is indicated.
예컨대, 에러 보정 코드로 새롭게 보정된 기억 소자들의 수는 에러 생성량에 대한 기준으로서 사용될 수도 있다. 보정 코드를 사용하는 보정 동작을 통하여 새롭게 발견된 많은 에러를 갖는 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에서, 최종 기록 동작후 오랜 기간이 경과하였다. 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에서 기억 소자들의 방전이 실질적으로 동일한 속도로 진행되면, 전하량에 대한 임계값을 초과하고, 판독 동작시 에러를 생성시키는 많은 기억 소자들을 포함하는 확률이 높다.For example, the number of memory elements newly corrected by the error correction code may be used as a reference for the error generation amount. In the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn having many errors newly discovered through a correction operation using a correction code, a long time has passed since the last write operation. If the discharge of the memory elements in the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn proceeds at substantially the same speed, there is a high probability of exceeding the threshold for the amount of charge and including many memory elements that generate an error in a read operation.
또는, 전하량에 대한 미리 결정된 수의 임계값들을 초과하는 기억 소자들의 수는 에러 생성량에 대한 기준으로서 사용될 수도 있다. 예컨대, 4-값 기억 소자들의 경우에서, 전하량에 대한 복수의 임계값들을 초과하는 기억 소자들 수가 미리 결정된 임계값보다 큰 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에 리프레시 동작이 수행될 수도 있다.Alternatively, the number of memory elements exceeding a predetermined number of thresholds for the amount of charge may be used as a reference for the amount of error generation. For example, in the case of four-value memory elements, a refresh operation may be performed on the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn in which the number of memory elements exceeding a plurality of thresholds for the charge amount is larger than a predetermined threshold value.
충전량에 대한 복수의 임계값들의 초과는 거의 발생하지 않는다. 그러나, 이러한 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)은 최종 기록 동작 후 오랜 기간을 갖는다. 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에서의 기억 소자의 방전이 실질적으로 동일한 속도로 진행되면, 전하량에 대한 임계값을 초과하고 판독 동작시 에러를 생성시키는 많은 기억 소자들을 포함하는 확률이 높다.Exceeding the plurality of thresholds for the charge amount rarely occurs. However, these memory cell groups MC1 to MCn have a long period after the last write operation. If the discharge of the memory elements in the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn proceeds at substantially the same rate, there is a high probability of including many memory elements that exceed the threshold for the amount of charge and generate an error in a read operation.
또는, 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)의 정보 기억의 용량은 에러 생성량에 대한 기준으로서 사용될 수도 있다. 특히, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)이 제3 실시예에서 기억 유닛들(M1 내지 Mn) 간에 공유되는 경우에서, 보정 이력 기억 유닛(EL)은, 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)에서 발견된 에러수가 작아도, 기억 용량을 초과할 수도 있다.Alternatively, the capacity of the information storage of the correction history storage units EL1 to ELn may be used as a reference for the error generation amount. In particular, in the case where the correction history storage unit EL is shared between the storage units M1 to Mn in the third embodiment, the correction history storage unit EL is found in the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn. Even if the number of errors is small, the storage capacity may be exceeded.
이 경우, 리프레시될 메모리 셀 그룹들(MC1 내지 MCn)은 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL)을 공유하는 메모리 셀 그룹들로부터 임의로 선택될 수 있다. 그러나, 리프레시 동작은 최대수의 기억된 에러 보정 이력들을 갖는 메모리 셀 그룹에 수행될 수도 있으며, 대응하는 보정 이력이 지워진다. 따라서, 많은 에러를 갖는 메모리 셀 그룹들에 기억된 정보의 신뢰성이 유지될 수 있고, 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL)의 기억 영역이 적절하게 증가될 수 있다.In this case, the memory cell groups MC1 to MCn to be refreshed may be arbitrarily selected from the memory cell groups sharing the correction history storage units EL. However, the refresh operation may be performed on the memory cell group having the maximum number of stored error correction histories, and the corresponding correction history is erased. Therefore, the reliability of the information stored in the memory cell groups having many errors can be maintained, and the storage area of the correction history storage units EL can be increased appropriately.
다음, 제4 실시예에 따라 기억 매체 재생 장치(1100)에 의하여 수행될 기억 매체 재생 동작을 설명한다. 도 12는 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 동작의 흐름도이다.Next, a storage medium reproducing operation to be performed by the storage
단계 S1201 내지 단계 1205의 정보 판독 처리 및 정보 보정 처리는 제1 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)에서 수행될 단계 S601 내지 단계 S605의 것과 동일하므로, 그 설명을 여기서 반복하지 않는다.Since the information reading processing and the information correcting processing of steps S1201 to 1205 are the same as those of steps S601 to S605 to be performed in the storage
보정 유닛(103)이 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 정보를 보정한 후(단계 S1205), 리프레시 제어 유닛(1104)은, 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에 기록된 보정 이력들수가 미리 결정된 임계값보다 큰 지의 여부를 판정한다(단계 S1206).After the
보정 이력들의 수가 미리 결정된 임계값보다 크면(단계 S1206에서 “YES"), 리프레시 제어 유닛(1104)은 정보가 판독되었던 메모리 셀 그룹에 리프레시 동작을 수행하고, 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)에 보정 이력들을 지운다(단계 S1208).If the number of correction histories is larger than the predetermined threshold value (YES in step S1206), the
보정 이력들 수가 미리 결정된 임계값보다 크지 않으면(단계 S1206에서 “NO"), 보정 유닛(103)은 보정 이력 기억 유닛(ELk)에 보정 이력으로서 셀 ID와 보정 내용을 등록한다(단계 S1207).If the number of correction histories is not larger than the predetermined threshold value (“NO” in step S1206), the
단계 S1209와 단계 S1210의 정보 출력 처리는 제1 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치(100)에서 수행될 단계 S607 및 단계 S608과 동일하며, 따라서 그 설명을 반복하지 않는다.The information output processing of steps S1209 and S1210 is the same as that of steps S607 and S608 to be performed in the storage
보정 이력의 수가 도 12에서 에러 생성량으로서 사용되어도, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 새롭게 보정된 기억 소자들의 수, 전하량 임계값들의 미리 결정된 수를 초과하는 기억 소자들의 수, 또는 보정 이력 기억 유닛들(EL1 내지 ELn)의 정보 기억 용량으로 나타낸 에러 생성량에 따라 리프레시 동작이 필요한지에 대한 여부를 또한 판정할 수 있다.Although the number of correction histories is used as the error generation amount in FIG. 12, the number of memory elements newly corrected using the error correction code, the number of memory elements exceeding a predetermined number of charge amount thresholds, or the correction history memory units EL1. It is also possible to determine whether or not the refresh operation is necessary in accordance with the error generation amount indicated by the information storage capacity of ELn).
상술된 바와 같이, 제4 실시예에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 에러 생성량이 미리 결정된 임계값을 초과할 때, 리프레시 동작이 기억 소자들에 수행된다. 이러한 리프레시 동작은 에러 생성을 감소시킬 수 있고, 보정 동작에 요구되는 계산량이 따라서 감소될 수 있다.As described above, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the fourth embodiment, when the amount of error generation exceeds a predetermined threshold, a refresh operation is performed on the storage elements. This refresh operation can reduce error generation, and the amount of calculation required for the correction operation can be reduced accordingly.
제1 내지 제4 실시예의 기억 매체 재생 장치에서 수행될 기억 매채 재생 프로그램은 ROM(Read Only Memory)과 같은 메모리로 미리 통합된다.The storage medium reproduction program to be performed in the storage medium reproducing apparatuses of the first to fourth embodiments is previously incorporated into a memory such as a ROM (Read Only Memory).
제1 내지 제4 실시예의 기억 매채 재생 장치에서 수행될 기억 매체 재생 프로그램은 CD-ROM(Compact Disk Read Only Memory), 플렉서블 디스크(FD), CD-R(Compact Disk Recordable), 또는 DVD(Digital Versatile Disk)와 같은 컴퓨터-판독가능 기록 매채에 기록된 실행가능한 파일 또는 설치가능한 포맷으로 나타내질 수도 있다.The storage medium reproducing program to be executed in the storage medium reproducing apparatuses of the first to fourth embodiments is a compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM), a flexible disk (FD), a compact disk recordable (CD-R), or a digital versatile Or an executable file recorded on a computer-readable recording medium such as a disk.
제1 내지 제4 실시예의 기억 매채 재생 장치에서 수행될 기억 매채 재생 프로그램은 인터넷과 같은 네트워크에 접속된 컴퓨터에 기억될 수도 있고, 네트워크를 통하여 다운로드될 수도 있다. 제1 내지 제4 실시예의 기억 매채 재생 장치에서 수행될 기억 매채 재생 프로그램은 또한 인터넷과 같은 네트워크를 통하여 제공되거나 분배될 수도 있다.The storage medium reproduction program to be performed in the storage medium reproduction apparatuses of the first to fourth embodiments may be stored in a computer connected to a network such as the Internet, or may be downloaded via a network. The storage medium reproduction program to be executed in the storage medium reproduction apparatuses of the first to fourth embodiments may also be provided or distributed through a network such as the Internet.
제1 내지 제4 실시예의 기억 매채 재생 장치에서 수행될 기억 매채 재생 프로그램은 상술된 구성 요소들(제어 유닛, 보정 이력 실행 유닛, 보정 유닛, 및 리프레시 유닛)을 포함하는 모듈 구성을 갖는다. 실제 하드웨어에서, CPU(Central Processing Unit)은 ROM으로부터 기억 매채 재생 프로그램을 판독하고, 기억 매채 재생 프로그램을 실행한다. 따라서, 상술된 구성 요소들은 주 기억 장치에 장착되고 생성된다.The storage medium reproduction program to be executed in the storage medium reproduction apparatuses of the first to fourth embodiments has a module configuration including the above-described components (control unit, correction history execution unit, correction unit, and refresh unit). In real hardware, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) reads the storage medium reproduction program from the ROM and executes the storage medium reproduction program. Thus, the above-described components are mounted on the main memory device and created.
부가적인 이점 및 변형들은 당업자들에게 용이하게 행해질 것이다. 그러므로, 보다 광범위한 태양의 본 발명은 여기서 도시되고 설명된 특정 상세 및 대표적 인 실시예에 한정되지 않는다. 따라서, 첨부된 청구 범위 및 그 등가물에 의하여 정의된 바와 같은 일반적인 발명의 개념의 사상 또는 범위를 벗어나지 않고 다양한 변형이 행해질 수도 있다.Additional advantages and modifications will be readily made to those skilled in the art. Therefore, the invention in its broader aspects is not limited to the specific details and representative embodiments shown and described herein. Accordingly, various modifications may be made without departing from the spirit or scope of the general inventive concept as defined by the appended claims and their equivalents.
본 발명에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에 따르면, 에러 보정 코드를 사용하여 보정된 에러가 방전으로 인하여 유발된 에러로서 간주될 수 있을 때만, 에러 보정의 내용이 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억되어, 에러 보정의 내용이 이후의 보정 동작에 참조될 수 있어, 불필요한 보정 동작이 최소 가능한 회수로 제한될 수 있다.According to the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the present invention, the contents of the error correction are stored in the correction history storage unit only when the error corrected using the error correction code can be regarded as an error caused by the discharge. The contents can be referred to later correction operations, so that unnecessary correction operations can be limited to the minimum possible number of times.
또한, 본 발명에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 복수의 기억 유닛들의 보정 이력들이 단일 보정 이력 기억 유닛에 기억되므로, 보정 이력들을 기억하기 위하여 요구되는 기억 소자들의 수가 감소되어 기억 영역의 사용 효율성이 증가된다.Further, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the present invention, since the correction histories of the plurality of storage units are stored in a single correction history storage unit, the number of storage elements required for storing the correction histories is reduced, thereby increasing the use efficiency of the storage area. do.
또한, 본 발명에 따른 기억 매체 재생 장치에서, 에러 생성량이 미리 결정된 임계값을 초과할 때, 리프레시 동작이 기억 소자들에 수행되어 리프레시 동작은 에러 생성을 감소시킬 수 있고, 보정 동작에 요구되는 계산량이 감소될 수 있다.Further, in the storage medium reproducing apparatus according to the present invention, when the amount of error generation exceeds a predetermined threshold, a refresh operation is performed on the storage elements so that the refresh operation can reduce error generation and the amount of calculation required for the correction operation. This can be reduced.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060027853A KR100697792B1 (en) | 2005-09-20 | 2006-03-28 | Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPJP-P-2005-00272684 | 2005-09-20 | ||
| KR1020060027853A KR100697792B1 (en) | 2005-09-20 | 2006-03-28 | Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100697792B1 true KR100697792B1 (en) | 2007-03-21 |
Family
ID=41563862
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060027853A KR100697792B1 (en) | 2005-09-20 | 2006-03-28 | Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100697792B1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20100093739A (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of reading data in a non-volatile memory device |
| KR101574208B1 (en) | 2009-03-31 | 2015-12-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Nonvolatile memory device memory system including the same and operating method thereof |
| KR20160070014A (en) * | 2014-12-09 | 2016-06-17 | 캐논 가부시끼가이샤 | Radiation imaging system, control method therefor, and storage medium having stored thereon a program for executing the control method |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09128303A (en) * | 1995-10-31 | 1997-05-16 | Toshiba Corp | Memory management device |
| JP2001101087A (en) | 1999-09-29 | 2001-04-13 | Sharp Corp | Memory and memory controlling method |
-
2006
- 2006-03-28 KR KR1020060027853A patent/KR100697792B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09128303A (en) * | 1995-10-31 | 1997-05-16 | Toshiba Corp | Memory management device |
| JP2001101087A (en) | 1999-09-29 | 2001-04-13 | Sharp Corp | Memory and memory controlling method |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20100093739A (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of reading data in a non-volatile memory device |
| US8321765B2 (en) | 2009-02-17 | 2012-11-27 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method of reading data in non-volatile memory device |
| KR101588293B1 (en) | 2009-02-17 | 2016-01-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | method of reading data in a non-volatile memory device |
| KR101574208B1 (en) | 2009-03-31 | 2015-12-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Nonvolatile memory device memory system including the same and operating method thereof |
| KR20160070014A (en) * | 2014-12-09 | 2016-06-17 | 캐논 가부시끼가이샤 | Radiation imaging system, control method therefor, and storage medium having stored thereon a program for executing the control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4413840B2 (en) | Storage medium playback apparatus, storage medium playback method, and storage medium playback program | |
| US8464137B2 (en) | Probabilistic multi-tier error correction in not-and (NAND) flash memory | |
| KR100632952B1 (en) | Method and device capable of judging whether program operation is failed due to power failure | |
| US8255613B2 (en) | Wear-leveling and bad block management of limited lifetime memory devices | |
| US8756464B2 (en) | Flash memory device and flash memory programming method equalizing wear-level | |
| US10333558B2 (en) | Decoding device and decoding method | |
| TWI601148B (en) | Method for selecting bad columns and data storage device with? bad column summary table | |
| JP2004281037A (en) | Method and system for correcting data stored in storage medium and computer readable storage medium | |
| JP5805727B2 (en) | Data encoding and decoding to accommodate memory cells with stuck-at faults | |
| JP6957392B2 (en) | Memory system | |
| US10574272B2 (en) | Memory system | |
| US10210042B2 (en) | Memory system | |
| CN112256193A (en) | Method, device and storage medium for improving data security of solid state disk | |
| JP2010079486A (en) | Semiconductor recording device | |
| JP2019057812A (en) | Memory system | |
| KR100697792B1 (en) | Storage medium reproducing apparatus, storage medium reproducing method, and computer readable medium for reading information from storage medium | |
| US9928136B2 (en) | Message storage in memory blocks using codewords | |
| US11923028B2 (en) | Reference voltage adjustment based on post-decoding and pre-decoding state information | |
| KR20140125987A (en) | Encoder, decoder and semiconductor device including the same | |
| US20160071597A1 (en) | Storage device, memory controller and memory control method | |
| CN112988448A (en) | Error rate balancing method and device and reading method and device | |
| US11907047B2 (en) | Data storage device and error tolerance selecting method thereof | |
| US20240152326A1 (en) | Memory device and operating method thereof | |
| CN112992256B (en) | Error rate balancing method and device | |
| JP2013218525A (en) | Semiconductor memory system, memory controller, and memory control method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20120223 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |