KR100262944B1 - Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI - Google Patents
Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100262944B1 KR100262944B1 KR1019970069705A KR19970069705A KR100262944B1 KR 100262944 B1 KR100262944 B1 KR 100262944B1 KR 1019970069705 A KR1019970069705 A KR 1019970069705A KR 19970069705 A KR19970069705 A KR 19970069705A KR 100262944 B1 KR100262944 B1 KR 100262944B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- virtual
- virtual path
- network
- message
- incoming
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/58—Association of routers
- H04L45/586—Association of routers of virtual routers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/54—Store-and-forward switching systems
- H04L12/56—Packet switching systems
- H04L12/5601—Transfer mode dependent, e.g. ATM
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/02—Topology update or discovery
- H04L45/10—Routing in connection-oriented networks, e.g. X.25 or ATM
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L49/00—Packet switching elements
- H04L49/15—Interconnection of switching modules
- H04L49/1553—Interconnection of ATM switching modules, e.g. ATM switching fabrics
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L49/00—Packet switching elements
- H04L49/25—Routing or path finding in a switch fabric
- H04L49/256—Routing or path finding in ATM switching fabrics
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/54—Store-and-forward switching systems
- H04L12/56—Packet switching systems
- H04L12/5601—Transfer mode dependent, e.g. ATM
- H04L2012/5619—Network Node Interface, e.g. tandem connections, transit switching
- H04L2012/562—Routing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 비동기전달모드(ATM : Asynchronous Transfer Mode) 교환시스템의 망-망 접면에서 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 제공 방법에 관한 것으로서, 특히 광대역 종합정보통신망(B-ISDN : Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network)에서 타국의 발신 교환기 관리자가 발신 교환기와 착신 교환기 사이에 가상 통로(Virtual Tunnel), 즉 망-망 가상경로(Network-network Virtual Path)의 설정을 요구한 경우에 대하여 망-망 접면(NNI : Network-Node Interface)에서 중계선 신호 프로토콜인 광대역 종합정보통신망 사용자부(BISUP : B-ISDN User Part)를 사용하여 발신과 착신 교환기 사이에 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)의 설정을 제공하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method for providing a virtual path using an incoming call control procedure at a network-network interface of an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching system. Particularly, the present invention relates to a broadband integrated services network (B-ISDN). In the case of a digital exchange, the originating exchange manager of another station requests the establishment of a virtual tunnel (ie, a network-network virtual path) between the originating exchange and the destination exchange. Virtual channel (network-network virtual) using incoming call control procedure between originating and terminating exchange using BISIS User Part (BISUP), which is the trunk line signaling protocol in NNI: Network-Node Interface Route).
ATM 계층이 상위 계층에 제공하는 투명성 연결을 비동기전달모드 연결(ATM connection)이라고 하는데, ATM 연결은 연결 소자(connection element)들의 연쇄적인 연결에 의해서 종단(endpoint)간에 이어진다.The transparency connection that the ATM layer provides to the upper layer is called an asynchronous transfer mode connection, which is connected between endpoints by a chain of connection elements.
ATM 연결에는 가상채널(VC : Virtual Channel)과 가상경로(VP : Virtual Path) 두 가지가 있다.There are two types of ATM connections: Virtual Channel (VC) and Virtual Path (VP).
가상채널(VC)은 ATM 셀을 전달하는 링크 종단간의 논리적인 단방향 결합을 의미하고, 가상경로(VP)는 가상채널(VC)들의 논리적인 결합을 의미한다.The virtual channel VC refers to a logical unidirectional coupling between link ends carrying an ATM cell, and the virtual path VP refers to a logical combination of virtual channels VC.
가상채널(VC)에는 각각 하나의 가상채널 식별번호(VCI : Virtual Channel Identifier)가 부여되고, 가상경로(VP)에는 각각 하나의 가상경로 식별번호(VPI : Virtual Path Identifier)가 부여된다.One virtual channel identifier (VCI) is assigned to the virtual channel VC, and one virtual path identifier (VPI) is assigned to the virtual path VP.
가상경로(VP)안에는 서로 다른 가상채널(VC) 링크들이 존재할 수 있는데, 이들은 그 각각에 할당된 가상채널 식별번호(VCI)에 의해서 서로 구별된다.Within the virtual path VP there may be different virtual channel (VC) links, which are distinguished from each other by the virtual channel identification number (VCI) assigned to each of them.
한편, 서로 다른 가상경로(VP)에 속해 있는 가상채널(VC)중에는 가상채널 식별번호(VCI)가 동일한 것들도 있을 수 있다. 그러므로, 하나의 가상채널(VC)은 해당 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)와 가상채널 식별번호(VCI)의 결합에 의해서만 완전히 식별 가능하게 된다.Meanwhile, among the virtual channels VC belonging to different virtual paths VP, virtual channel identification numbers VCI may be the same. Therefore, one virtual channel VC can be fully identified only by combining the corresponding virtual path identification number VPI and the virtual channel identification number VCI.
가상경로(VP)는 가상채널링크(VCL : Virtual Channel Link)의 다발을 지칭하는 일반적인 용어로서, 이때 다발 안에 있는 모든 가상채널링크(VCL)들은 동일한 종단점을 갖는다.Virtual path (VP) is a general term for a bundle of virtual channel links (VCLs), where all virtual channel links (VCLs) in the bundle have the same endpoint.
ATM 셀에는 가상경로(VP)를 위한 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)가 명시적으로 할당되어 있는데, VPI는 동일한 가상경로(VP)를 공유하는 가상채널(VC) 링크 그룹을 식별한다.An ATM cell is explicitly assigned a virtual path identification number (VPI) for a virtual path (VP), which identifies a group of virtual channel (VC) links that share the same virtual path (VP).
ATM 망에서 가상경로(VP)가 교환될 때마다 특정한 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)가 할당된다. 가상경로링크(VPL : Virtual Path Link)는 가상경로 식별번호(VPI) 값이 번역되는 2개의 ATM 개체들 사이에 ATM 셀을 수송하기 위한 단방향성의 능력을 의미하는 것으로, 가상경로링크(VPL)는 가상경로 식별번호(VPI) 값을 할당하는 것에 의해서 발생하고, 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)를 제거하면 종단된다.Each time a virtual path (VP) is exchanged in an ATM network, a specific virtual path identification number (VPI) is assigned. Virtual Path Link (VPL) refers to the unidirectional ability to transport an ATM cell between two ATM entities whose value is translated into a Virtual Path Identification Number (VPI). Is generated by assigning a virtual path identification number (VPI) value and terminates when the virtual path identification number (VPI) is removed.
가상경로(VP) 준위에서는 사용자-사용자간(User-User), 사용자-망간(User-Network), 그리고 망-망간(Network-Network)의 정보 전달을 위해서 가상경로(VP)가 제공된다.In the virtual path (VP) level, a virtual path (VP) is provided to transfer information between user-user, user-network, and network-network.
가상채널(VC)이 교환될 때에는 입력 가상채널링크를 지원하는 가상경로(VP)가 먼저 종단되고, 출력 가상채널링크를 지원하는 가상경로(VP)가 새로이 생성된다. 가상경로(VP)의 응용은 다음과 같다.When the virtual channel VC is exchanged, the virtual path VP supporting the input virtual channel link is terminated first, and a virtual path VP supporting the output virtual channel link is newly created. The application of the virtual path (VP) is as follows.
첫째, 사용자-사용자간 가상경로(VP)는 TB또는 SB기준점들간에 설정되며, 사용자들에게 가상경로(VP)를 제공한다. ATM 망 요소들은 이러한 가상경로(VP)에 관련된 모든 셀들을 동일한 경로(route)를 통해서 수송해 준다. 해당 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)들은 교차 연결 또는 교환 기능을 제공하는 ATM 망 요소에서 번역된다.First, the user-to-user virtual path (VP) is set between the T B or S B reference points and provides the user with the virtual path (VP). ATM network elements transport all cells related to this virtual path (VP) through the same route. Corresponding virtual path identification numbers (VPIs) are translated in ATM network elements that provide cross linking or switching functions.
둘째, 사용자-망 간 가상경로(VP)는 TB또는 SB기준점과 망 노드간에 설정되며, 사용자 장치들을 집단적으로 망 요소에 접속시키는데 사용된다.Second, the user-network virtual path (VP) is established between the T B or S B reference point and the network node, and is used to collectively connect user devices to the network element.
셋째, 망-망 간 가상경로(VP)는 두 개의 망 노드들 간에 설정되는데, 이는 망 트래픽(traffic) 관리나 경로 배정(route assignment) 등에 응용된다. 가상경로(VP)가 종단되는 망 노드에서는 가상경로(VP)내의 가상채널(VC)들이 다른 가상경로(VP)내의 가상채널(VC)들과 교환 또는 교차 연결된다.Third, a network-to-network virtual path (VP) is established between two network nodes, which is applied to network traffic management or route assignment. In the network node where the virtual path VP is terminated, the virtual channels VC in the virtual path VP are exchanged or cross-connected with the virtual channels VC in the other virtual path VP.
중계선 신호 프로토콜(BISUP)은 본래 망-망 접면(NNI)에서 가상채널을 설정 시키기 위한 호 제어 절차를 정의한 것이다. 가상채널(VC)은 발신 사용자가 요구할 때 마다 연결을 설정해야 하므로, 그 때마다 망 자원 할당, 내부 스위치 경로 등과 같은 연결 제어(connection control)를 반복적으로 수행해야 한다.The trunk line signaling protocol (BISUP) originally defined a call control procedure for establishing a virtual channel at the network-to-network interface (NNI). Since the virtual channel (VC) needs to establish a connection whenever the calling user requests, it must repeatedly perform connection control such as network resource allocation and internal switch path.
그러므로, 동일한 경로를 사용하는 가상채널(VC)을 설정해야 하는 경우 동일한 작업을 반복해야 하는 오버헤드(overhead)가 있다. 또한, 요구하는 가상채널(VC)의 서비스품질(QoS : Quality of Service)이 이미 전송 링크(transmission link)안에 설정되어 있는 가상채널(VC)의 QoS와 틀리므로 기존의 가상채널 연결의 서비스품질을 유지하면서 새로운 가상채널(VC)의 QoS를 만족시키기 위해서는 전송 링크에 있는 모든 가상채널(VC)을 고려하여 할당할 수 있는 망 자원을 계산하여야 하므로 망 자원 할당에 필요한 많은 시간과 노력이 요구된다.Therefore, there is an overhead of repeating the same operation when it is necessary to set up a virtual channel (VC) using the same path. In addition, since the quality of service (QoS) of the required virtual channel (VC) is different from the QoS of the virtual channel (VC) already set in the transmission link, the quality of service of the existing virtual channel connection is reduced. In order to satisfy the QoS of the new virtual channel (VC) while maintaining it, it is necessary to calculate network resources that can be allocated in consideration of all virtual channels (VC) in the transport link, which requires a lot of time and effort required for network resource allocation.
이를 해결하기 위하여, 가상경로를 이용하는 경우에 가상경로(VP)는 동일한 경로(route)의 가상채널을 한 다발로 묶어서 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)로만 ATM 셀 교환(switching)을 할 수 있으므로 추가 연결을 요구하는 가상채널(VC)에 대한 연결 제어가 필요하지 않다.In order to solve this problem, in case of using the virtual path, the virtual path (VP) bundles the virtual channels of the same route into a bundle so that only ATM cell switching can be performed with the virtual path identification number (VPI). No connection control is required for the virtual channel (VC) that requires.
또한, 가상경로(VP)에 미리 필요한 망 자원을 예약하므로 가상경로(VP)를 통하여 가상채널(VC)을 설정하는 경우, 가상채널(VC)의 설정을 위해 필요한 망 자원 할당을 빠른 시간내에 수행할 수 있다.In addition, since a network resource necessary for the virtual path VP is reserved in advance, when the virtual channel VC is set through the virtual path VP, network resource allocation required for setting the virtual channel VC is performed within a short time. can do.
현재, 신호 프로토콜을 이용하여 설정할 수 있는 가상경로(VP)의 응용은 사용자-사용자 가상경로에 국한되어 있고, 사용자-망과 망-망 가상경로는 교환기 관리자에 의해서만 설정할 수 있다.Currently, the application of the virtual path (VP) that can be set using the signaling protocol is limited to the user-user virtual path, and the user-network and network-network virtual paths can be set only by the exchange administrator.
종래에는 가상경로(VP)의 설정을 신호 절차없이 교환기 관리자에 의해서 반영구(Semi-permanent) 또는 영구가상경로(PVP : Permanent Virtual Path)의 형태로만 설정할 수 있으므로, 가상경로(VP) 설정을 위하여 가입자 정보, 망 형상(topology)과 구성(configuration)에 대한 많은 정보, 시간 그리고 노력이 필요하였다.Conventionally, since the setting of the virtual path (VP) can be set only in the form of a semi-permanent or permanent virtual path (PVP) by the exchange manager without a signaling procedure, a subscriber for the virtual path (VP) setting is required. Much information, time, and effort were required on information, topology and configuration.
그러므로, 교환기 관리자 또는 사용자가 원할 때 즉시 새로운 가상경로(VP)를 생성할 수 없는 문제점이 있었다.Therefore, there was a problem that a new virtual path (VP) could not be created immediately when the exchange manager or user wanted.
이러한 점을 해결하고자 국제 표준화 기구에서는 가입자 신호 프로토콜(DSS2)과 중계선 신호 프로토콜(BISUP)에 가상경로(VP)를 설정할 수 있는 신호 능력을 추가하였는데, 이는 가상 연결을 요구하는 셋업(SETUP) 메시지의 정보 요소인 광대역 전달 능력(BBC : Broadband Bearer Capability)에 가상경로(VP) 전달 등급(BC : Bearer Class)을 추가하고 연결 식별번호 정보 요소에는 가상채널 식별번호(VCI)를 무시하고 가상경로 식별번호(VPI)에 대해서만 연결 제어를 수행하는 것이다.To address this, the International Organization for Standardization added signaling capabilities for establishing virtual paths (VPs) in subscriber signaling protocols (DSS2) and trunk line signaling protocols (BISUP). Add Virtual Path (VP) bearer class (BC) to Broadband Bearer Capability (BBC) which is an information element, and ignore virtual channel identification number (VCI) in connection identification number information element and virtual path identification number (VPI) only performs connection control.
이 신호 프로토콜은 전달 등급이 가상경로(VP)인 경우만 가상경로 설정 절차를 수행하고, 전달 등급이 가상경로가 아닌 광대역 연결형 전달 서비스 형식-A(BCOB-ABroadband Connection Oriented Bearer-A)와, 광대역 연결형 전달 서비스 형식-C(BCOB-C : Broadband Connection Oriented Bearer-C), 및 광대역 연결형 전달 서비스 형식-X(BCOB-X : Broadband Connection Oriented Bearer-X)인 경우에는 기존의 가상채널 설정 절차를 수행한다.This signaling protocol performs the virtual path setup procedure only if the transmission class is virtual path (VP), and the transmission class is not the virtual path, and is connected with BCOB-ABroadband Connection Oriented Bearer-A and broadband. In case of the connection type forwarding service type-C (BCOB-C) and the connection type forwarding service type-X (BCOB-X: Broadband Connection Oriented Bearer-X), the existing virtual channel setup procedure is performed. do.
그러나, 이 신호 프로토콜을 이용하여 설정할 수 있는 가상경로(VP)의 응용은 사용자-사용자 가상경로에만 국한된다. 사용자-사용자 가상경로 설정 기능을 확장하기 위하여 가상경로 전달 등급을 사용자-사용자 가상경로(기존의 가상경로 전달 등급과 동일함)와, 사용자-망 가상경로, 및 망-망 가상경로의 세가지로 확장하였다.However, the application of virtual paths (VPs) that can be established using this signaling protocol is limited to user-user virtual paths. To extend the user-user virtual path setting function, the virtual path forwarding class is expanded into three types: user-user virtual path (same as the existing virtual path forwarding class), user-network virtual path, and network-network virtual path. It was.
사용자-사용자 가상경로와 망-망 가상경로의 가장 큰 차이점은 다음의 표 1 과 같다.The biggest difference between the user-user virtual path and the network-network virtual path is shown in Table 1 below.
그런데, 두 교환기간(착신과 발신 교환기) 또는 하나 이상의 중계 교환기를 경유하는 두 교환기 사이에 설정하는 반영구 또는 영구가상경로(PVC)를 특별히 가상 통로(virtual tunnel)라 하는데, 이 가상 통로는 상기에 기술한 바와 같이 설정을 하기 위해 많은 정보를 필요로 하고, 할당한 망 자원(대역)이 고정되어 있어 대역의 변경을 원할 때 가상 통로를 해제한 후 재 설정해야 하는 문제점이 있다.By the way, a semi-permanent or permanent virtual path (PVC) that is set up between two exchanges (incoming and outgoing exchanges) or between two exchanges via one or more relay exchanges is specifically called a virtual tunnel. As described above, a lot of information is required for setting, and the allocated network resources (bands) are fixed, so when a band is to be changed, the virtual path must be released and then reset.
따라서, 두 교환기 사이의 가상경로(VP)인 망-망 가상경로를 중계선 신호 프로토콜(BISUP)을 사용하여 설정함으로써, 두 교환기간의 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 제공할 수 있는 방안이 필수적으로 요구된다.Therefore, by establishing a network-network virtual path (VP), which is a virtual path between two exchanges, using a relay line signaling protocol (BISUP), a method for providing a virtual path (network-network virtual path) between two switching periods is provided. It is required.
따라서, 본 발명은 상기한 바와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 안출된 것으로서, 망-망 접속면에서 중계선 신호 프로토콜(BISUP)의 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용하여 두 교환기간의 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 제공함으로써, 망 자원의 효율을 높이기 위한 가상 통로의 제공 방법을 제공하는데 그 목적이 있다.Accordingly, the present invention has been made to solve the problems described above, the virtual path (network-network virtual) of the two exchange periods using the incoming call control procedure of the relay line signaling protocol (BISUP) in the network-network connection surface It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for providing a virtual path for improving the efficiency of network resources.
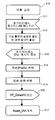
도 1 은 본 발명이 적용되는 망-망간 가상경로와 사용자-사용자간 가상경로의 개념을 비교한 설명도.1 is an explanatory diagram comparing the concept of a network-network virtual path and a user-user virtual path to which the present invention is applied.
도 2 는 본 발명이 적용되는 비동기전달모드(ATM) 교환시스템의 구성을 개략적으로 나타낸 블럭도.Figure 2 is a block diagram schematically showing the configuration of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switching system to which the present invention is applied.
도 3 은 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 비동기전달모드(ATM) 교환시스템의 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 제공을 위한 처리 블록도.3 is a processing block diagram for providing a virtual passage using an incoming call control procedure of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switching system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4 는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 설정을 위한 중계선 신호 프로토콜 메시지 처리 절차를 나타낸 설명도.4 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a relay line signal protocol message processing procedure for setting up a virtual path using an incoming call control procedure according to an embodiment of the present invention;
도 5a 내지 도 5f 는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 제공 방법에 대한 흐름도.5A to 5F are flowcharts illustrating a method for providing a virtual passage using an incoming call control procedure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
* 도면의 주요 부분에 대한 부호의 설명* Explanation of symbols for the main parts of the drawings
300 내지 302 : 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록300 to 302: switch link resource management processing block
310 내지 312 : 국번 번역 블록310 to 312: station number translation block
320 내지 322 : 망 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록320 to 322: network link resource management processing block
330 내지 332 : 광대역 신호 접속 처리 블록330 to 332: broadband signal connection processing block
340, 341 : 가입자 서비스 지정 조정 처리 블록340, 341: subscriber service designated coordination processing block
350, 351 : 가입자 연결 접속 블록350, 351: subscriber connection block
360, 361 : 가입자 연결 제어 블록360, 361: subscriber connection control block
370 : 중계선 서비스 지정 조정 처리 블록370: trunk line service specified adjustment processing block
380 : MTP 신호 메시지 처리 블록380: MTP signaling message processing block
381 : 중계선 연결 접속 블록 382 : 중계선 연결 제어 블록381 relay connection connection block 382 relay connection control block
390 : 번호 번역 블록 391 : 경로 지정 제어 블록390: number translation block 391: routing control block
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명은, 비동기전달모드(ATM) 교환시스템에서 발착신 교환기 사이에서 입중계 제어 절차를 이용하여 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 발신 교환기나 중계 교환기로부터 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 초기 어드레스 메시지(IAM)를 수신한 중계선 제어 블록의 주 프로세서(TCCF_main)가 입중계 중계선 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세서(TCCF_vpict)를 생성하고, 가상 통로의 설정을 위한 메시지(IAM_mc)를 상기 입중계 중계선 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세서(TCCF_vpict)에게 전달하는 제 1 단계; 상기 메시지(IAM_mc)를 수신한 상기 입중계 중계선 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세서(TCCF_vpict)가 망 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록(NLRHF)의 시스템 라이브러리를 호출하여 입중계 대역 및 가상채널 식별번호의 할당을 요구하고, 요구 결과에 따라 대국의 중계 교환기나 발신 교환기로 입중계 망자원이 유효함을 알리는 메시지(IAA)를 송신한 후, 착신 교환기 번호의 국번 번역을 수행하며, 착신 교환기 번호의 번역 결과를 통보받고, 상기 착신 교환기의 관리자에게 가상 통로의 설정 요구를 통보하는 메시지(VP_EstabSig)를 전달한 후에 초기 어드레스 응답 메시지 대기 상태(Await_IAA)로 천이하는 제 2 단계; 상기 착신 교환기의 관리자로부터 가상 통로의 설정 승인을 알리는 메시지(VP_EstabACK)가 수신된 경우에, 상기 입중계 중계선 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세서(TCCF_vpict)가 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록(SLRHF)으로부터 내부 스위치 링크 경로 정보를 추출하며, 중계선 접속 모듈 제어기(TIMC)로 점대점 연결 설정 요구 메시지(PtP_ConnEstabRQ)를 전달하여 가상경로 식별번호(VPI), 가상채널 식별번호(VCI), 망제어 파라미터 정보, 그리고 내부 스위치 링크 경로 정보를 등록하고, 대국으로 가상 통로 설정 완료 응답 메시지(ANM)를 송신한 후 통화중 상태로 천이하는 제 3 단계; 및 발착신 교환기 관리자의 가상 통로 해제 요구에 따라, 통화중 상태인 가상 통로 연결을 해제하는 제 4 단계를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 한다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a method for providing a virtual path (network-network virtual path) using an incoming call control procedure between an originating and receiving exchange in an asynchronous delivery mode (ATM) switching system. The main processor TCCF_main of the trunk line control block that receives the initial address message IAM requesting the establishment of the virtual path from the relay exchange creates the incoming trunk line virtual path connection control child processor TCCF_vpict and sets the virtual path. Transmitting a message IAM_mc to the incoming trunk trunk virtual path connection control child processor TCCF_vpict; The incoming relay trunk virtual path connection control child processor TCCF_vpict receiving the message IAM_mc calls the system library of the network link resource management processing block NLRHF to request the allocation of the incoming band and the virtual channel identification number. In response to the request result, a message (IAA) indicating that the incoming network resource is valid is transmitted to the relay or originating exchange of a large country, and then the station number of the destination exchange number is translated, and the translation result of the destination exchange number is notified. And a second step of transitioning to an initial address response message waiting state (Await_IAA) after delivering a message (VP_EstabSig) for notifying a request for setting a virtual path to an administrator of the destination exchange; When a message VP_EstabACK is received from the administrator of the destination exchange to inform the establishment of the virtual path, the incoming trunk virtual path connection control child processor TCCF_vpict receives an internal switch link from the switch link resource management processing block SLRHF. It extracts the route information and transmits the point-to-point connection establishment request message (PtP_ConnEstabRQ) to the trunk line connection module controller (TIMC) to send the virtual path identification number (VPI), virtual channel identification number (VCI), network control parameter information, and internal switch. Registering link path information, transmitting a virtual path establishment complete response message (ANM) to a power station, and then transitioning to a busy state; And a fourth step of releasing the virtual passage connection in the busy state according to the call release request of the originating exchange exchange manager.
본 발명은 ATM 교환시스템에 있어서 타국의 B-ISDN 발신 교환기 관리자가 망-망 접면(NNI)에서 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 경우, BISUP의 사용자-사용자 가상경로 설정 기능을 확장하여 망-망 접면에서 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 망-망 가상경로(가상 통로)를 제공함으로써, 설정한 가상 통로를 통하여 발신과 착신 교환기 사이에서 추가의 연결 제어 절차를 수행하지 않고 ATM 가상채널 연결 서비스를 제공할 수 있어 호 설정 처리 시간을 줄일 수 있고, 중계선 신호 프로토콜을 이용하여 이 가상 통로의 설정 및 해제를 용이하게 할 수 있으며, 가상 통로의 대역 이용률에 따라 그 대역을 변경 및 삭제할 수 있으므로 망 자원의 효율을 높일 수 있다.According to the present invention, when the B-ISDN originating exchange manager of another station in the ATM switching system requires the establishment of the virtual path at the network-network interface (NNI), the user-user virtual path setting function of BISUP is extended to the network-network interface. By providing the network-network virtual path (virtual path) using the incoming call control procedure, the ATM virtual channel connection service can be provided without performing additional connection control procedure between the originating and destination exchange through the established virtual path. It is possible to reduce the call setup processing time, to facilitate the setup and release of this virtual path using the relay line signal protocol, and to change and delete the band according to the bandwidth utilization of the virtual path, thus the efficiency of network resources. Can increase.
상술한 목적, 특징들 및 장점은 첨부된 도면과 관련한 다음의 상세한 설명을 통하여 보다 분명해 질 것이다. 이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명에 따른 바람직한 일실시예를 상세히 설명한다.The above objects, features and advantages will become more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1 은 본 발명이 적용되는 망-망간 가상경로와 사용자-사용자간 가상경로의 개념을 비교한 설명도이다.1 is an explanatory diagram comparing the concept of a network-network virtual path and a user-user virtual path to which the present invention is applied.
도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 사용자-사용자간 가상경로는 광대역 종합정보통신망 단말과 광대역 종합정보통신망 단말간의 가상경로(VP)를 말하며, 망-망간 가상경로는 발신 교환기와 중계 교환기간이나, 중계 교환기와 착신 교환기간, 또는 발신 교환기와 착신 교환기간을 말한다.As shown in FIG. 1, the user-user virtual path refers to a virtual path (VP) between the broadband general information network terminal and the broadband comprehensive information network terminal, and the network-network virtual path is a relay exchange period or relay period. Period of exchange and incoming exchange, or outgoing exchange and incoming exchange.
가상경로(VP)는 광대역 종합정보통신망의 가입자가 가상채널(VC)의 설정을 요구할 때 교환기 관리자가 중계선 신호 프로토콜을 사용하여 광대역 종합정보통신망의 가입자를 위한 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 미리 설정함으로써 발신 가입자와 착신 가입자 사이에 가상채널(VP) 설정을 용이하게 설정하도록 하는데 그 목적이 있다.A virtual path (VP) is a network manager that establishes a virtual path (network-network virtual path) for a subscriber of a broadband integrated telecommunication network using a relay line signaling protocol when a subscriber of the broadband integrated telecommunication network requests setting up a virtual channel (VC). It is an object of the present invention to easily set a virtual channel (VP) setting between the calling subscriber and the called subscriber by setting in advance.
가상경로(VP)는 사용자-사용자, 사용자-망, 그리고 망-망 사이에서 설정할 수 있는데, 본 발명은 특히 망-망 접면(NNI)에서 중계선 신호 프로토콜을 사용하여 입중계되는 망-망 가상경로를 발신 교환기와 착신 교환기 사이에서 제공함으로써, 신호 프로토콜을 사용하지 않고 순수하게 교환기 관리자에 의해서만 설정되는 영구적 가상 통로를 대체하고자 하는 것이다.The virtual path (VP) can be set up between user-user, user-network, and network-network. The present invention provides network-network virtual paths which are relayed using relay line signaling protocol, especially at network-network interface (NNI). By providing a between the originating exchange and the destination exchange, it is intended to replace a permanent virtual path that is purely set up by the exchange manager without using signaling protocols.
발신과 착신 교환기 사이에 미리 설정한 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 사용하면 이 가상 통로를 사용하는 가상채널들에 대해서 추가의 연결 제어가 필요 없게 된다.The use of a preset virtual path (network-network virtual path) between the originating and destination exchanges eliminates the need for additional connection control for the virtual channels using this virtual path.
도 2 는 본 발명이 적용되는 비동기전달모드(ATM) 교환시스템의 구성을 개략적으로 나타낸 블럭도이다.Figure 2 is a block diagram schematically showing the configuration of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switching system to which the present invention is applied.
도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, ATM 교환시스템은 기본적으로 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템(ALS : ATM Local Switching Subsystem)(210,220,230)과 ATM 중앙 교환 부 시스템(ACS : ATM Central Switching Subsystem)(200)으로 구성된다.As shown in FIG. 2, an ATM switching system basically includes an ATM Local Switching Subsystem (ALS) 210, 220, and 230 and an ATM Central Switching Subsystem (ACS) 200. .
상기 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템(210,220,230)은 상기 ATM 중앙 교환 부 시스템(200)과 함께 일정한 집선비를 갖는 집선 장치로서 동작한다. 따라서, 상기 ATM 중앙 교환 부 시스템(200)은 상기 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템(210,220,230)간의 상호 연결 기능을 수행하는 분배 장치로서 동작한다. 또한, 상기 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템(210,220,230)은 광대역 종합정보통신망 사용자 정합을 위한 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템/광대역 종합정보통신망 가입자(ALS/S : ALS/BISDN Subscriber)(220)와, 망 정합을 위한 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템/광대역 종합정보통신망 중계선(ALS/T : ALS/BISDN Trunk)(210), 및 사용자와 망 정합을 함께 수용하는 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템/ 광대역 종합정보통신망 가입자와 중계선(ALS/ST : ALS/BISDN Subscriber and Trunk)(230)으로 구성된다.The ATM
집선 장치로서 상기 ATM 국부 교환 부 시스템/광대역 종합정보통신망 가입자(ALS/S)(220)는 사용자측 링크 수를 n(155Mbps 기준)으로 하고, 스위치(상기 ATM 중앙 교환 부 시스템(200)) 측 링크 수를 m으로 하는 n*m의 집선비를 가질 수 있다.As a concentrator, the ATM local switching sub-system / broadband integrated information network subscriber (ALS / S) 220 sets the number of user-side links to n (155 Mbps), and switches (side the ATM central switching sub-system 200) side links. It can have a collection ratio of n * m in which the number m.
따라서, 상기 ATM 중앙 교환 부 시스템(200)은 호/연결 제어시 자국 및 입중계 호/연결일 경우에 착신 번호 번역을 수행하며, 출중계 호/연결일 경우에 각 중계선에 대한 경로(route) 제어를 수행한다.Accordingly, the ATM central
또한, 상기 ATM 중앙 교환 시스템(200)은 시스템 전체의 운용과 유지 보수를 위한 운용 보전 프로세서(OMP : Operation and Maintenance Processor)(201)를 두어 시스템 차원의 유지 보수, 시험, 측정 및 통계 기능 뿐만아니라 운용자와의 각종 입출력 제어 기능을 수행한다.In addition, the ATM
도 3 은 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 비동기전달모드(ATM) 교환시스템의 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 제공을 위한 처리 블록도이다.3 is a processing block diagram for providing a virtual path using an incoming call control procedure of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switching system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 시스템 라이브러리(System Library) 블록으로는 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록(SLRHF : Switch Link Resource Handling Function)(300,301,302)과, 국번 번역 블록(NTLF : Number Translation in ALS Function)(310,311,312), 및 망 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록(NLRHF : Network Link Resource Handling Function)(320,321,322)이 있다.As shown in FIG. 3, a system library block includes a switch link resource handling function (SLRHF) 300, 301, 302 and a number translation in ALS function (NTLF). 310, 311, 312, and a Network Link Resource Handling Function (NLRHF) (320, 321, 322).
상기 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블럭(300,301,302)은 내부 스위치 링크 경로 설정과 ATM 셀 헤더(Cell Header; VPI, VCI)의 경로(route) 정보를 생성하기 위한 블록이고, 상기 국번 번역 블록(310,311,312)은 착신 번호의 국번 번역을 수행하기 위한 블록이고, 상기 망 링크 자원 관리 처리 블럭(320,321,322)은 망-망 접면에서 중계선 링크의 VPI, VCI, 대역 할당, 및 대역 관리를 처리하기 위한 블록이다.The switch link resource management processing block (300,301,302) is a block for generating internal switch link path setting and route information of ATM cell header (VPI, VCI), and the station number translation block (310,311,312) is called A block for performing a station number translation of a number, and the network link resource management processing blocks 320, 321, and 322 are blocks for processing VPI, VCI, band allocation, and band management of a relay line link at a network-network interface.
또한, 광대역 신호 접속 처리 블록(BSIF : Broadband Signalling Interface Function)(330,331,332)은 ATM 호/연결 제어 메시지들의 신뢰성있는 전송을 위한 신호 연결(Signalling Connection)을 제어 및 관리하는 기능을 한다.In addition, the Broadband Signaling Interface Function (BSIF) 330, 331 and 332 functions to control and manage a signaling connection for reliable transmission of ATM call / connection control messages.
그리고, 가입자 서비스 지정 조정 처리 블록(SSCF : Subscriber Service Specific Coordination Function)(340,341)은 가입자 신호 메시지를 전달하기 위하여 상기 광대역 신호 접속 처리 블록(BSIF)(330,331,332)과 사용자 연결 접속 블록(UCIF : User Connection Interface Function)(350,351) 사이에서 조정 기능을 수행한다.A subscriber service specific coordination function (SSCF) 340, 341 may be configured to transmit a subscriber signal message with a BSIF (330, 331, 332) and a user connection access block (UCIF: User Connection). Interface Function (350, 351) performs an adjustment function.
또한, 상기 가입자 연결 접속 블록(UCIF)(350,351)은 가입자 신호 메시지의 접속 기능을 수행한다.In addition, the subscriber connection access blocks (UCIFs) 350 and 351 perform access functions of subscriber signal messages.
또한, 가입자 연결 제어 블록(UCCF : User Connection Control Function)(360,361)은 가입자 호/연결 제어를 수행한다.In addition, a user connection control function (UCCF) 360,361 performs subscriber call / connection control.
또한, 중계선 서비스 지정 조정 처리 블록(TSCF : Trunk Service Specific Coordination Function)(370)은 중계선 신호 메시지를 전달하기 위하여 상기 광대역 신호 접속 처리 블록(BSCF)(330,331,332)와 MTP 신호 메시지 처리 블록(SMHF : MTP-3 Signalling Message Handling Function)(380) 사이에서 조정 기능을 수행한다.Also, trunk service specific coordination function (TSCF) 370 is used to transmit the trunk line signal message to
또한, 상기 MTP 신호 메시지 처리 블록(SMHF)(380)은 No.7 신호 방식 중에서 MTP-3 기능을 수행한다.In addition, the MTP signal message processing block (SMHF) 380 performs an MTP-3 function among No. 7 signaling methods.
또한, 중계선 연결 접속 블록(TCIF : Trunk Connection Interface Function)(381)은 상기 MTP 신호 메시지 처리 블록(SMHF)(380)과 중계선 연결 제어 블록(TCCF : Trunk Connection Control Function)(382) 사이에서 MTP 신호 메시지 전달 기능을 수행한다.In addition, a trunk line connection connection block (TCIF) 381 is an MTP signal between the MTP signal message processing block (SMHF) 380 and a trunk line connection control block (TCCF) 382. Perform message passing.
또한, 상기 중계선 연결 제어 블록(TCCF)(382)은 광대역 종합정보통신망 사용자부(BISUP) 호/연결 제어를 수행한다.In addition, the trunk line connection control block (TCCF) 382 performs the BISUP call / connection control.
그리고, 착신 번호 번역을 위한 번호 번역 블록(NTCF : Number Translation in ACS)(390)과 경로 지정 제어를 수행하는 경로 지정 제어 블록(RTCF : Routing Control Function)(391) 블록이 있다.There are a number translation block (NTCF) for receiving called number translation (NTCF) 390 and a routing control block (RTCF) 391 that performs routing control.
도 4 는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 설정을 위한 중계선 신호 프로토콜 메시지 처리 절차를 나타낸 설명도이다.4 is an explanatory diagram showing a relay line signal protocol message processing procedure for setting a virtual path using an incoming call control procedure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4에 도시된 바와 같이, 가상 통로의 설정은 발신 교환기 관리자가 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 VP_EstabRQ 메시지를 송신함으로써 시작된다. VP_EstabRQ 메시지를 수신한 중계선 연결 제어 블록(TCCF)은 망-망 가상경로 설정을 수행하는 출중계 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세스(TCCF_vpogt : Outgoing Trunk Virtual Path Connection Control Process)를 생성시키고, 망-망 가상경로 설정에 필요한 정보를 초기 어드레스 메시지(IAM : Initial Address Message)에 실어 TCCF_vpogt로 전달한다.As shown in Fig. 4, the establishment of the virtual passage begins by the originating exchange manager sending a VP_EstabRQ message requesting the establishment of the virtual passage. The trunk line connection control block (TCCF) that receives the VP_EstabRQ message creates an outgoing trunk virtual path connection control process (TCCF_vpogt) that performs network-network virtual path establishment, and creates a network-network virtual path. Information necessary for setting is transferred to an initial address message (IAM) and transferred to TCCF_vpogt.
TCCF_vpogt는 IAM_mc 메시지의 착신 번호 정보를 분석하여 중계 또는 착신 교환기로 망-망 가상경로의 설정을 요구하는 초기 어드레스 메시지를 전송한다.TCCF_vpogt analyzes the destination number information of the IAM_mc message and transmits an initial address message requesting the establishment of the network-network virtual path to the relay or destination exchange.
상기의 TCCF_vpogt로부터 IAM 메시지를 수신한 자국의 착신 교환기에 있는 TCCF는 TCCF_vpict를 생성시키고, TCCF_vpict로 IAM_mc 메시지를 전달한다.The TCCF in the terminating exchange of the own country that receives the IAM message from the TCCF_vpogt generates the TCCF_vpict and forwards the IAM_mc message to the TCCF_vpict.
IAM_mc 메시지를 수신한 입중계 가상경로 연결 제어 자식 프로세스(TCCF_vpict : Incoming Trunk Virtual Path Connection Control Process)는 입중계 링크에 대한 망 자원과 가상경로 번호를 할당받고, 그 결과가 유효하면 중계 또는 착신 교환기로부터의 가상 통로의 설정 요구에 대하여 입중계 망 자원이 유효함을 알리는 초기 어드레스 응답 메시지(IAA : IAM Acknowledge)를 전달한다. 그리고, 착신 교환기의 관리자에게 가상 통로의 설정을 통보한다.Incoming Trunk Virtual Path Connection Control Process (TCCF_vpict) that receives IAM_mc message is assigned a network resource and virtual path number for incoming link, and if the result is valid, it receives from the relay or destination exchange. An initial address response message (IAA: IAM Acknowledge) indicating that the incoming network resource is valid is transmitted to the request for setting up the virtual path. The manager of the destination exchange is notified of the setting of the virtual passage.
중계 교환기의 관리자로부터 가상 통로의 설정 요구에 대한 응답을 수신한 TCCF_vpict는 착신 번호 정보를 분석하여 착신 교환기 번호의 국번과 번호를 번역하고 내부 스위치 링크 경로 정보를 할당받는다.Receiving a response to the request for establishing the virtual path from the manager of the relay exchange, the TCCF_vpict analyzes the called number information, translates the station number and the number of the called exchange number, and is assigned internal switch link path information.
상기 절차가 성공적으로 끝나면, TCCF_vpict는 사용자 셀의 전달을 위한 셀 헤더(cell header) 정보를 중계선 접속 모듈 제어기(TIMC : Trunk Interface Module Controller)로 전달하여 셀 헤더 변환 테이블에 할당하고 대국 교환기로 응답 메시지(Answer Message, ANM)를 송신하면, 이때 발신과 착신 교환기 사이에 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)의 설정이 완료되고, 가상 통로의 상태는 통화중(conversation)으로 천이한다Upon successful completion of the above procedure, TCCF_vpict transfers cell header information for transmission of the user cell to the trunk interface module controller (TIMC) and assigns it to the cell header translation table and sends a response message to the counter exchange. When (Answer Message, ANM) is sent, the establishment of the virtual path (network-network virtual path) between the originating and destination exchange is completed, and the state of the virtual path transitions to conversation.
가상 통로의 해제는 발신 또는 착신 교환기 관리자의 요구에 의하여 VP_RelRQ 메시지를 TCCF_vpogt 또는 TCCF_vpict로 전달하여 시작된다. 가상 통로의 해제는 TCCF_vpogt 또는 TCCF_vpict가 통화중 상태인 가상 통로의 대역, VPCI 그리고 내부 스위치 링크 경로 정보의 반환과 셀 헤더 변환 테이블의 삭제 등을 수행하고 종료한다.The release of the virtual path is initiated by delivering a VP_RelRQ message to TCCF_vpogt or TCCF_vpict at the request of the originating or terminating exchange manager. The release of the virtual path is terminated by performing the return of the band, VPCI and internal switch link path information of the virtual path in which TCCF_vpogt or TCCF_vpict is in a call, and deletion of the cell header translation table.
도 5a 내지 도 5f 는 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 제공 방법에 대한 흐름도이다.5A to 5F are flowcharts illustrating a method for providing a virtual path using an incoming call control procedure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 5a에 도시된 바와 같이, 망-망 접면(NNI)에서 입중계 비동기전달모드 국부 교환 부 시스템에 위치하는 중계선 제어 블럭의 주 프로세스(main process)인 TCCF_main이 발신 또는 중계 교환기의 출중계 TCCF_vpogt가 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하기 위하여 전달하는 초기 어드레스 메시지에 대하여 TCCF_vpict를 생성하고 IAM_mc 메시지를 전달하는 절차는, 상기 TCCF_main 상태가 유휴 상태에서(500) 발신 교환기 관리자로부터의 가상 통로 설정 요구에 대하여 중계 또는 발신 교환기의 TCCF_vpogt가 전달하는 입중계 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 초기 어드레스 메시지르르 수신하면(501), 전달 등급이 가상 등급인지를 판단하여(502), 전달 등급이 가상 등급이면 입중계 가상경로 제어 자식 프로세스인 TCCF_vpict를 생성하고(503), 전달 등급이 가상 등급이 아니면 입중계 가상채널 연결 제어 자식 프로세스인 TCCF_vpict를 생성한다(506).As shown in Fig. 5A, TCCF_main, which is the main process of the trunk line control block located in the incoming asynchronous transfer mode local switching system at the network-network interface (NNI), is the originating or outgoing TCCF_vpogt of the relay exchange. The procedure of generating a TCCF_vpict for the initial address message delivered to request the establishment of the virtual path and delivering the IAM_mc message may be performed by relaying or requesting the virtual path establishment request from the originating exchange manager when the TCCF_main state is idle (500). If an initial address message requesting the establishment of an incoming virtual path forwarded by TCCF_vpogt of the originating exchange is received (501), it is determined whether the forwarding class is a virtual level (502), and the incoming virtual path control if the forwarding level is a virtual level. Create a child process TCCF_vpict (503), and if the delivery class is not virtual, connect the incoming virtual channel. A TCCF_vpict, which is a control child process, is created (506).
상기 TCCF_vpict를 생성한 후에는 IAM_mc 메시지를 TCCF_vpict로 전달한다(504).After generating the TCCF_vpict, the IAM_mc message is transferred to the TCCF_vpict (504).
그리고, 휴지 상태를 유지한다(505).The idle state is maintained (505).
도 5b 내지 도 5f에 도시된 바와 같이, TCCF_vpict가 망-망 접면에서 입중계 호 제어 절차를 이용한 가상 통로의 설정과 해제 절차는, 유휴 상태에서(510) TCCF_vpict는 TCCF_main으로부터 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 초기 어드레스 메시지(Main-to-Child IAM, IAM_mc) 메시지를 수신하면(511), 중계선 자원 처리 블록으로부터 가상 통로의 설정에 필요한 대역 및 가상경로 번호를 할당받고(512), 중계 또는 착신 교환기로 요구한 가상 통로 설정 요구에 대하여 입중계 가상 통로의 망 자원이 유효하다는 초기 메시지 응답 메지지를 통보한 후에(513), 국번 번역 블록을 호출하여 국번을 번역하고(514), 번호 번역 블록을 호출하여 번호를 번역하며(516), 착신 교환기의 관리자에게 가상 통로의 설정을 요구하는 메시지 VP_Estabrq를 송신하고(516), 초기 메시지 응답 메시지 대기 상태(Await_IAA)로 천이한다(517).As shown in FIGS. 5B-5F, the procedure for establishing and releasing the virtual passage using the incoming call control procedure at the network-network interface, TCCF_vpict requires setting up the virtual passage from TCCF_main in idle state (510). When receiving an initial address message (Main-to-Child IAM, IAM_mc) message (511), a band and a virtual path number required for the establishment of the virtual path from the relay line resource processing block is allocated (512), the relay or destination exchange After notifying an initial message response message indicating that the network resource of the incoming virtual path is valid for the requested virtual path setting request (513), the station number translation block is called to translate the station number (514), and the number translation block is called. Translates the number (516), sends a message VP_Estabrq requesting the establishment of the virtual path to the manager of the destination exchange (516), and the initial message response message waiting state (Await_). IAA) (517).
TCCF_vpict는 Await_IAA 상태에서(520) 착신 교환기의 관리자로부터 가상 통로의 설정 요구에 대한 응답으로 VP_EstabRP 메시지를 수신하면(521), 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록을 호출하여 내부 스위치 링크 경로 설정하고(522), 중계선 접속 모듈 제어기로 연결 식별자 및 망 파라미터 제어용 정보 메시지를 전달하고(523), 요구한 가상 통로의 설정이 완료되었음을 알리는 응답 메시지(Answer, ANM)를 중계 또는 발신 교환기로 전달한 후에(524), 통화 중 상태(conversation)로 천이한다(525).When TCCF_vpict receives a VP_EstabRP message in response to a request for setting up a virtual path from the destination exchange manager in the Await_IAA state (520) (521), it calls the switch link resource management processing block to set the internal switch link path (522), After transmitting the connection identifier and the information message for network parameter control to the relay line connection module controller (523), and after transmitting a response message (Answer, ANM) indicating that the setting of the requested virtual path is completed (524), the call Transition to conversation (525).
이때부터 설정된 가상 통로를 통과하는 가상채널의 설정 요구에 대하여 호 제어 절차를 수행할 수 있다.At this point, a call control procedure may be performed for a request for setting a virtual channel passing through the set virtual passage.
가상 통로의 해제 절차는 발신 또는 착신 교환기의 관리자 요구에 의하여 수행될 수 있는데, TCCF_vpogt는 통화 중 상태(530)에서 VP_RelRQ 메시지를 수신하면(531), TCCF_vpogt는 가상 통로를 해제하기 전에 가상 통로 내에 가상채널이 존재하는지 검사하고(532), 그 결과 가상채널 존재하는 경우 가상채널을 먼저 해제한 후에 가상 통로의 해제 절차를 시작한다(538).The procedure for releasing the virtual passage may be performed by an administrator request of the originating or terminating exchange. If TCCF_vpogt receives a VP_RelRQ message in a busy state 530 (531), TCCF_vpogt may be in the virtual passage before releasing the virtual passage. In
TCCF_vpict는 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블록의 시스템 라이브러리를 호출하여 가상 통로에 해당하는 내부 스위치 경로를 해제하고(533), 중계선 접속 모듈 제어기로 연결 식별자 해제를 요구한다(534).TCCF_vpict calls the system library of the switch link resource management processing block to release the internal switch path corresponding to the virtual path (533), and requests the connection identifier release to the trunk line connection module controller (534).
또한 중계선 링크 자원 관리 처리 블럭을 호출하여 입중계 링크에 할당된 대역 및 가상경로 번호를 해제한다(535). 그리고 중계 또는 발신 교환기로 가상 통로의 해제를 요구하기 위하여 가상 통로 해제 요구 메시지(REL)를 전달하고(536) 가상 통로 해제 완료(Release Complete, RLC) 대기 상태(Await_RLC)로 천이한다(537).The relay line link resource management processing block is called to release the band and virtual path number allocated to the incoming link (535). In order to request the release of the virtual path to the relay or originating exchange, the virtual path release request message REL is transmitted (536), and the virtual path release complete (Release Complete, RLC) transitions to the wait state (Await_RLC) (537).
TCCF_vpict는 중계 또는 발신 교환기로부터 가상 통로의 해제가 완료되었음을 통보하는 가상 통로 해제 완료 메시지를 수신하면(538), 착신 교환기 관리자에게 VP_RelRP를 전달하고(539), 종료한다.When TCCF_vpict receives a virtual path release completion message from the relay or originating exchange notifying that the release of the virtual path is completed (538), the TCCF_vpict sends a VP_RelRP to the destination exchange manager (539) and terminates.
발신 교환기 관리자의 요구에 의하여 가상 통로의 해제 절차를 수행하는 경우는, TCCF_vpict는 중계 또는 발신 교환기로부터 가상경로 해제 완료 메시지를 수신하면(540), 가상 통로를 해제하기 전에 가상 통로 내에 가상채널이 존재하는지 검사하고(541), 그 결과로서 가상채널이 존재하는 경우 가상채널을 먼저 해제한 후 가상 통로의 해제 절차를 시작한다(542).When the virtual channel release procedure is performed at the request of the originating exchange manager, when TCCF_vpict receives the virtual path release completion message from the relay or originating exchange (540), the virtual channel exists in the virtual passage before releasing the virtual passage. If the virtual channel exists as a result (541), the virtual channel is released first, and then a release procedure of the virtual channel is started (542).
TCCF_vpict는 스위치 링크 자원 관리 처리 블럭의 시스템 라이브러리를 호출하여 가상 통로에 해당하는 내부 스위치 링크 경로를 해제하고(543), 중계선 접속 모듈 제어기로 연결 식별자의 삭제를 요구하며(544), 경로 지정 제어 블록으로 메시지를 전달하여 착신 교환기로의 경로 및 대역을 해제한다(545).TCCF_vpict calls the system library of the switch link resource management processing block to release the internal switch link path corresponding to the virtual path (543), requests the relay line connection module controller to delete the connection identifier (544), and the routing control block. The message is forwarded to release the path and band to the destination exchange (545).
그리고, 중계선 링크 자원 관리 처리 블럭을 호출하여 입중계 링크에 할당된 대역 및 가상경로 번호를 해제한 후(546), 착신 교환기 관리자에게 VP_Relrp를 전달하고(547), 중계 또는 발신 교환기로 가상 통로의 해제가 완료되었음을 통보하는 가상 통로 해제 완료 메시지를 전달한 후에(548), TCCF_vpict는 종료한다.Then, the relay line resource management processing block is called to release the band and virtual path number assigned to the incoming link (546), and then the VP_Relrp is transmitted to the destination exchange manager (547), and the virtual path is forwarded to the relay or originating exchange. After passing the virtual path
이상에서 설명한 본 발명은, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 있어 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경이 가능하므로 전술한 실시예 및 첨부된 도면에 한정되는 것이 아니다.The present invention described above is capable of various substitutions, modifications, and changes without departing from the spirit of the present invention for those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains, and the above-described embodiments and accompanying It is not limited to the drawing.
상기와 같은 본 발명은, 중계선 신호 프로토콜을 사용하여 광대역 종합정보통신망 가입자를 위한 가상 통로(망-망 가상경로)를 미리 설정함으로써 발신 가입자와 착신 가입자 사이에 가상 채널 설정을 용이하게 할 수 있고, 발신과 착신 교환기 사이에 미리 설정한 가상 통로를 사용하면 이 가상 통로를 사용하는 가상 채널들에 대해서 추가의 연결 제어가 필요없게 되며, 기존의 영구 연결 형태의 가상 통로에 비하여 연결 및 해제가 단순하고 착신 교환기의 착신 번호만 알면 되므로 상대적으로 적은 정보를 사용하여 동일한 효과를 얻을 수 있다.The present invention as described above, by using the relay line signal protocol to set the virtual path (network-network virtual path) for the broadband integrated information network network subscriber in advance, it is easy to establish a virtual channel between the calling party and the called party, The use of a pre-configured virtual path between the originating and destination exchanges eliminates the need for additional connection control for virtual channels using this virtual path, and is simpler to connect and disconnect than the existing virtual connection type of permanent path. Since the destination number of the destination exchange only needs to be known, the same effect can be obtained by using relatively little information.
더욱이, 중계선 신호 프로토콜(BISUP)의 대역 변경 기능을 이용하여 가상 통로의 대역을 쉽게 변경할 수 있으므로 기존의 방식인 가상 통로 해제 후 재 설정 방법에 비하여 그 절차를 매우 단순화시키는 효과가 있다.In addition, since the band of the virtual path can be easily changed using the band change function of the relay line signal protocol (BISUP), the procedure is greatly simplified compared to the conventional method of releasing and resetting the virtual path.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1019970069705A KR100262944B1 (en) | 1997-12-17 | 1997-12-17 | Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1019970069705A KR100262944B1 (en) | 1997-12-17 | 1997-12-17 | Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR19990050573A KR19990050573A (en) | 1999-07-05 |
| KR100262944B1 true KR100262944B1 (en) | 2000-08-01 |
Family
ID=19527649
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1019970069705A KR100262944B1 (en) | 1997-12-17 | 1997-12-17 | Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100262944B1 (en) |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR19980049365A (en) * | 1996-12-19 | 1998-09-15 | 양승택 | Method of Providing User-User Exchange Virtual Path Connection at Incoming Connection |
-
1997
- 1997-12-17 KR KR1019970069705A patent/KR100262944B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR19980049365A (en) * | 1996-12-19 | 1998-09-15 | 양승택 | Method of Providing User-User Exchange Virtual Path Connection at Incoming Connection |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR19990050573A (en) | 1999-07-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5956334A (en) | Method for interfacing a telephony and an ATM network to establish voice communication | |
| JP2003163677A (en) | Broadband telecommunications system | |
| GB2338861A (en) | Communication system architecture | |
| CA2299686C (en) | System and method for establishing a communication connection | |
| CA2254821A1 (en) | Communications system with load sharing communications interface | |
| KR100262944B1 (en) | Method of providing virtual tunnel using incoming trunk call control procedures at NNI | |
| KR100265856B1 (en) | Method for providing virtual tunnel using outgoing trunk call control procedures at NNI | |
| KR100198446B1 (en) | Provision methods of user-user switched virtual path connection at outgoing interference | |
| KR100198445B1 (en) | Provision methods of user-user switched virtual path connection at incoming trunk interference | |
| Tirtaatmadja et al. | The application of virtual-paths to the interconnection of IEEE 802.6 metropolitan area networks | |
| KR100194627B1 (en) | How to Provide a User-to-User Exchange Virtual Path Connection at the Recipient User-Network Interface | |
| KR100198095B1 (en) | Virtual channel connection | |
| KR0121766B1 (en) | Bilateral path control in the atm switch | |
| KR100222407B1 (en) | Atm switching system for distributed processing for each signal layer and a method thereof | |
| KR19980055541A (en) | How to set / release PVC dynamically in ATM network | |
| KR100241885B1 (en) | Implementation method of soft pvc of atm network | |
| KR0123255B1 (en) | A method for point-to-point oneway traffic control in totally distributed atm switching system | |
| KR100205027B1 (en) | Tandem call suppling method of b-isdn bisup | |
| KR0129560B1 (en) | Atm system | |
| KR0147135B1 (en) | Dynamic virtual connection assignment method in broad band | |
| KR100205028B1 (en) | Trunk outgoing call supplying method of b-isdn bisup | |
| JP2000124919A (en) | Device and method for atm signaling | |
| Jeong et al. | The design and implementation of call/connection control software in ATM switching system for multimedia services | |
| JP2002152220A (en) | Atm-pon system and connection control method for the atm-pon system | |
| La Porta et al. | Design and implementation of a distributed call processing architecture |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20040401 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |