JP7305581B2 - Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program - Google Patents
Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7305581B2 JP7305581B2 JP2020032529A JP2020032529A JP7305581B2 JP 7305581 B2 JP7305581 B2 JP 7305581B2 JP 2020032529 A JP2020032529 A JP 2020032529A JP 2020032529 A JP2020032529 A JP 2020032529A JP 7305581 B2 JP7305581 B2 JP 7305581B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- work vehicle
- position information
- recording
- storage unit
- information recording
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 51
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 claims description 106
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 70
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 66
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 36
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 26
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000013339 cereals Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003028 elevating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003337 fertilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002828 fuel tank Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003502 gasoline Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003306 harvesting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009331 sowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003971 tillage Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Guiding Agricultural Machines (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
本発明は、作業車両の位置情報を記録する位置情報記録装置などに関する。 The present invention relates to a position information recording device and the like for recording position information of a work vehicle.
背景技術として、作業車両の位置情報を予め設定されたサンプリング間隔で記憶部に記録する技術が知られている。また、作業車両が圃場内に位置しているか否かに応じて位置情報のサンプリング間隔を切り替える技術も知られている(例えば特許文献1参照)。 As a background art, there is known a technique of recording position information of a work vehicle in a storage unit at preset sampling intervals. There is also known a technique of switching the sampling interval of position information depending on whether or not the work vehicle is positioned in a field (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
ところで、位置情報のサンプリング間隔が短いほど、密度の高い位置情報が記録され、当該位置情報に基づいて作業車両の作業対象領域を特定する際の精度が高くなるが、データ量が増加するため必要な記憶容量が大きくなるという問題が生じる。一方、位置情報のサンプリング間隔が長いほど、必要な記憶容量は抑制されるが、記録される位置情報の密度が低くなるため、当該位置情報に基づいて作業車両の作業対象領域を特定する際の精度が低くなるという問題が生じる。 By the way, the shorter the sampling interval of the position information, the higher the density of the position information recorded, and the higher the accuracy when specifying the work target area of the work vehicle based on the position information. However, there is a problem that the storage capacity becomes large. On the other hand, the longer the sampling interval of the position information, the more the required storage capacity is suppressed, but the density of the recorded position information becomes lower. A problem arises that the accuracy is lowered.
本発明の目的は、必要な記憶容量を抑制しつつ作業車両の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定可能な位置情報を記録することができる、位置情報記録装置、走行車両、位置情報記録方法、及び位置情報記録プログラムを提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a position information recording device, a traveling vehicle, a position information recording method, and a position information recording device capable of recording position information capable of specifying a work target area of a work vehicle with high accuracy while suppressing the required storage capacity. An object of the present invention is to provide a position information recording program.
本発明に係る位置情報記録装置は、取得処理部及び記録処理部を備える。前記取得処理部は、作業車両の位置情報を取得する。前記記録処理部は、前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録する。 A position information recording device according to the present invention includes an acquisition processing unit and a recording processing unit. The acquisition processing unit acquires position information of the work vehicle. The recording processing unit records the position information at different sampling intervals according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle in the storage unit.
本発明に係る作業車両は、前記位置情報記録装置と、当該位置情報記録装置により前記位置情報が記録される記憶部とを備える。 A work vehicle according to the present invention includes the position information recording device and a storage section in which the position information is recorded by the position information recording device.
本発明に係る位置情報記録方法は、一又は複数のプロセッサーにより、作業車両の位置情報を取得することと、前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、を実行する方法である。 A position information recording method according to the present invention acquires position information of a work vehicle by one or more processors, and records the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle. and how to do it.
本発明に係る位置情報記録プログラムは、作業車両の位置情報を取得することと、前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、をプロセッサーに実行させるためのプログラムである。 A position information recording program according to the present invention causes a processor to acquire position information of a work vehicle and record the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle. It is a program for
本発明によれば、必要な記憶容量を抑制しつつ作業車両の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定可能な位置情報を記録することができる、位置情報記録装置、走行車両、位置情報記録方法、及び位置情報記録プログラムを提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to the present invention, a position information recording device, a traveling vehicle, a position information recording method, and a position information recording apparatus capable of recording position information capable of specifying a work target area of a work vehicle with high accuracy while suppressing a required storage capacity. A location information recording program can be provided.
以下の実施形態は、本発明を具体化した一例であって、本発明の技術的範囲を限定するものではない。 The following embodiments are specific examples of the present invention, and do not limit the technical scope of the present invention.
図1に示されるように、本発明の実施形態に係る位置情報記録システム1は、一又は複数の作業車両10及び管理サーバー20を備える。作業車両10及び管理サーバー20は、携帯電話回線網、パケット回線網、又は無線LANなどの通信網N1を介して通信可能である。
As shown in FIG. 1, a positional information recording system 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention includes one or
本実施形態では、作業車両10がトラクタである場合を例に挙げて説明する。なお、他の実施形態として、作業車両10は、田植機、コンバイン、建設機械、又は除雪車などであってもよい。
In this embodiment, a case where the
[作業車両10の概略構成]
図1及び図2に示されるように、作業車両10は、車両制御装置11、走行装置12、作業装置13、状態検出装置14、エンジンON/OFFキー15、及び位置情報記録装置16などを備える。車両制御装置11は、走行装置12、作業装置13、状態検出装置14、エンジンON/OFFキー15、及び位置情報記録装置16などに電気的に接続されている。なお、車両制御装置11及び位置情報記録装置16は、無線通信可能であってもよい。
[Schematic configuration of work vehicle 10]
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the
車両制御装置11は、一又は複数のプロセッサーと、不揮発性メモリ及びRAMなどの記憶メモリとを備えるコンピュータシステムである。そして、車両制御装置11は、作業車両10に対する各種のユーザー操作に応じて当該作業車両10の動作を制御する。
The
走行装置12は、作業車両10を走行させる駆動部である。図2に示されるように、走行装置12は、エンジン121、前輪122、後輪123、トランスミッション124、フロントアクスル125、リアアクスル126、ハンドル127などを備える。なお、前輪122及び後輪123は、作業車両10の左右にそれぞれ設けられている。また、走行装置12は、前輪122及び後輪123を備えるホイールタイプに限らず、作業車両10の左右に設けられるクローラを備えるクローラタイプであってもよい。
The
エンジン121は、不図示の燃料タンクに補給される燃料を用いて駆動するディーゼルエンジン又はガソリンエンジンなどの駆動源である。走行装置12は、エンジン121と共に、又はエンジン121に代えて、電気モーターを駆動源として備えてもよい。なお、エンジン121には、不図示の発電機が接続されており、当該発電機から作業車両10に設けられた車両制御装置11等の電気部品及びバッテリー等に電力が供給される。なお、前記バッテリーは、前記発電機から供給される電力によって充電される。そして、作業車両10に設けられている車両制御装置11及び位置情報記録装置16等の電気部品は、エンジン121の停止後も前記バッテリーから供給される電力により駆動可能である。
The
エンジン121の駆動力は、トランスミッション124及びフロントアクスル125を介して前輪122に伝達され、トランスミッション124及びリアアクスル126を介して後輪123に伝達される。また、エンジン121の駆動力は、不図示のPTO軸を介して作業装置13にも伝達される。
The driving force of the
作業装置13は、例えば耕耘機、プラウ、施肥機、草刈機、又は播種機などであって、作業車両10に着脱可能である。これにより、作業車両10は、作業装置13各々を用いて各種の作業を行うことが可能である。
The
具体的に、図2に示される作業装置13は、エンジン121からの駆動力によって回転軸131を中心に回転して圃場を耕耘する複数の耕耘爪132を備える耕耘機である。また、作業装置13は、作業車両10において、不図示の昇降機構により昇降可能に支持されている。そして、車両制御装置11は、ユーザーによる昇降操作に応じて前記昇降機構を制御して作業装置13を昇降させる。例えば、ユーザーは、作業車両10が圃場の作業対象領域において前進する場合に作業装置13を下降させ、作業車両10が後進する場合には作業装置13を上昇させる。
Specifically, the
ハンドル127は、ユーザーによって操作される操作部である。走行装置12では、ユーザーによるハンドル127の操作に応じて、不図示の油圧式パワーステアリング機構などによって前輪122の角度が変更され、作業車両10の進行方向が変更される。
The
また、走行装置12は、ハンドル127の他に、ユーザーによって操作される不図示のシフトレバー、アクセル、ブレーキ等を備える。そして、走行装置12では、ユーザーによる前記シフトレバーの操作に応じて、トランスミッション124のギアが前進ギア又はバックギアなどに切り替えられ、作業車両10の走行態様が前進又は後進などに切り替えられる。なお、前記シフトレバーは、作業車両10の前後進を切り替える操作具の一例である。また、車両制御装置11は、ユーザーによる前記アクセルの操作に応じてエンジン121の回転数を制御する。一方、車両制御装置11は、ユーザーによる前記ブレーキの操作に応じて、電磁ブレーキを用いて前輪122及び後輪123の回転を制動する。
In addition to the
状態検出装置14は、作業車両10の状態を検出する各種の検出部を備え、当該状態検出装置14による検出結果は車両制御装置11に入力される。具体的に、状態検出装置14は、ハンドル127の操作角度を検出するハンドル角度検出部141、及び前記シフトレバーの位置を検出するシフト検出部142などを備える。
The
ハンドル角度検出部141は、例えばハンドル127の回転軸の回転角度を当該ハンドル127の操作角度として検出するロータリーエンコーダー等を備える。ハンドル角度検出部141により検出されるハンドル127の操作角度は、前輪122が作業車両10における前後方向と平行な状態である場合を基準の0度とした場合の操作角度であり、右方向の回転操作時にプラス、左方向の回転操作時にマイナスとなる。また、シフト検出部1
42は、例えば前記シフトレバーの位置を検出する機械式スイッチ又は磁気センサ等を備える。
The handle
42 is provided with, for example, a mechanical switch or a magnetic sensor for detecting the position of the shift lever.
エンジンON/OFFキー15は、走行装置12のエンジン121の始動及び停止を切り替えるためのキースイッチ又はボタンスイッチなどである。車両制御装置11は、エンジンON/OFFキー15がオンに切り替えられた場合にエンジン121を始動させ、エンジンON/OFFキー15がオフに切り替えられた場合にエンジン121を停止させる。なお、前述したように車両制御装置11には前記バッテリーが接続されており、当該車両制御装置11は、エンジン121の停止中も稼働可能である。
The engine ON/
位置情報記録装置16は、制御部161、記憶部162、通信部163、及び位置検出部164などを備える通信端末である。例えば、位置情報記録装置16は、図2に示されるように、ユーザーが搭乗するキャビン17内に設けられている。また、位置情報記録装置16の設置場所はキャビン17内に限らない。さらに、位置情報記録装置16の制御部161、記憶部162、通信部163、及び位置検出部164は、作業車両10において異なる位置に分散して配置されていてもよい。なお、前述したように位置情報記録装置16には前記バッテリーが接続されており、当該位置情報記録装置16は、エンジン121の停止中も稼働可能である。また、位置情報記録装置16として、例えば携帯電話端末、スマートフォン、又はタブレット端末などが代用されてもよい。
The position
制御部161は、一又は複数のプロセッサーと、不揮発性メモリ及びRAMなどの記憶メモリとを備えるコンピュータシステムである。記憶部162は、制御部161に後述の位置情報記録処理(図3参照)を実行させるための位置情報記録プログラム、及び後述の位置情報などを記憶する不揮発性メモリなどである。
The
通信部163は、近距離無線通信又は有線通信により車両制御装置11との間で各種のデータの送受信が可能である。具体的に、制御部161は、通信部163により車両制御装置11から作業車両10における各種の稼働状態を示す稼働情報を取得することが可能である。
The
前記稼働情報には、ハンドル角度検出部141によって検出されるハンドル127の操作角度を示すハンドル操作情報、及びシフト検出部142によって検出される前記シフトレバーの操作状態を示すシフト情報などが含まれる。また、前記稼働情報には、作業車両10のエンジンON/OFFキー15のON/OFF状態を示すエンジン情報も含まれる。さらに、前記稼働情報には、エンジン121の回転数を示す回転数情報、車速情報、前記ブレーキの操作状態を示すブレーキ情報が含まれていてもよい。なお、作業車両10が穀物などを収穫するものである場合には、当該作業車両10による収穫量などを示す収穫量情報が含まれていてもよい。
The operation information includes steering wheel operation information indicating the operation angle of the
また、通信部163は、通信網N1を介して管理サーバー20との間で各種のデータの送受信が可能である。管理サーバー20は、図1に示されるように、制御部21及び記憶部22などを備えるコンピュータシステムである。管理サーバー20では、制御部21が、作業車両10各々から通信網N1を介して受信する位置情報などを記憶部22に蓄積して記憶する。また、制御部21は、ユーザー操作に応じて、記憶部22に記憶されている前記位置情報などを表示又は送信することが可能である。
Also, the
位置検出部164は、GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)等の衛星測位システムを用いて、位置情報記録装置16が搭載された作業車両10の位置情報を検出する。前記位置情報には、作業車両10の位置を示す緯度及び経度の情報が含まれる。なお、位置検出部164による作業車両10の位置情報
の取得手法は特に限定されない。また、前記位置情報は、緯度及び経度に限らず、作業車両10の位置を特定可能な他の形式の情報であってもよい。他の実施形態として、前記位置情報は、作業車両10の作業開始位置又はエンジン始動位置などの特定の位置を基準位置として、当該基準位置に対する相対的な位置を示す情報であってもよい。
The
ところで、予め設定されたサンプリング間隔で作業車両10の位置情報を記録する技術が知られている。ここで、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔が短いほど、密度の高い位置情報が記録され、当該位置情報に基づいて作業車両10の作業対象領域を特定する際の精度が高くなるが、データ量が増加するため必要な記憶容量が大きくなるという問題が生じる。一方、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔が長いほど、必要な記憶容量は抑制されるが、記録される位置情報の密度が低くなるため、当該位置情報に基づいて作業車両10の作業対象領域を特定する際の精度が低くなるという問題が生じる。
By the way, there is known a technique of recording the position information of the
これに対し、以下に説明するように、本実施形態に係る作業車両10では、必要な記憶容量を抑制しつつ作業車両10の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定可能な位置情報を記録することができる。
On the other hand, as described below, in the
具体的に、本実施形態に係る作業車両10に搭載される位置情報記録装置16の制御部161は、計時処理部171、取得処理部172、及び記録処理部173などの各種の処理部を含む。なお、制御部161は、前記位置情報記録プログラムに従って各種の処理を実行することにより前記各種の処理部として機能する。また、他の実施形態として、計時処理部171、取得処理部172、及び記録処理部173の一部又は全部が電子回路で構成されていてもよい。
Specifically, the
計時処理部171は、現在の時刻を計時するための計時処理を実行する。前記時刻には、年、月、日、時、分、秒が含まれる。位置情報記録装置16は、前記バッテリーに接続されており、計時処理部171は、作業車両10のエンジン121がOFF状態でも、前記バッテリーから供給される電力により計時処理を実行することが可能である。
The
取得処理部172は、作業車両10の前記位置情報及び前記稼働情報を取得する情報取得処理を実行する。具体的に、取得処理部172は、計時処理部171により計時される時刻に基づいて、予め設定された情報取得間隔で、前記位置情報を位置検出部164から取得し、前記稼働情報を車両制御装置11から取得する。
The
記録処理部173は、取得処理部172によって取得される前記位置情報のうち、予め設定されたサンプリング間隔の位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。特に、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。なお、前記走行態様には、旋回又は後進の少なくとも一方と直進とが含まれる。
The
特に、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合は、予め設定された第1サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。また、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合は、前記第1サンプリング間隔よりも短い予め設定された第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。例えば、前記第1サンプリング間隔が10秒であり、前記第2サンプリング間隔が1秒である。
In particular, when the
なお、本実施形態では、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合に対応するサンプリング間隔が共通の前記第2サンプリング間隔である場合を例に挙げて説明する。一方、他の実施形態として、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回である場合に対応するサンプ
リング間隔と、作業車両10の走行態様が後進である場合に対応するサンプリング間隔とが異なっていてもよい。
In the present embodiment, an example will be described in which the sampling interval corresponding to the traveling mode of the
[位置情報記録処理]
以下、図3を参照しつつ、作業車両10に搭載される位置情報記録装置16の制御部161によって実行される前記位置情報記録処理の一例について説明する。例えば、前記位置情報記録処理は、エンジンON/OFFキー15により作業車両10のエンジン121がON状態にされた場合に制御部161によって開始される。また、前記位置情報記録処理は、作業車両10又は位置情報記録装置16に対する所定のユーザー操作に応じて開始されてもよい。
[Position information recording process]
An example of the position information recording process executed by the
なお、本願発明は、制御部161により前記位置情報記録処理の一部又は全部を実行する位置情報記録処理方法の発明、又は、当該位置情報記録方法の一部又は全部を制御部161に実行させるための位置情報記録プログラムの発明として捉えてもよい。また、前記位置情報記録処理は、一又は複数のプロセッサーによって実行されてもよい。例えば、前記位置情報記録処理は、制御部161及び車両制御装置11によって協働して実行されてもよい。
In addition, the present invention is an invention of a position information recording processing method in which the
<ステップS1>
ステップS1において、制御部161の取得処理部172は、前記位置情報及び前記稼働情報を取得する情報取得処理を実行する。具体的に、取得処理部172は、前記位置情報を位置検出部164から取得し、前記稼働情報を車両制御装置11から取得する。このとき、制御部161は、前記位置情報及び前記稼働情報を取得したときの時刻を示す時刻情報を前記計時処理部171から取得し、当該位置情報及び当該稼働情報に対応付ける。
<Step S1>
In step S1, the
なお、位置検出部164から所定時間ごとに前記位置情報が制御部161に入力され、車両制御装置11から所定時間ごとに前記稼働情報が制御部161に入力されていてもよい。この場合、制御部161では、位置検出部164及び車両制御装置11から入力される最新の前記位置情報及び前記稼働情報が当該制御部161のRAMに一時的に記憶されており、当該ステップS1では、前記RAMに記憶されている最新の前記位置情報及び前記稼働情報が参照されてもよい。
The position information may be input to the
<ステップS2>
ステップS2において、制御部161は、作業車両10のエンジン121がOFF状態であるか否かを判定する。具体的に、制御部161は、エンジンON/OFFキー15がON状態である場合に作業車両10のエンジン121がON状態であり、エンジンON/OFFキー15がOFF状態である場合に作業車両10のエンジン121がOFF状態であると判定する。そして、作業車両10のエンジン121がOFF状態であると判定されると(S2:Yes)、処理がステップS21に移行し、作業車両10のエンジン121がOFF状態になるまでの間は(S2:No)、処理がステップS3に移行する。
<Step S2>
In step S2, the
<ステップS21>
ステップS21において、制御部161は、後述のステップS6で記憶部162に記録される前記位置情報、前記稼働情報、及び前記時刻情報を管理サーバー20に送信し、前記位置情報記録処理を終了する。なお、制御部161は、管理サーバー20から前記位置情報などの受信確認信号を受信すると、当該位置情報などを記憶部162から消去する。
<Step S21>
In step S21, the
<ステップS3>
ステップS3において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否かを判定する。具体的に、記録処理部173は、前記ステップS1で取
得された前記稼働情報に含まれる前記ハンドル操作情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否かを判定する。例えば、前記ハンドル操作情報に基づいて、ハンドル127の操作角度が-5度以上+5度以下などの予め設定された特定範囲を超えている場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定される。そして、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定されると(S3:Yes)、処理がステップS31に移行し、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回でないと判定されると(S3:No)、処理がステップS4に移行する。
<Step S3>
In step S3, the
<ステップS4>
ステップS4において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であるか否かを判定する。具体的に、記録処理部173は、前記ステップS1で取得された前記稼働情報に含まれる前記シフト情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であるか否かを判定する。例えば、前記シフト情報に基づいて、前記シフトレバーの位置が作業車両10のギアの状態がバックギアとなるバック位置である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であると判定される。そして、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であると判定されると(S4:Yes)、処理がステップS31に移行し、作業車両10の走行態様が後進でないと判定されると(S4:No)、処理がステップS5に移行する。
<Step S4>
In step S4, the
<ステップS5>
ステップS5において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したか否かを判定する。そして、前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定された場合(S5:Yes)、処理はステップS6に移行し、前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過していないと判定された場合(S5:No)、処理はステップS7に移行する。即ち、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回及び後進のいずれでもない場合には(S3及びS4:No)、前記第1サンプリング間隔で前記ステップS6が実行されることになる。
<Step S5>
In step S5, the
例えば、前記第1サンプリング間隔が10秒である場合、記録処理部173は、現在の時刻の秒の情報について、十の位が0~5のいずれかであり、且つ、一の位が0である場合に、前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00秒、10秒、20秒、30秒、40秒、50秒となる10秒ごとのタイミングで前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。また、前記第1サンプリング間隔が1分である場合、記録処理部173は、現在の時刻の秒の情報について、十の位及び一の位が共に0である場合に、前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00秒となる1分ごとのタイミングで前記第1サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。
For example, when the first sampling interval is 10 seconds, the
<ステップS31>
一方、前記ステップS3又はS4において、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進であると判定された場合には(S3又はS4:Yes)、ステップS31が実行される。ステップS31において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したか否かを判定する。そして、前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定された場合(S31:Yes)、処理はステップS6に移行し、前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過していないと判定された場合(S31:No)、処理はステップS7に移行する。即ち、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合には、前記第2サンプリング間隔で前記ステップS6が実行されることになる。
<Step S31>
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S3 or S4 that the traveling mode of the
例えば、前記第2サンプリング間隔が1秒である場合、記録処理部173は、計時処理部171で計時されている現在の時刻の秒の情報について、一の位が0~9のいずれかである場合に、前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00秒、01秒、02秒、03秒、04秒、05秒・・・、59秒となる1
秒ごとのタイミングで前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。また、前記第2サンプリング間隔が2秒である場合、記録処理部173は、計時処理部171で計時されている現在の時刻の秒の情報について、一の位が0、2、4、6、8のいずれかである場合に、前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00秒、02秒、04秒、06秒、08秒、10秒・・・、58秒となる2秒ごとのタイミングで前記第2サンプリング間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。
For example, when the second sampling interval is 1 second, the
It is determined that the second sampling interval has passed at the timing of every second. Further, when the second sampling interval is 2 seconds, the
<ステップS6>
ステップS6において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、前記ステップS1で取得された前記位置情報、前記稼働情報、及び前記時刻情報を記憶部162に記録する。なお、図4は、前記ステップS6において記憶部162に記録される前記位置情報、前記稼働情報、及び前記時刻情報の一例を示す図である。図4では、前記位置情報がX1~X9及びY1~Y9で示されているが、実際の前記位置情報には、X1~X9及びY1~Y9に代えて作業車両10の位置を示す数値などが含まれる。また、他の実施形態として、前記第1サンプリング間隔で前記位置情報が記録される場合には前記稼働情報が共に記録され、前記第2サンプリング間隔で前記位置情報が記録される場合には前記稼働情報が記録されないことも考えられる。
<Step S6>
In step S<b>6 , the
<ステップS7>
ステップS7において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、前記情報取得間隔が経過したか否かを判定する。そして、前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定された場合(S7:Yes)、処理はステップS1に戻され、前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定されるまでの間は(S7:No)、処理がステップS7で待機する。即ち、作業車両10では、エンジン121がON状態となった後、エンジン121がOFF状態となるまでの間、前記情報取得間隔で前記ステップS1以降の前記位置情報記録処理が繰り返し実行されることになる。前記情報取得間隔は、前記第2サンプリング間隔と同じ又は当該第2サンプリング間隔よりも短い時間である。また、前記情報取得間隔は、前記第1サンプリング間隔及び前記第2サンプリング間隔の公約数となる時間である。
<Step S7>
In step S7, the
例えば、前記情報取得間隔が1秒である場合、記録処理部173は、計時処理部171で計時されている現在の時刻の秒の情報について、一の位が0~9のいずれかであり、且つ、小数点以下の位が0である場合に、前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00秒、01秒、02秒、03秒、04秒、05秒・・・、59秒となる1秒ごとのタイミングで前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。また、前記情報取得間隔が0.1秒である場合、記録処理部173は、計時処理部171で計時されている現在の時刻の秒の情報について、100m秒の位が0~9のいずれかであり、10m秒以下の位が0である場合に、前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定する。この場合、現在の時刻の秒の情報が、00.00秒、00.10秒、00.20秒、00.30秒、00.40秒、00.50秒・・・、00.90秒となる0.1秒ごとのタイミングで前記情報取得間隔が経過したと判定されることになる。
For example, when the information acquisition interval is 1 second, the
また、ステップS5、S31、及びS7における前記第1サンプリング間隔、前記第2サンプリング間隔、及び前記情報取得間隔の判定手法はここで説明する方法に限らない。例えば、記録処理部173は、初期値が0でありステップS6が実行されるごとに0にリセットされる第1経過時間を計時することが考えられる。この場合、記録処理部173は、ステップS5又はS31において、前記第1経過時間が前記第1サンプリング間隔又は前記第2サンプリング間隔に達したか否かに応じて、前記第1サンプリング間隔又は前記第2サンプリング間隔の経過の有無を判定可能である。また、記録処理部173は、初期値が0であり前記ステップS1が実行されるごとに0にリセットされる第2経過時間を計
時することが考えられる。この場合、記録処理部173は、前記第2経過時間が前記情報取得間隔に達したか否かに応じて、前記情報取得間隔の経過の有無を判定可能である。なお、前記ステップS7は省略されてもよい。
Also, the method of determining the first sampling interval, the second sampling interval, and the information acquisition interval in steps S5, S31, and S7 is not limited to the method described here. For example, the
以上説明したように、位置情報記録装置16において、制御部161の記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。これにより、位置情報記録装置16では、必要な記憶容量を抑制しつつ作業車両10の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定することが可能な前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録することが可能である。
As described above, in the position
具体的に、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合には(S3及びS4:No)、前記第2サンプリング間隔よりも長い前記第1サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記憶部162に記録される。これにより、常に前記第2サンプリング間隔で前記位置情報が記録される場合に比べて記憶部162に必要な記憶容量が抑制される。また、常に前記第2サンプリング間隔で前記位置情報が記録される場合に比べて、前記ステップS21において位置情報記録装置16から管理サーバー20に送信される前記位置情報の情報量が抑制されることになるため通信負荷も抑制される。また、前記位置情報記録処理では、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合には(S3又はS4:Yes)、前記第1サンプリング間隔よりも短い前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記憶部162に記録される。これにより、常に前記第1サンプリング間隔で前記位置情報が記録される場合に比べて、密度の高い前記位置情報が記録されることになり、作業車両10の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定することが可能となる。
Specifically, when the
[位置情報のサンプリング結果の一例]
以下、図5~図10を参照しつつ、作業車両10が圃場F1において作業を行う場合に、位置情報記録装置16による記憶部162への前記位置情報の記録結果の一例について説明する。
[Example of location information sampling results]
An example of the result of recording the position information in the
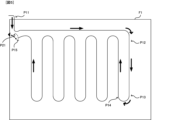
<作業車両10の走行軌跡>
まず、図5及び図6を参照しつつ、作業車両10の走行軌跡の一例について説明する。なお、図5及び図6において、実線は、作業車両10の直進時又は旋回時の走行軌跡を示し、破線は、作業車両10の後進時の走行軌跡を示し、矢印は、作業車両10の進行方向を示す。
<Travel locus of
First, an example of the travel locus of the
また、作業車両10には、耕耘機である作業装置13が装着されており、圃場F1内において、走行態様が直進又は旋回である場合には作業装置13が下降した状態にされ、走行態様が後進である場合には作業装置13が上昇した状態にされるものとする。なお、作業車両10では、当該作業車両10に装着される作業装置13の種類によって、作業車両10の旋回時にも当該作業装置13が上昇した状態にされることがある。
The working
図5に示されるように、作業車両10は、作業装置13が上昇した状態で、入口P11から圃場F1に入った後、直進及び旋回により第1作業開始位置P12まで走行する。そして、作業車両10は、第1作業開始位置P12から旋回開始位置P13まで直進する。次に、作業車両10は、旋回開始位置P13から旋回終了位置P14まで旋回する。その後、作業車両10は、同様に直進及び旋回を繰り返して第1作業終了位置P15まで走行すると、第1作業終了位置P15から第2作業開始位置P21まで後進する。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
続いて、図6に示されるように、作業車両10は、第2作業開始位置P21から旋回開始位置P22まで直進する。そして、作業車両10は、旋回開始位置P22から旋回終了位置P23まで旋回する。次に、作業車両10は、旋回終了位置P23から作業再開位置
P24まで後進した後、旋回開始位置P25まで直進する。その後、作業車両10は、同様に直進、旋回、後進などを繰り返して第2作業終了位置P26まで走行すると、第2作業終了位置P26から旋回及び後進により第3作業開始位置P31まで走行する。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 6, the
また、図6に示されるように、作業車両10は、第2作業開始位置P21から第2作業終了位置P26までの移動と同様に、直進、旋回、後進などを繰り返し、第3作業開始位置P31から第3作業終了位置P32まで走行する。そして、作業車両10は、第3作業終了位置P32から旋回及び後進により第4作業終了位置P33まで走行する。その後、作業車両10は、圃場F1の入口P11から圃場F1外に向けて走行する。
Further, as shown in FIG. 6, the
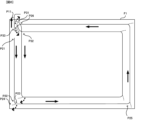
<位置情報のサンプリング結果の比較例>
図7及び図8には、作業車両10が図5及び図6に示される走行軌跡に沿って走行する場合であり、記憶部162に必要な記憶容量を抑制するために、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔がある程度長い場合のサンプリング結果の一例が示されている。なお、図7及び図8に示される黒点は、記憶部162に記録される作業車両10の前記位置情報を表すものであり、当該黒点を結ぶ一点鎖線は、前記位置情報及び前記時刻情報に基づいて再現される走行軌跡を表す仮想線である。
<Comparison example of location information sampling results>
FIGS. 7 and 8 show the case where the
図7及び図8に示されるように、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔がある程度長ければ前記位置情報の密度が低くなる。特に、作業車両10の走行軌跡のうち旋回又は後進が行われる角部分における前記位置情報の密度が低い場合には、当該位置情報に基づいて再現される角部分の走行軌跡の精度が低くなる。そのため、前記位置情報に基づいて圃場F1における作業車両10の作業対象領域を特定する際の精度が低くなる。
As shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, if the sampling interval of the position information is long to some extent, the density of the position information becomes low. In particular, when the density of the positional information is low at the corner portion where the
<本実施形態に係る位置情報のサンプリング結果>
一方、図9及び図10には、作業車両10が図5及び図6に示される走行軌跡に沿って走行する場合であり、本実施形態に係る作業車両10のように、走行態様に応じて前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔が変更される場合のサンプリング結果の一例が示されている。なお、図9及び図10に示される黒点は、記憶部162に記録される作業車両10の前記位置情報を表すものであり、当該黒点を結ぶ一点鎖線は、前記位置情報及び前記時刻情報に基づいて再現される走行軌跡を表す仮想線である。
<Sampling result of position information according to the present embodiment>
On the other hand, FIGS. 9 and 10 show the case where the
図9及び図10に示されるように、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合には、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔がある程度長くなっているが、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合には、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔が短くなっている。そのため、作業車両10の走行軌跡のうち直進が行われる部分については走行軌跡の精度が低いが、旋回又は後進が行われる角部分の走行軌跡の精度は高くなっている。このように、本実施形態に係る作業車両10では、圃場F1における作業車両10の作業対象領域を高い精度で特定することが可能な前記位置情報が記録されていることがわかる。
As shown in FIGS. 9 and 10, when the
[他の実施形態]
以下、本実施形態に係る作業車両10の他の実施形態について説明する。
[Other embodiments]
Other embodiments of the
前記実施形態では、前記ステップS3及びS4において、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否か、及び、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であるか否かの両方の判定が行われる場合について説明した。一方、他の実施形態として、前記ステップS3又はS4のいずれか一方が実行され、他方が省略されてもよい。例えば、制御部161が、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合と作業車両10の走行態様が旋回である場合とで前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔を切り替えることが考えられる。また、制御部161が、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合と作業車両10の走行態様が後進である場合とで前記
位置情報のサンプリング間隔を切り替えることも考えられる。
In the above embodiment, in steps S3 and S4, it is determined whether or not the traveling mode of the
さらに、他の実施形態として、前記ステップS3及びS4に代えて、作業車両10の走行態様が直進であるか否かが判定されてもよい。例えば、制御部161は、前記ハンドル操作情報及び前記シフト情報に基づいて、ハンドル127の操作角度が-5度以上+5度の特定範囲内であり、且つ、作業車両10の前記シフトレバーの位置が前進位置である場合に直進であると判定する。そして、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合は処理がステップS5に移行し、直進でない場合には処理がステップS31に移行する。この場合でも、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である場合と作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合とで前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔が切り替えられることになる。
Furthermore, as another embodiment, instead of steps S3 and S4, it may be determined whether or not the
また、前記実施形態では、作業車両10が、ユーザーによって手動で操作される場合について説明した。一方、作業車両10は、予め設定される経路情報に基づいて自動走行する自動走行型の作業車両であってもよい。作業車両10が自動走行型の作業車両である場合、制御部161は、前記経路情報に基づいて作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが可能である。そこで、前記位置情報記録処理において、制御部161は、前記経路情報に基づいて各タイミングにおける作業車両10の走行態様を判定し、当該走行態様に応じて前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔を変更してもよい。
Moreover, in the above-described embodiment, the case where the
また、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様の切り替え後の特定期間については、当該走行態様の切り替え前後の前記走行態様各々に対応する前記サンプリング間隔のうち短い方のサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録してもよい。具体的に、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様が、旋回から直進又は後進に切り替えられた後は、前記特定期間が経過するまでの間だけ、前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録し、その後は、前記第1サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。これにより、前記特定期間については、前記第1サンプリング間隔よりも短い前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記憶部162に記録された状態となる。従って、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進となる前後の走行軌跡の再現精度が高くなる。
Further, the
また、前記実施形態では、前記位置情報記録処理において、取得処理部172によって取得される前記位置情報のうち、前記走行態様ごとに対応するサンプリング間隔で取得された前記位置情報のみが記憶部162に記録される場合について説明した。一方、記録処理部162が、取得処理部172によって取得された前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録した後、特定のタイミングで記憶部162から不要な前記位置情報を消去する消去処理を実行してもよい。具体的に、記録処理部173は、記憶部162に記録された前記位置情報のデータ量が予め設定されたデータ量に達した場合に前記消去処理を実行する。例えば、前記消去処理において、作業車両10の走行態様が直進である期間については、前記第1サンプリング間隔の位置情報が残され、他の位置情報が消去される。一方、前記消去処理において、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である期間については、前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が残され、他の位置情報が消去される。これにより、結果的に、記憶部162には、作業車両10の走行態様ごとに対応するサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記録された状態となる。
In the above embodiment, in the position information recording process, of the position information acquired by the
特に、前記消去処理が実行される場合、記録処理部173は、作業車両10の走行態様の切り替え前の特定期間についても、前記位置情報のサンプリング間隔を短縮することが可能である。具体的に、記録処理部173は、前記特定期間については、作業車両10の走行態様の切り替え前後の前記走行態様各々に対応する前記サンプリング間隔のうち短い方のサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録する。例えば、記録処理部173は、前記消去処理において、作業車両10の走行態様が直進から旋回又は後進に切り
替えられる直前の前記特定期間は、前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162から消去せず、他の位置情報を消去する。また、前記消去処理において、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進から直進に切り替えられた直後の前記特定期間は、前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162から消去せず、他の位置情報を消去する。これにより、結果的に、前記特定期間については、前記第1サンプリング間隔よりも短い前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記憶部162に記録された状態となる。従って、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進となる前後の走行軌跡の再現精度が高くなる。
In particular, when the erasing process is executed, the
なお、制御部161は、作業車両10が圃場内に位置しているか否かを判定し、当該作業車両10が圃場内に位置する場合に、前記位置情報記録処理を実行し、当該作業車両10が圃場内に位置しない場合は、前記位置情報記録処理が実行しないことも考えられる。また、制御部161は、作業車両10が圃場内に位置する場合であって、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進である場合にのみ、前記第2サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部162に記録することが考えられる。即ち、作業車両10が圃場内に位置しない場合には、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進であっても、前記第1サンプリング間隔の前記位置情報が記憶部162に記録されてもよい。
Note that the
ところで、前記実施形態では、ハンドル127の操作角度に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否かが判定される場合について説明した。また、前記実施形態では、作業車両10の前後進を切り替える操作具の一例である前記シフトレバーの位置がバック位置であるか否かに基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であるか否かが判定される場合について説明した。一方、作業車両10の走行態様の判定手法はこれらに限らない。以下、作業車両10の走行態様の判定手法の他の例について説明する。
By the way, in the above embodiment, the case where it is determined whether or not the traveling mode of the
例えば、クローラタイプの作業車両10には、左側のクローラへの駆動力の伝達の有無を切り替える左クラッチと、右側のクローラへの駆動力の伝達の有無を切り替える右クラッチとが設けられることがある。また、前記左クラッチ及び前記右クラッチには、操作状態を検出可能なセンサがそれぞれ設けられており、前記稼働情報には、前記センサ各々による検出結果を示すクラッチ情報が含まれる。この場合、制御部161は、前記クラッチ情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが可能である。例えば、制御部161は、前記左クラッチ及び前記右クラッチのいずれか一方のみが操作されている場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定する。
For example, the crawler-
また、ホイールタイプの作業車両10には、左側の後輪123に対応する左ブレーキと、右側の後輪123に対応する右ブレーキとが設けられることがある。さらに、前記左ブレーキ及び前記右ブレーキには、操作状態を検出可能なセンサがそれぞれ設けられており、前記稼働情報には、前記センサ各々による検出結果を示すブレーキ情報が含まれる。この場合、制御部161は、前記ブレーキ情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが可能である。例えば、制御部161は、前記左ブレーキ及び前記右ブレーキのいずれか一方のみが操作されている場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定する。
In some cases, the wheel-
また、クローラタイプの作業車両10には、クローラの回転方向を検出可能なセンサが設けられており、前記稼働情報に当該センサ各々による検出結果を示す走行情報が含まれることがある。この場合、作業車両10では、制御部161が、前記走行情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が、直進、旋回、後進のいずれであるかを判定することが可能である。例えば、制御部161は、右側のクローラと左側のクローラとの回転方向が反対である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定する。また、制御部161は、右側のクローラと左側のクローラとの回転方向が共に前方である場合に、作業車両10
の走行態様が直進であると判定する。また、制御部161は、右側のクローラと左側のクローラとの回転方向が共に後方である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であると判定する。さらに、制御部161は、右側のクローラと左側のクローラとの回転速度が異なる場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定してもよい。
Further, the crawler-
is determined to be straight running. Further, the
また、作業車両10には、作業車両10の前方又は後方を撮影する第1撮影部、或いは、作業車両10に搭乗しているユーザーの操作状態を撮影する第2撮影部が設けられることがある。この場合、作業車両10では、制御部161が、前記撮影部により撮影される映像に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが考えられる。例えば、制御部161は、前記第1撮影部により撮影される作業車両10の前方又は後方の映像の変化態様に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が、直進、旋回、後進のいずれであるかを判定することが可能である。また、制御部161は、前記第2撮影部により撮影される映像に基づいてハンドル127の操作状態を認識し、当該ハンドル127の操作状態に応じて作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否かを判定することが可能である。さらに、制御部161は、前記第2撮影部により撮影される映像に基づいて前記シフトレバーの操作状態を認識し、当該シフトレバーの操作状態に応じて作業車両10の走行態様が後進であるか否かを判定することも可能である。
In addition, the
また、位置情報記録システム1は、作業車両10を上空から撮影可能な飛行撮影装置を備えることが考えられる。この場合、制御部161は、前記飛行撮影装置により撮影される画像又は映像に基づいて、作業車両10の走行方向を特定し、当該走行方向に応じて作業車両10の走行態様が、直進、旋回、後進のいずれであるかを判定することが考えられる。さらに、制御部161は、位置検出部164で検出される所定期間ごとの位置情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行方向を特定し、当該走行方向に応じて作業車両10の走行態様が、直進、旋回、後進のいずれであるかを判定することも考えられる。
Further, the position information recording system 1 may be equipped with an aerial photographing device capable of photographing the
また、作業車両10には、前記稼働情報に、前記油圧式パワーステアリング機構などを制御するための油圧信号の内容を示す油圧信号情報が含まれることがある。この場合、制御部161は、前記油圧信号情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であるか否かを判定することが可能である。
Further, in the
また、作業車両10では、ハンドル127にユーザーが握っている当該ハンドル127の位置を検出するための圧力センサが設けられることがあり、前記稼働情報に、前記圧力センサによる検出結果を示す握り位置情報が含まれることがある。この場合、制御部161は、前記握り位置情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが考えられる。例えば、制御部161は、ユーザーが握っているハンドル127の位置が、当該ハンドル127の回転操作が行われる場合の位置として予め定められた旋回操作位置である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回であると判定する。同様に、制御部161は、ユーザーが握っているハンドル127の位置が、当該ハンドル127の回転操作が行われない場合の位置として予め定められた直進操作位置である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が直進であると判定する。
In the
また、前記稼働情報に、作業装置13の昇降状態を示す作業機情報が含まれることがある。この場合、制御部161は、前記作業機情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが考えられる。例えば、制御部161は、作業装置13が下降した状態である場合には、作業車両10の走行態様が直進であると判定する。また、制御部161は、作業装置13が上昇した状態である場合には、作業車両10の走行態様が後進であると判定する。また。作業車両10に装着されている作業装置13が作業車両10の旋回時にも上昇した状態となるものである場合には、制御部161は、作業装置13が上昇した状態である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進であると判定することが考えられる。
Further, the operation information may include working machine information indicating the lifting state of the working
また、作業車両10が直進する場合に比べて、作業車両10が旋回又は後進する場合には、作業車両10の走行速度が低下することがある。そして、前記稼働情報には、作業車両10の走行速度を示す速度情報が含まれることがある。この場合、制御部161は、前記速度情報に基づいて、作業車両10の走行態様を判定することが考えられる。例えば、制御部161は、作業車両10の走行速度が予め設定された特定速度以上である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が直進であり、作業車両10の走行速度が前記特定速度未満である場合に、作業車両10の走行態様が旋回又は後進であると判定することが考えられる。
In addition, the running speed of the
1 位置情報記録システム
10 作業車両
11 車両制御装置
12 走行装置
13 作業装置
14 状態検出装置
15 エンジンON/OFFキー
16 位置情報記録装置
17 キャビン
20 管理サーバー
21 制御装置
22 記憶部
1 position
Claims (8)
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録する記録処理部と、を備え、
前記記録処理部は、前記作業車両の走行態様が後進である場合に、前記作業車両の走行態様が直進である場合よりも短いサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、
位置情報記録装置。 an acquisition processing unit that acquires position information of the work vehicle;
a recording processing unit that records the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle ;
When the work vehicle travels backward, the recording processing unit records the position information at sampling intervals shorter than when the work vehicle travels straight in the storage unit.
Location information recording device.
請求項1に記載の位置情報記録装置。 The recording processing unit determines whether or not the work vehicle is traveling in reverse according to the position of the operation tool that switches between forward and backward travel of the work vehicle.
The position information recording device according to claim 1 .
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録する記録処理部と、を備え、
前記記録処理部は、前記作業車両の走行態様の切り替え前又は切り替え後の特定期間については、当該走行態様の切り替え前後の前記走行態様各々に対応する前記サンプリング間隔のうち短い方のサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、
位置情報記録装置。 an acquisition processing unit that acquires position information of the work vehicle;
a recording processing unit that records the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle;
For a specific period before or after switching the traveling mode of the work vehicle, the recording processing unit selects the shorter sampling interval among the sampling intervals corresponding to each of the traveling modes before and after switching the traveling mode. recording position information in the storage unit ;
Location information recording device.
前記位置情報記録装置により前記位置情報が記録される記憶部と、
を備える、作業車両。 a position information recording device according to any one of claims 1 to 3 ;
a storage unit in which the position information is recorded by the position information recording device;
A work vehicle comprising:
作業車両の位置情報を取得することと、
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、を実行し、
前記位置情報の記録に際して、前記作業車両の走行態様が後進である場合に、前記作業車両の走行態様が直進である場合よりも短いサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、
位置情報記録方法。 by one or more processors,
Acquiring position information of the work vehicle;
recording the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle ;
When recording the position information, when the work vehicle travels backward, the position information is recorded in the storage unit at sampling intervals shorter than when the work vehicle travels straight.
Location information recording method.
作業車両の位置情報を取得することと、 Acquiring position information of the work vehicle;
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、を実行し、 recording the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle;
前記位置情報の記録に際して、前記作業車両の走行態様の切り替え前又は切り替え後の特定期間については、当該走行態様の切り替え前後の前記走行態様各々に対応する前記サンプリング間隔のうち短い方のサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、 When recording the position information, for a specific period before or after switching the travel mode of the work vehicle, the sampling interval corresponding to each of the travel modes before and after the switching of the travel mode is set to the shorter sampling interval. recording the position information in the storage unit;
位置情報記録方法。 Location information recording method.
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、
をプロセッサーに実行させるための位置情報記録プログラムであって、
前記位置情報の記録に際して、前記作業車両の走行態様が後進である場合に、前記作業車両の走行態様が直進である場合よりも短いサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、
位置情報記録プログラム。 Acquiring position information of the work vehicle;
recording the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle;
A location information recording program for causing a processor to execute
When recording the position information, when the work vehicle travels backward, the position information is recorded in the storage unit at sampling intervals shorter than when the work vehicle travels straight.
Location information recording program.
前記作業車両の走行態様に応じて異なるサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を記憶部に記録することと、 recording the position information at different sampling intervals in a storage unit according to the traveling mode of the work vehicle;
をプロセッサーに実行させるための位置情報記録プログラムであって、 A location information recording program for causing a processor to execute
前記位置情報の記録に際して、前記作業車両の走行態様の切り替え前又は切り替え後の特定期間については、当該走行態様の切り替え前後の前記走行態様各々に対応する前記サンプリング間隔のうち短い方のサンプリング間隔の前記位置情報を前記記憶部に記録する、 When recording the position information, for a specific period before or after switching the travel mode of the work vehicle, the sampling interval corresponding to each of the travel modes before and after the switching of the travel mode is set to the shorter sampling interval. recording the position information in the storage unit;
位置情報記録プログラム。 Location information recording program.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020032529A JP7305581B2 (en) | 2020-02-28 | 2020-02-28 | Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020032529A JP7305581B2 (en) | 2020-02-28 | 2020-02-28 | Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021132598A JP2021132598A (en) | 2021-09-13 |
| JP7305581B2 true JP7305581B2 (en) | 2023-07-10 |
Family
ID=77659512
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020032529A Active JP7305581B2 (en) | 2020-02-28 | 2020-02-28 | Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7305581B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7571071B2 (en) | 2022-02-21 | 2024-10-22 | ヤンマーホールディングス株式会社 | Work area management method, work area management system, and work area management program |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050066738A1 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2005-03-31 | Moore Mark Ramon | Mapping techniques |
| JP2010009443A (en) | 2008-06-30 | 2010-01-14 | Nissan Diesel Motor Co Ltd | Onboard device, and vehicle operation control system using the same |
| JP2016183936A (en) | 2015-03-26 | 2016-10-20 | 株式会社ゼンリンデータコム | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP2019091353A (en) | 2017-11-16 | 2019-06-13 | ヤンマー株式会社 | Information acquisition device and information management system |
| JP2019162053A (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | ヤンマー株式会社 | Field registration device |
-
2020
- 2020-02-28 JP JP2020032529A patent/JP7305581B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050066738A1 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2005-03-31 | Moore Mark Ramon | Mapping techniques |
| JP2010009443A (en) | 2008-06-30 | 2010-01-14 | Nissan Diesel Motor Co Ltd | Onboard device, and vehicle operation control system using the same |
| JP2016183936A (en) | 2015-03-26 | 2016-10-20 | 株式会社ゼンリンデータコム | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP2019091353A (en) | 2017-11-16 | 2019-06-13 | ヤンマー株式会社 | Information acquisition device and information management system |
| JP2019162053A (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | ヤンマー株式会社 | Field registration device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021132598A (en) | 2021-09-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6924542B2 (en) | Information acquisition device and information management system | |
| JP7305581B2 (en) | Location information recording device, work vehicle, location information recording method, location information recording program | |
| US20210263523A1 (en) | Autonomous work machine, method of controlling the same, and storage medium | |
| WO2022130945A1 (en) | Automatic traveling system, automatic traveling method, and automatic traveling program | |
| US20230070542A1 (en) | Automatic Traveling Method, Automatic Traveling System, And Automatic Traveling Program | |
| US20240103527A1 (en) | Automatic traveling system, automatic traveling method, and automatic traveling program | |
| EP4094555A1 (en) | Bale retriever that generates driveable path for efficiency and to reduce compaction | |
| WO2022118773A1 (en) | Automatic traveling system, automatic traveling method, and automatic traveling program | |
| EP4029365A1 (en) | Agricultural vehicle with controller for determining sufficiently sized bale drop zone | |
| CN116419667A (en) | Autonomous traveling system, autonomous traveling method, and autonomous traveling program | |
| JP7492469B2 (en) | Autonomous driving method, automatic driving system, and automatic driving program | |
| JP2020119379A (en) | Management device, and control method and program for management device | |
| JPWO2020161856A1 (en) | Work equipment, work equipment control methods, and programs | |
| US20240012414A1 (en) | Route generation method, route generation system, and route generation program | |
| EP4388848A1 (en) | System and method for operating a mowing implement having sensors that track a mowing operation | |
| US20240096137A1 (en) | Display method, display terminal, and display program | |
| US20230026246A1 (en) | Travel Control Method, Travel Control System, And Travel Control Program | |
| WO2024179273A1 (en) | Control method, apparatus, and vehicle | |
| WO2022102366A1 (en) | Work region setting system, work region setting method, and work region setting program | |
| US20240085906A1 (en) | Travel Control Method, Travel Control System, And Travel Control Program | |
| CN116867357A (en) | Harvester | |
| KR20230122972A (en) | Field registering method, field registering system, and field registering program | |
| JP2023078841A (en) | Automatic travel method, automatic travel system, and automatic travel program | |
| JP2022061394A (en) | Autonomous traveling system, autonomous traveling method, and autonomous traveling program | |
| JP2023127874A (en) | Automatic travelling method, automatic travelling system, and automatic travelling program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20201013 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20220225 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20221130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20221206 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20230127 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230221 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20230620 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20230628 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7305581 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |