JP7157990B1 - Electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls - Google Patents
Electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7157990B1 JP7157990B1 JP2022552495A JP2022552495A JP7157990B1 JP 7157990 B1 JP7157990 B1 JP 7157990B1 JP 2022552495 A JP2022552495 A JP 2022552495A JP 2022552495 A JP2022552495 A JP 2022552495A JP 7157990 B1 JP7157990 B1 JP 7157990B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- grinding
- grinding wheel
- electrolytic dressing
- power supply
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims abstract description 40
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 40
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 25
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 32
- 238000011900 installation process Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 25
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 14
- 229910000997 High-speed steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000006061 abrasive grain Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000005097 cold rolling Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005098 hot rolling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001208 Crucible steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001315 Tool steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Vinyl chloride Chemical compound ClC=C BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003082 abrasive agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005275 alloying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005868 electrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000601 superalloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23H—WORKING OF METAL BY THE ACTION OF A HIGH CONCENTRATION OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ON A WORKPIECE USING AN ELECTRODE WHICH TAKES THE PLACE OF A TOOL; SUCH WORKING COMBINED WITH OTHER FORMS OF WORKING OF METAL
- B23H3/00—Electrochemical machining, i.e. removing metal by passing current between an electrode and a workpiece in the presence of an electrolyte
- B23H3/04—Electrodes specially adapted therefor or their manufacture
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23H—WORKING OF METAL BY THE ACTION OF A HIGH CONCENTRATION OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ON A WORKPIECE USING AN ELECTRODE WHICH TAKES THE PLACE OF A TOOL; SUCH WORKING COMBINED WITH OTHER FORMS OF WORKING OF METAL
- B23H9/00—Machining specially adapted for treating particular metal objects or for obtaining special effects or results on metal objects
- B23H9/04—Treating surfaces of rolls
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B53/00—Devices or means for dressing or conditioning abrasive surfaces
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Electrical Discharge Machining, Electrochemical Machining, And Combined Machining (AREA)
- Grinding-Machine Dressing And Accessory Apparatuses (AREA)
Abstract
鋼製ロールの円筒研削に適した電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法を提供する。圧延用の鋼製ロールの研削加工に用いる導電性の研削砥石と、研削砥石と間隙をもって対向する電極と、研削砥石及び電極に給電する電源と、を備え、研削砥石と電極との間の間隙に導電性の研削液を供給して研削加工中の研削砥石の表面に付着した鋼製ロールの研削粉を電解除去する電解ドレッシング装置であって、電極は、研削砥石に対向する面が金属製の薄板で構成され、研削砥石に対向する面以外の部分が絶縁材料で構成される。Provided are an electrolytic dressing device and an electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls. Equipped with a conductive grinding wheel used for grinding a steel roll for rolling, an electrode facing the grinding wheel with a gap, and a power supply for supplying power to the grinding wheel and the electrode, the gap between the grinding wheel and the electrode An electrolytic dressing device that supplies a conductive grinding fluid to the electrode to electrolytically remove the grinding powder of the steel roll adhering to the surface of the grinding wheel during grinding, wherein the electrode has a metal surface facing the grinding wheel and a portion other than the surface facing the grinding wheel is made of an insulating material.
Description
本発明は、圧延用の鋼製ロールの円筒研削に適した電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an electrolytic dressing apparatus and an electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls for rolling.
鋼製圧延ロールには鋳鋼、工具鋼(ダイス鋼、ハイス鋼)などの種類がある。熱い素材を圧延する熱間圧延は素材が加熱され高温のため軟らかい。熱間圧延は高温の間にできるだけ素材を潰して板厚を下げるのを目的とする。熱間圧延には大径の鋳鋼ロールが使用される。熱間圧延後は板やコイルの形状になり、厚板製品となる。熱間圧延後の厚板製品を、薄板や薄帯の製品にするための圧延が冷間圧延である。板やコイルは既に冷却されており室温になっている。素材は高温より室温の方が高強度で圧延に要する力も大きい。冷間圧延に使われるロールは素材の強度に負けない、より高強度の鋼で造られる。そのため、ダイス鋼やハイス鋼といった高合金の工具鋼も使用される。高合金とすることでロールはより高強度と強靭性が付与され、高強度材の圧延を可能とする。特に高強度のステンレス鋼などの磨き帯鋼はバネなどに使用されるもので、代表的な高硬度の材料と言える。これを冷間圧延するためには高合金のハイス鋼ロールが適しているが、繰り返し冷間圧延するには定期的に再研削が必要となる。しかしながら、ハイス鋼は高強度かつ強靭性なので、再研削は難加工工程となっている。 Steel rolling rolls include types such as cast steel and tool steel (die steel, high-speed steel). Hot rolling, which rolls a hot material, heats the material to a high temperature and makes it soft. The purpose of hot rolling is to reduce the sheet thickness by crushing the material as much as possible while it is still hot. Large diameter cast steel rolls are used for hot rolling. After hot rolling, it becomes a plate or coil, and becomes a thick plate product. Cold rolling is the process of rolling hot-rolled thick plate products into thin plates and ribbon products. The plates and coils are already cooled and at room temperature. The strength of the material is higher at room temperature than at high temperature, and the force required for rolling is greater. The rolls used for cold rolling are made of higher strength steel that is as strong as the raw material. Therefore, high-alloy tool steels such as die steels and high-speed steels are also used. The high alloy gives the rolls higher strength and toughness, making it possible to roll high-strength materials. In particular, polished strip steel such as high-strength stainless steel is used for springs and the like, and can be said to be a representative high-hardness material. High-alloy high-speed steel rolls are suitable for cold-rolling this, but repeated cold-rolling requires periodic regrinding. However, since high-speed steel has high strength and toughness, regrinding is a difficult process.
鋼製ロールで板や帯の素材を圧延すると素材とロールが接触する面には跡が残る。この跡をそのままにしておけば引き続き圧延される素材に形状不良や疵が発生し不具合となる。そのためロールは定期的に再研削される。しかしながらダイス鋼やハイス鋼は高強度、強靭性のため研削砥石表面にロール研削粉が付着して目詰まりを起こしやすく、研削が難くなる。これにより、1本のロールを研削するのに長時間を要する課題が存在していた。研削性が悪いと研削効率が下がり、結果として板や帯の生産効率も落ちる。特にダイス鋼よりも添加合金元素数と添加量の多いハイス鋼は、上述のように素材自体が高強度のステンレス鋼の薄板や薄帯を製造する際の圧延に用いられることが多い。ハイス鋼ロールにより圧延すれば、圧延後の板や帯の表面性状が良く、美麗な外観を得ることができる。しかし上述のようにハイス鋼ロールは研削性が悪いため、ダイス鋼と比べて使用される頻度が低く、ハイス鋼ロールが普及する上での課題となっている。圧延ロールの再研削の工程を改善することで、金属の板、帯の製品の品質を向上させることにもつながる。 Rolling a plate or band material with steel rolls leaves marks on the surface where the material and the roll come into contact. If this mark is left as it is, the material that is subsequently rolled will have a shape defect or a flaw, resulting in a problem. The rolls are therefore regularly reground. However, since die steel and high-speed steel have high strength and toughness, roll grinding powder tends to adhere to the surface of the grinding wheel, causing clogging and making grinding difficult. As a result, there is a problem that it takes a long time to grind one roll. If the grindability is poor, the grinding efficiency decreases, and as a result, the production efficiency of plates and strips also decreases. In particular, high-speed steel, which contains more alloying elements and amounts than die steel, is often used for rolling when producing high-strength stainless steel sheets and strips, as described above. By rolling with high-speed steel rolls, the rolled sheet or strip has good surface properties and a beautiful appearance. However, as described above, high-speed steel rolls have poor grindability and are used less frequently than die steel. Improving the process of regrinding the rolling rolls leads to improving the quality of metal plate and band products.
上述の研削性を向上する技術として、研削加工と同時に(インプロセスで)砥石の表面を電解ドレッシングする技術が存在する。従来の電解ドレッシング装置の典型的な構成を示したのが図7である。また、例えば、特許文献1に開示される技術も存在する。特許文献1に開示される研削加工装置は、ワークを研削加工する砥石と、砥石の研削面と研削液を介在させる間隙を隔てて電極面が対向する電解ドレッシング用電極と、研削液を介在して砥石と電解ドレッシング用電極とを通電する電源とを備え、砥石の表面を電解ドレッシングしつつワークを研削加工するものである。しかしながら、特許文献1に開示されるような従来の技術は、砥石そのものを電解ドレッシングするものであり、砥石の表面に付着した研削粉を電解により除去するものではなかった。 As a technique for improving the above-described grindability, there is a technique for performing electrolytic dressing (in-process) on the surface of the grindstone at the same time as the grinding process. FIG. 7 shows a typical configuration of a conventional electrolytic dressing device. Also, for example, there is a technique disclosed in Patent Document 1. The grinding apparatus disclosed in Patent Document 1 includes a grindstone for grinding a workpiece, an electrode for electrolytic dressing in which the electrode surface is opposed to the grinding surface of the grindstone with a gap for interposing the grinding fluid, and the grinding fluid is interposed. The machine is equipped with a power supply for energizing the grindstone and the electrode for electrolytic dressing, and grinds the workpiece while electrolytically dressing the surface of the grindstone. However, the conventional technique disclosed in Patent Document 1 is for electrolytically dressing the grindstone itself, and is not for electrolytically removing the grinding powder adhering to the surface of the grindstone.
また、図7に示されるような従来の電解ドレッシング装置に用いられる電極は金属製のブロックであったため、重量があるために製作性、可搬性や設置性が悪く、高いコストも要していた。 In addition, since the electrodes used in the conventional electrolytic dressing apparatus as shown in FIG. 7 are metal blocks, they are heavy and therefore have poor manufacturability, portability, and installation properties, and require high costs. .
そこで、本発明は、鋼製ロールの円筒研削に適した電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法を提供することを目的とする。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide an electrolytic dressing apparatus and an electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls.
上記の課題を解決するために、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置は、圧延用の鋼製ロールの研削加工に用いる導電性の研削砥石と、研削砥石と間隙をもって対向する電極と、研削砥石及び電極に給電する電源と、を備え、研削砥石と電極との間の間隙に導電性の研削液を供給して研削加工中の研削砥石の表面に付着した鋼製ロールの研削粉を電解除去する電解ドレッシング装置であって、電極は、研削砥石に対向する面が金属製の薄板で構成され、研削砥石に対向する面以外の部分が絶縁材料で構成される。 In order to solve the above problems, the electrolytic dressing apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductive grinding wheel used for grinding steel rolls for rolling, an electrode facing the grinding wheel with a gap, and a grinding wheel and the electrode. and an electrolysis that supplies a conductive grinding fluid to the gap between the grinding wheel and the electrode to electrolytically remove the grinding powder of the steel roll adhering to the surface of the grinding wheel during grinding. In the dressing device, the surface of the electrode facing the grinding wheel is made of a thin metal plate, and the portion other than the surface facing the grinding wheel is made of an insulating material.
電極は、その内部が中空に構成され、薄板は、複数の微小な研削液供給孔を備え、研削液は、電極の内部及び研削液供給孔を通過して間隙に供給されても良い。 The electrode may have a hollow interior, the thin plate may have a plurality of minute grinding fluid supply holes, and the grinding fluid may be supplied to the gap through the inside of the electrode and the grinding fluid supply holes.
電極の内部は、少なくとも一つの隔壁によって分割されており、研削液供給孔は、その孔径が、隔壁によって大きく分割された電極の内部に対応する研削液供給孔と、隔壁によって小さく分割された電極の内部に対応する研削液供給孔とで異なるように形成されても良い。 The inside of the electrode is divided by at least one partition wall, and the grinding liquid supply hole has a hole diameter corresponding to the inside of the electrode largely divided by the partition wall, and the electrode is divided into small parts by the partition wall. may be formed differently from the corresponding grinding liquid supply holes.
上述の電極を第1電極としたときに、第1電極とは異なる位置に研削砥石と間隙をもって対向するようにして、第1電極と同じ電極を第2電極として更に備え、電源は、研削砥石に代えて第2電極に給電しても良い。 When the above electrode is used as the first electrode, the same electrode as the first electrode is further provided as a second electrode so as to face the grinding wheel at a position different from the first electrode with a gap, and the power source is the grinding wheel. Alternatively, power may be supplied to the second electrode.
どちらか一方の電極が、研削砥石の鉛直上方に設けられても良い。 Either one of the electrodes may be provided vertically above the grinding wheel.
どちらか一方の電極が、研削砥石の鉛直下方に設けられても良い。 Either one of the electrodes may be provided vertically below the grinding wheel.
アウターレースが給電線によって電源と電気的に接続される導電性を備えたベアリングを更に備え、ベアリングは、研削砥石の軸に通電可能に固定され、ベアリングを介して電源から研削砥石に給電しても良い。 The bearing further comprises a conductive bearing, the outer race of which is electrically connected to the power supply by a power supply line, the bearing being electrically fixed to the shaft of the grinding wheel, and the power supply supplying power to the grinding wheel through the bearing. Also good.
研削砥石のボンド材は、レジンボンド材に金属ファイバーを含有させて通電性を付与したメタルレジンボンド材でも良い。 The bond material of the grinding wheel may be a metal resin bond material obtained by adding metal fibers to the resin bond material to impart electrical conductivity.
研削砥石は、その番手が♯400から♯2,000のものでも良い。 The grinding wheel may have a count of #400 to #2,000.
研削砥石は、その砥粒がCBN砥粒でも良い。 The abrasive grains of the grinding wheel may be CBN abrasive grains.
薄板は、その円弧長が研削砥石の円周長の15パーセントを超えても良い。 The slats may have an arc length greater than 15 percent of the circumference of the grinding wheel.
また、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング方法は、圧延用の鋼製ロールの研削加工に用いる導電性の研削砥石と、研削砥石と間隙をもって対向する電極との間の間隙に導電性の研削液を供給し、研削砥石と電極とに電源より給電して、研削加工中の研削砥石の表面に付着した鋼製ロールの研削粉を電解除去する電解ドレッシング方法であって、電極は、研削砥石に対向する面が複数の微小な研削液供給孔を備える金属製の薄板で構成され、研削砥石に対向する面以外の部分が絶縁材料で中空に構成されており、研削液を、電極の内部及び研削液供給孔を通して間隙に供給する研削液供給工程を備える。 In addition, the electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention supplies a conductive grinding fluid to the gap between a conductive grinding wheel used for grinding a steel roll for rolling and an electrode facing the grinding wheel with a gap. An electrolytic dressing method for electrolytically removing grinding powder from a steel roll adhering to the surface of the grinding wheel during grinding by supplying power to the grinding wheel and the electrode from a power supply, wherein the electrode faces the grinding wheel. The surface is composed of a thin metal plate with a plurality of minute grinding fluid supply holes, and the part other than the surface facing the grinding wheel is hollow with an insulating material, and the grinding fluid is supplied to the inside of the electrode and the grinding fluid. A grinding liquid supply step of supplying the grinding fluid to the gap through the supply hole is provided.
上述の電極を第1電極としたときに、第1電極とは異なる位置に、研削砥石と間隙をもって対向するようにして、第1電極と同じ電極を第2電極として設置する第2電極設置工程と、研削砥石への給電を第2電極への給電に切り替える給電切替工程と、を更に備えても良い。 When the above electrode is used as the first electrode, a second electrode installation step of installing the same electrode as the first electrode as the second electrode at a position different from the first electrode so as to face the grinding wheel with a gap. and a power supply switching step of switching power supply to the grinding wheel to power supply to the second electrode.
アウターレースが給電線によって電源と電気的に接続される導電性を備えたベアリングを準備する給電用ベアリング準備工程と、ベアリングを、研削砥石の軸に通電可能に設ける給電用ベアリング設置工程と、を更に備え、ベアリングを介して電源から砥石に給電しても良い。 a feed bearing preparation step of preparing a conductive bearing whose outer race is electrically connected to a power supply by a feed line; In addition, power may be supplied to the grindstone from a power source through the bearing.
本発明によれば、鋼製ロールの円筒研削に適した電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法を提供できる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the electrolytic dressing apparatus and electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of a steel roll can be provided.
以下、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法を説明する。なお、各図を通して、同一の参照符号が付されているものは、同一または同等のものである。 An electrolytic dressing apparatus and an electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention will be described below. It should be noted that, throughout each figure, the same reference numerals denote the same or equivalent parts.
まず、本発明の第一実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置100について説明する。
First, an
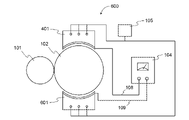
図1は、本発明の第一実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置100の構成を示した図である。電解ドレッシング装置100は、研削砥石102と、電極103と、電源104とを備えている。なお、参照符号101は圧延用の鋼製ロールである。また、参照符号105は研削液供給源(タンク)、参照符号106は研削液を吐出するノズルであり、チューブ(ホース)によって研削液供給源(タンク)に接続されている。
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the configuration of an
研削砥石102は、鋼製ロール101の研削加工に用いる円柱状の導電性の砥石であり、図示しない円筒研削盤等の装置に支持された回転軸によって回転駆動される。研削砥石102のボンド材としては既存の種々のものが適用可能だが、メタルボンドは硬いために鋼製ロールと反発し合い、鋼製ロールの表面にタタキのような欠陥が生じる場合がある。そのため、研削砥石102のボンド材としては、レジンボンド材に金属ファイバーを含有させて通電性(導電性)を付与したメタルレジンボンド材が好適である。研削砥石102の番手としては既存の種々の番手が適用可能だが、本願出願人が鋭意実験した結果、♯200から♯4,000の範囲、より限定するならば#400から#2,000の範囲が好適であるとの知見を得た。なお、本明細書に記載する番手(粒度)は、JIS R 6001-1:2017(研削といし用研削材の粒度-第1部:粗粒)及びJIS R 6001-2:2017(研削といし用研削材の粒度-第2部:微粉)、並びに、研削砥石を製造及び販売する業界で通常使用されている表記に従う又は準ずる。研削砥石102の砥粒としては既存の種々の種類が適用可能だが、本願出願人が鋭意実験した結果、CBNが好適であるとの知見を得た。
The
電極103は、研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉を電解除去するための電極である。電極103は、図示されるようにブロック状であって、断面円弧状の電極面を備えている。この電極面は、研削砥石102の外周面と対向する長い矩形で、且つ、研削砥石102の外周面との間に導電性の研削液の介在を許容する間隙、例えば0.5mmから7.0mm程度の間隙が形成されるように円筒内周面状に形成されている。なお、図1では電極103が研削砥石102の横に並ぶようにして設けられた状態を示しているが、電極103を設ける位置はこれに限定されない。
The
ここで、図2A乃至図2Cを参照しながら、電極103について更に説明する。図2Aは電極103の正面図であり、図2Bは電極103の側面図であり、図2Cは電極103のA-A線断面図である。図示されるように、電極103は、研削砥石102に対向する面、即ち断面円弧状の電極面が、金属製の薄板201によって構成されている。また、電極103は、研削砥石102に対向する面以外の部分が、絶縁材料200で構成されている。薄板201の具体的な素材としては、チタン、銅など種々の金属が適用可能である。薄板201の巾(図2Bにおける横方向の幅)は、研削砥石102の巾と同じかそれ以上であることが好ましい。絶縁材料200の具体的な材料としては、例えば塩化ビニル、ポリカーボネートなど種々のプラスチックが適用可能である。電極103を以上に述べた構成とすることで、全体が金属で構成されていた従来の電極と比較して大幅に軽量化される他、製作性、可搬性や設置性の向上やコストの削減の効果が得られる。なお、電極面の大きさについては特に限定されないが、本願出願人が鋭意実験した結果、電極面の周方向の長さ、即ち薄板201の円弧長が研削砥石102の円周長(外周長)の15パーセントを超える(即ち、周方向において薄板201が研削砥石102をカバーする比率が15パーセントを超える)場合に良好な効果が得られるとの知見を得た。
The
電源104は、研削条件に応じた適正な電圧、電流を研削砥石102及び電極103に供給(給電)する電源である。電源104としては、直流電源、直流パルス電源、交流電源、バイポーラ増幅器など種々の方式の電源が適用可能である。本実施形態では、電極103(薄板201)に対しては給電線(配線)108を介して、研削砥石102に対しては給電線(配線)109を介して給電が行われる。なお、研削砥石102に対しては、給電線109の先端に設けられるブラシによって給電が行われても良いが、後述する給電用のアタッチメント107(ベアリング301)を介して給電する形態とすれば、より安定して給電することができる。
The
次に、図3A及び図3Bを参照しながら、砥石102への安定した給電を可能とするアタッチメント107について説明する。図3Aはアタッチメント107の側面図であり、図3Bはアタッチメント107の正面図である。図示されるように、アタッチメント107は、主要部品としてベアリング301を備えており、また、ベアリング301を内部に収容するスリーブ300を備えている。ただし、スリーブ300は適宜省略しても良い。ベアリング301は導電性(通電性)を備えており、研削砥石102の軸(回転軸)に通電可能に固定されるものである。ベアリング301への導電性(通電性)の付与は、例えばベアリング301を組み立てる際に導電性(通電性)のグリスを用いることにより実現される。ベアリング301は、給電線(配線)109がアウターレースに対して固定されることにより、電源104と電気的に接続される。給電線(配線)109をアウターレースに対して固定する方法は特に限定されず、例えば参照符号302に示すような穴に給電線(配線)109を差し込んで固定する方法や、半田付けによってアウターレースに対して直接固定する方法が適用可能である。ベアリング301を介して研削砥石102に対して給電する形態とすることで、使用に伴って消耗するブラシによる給電と比較して、安定した給電が可能となる。また、廃棄部品の削減の効果も得られる。
Next, the
以上のとおり説明した電解ドレッシング装置100の動作について説明する。まず、鋼製ロール101の研削加工に用いる導電性の研削砥石102に対して、導電性の研削液の介在を許容する間隙をもって対向するようにして電極103を固定する。続いて、研削砥石102と電極103との間隙にノズル106から研削液を供給し、電源104より研削砥石102と電極103とに給電する。これにより、研削加工中の研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉が連続的に電解除去(電解ドレッシング)され、研削砥石102の砥粒が鋼製ロール101と接する状態を保つことができ、研削性が向上する。なお、アウターレースが給電線(配線)109によって電源104と電気的に接続された導電性(通電性)のベアリング301を準備して研削砥石102の軸に通電可能に設け、ベアリング301を介して電源104から研削砥石102に給電すれば、安定した給電が可能となる。
The operation of the
次に、本発明の第二実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置400について説明する。
Next, an
図4は、本発明の第二実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置400の構成を示した図である。電解ドレッシング装置400は、研削砥石102と、電極401と、電源104とを備えている。鋼製ロール101、研削砥石102、電源104、研削液供給源(タンク)105、アタッチメント107、給電線(配線)108及び給電線(配線)109は、第一実施形態と同様である。
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the configuration of an
電極401は、研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉を電解除去するための電極である。電極401は、図示されるようにブロック状であって、断面円弧状の電極面を備えている。この電極面は、研削砥石102の外周面と対向する長い矩形で、且つ、研削砥石102の外周面との間に導電性の研削液の介在を許容する間隙、例えば0.5mmから7.0mm程度の間隙が形成されるように円筒内周面状に形成されている。なお、図4では電極401が研削砥石102の横に並ぶようにして設けられた状態を示しているが、電極401を設ける位置はこれに限定されない。
The
次に、図5A乃至図5Cを参照しながら、電極401について更に説明する。図5Aは電極401の正面図であり、図5Bは電極401の側面図であり、図5Cは電極401のB-B線断面図である。図示されるように、電極401は、研削砥石102に対向する面、即ち断面円弧状の電極面が、金属製の薄板502によって構成されている。また、電極401は、研削砥石102に対向する面以外の部分が、絶縁材料500で構成されている。薄板502の具体的な素材としては、チタン、銅など種々の金属が適用可能である。薄板502の巾(図5Bにおける横方向の幅)は、研削砥石102の巾と同じかそれ以上であることが好ましい。絶縁材料500の具体的な材料としては、例えば塩化ビニル、ポリカーボネートなど種々のプラスチックが適用可能である。電極401を以上に述べた構成とすることで、全体が金属で構成されていた従来の電極と比較して大幅に軽量化される他、製作性、可搬性や設置性の向上やコストの削減の効果が得られる。なお、電極面の大きさについては特に限定されないが、本願出願人が鋭意実験した結果、電極面の周方向の長さ、即ち薄板502の円弧長が研削砥石102の円周長(外周長)の15パーセントを超える(即ち、周方向において薄板502が研削砥石102をカバーする比率が15パーセントを超える)場合に良好な効果が得られるとの知見を得た。
The
ここで、電極401は、その内部504が中空に構成されている点、研削液導入口501が絶縁材料500に少なくとも一つ設けられている点及び薄板502に複数の微小な研削液供給孔503が設けられている点が、第一実施形態に係る電極103と異なっている。研削液導入口501は、電極401の内部504に研削液を導入するための開口であり、チューブ(ホース)によって研削液供給源(タンク)に接続されている。なお、電極401においては研削液導入口501が正面に設けられているが、背面など他の面に設けられても良い。電極401を以上に述べた構成とすることで、電極401の内部504及び研削液供給孔503を通過して、研削砥石102と電極401との間隙に研削液が均一に供給される(研削液供給工程)。これにより、電極面における研削液の流れの局所的な不均一が解消され、研削砥石102の表面性状を一定に保つことができる。なお、電極401を図4に示すような位置に設けるときは、下方の研削液供給孔503ほど孔径を小さく(上方の研削液供給孔503ほど孔径を大きく)することができる。下方の研削液供給孔503ほど孔径を小さくすることで、下方から上方にかけての研削液の供給の不均一を解消することができる。
Here, the
また、電極401は、図5Dに示すような形態とすることもできる。即ち、電極401の内部504に、内部504を分割する隔壁505を少なくとも一つ設けることができる。電極401の内部504に隔壁505を設けることで、電極401の剛性を高めることができる他、研削液導入口501より導入された研削液を、電極401の内部504においてバランスよく分布させることができる。また、隔壁505によって電極401の内部504が異なる大きさ(容積)に分割されるときは、隔壁505によって大きく分割された内部504(504L)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503L)と、隔壁505によって小さく分割された内部504(504S)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503S)とで、研削液供給孔503の孔径を異なる大きさとすることができる。例えば、隔壁505によって大きく分割された内部504(504L)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503L)を小さな孔径とし、隔壁505によって小さく分割された内部504(504S)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503S)を大きな孔径とすることができる。この反対も可能である。電極401を設ける位置、向きや角度、研削液の粘度などの条件に応じて、隔壁505によって大きく分割された内部504(504L)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503L)と隔壁505によって小さく分割された内部504(504S)に対応する研削液供給孔503(503S)とで研削液供給孔503の孔径を異なる大きさとすることで、研削砥石102と電極401との間隙への研削液の供給の不均一を解消することができる。
以上のとおり説明した本発明の第二実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置400によれば、研削加工中の研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉が連続的に電解除去(電解ドレッシング)され、研削砥石102の砥粒が鋼製ロール101と接する状態を保つことができ、研削性が向上する。なお、本発明の第一実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置100と同様に、アウターレースが給電線(配線)109によって電源104と電気的に接続された導電性(通電性)のベアリング301を準備して研削砥石102の軸に通電可能に設け、ベアリング301を介して電源104から研削砥石102に給電すれば、安定した給電が可能となる。
According to the
次に、本発明の第三実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置600について説明する。
Next, an
図6Aは、本発明の第三実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置600の構成を示した図である。電解ドレッシング装置600は、研削砥石102と、電極401と、電極601と、電源104とを備えている。電極401は、第一実施形態と同様である。また、鋼製ロール101、研削砥石102、電源104、研削液供給源(タンク)105及び給電線(配線)108は、第一実施形態と同様である。
FIG. 6A is a diagram showing the configuration of an
電極401は、研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉を電解除去するための電極(第1電極)である。電極401の構成は第二実施形態と同様である。なお、図6Aでは電極401が研削砥石102の横に並ぶようにして設けられた状態を示しているが、電極401を設ける位置はこれに限定されない。また、本実施形態では第二実施形態に係る電極401を第1電極としているが、第1電極は、第一実施形態に係る電極103でも良い。
The
電極601は、第1電極としての電極401と同じ構成からなる電極(第2電極)である。第2電極としての電極601は、第1電極としての電極401とは異なる位置に、研削砥石102と間隙をもって対向するように設けられている(第2電極設置工程)。なお、図6Aでは電極601が研削砥石102の鉛直下方に設けられた状態を示しているが、電極601を設ける位置はこれに限定されない。
The
本発明の第三実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置600では、電源104は給電線(配線)109を介して、研削砥石102に代えて電極601(第2電極)に給電する(給電切替工程)。
In the
以上のとおり説明した本発明の第三実施形態に係る電解ドレッシング装置600によれば、研削加工中の研削砥石102の表面に付着した鋼製ロール101の研削粉が連続的に電解除去(電解ドレッシング)され、研削砥石102の砥粒が鋼製ロール101と接する状態を保つことができ、研削性が向上する。また、電源104からの給電先を電極401(第1電極)及び電極601(第2電極)としたことで、回転駆動する研削砥石102に対してのブラシによる直接的な給電やベアリング301を介しての給電が不要となる。
According to the
ここで、電極401(第1電極)及び電極601(第2電極)を設ける位置は特に限定されないが、どちらか一方の電極を研削砥石102の鉛直下方に設けることとすれば、研削砥石102の周囲の空間を圧迫することがなく、また、電極を置くだけで容易に設置することができる。また、図6Bに示す変形例のように、どちらか一方の電極を研削砥石102の鉛直上方に設けることとすれば、言うなればシャワーのように重力を利用して、研削砥石102と電極との間隙に研削液を効率良く供給することができる。
Here, the positions where the electrode 401 (first electrode) and the electrode 601 (second electrode) are provided are not particularly limited. It does not occupy the surrounding space and can be easily installed just by placing the electrodes. Also, if one of the electrodes is provided vertically above the
以上、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上記の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の改変が可能である。 Although the preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described above, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various modifications are possible without departing from the scope of the present invention.
例えば、研削液が流れることができる細かい溝を電極面に形成し、研削液供給孔503から供給された研削液が溝を伝って電極面の全体に行き届くようにすることができる。これにより、研削砥石と電極との間隙への研削液の供給の均一性がより高まる。
For example, fine grooves through which the grinding liquid can flow can be formed on the electrode surface so that the grinding liquid supplied from the grinding
本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法によれば、ハイス鋼の圧延ロールへの使用頻度が拡大し、高機能表面を有する板および帯の製造の難易度が下がる。また、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法は、工具鋼以外の高機能ロール(例えば超硬ロールやセラミックロール)への応用も可能である。また、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法によれば、ステンレス鋼などの高硬度、強靭性の材料を冷間圧延する場面において表面品質の向上が可能となる他、ステンレス鋼以外の高硬度、強靭性の材料を冷間圧延する可能性が拡大し、ステンレス鋼以外の高硬度、強靭性の材料の用途が拡大する。また、本発明に係る電解ドレッシング装置及び電解ドレッシング方法によれば、鋼よりも高強度、高靭性の材料(例えば超合金)を熱間圧延ロールの材料として利用する可能性が生じる。 According to the electrolytic dressing apparatus and the electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention, the frequency of use of high-speed steel rolling rolls is increased, and the difficulty of manufacturing plates and strips having high-performance surfaces is reduced. The electrolytic dressing apparatus and electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention can also be applied to high-performance rolls other than tool steel (for example, cemented carbide rolls and ceramic rolls). In addition, according to the electrolytic dressing apparatus and the electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention, it is possible to improve the surface quality when cold-rolling a material with high hardness and toughness such as stainless steel. Possibilities for cold rolling hard and tough materials will expand, and applications of hard and tough materials other than stainless steel will expand. Further, according to the electrolytic dressing apparatus and the electrolytic dressing method according to the present invention, there arises a possibility of using a material (for example, a superalloy) having higher strength and toughness than steel as the material of the hot rolling rolls.
100 電解ドレッシング装置
101 鋼製ロール
102 研削砥石
103 電極(第1電極)
104 電源
105 研削液供給源(タンク)
106 ノズル
107 アタッチメント
108 給電線(配線)
109 給電線(配線)
200 絶縁材料
201 薄板
300 スリーブ
301 ベアリング
302 穴
400 電解ドレッシング装置
401 電極(第1電極)
500 絶縁材料
501 研削液導入口
502 薄板
503 研削液供給孔
503L 研削液供給孔
503S 研削液供給孔
504 内部(内部空間)
504L 内部(内部空間)
504S 内部(内部空間)
505 隔壁
600 電解ドレッシング装置
601 電極(第2電極)
700 電解ドレッシング装置
701 電極
702 直流電源
703 給電線(配線)
704 給電線(配線)100
104
106
109 feed line (wiring)
200 insulating
500 insulating
504L inside (internal space)
504S inside (internal space)
505
700
704 power supply line (wiring)
Claims (1)
前記電極は、前記研削砥石に対向する面が複数の微小な研削液供給孔を備える金属製の薄板で構成され、前記研削砥石に対向する面以外の部分が絶縁材料で中空に構成されており、
前記研削液を、前記電極の内部及び前記研削液供給孔を通して前記間隙に供給する研削液供給工程と、
前記電極を第1電極としたときに、該第1電極とは異なる位置に、前記研削砥石と間隙をもって対向するようにして、該第1電極と同じ電極を第2電極として設置する第2電極設置工程と、
前記研削砥石への給電を前記第2電極への給電に切り替える給電切替工程と、を備える、
電解ドレッシング方法。 A conductive grinding fluid is supplied to the gap between a conductive grinding wheel used for grinding a steel roll for rolling and an electrode facing the grinding wheel with a gap, and the grinding wheel and the electrode are separated. is powered from a power supply to electrolytically remove grinding powder of the steel roll adhering to the surface of the grinding wheel during the grinding process,
The surface of the electrode facing the grinding wheel is composed of a thin metal plate having a plurality of fine grinding liquid supply holes, and the portion other than the surface facing the grinding wheel is hollow with an insulating material. ,
a grinding liquid supply step of supplying the grinding liquid to the gap through the interior of the electrode and the grinding liquid supply hole ;
When the electrode is used as the first electrode, a second electrode that is the same electrode as the first electrode is provided as a second electrode at a position different from the first electrode so as to face the grinding wheel with a gap. an installation process;
a power supply switching step of switching power supply to the grinding wheel to power supply to the second electrode;
Electrolytic dressing method.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/025493 WO2024003977A1 (en) | 2022-06-27 | 2022-06-27 | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suited for cylindrical grinding of steel roll |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP7157990B1 true JP7157990B1 (en) | 2022-10-21 |
| JPWO2024003977A1 JPWO2024003977A1 (en) | 2024-01-04 |
| JPWO2024003977A5 JPWO2024003977A5 (en) | 2024-06-04 |
Family
ID=83691982
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022552495A Active JP7157990B1 (en) | 2022-06-27 | 2022-06-27 | Electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7157990B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN118401344A (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI837030B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2024003977A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7374542B1 (en) * | 2023-03-10 | 2023-11-07 | 株式会社シントク | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS468783Y1 (en) * | 1967-06-23 | 1971-03-29 | ||
| JPS5932315A (en) * | 1982-08-12 | 1984-02-21 | 株式会社 サタケ | Cord reel |
| JPH01175160U (en) * | 1988-05-26 | 1989-12-13 | ||
| JPH07132458A (en) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-23 | Nippon Steel Corp | Grinding wheel dressing method |
| JPH0733554U (en) * | 1993-12-10 | 1995-06-20 | セイコー精機株式会社 | Electrode for electrolytic in-process dressing |
| JP2001252869A (en) * | 2000-03-09 | 2001-09-18 | Inst Of Physical & Chemical Res | Removable electrode |
| KR101490745B1 (en) * | 2014-12-01 | 2015-02-06 | 주식회사 21세기 | A grinding apparatus for electrolytic in-process dressing |
| JP5932315B2 (en) | 2011-12-02 | 2016-06-08 | キヤノン株式会社 | Strobe device and camera system |
| JP2019021549A (en) * | 2017-07-20 | 2019-02-07 | 株式会社小糸製作所 | Lamp unit |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3214694B2 (en) * | 1997-12-02 | 2001-10-02 | 理化学研究所 | Dynamic pressure generating electrode |
| TWI669189B (en) * | 2018-10-23 | 2019-08-21 | 財團法人金屬工業研究發展中心 | Apparatus for grinding wheel chip removing and sharpening |
-
2022
- 2022-06-27 WO PCT/JP2022/025493 patent/WO2024003977A1/en active Application Filing
- 2022-06-27 JP JP2022552495A patent/JP7157990B1/en active Active
- 2022-06-27 CN CN202280083074.9A patent/CN118401344A/en active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-06-27 TW TW112123752A patent/TWI837030B/en active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS468783Y1 (en) * | 1967-06-23 | 1971-03-29 | ||
| JPS5932315A (en) * | 1982-08-12 | 1984-02-21 | 株式会社 サタケ | Cord reel |
| JPH01175160U (en) * | 1988-05-26 | 1989-12-13 | ||
| JPH07132458A (en) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-23 | Nippon Steel Corp | Grinding wheel dressing method |
| JPH0733554U (en) * | 1993-12-10 | 1995-06-20 | セイコー精機株式会社 | Electrode for electrolytic in-process dressing |
| JP2001252869A (en) * | 2000-03-09 | 2001-09-18 | Inst Of Physical & Chemical Res | Removable electrode |
| JP5932315B2 (en) | 2011-12-02 | 2016-06-08 | キヤノン株式会社 | Strobe device and camera system |
| KR101490745B1 (en) * | 2014-12-01 | 2015-02-06 | 주식회사 21세기 | A grinding apparatus for electrolytic in-process dressing |
| JP2019021549A (en) * | 2017-07-20 | 2019-02-07 | 株式会社小糸製作所 | Lamp unit |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7374542B1 (en) * | 2023-03-10 | 2023-11-07 | 株式会社シントク | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls |
| WO2024189672A1 (en) * | 2023-03-10 | 2024-09-19 | 株式会社シントク | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suited for cylindrical grinding of steel roll |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2024003977A1 (en) | 2024-01-04 |
| CN118401344A (en) | 2024-07-26 |
| TW202400331A (en) | 2024-01-01 |
| TWI837030B (en) | 2024-03-21 |
| WO2024003977A1 (en) | 2024-01-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Lim et al. | A fundamental study on the mechanism of electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding | |
| US7189145B2 (en) | Method of and apparatus for producing roll | |
| JP7157990B1 (en) | Electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls | |
| EP2270263B1 (en) | Stainless steel and surface treatment method for stainless steel | |
| JPS5854945B2 (en) | Satin electrical discharge machining equipment for roll-shaped workpieces | |
| Qian et al. | Cylindrical grinding of bearing steel with electrolytic in-process dressing | |
| JP7374542B1 (en) | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel rolls | |
| Hocheng et al. | The application of a turning tool as the electrode in electropolishing | |
| CN118946431A (en) | Electrolytic dressing device and electrolytic dressing method suitable for cylindrical grinding of steel roller | |
| JP2648999B2 (en) | Electrolytic compound polishing machine for cylindrical workpiece outer surface | |
| KR101900531B1 (en) | Method for producing steel | |
| JP4859538B2 (en) | Stainless steel sheet manufacturing method | |
| US3236009A (en) | Apparatus for surfacing | |
| JP3483866B2 (en) | Online rolling roll grinding method and apparatus and rolling mill train | |
| JPS6279954A (en) | Grinding method | |
| JP5394962B2 (en) | Grinding apparatus and grinding method | |
| Ohmori et al. | Highly efficient and precision fabrication of cylindrical parts from hard materials with the application of ELID (electrolytic in-process dressing) | |
| Sudiarso et al. | In-Process Electrical Dressing of Metal-Bonded Diamond Grinding Wheels. | |
| JPH0679314A (en) | Method and device for electric discharge machining roll surface | |
| JP2003181507A (en) | Control method for surface roughness of cold rolling work roll, cold rolling work roll, and material to be rolled | |
| KR100227089B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of stone finish materials | |
| JP2004042261A (en) | Grinding method and cold rolling method of rolling-mill roll | |
| JPH02218554A (en) | Inprocess electrolytic dressing method by plural electrodes | |
| KR950015117B1 (en) | Electroerosion machine having cylindrical aspects works | |
| JPH0866869A (en) | Segment grinding wheel unit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220831 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20220831 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20220831 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220930 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220930 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7157990 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |