JP7012394B1 - Turbine emergency stop control device - Google Patents
Turbine emergency stop control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7012394B1 JP7012394B1 JP2021004206A JP2021004206A JP7012394B1 JP 7012394 B1 JP7012394 B1 JP 7012394B1 JP 2021004206 A JP2021004206 A JP 2021004206A JP 2021004206 A JP2021004206 A JP 2021004206A JP 7012394 B1 JP7012394 B1 JP 7012394B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- port
- pipe
- solenoid valve
- valves
- port solenoid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000010720 hydraulic oil Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 42
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011835 investigation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005461 lubrication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Turbines (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】 タービンの回転速度の検出結果に基づいて動作する2oo3論理回路を採用した危急停止制御装置において、危急停止制御装置を停止させることなく、2oo3論理回路を構成する4ポート電磁弁を交換することを可能にする。【解決手段】 作動油の供給源に接続された第1のパイプ22Pと3個の4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のポートPとの間に開閉操作が可能な止め弁NV1P、NV2PおよびNV3Pを挿入し、回油部30に接続された第2のパイプ22Tと3個の4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のポートTとの間に開閉操作が可能な止め弁NV1T、NV2TおよびNV3Tを挿入した。【選択図】図1PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To replace a 4-port solenoid valve constituting a 2oo3 logic circuit in an emergency stop control device adopting a 2oo3 logic circuit which operates based on a detection result of a turbine rotation speed, without stopping the emergency stop control device. Make it possible. SOLUTION: Stop valves NV1P, NV2P and NV3P which can be opened and closed between a first pipe 22P connected to a hydraulic oil supply source and ports P of three 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3. The stop valves NV1T, NV2T and NV3T that can be opened and closed between the second pipe 22T connected to the oil turning unit 30 and the ports T of the three 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3. I inserted it. [Selection diagram] Fig. 1
Description
この発明は、発電設備等に用いられるタービンの危急停止制御装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an emergency stop control device for a turbine used in a power generation facility or the like.
タービンを利用した発電設備等では、安全を確保するため、タービンの回転速度をセンサにより測定し、回転速度が上限を超過したときにタービンを停止させる危急停止制御装置が設けられる。ここで、タービンの回転速度を測定するセンサは、過酷な環境下で動作するため、誤動作する可能性がある。そこで、3個のセンサによりタービンの回転速度を測定し、3個のうちの任意の2個のセンサが回転速度の上限超過を検出した場合に、タービンを停止させる2oo3(2 out of 3;3者2択)論理回路を備えた危急停止制御装置が提供されている。なお、この種の危急停止制御装置は、例えば特許文献1に開示されている。
In power generation equipment using a turbine, in order to ensure safety, an emergency stop control device is provided that measures the rotation speed of the turbine with a sensor and stops the turbine when the rotation speed exceeds the upper limit. Here, the sensor that measures the rotational speed of the turbine operates in a harsh environment, and therefore may malfunction. Therefore, the rotation speed of the turbine is measured by three sensors, and when any two of the three sensors detect that the upper limit of the rotation speed is exceeded, the turbine is stopped 2oo3 (2 out of 3; 3). 2) An emergency stop control device equipped with a logic circuit is provided. It should be noted that this kind of emergency stop control device is disclosed in, for example,
上述した危急停止制御装置の2oo3論理回路は、3個のセンサからの検出信号により開閉制御される3個の電磁弁を用いた油圧回路により構成される。ここで、危急停止制御装置は、長期に亙って動作し、その間にタービンの回転速度超過が発生した場合には確実にタービンを危急停止させねばならない。このため、危急停止制御装置では、2oo3論理回路の電磁弁のメンテナンスを頻繁に行う必要がある。従来、この電磁弁のメンテナンスの際に危急停止制御装置の動作を停止させていたため、危急停止制御装置およびそれを利用した発電設備等の稼働率の低下を招いていた。 The 2oo3 logic circuit of the above-mentioned emergency stop control device is composed of a hydraulic circuit using three solenoid valves controlled to open and close by detection signals from three sensors. Here, the emergency stop control device must operate for a long period of time, and if the rotation speed of the turbine is exceeded during that period, the turbine must be reliably stopped. Therefore, in the emergency stop control device, it is necessary to frequently perform maintenance of the solenoid valve of the 2oo3 logic circuit. In the past, the operation of the emergency stop control device was stopped during the maintenance of this solenoid valve, which caused a decrease in the operating rate of the emergency stop control device and the power generation equipment using the emergency stop control device.
この発明は以上のような事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、動作を停止させることなく2oo3論理回路の電磁弁のメンテナンスを行うことが可能な危急停止制御装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide an emergency stop control device capable of performing maintenance of a solenoid valve of a 2oo3 logic circuit without stopping the operation.
この発明は、タービンの回転速度が上限を超えるのに応じて前記タービンを停止させる危急停止制御装置において、作動油の供給源から作動油が供給される第1のパイプと、回油部に作動油を供給する第2のパイプと、前記第1のパイプの作動油の油圧が低下することにより閉状態から開状態に切り換えられ、開状態となることによりタービンを停止させる急速停止弁と、各々ポートP、T、AおよびBを有し、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間における作動油の通過を遮断する遮断状態、および、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間において作動油を通過させる通過状態の相互間の切り換えが可能な第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁であって、各々のポートPが前記第1のパイプに接続され、各々のポートTが前記第2のパイプに接続され、第1の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第2の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第1の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、第2の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第3の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第2の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、第3の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第1の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第1の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、各々別個のセンサにより測定される前記タービンの回転速度が上限を超過することにより前記遮断状態から前記通過状態に各々切り換えられる第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁からなる2oo3論理回路と、を具備し、前記第1のパイプと前記第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁の各ポートPとの間に開閉操作が可能な第1~第3の止め弁が挿入され、前記第2のパイプと前記第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁の各ポートTとの間に開閉操作が可能な第4~第6の止め弁が挿入された危急停止制御装置を提供する。 According to the present invention, in an emergency stop control device for stopping the turbine when the rotation speed of the turbine exceeds the upper limit, the first pipe to which the hydraulic oil is supplied from the hydraulic oil supply source and the lubrication section are operated. A second pipe that supplies oil and a quick stop valve that switches from the closed state to the open state when the hydraulic oil of the hydraulic oil of the first pipe drops and stops the turbine when the open state is reached, respectively. A shut-off state that has ports P, T, A and B and blocks the passage of hydraulic fluid in both the sections between ports P and A and between ports B and T, and between ports P and A and port B. 1st to 3rd 4-port solenoid valves capable of switching between passing states through which hydraulic oil is passed in both sections between and T, and each port P is connected to the first pipe. , Each port T is connected to the second pipe, and the port A of the first 4-port solenoid valve and the port B of the second 4-port solenoid valve are connected by the first solenoid valve-to-valve pipe. The port A of the 2 4-port solenoid valve and the port B of the 3rd 4-port solenoid valve are connected by a second solenoid valve-to-valve pipe, and the port A of the 3rd 4-port solenoid valve and the 1st 4-port solenoid valve are connected. A first solenoid valve is connected between the ports B of the valves by a first solenoid valve pipe, and the shutoff state is switched to the passing state when the rotation speed of the turbine, which is measured by a separate sensor, exceeds the upper limit. A second is provided with a 2oo3 logic circuit including a third 4-port solenoid valve, and can be opened and closed between the first pipe and each port P of the first to third 4-port solenoid valves. The first to third stop valves are inserted, and the fourth to sixth stop valves that can be opened and closed between the second pipe and each port T of the first to third four-port solenoid valves are Provide an inserted emergency stop control device.
以下、図面を参照し、この発明の実施形態について説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
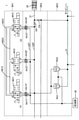
図1はこの発明の一実施形態であるタービンの危急停止制御装置1の油圧回路の構成を示す回路図である。図1に示すように、危急停止制御装置1は、電磁弁モジュールBK1と、止め弁モジュールBK2と、カートリッジバルブモジュールBK3とを含む。
FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a configuration of a hydraulic circuit of a turbine emergency
電磁弁モジュールBK1は、3個の4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3を含む。4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の各々は、ポートP、A、BおよびTを有している。これらの各電磁弁は、互いに独立した3個のセンサによるタービンの回転速度の測定結果に基づいて切り換えられる。例えば4ポート電磁弁MV1は、1つのセンサにより測定されるタービンの回転速度が上限以内である場合に、コイルへの通電が行われ、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間における作動油の通過が遮断された遮断状態となり、同センサにより測定されるタービンの回転速度が上限を超過した場合に、コイルが非通電となり、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間において作動油の通過が許可される通過状態となる。他の4ポート電磁弁MV2およびMV3も同様であり、他のセンサによる回転速度の測定結果に基づいて遮断状態または通過状態に切り換えられる。また、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3は、弁芯位置スイッチS1、S2およびS3を各々有する。これらの弁芯位置スイッチS1、S2およびS3により4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の弁芯位置を各々検出し、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3が正常に動作しているか否かを確認することができる。 The solenoid valve module BK1 includes three 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3. Each of the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 has ports P, A, B and T. Each of these solenoid valves is switched based on the measurement result of the rotational speed of the turbine by three sensors independent of each other. For example, in the 4-port solenoid valve MV1, when the rotation speed of the turbine measured by one sensor is within the upper limit, the coil is energized and both between ports P and A and between ports B and T. When the passage of hydraulic oil in the section is blocked and the rotation speed of the turbine measured by the sensor exceeds the upper limit, the coil is de-energized and between ports P and A and between ports B and T. In both sections, the passage state is such that the passage of hydraulic oil is permitted. The same applies to the other 4-port solenoid valves MV2 and MV3, which are switched to a cutoff state or a passing state based on the measurement result of the rotation speed by another sensor. Further, the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 have valve core position switches S1, S2 and S3, respectively. These valve core position switches S1, S2 and S3 detect the valve core positions of the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3, respectively, and confirm whether the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 are operating normally. can do.
4ポート電磁弁MV1のポートAと4ポート電磁弁MV2のポートBは、電磁弁間パイプAB12により接続されている。また、4ポート電磁弁MV2のポートAと4ポート電磁弁MV3のポートBは、電磁弁間パイプAB23により接続されている。また、4ポート電磁弁MV3のポートAと4ポート電磁弁MV1のポートBは、電磁弁間パイプAB31により接続されている。このように各4ポート電磁弁間を接続する電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31と、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3は、2oo3論理回路を構成している。 The port A of the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 and the port B of the 4-port solenoid valve MV2 are connected by a solenoid valve inter-valve pipe AB12. Further, the port A of the 4-port solenoid valve MV2 and the port B of the 4-port solenoid valve MV3 are connected by a solenoid valve inter-valve pipe AB23. Further, the port A of the 4-port solenoid valve MV3 and the port B of the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 are connected by a solenoid valve intervalving pipe AB31. In this way, the solenoid valve spacing pipes AB12, AB23 and AB31 connecting the four-port solenoid valves and the four-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 form a 2oo3 logic circuit.
止め弁モジュールBK2は、各々ニードル型止め弁である止め弁NV1T~NV3TおよびNV1P~NV3Pと、オリフィスOAおよびO0とを含む。ポンプ等の作動油供給源20から供給される作動油は、パイプ21を介してオリフィスOAおよびO0に与えられる。
The stop valve module BK2 includes stop valves NV1T to NV3T and NV1P to NV3P, which are needle type stop valves, and orifices OA and O0, respectively. The hydraulic oil supplied from the hydraulic
パイプ21からオリフィスOAを通過した作動油は、パイプ31に供給される。このパイプ31の作動油は、安全油としてタービンに供給される。この安全油の油圧が十分に高い状態ではタービンは通常動作する。
The hydraulic oil that has passed through the orifice OA from the
パイプ21からオリフィスO0を通過した作動油は、第1のパイプ22Pに供給され、この第1のパイプ22Pの作動油は、止め弁NV1P、NV2PおよびNV3Pを各々介すことにより4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のポートPに各々与えられる。
The hydraulic oil that has passed through the orifice O0 from the
4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のポートTから出る作動油は、止め弁NV1T、NV2TおよびNV3Tを各々介すことにより第2のパイプ22Tに供給される。第2のパイプ22Tに供給された作動油は、回油部30へ送られる。
The hydraulic oil discharged from the port T of the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 is supplied to the
カートリッジバルブモジュールBK3は、各々2方向カートリッジバルブである急速停止弁NG1およびNG2を含む。この急速停止弁NG1およびNG2は、第2のパイプ22Tとパイプ31との間に挿入されており、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の状態により開閉状態が制御される。
The cartridge valve module BK3 includes rapid stop valves NG1 and NG2, which are two-way cartridge valves, respectively. The rapid stop valves NG1 and NG2 are inserted between the
急速停止弁NG1およびNG2が閉じた状態では、パイプ31の作動油の油圧が十分に高く、タービンは通常動作する。一方、急速停止弁NG1およびNG2が開くと、回油部30に接続された第2のパイプ22Tが急速停止弁NG1およびNG2によりパイプ31に接続されるため、パイプ31の作動油の油圧が低下する。これによりタービンが急速停止する。
When the rapid stop valves NG1 and NG2 are closed, the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil in the
図1に示す例では、3個のセンサにより測定されるタービンの回転速度がいずれも上限以内であるため、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3は、全て遮断状態となっている。この場合、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22T間が遮断された状態となる。このため、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油が高い油圧を維持し、急速停止弁NG1およびNG2は閉状態となる。
In the example shown in FIG. 1, since the rotational speeds of the turbines measured by the three sensors are all within the upper limit, the four-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2, and MV3 are all shut off. In this case, the space between the
図2に示す例では、1つのセンサにより測定されたタービンの回転速度が上限を超過し、4ポート電磁弁MV1が通過状態、他の4ポート電磁弁MV2およびMV3が遮断状態となっている。この場合、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油は、止め弁NV1Pを介して4ポート電磁弁MV1のポートPに与えられるが、この4ポート電磁弁MV1のAポートに電磁弁間パイプAB12を介して接続された4ポート電磁弁MV2のポートBおよびT間が遮断状態である。このため、4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV2を介した第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22T間の作動油の移動は生じず、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22T間は遮断状態となり、急速停止弁NG1およびNG2は閉状態となる。
In the example shown in FIG. 2, the rotation speed of the turbine measured by one sensor exceeds the upper limit, the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 is in the passing state, and the other 4-port solenoid valves MV2 and MV3 are in the shutoff state. In this case, the hydraulic oil of the
図3に示す例では、2つのセンサにより測定された回転速度が上限を超え、4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV3が通過状態、4ポート電磁弁MV2が遮断状態となっている。この場合、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油は、止め弁NV3Pを介して4ポート電磁弁MV3のポートPに与えられるが、この4ポート電磁弁MV3のAポートに電磁弁間パイプAB31を介して接続された4ポート電磁弁MV1のポートBおよびT間が通過状態である。このため、4ポート電磁弁MV3およびMV1を介した第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22T間の作動油の移動が可能であり、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22T間は接続された状態となり、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油の油圧が低下する。この結果、急速停止弁NG1およびNG2が開状態となり、パイプ31の作動油の油圧が低下し、タービンが急速停止する。
In the example shown in FIG. 3, the rotation speed measured by the two sensors exceeds the upper limit, and the 4-port solenoid valves MV1 and MV3 are in the passing state and the 4-port solenoid valve MV2 is in the shutoff state. In this case, the hydraulic oil of the
さて、本願発明者が調査したところ、図1に示す構成では、次のような問題が発生することが分った。すなわち、3個の4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のうちの1つが通過状態から遮断状態に復帰し、その後、他の2つが通過状態になると、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油の油圧およびパイプ31の作動油の油圧が短時間で突然降下し、システムエラーによる遮断(タービンの急速停止)とエラーの誤報を引き起こす。
As a result of investigation by the inventor of the present application, it was found that the following problems occur in the configuration shown in FIG. That is, when one of the three 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 returns from the passing state to the shutoff state, and then the other two return to the passing state, the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil of the
数多くの実験を行った結果、この問題の原因として、次のことが分った。1つの4ポート電磁弁(例えば4ポート電磁弁MV1とする)が通過状態から遮断状態に復帰した後、この4ポート電磁弁MV1のポートBと、これに隣接する4ポート電磁弁MV3のポートAに接続された電磁弁間パイプAB31内にエアキャビティが形成され、4ポート電磁弁MV3が通過状態になる際に、電磁弁間パイプAB31内の作動油がエアキャビティを充填する。この作動油によるエアキャビティの充填により、第1のパイプ22Pの作動油の油圧が瞬時に低下し、回復する。この結果、急速停止弁NG1およびNG2が瞬時に開閉し、パイプ31の作動油の油圧が瞬時に低下し、システムエラーによる遮断と誤報を引き起こす。
As a result of many experiments, we found the following as the cause of this problem. After one 4-port solenoid valve (for example, a 4-port solenoid valve MV1) returns from the passing state to the cutoff state, the port B of the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 and the port A of the adjacent 4-port solenoid valve MV3. An air cavity is formed in the solenoid valve inter-valve pipe AB31 connected to the above, and when the 4-port solenoid valve MV3 is in a passing state, the hydraulic oil in the solenoid valve inter-valve pipe AB31 fills the air cavity. By filling the air cavity with this hydraulic oil, the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil of the
多くの実験と理論実証の結果、異常な圧力降下の持続時間は、降下の深さとエアキャビティの形成される電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31の容積に比例し、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の内部漏れ量に反比例することが分かった。 As a result of many experiments and theoretical demonstrations, the duration of the abnormal pressure drop is proportional to the depth of the drop and the volume of the solenoid valve intervalving pipes AB12, AB23 and AB31 in which the air cavity is formed, and the 4-port solenoid valves MV1 and MV2. And it was found to be inversely proportional to the amount of internal leakage of MV3.
本実施形態による危急制御装置は、以上の実験および理論実証の結果を踏まえて設計されたものである。本実施形態では、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31の容積を最小化する設計を行った。具体的には、本実施形態では、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31を同じ長さとし、かつ、最短化した。また、本実施形態では、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3として、内部漏れ量の大きいものを採用した。ここで、内部漏れとは、遮断状態の4ポート電磁弁のポートPおよびA間、ポートBおよびT間の漏れ量を指す。この漏れ量は、バルブのバルブコアのタイプに関係する。電磁スライドバルブの内部漏れ量は、電磁シートバルブの内部漏れ量よりも大きい。このため、本実施形態では、電磁スライドバルブを4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3として採用した。 The emergency control device according to this embodiment is designed based on the results of the above experiments and theoretical proofs. In this embodiment, the design is made to minimize the volume of the solenoid valve intervalve pipes AB12, AB23 and AB31. Specifically, in the present embodiment, the solenoid valve pipes AB12, AB23 and AB31 have the same length and are shortened. Further, in the present embodiment, as the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3, those having a large internal leakage amount are adopted. Here, the internal leakage refers to the amount of leakage between ports P and A and between ports B and T of the 4-port solenoid valve in the shutoff state. This amount of leakage is related to the type of valve core of the valve. The amount of internal leakage of the electromagnetic slide valve is larger than the amount of internal leakage of the electromagnetic seat valve. Therefore, in this embodiment, the solenoid slide valve is adopted as the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3.
図4は本実施形態による危急停止制御装置1の外観を示す正面図である。また、図5は危急停止制御装置を上方から見た平面図である。これらの図に示すように、本実施形態による危急停止制御装置1は、電磁弁モジュールBK1と、止め弁モジュールBK2と、カートリッジバルブモジュールBK3とを上下方向に縦積みした構成となっている。
FIG. 4 is a front view showing the appearance of the emergency
図5に示すように、電磁弁モジュールBK1の3個の4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3は、互いに同じ形状およびサイズを有しており、電磁弁モジュールBK1において、最大限に接近した状態で配置されている。本実施形態において、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3は、危急停止制御装置1の筐体に対し、外部から着脱が可能である。電磁弁モジュールBK1には、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31の各パイプ内の油圧を測定する油圧センサM1、M2およびM3が設けられている。この油圧センサM1、M2およびM3の出力信号を監視することにより4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の故障を検知することが可能である。また、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3には、上述した弁芯位置スイッチS1、S2およびS3があるので、この弁芯位置スイッチS1、S2およびS3により、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3に故障があるか否かを判定することができる。
As shown in FIG. 5, the three 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 of the solenoid valve module BK1 have the same shape and size as each other, and are in the maximum close contact state in the solenoid valve module BK1. Have been placed. In the present embodiment, the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 can be attached to and detached from the outside to the housing of the emergency
図6は、危急停止制御装置1の電磁弁モジュールBK1内のパイプのレイアウトを示す斜視図である。図6に示すように、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31は、正三角形の各辺をなすように、電磁弁モジュールBK1内に配置されている。この電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31の長さは、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3を最大限に接近させて配置した場合の1の4ポート電磁弁のAポートと隣接する4ポート電磁弁のBポートとの間の長さに等しい。
FIG. 6 is a perspective view showing the layout of the pipe in the solenoid valve module BK1 of the emergency
本願発明者は、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31の形状、サイズ、レイアウトを図6に示すものにすることにより、異常な油圧低下の持続時間を50ms以内に制御できることを確認した。また、本願発明者は、降下幅を2bar未満、作動油供給源20の作動油の油圧を20barとした場合、4ポート電磁弁MV1~MV3が遮断状態に復帰した3分後に電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31のエアキャビティを充填できることを確認した。このように、電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB31を改善することにより、安全油圧が短時間で突然降下することがなくなり、使用要件を完全に満たすものとなった。
The inventor of the present application has confirmed that the duration of the abnormal hydraulic pressure drop can be controlled within 50 ms by making the shapes, sizes, and layouts of the solenoid valve intervalbular pipes AB12, AB23, and AB31 as shown in FIG. Further, the inventor of the present application has set the descent width to less than 2 bar and the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil of the hydraulic
危急停止制御装置1の信頼性を高めるためには、2oo3論理回路を構成する4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のメンテナンスを頻繁に行う必要がある。従来技術の下では、危急停止制御装置1を停止させて4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のメンテナンスを行っていたため、危急停止制御装置1およびこれを利用した発電システム全体の稼働率の低下を招いていた。そこで、本実施形態では、危急停止制御装置1を停止させることなく、その動作を維持した状態で、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の交換を行うことを可能にする手段を提供する。
In order to improve the reliability of the emergency
図1に示すように、危急停止制御装置1において、第1のパイプ22Pと4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の各ポートPとの間には、開閉操作が可能な止め弁NV1P、NV2PおよびNV3Pが挿入され、第2のパイプ22Tと4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の各ポートTとの間には、開閉操作が可能な止め弁NV1T、NV2TおよびNV3Tが挿入されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, in the emergency
また、図4に示すように、危急停止制御装置1の筐体には、止め弁NV1P~NV3P、NV1T~NV3Tに開閉操作のための電気信号を供給するプラグが設けられている。本実施形態では、このプラグから止め弁NV1P~NV3P、NV1T~NV3Tに電気信号を送り、止め弁NV1P~NV3P、NV1T~NV3Tの開閉操作を行うことにより、危急停止制御装置1を停止させることなく、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3の交換を行うことが可能である。
Further, as shown in FIG. 4, the housing of the emergency
図7は、本実施形態における4ポート電磁弁の交換のための操作を示す図である。4ポート電磁弁MV1を交換する場合には、止め弁NV1P、NV1T、NV2TおよびNV3Pを閉状態とし、止め弁NV2PおよびNV3Tを開状態とする。この状態では、4ポート電磁弁MV1は、強制的に遮断状態となり、センサによる回転速度の測定結果に反応しない。4ポート電磁弁MV2およびMV3は、各々に対応付けられた2つのセンサにより測定される回転速度が両方とも上限を超える場合に限り、両方が通過状態となって、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22Tを接続する。このように4ポート電磁弁MV2およびMV3は、2oo2(2 out of 2)論理回路として機能する。4ポート電磁弁MV1の交換が終わると、止め弁NV1P、NV1T、NV2TおよびNV3Pは開状態に切り換えられる。これにより2oo3論理回路としての動作が再開される。
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing an operation for replacing the 4-port solenoid valve in the present embodiment. When replacing the 4-port solenoid valve MV1, the stop valves NV1P, NV1T, NV2T and NV3P are closed and the stop valves NV2P and NV3T are open. In this state, the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 is forcibly shut off and does not react to the measurement result of the rotation speed by the sensor. The four-port solenoid valves MV2 and MV3 are both in the passing state only when the rotation speed measured by the two sensors associated with each exceeds the upper limit, and the
4ポート電磁弁MV2を交換する場合には、止め弁NV1P、NV2P、NV2TおよびNV3Tを閉状態とし、止め弁NV1TおよびNV3Pを開状態とする。この状態では、4ポート電磁弁MV2は、強制的に遮断状態となり、センサによる回転速度の測定結果に反応しない。4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV3は、各々に対応した2つのセンサにより測定される回転速度が両方とも上限を超えた場合に限り、両方が通過状態となって、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22Tを接続する。このように4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV3は、2oo2論理回路として機能する。4ポート電磁弁MV2の交換が終わると、止め弁NV1P、NV2P、NV2TおよびNV3Tは開状態に切り換えられる。これにより2oo3論理回路としての動作が再開される。
When replacing the 4-port solenoid valve MV2, the stop valves NV1P, NV2P, NV2T and NV3T are closed and the stop valves NV1T and NV3P are open. In this state, the 4-port solenoid valve MV2 is forcibly shut off and does not react to the measurement result of the rotation speed by the sensor. The four-port solenoid valves MV1 and MV3 are both in the passing state only when the rotation speed measured by the two sensors corresponding to each exceeds the upper limit, and the
4ポート電磁弁MV3を交換する場合には、止め弁NV1T、NV2P、NV3PおよびNV3Tを閉状態とし、止め弁NV1PおよびNV2Tを開状態とする。この状態では、4ポート電磁弁MV3は、強制的に遮断状態となり、センサによる回転速度の測定結果に反応しない。4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV2は、各々に対応した2つのセンサにより測定される回転速度が両方とも上限を超えた場合に限り、両方が通過状態となって、第1のパイプ22Pおよび第2のパイプ22Tを接続する。このように4ポート電磁弁MV1およびMV2は、2oo2論理回路として機能する。4ポート電磁弁MV3の交換が終わると、止め弁NV1T、NV2P、NV3PおよびNV3Tは開状態に切り換えられる。これにより2oo3論理回路としての動作が再開される。
When replacing the 4-port solenoid valve MV3, the stop valves NV1T, NV2P, NV3P and NV3T are closed and the stop valves NV1P and NV2T are open. In this state, the 4-port solenoid valve MV3 is forcibly shut off and does not react to the measurement result of the rotation speed by the sensor. The four-port solenoid valves MV1 and MV2 are both in the passing state only when the rotation speed measured by the two sensors corresponding to each exceeds the upper limit, and the
以上のように、本実施形態によれば、危急停止制御装置1を停止させることなく、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3を交換することができる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 can be replaced without stopping the emergency
4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3のうちの1個(例えば4ポート電磁弁MV1とする)を交換した場合、その4ポート電磁弁MV1は長期に亙る非通電状態(すなわち、通過状態)から通電状態(すなわち、遮断状態)に復帰することとなる。しかしながら、本実施形態では、3本の電磁弁間パイプAB12、AB23およびAB23を同じ長さとすることにより最短化し、かつ、4ポート電磁弁MV1、MV2およびMV3として電磁スライドバルブを採用している。このため、4ポート電磁弁MV1の通過状態から遮断状態への復帰後、他の4ポート電磁弁MV2およびMV3が通過状態となっても、上述した第1のパイプ22Pの作動油の油圧およびパイプ31の作動油の油圧が短時間で突然降下する問題が発生しない。
When one of the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3 (for example, the 4-port solenoid valve MV1) is replaced, the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 is energized from a long-term non-energized state (that is, a passing state). It will return to the state (that is, the cutoff state). However, in the present embodiment, the three solenoid valve intervalve pipes AB12, AB23 and AB23 are shortened by having the same length, and the solenoid slide valve is adopted as the 4-port solenoid valves MV1, MV2 and MV3. Therefore, even if the other 4-port solenoid valves MV2 and MV3 are in the passing state after returning from the passing state of the 4-port solenoid valve MV1 to the shut-off state, the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil of the
1……危急停止制御装置、BK1……電磁弁モジュール、BK2……止め弁モジュール、BK3……カートリッジバルブモジュール、MV1,MV2,MV3……4ポート電磁弁、NV1P~NV3P,NV1T~NV3T……止め弁、……、AB12,AB23,AB31……電磁弁間パイプ、22P……第1のパイプ、22T……第2のパイプ、NG1,NG2……急速停止弁、20……作動油供給部、30……回油部、31……パイプ。
1 ... Emergency stop control device, BK1 ... Solenoid valve module, BK2 ... Stop valve module, BK3 ... Cartridge valve module, MV1, MV2, MV3 ... 4-port solenoid valve, NV1P to NV3P, NV1T to NV3T ... Stop valve, ..., AB12, AB23, AB31 ... Solenoid valve inter-valve pipe, 22P ... 1st pipe, 22T ... 2nd pipe, NG1, NG2 ... Rapid stop valve, 20 ... Hydraulic oil supply unit , 30 ... Oil section, 31 ... Pipe.
Claims (3)
作動油の供給源から作動油が供給される第1のパイプと、
回油部に作動油を供給する第2のパイプと、
前記第1のパイプの作動油の油圧が低下することにより閉状態から開状態に切り換えられ、開状態となることによりタービンを停止させる急速停止弁と、
各々ポートP、T、AおよびBを有し、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間における作動油の通過を遮断する遮断状態、および、ポートPおよびA間と、ポートBおよびT間の両方の区間において作動油を通過させる通過状態の相互間の切り換えが可能な第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁であって、各々のポートPが前記第1のパイプに接続され、各々のポートTが前記第2のパイプに接続され、第1の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第2の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第1の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、第2の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第3の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第2の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、第3の4ポート電磁弁のポートAおよび第1の4ポート電磁弁のポートB間が第1の電磁弁間パイプにより接続され、各々別個のセンサにより測定される前記タービンの回転速度が上限を超過することにより前記遮断状態から前記通過状態に各々切り換えられる第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁からなる2oo3論理回路と、を具備し、
前記第1のパイプと前記第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁の各ポートPとの間に開閉操作が可能な第1~第3の止め弁が挿入され、前記第2のパイプと前記第1~第3の4ポート電磁弁の各ポートTとの間に開閉操作が可能な第4~第6の止め弁が挿入された危急停止制御装置。 In the emergency stop control device that stops the turbine when the rotation speed of the turbine exceeds the upper limit.
The first pipe to which the hydraulic oil is supplied from the hydraulic oil supply source,
A second pipe that supplies hydraulic oil to the oil circulation part,
A rapid stop valve that switches from the closed state to the open state when the hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic oil of the first pipe drops and stops the turbine when it becomes the open state.
A shut-off state that has ports P, T, A and B, respectively, and blocks the passage of hydraulic fluid in both the sections between ports P and A and between ports B and T, and between ports P and A and ports. 1st to 3rd 4-port solenoid valves capable of switching between passing states through which hydraulic oil is passed in both sections between B and T, and each port P is connected to the first pipe. Each port T is connected to the second pipe, and the port A of the first 4-port solenoid valve and the port B of the second 4-port solenoid valve are connected by the first solenoid valve-to-valve pipe. Port A of the second 4-port solenoid valve and port B of the third 4-port solenoid valve are connected by a second solenoid valve-to-valve pipe, and port A of the third 4-port solenoid valve and port B of the first 4 port. The ports B of the solenoid valves are connected by a first solenoid valve pipe, and when the rotational speed of the turbine measured by a separate sensor exceeds the upper limit, the shutoff state is switched to the passing state. It is equipped with a 2oo3 logic circuit consisting of 1st to 3rd 4-port solenoid valves.
A first to third stop valves capable of opening and closing operations are inserted between the first pipe and each port P of the first to third four-port solenoid valves, and the second pipe and the first stop valve are inserted. An emergency stop control device in which a fourth to sixth stop valve capable of opening and closing is inserted between each port T of the first to third four-port solenoid valves.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021004206A JP7012394B1 (en) | 2021-01-14 | 2021-01-14 | Turbine emergency stop control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021004206A JP7012394B1 (en) | 2021-01-14 | 2021-01-14 | Turbine emergency stop control device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP7012394B1 true JP7012394B1 (en) | 2022-01-28 |
| JP2022108955A JP2022108955A (en) | 2022-07-27 |
Family
ID=80735336
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021004206A Active JP7012394B1 (en) | 2021-01-14 | 2021-01-14 | Turbine emergency stop control device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7012394B1 (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN203906017U (en) | 2014-05-04 | 2014-10-29 | 上海汇益控制系统股份有限公司 | Emergency intercept device for isolating test signal |
| US20170152759A1 (en) | 2014-06-03 | 2017-06-01 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Hydraulic Control Device For An Emergency Stop Valve Of A Steam Turbine And Steam Turbine Arrangement |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2997605B2 (en) * | 1992-10-05 | 2000-01-11 | 株式会社東芝 | Steam valve drive for steam turbine |
-
2021
- 2021-01-14 JP JP2021004206A patent/JP7012394B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN203906017U (en) | 2014-05-04 | 2014-10-29 | 上海汇益控制系统股份有限公司 | Emergency intercept device for isolating test signal |
| US20170152759A1 (en) | 2014-06-03 | 2017-06-01 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Hydraulic Control Device For An Emergency Stop Valve Of A Steam Turbine And Steam Turbine Arrangement |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2022108955A (en) | 2022-07-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1854470B (en) | Electronically controllable and testable turbine trip system | |
| CN100443791C (en) | Valve state sensing module | |
| US7322270B2 (en) | Safety circuit for media-operated consumers and process for its operation | |
| RU2752786C2 (en) | Method for testing the solenoid valve and the corresponding device (versions) | |
| KR20120021139A (en) | Cutoff valve control apparatus | |
| JP2013543957A (en) | Hydraulic or pneumatic drive that operates control equipment with control valve or switching valve | |
| RU182432U1 (en) | COMBINED DRIVE CONTROL UNIT | |
| US3930518A (en) | Valves | |
| CZ282722B6 (en) | Hydraulic safety and control system | |
| JPS6159078A (en) | Device for monitoring physical magnitude in device | |
| CN103477093B (en) | Electropneumatic position regulator | |
| JP7012394B1 (en) | Turbine emergency stop control device | |
| JP3592377B2 (en) | Hydraulic safety circuit | |
| CS633590A3 (en) | Filling valve drive | |
| KR101395931B1 (en) | Test block of oil leakage test for turbine valve actuator | |
| JP7113544B2 (en) | Turbine emergency stop control device | |
| US20090140191A1 (en) | Device for actuating a process valve for use in foodstuffs technology | |
| JP5193648B2 (en) | Control rod drive control device | |
| KR100564338B1 (en) | Safety valve bypass element tester | |
| CN211059452U (en) | Butterfly valve actuating mechanism safety interruption device and butterfly valve actuating mechanism thereof | |
| CN218062408U (en) | Two-out-one-speed closing valve control module capable of realizing online test of steam turbine | |
| KR101892387B1 (en) | Hydraulic actuator for turbine valve and turbine power sistem using the same | |
| JPH0255840B2 (en) | ||
| KR101800240B1 (en) | Monitoring block for estimation real-time integrity during driving of power plant hydraulic actuator | |
| KR20180045248A (en) | Emergency valve unit of valve assembly |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210114 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20211228 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220111 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7012394 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |