JP6851715B2 - Manufacturing method of optical member - Google Patents
Manufacturing method of optical member Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6851715B2 JP6851715B2 JP2015210143A JP2015210143A JP6851715B2 JP 6851715 B2 JP6851715 B2 JP 6851715B2 JP 2015210143 A JP2015210143 A JP 2015210143A JP 2015210143 A JP2015210143 A JP 2015210143A JP 6851715 B2 JP6851715 B2 JP 6851715B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- optical shape
- layer
- optical
- curable resin
- base material
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
Description
本発明は、光学部材の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing an optical member.
ヘッドアップディスプレイ(以下、「HUD」ともいう)は、インストルメントパネル内に配置された映像源からフロントウィンドウに映像光を投影し、運転者に対して各種の情報を表示する車両用の表示装置である。従来、車両のフロントウィンドウとしては、一対のガラス板の間に飛散防止用の中間層を挟み込んだ合わせガラスが使用されている。この合わせガラスにHUDの映像光を投影すると、光の屈折により映像光が二重像として運転者に視認されることがある。そこで、光の屈折を制御するために、中間層の断面を楔形状とした合わせガラスが提案されている(特許文献1参照)。 A head-up display (hereinafter, also referred to as "HUD") is a display device for vehicles that projects image light from an image source arranged in an instrument panel onto a front window and displays various information to the driver. Is. Conventionally, as a front window of a vehicle, laminated glass in which an intermediate layer for preventing scattering is sandwiched between a pair of glass plates has been used. When the image light of the HUD is projected on the laminated glass, the image light may be visually recognized by the driver as a double image due to the refraction of the light. Therefore, in order to control the refraction of light, a laminated glass having a wedge-shaped cross section of the intermediate layer has been proposed (see Patent Document 1).
車両のフロントウィンドウは、車種毎に取り付け角度が異なる。中間層の断面を楔形状とした場合、その厚み、楔角等は、車両への取り付け角度に応じて設計される。しかし、現状では、中間層の楔形状を車両への取り付け角度に応じて設計することは難しい。そのため、フロントウィンドウに使用される光学部材において、光学性能をより向上させることが要望されている。 The mounting angle of the front window of the vehicle differs depending on the vehicle model. When the cross section of the intermediate layer is wedge-shaped, its thickness, wedge angle, etc. are designed according to the mounting angle to the vehicle. However, at present, it is difficult to design the wedge shape of the intermediate layer according to the mounting angle to the vehicle. Therefore, it is required to further improve the optical performance of the optical member used for the front window.
本発明の課題は、光学性能をより向上させた光学部材の製造方法を提供することである。 An object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing an optical member having further improved optical performance.
本発明は、以下のような解決手段により前記課題を解決する。なお、理解を容易にするために、本発明の実施形態に対応する符号を付して説明するが、これに限定されない。
・第1の発明は、第1傾斜面(21b)及び第2傾斜面(21c)を有する単位光学形状(21a)が複数配列された第1光学形状層(21)を備え、映像源から投射された映像光の一部を少なくとも前記第1傾斜面で観察者側に反射させる光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記単位光学形状を賦形する賦形面を有する成形型(100)に、未硬化のエネルギー線硬化樹脂を充填するエネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程と、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂にエネルギー線を照射して、前記成形型に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を収縮可能な状態で硬化させて、前記第1光学形状層を成形する第1光学形状層成形工程と、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から第1光学形状層を得る第1光学形状層作製工程と、前記第1光学形状層に設けられた前記単位光学形状の少なくとも前記第1傾斜面に反射層(22)を形成する反射層形成工程と、前記第1光学形状層の反射層が形成された側の面に第2光学形状層(23)を形成する第2光学形状層形成工程と、を含む光学部材の製造方法である。
・第2の発明は、第1の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記第1光学形状層作製工程では、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記成形型(100)から剥離して、前記第1光学形状層(21)を得ることを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第3の発明は、第1の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記成形型(100)に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の収縮とともに変形可能な基材(220)を貼り付ける基材貼り付け工程を含み、前記第1光学形状層作製工程は、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から前記基材を剥離する基材剥離工程と、前記基材の剥離された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記成形型から剥離して、前記第1光学形状層(21)を得る第1光学形状層剥離工程と、を含むことを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第4の発明は、第1の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に基材(24)を貼り付ける基材貼り付け工程を含み、前記第1光学形状層作製工程では、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記基材とともに前記成形型(100)から剥離して、前記基材の接合された前記第1光学形状層(21)を得ることを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第5の発明は、第1の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記成形型(100)に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の収縮とともに変形可能な基材(24)を貼り付ける基材貼り付け工程を含み、前記第1光学形状層成形工程では、前記基材を介して、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂にエネルギー線を照射して、前記成形型に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を収縮可能な状態で硬化させ、前記第1光学形状層作製工程では、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記基材とともに前記成形型から剥離して、前記基材の接合された前記第1光学形状層(21)を得ることを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第6の発明は、第1の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記成形型(100)に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の収縮とともに変形可能な第1基材(220)を貼り付ける第1基材貼り付け工程を含み、前記第1光学形状層作製工程は、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から前記第1基材を剥離する第1基材剥離工程と、前記第1基材の剥離された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に第2基材(24)を貼り付ける第2基材貼り付け工程と、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記第2基材とともに前記成形型から剥離して、前記第2基材の接合された前記第1光学形状層(21)を得る第1光学形状層剥離工程と、を含むことを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第7の発明は、第1から第6の発明までのいずれかの光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記第1光学形状層(21)は、前記第1傾斜面(21b)の算術平均うねりWaが0.05μm以下に形成され、前記単位光学形状(21a)の厚み方向の頂部から谷部までの高さhが10〜300μmの範囲で形成され、前記単位光学形状の配列ピッチPが100〜1000μmの範囲で形成されることを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
・第8の発明は、第3、第5又は第6の発明の光学部材(20)の製造方法であって、前記第1光学形状層(21)は、前記単位光学形状(21a)の谷部から、前記単位光学形状が設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さd1が10〜200μmの範囲で形成され、前記単位光学形状の頂部から、前記単位光学形状が設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さd2が30〜800μmの範囲で形成され、前記基材(24)又は前記第1基材(220)の厚みが8〜100μmの範囲で形成されることを特徴とする光学部材の製造方法である。
The present invention solves the above problems by the following solutions. In addition, in order to facilitate understanding, the description will be given with reference numerals corresponding to the embodiments of the present invention, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
The first invention includes a first optical shape layer (21) in which a plurality of unit optical shapes (21a) having a first inclined surface (21b) and a second inclined surface (21c) are arranged, and is projected from an image source. A method for manufacturing an optical member (20) that reflects at least a part of the image light to the observer side on the first inclined surface, and is a molding die (100) having a shaped surface that shapes the unit optical shape. ), The energy ray-curable resin filling step of filling the uncured energy ray-curable resin, and the energy ray-curable resin can be shrunk by irradiating the energy ray-curable resin with energy rays. A first optical shape layer forming step of curing in a state to form the first optical shape layer, a first optical shape layer manufacturing step of obtaining a first optical shape layer from the cured energy ray-curable resin, and the above. A step of forming a reflective layer (22) on at least the first inclined surface of the unit optical shape provided on the first optical shape layer, and a side on which the reflective layer of the first optical shape layer is formed. This is a method for manufacturing an optical member including a second optical shape layer forming step of forming a second optical shape layer (23) on a surface.
The second invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the first invention, and in the first optical shape layer manufacturing step, the energy ray-curable resin after curing is obtained from the molding die (100). This is a method for manufacturing an optical member, which comprises peeling to obtain the first optical shape layer (21).
A third invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the first invention, in which the energy ray-curable resin shrinks on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding die (100). The first optical shape layer manufacturing step includes a base material sticking step of sticking a deformable base material (220) together with the base material peeling step of peeling the base material from the energy ray-curable resin after curing. An optical feature comprising a first optical shape layer peeling step of peeling the energy ray-curable resin from which the base material has been peeled off from the molding die to obtain the first optical shape layer (21). It is a method of manufacturing a member.
The fourth invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the first invention, which includes a base material sticking step of sticking the base material (24) on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin after curing. In the first optical shape layer manufacturing step, the cured energy ray-curable resin is peeled from the molding die (100) together with the base material, and the first optical shape layer (21) to which the base material is bonded is peeled off. ) Is a method for manufacturing an optical member.
A fifth invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the first invention, wherein the energy ray-curable resin shrinks on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding die (100). In the first optical shape layer molding step, the energy ray-curable resin is irradiated with energy rays through the base material, including a base material sticking step of sticking the deformable base material (24). The energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding die is cured in a shrinkable state, and in the first optical shape layer manufacturing step, the cured energy ray-curable resin is peeled from the molding die together with the base material. This is a method for manufacturing an optical member, which comprises obtaining the first optical shape layer (21) to which the base material is bonded.
A sixth aspect of the present invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the first invention, wherein the energy ray-curable resin shrinks on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding die (100). Including the first base material pasting step of sticking the deformable first base material (220) together with the first optical shape layer manufacturing step, the first base material is peeled from the energy ray-curable resin after curing. The first base material peeling step, the second base material sticking step of sticking the second base material (24) on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin from which the first base material has been peeled off, and the energy ray-curable resin. The first optical shape layer peeling step of peeling the second base material from the molding die together with the second base material to obtain the first optical shape layer (21) to which the second base material is bonded is included. This is a method for manufacturing an optical member.
A seventh invention is a method for manufacturing any of the optical members (20) from the first to the sixth invention, wherein the first optical shape layer (21) is the first inclined surface (21b). The arithmetic mean swell Wa of the above is formed to be 0.05 μm or less, and the height h from the top to the valley in the thickness direction of the unit optical shape (21a) is formed in the range of 10 to 300 μm, and the array of the unit optical shapes is formed. This is a method for manufacturing an optical member, characterized in that the pitch P is formed in the range of 100 to 1000 μm.
The eighth invention is the method for manufacturing the optical member (20) of the third, fifth or sixth invention, and the first optical shape layer (21) is a valley of the unit optical shape (21a). The depth d1 from the portion to the surface opposite to the side on which the unit optical shape is provided is formed in the range of 10 to 200 μm, and from the top of the unit optical shape to the side on which the unit optical shape is provided. The depth d2 to the opposite surface is formed in the range of 30 to 800 μm, and the thickness of the base material (24) or the first base material (220) is formed in the range of 8 to 100 μm. This is a method for manufacturing an optical member.
本発明によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学部材の製造方法を提供することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a method for manufacturing an optical member having further improved optical performance.
以下、本発明に係る光学部材の製造方法の実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、本発明に係る光学部材を、自動車のフロントウィンドウに搭載されるヘッドアップディスプレイ(HUD)の光学シートに適用した例について説明する。なお、図1を含め、以下に示す各図は、模式的に示した図であり、各部の大きさ、形状は、理解を容易にするために、適宜誇張されている。
本明細書中に記載する各部材の寸法等の数値及び材料名等は、実施形態としての一例であり、これに限定されるものではなく、適宜選択して使用してよい。
本明細書中において、形状や幾何学的条件を特定する用語、例えば、平行や直交等の用語については、厳密に意味するところに加え、同様の光学的機能を奏し、平行や直交と見なせる程度の誤差を有する状態も含むものとする。
Hereinafter, embodiments of a method for manufacturing an optical member according to the present invention will be described. In the present embodiment, an example in which the optical member according to the present invention is applied to an optical sheet of a head-up display (HUD) mounted on a front window of an automobile will be described. It should be noted that each of the figures shown below, including FIG. 1, is a diagram schematically shown, and the size and shape of each part are exaggerated as appropriate for easy understanding.
Numerical values such as dimensions of each member and material names described in the present specification are examples of embodiments, and are not limited thereto, and may be appropriately selected and used.
In the present specification, terms that specify a shape or a geometric condition, for example, terms such as parallel and orthogonal, have the same optical function in addition to their strict meanings, and can be regarded as parallel or orthogonal. It shall also include the state having the error of.
(第1実施形態)
図1は、第1実施形態の表示装置10を配置した自動車1の運転席周辺を示す図である。図1(a)は、自動車1の運転席からフロントウィンドウ2側(自動車の進行方向側)を見た状態を示す図である。図1(b)は、図1(a)のb部断面からの矢視図であり、図1(c)は、図1(a)のc部矢視図、すなわち運転席を上側から見た図である。
図2は、第1実施形態の表示装置10を説明する図である。図2(a)は、光学シート20の厚み方向の運転者側から見た正面図である。図2(b)は、光学シート20の左右方向の中心線上における断面、すなわち図2(a)のb部断面を示す図である。図2(c)は、厚み方向(Y方向)に平行であって、単位光学形状21aの配列方向に平行な断面における断面、すなわち図2(a)のc部断面を示す図である。
なお、図2を含め以下に示す図中及び以下の説明において、理解を容易にするために、光学シートの上下方向をZ方向とし、厚み方向をY方向とし、左右方向をX方向とする。ここで、上下方向(Z方向)のうち−Z側を下側とし、+Z側を上側とする。また、厚み方向(X方向)のうち−Y側を背面側とし、+Y側を運転者側とする。また、左右方向(X方向)のうち−X側を左側とし、+X側を右側とする。
(First Embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the vicinity of the driver's seat of the
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating the
In the drawings shown below including FIG. 2 and in the following description, in order to facilitate understanding, the vertical direction of the optical sheet is the Z direction, the thickness direction is the Y direction, and the horizontal direction is the X direction. Here, in the vertical direction (Z direction), the −Z side is the lower side and the + Z side is the upper side. Further, in the thickness direction (X direction), the −Y side is the back side and the + Y side is the driver side. Further, in the left-right direction (X direction), the −X side is the left side and the + X side is the right side.
本実施形態の自動車1は、図1に示すように、車内側から見て、フロントウィンドウ2の右側に運転席が設けられ、フロントウィンドウ2の下方側に内装パネル3が配置されている。また、自動車1には、表示装置10が設けられている。表示装置10を構成する光学シート20(後述)は、フロントウィンドウ2の内側(車内側)の面の右側に配置されている。
フロントウィンドウ2は、一対のガラス板の間に飛散防止用の中間層を挟み込んだ合わせガラスである。本実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2において、中間層(不図示)は、フロントウィンドウ2の上端部(+Z方向の最上端部)から下端部(−Z方向の最下端部)までの範囲において、層厚が均等となるように形成されている。すなわち、本実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2は、中間層の断面が楔形状ではなく、上端部から下端部までの範囲において層厚が均等な矩形状を有する。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
The
内装パネル3は、フロントウィンドウ2の下方側に配置された化粧パネルであり、その右側に自動車の操縦桿となるハンドル4や、自動車の速度計等の計器類5が配置されている。また、内装パネル3には、表示装置10を構成する映像源11(後述)等が配置されている。
表示装置10は、自動車1の速度や、方向指示器の状態等を、運転者の視線上に表示することができる装置、いわゆるヘッドアップディスプレイ装置であり、自動車1を運転する運転者が視線を反らすことなく、自動車1の速度等の状態を把握することができる。
表示装置10は、映像源11、投射光学系12、光学シート20等を備えている。表示装置10は、映像源11から出射した速度情報等の映像光を、光学シート20を介して運転者側に投影する。具体的には、表示装置10は、映像源11から出射された映像光を、投射光学系12を介して光学シート20へ入射させて運転者側に映像情報を反射する。本実施形態では、表示装置10は、自動車1の運転席に搭載されるヘッドアップディスプレイとして説明するが、これに限定されるものでなく、他の乗り物、例えば、航空機や、鉄道等に搭載されるヘッドアップディスプレイであってもよい。
The
The
The
映像源11は、映像光を表示するディスプレイであり、例えば、透過型の液晶表示デバイスや、反射型の液晶表示デバイス、有機EL等を使用することができる。本実施形態の映像源11は、図1(a)に示すように、運転席からフロントウィンドウ2側を見て、光学シート20の下方側であって、光学シート20よりも左側の位置に投射光学系12とともに配置されている。
具体的には、映像源11は、図2(a)に示すように、光学シート20の厚み方向(Y方向)から見た状態において、映像源11の映像光Lの出射位置11aと光学シート20の幾何学的中心C1とを結ぶ線分が、光学シート20の幾何学的中心C1を通り、上下方向(Z方向)に平行な線に対して右側に傾斜するようにして配置されている。これにより、表示装置10は、運転席のハンドル4や計器類5の周囲を避けて映像源11を配置することができ、運転席内における映像源11の配置位置の自由度を向上させることができる。ここで、映像源11の出射位置11aとは、映像源11の映像光Lが出射する面の幾何学的中心となる位置である。
投射光学系12は、映像源11の出射位置11aの近くに配置され、映像源11から出射された映像光を投射する複数のレンズ群から構成される光学系である。
The
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2A, the
The projection
光学シート20は、光透過性を有する層であり、図1に示すように、フロントウィンドウ2の内側(車内側)の面の右側(運転席前)に貼り付けられている。光学シート20は、図2(b)に示すように、運転者側(+Y側)から順に光学形状層(第1光学形状層)21、反射層22、背面層(第2光学形状層)23が積層されている。光学シート20は、運転者の視界を妨げない観点から、フロントウィンドウ2を通して運転席から見える自動車の進行方向の光の一部を、光学シート20の背面側から運転者側へ透過させて、その光と映像光とを重ねて見せる、いわゆるシースルー機能を備えている。
光学形状層21は、光透過性を有する層であり、図2(a)に示すように、単位光学形状21aが平行に複数配列されたリニアフレネルレンズ形状を、その背面側(−Y側)の面に有している。なお、光学形状層21の単位光学形状21aは、リニアフレネルレンズ形状に限定されない。例えば、単位光学形状21aが同心円状に複数配列されたサーキュラーフレネルレンズ形状であってもよい。
The
The
単位光学形状21aは、図2(c)に示すように、シート面(XZ面)に直交する方向(厚み方向、Y方向)に平行であって、単位光学形状21aの配列方向R1に平行な断面における断面形状が、略三角形状(プリズム形状)である。
単位光学形状21aは、背面側に凸であり、映像光が直接入射する第1傾斜面21bと、この第1傾斜面21bと対向する第2傾斜面21cとを備えている。本実施形態において、単位光学形状21aは、第1傾斜面21bが頂部tを挟んで第2傾斜面21cよりも上側(+Z側)に位置している。
この単位光学形状21aは、光学シート20のシート面内(XZ面内)において、その配列方向R1と直交する方向に延在している。
As shown in FIG. 2C, the unit
The unit
The unit
単位光学形状21aの配列方向R1は、図2(a)に示すように、光学シート20を厚み方向(Y方向)から見た場合において、映像源11の映像光Lの出射位置11aと光学シート20の幾何学的中心C1とを通る線分と同じ側、すなわち本実施形態では右側(+X側)に傾斜している。このような構成にすることによって、光学シート20は、光学シート20に対して左側斜め下側に配置される映像源11から投射される映像光を効率よく運転者側に反射することができる。
ここで、図2(c)に示すように、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bが、シート面(XZ面)に平行な面となす角度は、αである。第2傾斜面21cがシート面に平行な面となす角度は、β(β>α)である。単位光学形状21aの配列ピッチは、Pである。単位光学形状21aの高さ(厚み方向における頂部tから単位光学形状21a間の谷部vまでの寸法)は、hである。単位光学形状21aの谷部vから、単位光学形状21aが設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さは、d1である。単位光学形状21aの頂部tから、単位光学形状21aが設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さは、d2である。深さd2は、光学形状層21の最も深い厚み寸法である。
As shown in FIG. 2A, the arrangement direction R1 of the unit
Here, as shown in FIG. 2C, the angle formed by the first
光学形状層21において、配列ピッチPは、100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。角度αは25°≦α≦40°、角度βは80°≦β≦90°の範囲で形成することが望ましい。高さhは10≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。深さd1及びd2は、それぞれ5μm≦d1≦100μm、15μm≦d2≦400μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。
後述するように、本実施形態の単位光学形状21aは、高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaが0.05μm以下となるように形成される。
なお、理解を容易にするために、図2では、単位光学形状21aの配列ピッチP、角度α、βは、単位光学形状21aの配列方向において一定であるように示している。本実施形態の単位光学形状21aは、配列ピッチP、角度β等が一定であるが、角度αが単位光学形状21aの配列方向において映像源11から離れるにつれて次第に大きくなってもよく、また、それに伴い高さhも変動してもよい。
また、これに限らず、配列ピッチPは、単位光学形状21aの配列方向に沿って次第に変化する形態等としてもよく、映像源から投影される映像の大きさや、映像源11の投射角度(光学シート20の運転者側の面への映像光の入射角度)、運転者側に反射する映像のサイズ、各層の屈折率等に応じて、適宜変更可能である。
In the
As will be described later, the unit
For ease of understanding, FIG. 2 shows that the arrangement pitch P, angles α, and β of the unit
Further, the arrangement pitch P may be not limited to this, and may be in a form that gradually changes along the arrangement direction of the unit
光学形状層21は、ウレタンアクリレートやエポキシアクリレート等の紫外線硬化性樹脂によりUV成形法等によって形成されている。なお、光学形状層21は、電子線硬化性樹脂等の他の電離放射線硬化性樹脂により形成されてもよい。また、光学形状層21は、熱可塑性樹脂、熱硬化性樹脂、紫外線硬化性樹脂と熱硬化性樹脂とを組み合わせた樹脂、熱可塑性樹脂と紫外線硬化性樹脂とを組み合わせた樹脂等によって形成されてもよい。
The
反射層22は、入射した光の一部を反射し、その他を透過する半透過型の反射層、いわゆるハーフミラーである。反射層22の反射率と透過率の割合は、適宜設定することができる。なお、映像光を良好に反射させるとともに、自動車の進行方向側から入射する光を十分に透過させて、運転者の視界を良好にする観点から、透過率が70%以上の範囲であることが望ましい。
反射層22は、光反射性の高い金属、例えば、アルミニウムや、銀、ニッケル等により形成されている。本実施形態では反射層22は、アルミニウムを蒸着することにより形成されている。また、これに限らず反射層22は、光反射性の高い金属をスパッタリングしたり、金属箔を転写したり、金属薄膜片を含有した塗料を塗布したりする等により形成されてもよい。
本実施形態の反射層22は、アルミニウムの蒸着によって約40〜60Åの厚みに形成されているが、光の透過率を上述の好ましい範囲に設定できるのであれば、その材料等に応じて厚さを自由に設定することができる。
なお、本実施形態の反射層22は、第1傾斜面21bの全面に形成されるが、これに限らず、第1傾斜面21bの一部に形成されていてもよい。
The
The
The
The
背面層23は、光学形状層21の背面側(−Y側)の面に設けられた層であり、光学シート20の最背面を平坦にするために設けられている。背面層23は、光透過性の高いウレタンアクリレート樹脂、エポキシアクリレート樹脂等から形成され、その屈折率は光学形状層21と同等である。背面層23の背面側の面は、不図示の接合層を介してフロントウィンドウ2に接合される面であり、フロントウィンドウ2を介して背面側から光学シート20内に入射する光の入射面である。
なお、光学シート20をフロントウィンドウ2に接合する接合層は、光透過性を有する粘着剤や接着剤を用いることができ、例えば、アクリル樹脂や、ウレタン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、フェノール樹脂、シリコーン樹脂等を用いることが可能である。
The
A light-transmitting pressure-sensitive adhesive or adhesive can be used as the bonding layer for bonding the
次に、本実施形態の光学シート20へ入射する映像光L及び外界からの光Gについて説明する。
図1(b)に示すように、映像源11から投射された映像光Lは、投射光学系12を介して、光学シート20の運転者側の面へ入射する。光学シート20に入射した映像光Lの一部の光L1は、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bに入射し、反射層22において運転者側へ反射する。そして、外界からの光Gは、その一部が光学シート20の背面側から運転者側へ透過する。そのため、運転者は、外界からの光Gと映像光Lとを重ねて見ることができる。また、映像光Lの他の一部の光L2は、反射層22を透過した後、背面層23を透過して、光学シート20の背面側(−Y側)の面から出射する。
Next, the image light L incident on the
As shown in FIG. 1B, the image light L projected from the
次に、第1実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法について説明する。
図3は、第1実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法を説明する図である。図3の各分図は、光学シート20が製造されるまでの過程を示す図である。
まず、図3(a)に示すように、単位光学形状21a(第1傾斜面21b、第2傾斜面21c)に対応する凹凸形状が設けられた成形型(不図示)を使用して、光学シート20を構成する光学形状層21をUV成形法等により成形する。この光学形状層21の成形工程については、後に詳細に説明する。
次に、図3(b)に示すように、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21b上に、真空蒸着法により蒸着金属(アルミニウム)ALを蒸着して反射層22を形成する。本実施形態では、真空蒸着装置を使用し、真空状態下においてアルミニウムを加熱、溶融して、光学形状層21の第1傾斜面21bに対してそのアルミニウムを蒸着する。
続いて、図3(c)に示すように、光学形状層21の単位光学形状21aが形成された側の面に、背面層23を構成する樹脂を充填し、平坦面が形成された金型によって押圧する。そして、硬化させた後に離型することにより、背面層23を形成することができる。以上の過程により、光学形状層21、反射層22、背面層23が順に積層された光学シート20が完成する。
Next, the method of manufacturing the
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a method of manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 3A, optics are performed using a molding die (not shown) provided with a concavo-convex shape corresponding to the unit
Next, as shown in FIG. 3B, a vapor-deposited metal (aluminum) AL is vapor-deposited on the first
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 3C, a mold in which the surface of the
次に、光学シート20を構成する光学形状層21の製造方法について説明する。
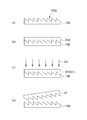
図4は、第1実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法を説明する図である。なお、本実施形態及び後述する他の実施形態の図面においては、部材の断面を示すハッチングを省略する。
まず、図4(a)に示すように、製造する光学形状層21の形状に対応した賦形面100aを有する成形型100を用意し、賦形面100aが上方(重力方向の天側)を向くように配置する。なお、成形型100は、金型でもよいし、樹脂型でもよい(他の実施形態も同様)。
次に、図4(b)に示すように、賦形面100a上に未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210を充填する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程)。ここでは、例えば、紫外線硬化樹脂210を、賦形面100a上の一辺に沿って点状又は線状に塗布し、不図示のローラ等で引き延ばすことにより、賦形面100a上に均一に充填できる(他の実施形態も同様)。
次に、図4(c)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210に対して紫外線UVを照射する(第1光学形状層成形工程)。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化して光学形状層21となる。
紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化した後、図4(d)に示すように、硬化後の紫外線硬化樹脂210を成形型100から剥離して、光学形状層21を得る(第1光学形状層作製工程)。
このようにして得られた光学形状層21を、図3に示した光学シート20の製造方法に用いることによって、本実施形態の光学シート20が完成する。
Next, a method of manufacturing the
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a method for manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 4A, a
Next, as shown in FIG. 4B, the uncured ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 4C, the uncured ultraviolet
After the ultraviolet
By using the
以上説明したように、第1実施形態の表示装置10によれば、映像源11から投射された映像光Lのうち、運転者側に届く光のほとんどは、光学シート20の単位光学形状21aで反射した光となる(図2(b)参照)。そのため、表示装置10においては、従来の合わせガラスにHUDの映像光を投影したときのように、光の屈折により映像光が二重像として運転者に視認される不具合が抑制されるため、運転者に対して鮮明な映像を表示することができる。
As described above, according to the
また、光学シート20の単位光学形状21aにおいて、第1傾斜面21bがシート面(XZ面)に平行な面となす角度α及び第2傾斜面21cがシート面に平行な面となす角度βは、光学シート20が貼り付けられたフロントウィンドウ2を自動車1に取り付けたときの傾斜角度、映像源11からの映像光の投射角度等に応じて容易に設計できる。また、光学形状層21は、例えば、ロールツーロール方式等の手法を用いることにより、設計通りの形状を容易に製造することができる。すなわち、第1実施形態の光学シート20は、設計及び製造が容易であり、低コストで製造することができる。
また、光学シート20を貼り付けるフロントウィンドウ2は、中間層の断面を矩形状とした一般的な合わせガラスでよいため、光学シート20を、より多くの車種に取り付けることができる。
Further, in the unit
Further, since the
また、光学形状層21の製造方法においては、紫外線硬化樹脂210に基材を貼り付けない状態で紫外線を照射するため、紫外線硬化樹脂210を収縮可能な状態で硬化させることができる。これによれば、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されないため、光学形状層21を成形型100から剥離した時に、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bにおけるうねりの発生を抑制できる。
そのため、単位光学形状21aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下にすることができる。
Further, in the method of manufacturing the
Therefore, in the shape in which the height h of the unit
これに対して、紫外線硬化樹脂210に基材を貼り付けた状態で紫外線を照射する従来の製造方法では、成形型100と基材(不図示)との間に挟まれた紫外線硬化樹脂210は収縮することができず、その収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されていた。そのため、成形型100から剥離した時に、紫外線硬化樹脂210に蓄積された残留応力により、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bにうねりが生じることがあった。第1傾斜面21bにうねりが生じると、その表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側(+Y側)に設計通りの角度で反射させることが難しくなる。その結果、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として運転者に視認されやすくなる。
On the other hand, in the conventional manufacturing method of irradiating ultraviolet rays with the base material attached to the ultraviolet
しかし、本実施形態の製造方法によれば、上述した理由により、光学形状層21の第1傾斜面21bにおける算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下にできるため、第1傾斜面21bの表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができる。これによれば、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として運転者に視認される不具合が更に抑制されるため、運転者に対してより鮮明な映像を表示することができる。
したがって、本実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
However, according to the manufacturing method of the present embodiment, the arithmetic mean waviness Wa on the first
Therefore, according to the method for manufacturing the
(第2実施形態)
次に、第2実施形態について説明する。第2実施形態の光学シート20は、光学形状層21の製造工程が第1実施形態と異なる。それ以外の光学シート20の構成は、第1実施形態と同じであるため、共通する説明を適宜に省略して、相違点のみを説明する。また、第1実施形態と共通する構成部分には、同じ符号を付して説明する。
図5は、第2実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法を説明する図である。
まず、図5(a)に示すように、製造する光学形状層21の形状に対応した賦形面100aを有する成形型100を用意し、賦形面100aが上方を向くように配置する。
第2実施形態において、賦形面100aにより賦形される光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2は、それぞれ、20μm≦d1≦100μm、30μm≦d2≦400μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさは、深さd1及びd2の差に比例する。すなわち、深さd1とd2との差が大きいほど、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮は大きくなる。したがって、光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2を上述した範囲とし、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて基材220(後述)の厚みs1を後述する範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。なお、本実施形態において、光学形状層21における配列ピッチP、高さhは、第1実施形態と同じである。
(Second Embodiment)
Next, the second embodiment will be described. The
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a method for manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 5A, a
In the second embodiment, it is desirable that the depths d1 and d2 of the
次に、図5(b)に示すように、賦形面100a上に紫外線硬化樹脂210を充填する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程)。
次に、図5(c)に示すように、賦形面100a上に充填された未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に、基材220を貼り付ける(基材貼り付け工程)。本実施形態の基材220は、紫外線硬化樹脂210の収縮とともに変形可能な基材である。そのため、基材220の厚みs1は、上述した単位光学形状21aの深さd1及びd2に合わせて、8μm≦s1≦50μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。基材220の厚みs1をこのような範囲とすることにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮に応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。
次に、図5(d)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、基材220を介して、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210に対して紫外線UVを照射する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂照射工程)。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化して光学形状層21となる。
紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化した後、図5(e)に示すように、硬化後の紫外線硬化樹脂210から基材220を剥離する(基材剥離工程)。
次に、図5(f)に示すように、光学形状層21を成形型100から剥離して、光学形状層21を得る(第1光学形状層剥離工程)。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5B, the UV
Next, as shown in FIG. 5C, the
Next, as shown in FIG. 5D, the uncured ultraviolet
After the ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 5 (f), the
第2実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法においては、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮に応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。これによれば、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されないため、成形型100から剥離した時に、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bにおけるうねりの発生を抑制できる。そのため、単位光学形状21aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが10μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下にすることができる。その結果、第1傾斜面21bの表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができる。したがって、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として観察者に視認される不具合を抑制できる。
また、光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2を、それぞれ、20μm≦d1≦100μm、30μm≦d2≦400μmの範囲で形成し、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて、基材220の厚みs1を8μm≦s1≦50μmの範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。
したがって、第2実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
In the method for producing the
Further, the depths d1 and d2 of the
Therefore, according to the method for manufacturing the
(第3実施形態)
次に、第3実施形態の表示装置10Aについて説明する。
図6は、第3実施形態の表示装置10を説明する図である。図6(a)は、光学シート20の左右方向の中心線上における断面図であり、図2(b)のb部断面に相当する部分断面図である。また、図6(b)は、第3実施形態における光学シート20の他の構成を示す断面図である。
第3実施形態の表示装置10Aは、映像源11、投射光学系12、光学シート20を含むフロントウィンドウ2を備えている。このうち、映像源11、投射光学系12の構成は、第1実施形態の表示装置10と同じであるため、ここでは第1実施形態との相違点についてのみ説明する。
(Third Embodiment)
Next, the
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating the
The
第3実施形態の表示装置10Aにおいて、光学シート20は、フロントウィンドウ2の内部に配置されている。すなわち、本実施形態の光学シート20は、後述する2枚のガラス(31、34)の間に挟まれてフロントウィンドウ2と一体に成形された、いわゆる合わせガラスの形態で使用される。また、本実施形態の光学シート20は、フロントウィンドウ2の全面に配置されている。
図6(a)に示すように、本実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2は、運転者側(+Y側)から順に、第1ガラス31、第1中間層32、光学シート20、第2中間層33及び第2ガラス34を備えている。
第1ガラス31は、フロントウィンドウ2の最も運転席側に配置された透明な部材である。第1ガラス31としては、例えば、ソーダライムガラス(青板ガラス)、硼珪酸ガラス(白板ガラス)、石英ガラス、ソーダガラス、カリガラス等の材料を用いることができる。また、第1ガラス31の厚みは、2〜3mmの範囲とすることが好ましい。
In the
As shown in FIG. 6A, the
The
第1中間層32は、第1ガラス31と光学シート20との間に配置された層である。第1ガラス31及び光学シート20は、第1中間層32により接合されている。第1中間層32は、フロントウィンドウ2の破損時に、第1ガラス31の破片が飛散するのを防止するために配置されている。第1中間層32としては、例えば、PVB(ポリビニルブラチール)を用いることができる。第1中間層32の厚みは、0.3〜0.8mmの範囲とすることが好ましい。また、第1中間層32の屈折率は、第1ガラス31、光学形状層21(光学シート20)と同等であることが望ましい。
The first
光学シート20は、第1実施形態の光学シート20と同じく、入射した光の一部を運転者側に反射し、その他の光を透過させるシートである。光学シート20の基本的な構成は、第1実施形態と同じである。本実施形態の光学シート20は、光学形状層21の運転者側(+Y側)に基材層24を備えている点において、第1実施形態と相違する。
基材層24は、光学形状層21を形成する際のベースとなる平板状の部材である。基材層24は、例えば、光透過性の高いPET等のポリエステル樹脂、アクリル樹脂、スチレン樹脂、アクリルスチレン樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、脂環式ポリオレフィン樹脂等から形成される。
Like the
The
第2中間層33は、第2ガラス34と光学シート20との間に配置された層である。第2ガラス34及び光学シート20は、第2中間層33により接合されている。第2中間層33は、フロントウィンドウ2の破損時に、第2ガラス34の破片が飛散するのを防止するために配置されている。第2中間層33としては、第1中間層32と同じく、PVBを用いることができる。第2中間層33の厚みは、0.3〜0.8mmの範囲とすることが好ましい。また、第2中間層33の屈折率は、第1ガラス31、光学形状層21と同等であることが望ましい。
第2ガラス34は、光学シート20の最も背面側(+Z側)に配置された透明な部材である。第2ガラス34としては、第1ガラス31と同じ材料を用いることができる。また、第2ガラス34の厚みは、2〜3mmの範囲とすることが好ましい。
The second
The
本実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2において、第1中間層32及び第2中間層33は、フロントウィンドウ2の上端部(+Z方向の最上端部)から下端部(−Z方向の最下端部)までの範囲において、それぞれ層厚が均等となるように形成されている。すなわち、フロントウィンドウ2において、第1中間層32及び第2中間層33の断面は楔形状ではなく、上端部から下端部までの範囲において層厚が均等な矩形状となる。したがって、中間層の断面を楔形状とした従来の合わせガラスに比べて、光学シート20を含むフロントウィンドウ2の設計及び製造が容易となる。
In the
次に、本実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2に入射する映像光L及び外界からの光Gの動きについて説明する。
図6(a)に示すように、映像源11から投射された映像光Lは、投射光学系12を介して、フロントウィンドウ2の運転者側の面へ入射する。フロントウィンドウ2に入射した映像光Lの一部の光L1は、第1ガラス31、第1中間層32及び基材層24を透過して、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bに入射し、反射層22において運転者側へ反射する。そして、外界からの光Gは、その一部がフロントウィンドウ2の背面側から運転者側へ透過する。そのため、運転者は、外界からの光Gと映像光Lとを重ねて見ることができる。また、映像光Lの他の一部の光L2は、反射層22を透過した後、背面層23、第2中間層33及び第2ガラス34を透過して、フロントウィンドウ2の背面側(+Z側)の面から出射する。更に、映像光Lの他の一部の光L3は、フロントウィンドウ2の第1ガラス31により、斜め上側(+Y側)へ反射する。そのため、光L3は、そのほとんどが運転者側に届くことはない。
Next, the movements of the image light L incident on the
As shown in FIG. 6A, the image light L projected from the
次に、第3実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法について説明する。
先に説明したように、第3実施形態の光学シート20は、光学形状層21の運転者側(+Y側)に基材層24を備えている点において、第1実施形態と相違する。ここでは、基材層24を備えた光学形状層21の製造方法について説明する。
図7は、第3実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法を説明する図である。
まず、図7(a)に示すように、製造する光学形状層21の形状に対応した賦形面100aを有する成形型100を用意し、賦形面100aが上方を向くように配置する。
第3実施形態において、賦形面100aにより賦形される光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2は、それぞれ、5μm≦d1≦200μm、45μm≦d2≦800μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。
後述するように、本実施形態の単位光学形状21aは、高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaが0.05μm以下となるように形成される。
Next, a method of manufacturing the
As described above, the
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a method for manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 7A, a
In the third embodiment, it is desirable that the depths d1 and d2 of the
As will be described later, the unit
次に、図7(b)に示すように、賦形面100a上に未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210を充填する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程)。
次に、図7(c)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210に対して紫外線UVを照射する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂照射工程)。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化して光学形状層21となる。
紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化した後、図7(d)に示すように、紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に、基材層24を貼り付ける(基材貼り付け工程)。基材層24の厚みs2は、光学シート20の仕様により異なるが、およそ100μm≦s2≦1000μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。また、基材層24の背面側の面は、入射する光の拡散を抑制する観点から平滑(例えば、60度の光沢度で90以上)に形成することが望ましい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7B, the uncured ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 7 (c), the uncured ultraviolet
After the ultraviolet
図示していないが、上述した基材層24の貼り付けは、例えば、以下のような手順で行うことができる。まず、硬化した紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に、紫外線硬化樹脂210と同じ材質の未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂を一辺に沿って点状又は線状に塗布する。そして、不図示のローラ等で引き延ばすことにより、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂を、硬化した紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に均一に塗布する。次に、重ねて塗布した未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂の上に基材層24を積層する。これにより、硬化した紫外線硬化樹脂210と基材層24との間に未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂が均一に充填される。
Although not shown, the above-mentioned
次に、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂に対し、基材層24を介して紫外線UVを照射する。これにより、重ねて塗布した未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂が硬化して、紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に基材層24が貼り付けられる。
なお、基材層24を未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂の上に積層した後、不図示のローラ等を基材層24に圧着させながら、基材層24の上を移動させることにより、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂を引き延ばしてもよい。この場合、塗布した未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂に気泡等が含まれていても、それらの気泡等は、ローラ等の進行方向に沿って移動し、外部に押し出される。これによれば、硬化した紫外線硬化樹脂210と基材層24との間に未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂を均一に充填できるだけでなく、気泡等を効率良く排除できるので、より好ましい。また、重ねて塗布する未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂として、硬化後に紫外線硬化樹脂210と同じ屈折率となる他の紫外線硬化樹脂を用いてもよい。
次に、図7(e)に示すように、光学形状層21を基材層24とともに成形型100から剥離して、基材層24と接合された光学形状層21を得る(第1光学形状層作製工程)。
Next, the uncured ultraviolet curable resin is irradiated with ultraviolet UV through the
After laminating the
Next, as shown in FIG. 7E, the
第3実施形態のフロントウィンドウ2は、上端部から下端部までの範囲において、それぞれ層厚が均等であるため、中間層の断面を楔形状とした従来の合わせガラスに比べて設計及び製造が容易であり、低コストで製造することができる。
また、第3実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法においては、紫外線硬化樹脂210に基材層24を貼り付けない状態で紫外線を照射するため、紫外線硬化樹脂210を収縮可能な状態で硬化させることができる。これによれば、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されないため、光学形状層21を成形型100から剥離した時に、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bにおけるうねりの発生を抑制できる。
そのため、単位光学形状21aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下にすることができる。これによれば、第1傾斜面21bの表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができるため、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として運転者に視認される不具合が更に抑制され、運転者に対してより鮮明な映像を表示することができる。
したがって、本実施形態の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
Since the
Further, in the method for manufacturing the
Therefore, in the shape in which the height h of the unit
Therefore, according to the manufacturing method of the present embodiment, it is possible to manufacture the
なお、第3実施形態における光学シート20は、図6(b)に示すような層構成としてもよい。図6(b)に示す光学シート20は、光学形状層21と第1中間層32との間及び背面層23と第2中間層33との間に、それぞれ基材層24が設けられている点において、図6(a)に示す光学シート20と相違する。その他の層構成は、図6(a)に示す光学シート20と同じである。本実施形態の光学シート20を備えたフロントウィンドウ2においても、図6(a)に示すフロントウィンドウ2と同様の光学特性が得られる。
また、図6(b)に示す層構成では、基材層24が運転者側に配置されているため、光学シート20の運転席側の平坦性を向上させることができる。そのため、光学シート20の光学性能をより向上させることができる。
The
Further, in the layer structure shown in FIG. 6B, since the
(第4実施形態)
第4実施形態は、光学形状層21の製造過程が第3実施形態と異なる。それ以外の光学シート20の構成は、第3実施形態と同じであるため、共通する説明を適宜に省略して、相違点のみを説明する。また、第3実施形態と共通する構成部分には、同じ符号を付して説明する。
図8は、第4実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法を説明する図である。
まず、図8(a)に示すように、製造する光学形状層21の形状に対応した賦形面100aを有する成形型100を用意し、賦形面100aが上方を向くように配置する。
第4実施形態において、賦形面100aにより賦形される光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2は、それぞれ、10μm≦d1≦200μm、50μm≦d2≦800μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2を上述した範囲とし、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて基材層24の厚みs2を後述する範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材層24をより適切に変形させることができる。なお、本実施形態において、光学形状層21における配列ピッチP、高さhは、第1実施形態と同じである。
(Fourth Embodiment)
In the fourth embodiment, the manufacturing process of the
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a method of manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 8A, a
In the fourth embodiment, it is desirable that the depths d1 and d2 of the
次に、図8(b)に示すように、賦形面100a上に紫外線硬化樹脂210を充填する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程)。
次に、図8(c)に示すように、賦形面100a上に充填された未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に、基材層24を貼り付ける(基材貼り付け工程)。本実施形態の基材層24は、紫外線硬化樹脂210の収縮とともに変形可能な基材である。そのため、基材層24の厚みs2は、上述した単位光学形状21aの深さd1及びd2に合わせて、10μm≦s2≦100μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。基材層24の厚みs2をこのような範囲とすることにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮に応じて、基材層24をより適切に変形させることができる。
次に、図8(d)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、基材層24を介して、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210に対して紫外線UVを照射する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂照射工程)。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化して光学形状層21となる。
紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化した後、図8(e)に示すように、光学形状層21を基材層24とともに成形型100から剥離して、基材層24と接合された光学形状層21を得る(第1光学形状層作製工程)。
Next, as shown in FIG. 8B, the UV
Next, as shown in FIG. 8C, the
Next, as shown in FIG. 8D, the uncured ultraviolet
After the ultraviolet
第4実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法においては、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮に応じて、基材層24をより適切に変形させることができる。これによれば、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されないため、成形型100から剥離した時に、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21bにおけるうねりの発生を抑制できる。そのため、単位光学形状21aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが10μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下にすることができる。その結果、第1傾斜面21bの表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができる。したがって、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として観察者に視認される不具合を抑制できる。
また、光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2を、それぞれ、10μm≦d1≦200μm、50μm≦d2≦800μmの範囲で形成し、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて、基材層24の厚みs2を10μm≦s2≦100μmの範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材層24をより適切に変形させることができる。
したがって、第4実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
In the method for producing the
Further, the depths d1 and d2 of the
Therefore, according to the method for manufacturing the
(第5実施形態)
第5実施形態は、光学形状層21の製造過程が第3実施形態と異なる。それ以外の光学シート20の構成は、第3実施形態と同じであるため、共通する説明を適宜に省略して、相違点のみを説明する。また、第3実施形態と共通する構成部分には、同じ符号を付して説明する。
図9は、第5実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法を説明する図である。
まず、図9(a)に示すように、製造する光学形状層21の形状に対応した賦形面100aを有する成形型100を用意し、賦形面100aが上方を向くように配置する。
第5実施形態において、光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2は、それぞれ、10μm≦d1≦200μm、50μm≦d2≦800μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。また、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて、基材220の厚みs1を後述する範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。なお、本実施形態において、光学形状層21における配列ピッチP、高さhは、第1実施形態と同じである。
(Fifth Embodiment)
In the fifth embodiment, the manufacturing process of the
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating a method of manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 9A, a
In the fifth embodiment, it is desirable that the depths d1 and d2 of the
次に、図9(b)に示すように、賦形面100a上に紫外線硬化樹脂210を充填する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程)。
次に、図9(c)に示すように、賦形面100a上に充填された未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210の上に、基材(第1基材)220を貼り付ける(第1基材貼り付け工程)。本実施形態の基材220は、紫外線硬化樹脂210の収縮とともに変形可能な基材である。そのため、基材220の厚みs1は、上述した単位光学形状21aの深さd1及びd2に合わせて、10μm≦s1≦100μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。基材220の厚みs1をこのような範囲とすることにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮に応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。
次に、図9(d)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、基材220を介して、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂210に対して紫外線UVを照射する(エネルギー線硬化樹脂照射工程)。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化して光学形状層21となる。
Next, as shown in FIG. 9B, the UV
Next, as shown in FIG. 9C, the base material (first base material) 220 is attached onto the uncured ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 9D, the uncured ultraviolet
紫外線硬化樹脂210が硬化した後、図9(e)に示すように、硬化後の紫外線硬化樹脂210から基材220を剥離する。
次に、図9(f)に示すように、硬化後の紫外線硬化樹脂210の表面に基材層(第2基材)24を貼り付ける(第2基材貼り付け工程)。基材層24の厚みs2は、光学シート20の仕様により異なるが、およそ100μm≦s2≦1000μmの範囲で形成することが望ましい。また、基材層24の背面側の面は、入射する光の拡散を抑制する観点から平滑(例えば、60度の光沢度で90以上)に形成することが望ましい。
次に、図9(g)に示すように、光学形状層21を成形型100から剥離して、基材層24と接合された光学形状層21を得る(第1光学形状層剥離工程)。
After the ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 9 (f), the base material layer (second base material) 24 is attached to the surface of the cured ultraviolet curable resin 210 (second base material pasting step). The thickness s2 of the
Next, as shown in FIG. 9 (g), the
第5実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法においても、第4実施形態と同様の理由により、第1傾斜面21bの表面に形成される反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができる。したがって、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として観察者に視認される不具合を抑制できる。
また、光学形状層21の深さd1及びd2を、それぞれ、10μm≦d1≦200μm、50μm≦d2≦800μmの範囲で形成し、この深さd1及びd2に合わせて、基材(第1基材)220の厚みs1を10μm≦s1≦100μmの範囲で形成することにより、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮の大きさに応じて、基材220をより適切に変形させることができる。
したがって、第5実施形態の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
Also in the method for manufacturing the
Further, the depths d1 and d2 of the
Therefore, according to the manufacturing method of the fifth embodiment, the
(第6実施形態)
第6実施形態では、成形型100において収縮可能な状態で硬化させた光学形状層(第1光学形状層)21と、同じく成形型100において収縮可能な状態で硬化させた背面層(第2光学形状層)23と、を接合した光学シート20について説明する。第6実施形態の光学シート20の基本的な構成は、第3実施形態の光学シート20と同じであるため、共通する説明を適宜に省略して、相違点のみを説明する。また、第3実施形態と共通する構成部分には、同じ符号を付して説明する。
図10は、第6実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法を説明する図である。
まず、図10(a)に示すように、別の製造過程により得られた光学形状層21(単位光学形状21a)の表面に蒸着金属を付着させて、反射層22を形成する。ここで、光学形状層21は、例えば、第3実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法(図7参照)により得られた光学形状層21である。
(Sixth Embodiment)
In the sixth embodiment, the optical shape layer (first optical shape layer) 21 cured in the
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating a method of manufacturing the
First, as shown in FIG. 10A, a vapor-deposited metal is adhered to the surface of the optical shape layer 21 (unit
次に、図10(b)に示すように、光学形状層21の単位光学形状21aが設けられた側の面に、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂250を充填する。ここでは、例えば、紫外線硬化樹脂250を、光学形状層21の一辺に沿って点状又は線状に塗布し、不図示のローラ等で引き延ばすことにより、均一に充填できる。
次に、図10(c)に示すように、光学形状層21の上に、別の製造過程により得られた背面層23を積層する。具体的には、光学形状層21の単位光学形状21aが設けられた側の面と、背面層23の背面側単位光学形状23aが設けられた側の面とが対向するように、背面層23を積層する。ここでは、例えば、第1実施形態の光学形状層21の製造方法(図4参照)により得られた光学形状層21を背面層23として用いることができる。背面層23の背面側単位光学形状23aは、光学形状層21の単位光学形状21aに対応する。背面側単位光学形状23aには、図10(c)に示すように、光学形状層21の第1傾斜面21bに対応する第3傾斜面23bが形成されている。
Next, as shown in FIG. 10B, the surface of the
Next, as shown in FIG. 10 (c), the
そして、不図示のローラを背面層23の背面(背面側単位光学形状23aが設けられた側の反対面)に圧着させながら、背面層23の上を移動させることにより、光学形状層21と背面層23との層厚を調整する。不図示のローラを背面層23の背面に圧着させながら、背面層23の上を移動させると、余分な紫外線硬化樹脂250(及び気泡等)は、背面層23と光学形状層21との接合面から外部に押し出される。そのため、不図示のローラを背面層23の背面に圧着する際の圧力を適宜に設定することにより、光学形状層21と背面層23との層厚を所望の間隔に調整することができる。
次に、図10(d)に示すように、紫外線照射部(不図示)から、未硬化の紫外線硬化樹脂250に対して紫外線UVを照射する。これにより、紫外線硬化樹脂250が硬化して接合層25となる。
次に、図10(e)に示すように、背面層23の背面に基材層24を貼り付ける。
以上の過程により、基材層24、光学形状層21、反射層22、接合層25、背面層23、基材層24が順に積層された光学シート20が完成する。本実施形態の光学シート20は、例えば、図6(b)に示すフロントウィンドウ2に適用することができる。
Then, while the roller (not shown) is crimped to the back surface of the back surface layer 23 (the opposite surface on the side where the back side unit
Next, as shown in FIG. 10D, the uncured ultraviolet
Next, as shown in FIG. 10 (e), the
Through the above process, the
第6実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法においては、光学形状層21及び背面層23を成形する際に、紫外線硬化樹脂210に基材層24を貼り付けない状態で紫外線UVを照射するため、紫外線硬化樹脂210を収縮可能な状態で硬化させることができる。これによれば、紫外線硬化樹脂210の硬化時に生じる収縮が残留応力として内部に蓄積されないため、成形型100から剥離した時に、単位光学形状21aの第1傾斜面21b及び背面側単位光学形状23aの第3傾斜面23bにおけるうねりの発生をそれぞれ抑制できる。そのため、単位光学形状21aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状(第3実施形態の光学形状層21を用いた場合)において、第1傾斜面21bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下に抑えることができる。同様に、背面側単位光学形状23aの高さhが10μm≦h≦300μmの範囲で形成され、配列ピッチPが100μm≦P≦1000μmの範囲で形成された形状(第1実施形態の光学形状層21を用いた場合)において、第3傾斜面23bの算術平均うねりWaを0.05μm以下に抑えることができる。
このように、本実施形態の製造方法によれば、上述した理由により、光学形状層21の第1傾斜面21b及び背面層23の第3傾斜面23bにおける算術平均うねりWaをそれぞれ0.05μm以下にできる。そのため、第1傾斜面21bと第3傾斜面23bとの間に設けられた反射層22において、映像光を運転者側に設計通りの角度で反射させることができる。これによれば、光学シート20で反射した映像光が二重像として運転者に視認される不具合が抑制されるため、運転者に対してより鮮明な映像を表示することができる。
したがって、第6実施形態の光学シート20の製造方法によれば、光学性能をより向上させた光学シート20を製造することができる。
In the method for manufacturing the
As described above, according to the manufacturing method of the present embodiment, the arithmetic mean swell Wa on the first
Therefore, according to the method for manufacturing the
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、本発明は、前述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、後述する変形形態のように種々の変形や変更が可能であって、それらも本発明の技術的範囲内である。なお、各実施形態に記載した効果は、本発明から生じる最も好適な効果を列挙したに過ぎず、実施形態に記載した効果に限定されない。また、前述した実施形態及び後述する変形形態の構成は、適宜に組み合わせることもできるが、詳細な説明は省略する。以下、各実施形態に共通の変形形態については、第1〜第6実施形態を総称して「実施形態」という。 Although the embodiments of the present invention have been described above, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and various modifications and changes can be made as in the modified forms described later, and these are also the present invention. Is within the technical scope of. The effects described in each embodiment are merely a list of the most suitable effects resulting from the present invention, and are not limited to the effects described in the embodiments. Further, the configurations of the above-described embodiment and the later-described modified embodiment can be appropriately combined, but detailed description thereof will be omitted. Hereinafter, the modified forms common to each embodiment will be collectively referred to as "embodiments" from the first to sixth embodiments.
(変形形態)
(1)上述の実施形態において、単位光学形状21aの配列方向R1(図2(a)参照)に平行な断面における断面形状は、多角形、半球形、レンズ形等によるプリズム形状であってもよい。また、プリズム形状は、断面が単位光学形状21aの配列方向R1と直交する方向に延在していてもよいし、ディンプル形、ピラミッド形(三角錐、四角錐等)であってもよい。
(2)上述の実施形態において、反射層22は、アルミニウムの蒸着により形成する例に限定されるものではなく、例えば、光反射性の高い金属をスパッタリングしたり、金属箔を転写したり、金属薄膜を含有した塗料を塗布したりする等の手法により形成してもよい。
(3)上述の実施形態において、単位光学形状21aの第2傾斜面21cに微細な凹凸形状を形成してもよい。光学形状層21及び背面層23が同一の屈折率を有する材料により形成されていても、両者に微小な屈折率差が生じる場合がある。その場合、第2傾斜面21cを透過する光の一部が、その第2傾斜面21cにおいて反射して、2重像(ゴースト)として運転者に視認されることがある。しかし、第2傾斜面21cに微細な凹凸形状を形成することによって、第2傾斜面21cに入射した光を拡散させて2重像の発生を抑制することができる。
(Transformed form)
(1) In the above-described embodiment, the cross-sectional shape in the cross section parallel to the arrangement direction R1 (see FIG. 2A) of the unit
(2) In the above-described embodiment, the
(3) In the above-described embodiment, a fine uneven shape may be formed on the second
(4)上述の第1及び第2実施形態において、フロントウィンドウ2の内側の面に貼り付けられる光学シート20は、フロントウィンドウ2の下側全面を覆う大きさであってもよいし、フロントウィンドウ2の全面を覆う大きさであってもよい。
上述の第3〜第6実施形態において、フロントウィンドウ2の内部に配置される光学シート20は、例えば、第1実施形態の光学シート20(図1(a)参照)のように、フロントウィンドウ2の右側(運転席前)のみを覆う大きさであってもよいし、フロントウィンドウ2の下側全面を覆う大きさであってもよい。このように、フロントウィンドウ2の特定の領域のみを光学シート20で覆うようにした場合には、光学シート20が配置されていない領域に、例えば、第3実施形態の第1中間層32と同じ材質の中間層を配置すればよい。また、第3〜第6実施形態において、光学シート20をフロントウィンドウ2の全面に配置し、光学シート20として機能させたい領域のみに反射層22を形成してもよい。この場合、光学シート20として機能させたい領域を除く領域において、より高い透過率を得ることができる。
(4) In the first and second embodiments described above, the
In the third to sixth embodiments described above, the
(5)上述の実施形態において、表示装置10は、自動車1の運転席に配置される例を示したが、これに限定されず、他の乗り物の運転席等に配置されてもよい。また、表示装置10は、自動車1のフロントウィンドウ2に限らず、サイドウィンドウ、リアウィンドウ等に配置されてもよい。更に、表示装置10は、背景等の外界の光を透過する店舗等のショーウィンドウ等に適用することもできる。この場合、例えば、ショーウィンドウの内側の面に光学シート20(第1及び第2実施形態)を貼り付けて、光学シート20の左側又は右側の斜め下方又は上方に映像源11を配置することによって、店舗の外側からショーウィンドウに展示される商品を見せるとともに、映像源11から商品の情報等を表示することができる。
(6)上述の第1及び第2実施形態において、光学シート20の運転者側(+Y側)の面に、傷つき防止を目的としたハードコート処理を施してもよい。このハードコート処理は、例えば、光学シート20の運転者側の面に、ハードコート機能を有する紫外線硬化型樹脂(例えば、ウレタンアクリレート等)を塗布してハードコート層を形成してもよい。
(5) In the above-described embodiment, the
(6) In the first and second embodiments described above, the surface of the
20 光学シート
21 光学形状層
21a 単位光学形状
21b 第1傾斜面
21c 第2傾斜面
22 反射層
23 背面層
24 基材層
100 成形型
100a 賦形面
210 紫外線硬化樹脂
220 基材
20
Claims (3)
前記単位光学形状を賦形する賦形面を有する成形型に、未硬化のエネルギー線硬化樹脂を充填するエネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程と、
前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂にエネルギー線を照射して、前記成形型に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を収縮可能な状態で硬化させて、前記第1光学形状層を成形する第1光学形状層成形工程と、
硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から第1光学形状層を得る第1光学形状層作製工程と、
前記第1光学形状層に設けられた前記単位光学形状の少なくとも前記第1傾斜面に反射層を形成する反射層形成工程と、
前記第1光学形状層の反射層が形成された側の面に第2光学形状層を形成する第2光学形状層形成工程と、
を含む光学部材の製造方法であって、
前記成形型に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に、前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の収縮とともに変形可能な基材を貼り付ける基材貼り付け工程を含み、
前記第1光学形状層作製工程は、
硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から前記基材を剥離する基材剥離工程と、
前記基材の剥離された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記成形型から剥離して、前記第1光学形状層を得る第1光学形状層剥離工程と、を含み、
前記第1光学形状層は、
前記単位光学形状の谷部から、前記単位光学形状が設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さd1が20μm≦d1≦100μmの範囲で形成され、
前記単位光学形状の頂部から、前記単位光学形状が設けられた側と反対側の面までの深さd2が30μm≦d2≦400μmの範囲で形成され、
前記基材の厚みが8μm≦s1≦50μmの範囲で形成されること、
を特徴とする光学部材の製造方法。 A first optical shape layer in which a plurality of unit optical shapes having a first inclined surface and a second inclined surface are arranged is provided, and a part of the image light projected from the image source is directed to the observer side at least on the first inclined surface. It is a method of manufacturing an optical member that reflects light.
An energy ray-curable resin filling step of filling an uncured energy ray-curable resin into a molding die having a shaped surface that shapes the unit optical shape.
First optical shape layer molding in which the energy ray-curable resin is irradiated with energy rays to cure the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding mold in a shrinkable state to form the first optical shape layer. Process and
A first optical shape layer manufacturing step of obtaining a first optical shape layer from the cured energy ray-curable resin, and
A reflection layer forming step of forming a reflection layer on at least the first inclined surface of the unit optical shape provided on the first optical shape layer.
The second optical shape layer forming step of forming the second optical shape layer on the surface on the side where the reflection layer of the first optical shape layer is formed, and
It is a manufacturing method of an optical member including
A base material sticking step of sticking a base material deformable with shrinkage of the energy ray-curable resin on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding mold is included.
The first optical shape layer manufacturing step is
A base material peeling step of peeling the base material from the energy ray-curable resin after curing,
And peeled peeled said energy ray-curable resin of the substrate from the mold, a first optical shape layer peeling step of obtaining the first optical shape layer, only including,
The first optical shape layer is
The depth d1 from the valley portion of the unit optical shape to the surface opposite to the side on which the unit optical shape is provided is formed in the range of 20 μm ≦ d1 ≦ 100 μm.
The depth d2 from the top of the unit optical shape to the surface opposite to the side on which the unit optical shape is provided is formed in the range of 30 μm ≦ d2 ≦ 400 μm.
The thickness of the base material is formed in the range of 8 μm ≦ s1 ≦ 50 μm.
A method for manufacturing an optical member.
前記単位光学形状を賦形する賦形面を有する成形型に、未硬化のエネルギー線硬化樹脂を充填するエネルギー線硬化樹脂充填工程と、
前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂にエネルギー線を照射して、前記成形型に充填された前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を収縮可能な状態で硬化させて、前記第1光学形状層を成形する第1光学形状層成形工程と、
硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂から第1光学形状層を得る第1光学形状層作製工程と、
前記第1光学形状層に設けられた前記単位光学形状の少なくとも前記第1傾斜面に反射層を形成する反射層形成工程と、
前記第1光学形状層の反射層が形成された側の面に第2光学形状層を形成する第2光学形状層形成工程と、
を含む光学部材の製造方法であって、
硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂の表面に、前記観察者側とは反対側である背面側の面が60度の光沢度で90以上である基材を貼り付ける基材貼り付け工程を含み、
前記第1光学形状層作製工程では、硬化後の前記エネルギー線硬化樹脂を前記基材とともに前記成形型から剥離して、前記基材の接合された前記第1光学形状層を得ること、
を特徴とする光学部材の製造方法。 A first optical shape layer in which a plurality of unit optical shapes having a first inclined surface and a second inclined surface are arranged is provided, and a part of the image light projected from the image source is directed to the observer side at least on the first inclined surface. It is a method of manufacturing an optical member that reflects light.
An energy ray-curable resin filling step of filling an uncured energy ray-curable resin into a molding die having a shaped surface that shapes the unit optical shape.
First optical shape layer molding in which the energy ray-curable resin is irradiated with energy rays to cure the energy ray-curable resin filled in the molding mold in a shrinkable state to form the first optical shape layer. Process and
A first optical shape layer manufacturing step of obtaining a first optical shape layer from the cured energy ray-curable resin, and
A reflection layer forming step of forming a reflection layer on at least the first inclined surface of the unit optical shape provided on the first optical shape layer.
The second optical shape layer forming step of forming the second optical shape layer on the surface on the side where the reflection layer of the first optical shape layer is formed, and
It is a manufacturing method of an optical member including
A base material sticking step of sticking a base material having a glossiness of 60 degrees and a glossiness of 90 or more on the back surface side opposite to the observer side on the surface of the energy ray-curable resin after curing is included.
In the first optical shape layer manufacturing step, the cured energy ray-curable resin is peeled off from the molding mold together with the base material to obtain the first optical shape layer to which the base material is bonded.
A method for manufacturing an optical member.
前記第1光学形状層は、
前記第1傾斜面の算術平均うねりWaが0.05μm以下に形成され、
前記単位光学形状の厚み方向の頂部から谷部までの高さhが10〜300μmの範囲で形成され、
前記単位光学形状の配列ピッチPが100〜1000μmの範囲で形成されること、
を特徴とする光学部材の製造方法。 The method for manufacturing an optical member according to claim 1 or 2.
The first optical shape layer is
The arithmetic mean swell Wa of the first inclined surface is formed to be 0.05 μm or less.
The height h from the top to the valley in the thickness direction of the unit optical shape is formed in the range of 10 to 300 μm.
The array pitch P of the unit optical shape is formed in the range of 100 to 1000 μm.
A method for manufacturing an optical member.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015210143A JP6851715B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2015-10-26 | Manufacturing method of optical member |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015210143A JP6851715B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2015-10-26 | Manufacturing method of optical member |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017083587A JP2017083587A (en) | 2017-05-18 |
| JP6851715B2 true JP6851715B2 (en) | 2021-03-31 |
Family
ID=58710929
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015210143A Active JP6851715B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2015-10-26 | Manufacturing method of optical member |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6851715B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2020071169A1 (en) * | 2018-10-01 | 2021-09-02 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | display |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2797487B2 (en) * | 1989-07-27 | 1998-09-17 | 株式会社島津製作所 | Head-up display |
| JPH11142627A (en) * | 1997-11-07 | 1999-05-28 | Nitto Denko Corp | Prism type translucent reflecting plate and lighting device |
| JP2004162000A (en) * | 2002-09-17 | 2004-06-10 | Toyo Ink Mfg Co Ltd | Hard coat film and method for producing the same |
| JP2004151406A (en) * | 2002-10-31 | 2004-05-27 | Nitto Denko Corp | Method for manufacturing optical film and liquid crystal display device |
| JP2004361835A (en) * | 2003-06-06 | 2004-12-24 | Three M Innovative Properties Co | Optical film and its manufacturing method |
| US20060132945A1 (en) * | 2003-06-06 | 2006-06-22 | Koichi Sano | Microstructured optical film and production process thereof |
| JP2006193675A (en) * | 2005-01-17 | 2006-07-27 | Nippon Zeon Co Ltd | Method for producing laminated film |
| JP2007199363A (en) * | 2006-01-26 | 2007-08-09 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | Light reflection member and straight down type surface light emitting device using same |
| JP2008213398A (en) * | 2007-03-07 | 2008-09-18 | Eiwa Kako Kk | Laminating device and method for processing long sheet |
| JP2008268940A (en) * | 2007-03-27 | 2008-11-06 | Toray Ind Inc | Reflection type polarizing plate and liquid crystal display device using same |
| JP5725335B2 (en) * | 2011-03-16 | 2015-05-27 | Dic株式会社 | Prism sheet and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2012022336A (en) * | 2011-10-03 | 2012-02-02 | Nitto Denko Corp | Optical film and liquid crystal display device |
| JP2013197083A (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-30 | Fujifilm Corp | Multilayer film for supporting optical function member, prism sheet, light source unit, and display device |
-
2015
- 2015-10-26 JP JP2015210143A patent/JP6851715B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017083587A (en) | 2017-05-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2016088389A1 (en) | Semi-transmissive reflective sheet, light guide plate, and display device | |
| JP6821918B2 (en) | Light guide plate and display device | |
| JP6660008B2 (en) | Display device | |
| JP2021099515A (en) | Reflection screen and video display device | |
| JP6659994B2 (en) | Display device | |
| JP5843043B1 (en) | Light guide plate, display device | |
| JPWO2019123896A1 (en) | Transparent screen, video projection mating board, and video display system | |
| JP2018163252A (en) | Light guide plate and display device | |
| JP2016200682A (en) | Optical member and display | |
| JP7003971B2 (en) | Display device | |
| JP6851715B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of optical member | |
| JP6988069B2 (en) | Reflective screen, video display device | |
| JP2020046676A (en) | Method for producing resin sheet | |
| JP6540249B2 (en) | Display device | |
| WO2018131684A1 (en) | Transparent screen, video projection laminated plate, video display system, and method for manufacturing transparent screen | |
| JP6759618B2 (en) | Optical member, display device | |
| JP2017003664A (en) | Optical member and display device | |
| JP7293731B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing optical member | |
| JP5910177B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing transmission screen | |
| JP6668803B2 (en) | Optical members, display devices | |
| JP6805491B2 (en) | Resin sheet manufacturing method | |
| JP6756089B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of transflective reflective sheet | |
| JP6699092B2 (en) | Resin sheet manufacturing method | |
| JP6836099B2 (en) | Optical seats, vehicle windows | |
| JP6665566B2 (en) | Light guide plate and display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20160928 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180827 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190725 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190820 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190924 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20200303 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200325 |
|
| C60 | Trial request (containing other claim documents, opposition documents) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C60 Effective date: 20200325 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20200402 |
|
| C21 | Notice of transfer of a case for reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C21 Effective date: 20200407 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20200619 |
|
| C211 | Notice of termination of reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C211 Effective date: 20200623 |
|
| C22 | Notice of designation (change) of administrative judge |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C22 Effective date: 20200811 |
|
| C23 | Notice of termination of proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C23 Effective date: 20210119 |
|
| C03 | Trial/appeal decision taken |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C03 Effective date: 20210309 |
|
| C30A | Notification sent |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C3012 Effective date: 20210309 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210310 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6851715 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |