JP6719104B2 - Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and recording medium - Google Patents
Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and recording medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6719104B2 JP6719104B2 JP2016049515A JP2016049515A JP6719104B2 JP 6719104 B2 JP6719104 B2 JP 6719104B2 JP 2016049515 A JP2016049515 A JP 2016049515A JP 2016049515 A JP2016049515 A JP 2016049515A JP 6719104 B2 JP6719104 B2 JP 6719104B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- resolution image
- evaluation value
- resolution
- display device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 title claims description 111
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 26
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 claims description 238
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 53
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 59
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 43
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 43
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 40
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 35
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 33
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 30
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 23
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 22
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 14
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 12
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 11
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 10
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 10
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 238000010827 pathological analysis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000012120 mounting media Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000004522 Pentaglottis sempervirens Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003708 edge detection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000008393 encapsulating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012466 permeate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001356 surgical procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- 240000004050 Pentaglottis sempervirens Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001574 biopsy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004171 remote diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012192 staining solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01Q—SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES OR APPARATUS; APPLICATIONS OF SCANNING-PROBE TECHNIQUES, e.g. SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY [SPM]
- G01Q30/00—Auxiliary means serving to assist or improve the scanning probe techniques or apparatus, e.g. display or data processing devices
- G01Q30/02—Non-SPM analysing devices, e.g. SEM [Scanning Electron Microscope], spectrometer or optical microscope
Landscapes
- Microscoopes, Condenser (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Closed-Circuit Television Systems (AREA)
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Facsimiles In General (AREA)
- Television Systems (AREA)
- Facsimile Scanning Arrangements (AREA)
- Editing Of Facsimile Originals (AREA)
- Image Input (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本開示は、画像出力装置、画像送信装置および画像受信装置などに関する。 The present disclosure relates to an image output device, an image transmission device, an image reception device, and the like.
従来、生体組織などにおけるミクロ構造を観察するために光学顕微鏡が用いられてきた。光学顕微鏡は、観察対象を透過した光、あるいは反射した光を利用する。観察者は、レンズによって拡大された像を観察する。顕微鏡のレンズで拡大された像を撮影してディスプレイ上に表示するデジタル顕微鏡も知られている。デジタル顕微鏡を利用することにより、複数人での同時観察、遠隔地での観察などが可能である。 Conventionally, an optical microscope has been used to observe a microstructure in a living tissue or the like. The optical microscope uses light that has passed through or is reflected by the observation target. The observer observes the image magnified by the lens. A digital microscope is also known in which an image magnified by a lens of a microscope is photographed and displayed on a display. By using a digital microscope, it is possible for multiple people to observe at the same time and to observe at a remote place.
近年、CIS(Contact Image Sensing)方式によってミクロ構造を観察する技術が注
目されている。CIS方式による場合、観察対象は、イメージセンサの撮像面に近接して配置される。イメージセンサとしては、一般に、多数の光電変換部が撮像面内に行および列状に配列された2次元イメージセンサが用いられる。光電変換部は、典型的には、半導体層または半導体基板に形成されたフォトダイオードであり、入射光を受けて電荷を生成する。
In recent years, a technique for observing a microstructure by a CIS (Contact Image Sensing) method has been attracting attention. In the case of the CIS method, the observation target is placed close to the imaging surface of the image sensor. As the image sensor, generally, a two-dimensional image sensor in which a large number of photoelectric conversion units are arranged in rows and columns in the imaging surface is used. The photoelectric conversion unit is typically a photodiode formed on a semiconductor layer or a semiconductor substrate, and receives incident light to generate charges.
イメージセンサによって取得される画像は、多数の画素によって規定される。各画素は、1つの光電変換部を含む単位領域によって区画されている。したがって、2次元イメージセンサにおける分解能(解像度)は、通常、撮像面上における光電変換部の配列ピッチに依存する。本明細書では、光電変換部の配列ピッチによって決まる分解能を、イメージセンサの「固有分解能」と呼ぶことがある。個々の光電変換部の配列ピッチは、可視光の波長程度まで短くなっているので、固有分解能をさらに向上させることは困難である。 The image acquired by the image sensor is defined by a large number of pixels. Each pixel is partitioned by a unit area including one photoelectric conversion unit. Therefore, the resolution in the two-dimensional image sensor usually depends on the arrangement pitch of the photoelectric conversion units on the imaging surface. In this specification, the resolution determined by the arrangement pitch of the photoelectric conversion units may be referred to as the “specific resolution” of the image sensor. Since the array pitch of the individual photoelectric conversion units is as short as the wavelength of visible light, it is difficult to further improve the specific resolution.
イメージセンサの固有分解能を超える分解能(即ち、高解像度)を実現する技術が提案されている。特許文献1は、被写体の結像位置をシフトさせて得られる複数の画像を用いて当該被写体の画像(即ち、高解像度の画像)を形成する技術を開示している。
Techniques have been proposed for realizing a resolution (that is, high resolution) that exceeds the inherent resolution of the image sensor.
しかしながら、高解像度の画像はデータサイズが大きく、その画像の送受信または保存などの取り扱いには負担がかかるという問題がある。 However, a high-resolution image has a large data size, and there is a problem in that handling such as transmission/reception or storage of the image is burdensome.
そこで本開示では、高解像度画像の送受信または保存などの取り扱いの負担を軽減する画像出力装置、画像送信装置および画像受信装置などを提供する。 Therefore, the present disclosure provides an image output device, an image transmission device, an image reception device, and the like that reduce the burden of handling such as transmission/reception or storage of high-resolution images.
本開示の一態様にかかる画像出力装置は、少なくとも1つのプロセッサと、実行可能な命令を保持する非一時的な記録媒体とを備え、前記命令は、デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得し、前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を外部装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信しない、ことを前記少なくとも1つのプロセッサに実行させる。 An image output apparatus according to an aspect of the present disclosure includes at least one processor and a non-transitory recording medium that holds executable instructions, and the instructions are for a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope. Obtaining a first resolution image that is an image, an image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope, An enlargement ratio for the first resolution image displayed on the display device is accepted, and an evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether or not it is higher than a predetermined value, and the evaluation value is the predetermined value. If it is determined that the second resolution image is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to an external device. Cause the at least one processor to do not send to an external device.
なお、これらの包括的または具体的な態様は、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラムまたはコンピュータ読み取り可能なCD−ROMなどの記録媒体で実現されてもよく、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラムまたは記録媒体の任意な組み合わせで実現されてもよい。 Note that these comprehensive or specific aspects may be realized by a recording medium such as a system, a method, an integrated circuit, a computer program or a computer-readable CD-ROM, and the system, the method, the integrated circuit, the computer program. Alternatively, it may be realized by any combination of recording media.
本開示によれば、高解像度画像の送受信または保存などの取り扱いの負担を軽減することができる。 According to the present disclosure, it is possible to reduce the burden of handling such as transmission/reception or storage of high-resolution images.
(本発明の基礎となった知見)
本発明者は、「背景技術」の欄において記載した高解像度化の技術に関し、以下の問題が生じることを見出した。
(Findings that form the basis of the present invention)
The present inventor has found that the following problems occur with respect to the high resolution technology described in the “Background Art” section.
顕微鏡を用いた病理検査では、観察対象となる個々の検体(病理検体ともいう)の病状によって使用するレンズの倍率が異なる。例えば癌の検査では、まず、対物10倍のレンズで観察を行う。癌の疑いが高い領域がない検体に対しては対物10倍のレンズの観察のみで観察を終了するが、癌の疑いが高い領域があれば対物レンズを40倍のレンズに切り替えて検査を行う。このように、検体に応じてレンズの拡大率が変更される。高い拡大率が必要になるか否かは検査をする前には不明であるため、高い拡大率から低い拡大率までの事前に決めた各拡大率で検体の撮影が行われる。 In a pathological examination using a microscope, the magnification of a lens used varies depending on the condition of each specimen (also referred to as a pathological specimen) to be observed. For example, in a cancer examination, first, observation is performed with a lens having a 10-fold objective. For specimens that do not have a region with a high suspicion of cancer, the observation is completed only by observing with a 10× objective lens, but if there is a region with a high suspicion of cancer, the objective lens is switched to a 40× lens for examination. .. In this way, the magnification of the lens is changed according to the sample. Since it is not known before the examination whether a high magnification is required, the specimen is imaged at each predetermined magnification from a high magnification to a low magnification.
デジタル顕微鏡によって検体の画像を撮影する場合、その画像の解像度が高くなるに従って撮影時間および画像サイズが増大する。デジタル顕微鏡によって得られる対物10倍相当の画像のサイズを100Mバイトとすると、対物40倍相当の画像のサイズは1.6Gバイトとなる。 When an image of a sample is taken with a digital microscope, the taking time and the image size increase as the resolution of the image increases. If the size of the image corresponding to the objective 10 times obtained by the digital microscope is 100 Mbytes, the size of the image corresponding to the objective 40 times is 1.6 Gbytes.
また、検査しなければならない病理検体の数が増える一方で、病理医の増加が追いついていない。したがって、今後、デジタル顕微鏡によって得られる画像である病理画像を遠隔地に送信して、遠隔地にいる病理医によって病理診断が行われることが増加していくと想定される。また、医療全体の高度化に伴い、一名の病理医で全ての臓器または症状の診断を行うことは困難になってきている。そのため、現場の病理医で診断が困難な検体の画像を、遠隔地にいる専門知識を有する病理医に送信して行う遠隔診断が行われていくようになる。しかし、高解像度の病理画像の送信には時間がかかるという問題がある。 Moreover, while the number of pathological specimens that must be examined increases, the number of pathologists has not kept up. Therefore, in the future, it is expected that the pathological image, which is an image obtained by a digital microscope, will be transmitted to a remote place and pathologists at the remote place will perform a pathological diagnosis. Further, with the advancement of medical treatment as a whole, it has become difficult for one pathologist to diagnose all organs or symptoms. Therefore, remote diagnosis is performed by transmitting an image of a sample that is difficult to be diagnosed by a pathologist at the site to a pathologist having remote expertise at a remote location. However, there is a problem that it takes time to transmit a high-resolution pathological image.
このような問題を解決するために、本発明の一態様に係る画像出力装置は、デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得する画像取得部と、前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する高解像度画像取得部と、表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付ける拡大受付部と、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する判定部と、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を外部装置に送信し、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信しない送信部とを備える。 In order to solve such a problem, an image output apparatus according to an aspect of the present invention includes an image acquisition unit that acquires a first resolution image that is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, A high-resolution image acquisition unit that acquires a second resolution image that is an image of a higher resolution than a one-resolution image and that is an image of the subject that is obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope, and that is displayed on a display device. An enlargement accepting unit that receives an enlargement ratio for the first resolution image, a determination unit that determines whether or not an evaluation value based on the enlargement ratio accepted by the enlargement accepting unit is higher than a predetermined value, and the determination unit When it is determined that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to an external device, and the evaluation unit determines that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. In this case, the transmission unit does not transmit the second resolution image to the external device.
これにより、評価値が高い場合にのみ第二解像度画像が送信される。つまり、十分な診断が必要な検体(被写体)のみ、その検体の画像を高解像度で例えば遠隔地に送信することができる。したがって、例えば短時間で診断できるような重要度の低い検体の高解像度画像の送信のために、十分な診断が必要な検体の高解像度画像の送信が遅れてしまうことを抑えることができる。また、評価値の低い検体の高解像度画像の送信は行われないため、高解像度画像の取り扱いの負担を軽減することができる。 As a result, the second resolution image is transmitted only when the evaluation value is high. In other words, only the sample (subject) for which sufficient diagnosis is necessary, the image of the sample can be transmitted with high resolution, for example, to a remote place. Therefore, for example, in order to transmit a high-resolution image of a sample of low importance that can be diagnosed in a short time, it is possible to prevent delay in transmission of a high-resolution image of a sample that requires sufficient diagnosis. Further, since the high resolution image of the sample having a low evaluation value is not transmitted, the burden of handling the high resolution image can be reduced.
また、前記送信部は、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第一解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信してもよい。 Further, the transmitting unit may transmit the first resolution image to the external device when the determining unit determines that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value.
これにより、例えば遠隔地にいる病理医も、送信された低解像度画像である第一解像度画像を用いた検体の診断を行うことができる。 Thereby, for example, a pathologist at a remote place can also diagnose a sample using the transmitted first resolution image which is a low resolution image.
また、前記画像出力装置は、さらに、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を記録媒体に出力して保存し、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記記録媒体に出力しない第一出力部を備えてもよい。 In addition, the image output device further outputs the second resolution image to a recording medium and saves it when the evaluation value is determined by the determination unit to be higher than the predetermined value. A first output unit may be provided that does not output the second resolution image to the recording medium when the unit determines that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value.
高解像度画像(第二解像度画像)の画像サイズは大きく、病理検査では、検査に用いた検体の画像は10年単位で保存される。また、人体から検体を取得する技術が向上している今日、撮影される検体の数は今後とも上昇していくと考えられる。したがって、デジタル顕微鏡で撮影した画像、特に高解像度画像の保存は重要な問題となる。 The image size of the high-resolution image (second resolution image) is large, and in the pathological examination, the image of the specimen used for the examination is stored every 10 years. In addition, as the technology for acquiring specimens from the human body is improving, the number of specimens to be imaged is expected to increase in the future. Therefore, storage of images taken with a digital microscope, especially high-resolution images, becomes an important issue.
そこで、本発明の一態様では、評価値が高い場合にのみ第二解像度画像が保存される。つまり、十分な診断が必要な検体(被写体)のみ、その検体の画像を高解像度で保存しておくことができる。したがって、例えば短時間で診断できるような重要度の低い検体の高解像度画像の保存のために、記録媒体の空き容量が制限されてしまうことを抑えることができる。また、評価値の低い検体の高解像度画像の保存は行われないため、高解像度画像の取り扱いの負担を軽減することができる。 Therefore, in one aspect of the present invention, the second resolution image is stored only when the evaluation value is high. That is, it is possible to store the image of the sample in high resolution only for the sample (subject) for which sufficient diagnosis is necessary. Therefore, for example, it is possible to prevent the free space of the recording medium from being limited in order to store a high-resolution image of a less important sample that can be diagnosed in a short time. Further, since the high resolution image of the sample having a low evaluation value is not stored, the burden of handling the high resolution image can be reduced.
また、例えば、前記判定部は、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた1つまたは複数の前記拡大率のうち、最大の拡大率を前記評価値として導出する。または、前記判定部は、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた回数が多いほど、または、前記被写体の画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、高い前記評価値を導出してもよい。または、前記判定部は、閾値よりも高い前記拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記被写体の面積が広いほど高い前記評価値を算出してもよい。 Further, for example, the determination unit derives, as the evaluation value, the maximum enlargement ratio among the one or more enlargement ratios accepted by the enlargement accepting unit. Alternatively, the determination unit may display the image of the subject on the display device as the number of times a high magnification rate, which is a magnification rate higher than a threshold value, is received by the enlargement acceptance section. The higher the evaluation time, the higher the evaluation value may be derived. Alternatively, the determination unit may calculate the evaluation value that is higher as the area of the subject displayed on the display device is larger at the enlargement ratio higher than a threshold value.
これにより、被写体の画像の用途に応じて適切な評価値を導出することができ、最適な高解像度画像(第二解像度画像)のみを送信することができる。 This makes it possible to derive an appropriate evaluation value according to the intended use of the image of the subject, and to transmit only the optimum high resolution image (second resolution image).
また、本発明の他の態様に係る画像出力装置は、画像送信装置と、前記画像送信装置と通信回線を介して接続された画像受信装置とを有する画像出力装置であって、前記画像送信装置は、デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得する画像取得部と、前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する高解像度画像取得部と、前記画像受信装置から通知される評価値関連情報によって示される評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する判定部と、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第一解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信する送信部とを備え、前記画像受信装置は、表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付ける拡大受付部と、前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像または前記第二解像度画像を取得し、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき拡大された前記第一解像度画像または前記第二解像度画像を前記表示装置に表示させる表示用出力部とを備え、前記表示用出力部は、さらに、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく前記評価値関連情報を、前記画像送信装置に送信する。 An image output device according to another aspect of the present invention is an image output device having an image transmission device and an image reception device connected to the image transmission device via a communication line. Is an image acquisition unit that acquires a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and an image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, based on photographing by the digital microscope. Whether the evaluation value indicated by the high-resolution image acquisition unit that acquires the second resolution image, which is the image of the subject obtained by the above, and the evaluation value-related information notified from the image receiving device is higher than a predetermined value. If a determination unit that determines whether or not the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value by the determination unit, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, the determination unit When it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value, the image receiving device includes a transmitting unit that transmits the first resolution image to the image receiving device, and the image receiving device is displayed on a display device. An enlargement accepting unit that receives an enlargement factor for the first resolution image, and the first resolution image or the second resolution image from the image transmission device, and the image is enlarged based on the enlargement factor accepted by the enlargement accepting unit. A display output unit for displaying the first resolution image or the second resolution image on the display device, wherein the display output unit is further based on the enlargement ratio accepted by the enlargement accepting unit. The evaluation value related information is transmitted to the image transmitting device.
または、本発明の他の態様に係る画像出力装置は、画像送信装置と、前記画像送信装置と通信回線を介して接続された画像受信装置とを有する画像出力装置であって、前記画像送信装置は、デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得する画像取得部と、前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する高解像度画像取得部と、前記第一解像度画像または前記第二解像度画像を、前記画像受信装置に送信する送信部とを備え、前記画像受信装置は、表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付ける拡大受付部と、前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像または前記第二解像度画像を取得し、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき拡大された前記第一解像度画像または前記第二解像度画像を前記表示装置に表示させる表示用出力部と、前記拡大受付部によって受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、判定結果を前記画像送信装置に通知する判定部とを備え、前記送信部は、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いことを示す前記判定結果である場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないことを示す前記判定結果である場合には、前記第一解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信する。なお、評価値関連情報は、拡大受付部によって受け付けられた拡大率、拡大率が受け付けられた回数、被写体の画像が表示されている時間、または、表示される被写体の面積などを含む情報である。 Alternatively, an image output device according to another aspect of the present invention is an image output device having an image transmission device and an image reception device connected to the image transmission device via a communication line. Is an image acquisition unit that acquires a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and an image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, based on photographing by the digital microscope. A high-resolution image acquisition unit that acquires a second resolution image that is the image of the subject obtained by the above; and a transmission unit that transmits the first resolution image or the second resolution image to the image reception device, The image receiving device acquires an enlargement accepting unit that receives an enlargement ratio for the first resolution image displayed on a display device, and acquires the first resolution image or the second resolution image from the image transmitting device, and the enlargement accepting unit. A display output unit for displaying the first resolution image or the second resolution image enlarged on the basis of the enlargement ratio accepted by the display device, and an evaluation based on the enlargement ratio accepted by the enlargement accepting unit. A determination unit that determines whether or not the value is higher than a predetermined value and notifies the image transmission device of the determination result, wherein the transmission unit determines that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value. In the case of the determination result showing, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and in the case of the determination result showing that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value, The one-resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device. The evaluation value related information is information including the enlargement ratio received by the enlargement receiving unit, the number of times the enlargement ratio is received, the time during which the image of the subject is displayed, the area of the displayed subject, and the like. ..
これにより、例えば被写体である検体が置かれた地点に病理医がいなくても、遠隔地にいる病理医は、その地点に設置された画像送信装置から送信される検体の画像を画像受信装置で取得して、その画像に基づく検体の診断を行うことができる。このときにも、不要な高解像度画像が画像受信装置に送信されることはないため、高解像度画像の取り扱いの負担を軽減することができる。 As a result, for example, even if there is no pathologist at the point where the sample, which is the subject, is placed, the pathologist at the remote location can use the image receiving apparatus to display the image of the sample transmitted from the image transmitting apparatus installed at that point. It is possible to obtain and diagnose the sample based on the image. Even at this time, an unnecessary high-resolution image is not transmitted to the image receiving device, so that the burden of handling the high-resolution image can be reduced.
また、前記画像送信装置は、さらに、前記判定部によって前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を記録媒体に出力して保存する第二出力部を備えてもよい。 Further, the image transmitting device further outputs the second resolution image to a recording medium and stores the second resolution image when the evaluation unit determines that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. An output unit may be provided.
これにより、評価値が低いために高解像度画像(第二解像度画像)が遠隔地の病理医に送信されなかった場合でも、その高解像度画像は保存されている。したがって、その病理医が高解像度画像を必要とする場合には、迅速に、その高解像度画像を記録媒体から読み出して病理医に送信することができる。 As a result, even if the high-resolution image (second resolution image) is not transmitted to the pathologist at the remote location due to the low evaluation value, the high-resolution image is stored. Therefore, when the pathologist needs a high resolution image, the high resolution image can be quickly read from the recording medium and transmitted to the pathologist.
なお、本発明の一態様に係る画像出力装置、画像送信装置および画像受信装置のそれぞれは、少なくとも1つのプロセッサと、実行可能な命令を保持する非一時的な記録媒体とを備えて構成されていてもよい。この場合、上述の各装置に備えられている各構成要素は、その記録媒体に保持されている命令がその少なくとも1つのプロセッサによって実行されることによって実現される。 Note that each of the image output device, the image transmission device, and the image reception device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes at least one processor and a non-transitory recording medium holding an executable instruction. May be. In this case, each component provided in each of the above-described devices is realized by the instruction stored in the recording medium being executed by the at least one processor.
以下、実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
なお、以下で説明する実施の形態は、いずれも包括的または具体的な例を示すものである。以下の実施の形態で示される数値、形状、材料、構成要素、構成要素の配置位置及び接続形態、ステップ、ステップの順序などは、一例であり、本発明を限定する主旨ではない。また、以下の実施の形態における構成要素のうち、最上位概念を示す独立請求項に記載されていない構成要素については、任意の構成要素として説明される。 It should be noted that each of the embodiments described below shows a comprehensive or specific example. Numerical values, shapes, materials, constituent elements, arrangement positions and connection forms of constituent elements, steps, order of steps, and the like shown in the following embodiments are examples, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Further, among the constituent elements in the following embodiments, constituent elements not described in the independent claim showing the highest concept are described as arbitrary constituent elements.
(実施の形態1)
図1は、実施の形態1における画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。
(Embodiment 1)
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram showing an example of an image processing system including the image output device according to the first embodiment.
画像処理システム100Sは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置1001、および表示装置1501からなる。
The image processing system 100S includes a
デジタル顕微鏡1500は、後述の画像取得装置であって、病理検体を被写体として撮影する。ここで、本明細書において「デジタル顕微鏡」とは、病理組織プレパラート標本の少なくとも一部をデジタル画像化する装置である。例えば、デジタル顕微鏡は、前記標本をコンタクトイメージセンシング(CIS:Contact Image Sensing)方式で撮影する
後述の画像取得装置、またはバーチャルスライドスキャナ等である。ここで、CIS方式で撮影する画像取得装置は、イメージセンサの上に被写体を直接配置して撮影を行うことによって、被写体の画像である第一解像度画像および第二解像度画像を取得する装置である。具体的には、前記画像取得装置は、複数の異なる照射方向より光を被写体に照射してその被写体を撮影することで複数の第一解像度画像を生成する。そして、前記画像取得装置は、それらの複数の第一解像度画像の各画素を再配置することによって、各第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の第二解像度画像を生成する。また、デジタル顕微鏡1500は、後述の画像取得装置の代わりに、複数の解像度の拡大画像を生成するバーチャルスライドスキャナ等のデジタル顕微鏡であっても構わない。バーチャルスライドスキャナは、顕微鏡越しに検体を撮影する装置である。顕微鏡に対するスライドの相対位置をずらす操作と撮影する操作を繰り返し、得られる複数の画像をつなぎ合わせて広範囲の検体の画像を生成する。バーチャルスライドスキャナでは、顕微鏡に装着する対物レンズを変えることで、取得する画像の解像度を選択する。低い倍率の対物レンズを用いると、解像度は低くなるが、1枚の画像に撮影される検体の範囲が広くなるので撮影箇所は少なくてすみ撮影時間は短くなる。画像取得装置については、実施の形態4において詳細に説明する。
The
表示装置1501は、デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる画像を操作者(例えば病理医)に表示する装置であて、例えば、液晶ディスプレイまたはプロジェクター等である。
The
画像出力装置1001は、デジタル顕微鏡1500による撮影によって得られた画像を取得して、その画像を表示装置1501に表示させる。さらに、画像出力装置1001は、通信回線を介して、例えば遠隔地の病理医によって扱われる装置にその画像を送信する。
The
この画像出力装置1001は、画像取得部1101と、高解像度画像取得部1102と、拡大受付部1201と、判定部1202と、表示用出力部1203と、送信部1204とを備える。
The
画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得する。なお、デジタル顕微鏡1500による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像は、その撮影によって直接的に得られる画像であってもよく、直接的に得られた画像に対して処理を行うことによって得られる画像であってもよい。ここでは、画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500における例えばコンタクトイメージセンサによる撮影によって得られたサブ画像を第一解像度画像として取得する。なお、第一解像度画像の解像度を第一解像度と呼ぶ。
The
高解像度画像取得部1102は、第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像(高解像度画像)であって、デジタル顕微鏡1500による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する。高解像度画像取得部1102は、複数のサブ画像から第二解像度画像を生成することによって、その第二解像度画像を取得してもよく、第二解像度画像をデジタル顕微鏡1500から取得してもよい。なお、第二解像度画像の解像度を第二解像度と呼ぶ。ここでは、第一解像度は画素ピッチが0.9μm、第二解像度は画素ピッチが0.3μmとする。また、第二解像度の画素ピッチに対する第一解像度の画素ピッチの比を解像度比とするとき、解像度比は3となる。
The high-resolution
拡大受付部1201は、表示装置1501に表示される第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付ける。具体的には、拡大受付部1201は、例えばキーボードの操作を介して拡大率Kを数値として取得する。また、拡大受付部1201は、例えばホイールを有するマウスの回転数を拡大率の変化値として用い、拡大率Kを更新してもよい。
The
表示用出力部1203は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づき拡大された第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像を表示装置1501に出力する。これにより、拡大された第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像が表示装置1501に表示される。なお、本実施の形態における画像出力装置1001は、表示用出力部1203を備えるが、この表示用出力部1203を備えていなくてもよい。
The
判定部1202は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する。ここで、所定の値とは、例えば病理医または操作者によって任意に設定される値であっても、予め定められた値であってもよい。具体的には、評価値が、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた1つまたは複数の拡大率のうち、最大の拡大率として導出される場合には、所定の値は例えば解像度比(つまり、上述の例の場合には3)と等しい値であってもよい。
The
なお、所定の値は1よりも大きい値である。ただし、所定の値を低い値にしてしまうと、後述の出力が頻繁に行われる事になる。これを避けるためには所定の値はできるだけ高い値であるこが望ましい。後述の出力は、送信部1204による送信、または、第一出力部1205による出力である。そこで、通信回線の太さや回線の混雑状況によって所定の値を切り替える構成としても良い。例えば、回線が細い携帯電話の回線を用いる場合には、所定の値を高い値10にし、回線が太い光回線を用いる場合には、所定の値を低い値3にする。また回線が混雑している場合には、所定の値を高い値10にし、回線が空いている場合には所定の値を低い値3にする。また、保存に用いるストレージ(例えば、後述する図8および図12〜図14の何れかの記録媒体1502)のサイズによって、所定の値を切り替える構成としても良い。例えば、そのストレージが大容量HDD(Hard Disk Drive)である場合には、所定の値を3とし、そのストレージが小容量のSSD(Solid State Drive)である場合には、所定の値を10としても良い。
The predetermined value is a value greater than 1. However, if the predetermined value is set to a low value, the output described below will be frequently performed. In order to avoid this, it is desirable that the predetermined value is as high as possible. The output described below is transmission by the
送信部1204は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を送信する。一方、送信部1204は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を送信しない。このとき、つまり、判定部1202によって評価値が高くないと判定される場合には、送信部1204は、第一解像度画像を送信する。第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像は、通信回線を介して、例えば遠隔地の病理医に扱われる装置に送信される。
When the
図2は、表示装置1501によって表示される表示画面の一例を示す図である。
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of a display screen displayed by the
表示装置1501は、終了ボタン602、俯瞰画像表示部603、所見入力欄604、読込ボタン605、および拡大画像表示部606を含む表示画面601を表示する。
The
終了ボタン602が選択されると、表示装置1501は、画像の表示を終了すべきことを知らせる信号を画像出力装置1001に送信する。俯瞰画像表示部603には、第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像の全体が表示される。所見入力欄604には、例えば病理医による所見が書き込まれる。読込ボタン605が選択されると、表示装置1501は、例えば、第一解像度画像の表示を終了し、第二解像度画像の読み込みを指示する信号を画像出力装置1001に送信する。拡大画像表示部606には、第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像が拡大されて表示される。
When the
図3は、画像出力装置1001の処理動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing an example of the processing operation of the
まず、画像出力装置1001の画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得する(ステップS11)。次に、拡大受付部1201は、操作者による例えばキーボードなどへの操作に応じて画像の拡大率を受け付ける(ステップS12)。そして、表示用出力部1203は、受け付けられた拡大率で第一解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。その出力によって、表示用出力部1203は、受け付けられた拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS13)。
First, the
次に、表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602または読込ボタン605が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第一解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS14)。ここで、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS14のNo)、拡大受付部1201は、さらに、新たな拡大率を受け付ける。つまり、表示装置1501に表示された画像を観察する操作者は、検体に応じて拡大率を変更して観察を行う。
Next, the
一方、表示を終了すべきと判定されると(ステップS14のYes)、判定部1202は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づく評価値を導出し、その評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する(ステップS15)。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the display should be ended (Yes in step S14), the
評価値は、例えば、ステップS12で受け付けられた1つまたは複数の拡大率のうちの、直前に受け付けられた拡大率(直前拡大率)、または最大の拡大率(最大拡大率)である。つまり、判定部1202は、直前拡大率または最大拡大率を評価値として導出する。または、判定部1202は、他の要件に基づいて評価値を導出してもよい。例えば、他の要件は、ステップS13によって拡大率が受け付けられた回数(受付回数)、表示装置1501に画像が表示されている時間(表示時間)、および、表示装置1501に表示された画像の面積(表示面積)のうちの少なくとも1つである。
The evaluation value is, for example, the expansion ratio received immediately before (immediate expansion ratio) or the maximum expansion ratio (maximum expansion ratio) of the one or more expansion ratios received in step S12. That is, the
また、判定部1202は、最大拡大率、受付回数、表示時間、および表示面積のそれぞれに係数を乗算し、それらを積算することによって評価値を導出してもよい。
Further, the
ここで、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定されると(ステップS15のNo)、送信部1204は、通信回線を介して第二解像度画像を送信することなく第一解像度画像を送信する(ステップS16)。一方、評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定されると(ステップS15のYes)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS17)。さらに、送信部1204は、その高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得された第二解像度画像を、通信回線を介して送信する(ステップS18)。
Here, if it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value (No in step S15), the
図3のフローチャートでは、受け付けられた拡大率で拡大されて表示される画像は第一解像度画像だけであるが、図4のフローチャートに示すように、第二解像度画像もその拡大率で拡大して表示してもよい。 In the flowchart of FIG. 3, only the first resolution image is enlarged and displayed at the accepted enlargement ratio, but as shown in the flowchart of FIG. 4, the second resolution image is also enlarged at that enlargement ratio. It may be displayed.
図4は、画像出力装置1001の処理動作の他の例を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing another example of the processing operation of the
まず、画像出力装置1001の画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得する(ステップS21)。そして、表示用出力部1203は、その第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に出力することによって、その第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS22)。
First, the
次に、拡大受付部1201は、操作者による例えばキーボードなどへの操作に応じて画像の拡大率を受け付ける(ステップS23)。判定部1202は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づく評価値を導出し、その評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する(ステップS24)。
Next, the
ここで、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定されると(ステップS24のNo)、表示用出力部1203は、ステップS23で受け付けられた拡大率に第一解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。この出力によって、表示用出力部1203は、拡大された第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS25)。このときには、第二解像度画像が送信されることはない。そして、表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602または読込ボタン605が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第一解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS26)。ここで、表示を終了すべきと判定されると(ステップS26のYes)、画像出力装置1001は処理を終了する。一方、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS26のNo)、画像出力装置1001はステップS23からの処理を繰り返し実行する。
Here, if it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value (No in step S24), the
また、ステップS24において、評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定されると(ステップS24のYes)、判定部1202は、その判定が検体に対して初回であるか否かを判別する(ステップS27)。ここで、初回であると判別されると(ステップS27のYes)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS28)。さらに、送信部1204は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得されたその第二解像度画像を、通信回線を介して送信する(ステップS29)。
When it is determined in step S24 that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value (Yes in step S24), the
ステップS29で第二解像度画像が送信された後、または、ステップS27において初回ではないと判別されると(ステップS27のNo)、表示用出力部1203は、ステップS23で受け付けられた拡大率に第二解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。その出力によって、表示装置1501は、拡大された第二解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS30)。このとき、第二解像度画像を、ステップS23で受け付けられた拡大率で拡大するのではなく、その拡大率を解像度比で除算することによって得られる値で拡大してもよい。例えば、受け付けられた拡大率が3であって、解像度比が3の場合には、第二解像度画像は1倍に拡大される。
After the second resolution image is transmitted in step S29, or when it is determined that it is not the first time in step S27 (No in step S27), the
次に、表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第二解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS31)。ここで、表示を終了すべきと判定されると(ステップS31のYes)、画像出力装置1001は処理を終了する。一方、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS31のNo)、画像出力装置1001はステップS23からの処理を繰り返し実行する。
Next, the
(効果)
このように、本実施の形態では、評価値が高い場合にのみ第二解像度画像が送信される。つまり、十分な診断が必要な検体(被写体)のみ、その検体の画像を高解像度で例えば遠隔地に送信することができる。したがって、例えば短時間で診断できるような重要度の低い検体の高解像度画像の送信のために、十分な診断が必要な検体の高解像度画像の送信が遅れてしまうことを抑えることができる。また、評価値の低い検体の高解像度画像の送信は行われないため、高解像度画像の取り扱いの負担を軽減することができる。
(effect)
As described above, in the present embodiment, the second resolution image is transmitted only when the evaluation value is high. In other words, only the sample (subject) for which sufficient diagnosis is necessary, the image of the sample can be transmitted with high resolution, for example, to a remote place. Therefore, for example, in order to transmit a high-resolution image of a sample of low importance that can be diagnosed in a short time, it is possible to prevent delay in transmission of a high-resolution image of a sample that requires sufficient diagnosis. Further, since the high resolution image of the sample having a low evaluation value is not transmitted, the burden of handling the high resolution image can be reduced.
具体的には、本実施の形態における画像出力装置1001が、経験の少ない病理医しかいない、または外科しかいない地方病院におかれて使用されることが考えられる。このケースでは、診断が難しい検体の第二解像度画像を、送信部1204によって、経験が豊富な病理医のいる遠隔地に送信するこができる。病理医には、まず低解像度の第一解像度画像が送信される。そして、高い評価値が得られたとき、つまり、検体に対してより詳細な診断が必要なときにのみ、高解像度の第二解像度画像を送信することができる。第一解像度画像を100Mバイト(=800Mビット)、第二解像度画像を1.6Gバイト、通信速度を50Mbpsとする場合、第一解像度画像は16秒で送信することができるが、高解像度画像の送信には256秒かかる。全ての画像を高解像度で送信すると時間がかかる。しかし、健康診断などで行われる生検では、ほとんどが低解像度の画像で異常がないことが判断できるため、必要な検体に対してのみ高解像度画像を送信することで診断を効率化することができる。また、画像出力装置1001は、病理医が一人しかいない小病院におかれ、重要な画像は遠隔地にいる病理医に送信されてダブルチェックを行う際の送信画像を選択する際に利用することができる。
Specifically, it is conceivable that the
(評価値の詳細)
ここで、上述の評価値について詳細に説明する。
(Details of evaluation value)
Here, the above-mentioned evaluation value will be described in detail.
上述のように、判定部1202は、受付回数、表示時間および表示面積のうちの少なくとも1つに基づいて評価値を導出してもよい。
As described above, the
これらの受付回数、表示時間または表示面積に基づく評価値は、診断において必須ではないのに高倍率での検体観察が行われたか、診断において必要なために高倍率での検体観察が行われたかを判定する際に有効である。つまり、通常の顕微鏡での診断では、レンズを交換する手間が大きいため、低倍率の観察を行った段階で検体が正常であることが分かれば、高倍率の観察は行われない。なお、検体が正常であるか否かの判断では、検体に腫瘍がない、または、診断上必要とされる検査項目が残っていない場合に、検体が正常であると判断される。一方、本実施の形態のデジタル顕微鏡1500のような電子顕微鏡によって取得された画像の高倍率の拡大は、マウスまたはキーボードのみの簡単な操作で行うことができる。したがって、デジタル顕微鏡1500では、通常の顕微鏡による低倍率の観察しか行わなかった検体に対しても、高倍率での観察を行う場合が極めて多い。
The evaluation value based on the number of times of reception, display time, or display area is not essential for diagnosis, but is the sample observed at high magnification, or is the sample observed at high magnification because it is necessary for diagnosis? It is effective in determining. That is, in a diagnosis with a normal microscope, it takes a lot of time to replace the lens, and therefore, if it is known that the specimen is normal at the stage of observing at a low magnification, the observation at a high magnification is not performed. In the determination of whether the sample is normal, the sample is determined to be normal when the sample does not have a tumor or when there are no test items required for diagnosis. On the other hand, high-magnification enlargement of an image acquired by an electron microscope such as the
これは、病理医、医師または検査技師などの診断者が、高倍率で拡大された画像を見ることによって、検体の撮影が適切に行われているかを確認しているためであると考えられる。また、診断者が、正常な検体についても、その検体に含まれる小さな領域を、高倍率で拡大された像として見ておきたいという要求によるものであると考えられる。 It is considered that this is because a diagnostician such as a pathologist, a doctor or a laboratory technician confirms whether or not the imaging of the sample is appropriately performed by looking at the image magnified at high magnification. Further, it is considered that the diagnostician wants to see a small region included in the normal sample as an image magnified at a high magnification even for a normal sample.
このような診断に必要ではない高倍率での観察における受付回数、表示時間、または表示面積などのパラメータは、診断者の好みまたは経験によって異なる。しかし、これらのパラメータの数値は、診断に必須な高倍率での観察のパラメータと比べると極めて小さい。よって、本実施の形態では、受付回数、表示時間または表示面積に基づく評価値を用いることで、高倍率での観察が、診断に必要か否かを判定することができる。限られ通信帯域を有効に活用するためには、このような診断に必要ではない高倍率での観察が行われた際には、高解像度画像の送信を行わないことが望ましい。 Parameters such as the number of times of reception, display time, or display area in observation at high magnification, which are not necessary for such diagnosis, differ depending on the preference or experience of the diagnostician. However, the numerical values of these parameters are extremely small compared to the parameters of observation at high magnification, which is essential for diagnosis. Therefore, in the present embodiment, by using the evaluation value based on the number of receptions, the display time, or the display area, it is possible to determine whether or not observation at high magnification is necessary for diagnosis. In order to effectively utilize the limited communication band, it is desirable not to transmit a high-resolution image when an observation at a high magnification, which is not necessary for such diagnosis, is performed.
また、受付回数、表示時間および表示面積のうちの少なくとも1つに基づいて評価値が導出されて、高解像度画像が送信されるときには、送信部1204は、その高解像度画像にタグを付けてもよい。つまり、送信部1204は、その評価値に用いられたパラメータ(受付回数、表示時間および表示面積のうちの少なくとも1つ)の種類と、その評価値とを示すタグを高解像度画像に付加し、そのタグ付けされた高解像度画像を送信する。これにより、その高解像度画像を受信する画像受信装置は、複数の高解像度画像の中から、パラメータの種類として例えば受付回数を示すタグが付加された高解像度画像を抽出することができる。また、画像受信装置は、抽出された高解像度画像が複数あれば、それらのタグに示される評価値に基づいて、それらの高解像度画像を評価値の昇順または降順に並べることができる。これにより、診断者は、容易に観察すべき高解像度画像を選択することができる。
Further, when the evaluation value is derived based on at least one of the number of receptions, the display time, and the display area and the high resolution image is transmitted, the
(評価値の詳細:受付回数)
受付回数は、具体的には、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた回数である。この閾値は、例えば上述の解像度比(具体的には3)である。判定部1202は、その受付回数が多いほど高い評価値を導出する。例えば、評価値は受付回数そのものであってもよい。この場合、判定部1202は、その評価値である受付回数が1回(所定の値=1)よりも多いか否かを判定する。つまり、受付回数が1回であれば、高拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像の表示は、診断に必要でない表示である可能性が高い。言い換えれば、高拡大率よりも低い拡大率の第一解像度画像によって、検体が正常であると判断されている可能性が高い。逆に、受付回数が2回以上であれば、高拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像の表示は、診断に必要な表示である可能性が高い。つまり、検体が正常であるか否かの判断が疑わしい可能性が高い。したがって、このように、受付回数が1回よりも多いか否かを判定して、多いと判定されたときに高解像度画像の送信を行うことによって、限られ通信帯域を有効に活用することができる。
(Details of evaluation value: Number of receptions)
The number of receptions is, specifically, the number of times that the
あるいは、判定部1202は、その評価値である受付回数が2回(所定の値=2)よりも多い否かを判定してもよい。具体的には、悪性腫瘍を診断する場合には、腫瘍の様態およびサイズを確認するために3回以上の診断を行うことが多い。例えば、腫瘍の中心、左端、および右端のそれぞれの診断が行われることが多い。したがって、上述のように所定の値を「2」とすることによって、悪性腫瘍の疑いが高い検体の高解像度画像だけを送信することができる。
Alternatively, the
このように、評価値が受付回数に基づいて導出される場合には、高倍率での検体観察が1回または2回以下の回数しか行われていないにもかかわらず、高解像度画像が送信されてしまうことを抑えることができる。すなわち、診断に必要でない高倍率での検体観察が行われたことによって、高解像度画像が送信されてしまうことを抑えることができる。 In this way, when the evaluation value is derived based on the number of times of acceptance, the high-resolution image is transmitted even though the sample observation at high magnification is performed only once or twice or less. It can be suppressed. That is, it is possible to suppress the transmission of the high-resolution image due to the observation of the sample at a high magnification which is not necessary for the diagnosis.
(評価値の詳細:表示時間)
表示時間は、具体的には、被写体の画像が高拡大率で表示装置1501に表示されている時間である。判定部1202は、その表示時間が長いほど高い評価値を導出する。例えば、評価値は、被写体の画像が上述の解像度比(具体的には3)以上の高拡大率で表示装置1501に表示されている表示時間であってもよい。この場合、判定部1202は、その評価値である表示時間が例えば10秒(所定の値=10秒)よりも長いか否かを判定する。つまり、その表示時間が10秒以下であれば、高拡大率に拡大された画像の表示は、診断に必要でない表示である可能性が高い。これにより、診断に必要でない高倍率での検体観察が行われたことによって、高解像度画像が送信されてしまうことを抑えることができる。
(Details of evaluation value: Display time)
Specifically, the display time is the time during which the image of the subject is displayed on the
また、悪性腫瘍の診断にかかる時間は、診断者または観察する部位によって差がある。したがって、診断者、観察する部位、あるいは検体の取得作成方法によって、その所定の値(上述の例では10秒)を変えもよい。例えば、通常の方法で作成した検体に対しては、その所定の値を10秒とし、術中迅速診断用に短時間で作成した検体に対しては、その所定の値を30秒としてもよい。 Further, the time required for diagnosing a malignant tumor varies depending on the diagnostician or the site to be observed. Therefore, the predetermined value (10 seconds in the above example) may be changed depending on the diagnostician, the site to be observed, or the method for obtaining and creating the sample. For example, the predetermined value may be set to 10 seconds for a sample created by a normal method, and the predetermined value may be set to 30 seconds for a sample created in a short time for intraoperative rapid diagnosis.
また、上述の例では、所定の値を10秒または30秒としたが、正常な検体の観察にかかる平均的な表示時間のm倍(mは1より大きい実数)の時間などを所定の値としてもよい。 Further, in the above example, the predetermined value is set to 10 seconds or 30 seconds, but a time that is m times (m is a real number larger than 1) the average display time required for observing a normal sample is set to the predetermined value. May be
また、判定部1202は、受け付けられた拡大率(つまり、3以上の高拡大率)ごとに、その拡大率での表示時間に重みを乗じ、それぞれの重み付けされた表示時間の総和を、評価値として導出してもよい。この重みは、拡大率が高いほど大きい値である。具体的には、判定部1202は、拡大率そのものを重みとして扱い、評価値=Σ[拡大率(k)×表示時間(k)]によって、評価値を導出する。なお、拡大率(k)は、k番目に受け付けられた3以上の拡大率であり、表示時間(k)は、k番目の拡大率で拡大された第一解像度画像が表示された表示時間である。つまり、解像度比以上の拡大率がn回受け付けられた場合、評価値は、kが1〜nまでの拡大率(k)×表示時間(k)の総和として導出される。例えば、受け付けられた拡大率Qと、そのときの表示時間T(秒)とは、(Q,T)=(3,7)、(4,6)、(5,5)、および(6,4)であったとする。このような場合、判定部1202は、評価値=(3×7)+(4×6)+(5×5)+(6×4)によって、評価値を導出する。なお、評価値の算出において、拡大率(k)の代わりに、「拡大率(k)−解像度比(具体的には3)+1」を用いてもよい。この場合には、判定部1202は、評価値=(1×7)+(2×6)+(3×5)+(4×4)によって、評価値を導出する。このような評価値を用いれば、観察時間が長いほど、また観察時の拡大率(倍率)が高いほど、高い評価値が導出される。また、この場合には、判定部1202は、評価値が例えば30(所定の値=30)を越えるか否かを判定してもよい。
Further, the
なお、判定部1202は、各拡大率での表示時間を計算した後に、評価値を導出するが、観察時における評価値を随時更新してもよい。つまり、判定部1202は、一定時間の経過ごとに、観察時の拡大率を取得し、その取得された拡大率と一定時間との乗算結果を、直前に導出された評価値に加算することによって、その評価値を更新してもよい。これにより、一定時間の経過ごとに、新たな評価値が導出される。
Although the
また、判定部1202は、拡大率を表示時間に乗じる代わりに、拡大率に対して単調増加する値を表示時間に乗じてもよい。拡大率に対して単調増加する値は、関数によって得られる値であって、例えば、拡大率の対数である。つまり、判定部1202は、評価値=Σ[log拡大率(k)×表示時間(k)]によって、評価値を導出する。
Further, the
また、判定部1202は、上述のような総和によって評価値を導出する代わりに、拡大率または拡大率の対数を表示時間で積分した値を評価値として導出してもよい。
Further, the
(評価値の詳細:表示面積)
表示面積は、具体的には、その高拡大率で表示装置1501に表示される被写体の面積である。例えば、判定部1202は、一枚のフレームにおいて被写体が映し出されている領域を、エッジ検出を用いて特定し、その特定された領域の面積を、被写体の画像の面積として算出する。また、エッジ検出で一枚のフレームにおいて複数の領域が検出される場合には、判定部1202は、その複数の領域のうち、例えば、ユーザがマウスで指示した場所(座標)を含む領域の面積を被写体の画像の面積としてもよい。ここで、その表示されている画像がずらされると、新たなに表示される画像の面積だけ表示面積は広くなる。つまり、ユーザがマウスで指示した場所(即ち、座標)を含む領域が連続する場合(即ち、エッジがない場合)、ユーザが、画像をずらすと、その領域に連続する新たに領域が出現する。そこで、判定部1202は、その新たに出現した領域であって、かつ、ユーザがマウスで指示した場所を含む領域に連続する領域の面積を、被写体の画像の面積に加算してもよい。なお、表示面積である被写体の面積は、上述のように算出される被写体の画像の面積を実際の拡大率で除算することによって得られる値(商)である。判定部1202は、その表示面積が広いほど高い評価値を導出する。
(Details of evaluation value: display area)
The display area is specifically the area of the subject displayed on the
例えば、評価値は、解像度比(具体的には3)以上の高拡大率で表示される被写体の表示面積である。この場合、判定部1202は、その評価値である表示面積が10,000μm2よりも広いか否かを判定する。解像度比が3の際に、隣接する2つの画素に対応する検体の位置の間隔が1/3μm(=0.333μm)とすると、1つの画素で撮影される検体の面積は1/9μm2となり、10,000μm2に対応する検体のサイズは10,000μm2/(1/9μm2)=9×104ピクセルとなる。すなわち、判定部1202は、9×104ピクセル(所定の値=9×104ピクセル)よりも広いか否かを判定する。つまり、その表示面積が9×104ピクセル以下であれば、高拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像の表示は、診断に必要でない表示である可能性が高い。これにより、診断に必要でない高倍率での検体観察が行われたことによって、高解像度画像が送信されてしまうことを抑えることができる。
For example, the evaluation value is the display area of the subject displayed at a high magnification ratio equal to or higher than the resolution ratio (specifically, 3). In this case, the
また、上述の例では、所定の値を10,000μm2(すなわち、9×104ピクセル)としたが、正常な検体の観察にかかる平均的な表示面積のm倍(mは1よりも大きい実数)の面積などを所定の値としてもよい。 Further, in the above example, the predetermined value is set to 10,000 μm 2 (that is, 9×10 4 pixels), but m times the average display area required for observing a normal sample (m is larger than 1). The area of (real number) may be set as a predetermined value.
また、判定部1202は、受け付けられた拡大率(つまり、3以上の高拡大率)ごとに、その拡大率での表示面積に重みを乗じ、それぞれの重み付けされた表示面積の総和を、評価値として導出してもよい。この重みは、拡大率が高いほど大きい値である。具体的には、判定部1202は、拡大率の二乗を重みとして扱い、判定部1202は、評価値=Σ[拡大率(k)^2×表示面積(k)]によって、評価値を導出する。なお、拡大率(k)は、上述と同様、k番目に受け付けられた3以上の拡大率であり、表示面積(k)は、k番目の拡大率で拡大された被写体の表示面積である。なお、A^Bは、AのB乗の計算を示す。つまり、解像度比以上の拡大率がn回受け付けられた場合、評価値は、kが1〜nまでの拡大率(k)^2×表示面積(k)の総和として導出される。例えば、拡大率Qと、そのときの表示面積S(1×104ピクセル)とは、(Q,S)=(3, 2)、(4, 0.5)、(5, 1.5)、(6,1)であったとする。このような場合、判定部1202は、評価値=[(3^2)×2×104]+[(4^2)×0.5×104]+[(5^2)×1.5×104]+[(6^2)×1×104]によって、評価値を導出する。なお、評価値の算出において、拡大率(k)の二乗の代わりに、「拡大率(k)−解像度比(具体的には3)+1」の二乗を重みとして用いてもよい。この場合には、判定部1202は、評価値=[(1^2)×2×104]+[(2^2)×0.5×104]+[(3^2)×1.5×104]+[(4^2)×1×104]によって、評価値を導出する。このような評価値を用いれば、観察される被写体の面積が広いほど、また観察時の拡大率(倍率)が高いほど、高い評価値が導出される。また、この場合には、判定部1202は、評価値が例えば8.1×105(所定の値=8.1×105)を越えるか否かを判定してもよい。
Further, the
なお、重みは、拡大率が高いほど大きい値であればよく、そのような値が算出される関数であれば、拡大率の二乗に限らず、どのような関数を用いてもよい。例えば、判定部1202は、評価値=Σ[拡大率(k)^3×表示面積(k)]によって、評価値を導出してもよい。
It should be noted that the weight may have a larger value as the enlargement ratio is higher, and any function that calculates such a value is not limited to the square of the enlargement ratio, and any function may be used. For example, the
また、判定部1202は、上述のような総和によって評価値を導出する代わりに、拡大率のべき乗を表示面積で積分した値を評価値として導出してもよい。
Further, the determining
(変形例)
ここで、実施の形態1における画像出力装置の変形例について説明する。本変形例にかかる画像出力装置は、評価値が高い場合には、第二解像度画像を送信するとともに保存する。
(Modification)
Here, a modified example of the image output device according to the first embodiment will be described. When the evaluation value is high, the image output device according to the present modification transmits and saves the second resolution image.
図5は、本変形例に係る画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing an example of an image processing system including an image output device according to this modification.
本変形例に係る画像処理システム100Saは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置1001a、表示装置1501、および記録媒体1502からなる。
An image processing system 100Sa according to this modification includes a
記録媒体1502は、画像出力装置1001aから出力された画像を保持する。この記録媒体1502は、例えば、ハードディスク、BD(Blu−ray(登録商標) Disc)、DVD、SDカード(登録商標)、RAM(Random Access Memory)、またはキャッシュ等の記憶装置によって実現される。
The
画像出力装置1001aは、上記実施の形態1の画像出力装置1001が備えている各構成要素の他に、さらに、第一出力部1205を備える。
The
第一出力部1205は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する。一方、第一出力部1205は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力しない。
When the
言い換えれば、第一出力部1205は、送信部1204から送信される画像を記録媒体1502に出力することによって、その画像を記録媒体1502に保存する。つまり、第一出力部1205は、図3のステップS16,S18または図4のステップS29において送信される第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に保存する。
In other words, the
(効果)
このような本変形例にかかる画像出力装置1001aでは、高解像度での診断が必要な検体に対しては、高解像度画像(第二解像度画像)を自動的に保存することができる。高解像度画像を保存するか否かを選択するボタンを設けることも考えられるが、病理医は一時間に60検体以上の診断を行うような場合があり、ボタン操作を忘れることが考えられる。しかし、本変形例にかかる画像出力装置1001aを用いれば、操作忘れを防止することができ、重要な高解像度画像を確実に保存することができる。
(effect)
The
また、本変形例にかかる画像出力装置1001aを用いれば、高解像度画像で診断が行われた検体に対してはその高解像度画像が保存および送信され、低解像度画像(第一解像度画像)で診断が行われた検体に対してはその低解像度画像が保存および送信される。これにより、保存および送信される画像のサイズを検体に応じたサイズにすることで、保存される画像のサイズ、送信(転送)される画像のサイズおよび転送時間を削減することができる。
Further, when the
(実施の形態2)
本実施の形態における画像出力装置は、互いに通信回線を介して接続される画像送信装置と画像受信装置とから構成される。なお、本実施の形態における装置およびその構成要素のうち、実施の形態1と同じ装置およびその構成要素に対しては、実施の形態1と同じ符号を付し、それらの詳細な説明を省略する。
(Embodiment 2)
The image output device according to the present embodiment is composed of an image transmitting device and an image receiving device which are connected to each other via a communication line. It should be noted that, of the devices and their components in the present embodiment, the same devices and their components as in the first embodiment will be assigned the same reference numerals as in the first embodiment, and detailed explanations thereof will be omitted. ..
図6は、実施の形態2における画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 6 is a configuration diagram showing an example of an image processing system including the image output device according to the second embodiment.
画像処理システム200Sは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置2001、表示装置1501、記録媒体1502、および記録媒体1503からなる。
The image processing system 200S includes a
記録媒体1502は、画像出力装置2001の画像受信装置1200から出力された画像を保持する。
The
記録媒体1503は、画像出力装置2001の画像送信装置1100から出力された画像を保持する。この記録媒体1503は、記録媒体1502と同様、例えば、ハードディスク、BD(Blu−ray(登録商標) Disc)、DVD、SDカード(登録商標)、RAM、またはキャッシュ等の記憶装置によって実現される。
The
画像出力装置2001は、通信回線を介して互いに接続される画像送信装置1100および画像受信装置1200を備える。なお、画像出力装置2001は全体として、実施の形態1の画像出力装置1001と同様の機能を有する。また、例えば、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像送信装置1100および記録媒体1503を含むセットは、病理医のいない病院などの施設に配置される。画像受信装置1200、表示装置1501および記録媒体1502を含むセットは、例えば、その病院から遠く離れた、病理医がいる施設に配置される。
The
画像送信装置1100は、画像取得部1101、高解像度画像取得部1102、送信部1204、および第二出力部1103を備える。
The
第二出力部1103は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得された第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力することによって、その第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に保存する。つまり、この第二出力部1103は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力して保存する。
The
画像受信装置1200は、拡大受付部1201、判定部1202、表示用出力部1203、および第一出力部1205を備える。
The
表示用出力部1203は、画像送信装置1100から通信回線を介して第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像を取得する。そして、実施の形態1と同様に、表示用出力部1203は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づき拡大された第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像を表示装置1501に出力する。これにより、表示用出力部1203は、拡大された第一解像度画像または第二解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる。
The
判定部1202は、実施の形態1と同様に、評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する。そして、判定部1202は、通信回線を介してその判定結果を画像送信装置1100に通知する。
The
画像送信装置1100の送信部1204は、評価値が高いことを示す判定結果である場合には、通信回線を介して第二解像度画像を画像受信装置1200に送信する。一方、送信部1204は、評価値が高くないことを示す判定結果である場合には、通信回線を介して第一解像度画像を第二解像度画像の代わりに送信する。
When the determination result indicates that the evaluation value is high, the
図7は、画像送信装置1100および画像受信装置1200の処理動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the processing operation of the
画像送信装置1100の画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得する(ステップS41)。送信部1204は、通信回線を介して第一解像度画像を画像受信装置1200に送信する(ステップS42)。
The
画像受信装置1200の表示用出力部1203は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100から送信される第一解像度画像を受信する(ステップS51)。次に、画像受信装置1200の拡大受付部1201は、操作者による例えばキーボードなどへの操作に応じて画像の拡大率を受け付ける(ステップS52)。そして、表示用出力部1203は、受け付けられた拡大率で第一解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。表示用出力部1203は、その出力によって、受け付けられた拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS53)。
The
次に、画像受信装置1200の表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602または読込ボタン605が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第一解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS54)。ここで、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS54のNo)、拡大受付部1201は、さらに、新たな拡大率を受け付ける。つまり、表示装置1501に表示された画像を観察する操作者(病理医)は、検体に応じて拡大率を変更して観察を行う。
Next, the
一方、表示を終了すべきと判定されると(ステップS54のYes)、判定部1202は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づく評価値を導出し、その評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する(ステップS55)。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the display should be ended (Yes in step S54), the
ここで、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定されると(ステップS55のNo)、画像受信装置1200の第一出力部1205は、第一解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する(ステップS59)。一方、評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定されると(ステップS55のYes)、第一出力部1205は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100に第二解像度画像を要求する(ステップS56)。
Here, if it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value (No in step S55), the
画像送信装置1100の送信部1204は、画像受信装置1200から第二解像度画像が要求されているか否かを判定する(ステップS43)。ここで、要求されていないと判定されると(ステップS43のNo)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS44)。そして、第二出力部1103は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得されたその第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力して保存する(ステップS45)。したがって、この第二出力部1103は、判定部1202によって評価値が高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力して保存する。
The
一方、第二解像度画像が要求されていると判定すると(ステップS43のYes)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS46)。そして、送信部1204は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得されたその第二解像度画像を、通信回線を介して画像受信装置1200に送信する(ステップS47)。したがって、送信部1204は、実施の形態1と同様、判定部1202によって評価値が高いと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を送信し、判定部1202によって評価値が高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を送信しない。
On the other hand, when determining that the second resolution image is requested (Yes in step S43), the high resolution
なお、上述の例では、ステップS43の判定の後に、ステップS44およびステップS46の処理が行われるが、ステップS43の判定の前に行われていてもよい。 In the above example, the processes of steps S44 and S46 are performed after the determination of step S43, but they may be performed before the determination of step S43.
ステップS47で第二解像度画像が送信されると、画像受信装置1200の第一出力部1205は、その第二解像度画像を受信する(ステップS57)。そして、第一出力部1205は、その第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する(ステップS58)。
When the second resolution image is transmitted in step S47, the
(効果)
このような本実施の形態における画像出力装置2001では、被写体の画像を取得する施設と、その画像を観察する施設とが離れていても、実施の形態1と同様の効果を奏することができる。
(effect)
In the
(変形例1)
ここで、実施の形態2における画像出力装置の第1の変形例について説明する。本変形例では、複数の検体に対して評価値が高いと判定された場合に、高い評価値の検体に対応する第二解像度画像から順に、複数の第二解像度画像を送信する。
(Modification 1)
Here, a first modification of the image output device according to the second embodiment will be described. In this modification, when it is determined that the evaluation values are high for the plurality of samples, the plurality of second resolution images are transmitted in order from the second resolution image corresponding to the sample having the high evaluation value.
図8は、本変形例に係る画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 8 is a configuration diagram showing an example of an image processing system including an image output device according to this modification.
本変形例に係る画像処理システム200Saは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置2001a、表示装置1501、記録媒体1502、および記録媒体1503からなる。
An image processing system 200Sa according to this modification includes a
画像出力装置2001aは、通信回線を介して互いに接続される画像送信装置1100aおよび画像受信装置1200aを備える。
The
画像受信装置1200aは、実施の形態2における画像受信装置1200が備えている各構成要素の他に、さらに評価値蓄積部1206を備える。この評価値蓄積部1206には、各検体(被写体)に対して導出された評価値が蓄積される。また、第一出力部1205は、評価値蓄積部1206に蓄積されている各評価値に対応する第二解像度画像を画像送信装置1100aに要求する。
The
画像送信装置1100aは、実施の形態2における送信部1204の代わりに、送信部1204aを備える。この送信部1204aは、実施の形態2における送信部1204と同様の機能を有するだけでなく、第一出力部1205からの要求を受けた場合には、高い評価値の検体に対応する第二解像度画像から順に、複数の第二解像度画像を送信する。
The
図9は、画像送信装置1100aおよび画像受信装置1200aの処理動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing the processing operation of the
画像送信装置1100aの画像取得部1101および高解像度画像取得部1102は、被写体の第一解像度画像および第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS71)。送信部1204aは、通信回線を介して第一解像度画像を画像受信装置1200aに送信する(ステップS72)。そして、画像取得部1101および高解像度画像取得部1102は、次の被写体があるか否かを判定する(ステップS73)。次の被写体があると判定されると(ステップS73)、画像送信装置1100aは、ステップS71からの処理を繰り返す。
The
画像受信装置1200aの表示用出力部1203は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100aから送信される第一解像度画像を受信する(ステップS81)。次に、画像受信装置1200aの拡大受付部1201は、操作者による例えばキーボードなどへの操作に応じて画像の拡大率を受け付ける(ステップS82)。そして、表示用出力部1203は、受け付けられた拡大率で第一解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。表示用出力部1203は、その出力によって、受け付けられた拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS83)。
The
次に、画像受信装置1200aの表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602または読込ボタン605が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第一解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS84)。ここで、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS84のNo)、拡大受付部1201は、さらに、新たな拡大率を受け付ける。つまり、表示装置1501に表示された画像を観察する操作者(病理医)は、検体に応じて拡大率を変更して観察を行う。
Next, whether the
一方、表示を終了すべきと判定されると(ステップS84のYes)、判定部1202は、拡大受付部1201によって受け付けられた拡大率に基づく評価値を導出し、その評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定する(ステップS85)。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the display should be ended (Yes in step S84), the
ここで、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定されると(ステップS85のNo)、画像受信装置1200aの第一出力部1205は、第一解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する(ステップS87)。一方、評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定されると(ステップS85のYes)、判定部1202は、その所定の値よりも高い評価値を被写体に関連付けて評価値蓄積部1206に保存する(ステップS86)。
Here, if it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value (No in step S85), the
次に、画像受信装置1200aの表示用出力部1203は、次の被写体があるか否かを判定する(ステップS88)。ここで、次の被写体があると判定されると(ステップS88のYes)、画像受信装置1200aはステップS81からの処理を繰り返し実行する。一方、次の被写体がないと判定されると(ステップS88のNo)、画像受信装置1200aの第一出力部1205は、評価値蓄積部1206に保存されている評価値を参照する。そして、第一出力部1205は、高い評価値から順に、その評価値に関連付けられている被写体の第二解像度画像を送信するように、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100に要求する(ステップS89)。
Next, the
画像送信装置1100aの送信部1204aは、画像受信装置1200aから第二解像度画像が要求されているか否かを判定する(ステップS74)。ここで、要求されていないと判定されると(ステップS74のNo)、第二出力部1103は、ステップS71で取得された各被写体の第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力して保存する(ステップS75)。一方、送信部1204aは、第二解像度画像が要求されていると判定すると(ステップS74のYes)、ステップS71で取得された各被写体の第二解像度画像のうち、所定の値よりも高い評価値に対応する第二解像度画像を画像受信装置1200aに送信する。このとき、送信部1204aは、高い評価値の第二解像度画像から順に、それらの第二解像度画像を、通信回線を介して画像受信装置1200aに送信する(ステップS76)。
The transmission unit 1204a of the
画像受信装置1200aの第一出力部1205は、所定の値よりも高い評価値に対応する各第二解像度画像を、評価値の高い第二解像度画像から順に受信して記録媒体1502に出力する(ステップS90)。これにより、所定の値よりも高い評価値の各第二解像度画像が記録媒体1502に保存される。
The
(効果)
このように、本変形例では、評価値が高いと判定された複数の被写体の第二解像度画像をまとめて送信するときには、評価値が高い第二解像度画像から順に送信される。したがって、重要度の高い第二解像度画像を迅速に送信することができる。その結果、病理医は、重要度の高い第二解像度画像から順に、その第二解像度画像を用いた検体の診断を行うことができる。
(effect)
As described above, in the present modification, when the second resolution images of a plurality of subjects determined to have a high evaluation value are collectively transmitted, the second resolution images having a high evaluation value are transmitted in order. Therefore, it is possible to quickly transmit the second resolution image having high importance. As a result, the pathologist can diagnose the specimen using the second resolution images in order from the second resolution image with the highest importance.
つまり、画像送信装置1100aは、経験の少ない病理医しかいない、または外科しかいない地方病院におかれて使用されることが考えられる。このケースでは、診断が難しい検体の第二解像度画像が、送信部1204aによって、経験が豊富な病理医のいる大病院に送信される。通信回線は限りがあるが、本変形例における画像出力装置2001aを用いれば、診断が難しかった検体の第二解像度画像を優先して地方病院から大病院に送信することができる。また、画像送信装置1100aは、病理医が一人しかいない小病院におかれ、重要な画像は遠隔地にいる病理医に送信されてダブルチェックを行う際の送信画像を選択する際に利用することができる。
That is, it is conceivable that the
なお、病理検査では、同一患者から複数の検体を撮影する場合がある。例えば、癌の検査では、臓器の一部分を取得し、その一部分の異なる断面の切片を観察することがある。すなわち、上下方向の異なる位置(便宜上、異なる高さと呼ぶ)の検体切片を撮影することで、複数の2次元の画像を取得し、それらの画像によって、三次元的な癌の範囲を確認する。ここで、何れかの高さにおける画像において癌の疑いがある場合、その画像を含めて、他の高さにおける画像も、高解像度で送信または保持しておくことが望まれる。 In the pathological examination, a plurality of specimens may be imaged from the same patient. For example, in the examination for cancer, a part of an organ may be acquired and sections of different cross sections of the part may be observed. That is, a plurality of two-dimensional images are acquired by imaging specimen sections at different positions in the vertical direction (referred to as different heights for convenience), and the three-dimensional cancer range is confirmed by these images. Here, when there is a suspicion of cancer in an image at any height, it is desirable to transmit or hold images at other heights including that image with high resolution.
そこで、高解像度画像取得部1102は、同一患者の同一臓器から得られた複数の第二解像度画像に対して同一の画像群識別子を付与してもよい。この場合、送信部1204aは、第二解像度画像を送信するときには、その第二解像度画像に付与された画像群識別子に関連付けられている他の第二解像度画像も画像受信装置1200aに送信する。これにより、画像受信装置1200aを扱う病理医は、同一患者の同一臓器に対して得られた複数の第二解像度画像をそれぞれ選択することなく、まとめて取得することができ、癌の範囲などを三次元的に簡単に確認することができる。
Therefore, the high resolution
(変形例2)
上記実施の形態2およびその変形例1では、判定部1202は画像受信装置に備えられているが、画像送信装置に備えられていてもよい。第2の変形例における画像送信装置は、判定部1202を備える。
(Modification 2)
Although the
図10は、本変形例に係る画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing an example of an image processing system including an image output device according to this modification.
本変形例に係る画像処理システム200Sbは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置2001b、表示装置1501、記録媒体1502、および記録媒体1503からなる。
An image processing system 200Sb according to this modification includes a
画像出力装置2001bは、通信回線を介して互いに接続される画像送信装置1100bおよび画像受信装置1200bを備える。
The
画像送信装置1100bは、実施の形態2およびその変形例1における画像送信装置1100aが備えている各構成要素の他に、さらに、判定部1202を備える。
The
画像受信装置1200bは、判定部1202を備えず、拡大受付部1201、表示用出力部1203および第一出力部1205を備える。
The
図11は、画像送信装置1100bおよび画像受信装置1200bの処理動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing the processing operation of the
画像送信装置1100bの画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得する(ステップS101)。送信部1204は、通信回線を介して第一解像度画像を画像受信装置1200に送信する(ステップS102)。
The
画像受信装置1200bの表示用出力部1203は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100bから送信される第一解像度画像を受信する(ステップS121)。次に、画像受信装置1200bの拡大受付部1201は、操作者による例えばキーボードなどへの操作に応じて画像の拡大率を受け付ける(ステップS122)。そして、表示用出力部1203は、受け付けられた拡大率で第一解像度画像を拡大して表示装置1501に出力する。表示用出力部1203は、その出力によって、受け付けられた拡大率に拡大された第一解像度画像を表示装置1501に表示させる(ステップS123)。
The
次に、画像受信装置1200bの表示用出力部1203は、終了ボタン602または読込ボタン605が選択されることによって表示装置1501から出力される信号に基づいて、第一解像度画像の表示を終了すべきか否かを判定する(ステップS124)。ここで、表示を終了すべきでないと判定されると(ステップS124のNo)、拡大受付部1201は、さらに、新たな拡大率を受け付ける。つまり、表示装置1501に表示された画像を観察する操作者(病理医)は、検体に応じて拡大率を変更して観察を行う。一方、表示用出力部1203は、表示を終了すべきと判定すると(ステップS124のYes)、評価値の導出に必要となる評価値関連情報を、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100bに送信する(ステップS126)。この評価値関連情報は、例えば、上述の直前拡大率、最大拡大率、表示回数、表示時間および表示面積のうちの少なくとも1つである。
Next, the
画像送信装置1100bの判定部1202は、その評価値関連情報を受信する(ステップS104)。そして、判定部1202は、その評価値関連情報に基づいて評価値を導出する。さらに、判定部1202は、導出された評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、通信回線を介してその判定結果を画像受信装置1200bに通知する(ステップS105)。
The
画像受信装置1200bの第一出力部1205は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100bから通知された判定結果を受けると(ステップS127)、その判定結果が肯定的(Yes)であるか否かを確認する(ステップS128)。ここで、判定結果が否定的であること、つまり、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないことが確認されると(ステップS128のNo)、画像受信装置1200bの第一出力部1205は、第一解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する(ステップS132)。一方、判定結果が肯定的であること、つまり、評価値が所定の値よりも高いことが確認されると(ステップS128のYes)、画像受信装置1200bの第一出力部1205は、通信回線を介して画像送信装置1100に第二解像度画像を要求する(ステップS129)。
When the
画像送信装置1100bの送信部1204は、画像受信装置1200bから第二解像度画像が要求されているか否かを判定する(ステップS106)。ここで、要求されていないと判定されると(ステップS106のNo)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS107)。さらに、第二出力部1103は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得されたその第二解像度画像を記録媒体1503に出力して保存する(ステップS108)。
The
一方、第二解像度画像が要求されていると判定されると(ステップS106のYes)、高解像度画像取得部1102は、第二解像度画像を取得する(ステップS109)。そして、送信部1204は、高解像度画像取得部1102によって取得されたその第二解像度画像を、通信回線を介して画像受信装置1200bに送信する(ステップS110)。
On the other hand, when it is determined that the second resolution image is requested (Yes in step S106), the high resolution
なお、上述の例では、ステップS106の判定の後に、ステップS107およびステップS109の処理が行われるが、ステップS106の判定の前に行われていてもよい。 In the above example, the processes of steps S107 and S109 are performed after the determination of step S106, but may be performed before the determination of step S106.
ステップS110で第二解像度画像が送信されると、画像受信装置1200bの第一出力部1205は、その第二解像度画像を受信する(ステップS130)。そして、第一出力部1205は、その第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する(ステップS131)。
When the second resolution image is transmitted in step S110, the
(効果)
このように、本変形例では、判定部1202が画像送信装置1100bに備えられていても、上記実施の形態1および2と同様の効果を奏することができる。
(effect)
As described above, in the present modification, even if the
また、本変形例においても変形例1と同様に、所定の値よりも高い評価値に関連付けられた複数の被写体のそれぞれの第二解像度画像を、その評価値の高い第二解像度画像から順に送受信してもよい。 Also in the present modification example, similarly to the modification example 1, the second resolution images of the plurality of subjects associated with the evaluation value higher than the predetermined value are transmitted and received in order from the second resolution image with the highest evaluation value. You may.
(実施の形態3)
上記実施の形態1および2とそれらの変形例では、評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かに応じて、第二解像度画像を送信するか、送信しないかを切り替える。本実施の形態では、評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かに応じて、その送信と非送信との切り替えを行うことなく、第二解像度画像を保存するか、保存しないかを切り替える。なお、本実施の形態における装置およびその構成要素のうち、実施の形態1または2と同じ装置およびその構成要素に対しては、実施の形態1または2と同じ符号を付し、それらの詳細な説明を省略する。
(Embodiment 3)
In the first and second embodiments and their modifications, the second resolution image is transmitted or not transmitted depending on whether or not the evaluation value is higher than a predetermined value. In the present embodiment, depending on whether or not the evaluation value is higher than a predetermined value, the second resolution image is saved or not saved without switching between the transmission and the non-transmission. It should be noted that, of the devices and their components in the present embodiment, the same devices and their components as those in the first or second embodiment are designated by the same reference numerals as those in the first or second embodiment, and their detailed description is omitted. The description is omitted.
図12は、実施の形態3における画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 12 is a configuration diagram showing an example of an image processing system including the image output device according to the third embodiment.
画像処理システム300Sは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置3001、表示装置1501、および記録媒体1502からなる。
The image processing system 300S includes a
画像出力装置3001は、画像取得部1101と、高解像度画像取得部1102と、拡大受付部1201と、判定部1202と、表示用出力部1203と、第一出力部1205とを備える。つまり、本実施の形態における画像出力装置3001は、実施の形態1の画像出力装置1001が備える各構成要素のうちの送信部1204に代えて第一出力部1205を備える。なお、本実施の形態における画像出力装置3001は、表示用出力部1203を備えるが、実施の形態1と同様に、この表示用出力部1203を備えていなくてもよい。
The
第一出力部1205は、実施の形態1の変形例と同様、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する。一方、第一出力部1205は、判定部1202によって評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力しない。
When the
(効果)
これにより、本実施の形態では、実施の形態1の変形例と同様、高解像度での診断が必要な検体に対しては、高解像度画像(第二解像度画像)を自動的に保存することができる。また、高解像度での診断が不要な検体に対しては、高解像度画像は保存されないため、記録媒体1502の空き容量が制限されてしまうことを抑えることができる。
(effect)
As a result, in the present embodiment, similarly to the modification of the first embodiment, a high resolution image (second resolution image) can be automatically saved for a sample that requires high resolution diagnosis. it can. Further, since a high resolution image is not stored for a sample that does not require diagnosis at high resolution, it is possible to prevent the free space of the
(変形例1)
上記実施の形態3における画像出力装置3001は1つの装置として構成されているが、実施の形態2のように、2つの装置から構成されていてもよい。本変形例にかかる画像出力装置は、互いに通信回線を介して接続される画像送信装置と画像受信装置とから構成される。
(Modification 1)
Although the
図13は、実施の形態3における第1の変形例に係る画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの一例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 13 is a configuration diagram showing an example of an image processing system including an image output device according to a first modification of the third embodiment.
画像処理システム300Saは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置3001a、表示装置1501、および記録媒体1502からなる。
The image processing system 300Sa includes a
画像出力装置3001aは、通信回線を介して互いに接続される画像送信装置3100aおよび画像受信装置3200aを備える。なお、画像出力装置3001aは全体として、実施の形態3の画像出力装置3001と同様の機能を有する。また、例えば、デジタル顕微鏡1500および画像送信装置3100aを含むセットは、病理医のいない病院などの施設に配置される。画像受信装置3200a、表示装置1501および記録媒体1502を含むセットは、例えば、その病院から遠く離れた、病理医がいる施設に配置される。
The
画像送信装置3100aは、画像取得部1101を備える。画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得し、通信回線を介して、その第一解像度画像を画像受信装置3200aに送信する。
The
画像受信装置3200aは、高解像度画像取得部1102、拡大受付部1201、判定部1202、表示用出力部1203、および第一出力部1205を備える。本変形例に係る高解像度画像取得部1102は、第一出力部1205からの要求に応じて、複数の第一解像度画像を、通信回線を介して画像送信装置3100aから取得する。そして、高解像度画像取得部1102は、それらの第一解像度画像に基づいて第二解像度画像を生成することによって、その第二解像度画像を取得する。
The
第一出力部1205は、評価値が所定の値よりも高いと判定部1202によって判定された場合に、高解像度画像取得部1102に第二解像度画像を要求し、高解像度画像取得部1102から第二解像度画像を取得する。そして、第一出力部1205は、その第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する。一方、第一出力部1205は、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないと判定部1202によって判定された場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力しない。
When the
(効果)
このような本変形例における画像出力装置3001aでは、被写体の画像を取得する施設と、その画像を観察する施設とが離れていても、実施の形態3と同様の効果を奏することができる。
(effect)
In the
(変形例2)
上記実施の形態3における第1の変形例では、判定部1202は画像受信装置に備えられているが、画像送信装置に備えられていてもよい。第2の変形例における画像送信装置は、判定部1202を備える。
(Modification 2)
In the first modification of the third embodiment described above, the
図14は、実施の形態3における第2の変形例に係る画像出力装置を含む画像処理システムの他の例を示す構成図である。 FIG. 14 is a configuration diagram showing another example of the image processing system including the image output device according to the second modification of the third embodiment.
画像処理システム300Sbは、デジタル顕微鏡1500、画像出力装置3001b、表示装置1501、および記録媒体1502からなる。
The image processing system 300Sb includes a
画像出力装置3001bは、通信回線を介して互いに接続される画像送信装置3100bおよび画像受信装置3200bを備える。なお、画像出力装置3001bは全体として、実施の形態3の画像出力装置3001と同様の機能を有する。また、例えば、デジタル顕微鏡1500および画像送信装置3100bを含むセットは、病理医のいない病院などの施設に配置される。画像受信装置3200b、表示装置1501および記録媒体1502を含むセットは、例えば、その病院から遠く離れた、病理医がいる施設に配置される。
The
画像送信装置3100bは、画像取得部1101および判定部1202を備える。画像取得部1101は、デジタル顕微鏡1500から第一解像度画像を取得し、通信回線を介して、その第一解像度画像を画像受信装置3200bに送信する。判定部1202は、画像受信装置3200bから通信回線を介して送信される上述の評価値関連情報を取得し、その評価値関連情報に基づいて評価値を導出する。そして、判定部1202は、その評価値が所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、その判定結果を、通信回線を介して画像受信装置3200bに通知する。
The
画像受信装置3200bは、高解像度画像取得部1102、拡大受付部1201、表示用出力部1203、および第一出力部1205を備える。
The
高解像度画像取得部1102は、第一出力部1205からの要求に応じて、複数の第一解像度画像を、通信回線を介して画像送信装置3100bから取得する。そして、高解像度画像取得部1102は、それらの第一解像度画像に基づいて第二解像度画像を生成することによって、その第二解像度画像を取得する。
The high resolution
表示用出力部1203は、通信回線を介して評価値関連情報を画像送信装置3100bに送信する。これによって、画像送信装置3100bの判定部1202による判定が行われる。
The
第一出力部1205は、画像送信装置3100bから通知された判定結果が肯定的であること、つまり、評価値が所定の値よりも高いことが確認された場合に、高解像度画像取得部1102に第二解像度画像を要求する。そして、第一出力部1205は、高解像度画像取得部1102から第二解像度画像を取得し、その第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力して保存する。一方、第一出力部1205は、画像送信装置3100bから通知された判定結果が否定的であること、つまり、評価値が所定の値よりも高くないことが確認された場合には、第二解像度画像を記録媒体1502に出力しない。
The
(効果)
このように、本変形例では、判定部1202が画像送信装置3100bに備えられていても、上記実施の形態3およびその変形例1と同様の効果を奏することができる。
(effect)
As described above, in the present modification, even if the
(実施の形態4)
ここで、上記各実施の形態およびその変形例におけるデジタル顕微鏡1500について、以下、詳細に説明する。なお、デジタル顕微鏡1500を、以下、画像取得装置(デジタイザ)と称する。
(Embodiment 4)
Here, the
<高解像度画像形成の原理>
本開示では、照明光の照射方向を変えて複数回の撮影を実行することにより得られる複数の画像を用いて、それら複数の画像の各々よりも解像度(分解能)の高い画像(以下、「高解像度画像」または「高分解能画像」と呼ぶ。)を形成する。なお、高解像度画像は、上述の第二解像度画像に相当し、その高解像度画像の形成に用いられる複数の画像(サブ画像)のそれぞれは、上述の第一解像度画像に相当する。まず、図15A〜図20を参照して、高解像度画像形成の原理を説明する。ここでは、CCD(Charge Coupled Device)イメージセンサを例示して説明を行う。なお、以下の説明において、実質的に同じ機
能を有する構成要素は共通の参照符号で示し、説明を省略することがある。
<Principle of high resolution image formation>
In the present disclosure, by using a plurality of images obtained by changing the irradiation direction of the illumination light and performing a plurality of shootings, an image having a higher resolution (resolution) than each of the plurality of images (hereinafter, “high resolution”) is used. Resolution image" or "high resolution image"). The high resolution image corresponds to the second resolution image described above, and each of the plurality of images (sub-images) used to form the high resolution image corresponds to the first resolution image described above. First, the principle of high-resolution image formation will be described with reference to FIGS. 15A to 20. Here, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image sensor will be described as an example. In the following description, constituent elements having substantially the same function are designated by common reference numerals, and description thereof may be omitted.
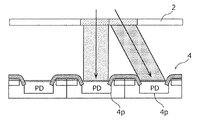
図15Aおよび図15Bを参照する。図15Aは、被写体の一部を模式的に示す平面図である。図15Aに示す被写体2は、例えば、生物組織の薄片(典型的には、数十μm以下の厚さを有する。)である。被写体2の画像の取得時、被写体2は、イメージセンサの撮像面に近接して配置されている。イメージセンサの撮像面から被写体2までの距離は、典型的には1mm以下であり、例えば1μm程度に設定され得る。
Please refer to FIG. 15A and FIG. 15B. FIG. 15A is a plan view schematically showing a part of the subject. The subject 2 shown in FIG. 15A is, for example, a thin piece (typically, having a thickness of several tens μm or less) of biological tissue. When the image of the subject 2 is acquired, the
図15Bは、イメージセンサのフォトダイオードのうち、図15Aに示されている領域の撮像に関わるフォトダイオードを抽出して模式的に示す平面図である。ここで説明する例では、イメージセンサ4に形成されたフォトダイオード4pのうち、6個のフォトダイオードが示されている。なお、参考のために、図15Bでは、互いに直交するx方向、y方向およびz方向を示す矢印が図示されている。z方向は、撮像面の法線方向を示している。図15Bでは、xy面内においてx軸からy軸に向かって45°回転した方向であるu方向を示す矢印も図示されている。他の図面においても、x方向、y方向、z方向またはu方向を示す矢印を図示することがある。
FIG. 15B is a plan view schematically showing, out of the photodiodes of the image sensor, the photodiodes involved in imaging the region shown in FIG. 15A. In the example described here, of the
イメージセンサ4におけるフォトダイオード4p以外の構成要素は、遮光層によって覆われている。図15B中、ハッチングされた領域は、遮光層によって覆われている領域を示している。CCDイメージセンサの撮像面上における1つのフォトダイオードの受光面の面積(S2)は、そのフォトダイオードを含む単位領域の面積(S1)よりも小さい。画素の面積S1に対する受光面積S2の比率(S2/S1)は、「開口率」と呼ばれている。ここでは、開口率が25%であるとして説明を行う。
The components other than the
図16Aおよび図16Bは、被写体2を透過してフォトダイオード4pに入射する光線の方向を模式的に示す。図16Aおよび図16Bは、撮像面に対して垂直な方向から光線を入射させた状態を示している。図16Aおよび図16Bにおいて模式的に示すように、ここでは、被写体2とイメージセンサ4との間に結像のためのレンズは配置されておらず、被写体2の画像は、被写体2を透過する実質的に平行な光線を用いて取得される。
16A and 16B schematically show directions of light rays that pass through the
図16Cは、図16Aおよび図16Bに示す照射方向のもとで取得される画像Sa(第1のサブ画像Sa)を模式的に示す。図16Cに示すように、第1のサブ画像Saは、6個のフォトダイオード4pによって取得される6個の画素Paから構成される。画素Paの各々は、個々のフォトダイオード4pに入射した光の量を示す値(画素値)を持つ。
FIG. 16C schematically shows the image Sa (first sub-image Sa) acquired under the irradiation direction shown in FIGS. 16A and 16B. As shown in FIG. 16C, the first sub-image Sa is composed of 6 pixels Pa acquired by the 6
図16Aおよび図16Bに示すように、撮像面に垂直な方向から被写体2を照射したときには、被写体2の全体のうち、フォトダイオード4pの直上に位置する領域を透過した光がフォトダイオード4pに入射する。この例では、第1のサブ画像Saは、被写体2の全体のうち、領域A1、A2、A3、A4、A5およびA6(図15A参照)の情報を有している。なお、フォトダイオード4pの直上に位置しない領域を透過した光は、フォトダイオード4pには入射しない。したがって、第1のサブ画像Saでは、被写体2の全体のうち、領域A1、A2、A3、A4、A5およびA6以外の領域の情報が欠落している。
As shown in FIGS. 16A and 16B, when the
図17Aおよび図17Bは、図16Aおよび図16Bに示す照射方向とは異なる照射方向から光線を入射させた状態を示している。図17Aおよび図17Bに示す光線は、z方向に対してx方向に傾斜している。このとき、被写体2の全体のうち、フォトダイオード4pの直上に位置する領域とは異なる領域を透過した光がフォトダイオード4pに入射する。
17A and 17B show a state in which light rays are incident from an irradiation direction different from the irradiation directions shown in FIGS. 16A and 16B. The rays shown in FIGS. 17A and 17B are inclined in the x direction with respect to the z direction. At this time, light that has passed through a region of the
図17Cは、図17Aおよび図17Bに示す照射方向のもとで取得される画像Sb(第2のサブ画像Sb)を模式的に示す。図17Cに示すように、第2のサブ画像Sbも、6個のフォトダイオード4pによって取得される6個の画素から構成されている。ただし、第2のサブ画像Sbを構成する画素Pbは、被写体2の全体のうち、領域A1、A2、A3、A4、A5およびA6とは異なる領域B1、B2、B3、B4、B5およびB6(図15A参照)に関する画素値を持つ。言い換えれば、第2のサブ画像Sbは、被写体2の全体のうち、領域A1、A2、A3、A4、A5およびA6の情報は有しておらず、代わりに、領域B1、B2、B3、B4、B5およびB6の情報を有している。ここでは、例えば領域B1は、被写体2において領域A1の右側に隣接する領域である(図15A参照)。
FIG. 17C schematically shows the image Sb (second sub-image Sb) acquired under the irradiation direction shown in FIGS. 17A and 17B. As shown in FIG. 17C, the second sub-image Sb is also composed of 6 pixels acquired by 6
図16Aおよび図16Bと、図17Aおよび図17Bとを比較することによって理解されるように、照射方向を適切に変更することにより、被写体2の異なる領域を透過した光線をフォトダイオード4pに入射させることができる。その結果、第1のサブ画像Saと第2のサブ画像Sbは、被写体2において異なる位置に対応する画素情報を含むことができる。
As can be understood by comparing FIGS. 16A and 16B with FIGS. 17A and 17B, by appropriately changing the irradiation direction, the light rays transmitted through different regions of the subject 2 are made incident on the
図18Aおよび図18Bは、図16Aおよび図16Bに示す照射方向ならびに図17Aおよび図17Bに示す照射方向とは異なる照射方向から光線を入射させた状態を示している。図18Aおよび図18Bに示す光線は、z方向に対してy方向に傾斜している。 18A and 18B show a state in which light rays are incident from an irradiation direction different from the irradiation directions shown in FIGS. 16A and 16B and the irradiation directions shown in FIGS. 17A and 17B. The light rays shown in FIGS. 18A and 18B are inclined in the y direction with respect to the z direction.
図18Cは、図18Aおよび図18Bに示す照射方向のもとで取得される画像Sc(第3のサブ画像Sc)を模式的に示す。図18Cに示すように、第3のサブ画像Scは、6個のフォトダイオード4pによって取得される6個の画素Pcから構成されている。図示するように、第3のサブ画像Scは、被写体2の全体のうち、図15Aに示す領域C1、C2、C3、C4、C5およびC6の情報を有している。ここでは、例えば領域C1は、被写体2において領域A1の上側に隣接する領域である(図15A参照)。
FIG. 18C schematically shows the image Sc (third sub-image Sc) acquired under the irradiation direction shown in FIGS. 18A and 18B. As shown in FIG. 18C, the third sub-image Sc is composed of 6 pixels Pc acquired by 6
図19Aは、図16Aおよび図16Bに示す照射方向、図17Aおよび図17Bに示す照射方向、ならびに図18Aおよび図18Bに示す照射方向とは異なる照射方向から光線を入射させた状態を示している。図19Aに示す光線は、z方向に対して、xy面内においてx軸と45°の角をなす方向に傾斜している。 FIG. 19A shows a state in which light rays are incident from an irradiation direction shown in FIGS. 16A and 16B, an irradiation direction shown in FIGS. 17A and 17B, and an irradiation direction different from the irradiation directions shown in FIGS. 18A and 18B. .. The light ray shown in FIG. 19A is inclined with respect to the z direction in a direction forming an angle of 45° with the x axis in the xy plane.
図19Bは、図19Aに示す照射方向のもとで取得される画像Sd(第4のサブ画像Sd)を模式的に示す。図19Bに示すように、第4のサブ画像Sdは、6個のフォトダイオード4pによって取得される6個の画素Pdから構成されている。第4のサブ画像Sdは、被写体2の全体のうち、図15Aに示す領域D1、D2、D3、D4、D5およびD6の情報を有している。ここでは、例えば領域D1は、領域C1の右側に隣接する領域である(図15A参照)。このように、サブ画像Sa、Sb、ScおよびSdの各々は、被写体2の異なる部分から構成される像を含んでいる。
FIG. 19B schematically shows the image Sd (fourth sub-image Sd) acquired under the irradiation direction shown in FIG. 19A. As shown in FIG. 19B, the fourth sub-image Sd is composed of six pixels Pd acquired by the six
図20は、4枚のサブ画像Sa、Sb、ScおよびSdから合成される高解像度画像HRを示している。図20に示すように、高解像度画像HRの画素数または画素密度は、4枚のサブ画像Sa、Sb、ScおよびSdの各々の画素数または画素密度の4倍である。 FIG. 20 shows a high resolution image HR composed of four sub images Sa, Sb, Sc and Sd. As shown in FIG. 20, the number of pixels or the pixel density of the high resolution image HR is four times the number of pixels or the pixel density of each of the four sub-images Sa, Sb, Sc and Sd.
例えば、被写体2における、図15Aに示す領域A1、B1、C1およびD1のブロックに着目する。これまでの説明からわかるように、図20に示すサブ画像Saの画素Pa1は、上述のブロック全体ではなく、領域A1のみの情報を有している。したがって、サブ画像Saは、領域B1、C1およびD1の情報が欠落した画像であるということができる。
For example, focus on the blocks of the areas A1, B1, C1, and D1 shown in FIG. 15A in the
しかしながら、被写体2において異なる位置に対応する画素情報を有するサブ画像Sb、ScおよびSdを用いることにより、図20に示すように、サブ画像Saにおいて欠落した情報を補完し、ブロック全体の情報を有する高解像度画像HRを形成することが可能である。個々のサブ画像の解像度がイメージセンサ4の固有解像度に等しいことに対し、この例では、イメージセンサ4の固有解像度の4倍の解像度が得られている。高解像度化(超解像)の程度は、イメージセンサの開口率に依存する。この例では、イメージセンサ4の開口率が25%であるため、異なる4方向からの光照射によって最大4倍の高解像度化が達成されている。Nを2以上の整数するとき、イメージセンサ4の開口率が近似的に1/Nに等しければ、最大N倍の高解像度化が可能である。
However, by using the sub-images Sb, Sc, and Sd having the pixel information corresponding to different positions in the
このように、被写体を基準にして複数の異なる照射方向から、順次、平行光を照射して被写体の撮像を行うことにより、被写体から「空間的」にサンプリングされる画素情報を増加させることができる。得られた複数のサブ画像を合成することにより、複数のサブ画像の各々よりも解像度の高い高解像度画像を形成することが可能である。もちろん、照射方向は、図16A〜図19Bを参照して説明した照射方向に限定されない。 In this way, by sequentially irradiating parallel light from a plurality of different irradiation directions with respect to the subject to image the subject, it is possible to increase pixel information that is “spatially” sampled from the subject. .. By combining the obtained plurality of sub-images, it is possible to form a high-resolution image having a higher resolution than each of the plurality of sub-images. Of course, the irradiation direction is not limited to the irradiation direction described with reference to FIGS. 16A to 19B.
なお、上記の例において、図20に示すサブ画像Sa、Sb、ScおよびSdは、被写体2における互いに異なる領域の画素情報を有しており、重なりを有していない。しかしながら、異なるサブ画像間において重なりを有していてもよい。また、上記の例では、被写体2において隣接する2つの領域を通過した光線は、いずれも、同一のフォトダイオードに入射している。しかしながら、照射方向の設定はこの例に限定されない。例えば、図21に示すように、被写体2の隣接する2つの領域を通過した光線が、それぞれ、異なるフォトダイオードに入射するように照射方向が調整されていてもよい。
Note that, in the above example, the sub-images Sa, Sb, Sc, and Sd shown in FIG. 20 have pixel information of different regions in the
<モジュール>
図15A〜図20を参照して説明した原理に基づく高解像度画像の形成において、サブ画像の取得は、被写体2がイメージセンサ4の撮像面に近接して配置された状態で実行される。本開示の実施形態では、被写体2およびイメージセンサ4が一体化された構造を有するモジュールを用いてサブ画像の取得を行う。以下、図面を参照して、モジュールの構成の一例およびモジュールの作製方法の一例を説明する。
<Module>
In the formation of the high-resolution image based on the principle described with reference to FIGS. 15A to 20, the acquisition of the sub-image is executed in the state where the
図22Aは、モジュールの断面構造の一例を模式的に示す。図22Aに示すモジュール10では、封入剤6によって覆われた被写体2がイメージセンサ4の撮像面4A上に配置されている。図示する例では、透明プレート(典型的にはガラス板)8が被写体2上に配置されている。すなわち、図22Aに例示する構成では、被写体2は、イメージセンサ4と透明プレート8との間に挟まれている。モジュール10が透明プレート8を有すると、作業性が向上するので有益である。透明プレート8としては、例えば、一般的なスライドガラスを使用することができる。なお、図中においては各要素が模式的に表されており、各要素における実際の大きさおよび形状は、図中に現された大きさおよび形状と必ずしも一致しない。以下において参照する他の図面においても同様である。
FIG. 22A schematically shows an example of the cross-sectional structure of the module. In the
図22Aに例示する構成において、イメージセンサ4は、パッケージ5に固定されている。図22Bは、図22Aに示すモジュール10をイメージセンサ4側から見たときの外観の一例を示す。図22Aおよび図22Bに示すように、パッケージ5は、透明プレート8とは反対側の面に裏面電極5Bを有する。この裏面電極5Bは、パッケージ5に形成された不図示の配線パターンを介してイメージセンサ4と電気的に接続されている。すなわち、裏面電極5Bを介して、イメージセンサ4の出力を取り出すことができる。本明細書では、パッケージとイメージセンサとが一体化された構造物を「撮像素子」と呼ぶ。
In the configuration illustrated in FIG. 22A, the
図23を参照して、モジュール10の作製方法の一例を説明する。ここでは、被写体2として生物組織の薄片(組織切片)を例示する。生物組織の薄片を被写体2として有するモジュール10は、病理診断に利用され得る。
An example of a method for manufacturing the
まず、図23に示すように、組織切片A02を透明プレート8に載せる。透明プレート8は、光学顕微鏡による試料の観察に用いられるスライドガラスであり得る。以下では、透明プレート8としてスライドガラスを例示する。次に、組織切片A02を透明プレート8ごと染色液Ssに漬けることにより、組織切片A02を染色する。次に、透明プレート8上に封入剤6を付与することにより、組織切片A02を染色することによって得られた被写体2を封入剤6によって覆う。封入剤6は、被写体2を保護する機能を有する。次に、撮像素子7を、イメージセンサ4の撮像面が被写体2に対向するようにして被写体2上に配置する。このようにして、モジュール10が得られる。
First, as shown in FIG. 23, the tissue section A02 is placed on the
モジュール10は、撮像の対象ごとに作製される。例えば病理診断の場面では、1つの検体から複数(例えば5〜20枚)の組織切片が用意される。そのため、同一の検体から得られた組織切片を被写体2として有する複数のモジュール10が作製され得る。これらの複数のモジュール10のそれぞれについて複数のサブ画像の取得を行えば、複数のモジュール10のそれぞれに対応した高解像度画像の形成が可能である。
The
図22Aに示すように、モジュール10は、光学顕微鏡による観察に用いられるプレパラートとは異なり、被写体2の画像を取得するイメージセンサ4を備えている。このようなモジュールを「電子プレパラート」と呼んでもよい。図22Aに示すように被写体2および撮像素子7が一体化された構造を有するモジュール10を用いることにより、被写体2とイメージセンサ4との間の配置を固定できるという利点が得られる。
As shown in FIG. 22A, the
モジュール10を用いて被写体2の画像の取得を実行するとき、透明プレート8を介して被写体2に照明光を照射する。被写体2を透過した照明光がイメージセンサ4に入射する。これにより、被写体2の画像が得られる。光源と被写体との相対的な配置を変えながら、順次、撮像を実行することにより、照射時において角度を変えて複数の異なる画像を取得することができる。例えば、図24Aに示すように、イメージセンサ4の直上に光源310を配置する。そして、コリメートされた光CLをイメージセンサ4の撮像面4Aの法線方向から被写体2に照射した状態で撮像を行えば、図26Cに示すサブ画像Saと同様のサブ画像が得られる。また、図24Bに示すように、モジュール10を傾けた状態でコリメートされた光CLを被写体2に照射して撮像を行えば、図17Cに示すサブ画像Sb(あるいは図18Cに示すサブ画像Sc)と同様のサブ画像が得られる。このように、光源に対するモジュール10の姿勢を変化させながら、順次、撮像を実行することにより、図15A〜図20を参照して説明した原理を適用して高解像度画像を得ることが可能である。
When the image of the subject 2 is acquired using the
<画像取得装置>
図25は、本開示の実施形態による画像取得装置の構成の一例の概略を示す。図25に示す画像取得装置100aは、照明システム30を有する。図25に例示する構成において、照明システム30は、照明光を生成する光源31、モジュール10が着脱自在に装填されるように構成されたステージ32、および、ステージ32の姿勢を変更可能に構成されたステージ駆動機構33を含んでいる。図25は、ステージ32にモジュール10が装填された状態を模式的に示している。ただし、モジュール10における封入剤6および透明プレート8の図示は省略している。モジュール10は、画像取得装置100aに必須の構成要素ではない。
<Image acquisition device>
FIG. 25 shows the outline of an example of the configuration of the image acquisition device according to the embodiment of the present disclosure. The
モジュール10は、ステージ32に接続された状態において、被写体2を透過した照明光が撮像素子7に入射するような配置を有する。照明システム30は、例えばステージ32の姿勢を変化させることにより、被写体2を基準とする照射方向を変化させる。本明細書における「姿勢」の変化は、基準面に対する傾斜の変化、基準方位に対する回転角度の変化、および、基準点に対する位置の変化などを広く含む。被写体2を基準とする複数の異なる照射方向から、順次、光源31によって生成された照明光で被写体2を照射する。照明システム30の構成の詳細および動作の例は後述する。照射方向を変えて被写体2を照射することにより、複数の異なる照射方向に応じて異なる複数の画像(サブ画像)が撮像素子7によって取得される。得られた複数の画像を用いて、高解像度画像の形成が可能である。
The
図25に示す画像取得装置100aは、照射方向決定部40aを有する。この照射方向決定部40aは、撮像素子7による複数のサブ画像の取得時における複数の異なる照射方向を決定する。本開示の実施形態では、サブ画像の取得は、照射方向決定部によって決定された複数の異なる照射方向のもとで実行される。言い換えれば、本開示の実施形態におけるサブ画像は、照射方向決定部によって決定された複数の異なる照射方向に対応した複数の異なる画像である。照射方向決定部40aの構成および動作の具体例は、後述する。
The
次に、図26A〜図27Bを参照して、被写体を基準とする照明光の照射方向を変更する方法の一例を説明する。 Next, with reference to FIGS. 26A to 27B, an example of a method of changing the irradiation direction of the illumination light with respect to the subject will be described.
図26Aおよび図26Bは、画像取得装置100aの例示的な外観を示す。図26Aに例示する構成において、画像取得装置100aは、光源31およびステージ32を含む本体110と、本体110に開閉可能に連結された蓋部120とを有している。蓋部120を閉じることにより、画像取得装置100aの内部に暗室を形成することができる(図26B参照)。
26A and 26B show an exemplary external appearance of the
図示する例では、ステージ32上にモジュール10を保持するためのソケット130が接続されている。ソケット130は、ステージ32に固定されていてもよいし、ステージ32に着脱可能に構成されていてもよい。ここでは、ソケット130がステージ32に着脱可能に構成されている構成を例示する。ソケット130は、例えば、モジュール10が着脱可能に構成された下部基材132と、開口部Apが形成された上部基材134とを含む。図26Aに例示する構成では、ソケット130は、下部基材132と上部基材134との間にモジュール10を挟むことにより、モジュール10を保持する。
In the illustrated example, a
下部基材132は、モジュール10の撮像素子7との電気的接続のための電気的接点を有する電気接続部を有し得る。被写体の画像の取得時、撮像素子7の撮像面が光源31に対向するようにしてモジュール10が下部基材132に載せられる。このとき、電気接続部の電気的接点と撮像素子7の裏面電極5B(図22Aおよび図22B参照)とが接触することにより、モジュール10の撮像素子7と下部基材132の電気接続部とが電気的に接続される。
The
図26Cは、画像取得装置100aのステージ32に対するソケット130の装填方法の一例を示す。図26Cに例示する構成において、ソケット130は、底面から突出する電極136を有している。この電極136は、下部基材132の電気接続部の一部であり得る。また、図26Cに示す例では、画像取得装置100aのステージ32は、ジャック36が設けられた取付部34を有している。図26Cに示すように、例えばモジュール10を保持した状態のソケット130は、ジャック36にソケット130の電極136が挿入されるようにしてステージ32に装填される。これにより、ソケット130に保持されたモジュール10中の撮像素子7と、画像取得装置100aとの間の電気的接続が確立される。ステージ32は、モジュール10を保持するソケット130が装填された状態においてイメージセンサ4の出力を受け取る回路を有し得る。本開示の実施形態では、画像取得装置100aは、ソケット130が有する電気接続部を仲立ちとして被写体2の画像を示す情報(画像信号あるいは画像データ)を取得する。
FIG. 26C shows an example of a method of loading the
なお、複数のモジュール10を用いて複数の被写体の撮像を行う場合、モジュール10と同数のソケット130を用意し、モジュール10を保持した状態のソケット130を換装することによって撮像の対象を変更してもよい。あるいは、ステージ32に1つのソケット130を取り付けた状態のままモジュール10を換装することにより、撮像の対象を変更してもよい。
When imaging a plurality of subjects using a plurality of
図26Cに示すように、ソケット130をステージ32に装填することにより、ソケット130の底面と、取付部34の上面とを密着させ得る。これにより、ステージ32に対するソケット130の配置が固定される。したがって、ステージ32と、ソケット130に保持されたモジュール10との配置をステージ32の姿勢の変化の前後において一定に保つことができる。典型的には、ステージ32にソケット130が装填された状態において、モジュール10の透明プレート8の主面とステージ32とは、ほぼ平行である。
As shown in FIG. 26C, by mounting the
図27Aは、照射方向を変更する方法の一例を示す。図示するように、ソケット130に保持されたモジュール10に、光源31から出射された照明光CLが照射される。照明光CLは、ソケット130に設けられた開口部Apを介して、モジュール10の被写体に入射する。被写体を透過した光が、モジュール10の撮像素子7の撮像面に入射する。
FIG. 27A shows an example of a method for changing the irradiation direction. As illustrated, the
光源31から出射される光は、典型的には、コリメートされた光である。ただし、被写体に入射する光が実質的に平行光であるとみなせる場合には、光源31から出射される光はコリメートされた光でなくてもよい。
The light emitted from the
光源31は、例えばLEDチップを含む。光源31は、各々が異なる波長帯域にピークを有する複数のLEDチップを含んでいてもよい。例えば、光源31が、青色の光を出射するLEDチップ、赤色の光を出射するLEDチップ、および緑色の光を出射するLEDチップを含んでいてもよい。複数の発光素子を近接(例えば100μm程度)して配置した場合には、これらを点光源とみなし得る。
The
互いに異なる色の光を出射する複数の発光素子を使用し、例えば、異なる色の光を照射方向ごとにタイムシーケンシャルに照射することにより、それぞれの色についての複数のサブ画像を取得することができる。例えば、青色サブ画像のセット、赤色サブ画像のセット、および緑色サブ画像のセットを取得してもよい。取得されたサブ画像のセットを用いれば、カラーの高解像度画像を形成することができる。例えば病理診断の場面では、カラーの高解像度画像を利用することにより、病変の有無などに関するより多くの有益な情報を得ることができる。光源31として白色LEDチップを用い、かつ、光路上にカラーフィルタを配置することによって、互いに異なる色の照明光をタイムシーケンシャルに得てもよい。また、イメージセンサ4としてカラー撮像用のイメージセンサを用いてもよい。ただし、イメージセンサ4の光電変換部に入射する光量の低減を抑制する観点からは、カラーフィルタを配置しない構成の方が有利である。
It is possible to obtain a plurality of sub-images for each color by using a plurality of light emitting elements that emit light of different colors and, for example, by sequentially irradiating light of different colors in each irradiation direction. .. For example, a set of blue sub-images, a set of red sub-images, and a set of green sub-images may be acquired. The acquired set of sub-images can be used to form a high resolution color image. For example, in a pathological diagnosis scene, more useful information regarding the presence or absence of a lesion can be obtained by using a high-resolution color image. By using a white LED chip as the
光源31は、LEDに限定されず、白熱電球、レーザ素子、ファイバーレーザ、放電管などであってもよい。光源31から出射される光は、可視光に限定されず、紫外線、赤外線などであってもよい。光源31が有する発光素子の数および配置も任意に設定可能である。
The
図25および図27Aに示すように、画像取得装置100aは、ステージ駆動機構33を有する。ステージ駆動機構33は、ゴニオ機構、回転機構などを含み、本体110に対するステージ32の傾斜および/またはステージ32の中心を通る軸に関する回転角を変化させる。ステージ駆動機構33が、ステージ32を基準面(典型的には水平面)内において平行移動させることが可能なスライド機構を含んでいてもよい。
As shown in FIGS. 25 and 27A, the
ステージ駆動機構33を動作させることにより、ステージ32の姿勢を変化させることができる。ここでは、モジュール10を保持した状態のソケット130がステージ32に取り付けられているので、ステージ32の姿勢を変化させることにより、モジュール10の姿勢を変化させることができる。例えば、ステージ32が基準面に対して傾斜していない時における照明光の入射方向がイメージセンサの撮像面の法線方向であるとする。ここでは、基準面に対するステージ32の傾斜と基準面に対するモジュール10の傾斜(透明プレート8の傾斜といってもよい。)との間の関係(例えば、平行)が、ステージ32の姿勢の変化の前後において一定に保たれている。そのため、図27Bに示すように、基準面に対してステージ32を角度θだけ傾斜させると、被写体に入射する光線の方向も角度θだけ傾斜する。なお、図27B中、破線Nは、イメージセンサの撮像面の法線を示している。
By operating the
このように、ステージ32とともにモジュール10の姿勢を変化させることにより、被写体2を基準として複数の異なる照射方向から、順次、照明光を被写体に照射することが可能である。したがって、被写体2を基準とする複数の異なる照射方向に応じた複数の画像をモジュール10の撮像素子7によって取得することができる。被写体2を基準とする照射方向は、例えば、イメージセンサの撮像面の法線Nと被写体2への入射光線とがなす角(図27Bに示す天頂角θ)、および撮像面上に設定した基準方位と入射光線の撮像面への射影とがなす角(方位角)の組によって表すことができる。
In this way, by changing the attitude of the
なお、光源31を画像取得装置100a内において移動させたり、互いに異なる場所に配置された複数の光源を順次に点灯させたりすることによっても、複数の異なる照射方向から被写体2を照射することが可能である。例えば、光源31と被写体2とを結ぶ方向に沿って光源31を移動させることにより、照射方向を変更してもよい。ステージ32の姿勢の変化と光源31の移動とを組み合わせることによって照射方向を変化させてもよい。
It is possible to illuminate the subject 2 from a plurality of different irradiation directions by moving the
<モジュールに用いられるイメージセンサ>
なお、本開示の実施形態において、イメージセンサ4は、CCDイメージセンサに限定されず、CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)イメージセンサ、また
は、その他のイメージセンサ(一例として、後述する光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサ)であってもよい。CCDイメージセンサおよびCMOSイメージセンサは、表面照射型または裏面照射型のいずれであってもよい。以下、イメージセンサの素子構造と、イメージセンサのフォトダイオードに入射する光の関係を説明する。
<Image sensor used in module>
In the embodiment of the present disclosure, the
図28は、CCDイメージセンサの断面構造と、被写体の相対的な透過率Tdの分布の例とを示す。図28に示すように、CCDイメージセンサは、概略的には、基板80と、基板80上の絶縁層82と、絶縁層82内に配置された配線84とを有している。基板80には、複数のフォトダイオード88が形成されている。配線84上には、遮光層(図28において不図示)が形成される。ここでは、トランジスタなどの図示は省略している。以下の図面においてもトランジスタなどの図示を省略する。なお、概略的には、表面照射型CMOSイメージセンサにおけるフォトダイオード近傍の断面構造は、CCDイメージセンサにおけるフォトダイオード近傍の断面構造とほぼ同様である。そのため、ここでは、表面照射型CMOSイメージセンサの断面構造の図示および説明を省略する。
FIG. 28 shows a sectional structure of the CCD image sensor and an example of the distribution of the relative transmittance Td of the subject. As shown in FIG. 28, the CCD image sensor roughly includes a
図28に示すように、照明光が撮像面の法線方向から入射する場合、被写体のうち、フォトダイオード88の直上にある領域R1を透過した照射光は、フォトダイオード88に入射する。一方、被写体のうち、配線84上の遮光層の直上にある領域R2を透過した照射光は、イメージセンサの遮光領域(遮光膜が形成された領域)に入射する。したがって、撮像面の法線方向から照射した場合には、被写体のうち、フォトダイオード88の直上にある領域R1を示す画像が得られる。
As shown in FIG. 28, when the illumination light is incident from the direction normal to the imaging surface, the irradiation light that has passed through the region R1 of the subject immediately above the
遮光膜の直上にある領域を示す画像を取得するためには、領域R2を透過した光がフォトダイオード88に入射するように、撮像面の法線方向に対して傾いた方向から照射を行えばよい。このとき、照射方向によっては、領域R2を透過した光のうちの一部が、配線84によって遮られることがある。図示する例では、ハッチングによって示す部分を通る光線はフォトダイオード88には届かない。そのため、斜め入射においては、画素値が幾分低下することがある。しかしながら、透過光の全てが遮られるわけではないので、このときに得られたサブ画像を用いた高解像度画像の形成は可能である。
In order to obtain an image showing a region immediately above the light-shielding film, irradiation is performed from a direction inclined with respect to the normal line direction of the imaging surface so that the light transmitted through the region R2 enters the
図29Aおよび図29Bは、裏面照射型CMOSイメージセンサの断面構造と、被写体の相対的な透過率Tdの分布の例とを示す。図29Aに示すように、裏面照射型CMOSイメージセンサでは、斜め入射の場合であっても透過光が配線84によって遮られることがない。ただし、被写体のうち、撮像を行いたい領域とは異なる他の領域を透過した光(図29Aおよび後述する図29B中、太い矢印BAで模式的に示す光)が基板80に入射することによってノイズが発生し、サブ画像の品質が劣化するおそれがある。このような劣化は、図29Bに示すように、基板においてフォトダイオードが形成された領域以外の領域上に遮光層90を形成することにより低減することが可能である。
29A and 29B show a cross-sectional structure of a backside illumination CMOS image sensor and an example of a distribution of relative transmittance Td of a subject. As shown in FIG. 29A, in the back-illuminated CMOS image sensor, the transmitted light is not blocked by the
図30は、有機材料または無機材料で形成した光電変換膜を備えるイメージセンサ(以下、「光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサ」と呼ぶ。)の断面構造と、被写体の相対的な透過率Tdの分布の例とを示す。 FIG. 30 is a cross-sectional structure of an image sensor including a photoelectric conversion film formed of an organic material or an inorganic material (hereinafter, referred to as “photoelectric conversion film stacked image sensor”) and a distribution of relative transmittance Td of a subject. And an example of.
図30に示すように、光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサは、概略的には、基板80と、複数の画素電極が設けられた絶縁層82と、絶縁層82上の光電変換膜94と、光電変換膜94上の透明電極96とを有している。図示するように、光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、半導体基板に形成されるフォトダイオードの代わりに、光電変換を行う光電変換膜94が基板80(例えば半導体基板)上に形成されている。光電変換膜94および透明電極96は、典型的には、撮像面の全体にわたって形成される。ここでは、光電変換膜94を保護する保護膜の図示を省略している。
As shown in FIG. 30, the photoelectric conversion film stacked image sensor is roughly composed of a
光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、光電変換膜94における入射光の光電変換によって発生した電荷(電子または正孔)が画素電極92によって集められる。これにより、光電変換膜94に入射した光の量を示す値が得られる。したがって、光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、撮像面において、1つの画素電極92を含む単位領域が1つの画素に相当するといえる。光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、裏面照射型CMOSイメージセンサと同様に斜め入射の場合であっても透過光が配線によって遮られることがない。
In the photoelectric conversion film stack type image sensor, charges (electrons or holes) generated by photoelectric conversion of incident light in the
図15A〜図20を参照して説明したように、高解像度画像の形成においては、被写体の異なる部分から構成される像を示す複数のサブ画像が用いられる。ところが、典型的な光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、撮像面の全体にわたって光電変換膜94が形成されているので、例えば垂直入射の場合であっても、被写体の所望の領域以外の領域を透過した光によっても光電変換膜94において光電変換が生じ得る。このときに発生した余分な電子または正孔が画素電極92に引き込まれると、適切なサブ画像が得られないおそれがある。したがって、画素電極92と透明電極96とが重なる領域(図30において網掛けされた領域)において発生した電荷を画素電極92に選択的に引き込むことが有益である。
As described with reference to FIGS. 15A to 20, in forming a high-resolution image, a plurality of sub-images showing images composed of different parts of the subject are used. However, in a typical photoelectric conversion film laminated type image sensor, the
図30に例示する構成では、画素電極92のそれぞれと対応して、画素内にダミー電極98が設けられている。被写体の像の取得時、画素電極92とダミー電極98との間には、適切な電位差が与えられる。これにより、画素電極92と透明電極96とが重なる領域以外の領域で発生した電荷をダミー電極98に引き込み、画素電極92と透明電極96とが重なる領域で発生した電荷を選択的に画素電極92に引き込むことができる。なお、透明電極96または光電変換膜94のパターニングによっても、同様の効果を得ることが可能である。このような構成においては、画素の面積S1に対する画素電極92の面積S3の比率(S3/S1)が、「開口率」に相当するということができる。
In the configuration illustrated in FIG. 30,
既に説明したように、Nを2以上の整数とするとき、イメージセンサ4の開口率が近似的に1/Nに等しければ、最大N倍の高解像度化が可能になる。言い換えれば、開口率が小さい方が高解像度化には有利である。光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサでは、画素電極92の面積S3を調整することによって、開口率に相当する比率(S3/S1)を調整することが可能である。この比率(S3/S1)は、例えば10%〜50%の範囲に設定される。比率(S3/S1)が上記の範囲内にある光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサは、超解像に用いられ得る。
As described above, when N is an integer of 2 or more, if the aperture ratio of the
なお、図28および図29Bからわかるように、CCDイメージセンサおよび表面照射型CMOSイメージセンサにおいて被写体と対向する表面は平坦ではない。例えば、CCDイメージセンサでは、その表面に段差が存在する。また、裏面照射型CMOSイメージセンサでは、高解像度画像を形成するためのサブ画像を取得するには、パターニングされた遮光層を撮像面上に設けることが必要であり、被写体と対向する表面は平坦ではない。 As can be seen from FIGS. 28 and 29B, the surface of the CCD image sensor and the front-illuminated CMOS image sensor facing the subject is not flat. For example, a CCD image sensor has a step on its surface. Further, in the back-illuminated CMOS image sensor, in order to obtain a sub-image for forming a high-resolution image, a patterned light-shielding layer needs to be provided on the imaging surface, and the surface facing the subject is flat. is not.
これに対し、光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサの撮像面は、図30からわかるように、ほぼ平坦な面である。したがって、撮像面上に被写体を配置した場合であっても、撮像面の形状に起因する被写体の変形がほとんど生じない。言い換えれば、光電変換膜積層型イメージセンサを用いてサブ画像を取得することによって、被写体のより詳細な構造を観察し得る。 On the other hand, the image pickup surface of the photoelectric conversion film stack type image sensor is a substantially flat surface as can be seen from FIG. Therefore, even when the subject is arranged on the image pickup surface, deformation of the subject due to the shape of the image pickup surface hardly occurs. In other words, by acquiring the sub-image using the photoelectric conversion film stack type image sensor, a more detailed structure of the subject can be observed.
以上、一つまたは複数の態様に係る画像出力装置について、いくつかの実施の形態に基づいて説明したが、本発明は、これらの実施の形態に限定されるものではない。本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない限り、当業者が思いつく各種変形を本実施の形態に施したものや、異なる実施の形態における構成要素を組み合わせて構築される形態も、本開示に含まれてもよい。 Although the image output device according to one or more aspects has been described above based on some embodiments, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. Without departing from the spirit of the present invention, the present disclosure may include various modifications that can be conceived by those skilled in the art to the present embodiment, and embodiments configured by combining components in different embodiments. ..
なお、上記各実施の形態において、各構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで構成されるか、各構成要素に適したソフトウェアプログラムを実行することによって実現されてもよい。各構成要素は、CPUまたはプロセッサなどのプログラム実行部が、ハードディスクまたは半導体メモリなどの記録媒体に記録されたソフトウェアプログラム(すなわち命令)を読み出して実行することによって実現されてもよい。ここで、上記各実施の形態の画像出力装置などを実現するソフトウェアは、図3、図4、図7、図9または図11のフローチャートにおける各ステップをコンピュータに実行させるプログラムである。なお、プログラム実行部は、1つのプロセッサから構成されていても、複数のプロセッサから構成されていてもよい。 In addition, in each of the above-described embodiments, each component may be configured by dedicated hardware, or may be realized by executing a software program suitable for each component. Each component may be realized by a program execution unit such as a CPU or a processor reading and executing a software program (that is, an instruction) recorded in a recording medium such as a hard disk or a semiconductor memory. Here, the software that realizes the image output device of each of the above-described embodiments is a program that causes a computer to execute each step in the flowcharts of FIGS. 3, 4, 7, 9, or 11. The program execution unit may be composed of one processor or plural processors.
また、本開示において、ユニット、デバイスの全部又は一部、又は図1、図5、図6、図8、図10、および図12〜図14に示されるブロック図の機能ブロックの全部又は一部は、半導体装置、半導体集積回路(IC)、又はLSI(large scale integration)
を含む一つ又は一つ以上の電子回路によって実行されてもよい。LSI又はICは、一つのチップに集積されてもよいし、複数のチップを組み合わせて構成されてもよい。例えば、記憶素子以外の機能ブロックは、一つのチップに集積されてもよい。ここでは、LSIやICと呼んでいるが、集積の度合いによって呼び方が変わり、システムLSI、VLSI(very large scale integration)、若しくはULSI(ultra large scale integration) と呼ばれるかもしれない。 LSIの製造後にプログラムされる、Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)、又はLSI内部の接合関係の再構成又はLSI内部の回路区画のセ
ットアップができるreconfigurable logic deviceも同じ目的で使うことができる。
Further, in the present disclosure, all or part of a unit or device, or all or part of the functional blocks of the block diagrams illustrated in FIGS. 1, 5, 6, 8, 10, and 12 to 14. Is a semiconductor device, a semiconductor integrated circuit (IC), or an LSI (large scale integration)
May be implemented by one or more electronic circuits including The LSI or IC may be integrated on one chip, or may be configured by combining a plurality of chips. For example, the functional blocks other than the memory element may be integrated in one chip. Although referred to as an LSI or an IC here, they may be called system LSI, VLSI (very large scale integration), or ULSI (ultra large scale integration) depending on the degree of integration. A Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) that is programmed after the manufacture of the LSI, or a reconfigurable logic device that can reconfigure the bonding relation inside the LSI or set up circuit sections inside the LSI can be used for the same purpose.
さらに、ユニット、装置、又は装置の一部の、全部又は一部の機能又は操作は、ソフトウエア処理によって実行することが可能である。この場合、ソフトウエアは一つ又は一つ以上のROM、光学ディスク、ハードディスクドライブ、などの非一時的記録媒体に記録され、ソフトウエアが、処理装置(processor)によって実行された場合に、ソフトウエ
アは、ソフトウエア内の特定の機能を、処理装置(processor)と周辺のデバイスに実行させる。システム又は装置は、ソフトウエアが記録されている一つ又は一つ以上の非一時的記録媒体、処理装置(processor)、及び必要とされるハードウエアデバイス、例えば
インターフェース、を備えていても良い。
Furthermore, all or some of the functions or operations of a unit, a device, or a part of a device can be performed by software processing. In this case, the software may be recorded on a non-transitory recording medium such as one or more ROMs, optical disks, hard disk drives, etc., and when the software is executed by a processor, the software Causes a processor and peripheral devices to perform specific functions within the software. The system or apparatus may include one or more non-transitory recording media on which software is recorded, a processor, and required hardware devices, such as interfaces.
本開示は、高解像度画像の取り扱いの負担を軽減することができるという効果を奏し、例えば、病理検体の高解像度画像を取り扱う画像出力装置などに適用することができる。 The present disclosure has the effect of reducing the burden of handling high-resolution images, and can be applied to, for example, an image output device that handles high-resolution images of pathological samples.
100S,100Sa,200S,200Sa,200Sb 画像処理システム
1001,1001a,2001,2001a 画像出力装置
1100,1100a,1100b 画像送信装置
1101 画像取得部
1102 高解像度画像取得部
1103 第二出力部
1200,1200a,1200b 画像受信装置
1201 拡大受付部
1202 判定部
1203 表示用出力部
1204,1204a 送信部
1205 第一出力部
1206 評価値蓄積部
1500 デジタル顕微鏡
1501 表示装置
1502,1503 記録媒体
100S, 100Sa, 200S, 200Sa, 200Sb
Claims (11)
少なくとも1つのプロセッサと、
実行可能な命令を保持する非一時的な記録媒体とを備え、
前記命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像を前記表示装置に表示し、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信せず、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数が多いほど、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つのプロセッサに実行させる
画像出力装置。 An image output device connected to a display device and connected to an external device via a communication line,
At least one processor,
And a non-transitory recording medium holding executable instructions,
The command is
Acquire the first resolution image, which is the image of the subject obtained based on the shooting with a digital microscope,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
Displaying the first resolution image on the display device,
Accepting the magnification for said first resolution image displayed on the display device,
An evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether it is higher than a predetermined value,
If the evaluation value is when it is determined to be higher than the predetermined value, it transmits the second resolution image to the external device, wherein the evaluation value is determined to not higher than the predetermined value Does not send the second resolution image to the external device,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) In the reception of the enlargement ratio, the larger the number of times the high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than the threshold, is received, (b) the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. The longer the time is, or (c) the larger the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
An image output device that causes the at least one processor to perform the above.
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第一解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つのプロセッサに実行させる
請求項1に記載の画像出力装置。 The instructions further include
When it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value, the first resolution image is transmitted to the external device,
The image output apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the image output apparatus causes the at least one processor to execute the following.
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を記録媒体に出力して保存し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記記録媒体に出力しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つのプロセッサに実行させる
請求項1または2に記載の画像出力装置。 The instructions further include
When it is determined that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is output to a recording medium and saved, and it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. In that case, the second resolution image is not output to the recording medium,
The image output apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the image output apparatus causes the at least one processor to execute the following.
前記画像送信装置は、
少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な送信用命令を保持する非一時的な送信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記送信用命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得して前記画像受信装置に送信し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
前記画像受信装置から通知される評価値関連情報によって導出される評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像受信装置は、表示装置に接続された装置であって、
少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な受信用命令を保持する非一時的な受信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記受信用命令は、
前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像を取得して前記表示装置に表示し、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき、前記表示装置に表示されている前記第一解像度画像を拡大し、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく前記評価値関連情報を前記画像送信装置に送信する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記評価値関連情報は、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積を示し、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記評価値関連情報が前記回数を示す場合には、前記回数が多いほど、(b)前記評価値関連情報が前記時間を示す場合には、前記時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記評価値関連情報が前記面積を示す場合には、前記面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
画像出力装置。 An image output device having an image transmitting device and an image receiving device connected to the image transmitting device via a communication line,
The image transmission device,
At least one transmitting processor,
And a non-transitory transmission recording medium that holds an executable transmission command,
The transmission instruction is
Acquiring a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and transmitting it to the image receiving device,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
The evaluation value derived by the evaluation value related information notified from the image receiving device, it is determined whether or not higher than a predetermined value,
When it is determined that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. Does not transmit the second resolution image to the image receiving device,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to:
The image receiving device is a device connected to a display device,
At least one receiving processor;
A non-transitory recording medium for holding an executable receiving command,
The receiving instruction is
Wherein the image transmitting apparatus to obtain the first-resolution image is displayed on the display device,
Accepting a magnification rate for the first resolution image displayed on the display device,
Enlarging the first resolution image displayed on the display device based on the accepted enlargement ratio,
Transmitting the evaluation value related information based on the received enlargement ratio to the image transmitting device,
And causing the at least one receiving processor to:
The evaluation value related information is
(A) The number of times a high magnification rate, which is a magnification rate higher than a threshold value, is accepted in the acceptance of the magnification rate, and (b) the time during which the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high magnification rate. Or (c) shows the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification ratio,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) When the evaluation value related information indicates the number of times, the greater the number of times, (b) When the evaluation value related information indicates the time, the longer the time, or (c ) When the evaluation value related information indicates the area, the higher the area, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
Image output device.
前記画像送信装置は、
少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な送信用命令を保持する非一時的な送信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記送信用命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得して前記画像受信装置に送信し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像受信装置は、表示装置に接続された装置であって、
少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な受信用命令を保持する非一時的な受信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記受信用命令は、
前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像を取得して前記表示装置に表示し、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき、前記表示装置に表示されている前記第一解像度画像を拡大し、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、判定結果を前記画像送信装置に通知し、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数が多いほど、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像送信装置の前記送信用命令は、さらに、
前記画像受信装置から通知される前記判定結果が、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いことを示す場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないことを示す場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させる
画像出力装置。 An image output device having an image transmitting device and an image receiving device connected to the image transmitting device via a communication line,
The image transmission device,
At least one transmitting processor,
And a non-transitory transmission recording medium that holds an executable transmission command,
The transmission instruction is
Acquiring a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and transmitting it to the image receiving device,
Acquiring a second resolution image, which is an image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and which is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to:
The image receiving device is a device connected to a display device,
At least one receiving processor;
A non-transitory recording medium for holding an executable receiving command,
The receiving instruction is
Wherein the image transmitting apparatus to obtain the first-resolution image is displayed on the display device,
Accepting the magnification for said first resolution image displayed on the display device,
Enlarging the first resolution image displayed on the display device based on the accepted enlargement ratio,
An evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether or not it is higher than a predetermined value, and the determination result is notified to the image transmission device,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) In the reception of the enlargement ratio, the larger the number of times the high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than the threshold, is received, (b) the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. The longer the time is, or (c) the larger the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
And causing the at least one receiving processor to:
The transmission instruction of the image transmission device further includes
When the determination result notified from the image receiving device indicates that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and the evaluation value is If it indicates that the second resolution image is not higher than a predetermined value, the second resolution image is not transmitted to the image receiving device,
An image output device that causes the at least one transmission processor to perform the above.
前記評価値の判定において、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を記録媒体に出力して保存する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させる
請求項4または5に記載の画像出力装置。 The transmission instruction further comprises:
In the determination of the evaluation value, if it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is output and stored on a recording medium,
The image output apparatus according to claim 4 or 5 to be executed by the at least one sending processor that.
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像を前記表示装置に表示し、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信せず、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数が多いほど、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
画像出力方法。 An image output method performed by an image output device connected to a display device and connected to an external device via a communication line,
Acquire the first resolution image, which is the image of the subject obtained based on the shooting with a digital microscope,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
Displaying the first resolution image on the display device,
Accepting the magnification for said first resolution image displayed on the display device,
An evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether it is higher than a predetermined value,
If the evaluation value is when it is determined to be higher than the predetermined value, it transmits the second resolution image to the external device, wherein the evaluation value is determined to not higher than the predetermined value Does not send the second resolution image to the external device ,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) In the reception of the enlargement ratio, the larger the number of times the high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than the threshold, is received, (b) the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. The longer the time is, or (c) the larger the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
Image output method.
前記プログラムは、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
前記第一解像度画像を前記表示装置に表示し、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記外部装置に送信せず、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数が多いほど、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
ことを、コンピュータに実行させる記録媒体。 A computer-readable non-transitory recording medium in which a program for a computer of an image output device connected to a display device and connected to an external device via a communication line is recorded.
The program is
Acquire the first resolution image, which is the image of the subject obtained based on the shooting with a digital microscope,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
Displaying the first resolution image on the display device,
Accepting the magnification for said first resolution image displayed on the display device,
An evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether it is higher than a predetermined value,
If the evaluation value is when it is determined to be higher than the predetermined value, it transmits the second resolution image to the external device, wherein the evaluation value is determined to not higher than the predetermined value Does not send the second resolution image to the external device ,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) In the reception of the enlargement ratio, the larger the number of times the high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than the threshold, is received, (b) the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. The longer the time is, or (c) the larger the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
A recording medium that causes a computer to execute the above.
前記画像送信装置は、
少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な送信用命令を保持する非一時的な送信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記送信用命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得して前記画像受信装置に送信し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
画像受信装置から通知される評価値関連情報によって導出される評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像受信装置は、
少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な受信用命令を保持する非一時的な受信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記受信用命令は、
前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像を取得して前記表示装置に表示させ、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき、前記表示装置に表示されている前記第一解像度画像を拡大し、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく前記評価値関連情報を前記画像送信装置に送信する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記評価値関連情報は、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積を示し、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記評価値関連情報が前記回数を示す場合には、前記回数が多いほど、(b)前記評価値関連情報が前記時間を示す場合には、前記時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記評価値関連情報が前記面積を示す場合には、前記面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
画像受信装置。 An image receiving device connected to a display device and connected to an image transmitting device via a communication line,
The image transmission device,
At least one transmitting processor,
And a non-transitory transmission recording medium that holds an executable transmission command,
The transmission instruction is
Acquiring a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and transmitting the image to the image receiving device,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
The evaluation value derived from the evaluation value related information notified from the image receiving device determines whether or not it is higher than a predetermined value,
When it is determined that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. Does not transmit the second resolution image to the image receiving device,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to:
The image receiving device,
At least one receiving processor;
A non-transitory recording medium for holding an executable receiving command,
The receiving instruction is
Wherein the image transmitting apparatus to obtain the first-resolution image is displayed on the display device,
Accepting a magnification rate for the first resolution image displayed on the display device,
Enlarging the first resolution image displayed on the display device based on the accepted enlargement ratio,
Transmitting the evaluation value related information based on the received enlargement ratio to the image transmitting device,
And causing the at least one receiving processor to :
The evaluation value related information is
(A) In the acceptance of the enlargement ratio, the number of times a high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than a threshold, is received, and (b) the time during which the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. Or (c) indicates the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification ratio,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) When the evaluation value related information indicates the number of times, the greater the number of times, (b) When the evaluation value related information indicates the time, the longer the time, or (c ) When the evaluation value related information indicates the area, the larger the area is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
Image receiving device.
前記画像送信装置は、
少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な送信用命令を保持する非一時的な送信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記送信用命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を取得して前記画像受信装置に送信し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像受信装置は、
少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な受信用命令を保持する非一時的な受信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記受信用命令は、
前記画像送信装置から前記第一解像度画像を取得して前記表示装置に表示させ、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき、前記表示装置に表示されている前記第一解像度画像を拡大し、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、判定結果を前記画像送信装置に通知し、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数が多いほど、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像送信装置の前記送信用命令は、さらに、
前記画像受信装置から通知される前記判定結果が、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いことを示す場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないことを示す場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させる。
画像受信装置。 An image receiving device connected to a display device and connected to an image transmitting device via a communication line,
The image transmission device,
At least one transmitting processor,
And a non-transitory transmission recording medium that holds an executable transmission command,
The transmission instruction is
Acquiring a first resolution image, which is an image of a subject obtained based on photographing by a digital microscope, and transmitting the image to the image receiving device,
Acquiring a second resolution image, which is an image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, which is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to:
The image receiving device,
At least one receiving processor;
A non-transitory recording medium for holding an executable receiving command,
The receiving instruction is
Wherein the image transmitting apparatus to obtain the first-resolution image is displayed on the display device,
Accepting the magnification for said first resolution image displayed on the display device,
Enlarging the first resolution image displayed on the display device based on the accepted enlargement ratio,
An evaluation value based on the received enlargement ratio is determined whether or not it is higher than a predetermined value, and the determination result is notified to the image transmission device ,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) In the reception of the enlargement ratio, the larger the number of times the high enlargement ratio, which is an enlargement ratio higher than the threshold, is received, (b) the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high enlargement ratio. The longer the time is, or (c) the larger the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
And causing the at least one receiving processor to:
The transmission instruction of the image transmission device further includes
When the determination result notified from the image receiving device indicates that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and the evaluation value is If the second resolution image is not higher than a predetermined value, the second resolution image is not transmitted to the image receiving device,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to perform the above.
Image receiving device.
前記画像受信装置は、
少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な受信用命令を保持する非一時的な受信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記受信用命令は、
デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる被写体の画像である第一解像度画像を、前記画像送信装置から取得して前記表示装置に表示させ、
前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像に対する拡大率を受け付け、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づき、前記表示装置に表示されている前記第一解像度画像を拡大し、
受け付けられた前記拡大率に基づく評価値関連情報を前記画像送信装置に送信する、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの受信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記画像送信装置は、
少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサと、
実行可能な送信用命令を保持する非一時的な送信用記録媒体とを備え、
前記送信用命令は、
前記第一解像度画像を取得して前記画像受信装置に送信し、
前記第一解像度画像よりも高い解像度の画像であって、前記デジタル顕微鏡による撮影に基づいて得られる前記被写体の画像である第二解像度画像を取得し、
前記画像受信装置から通知される前記評価値関連情報によって導出される評価値が、所定の値よりも高いか否かを判定し、
前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高いと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信し、前記評価値が前記所定の値よりも高くないと判定される場合には、前記第二解像度画像を前記画像受信装置に送信しない、
ことを前記少なくとも1つの送信用プロセッサに実行させ、
前記評価値関連情報は、
(a)前記拡大率の受け付けにおいて、閾値よりも高い拡大率である高拡大率が受け付けられた回数、(b)前記第一解像度画像が前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示されている時間、または、(c)前記高拡大率で前記表示装置に表示される前記第一解像度画像の面積を示し、
前記評価値の判定では、
(a)前記評価値関連情報が前記回数を示す場合には、前記回数が多いほど、(b)前記評価値関連情報が前記時間を示す場合には、前記時間が長いほど、または、(c)前記評価値関連情報が前記面積を示す場合には、前記面積が広いほど、高い前記評価値を導出する、
画像送信装置。 An image receiving device connected to a display device, and an image transmitting device connected via a communication line,
The image receiving device,
At least one receiving processor;
A non-transitory recording medium for holding an executable receiving command,
The receiving instruction is
The first resolution image of a subject obtained based on the photographing by a digital microscope, is displayed on the display device is obtained from the image transmitting apparatus,
Accepting a magnification rate for the first resolution image displayed on the display device,
Enlarging the first resolution image displayed on the display device based on the accepted enlargement ratio,
Transmitting evaluation value related information based on the received enlargement ratio to the image transmitting device,
And causing the at least one receiving processor to:
The image transmission device,
At least one transmitting processor,
And a non-transitory transmission recording medium that holds an executable transmission command,
The transmission instruction is
Acquiring the first resolution image and transmitting it to the image receiving device,
An image having a higher resolution than the first resolution image, and obtaining a second resolution image that is an image of the subject obtained based on photographing by the digital microscope,
Evaluation value derived by the evaluation value related information notified from the image receiving device, determines whether or not higher than a predetermined value,
When it is determined that the evaluation value is higher than the predetermined value, the second resolution image is transmitted to the image receiving device, and it is determined that the evaluation value is not higher than the predetermined value. Does not transmit the second resolution image to the image receiving device,
And causing the at least one transmitting processor to :
The evaluation value related information is
(A) The number of times a high magnification rate, which is a magnification rate higher than a threshold value, is accepted in the acceptance of the magnification rate, and (b) the time during which the first resolution image is displayed on the display device at the high magnification rate. Or (c) indicates the area of the first resolution image displayed on the display device at the high magnification ratio,
In the judgment of the evaluation value,
(A) When the evaluation value related information indicates the number of times, the greater the number of times, (b) When the evaluation value related information indicates the time, the longer the time, or (c ) When the evaluation value related information indicates the area, the larger the area is, the higher the evaluation value is derived.
Image transmission device.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/218,204 US10048485B2 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2016-07-25 | Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and non-transitory recording medium |
| CN201610644318.2A CN106483338A (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2016-08-09 | Image output device, picture transmitter device, image received device, image output method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015169822 | 2015-08-28 | ||
| JP2015169822 | 2015-08-28 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017046340A JP2017046340A (en) | 2017-03-02 |
| JP6719104B2 true JP6719104B2 (en) | 2020-07-08 |
Family
ID=58212293
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016049515A Expired - Fee Related JP6719104B2 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2016-03-14 | Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and recording medium |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6719104B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106483338A (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020170369A1 (en) * | 2019-02-20 | 2020-08-27 | オリンパス株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing system, information processing method and program |
| CN114268742B (en) * | 2022-03-01 | 2022-05-24 | 北京瞭望神州科技有限公司 | Sky eye chip processing apparatus |
Family Cites Families (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62137037A (en) * | 1985-12-11 | 1987-06-19 | 株式会社東芝 | X-ray photographing apparatus |
| US4777525A (en) * | 1985-12-23 | 1988-10-11 | Preston Jr Kendall | Apparatus and method for a multi-resolution electro-optical imaging, display and storage/retrieval system |
| JP3526880B2 (en) * | 1990-10-30 | 2004-05-17 | オムニプラナー,インコーポレーテッド | Multi-resolution machine readable symbol |
| JPH0730899A (en) * | 1993-07-12 | 1995-01-31 | Kyocera Corp | Hierarchical motion vector detection system |
| JPH0918764A (en) * | 1995-06-28 | 1997-01-17 | Canon Inc | Monitor system and image processing unit used for it |
| JPH1028222A (en) * | 1996-07-11 | 1998-01-27 | Canon Inc | Image processor and method thereof |
| JP3877474B2 (en) * | 1999-08-03 | 2007-02-07 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Electronic camera |
| JP2001128062A (en) * | 1999-10-29 | 2001-05-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Device and method for forming image |
| JP3882585B2 (en) * | 2001-11-07 | 2007-02-21 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and program |
| JP3882651B2 (en) * | 2002-03-20 | 2007-02-21 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and program |
| JP4563755B2 (en) * | 2003-09-16 | 2010-10-13 | シスメックス株式会社 | Specimen image display method, specimen image display program, recording medium recording the program, and specimen image display terminal device |
| FR2861525B1 (en) * | 2003-10-24 | 2006-04-28 | Winlight System Finance | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CAPTURING A LARGE FIELD IMAGE AND A REGION OF INTEREST THEREOF |
| JP2006191159A (en) * | 2004-12-28 | 2006-07-20 | Canon Inc | Method and apparatus for image processing |
| US20060159325A1 (en) * | 2005-01-18 | 2006-07-20 | Trestle Corporation | System and method for review in studies including toxicity and risk assessment studies |
| US8373652B2 (en) * | 2005-04-06 | 2013-02-12 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Image display apparatus and image display method |
| EP1969452A2 (en) * | 2005-12-30 | 2008-09-17 | Apple Inc. | Portable electronic device with multi-touch input |
| JP2007189503A (en) * | 2006-01-13 | 2007-07-26 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Terminal device and program |
| JP4874904B2 (en) * | 2007-09-13 | 2012-02-15 | 株式会社東芝 | Image processing apparatus and method |
| JP2009194896A (en) * | 2008-01-18 | 2009-08-27 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Image processing device and method, and imaging apparatus |
| JP4506854B2 (en) * | 2008-03-04 | 2010-07-21 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and image forming apparatus |
| JP5028328B2 (en) * | 2008-05-13 | 2012-09-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and image processing method |
| WO2009154438A1 (en) * | 2008-06-16 | 2009-12-23 | Optelec Development B.V. | Method and apparatus for automatically magnifying a text based image of an object |
| CN101320423A (en) * | 2008-06-26 | 2008-12-10 | 复旦大学 | Low resolution gait recognition method based on high-frequency super-resolution |
| CN102150418B (en) * | 2008-12-22 | 2014-10-15 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Image enlargement apparatus, method, and integrated circuit |
| JP5146335B2 (en) * | 2009-01-22 | 2013-02-20 | ソニー株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and method, and program |
| JP2011023886A (en) * | 2009-07-14 | 2011-02-03 | Panasonic Corp | Teleconferencing device and image display processing method |
| JP2011109397A (en) * | 2009-11-17 | 2011-06-02 | Sony Corp | Image transmission method, image reception method, image transmission device, image reception device, and image transmission system |
| JP5660273B2 (en) * | 2010-01-04 | 2015-01-28 | 日本電気株式会社 | Image diagnosis method, image diagnosis apparatus, and image diagnosis program |
| JP2011237997A (en) * | 2010-05-10 | 2011-11-24 | Sony Corp | Image processing device, and image processing method and program |
| JP2012175270A (en) * | 2011-02-18 | 2012-09-10 | Brother Ind Ltd | Controller |
| JP5903835B2 (en) * | 2011-04-28 | 2016-04-13 | 株式会社リコー | Transmission terminal, image display control method, image display control program, recording medium, and transmission system |
| JP5826606B2 (en) * | 2011-11-10 | 2015-12-02 | オリンパス株式会社 | Image distribution server |
| JP5497874B2 (en) * | 2011-12-22 | 2014-05-21 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Radiation image detector, radiation image capturing apparatus, and radiation image capturing system |
| US9304089B2 (en) * | 2013-04-05 | 2016-04-05 | Mitutoyo Corporation | System and method for obtaining images with offset utilized for enhanced edge resolution |
| CN104346770A (en) * | 2013-07-24 | 2015-02-11 | 联咏科技股份有限公司 | Data interpolation method and data interpolation system |
| KR101565926B1 (en) * | 2013-10-18 | 2015-11-04 | 주식회사 자원메디칼 | Method for compensating image for low vision person and apparatus for the same |
-
2016
- 2016-03-14 JP JP2016049515A patent/JP6719104B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-08-09 CN CN201610644318.2A patent/CN106483338A/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106483338A (en) | 2017-03-08 |
| JP2017046340A (en) | 2017-03-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6307770B2 (en) | Image sensor | |
| JP6631886B2 (en) | Image forming system, image forming method, image sensor, and program | |
| TW201126624A (en) | System and method for inspecting a wafer (2) | |
| JP5789765B2 (en) | Image acquisition apparatus, image acquisition method, and program | |
| JP2014142657A (en) | Whole slide fluorescence scanner | |
| JP6514832B2 (en) | Observation device | |
| JP6739061B2 (en) | Image generating apparatus, image generating method and program | |
| JP2014130221A (en) | Image processing apparatus, control method thereof, image processing system, and program | |
| US20150309301A1 (en) | Image forming apparatus, image forming method, image forming system, and recording medium | |
| JP7004808B2 (en) | Opposed edge system for scanning and processing glass slides | |
| WO2020003992A1 (en) | Learning device and learning method, and medical image processing device | |
| JP6719104B2 (en) | Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and recording medium | |
| JP2013109077A (en) | Image obtaining apparatus, image obtaining method, and image obtaining program | |
| JP2016052116A (en) | Image processing device, image processing method and computer program | |
| JP6562253B2 (en) | Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method and program | |
| US10048485B2 (en) | Image output device, image transmission device, image reception device, image output method, and non-transitory recording medium | |
| JP6004245B1 (en) | Image acquisition apparatus, image forming system, and image forming method | |
| US9778449B2 (en) | Preparation element set, preparation, manufacturing method of preparation, imaging apparatus, and imaging method | |
| JP2021501349A (en) | Carousel for 2x3 and 1x3 slides | |
| US9774771B2 (en) | Preparation, transparent plate, method for producing preparation, slide glass, imaging apparatus, imaging method, preparation producing apparatus, and preparation component set | |
| JP6867916B2 (en) | Observation device | |
| JP2017045430A (en) | Image processing device, image processing system, image processing method and program | |
| JP7112994B2 (en) | fluorescence imaging device | |
| JP2015228927A (en) | Imaging device for dermoscopy and method for using imaging device for dermoscopy | |
| WO2022209349A1 (en) | Lighting device for observation device, observation device, and observation system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190212 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20191128 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191224 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200225 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200519 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200602 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6719104 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |