JP6643033B2 - Railroad crossing machine - Google Patents
Railroad crossing machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6643033B2 JP6643033B2 JP2015200725A JP2015200725A JP6643033B2 JP 6643033 B2 JP6643033 B2 JP 6643033B2 JP 2015200725 A JP2015200725 A JP 2015200725A JP 2015200725 A JP2015200725 A JP 2015200725A JP 6643033 B2 JP6643033 B2 JP 6643033B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- motor
- brushless motor
- electromagnetic brake
- shaft
- output shaft
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 claims description 39
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 19
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000003028 elevating effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Motors That Do Not Use Commutators (AREA)
Description
本発明は、踏切しゃ断機に関する。 The present invention relates to a level crossing circuit breaker.
従来の踏切しゃ断機100の制御ブロックの一例を図5に示す。なお、図5中に示す矢印は、しゃ断棹の昇降動作時の信号の流れを示している。例えば図5に示すように、従来の踏切しゃ断機100は、不図示のしゃ断棹を昇降動作させるモータ300と、しゃ断棹を所定の上昇位置(垂直状態)又は所定の下降位置(水平状態)で保持するためのブレーキ500と、モータ300の駆動(三相駆動電力)を制御するモータドライバ600と、しゃ断棹を上昇動作又は下降動作させるための制御入力を行うしゃ断機回路700とを含んで構成される。
FIG. 5 shows an example of a control block of the conventional level
モータ300には、例えばホール素子、ロータリーエンコーダ、レゾルバ等の回転検出用のセンサ400が付設されており、センサ400は、モータ300の出力軸(モータ出力軸)の回転を検出する。センサ400の検出信号はモータドライバ600の回転角検出部605に出力され、モータ300の駆動制御に用いられる。
The
ブレーキ500は、しゃ断棹の停止時にはしゃ断機回路700により通電状態(ON)とされ、モータ出力軸の回転を制動させる。一方、図5に示すように、しゃ断棹の昇降動作時には、ブレーキ500は断電状態(OFF)とされ、その制動を解除するように構成されている。
The
モータドライバ600は、モータ300を駆動するモータ駆動部601と、モータ駆動部601を制御するモータ制御部603と、センサ400から入力される検出信号に基づきモータ出力軸の回転角を検出する回転角検出部605とを備える。モータ制御部603は、しゃ断機回路700からの上昇指令又は下降指令を受けてモータ300をしゃ断棹の上昇方向又は下降方向に駆動させ、しゃ断棹を昇降動作させる。そしてその際に、回転角検出部605が随時検出しているモータ出力軸の回転角(回転数を含む)を用いてモータ駆動部601を制御し、上昇動作時であればしゃ断棹が所定の上昇基準位置に達したこと、下降動作時であればしゃ断棹が所定の下降基準位置に達したことを検知してモータ駆動部601によるモータ300の駆動を停止させる。
The
図5に例示したように、従来の踏切しゃ断機100では、モータの駆動制御のために回転検出用のセンサ400を設けてモータ出力軸の回転角(回転数を含む)を検出していた。
As illustrated in FIG. 5, in the conventional level
本発明は、回転角検出用センサといったモータの駆動制御のための回転検出用の専用装置を不要とし、モータ出力軸の回転角に相応する信号を何らかの方法で取得してモータの駆動制御を行う技術を実現することを目的として考案されたものである。 The present invention eliminates the need for a dedicated device for rotation detection for motor drive control, such as a rotation angle detection sensor, and obtains a signal corresponding to the rotation angle of the motor output shaft in some way to perform drive control of the motor. It was devised for the purpose of realizing technology.
上記課題を解決するための第1の発明は、
モータ出力軸を高速軸とし、しゃ断棹のしゃ断棹軸を低速軸とする複数軸で構成された減速機構部(例えば、図1のモータ出力軸331、しゃ断棹軸11、回転伝達機構20)と、
前記モータ出力軸を回転させて前記しゃ断棹を昇降動作させるブラシレスモータ(例えば、図1のブラシレスモータ30)と、
前記ブラシレスモータの駆動が停止されて前記しゃ断棹が所定の上昇位置または所定の下降位置に位置した際に作動して前記モータ出力軸或いは他の高速軸(以下包括して「制動用高速軸」という)の回転を制動させる非接触式の電磁ブレーキ(例えば、図1の電磁ブレーキ50)と、
前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御して前記しゃ断棹を昇降動作させるモータ駆動制御部であって、昇降動作中に前記制動用高速軸の回転によって前記電磁ブレーキに発生する励磁電圧の周期的変化を用いて、前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御するモータ駆動制御部(例えば、図1のモータドライバ60)と、
を備えた踏切しゃ断機である。
A first invention for solving the above problems is
A deceleration mechanism (for example, the
A brushless motor (e.g., the
When the drive of the brushless motor is stopped and the cut-off rod is located at a predetermined raised position or a predetermined lowered position, the brushless motor is activated to operate the motor output shaft or another high-speed shaft (hereinafter collectively referred to as “braking high-speed shaft”). A non-contact type electromagnetic brake (for example, the
A motor drive control unit that controls the drive of the brushless motor to move the breaking rod up and down, using a periodic change in an excitation voltage generated in the electromagnetic brake by rotation of the braking high-speed shaft during the up and down operation. A motor drive control unit (for example, the
It is a level crossing machine equipped with.
第1の発明によれば、しゃ断棹の昇降動作時は、ブラシレスモータが駆動されてモータ出力軸が回転する。一方、昇降動作の停止にあたっては非接触式の電磁ブレーキが作動され、モータ出力軸或いはモータ出力軸の回転をしゃ断棹軸に伝達する他の高速軸である制動用高速軸の回転が制動される。そして、このような構成の踏切しゃ断機において、昇降動作中は、制動用高速軸の回転によって電磁ブレーキに励磁電圧が発生し、その励磁電圧が周期的に変化する。そこで、電磁ブレーキの励磁電圧の信号を、モータ出力軸の回転に相応する信号として利用することで、ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御することができる。従来の踏切しゃ断機のような、モータ出力軸の回転検出用の装置は不要である。 According to the first aspect, at the time of the elevating operation of the cut-off rod, the brushless motor is driven and the motor output shaft rotates. On the other hand, when stopping the elevating operation, the non-contact type electromagnetic brake is operated, and the rotation of the motor output shaft or the high-speed shaft for braking, which is another high-speed shaft transmitting the rotation of the motor output shaft to the cut-off rod shaft, is braked. . In the level crossing circuit breaker having such a configuration, during the elevating operation, the excitation voltage is generated in the electromagnetic brake by the rotation of the braking high-speed shaft, and the excitation voltage changes periodically. Therefore, the drive of the brushless motor can be controlled by using the excitation voltage signal of the electromagnetic brake as a signal corresponding to the rotation of the motor output shaft. There is no need for a device for detecting the rotation of the motor output shaft, such as a conventional level crossing circuit breaker.
第2の発明は、
前記電磁ブレーキは、前記制動用高速軸とともに回転する複数極の永久磁石が備えられた回転子を、複数の電磁石用コイルが通電されることで非接触に制動する回転電気機械であり、
前記モータ駆動制御部は、前記ブラシレスモータの極・相・スロットの構成と前記電磁ブレーキの極・相・スロットの構成との関係を用いて、前記電磁ブレーキに発生する励磁電圧の周期的変化から前記ブラシレスモータの制御用回転角を検出して、前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御する、
第1の発明の踏切しゃ断機である。
The second invention is
The electromagnetic brake is a rotating electric machine that non-contactly brakes a rotor provided with a plurality of permanent magnets that rotate with the high-speed shaft for braking, when a plurality of electromagnet coils are energized,
The motor drive control unit uses the relationship between the configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the brushless motor and the configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the electromagnetic brake to calculate a periodic change in the excitation voltage generated in the electromagnetic brake. Detecting the control rotation angle of the brushless motor and controlling the driving of the brushless motor,
1 is a crossing breaker according to the first invention.
第2の発明によれば、ブラシレスモータの極・相・スロットの構成と、電磁ブレーキの極・相・スロットの構成との関係を用いて、電磁ブレーキに発生する励磁電圧の周期的変化からブラシレスモータの制御用回転角を検出できる。 According to the second aspect of the present invention, the brushless motor is used to determine the brushless motor from the periodic change of the excitation voltage generated in the electromagnetic brake by using the relationship between the pole / phase / slot configuration of the brushless motor and the pole / phase / slot configuration of the electromagnetic brake. The control rotation angle of the motor can be detected.
第3の発明は、
前記モータ出力軸と前記制動用高速軸とは同軸であり、
前記ブラシレスモータは3相であり、
前記電磁ブレーキは2相である、
第1又は第2の発明の踏切しゃ断機である。
The third invention is
The motor output shaft and the braking high-speed shaft are coaxial,
The brushless motor has three phases,
The electromagnetic brake is two-phase,
It is a level crossing circuit breaker of the first or second invention.
第3の発明によれば、制動用高速軸をモータ出力軸とすることができ、ブラシレスモータを3相とし、電磁ブレーキを2相とすることができる。 According to the third aspect, the high-speed braking shaft can be used as the motor output shaft, the brushless motor can have three phases, and the electromagnetic brake can have two phases.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明する。なお、以下説明する実施形態によって本発明が限定されるものではなく、本発明を適用可能な形態が以下の実施形態に限定されるものでもない。また、図面の記載において、同一部分には同一の符号を付する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Note that the present invention is not limited by the embodiments described below, and the form to which the present invention can be applied is not limited to the following embodiments. In the description of the drawings, the same portions are denoted by the same reference numerals.
図1は、本実施形態の踏切しゃ断機1の制御ブロックの一例を示す図であり、(a)ではしゃ断棹10の昇降動作時の信号の流れを、(b)ではしゃ断棹10の停止時の信号の流れを矢印で示している。また、踏切しゃ断機1を構成するブラシレスモータ30の構成例を図2に示し、電磁ブレーキ50の構成例を図3に示す。
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of a control block of the level crossing circuit breaker 1 of the present embodiment. FIG. 1A illustrates a signal flow when the breaking
本実施形態の踏切しゃ断機1は、モータ出力軸331を回転させてしゃ断棹10を昇降動作させる三相のブラシレスモータ30と、直流のブレーキ作動信号が入力されることで作動して、しゃ断棹10を所定の上昇位置(垂直状態)又は所定の下降位置(水平状態)で保持するための非接触式の電磁ブレーキ50と、ブラシレスモータ30の駆動を制御するモータ駆動制御部としてのモータドライバ60と、しゃ断棹10を上昇動作又は下降動作させるための制御入力を行うしゃ断機回路70とを備える。
The crossing breaker 1 according to the present embodiment is operated by inputting a three-phase
モータ出力軸331の回転は、回転伝達機構20を介してしゃ断棹10の支持軸(しゃ断棹軸)11に伝達される。具体的には、回転伝達機構20は、複数の歯車等を有する減速機構部を構成しており、少なくとも高速軸であるモータ出力軸331および低速軸であるしゃ断棹軸11を備える。そして、この減速機構部によってモータ出力軸331の回転速度が減じて伝達され、しゃ断棹軸11を回転させる。これにより、しゃ断棹10は、ブラシレスモータ30の回転方向に応じて下降又は上昇する。
The rotation of the
また、回転伝達機構20の減速機構部が有する高速軸の1つが、電磁ブレーキ50の制動対象の軸(制動用高速軸)とされている。電磁ブレーキ50により制動用高速軸が制動されると、伝達機構の回転伝達が制止されるため、ブラシレスモータ30によるモータ出力軸331の回転やしゃ断棹軸11の回転も制止されたロック状態となる。ここで、高速軸とは、しゃ断棹軸11の回転に対して高速に回転する軸をいう。また、本実施形態では、電磁ブレーキ50の制動用高速軸と、モータ出力軸331とを同軸とする。すなわち、制動用高速軸は、モータ出力軸331である。なお、制動用高速軸は高速軸であればよく、モータ出力軸331とは別の高速軸としてもよい。
In addition, one of the high-speed shafts included in the speed reduction mechanism of the
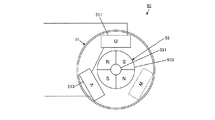
ブラシレスモータ30は、例えばインナーロータ型の構造を有した三相駆動の電動機であり、その構造の例を概略的に図2に示す。回転子33は、回転軸であるモータ出力軸331の周方向にN極の永久磁石とS極の永久磁石とが交互に配置された4極の永久磁石333を備え、モータ出力軸331を軸中心として回転する。一方、固定子31には、120°毎の等角度間隔で3つのスロットが画成されており、各スロットに配置された三相(U相、V相、W相)のコイル311,313,315を備える。各相のコイル311,313,315は、中性点において相互に接続されている。
The
電磁ブレーキ50は、構造的にはブラシレスモータ30と同様の回転電気機械であり、その構造の例を概略的に図3に示す。電磁ブレーキ50において、回転子53は、モータ出力軸331と同軸となる回転軸531と一体に構成され、4極の永久磁石533が回転軸531とともに回転するように構成されている。一方、固定子51は、三相(U相、V相、W相)のスロットのうちの2相にコイル(電磁石用コイル)511,513を配置して備え、各コイル511,513を直列接続して構成される。
The
この電磁ブレーキ50の作動時は、しゃ断機回路70からのブレーキ作動信号(DC)の入力によってコイル511,513が通電されることで固定子51と回転子53との間に制動力が生じ、モータ出力軸331の回転を非接触に制動する(図1(b))。一方で、電磁ブレーキ50の解除時(OFF)は、モータ出力軸331の回転に伴って回転子53が回転することから、電磁ブレーキ50に励磁電圧が発生する。すなわち、電磁ブレーキ50の励磁電圧の信号は、モータ出力軸331の回転に相応する信号と言える。但し、発生した励磁電圧そのものは振幅が大きい交流信号であるため、本実施形態では種々の信号処理を施した上で、ブラシレスモータ30の駆動制御に用いることとする。まず、発生した励磁電圧信号(AC)は、図1(a)に示すように、モータドライバ60を構成するブレーキ励磁波形変換部65の降圧回路部651に出力される。
When the
なお、ブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成は図2に例示した構成に限らない。また、電磁ブレーキ50についても同様に、図3に例示した極・相・スロットの構成に限定されない。ブラシレスモータ30および電磁ブレーキ50のいずれも、極数、相数、およびスロット数を適宜選択して構成してよい。
The configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the
モータドライバ60は、ブラシレスモータ30を駆動するモータ駆動部61と、モータ駆動部61を制御するモータ制御部63と、昇降動作中に電磁ブレーキ50に発生する励磁電圧波形の変化周期を検出するブレーキ励磁波形変換部65と、励磁電圧波形の変化周期に基づきブラシレスモータ30の回転角(制御用回転角。回転数を含む。)を検出する回転角検出部67とを備える。
The
モータ制御部63は、しゃ断機回路70からの上昇指令又は下降指令を受けてブラシレスモータ30をしゃ断棹10の上昇方向又は下降方向に駆動させ、しゃ断棹10を昇降動作させる。その際、モータ制御部63は、回転角検出部67が随時検出しているブラシレスモータ30の制御用回転角を用いてブラシレスモータ30の駆動を制御する。そして、上昇動作時であればしゃ断棹10が上昇基準位置に達したこと、下降動作時であればしゃ断棹10が下降基準位置に達したことを検知してブラシレスモータ30の駆動を停止させる。例えば、モータ制御部63は、検出された制御用回転角を用いてブラシレスモータ30の回転速度制御を行う。また、制御用回転角を用い、昇降動作開始時からのブラシレスモータ30の回転数を計数する等して上昇基準位置/下降基準位置に達したことを検知する。昇降動作を開始してから上昇基準位置/下降基準位置に達するまでのブラシレスモータ30の回転数は既知であるため、予め設定しておくことが可能である。
The
ブレーキ励磁波形変換部65は、降圧回路部651と、整流回路部653と、電圧検出部655とで構成される。降圧回路部651は、しゃ断棹10の昇降動作中に電磁ブレーキ50から入力される励磁電圧信号を降圧し、整流回路部653に出力する。整流回路部653は、降圧回路部651からの入力電圧信号を全波整流し、電圧検出部655に出力する。電圧検出部655は、整流回路部653からの入力電圧信号を所定の閾値Dth(図4(b)を参照)を境に2値の論理信号に変換し、回転角検出部67に出力する。
The brake
図4(a)に、励磁電圧波形の概略例を示す。また、(a)に示す励磁電圧波形の励磁電圧信号を降圧回路部651で降圧し、整流回路部653で整流した電圧波形を(b)に、これを電圧検出部655で変換した論理信号を(c)に示す。
FIG. 4A shows a schematic example of the excitation voltage waveform. Also, the excitation voltage signal having the excitation voltage waveform shown in (a) is stepped down by the step-down
電磁ブレーキ50の回転子53はモータ出力軸331の回転に伴って回転することから、電磁ブレーキ50が解除(OFF)され、モータ出力軸331が回転し始めると発生する励磁電圧は、図4(a)に示すように、電磁ブレーキ50の回転に合わせて周期的に変化する。本実施形態では、回転子53の永久磁石533が4極であり、固定子51が二相・2スロットであることから、励磁電圧波形の1回の変化周期で回転軸531(本実施形態ではモータ出力軸331)が半回転していることを示す。したがって、励磁電圧波形を図4(b)に示すように降圧・整流し、(c)に示すように論理信号に変換することで回転軸531の回転を180°単位で検出でき、その変化周期から、回転軸531の回転角すなわちモータ出力軸331の回転角を知ることができる。
Since the
なお、図4の波形の変化具合を補足的に説明すると、しゃ断棹10の昇降動作を開始した直後は、ブラシレスモータ30が回転開始した直後であるため励磁電圧波形がゆっくり変化しているが、すぐに定常回転速度となるため、励磁電圧波形が一定周期の波形となって表れる。
In addition, if the degree of change of the waveform in FIG. 4 is supplementarily described, immediately after the raising / lowering operation of the cut-off
また、モータ出力軸331(および制動対象軸である回転軸531)は高速軸であり、低速軸であるしゃ断棹軸11に比べて十分に高い回転比(例えば10倍以上)である。そのため、励磁電圧波形の変化周期から判別されるモータ出力軸331の回転角に誤差が生じたとしても、しゃ断棹10の昇降位置が大きくずれることはなく、制御上、問題とはならない。
In addition, the motor output shaft 331 (and the
また、ブラシレスモータ30と電磁ブレーキ50とでは、極・相・スロットの構成が異なる。そこで、回転角検出部67は、このブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成と電磁ブレーキ50の極・相・スロットの構成との関係を用いて励磁電圧波形の変化周期をブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成に応じた変化周期に変換し、ブラシレスモータ30の回転角を制御用回転角として検出する。
The configuration of the poles, phases, and slots differs between the
次に、踏切しゃ断機1の動作を説明する。踏切しゃ断機1において設置先の踏切に列車が接近した旨の通知を外部から受けると、図1(a)に示すように、しゃ断機回路70の制御のもと、不図示の電源部がモータ電源を供給してモータドライバ60を起動(ON)し、しゃ断棹10の下降動作を指示する下降指令を出力する。また、電磁ブレーキ50を解除(OFF)する。そして、モータドライバ60においてモータ制御部63が、下降指令に応答してブラシレスモータ30をしゃ断棹10の下降方向に駆動させ、しゃ断棹10を下降動作させる。
Next, the operation of the level crossing circuit breaker 1 will be described. When a notification that the train has approached the railroad crossing at the installation location is received from the outside at the level crossing circuit breaker 1, a power supply unit (not shown) is controlled by the power supply unit (not shown) under the control of the
下降動作中は、ブレーキ励磁波形変換部65が、電磁ブレーキ50に発生した励磁電圧波形の変化周期を随時検出する。そして、回転角検出部67が、励磁電圧波形の変化周期からブラシレスモータ30の制御用回転角を随時検出する。モータ制御部63は、この制御用回転角を用いてモータ駆動部61の駆動を制御するとともに、しゃ断棹10が下降基準位置に達したことを検知してモータ駆動部61によるブラシレスモータ30の駆動を停止させる。その後は、しゃ断機回路70が、モータ電源のモータドライバ60への供給を停止するとともに、電磁ブレーキ50を作動させてしゃ断棹10を下降位置で保持させる。
During the descending operation, the brake
続いて、列車が踏切を通過し終えた旨の通知を受けると、図1(a)に示すように、しゃ断機回路70は、再びモータ電源を供給させてモータドライバ60を起動し、しゃ断棹10の上昇動作を指示する上昇指令を出力するとともに、電磁ブレーキ50を解除(OFF)する。そして、モータドライバ60においてモータ制御部63が、上昇指令に応答してブラシレスモータ30をしゃ断棹10の上昇方向に駆動させ、しゃ断棹10を上昇動作させる。
Subsequently, upon receiving a notification that the train has passed the railroad crossing, as shown in FIG. 1A, the
上昇動作中は、ブレーキ励磁波形変換部65が電磁ブレーキ50に発生した励磁電圧波形の変化周期を随時検出し、回転角検出部67が励磁電圧波形の変化周期からブラシレスモータ30の制御用回転角を随時検出する。そして、モータ制御部63は、制御用回転角を用いてモータ駆動部61の駆動を制御するとともに、しゃ断棹10が上昇基準位置に達したことを検知してモータ駆動部61によるブラシレスモータ30の駆動を停止させる。その後は、しゃ断機回路70が、モータ電源のモータドライバ60への供給を停止するとともに、電磁ブレーキ50を作動させてしゃ断棹10を上昇位置で保持させる。
During the ascending operation, the brake excitation
以上説明したように、本実施形態によれば、しゃ断棹10の昇降動作中に電磁ブレーキ50に発生する励磁電圧波形の変化周期を用いてブラシレスモータ30の制御用回転角を検出することができる。そして、この制御用回転角を用いてブラシレスモータ30の駆動制御を行う。したがって、従来の踏切しゃ断機のような、モータ出力軸の回転検出用の装置は不要となる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the control rotation angle of the
また、制御用回転角の検出に際し、ブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成と、電磁ブレーキ50の極・相・スロットの構成との関係を用いて、励磁電圧波形の変化周期をブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成に応じた変化周期に変換することができる。したがって、ブラシレスモータ30と電磁ブレーキ50とで極数や相数、スロット数が異なる場合であっても、制御用回転角を適正に検出してブラシレスモータ30を駆動制御できる。
When detecting the control rotation angle, the change period of the excitation voltage waveform is determined using the relationship between the pole / phase / slot configuration of the
なお、本発明を適用した実施形態の一例を説明したが、本発明を適用可能な形態は上述した実施形態に限らない。
例えば、電磁ブレーキ50の制動対象軸は、高速軸であればモータ出力軸331でなくともよい。
Although an example of the embodiment to which the present invention is applied has been described, the form to which the present invention can be applied is not limited to the above-described embodiment.
For example, the braking target axis of the
また、上述した実施形態におけるブラシレスモータ30及び電磁ブレーキ50の極・相・スロットの構成は一例であり、他の構成でもよい。何れにせよ、ブラシレスモータ30の極・相・スロットの構成と、電磁ブレーキ50の極・相・スロットの構成との関係が既知であれば、その関係を用いて、励磁電圧波形の周期的変化から制御回転角を検出できる。
In addition, the configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the
1 踏切しゃ断機
10 しゃ断棹
11 しゃ断棹軸
20 回転伝達機構
30 ブラシレスモータ
31 固定子
311,313,315 コイル
33 回転子
331 モータ出力軸
333 永久磁石
50 電磁ブレーキ
51 固定子
511,513 コイル
53 回転子
60 モータドライバ
61 モータ駆動部
63 モータ制御部
65 ブレーキ励磁波形変換部
651 降圧回路部
653 整流回路部
655 電圧検出部
67 回転角検出部
70 しゃ断機回路
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Crossing-
Claims (3)
前記モータ出力軸を回転させて前記しゃ断棹を昇降動作させるブラシレスモータと、
前記ブラシレスモータの駆動が停止されて前記しゃ断棹が所定の上昇位置又は所定の下降位置に位置した際に作動して前記モータ出力軸或いは前記モータ出力軸以外の高速軸(以下包括して「制動用高速軸」という)の回転を制動させる非接触式の電磁ブレーキと、
前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御して前記しゃ断棹を昇降動作させるモータ駆動制御部であって、昇降動作中に前記制動用高速軸の回転によって前記電磁ブレーキに発生する励磁電圧の周期的変化を用いて、前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御するモータ駆動制御部と、
を備えた踏切しゃ断機。 A reduction mechanism comprising a plurality of rotation transmitting mechanisms for reducing the rotation speed of the motor output shaft and rotating the cut-off rod shaft of the cut-off rod , including the motor output shaft rotating at a higher speed than the cut-off rod shaft. A speed reduction mechanism having a plurality of high-speed axes ;
A brushless motor that rotates the motor output shaft to raise and lower the breaking rod,
When the drive of the brushless motor is stopped and the breaking rod is positioned at a predetermined raised position or a predetermined lowered position, the brushless motor is activated to operate the motor output shaft or a high-speed shaft other than the motor output shaft (hereinafter collectively referred to as “braking”). Non-contact type electromagnetic brake that brakes the rotation of
A motor drive control unit that controls the drive of the brushless motor to move the breaking rod up and down, using a periodic change in an excitation voltage generated in the electromagnetic brake by rotation of the braking high-speed shaft during the up and down operation. A motor drive control unit that controls the drive of the brushless motor;
Level crossing machine with.
前記モータ駆動制御部は、前記ブラシレスモータの極・相・スロットの構成と前記電磁ブレーキの極・相・スロットの構成との関係を用いて、前記電磁ブレーキに発生する励磁電圧の周期的変化から前記ブラシレスモータの制御用回転角を検出して、前記ブラシレスモータの駆動を制御する、
請求項1に記載の踏切しゃ断機。 The electromagnetic brake is a rotating electric machine that non-contactly brakes a rotor provided with a plurality of permanent magnets that rotate with the high-speed shaft for braking, when a plurality of electromagnet coils are energized,
The motor drive control unit uses the relationship between the configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the brushless motor and the configuration of the poles, phases, and slots of the electromagnetic brake to calculate a periodic change in the excitation voltage generated in the electromagnetic brake. Detecting the control rotation angle of the brushless motor and controlling the driving of the brushless motor,
The level crossing circuit breaker according to claim 1.
前記ブラシレスモータは3相であり、
前記電磁ブレーキは2相である、
請求項1又は2に記載の踏切しゃ断機。 The motor output shaft and the braking high-speed shaft are coaxial,
The brushless motor has three phases,
The electromagnetic brake is two-phase,
The level crossing circuit breaker according to claim 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015200725A JP6643033B2 (en) | 2015-10-09 | 2015-10-09 | Railroad crossing machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015200725A JP6643033B2 (en) | 2015-10-09 | 2015-10-09 | Railroad crossing machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017071353A JP2017071353A (en) | 2017-04-13 |
| JP6643033B2 true JP6643033B2 (en) | 2020-02-12 |
Family
ID=58539106
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015200725A Active JP6643033B2 (en) | 2015-10-09 | 2015-10-09 | Railroad crossing machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6643033B2 (en) |
-
2015
- 2015-10-09 JP JP2015200725A patent/JP6643033B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017071353A (en) | 2017-04-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109874390B (en) | Linear actuator with brushless DC motor | |
| JP5653906B2 (en) | Judgment of electrical machine rotor position | |
| US10122305B2 (en) | Motor control apparatus | |
| US10486936B2 (en) | Method for determining a stator current vector for starting a synchronous machine of a drive of a passenger transportation apparatus | |
| EP2824825B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for determining position for a permanent magnet elevator motor | |
| JP6643033B2 (en) | Railroad crossing machine | |
| JP2012165612A (en) | Dc motor ceiling fan | |
| JP2008271698A (en) | Motor drive | |
| CN111213314A (en) | Method for starting and operating a BLDC motor and BLDC motor | |
| EP2733841A2 (en) | Systems, methods, and assemblies for detecting stoppage of electric motors | |
| JP6440355B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for synchronizing rotor speed with stator rotating magnetic field | |
| JP6668034B2 (en) | Motor drive control device and level crossing circuit breaker | |
| CN108377113B (en) | Method for applying brake to crane in permanent magnet motor in electromagnetic mode | |
| WO2015008382A1 (en) | Elevator control device | |
| JP2009011014A (en) | Inverter controller, electric compressor, and home electrical equipment | |
| JP5707638B2 (en) | Three-phase brushless motor drive control device | |
| KR101684617B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for driving three phase motor | |
| JPWO2020059759A1 (en) | Motor drive controller, motor unit, and actuator | |
| JP5418281B2 (en) | Synchronous rotating machine control device and synchronous rotating machine control method | |
| JP6835256B2 (en) | Elevator controller | |
| KR100827414B1 (en) | Control apparatus and method for bldc hub motor | |
| KR101191355B1 (en) | Noise control apparatus for dc motor of vehicle | |
| JP2005333753A (en) | Control device of three-phase brushless motor | |
| JP2000287478A (en) | Elevator driven by permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| JP2006206196A (en) | Elevator repairing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180926 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190618 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190730 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20191224 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200106 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6643033 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |