JP6602687B2 - Opto-electric hybrid device - Google Patents
Opto-electric hybrid device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6602687B2 JP6602687B2 JP2016030997A JP2016030997A JP6602687B2 JP 6602687 B2 JP6602687 B2 JP 6602687B2 JP 2016030997 A JP2016030997 A JP 2016030997A JP 2016030997 A JP2016030997 A JP 2016030997A JP 6602687 B2 JP6602687 B2 JP 6602687B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- optical waveguide
- spacer
- cladding
- vertical optical
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 93
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 85
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 claims description 42
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 42
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 42
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 105
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 19
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000005357 flat glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009429 electrical wiring Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009191 jumping Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002210 silicon-based material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013464 silicone adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Couplings Of Light Guides (AREA)
- Optical Integrated Circuits (AREA)
Description
本発明は、光電気混載デバイスに関する。 The present invention relates to an opto-electric hybrid device.
従来、基板上に光回路と電子部品を混載した光電気混載デバイスが知られている。例えば特許文献1(図28)に開示された光電気混載デバイスでは、基板と基板上の薄板ガラスとの間に基板に対して立設した縦型光導波路が形成され、縦型光導波路の上端は薄板ガラスに接している。 Conventionally, an opto-electric hybrid device in which an optical circuit and an electronic component are mixedly mounted on a substrate is known. For example, in the opto-electric hybrid device disclosed in Patent Document 1 (FIG. 28), a vertical optical waveguide standing on the substrate is formed between the substrate and the thin glass on the substrate, and the upper end of the vertical optical waveguide is formed. Is in contact with thin glass.
しかしながら、上記のように構成された光電気混載デバイスでは、縦型光導波路の上端と薄板ガラスとの接合面において剥離が生じるおそれがある。 However, in the opto-electric hybrid device configured as described above, there is a possibility that peeling occurs at the joint surface between the upper end of the vertical optical waveguide and the thin glass plate.
本発明は、上記の点に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的の1つは、縦型光導波路の上端と薄板ガラスとの接合面において剥離を生じにくくさせることにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and one of its purposes is to make it difficult for separation to occur at the joint surface between the upper end of the vertical optical waveguide and the thin glass plate.
上述した課題を解決するために、本発明の一態様は、光信号の送信部と受信部の少なくとも何れか一方が設けられた基板と、前記基板上に搭載され、前記送信部と受信部の少なくとも何れか一方と電気信号を送受信する電子部品と、前記基板上に設置されたスペーサと、前記スペーサ上に前記スペーサから張り出す形で設置された透明な板材と、前記基板と前記板材の張り出した部分との間に形成された縦型光導波路と、前記電子部品上に開口を有して前記基板上の少なくとも一部分を覆うと共に、前記縦型光導波路のクラッドを構成する樹脂層と、を備え、前記スペーサと前記クラッドとの間に空隙が設けられていることを特徴とする光電気混載デバイスである。 In order to solve the above-described problem, one embodiment of the present invention includes a substrate provided with at least one of an optical signal transmission unit and a reception unit, mounted on the substrate, and the transmission unit and the reception unit. Electronic components that transmit / receive electrical signals to / from at least one of them, a spacer installed on the substrate, a transparent plate installed on the spacer so as to protrude from the spacer, and an extension of the substrate and the plate A vertical optical waveguide formed between the first and second portions, and a resin layer that has an opening on the electronic component and covers at least a part of the substrate, and that constitutes a cladding of the vertical optical waveguide. The opto-electric hybrid device is characterized in that a gap is provided between the spacer and the clad.
また、本発明の他の一態様は、上記一態様において、前記スペーサと前記板材が接着剤によって接着され、前記接着剤は、前記板材が温度変化による前記クラッドの収縮に応じて傾斜可能であるような柔軟性を有することを特徴とする光電気混載デバイスである。 According to another aspect of the present invention, in the above aspect, the spacer and the plate are bonded by an adhesive, and the adhesive can be inclined according to contraction of the clad due to a temperature change of the plate. It is an opto-electric hybrid device characterized by having such flexibility.
また、本発明の他の一態様は、上記一態様において、前記スペーサと前記板材が接着剤によって接着され、前記接着剤は、紫外光照射によって接着力が低下することを特徴とする光電気混載デバイスである。 According to another aspect of the present invention, in the above aspect, the spacer and the plate material are bonded by an adhesive, and the adhesive is reduced in adhesive strength by irradiation with ultraviolet light. It is a device.
また、本発明の他の一態様は、上記一態様において、前記板材は、前記空隙の上部箇所で切断されていることを特徴とする光電気混載デバイスである。 Another aspect of the present invention is the opto-electric hybrid device according to the above aspect, wherein the plate member is cut at an upper portion of the gap.
本発明によれば、縦型光導波路の上端と薄板ガラスとの接合面において剥離を生じにくくさせることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to make it difficult for peeling to occur at the joint surface between the upper end of the vertical optical waveguide and the thin glass plate.
以下、図面を参照しながら本発明の実施形態について詳しく説明する。図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る光電気混載デバイスの製造方法を示すフローチャートである。この製造方法は、第1〜13工程からなる。図2〜14は、各工程におけるデバイスの状態をそれぞれ示す図である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a flowchart showing a method for manufacturing an opto-electric hybrid device according to an embodiment of the present invention. This manufacturing method includes the first to thirteenth steps. 2-14 is a figure which shows the state of the device in each process, respectively.
まず、第1工程において、基板10上にIC(電子部品)12を実装する(図2)。基板10は、例えばSOI基板であり、その表面には予め光回路14が形成されている。光回路14の一例は、フォトダイオードやグレーティングカプラである。光回路14がフォトダイオードである場合、フォトダイオードはその受光面が上方を向くように配置され、基板10上には受光信号をIC12へ伝送するための電気配線(不図示)が更に設けられる。光回路14がグレーティングカプラである場合、基板10上には、光源と、光源からの光を変調する光変調器と、光変調器によって変調された光信号(送信光)をグレーティングカプラまで導く平面光導波路が更に設けられる(何れも不図示)。そして、グレーティングカプラは、平面光導波路を伝搬してきた光信号を上方へ跳ね上げる機能を有するように構成される。光回路14の上面には、更に、後述する露光工程の際に露光光の基板10からの反射を防止するための反射防止膜16が、予め形成されている。
First, in a first step, an IC (electronic component) 12 is mounted on the substrate 10 (FIG. 2). The
IC12は、上述の光変調器を電気的に駆動するためのドライバIC、又は上述のフォトダイオードからの受光信号(電流)をIV変換するためのトランスインピーダンスアンプ(TIA)である。IC12は、例えばボールグリッドアレイ(BGA)等の接続電極18を介してIC12側の各端子が基板10側の電気配線(光変調器又はフォトダイオードと電気接続する配線)と接続されるように、基板10上に実装される。
The
次に、第2工程において、基板10上にガラス基板(スペーサ)20を搭載する(図3)。ガラス基板20には一続きの大きな開口22が設けられており、この開口22の中にIC12と後述する縦型光導波路の形成領域(反射防止膜16の部分)とが収容されるようにして、ガラス基板20が搭載される。ガラス基板20はIC12の搭載高さ(基板10の表面からIC12の上面までの高さ)よりも大きい厚さを持ち、IC12の上面は開口22の上端よりも凹んだ位置にある。ガラス基板20は、更に貫通配線(TGV)24を有し、この貫通配線24は、基板10上に設けられた電気配線(不図示)と上述の接続電極18を介してIC12と接続される。
Next, in a second step, a glass substrate (spacer) 20 is mounted on the substrate 10 (FIG. 3). The
次に、第3工程において、搭載されたガラス基板20の開口22内の縦型光導波路形成領域上に、光導波路コア形成用の光硬化性樹脂26を供給する(図4)。縦型光導波路形成領域は、IC12と開口22の壁面との間の反射防止膜16部分である。コア用樹脂26は、IC12の側面と開口22の壁面との間の空間に、その液面が開口22の上端よりも少し飛び出た状態となるような高さまで充填される。
Next, in the third step, a
次に、第4工程において、ガラス基板20上に薄板ガラス(透明板材)28をその一部分が縦型光導波路形成領域上に張り出す形で搭載する(図5)。この時、薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20から張り出した部分が、上から見て縦型光導波路形成領域の全体を覆う(重なる)形となるようにする。これにより、搭載された薄板ガラス28の当該張り出した部分と縦型光導波路形成領域との間の空間全体が、コア用樹脂26によって満たされた状態となる。なお、薄板ガラス28をガラス基板20上に搭載する際に、余剰のコア用樹脂26はIC12の上面へと拡がり、また、薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20との接触面の間隙にも、コア用樹脂26の一部が入り込んでいく。この間隙に入り込んだコア用樹脂26によって、薄板ガラス28はガラス基板20と仮固定された状態となっている。
Next, in the fourth step, the thin glass (transparent plate material) 28 is mounted on the
次に、第5工程において、コア形成用マスク30を配置する(図6)。コア形成用マスク30は、ガラス板の一方の面に、縦型光導波路コア形成用透光部32、薄板ガラス接着部用透光部36、及び位置合わせ穴形成用透光部38を除いて、露光時の遮光用の金属膜が形成されて構成されている。縦型光導波路コア形成用透光部32は、基板10上の光回路14の位置及び数に対応して設けられている。薄板ガラス接着部用透光部36は、薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20との接触面に対応した位置に設けられている。位置合わせ穴形成用透光部38は、光電気混載デバイスが完成した後に光ファイバコネクタを接続する際の位置合わせ用の穴を形成するためのものである。
Next, in the fifth step, the
次に、第6工程において、コア形成用マスク30を介して露光を行う(図7)。露光光は、コア用樹脂26が感光して硬化する波長の光(例えばUV光)である。露光により、各透光部32、36、及び38の下部に存在するコア用樹脂26が硬化する。その結果、縦型光導波路コア形成用透光部32の下部には、薄板ガラス28と基板10上の光回路14との間に基板10に対して垂直に立設した、柱状の(縦型の)光導波路コア40が形成される。また、薄板ガラス接着部用透光部36の下部において、前述したように薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20との接触面の間隙にコア用樹脂26が入り込んでいるが、この部分のコア用樹脂26が露光されて硬化することによって、薄板ガラス28がガラス基板20に対して固着(本固定)される。
次に、第7工程において、コア形成用マスク30を取り外す(図8)。
Next, in a sixth step, exposure is performed through the core forming mask 30 (FIG. 7). The exposure light is light (for example, UV light) having a wavelength at which the
Next, in the seventh step, the
このように、縦型光導波路コア40の形成と薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20への固着を、同じ露光工程により一括して行うことができる。
In this way, the formation of the vertical
次に、第8工程において、露光後に未硬化のまま残ったコア用樹脂26を溶剤で洗い流して除去する(図9)。
Next, in the eighth step, the
次に、第9工程において、ガラス基板20の開口22内全体を満たすように、光導波路クラッド形成用の光硬化性樹脂44を供給する(図10)。この時、クラッド用樹脂44は、その液面が開口22の上端よりも少し飛び出た状態となるような高さまで充填されて、IC12の上面全体が、クラッド用樹脂44で完全に覆われた形となっている。
Next, in the ninth step, a
次に、第10工程において、クラッド形成用マスク46を配置する(図11)。クラッド形成用マスク46は、ガラス板の一方の面においてIC開口形成用遮光部48と、空隙形成用遮光部49と、ガラス基板20の開口22より外周側の部分に、露光時の遮光用の金属膜が形成されて構成されている。このIC開口形成用遮光部48は、後述するIC12上面の開口を形成するためのものであり、IC12の上面に対応した位置に、IC12の上面の略全面(IC12の上面全体よりも若干小さい広さ)を覆うような形状と大きさで設けられている。空隙形成用遮光部49は、薄板ガラス28の下部においてガラス基板20の開口22の壁面近傍部分を遮光するように設けられている。
Next, in a tenth step, a
次に、第11工程において、クラッド形成用マスク46を介して露光を行う(図12)。露光光は、コア用樹脂26の露光時と同様、クラッド用樹脂44が感光して硬化する波長の光(例えばUV光)である。露光により、ガラス基板20の開口22内に充填されているクラッド用樹脂44が、IC開口形成用遮光部48の下部と空隙形成用遮光部49の下部を除いて硬化する。その結果、縦型光導波路コア40の周囲にクラッド50が形成される。空隙形成用遮光部49の下部では露光光が遮蔽されてクラッド用樹脂44が硬化しないため、クラッド50は、ガラス基板20の開口22の壁面から離れて形成される。即ち、露光によって形成されたクラッド50とガラス基板20の開口22の壁面との間には未硬化のクラッド用樹脂が残っており、以下の第13工程においてこの未硬化樹脂が除去されると、樹脂で占められていない空隙51が出現する。一方、IC12の底部近傍では、IC12の底面と基板10との間の間隙(接続電極18が設置されている間隙)の周囲において硬化したクラッド用樹脂44aによって、IC12と基板10を電気接続している接続電極18が封止される。更に、IC12の上面部分では、クラッド形成用マスク46のIC開口形成用遮光部48の存在によって、IC12の周縁部分においてのみクラッド用樹脂44bが硬化することで当該周縁を取り囲むように壁面が形成され、この壁面の内側にはクラッド用樹脂44が未硬化のまま残っている。即ち、IC12の周縁を取り囲んだ硬化したクラッド用樹脂44bからなる壁面によって、IC12の上面には開口52が形成される。
次に、第12工程において、クラッド形成用マスク46を取り外す(図13)。
Next, in an eleventh step, exposure is performed through the cladding forming mask 46 (FIG. 12). The exposure light is light (for example, UV light) having a wavelength at which the clad
Next, in a twelfth step, the
このように、縦型光導波路クラッド50の形成と、IC12上面の開口52の形成と、接続電極18の封止を、同じ露光工程により一括して行うことができる。
In this way, the formation of the vertical
次に、第13工程において、露光後に未硬化のまま残っている開口52内のクラッド用樹脂を溶剤で洗い流して除去する(図14)。なお、IC12下部の接続電極部分に存在するクラッド用樹脂も、露光時にIC12で遮光されるため未硬化のままである。しかしながら、上述したようにIC12は周囲が既に硬化したクラッド用樹脂44aで囲まれているため、接続電極周囲の未硬化のクラッド用樹脂は、洗浄工程によって除去することができない。そこで、この部分の未硬化のクラッド用樹脂は、別途、加熱工程により硬化させる。なお、予めIC12の底面周囲にアンダーフィリングを施しておき、クラッド用樹脂がIC12の底面の間隙に入り込まないようにしてもよい。
Next, in the thirteenth step, the resin for cladding in the
以上の工程により、本発明の一実施形態に係る光電気混載デバイスが完成する。図14は光電気混載デバイスの完成形態を示している。本実施形態による光電気混載デバイスを使用する際には、開口52を通して、IC12上面に熱伝導性の良い樹脂を介してヒートシンクを接続することにより、IC12から効果的に放熱を行うことが可能である。
The opto-electric hybrid device according to one embodiment of the present invention is completed through the above steps. FIG. 14 shows a completed form of the opto-electric hybrid device. When using the opto-electric hybrid device according to the present embodiment, it is possible to effectively radiate heat from the
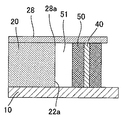
図15は、完成した光電気混載デバイスの縦型光導波路近傍の拡大図を示す。図示されるように、薄板ガラス28の下部において、縦型光導波路クラッド50はガラス基板20の開口22の壁面22aから離間して形成され、したがって縦型光導波路クラッド50と壁面22aとの間には空隙51が存在する。ここで、樹脂から成る縦型光導波路クラッド50(及び縦型光導波路コア40)の線膨張係数は、一般にガラス基板20の線膨張係数と比べて大きいので、光電気混載デバイスに温度変化が加えられた際には、縦型光導波路クラッド50とガラス基板20は異なる伸縮を示す。例えば、光電気混載デバイスが低温に曝されると、縦型光導波路クラッド50はガラス基板20よりも顕著に収縮し、縦型光導波路クラッド50の高さ方向の寸法は、ガラス基板20の高さ方向の寸法(即ち厚さ)より小さくなる。そのため、縦型光導波路クラッド50と薄板ガラス28との接合面には、縦型光導波路クラッド50を薄板ガラス28から剥離させようとする力が発生する。しかしながら、縦型光導波路クラッド50とガラス基板20の壁面22aとの間には空隙51が存在しているため、薄板ガラス28は、ガラス基板20の壁面22aが薄板ガラス28と接する箇所28aを支点として、収縮する縦型光導波路クラッド50によって下方向へ引っ張られる形で弾性的に変形する(撓む)ことが可能である。したがって、薄板ガラス28のこのような弾性変形によって、縦型光導波路クラッド50と薄板ガラス28との接合面にかかる応力(縦型光導波路クラッド50を剥離させようとする力)が緩和され、その結果、縦型光導波路クラッド50の薄板ガラス28からの剥離が生じにくくすることができる。
FIG. 15 shows an enlarged view of the vicinity of the vertical optical waveguide of the completed opto-electric hybrid device. As shown in the figure, in the lower part of the
なお、図12乃至14において縦型光導波路クラッド50はIC12と接して形成されているが、縦型光導波路クラッド50は、IC12から離間して(即ち縦型光導波路クラッド50とIC12との間にも空隙が介在するように)形成されてもよい。同様に、縦型光導波路クラッド50は、コア用樹脂で構成された位置合わせ穴(又は位置合わせ穴の側におけるガラス基板20の壁面)から離間して形成されてもよい。
12 to 14, the vertical
以上、本発明の実施形態を説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において様々な変更が可能である。変形例のいくつかを以下に述べる。 As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described, this invention is not limited to this, A various change is possible within the range which does not deviate from the summary. Some of the modifications will be described below.
上述した実施形態では、薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20への固定は、薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20との接触面の間隙にコア用樹脂26が入り込んで硬化することによってなされているが、コア用樹脂26ではなく、別途の接着剤を用いて薄板ガラス28をガラス基板20に対して接着することとしてもよい。このような接着剤として、例えばシリコーン系接着剤などの、柔軟性の高い接着剤を適用することが好適である。図16は、シリコーン系接着剤27を用いて薄板ガラス28をガラス基板20に接着することによって構成された光電気混載デバイスの、低温時における縦型光導波路近傍の拡大図を示す。図示されるように、縦型光導波路クラッド50は、収縮によって高さ方向の寸法がガラス基板20の厚さよりも小さくなっているが、薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20との間に介在するシリコーン系接着剤27が比較的高い柔軟性を持つため、薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20との接合部位は、シリコーン系接着剤27によってガラス基板20との接合を保持したまま、ガラス基板20の表面からわずかに浮くような形で可動する。これにより、薄板ガラス28は、コア用樹脂によってガラス基板20に接着される場合と比べて、撓みの少ない状態で縦型光導波路クラッド50の側が下がった姿勢に落ち着く。したがって、このようにシリコーン系接着剤27の柔軟性によって薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20との接合部位がわずかに変位可能とされることで、縦型光導波路クラッド50と薄板ガラス28との接合面にかかる応力が緩和され、その結果、縦型光導波路クラッド50の薄板ガラス28からの剥離を生じにくくさせることができる。
In the embodiment described above, the
薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20を接着する接着剤の別の例として、例えばUV光の照射によって接着力が低下又は消失する接着剤を適用してもよい。このような接着剤を用いて、上述した第4工程において、一旦薄板ガラス28はガラス基板20に対して接着(固定)される。その後更に、上述した第11工程(又は第13工程後の別工程)において、薄板ガラス28とガラス基板20で挟まれた部位の当該接着剤にも露光光を照射することで、薄板ガラス28はガラス基板20から剥離される(なお、接着剤は洗浄して除去することが好ましい)。この場合、低温時には、薄板ガラス28は、ガラス基板20に対して固定されていないことによって、元の平板形状を保ったまま縦型光導波路クラッド50の側が下がった状態に傾斜する。したがって、シリコーン系接着剤27を用いた場合と同じように、縦型光導波路クラッド50と薄板ガラス28との接合面にかかる応力が緩和され、その結果、縦型光導波路クラッド50の薄板ガラス28からの剥離を生じにくくさせることができる。
As another example of the adhesive that bonds the
更に別の変形例として、薄板ガラス28を、空隙51の上部の箇所で切断することとしてもよい。即ち、薄板ガラス28は、ガラス基板20側の部分と縦型光導波路クラッド50側の部分に分離されてもよい。このような光電気混載デバイスに温度変化が加えられた際には、ガラス基板20と縦型光導波路クラッド50のそれぞれの伸縮に応じて、薄板ガラス28のガラス基板20側の部分と縦型光導波路クラッド50側の部分は、互いに独立して可動する。したがって、縦型光導波路クラッド50と薄板ガラス28との接合面には応力がかからず、縦型光導波路クラッド50の薄板ガラス28からの剥離を完全に回避することができる。
As yet another modification, the
10 基板
12 IC(電子部品)
14 光回路
16 反射防止膜
18 接続電極
20 ガラス基板(スペーサ)
22 ガラス基板の開口
24 貫通配線
26 コア用樹脂
28 薄板ガラス(透明板材)
30 コア形成用マスク
32 縦型光導波路コア形成用透光部
36 薄板ガラス接着部用透光部
38 位置合わせ穴形成用透光部
40 縦型光導波路コア
44 クラッド用樹脂
46 クラッド形成用マスク
48 IC開口形成用遮光部
49 空隙形成用遮光部
50 縦型光導波路クラッド
51 空隙
52 IC上面の開口
10
14
22
30
Claims (3)
前記基板上に搭載され、前記送信部と受信部の少なくとも何れか一方と電気信号を送受信する電子部品と、
前記基板上に設置されたスペーサと、
前記スペーサ上に前記スペーサから張り出す形で設置された透明な板材と、
前記基板と前記板材の張り出した部分との間に形成された縦型光導波路と、
前記電子部品上に開口を有して前記基板上の少なくとも一部分を覆うと共に、前記縦型光導波路のクラッドを構成する樹脂層と、
を備え、前記スペーサと前記クラッドとの間に空隙が設けられており、
前記スペーサと前記板材が接着剤によって接着され、前記接着剤は、前記板材が温度変化による前記クラッドの収縮に応じて傾斜可能であるような柔軟性を有することを特徴とする、光電気混載デバイス。 A substrate provided with at least one of an optical signal transmitter and a receiver;
An electronic component that is mounted on the substrate and transmits / receives an electrical signal to / from at least one of the transmitter and the receiver,
A spacer installed on the substrate;
A transparent plate installed on the spacer so as to protrude from the spacer;
A vertical optical waveguide formed between the substrate and the protruding portion of the plate,
A resin layer having an opening on the electronic component and covering at least a part of the substrate, and constituting a cladding of the vertical optical waveguide;
A gap is provided between the spacer and the cladding ,
Said spacer and said plate member are bonded by an adhesive, the adhesive is characterized by having flexibility, such as the plate is tiltable in response to contraction of the cladding due to temperature change, the opto-electric hybrid device .
前記基板上に搭載され、前記送信部と受信部の少なくとも何れか一方と電気信号を送受信する電子部品と、
前記基板上に設置されたスペーサと、
前記スペーサ上に前記スペーサから張り出す形で設置された透明な板材と、
前記基板と前記板材の張り出した部分との間に形成された縦型光導波路と、
前記電子部品上に開口を有して前記基板上の少なくとも一部分を覆うと共に、前記縦型光導波路のクラッドを構成する樹脂層と、
を備え、前記スペーサと前記クラッドとの間に空隙が設けられており、
前記スペーサと前記板材が接着剤によって接着され、前記接着剤は、紫外光照射によって接着力が低下することを特徴とする、光電気混載デバイス。 A substrate provided with at least one of an optical signal transmitter and a receiver;
An electronic component that is mounted on the substrate and transmits / receives an electrical signal to / from at least one of the transmitter and the receiver,
A spacer installed on the substrate;
A transparent plate installed on the spacer so as to protrude from the spacer;
A vertical optical waveguide formed between the substrate and the protruding portion of the plate,
A resin layer having an opening on the electronic component and covering at least a part of the substrate, and constituting a cladding of the vertical optical waveguide;
A gap is provided between the spacer and the cladding,
The photoelectric hybrid device , wherein the spacer and the plate material are bonded by an adhesive, and the adhesive of the adhesive is reduced by irradiation with ultraviolet light.
前記基板上に搭載され、前記送信部と受信部の少なくとも何れか一方と電気信号を送受信する電子部品と、
前記基板上に設置されたスペーサと、
前記スペーサ上に前記スペーサから張り出す形で設置された透明な板材と、
前記基板と前記板材の張り出した部分との間に形成された縦型光導波路と、
前記電子部品上に開口を有して前記基板上の少なくとも一部分を覆うと共に、前記縦型光導波路のクラッドを構成する樹脂層と、
を備え、前記スペーサと前記クラッドとの間に空隙が設けられており、
前記板材は、前記空隙の上部箇所で切断されていることを特徴とする、光電気混載デバイス。 A substrate provided with at least one of an optical signal transmitter and a receiver;
An electronic component that is mounted on the substrate and transmits / receives an electrical signal to / from at least one of the transmitter and the receiver,
A spacer installed on the substrate;
A transparent plate installed on the spacer so as to protrude from the spacer;
A vertical optical waveguide formed between the substrate and the protruding portion of the plate,
A resin layer having an opening on the electronic component and covering at least a part of the substrate, and constituting a cladding of the vertical optical waveguide;
A gap is provided between the spacer and the cladding,
The opto- electric hybrid device, wherein the plate material is cut at an upper portion of the gap.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030997A JP6602687B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2016-02-22 | Opto-electric hybrid device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030997A JP6602687B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2016-02-22 | Opto-electric hybrid device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017151146A JP2017151146A (en) | 2017-08-31 |
| JP6602687B2 true JP6602687B2 (en) | 2019-11-06 |
Family
ID=59741763
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030997A Active JP6602687B2 (en) | 2016-02-22 | 2016-02-22 | Opto-electric hybrid device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6602687B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7112254B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2022-08-03 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor module and communication method using semiconductor module |
| JP2019219619A (en) | 2018-06-22 | 2019-12-26 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2020086046A (en) | 2018-11-21 | 2020-06-04 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor module and manufacturing method of the same, and communication method using semiconductor module |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4905252B2 (en) * | 2007-05-23 | 2012-03-28 | 日立電線株式会社 | Optical communication module |
| US20100034497A1 (en) * | 2008-08-05 | 2010-02-11 | Fujitsu Limited | Flexible Optical Pillars for an Optical Assembly |
| JP6461786B2 (en) * | 2013-03-29 | 2019-01-30 | アイオーコア株式会社 | Opto-electric hybrid device and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2016002712A1 (en) * | 2014-07-04 | 2016-01-07 | 技術研究組合光電子融合基盤技術研究所 | Optical-device manufacturing method and optical device |
-
2016
- 2016-02-22 JP JP2016030997A patent/JP6602687B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017151146A (en) | 2017-08-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6461786B2 (en) | Opto-electric hybrid device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN103069563B (en) | Method for producing at least one optoelectronic semiconductor component | |
| US20080311707A1 (en) | Process for producing a functional device-mounted module | |
| JP5746919B2 (en) | Semiconductor package | |
| EP1022822A1 (en) | Optical module and method of manufacture thereof | |
| US11611004B2 (en) | Opto-electronic integrated circuit and computing apparatus | |
| TW200409988A (en) | Optical sub-assembly packaging techniques that incorporate optical lenses | |
| JP6602687B2 (en) | Opto-electric hybrid device | |
| JP2011113039A (en) | Optical waveguide device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP3729240B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of optical module | |
| JP2013120821A (en) | Light-emitting device | |
| JP5849220B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP5029343B2 (en) | Optical substrate manufacturing method | |
| JP2013057720A (en) | Optical module | |
| JP5550535B2 (en) | Optical waveguide device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4782522B2 (en) | Optical functional device package and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US10681811B2 (en) | Connecting optical sub-assembly to main printed circuit board | |
| JP2010050443A (en) | Lens support, and wire-bond protector | |
| JPH0778953A (en) | Solid state image sensor | |
| JP5104039B2 (en) | Optical substrate manufacturing method | |
| JP2010152075A (en) | Optical transmission apparatus | |
| WO2020022428A1 (en) | Optical waveguide member connector and method therefor | |
| JP7372754B2 (en) | Optical/electrical hybrid board | |
| JP2005094701A (en) | Semiconductor device, manufacturing method for the semiconductor device, image reading unit and image forming apparatus having the device | |
| WO2010143389A1 (en) | Semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180904 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190711 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190718 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190906 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20191001 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20191009 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6602687 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |