JP6137955B2 - Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device - Google Patents
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6137955B2 JP6137955B2 JP2013125986A JP2013125986A JP6137955B2 JP 6137955 B2 JP6137955 B2 JP 6137955B2 JP 2013125986 A JP2013125986 A JP 2013125986A JP 2013125986 A JP2013125986 A JP 2013125986A JP 6137955 B2 JP6137955 B2 JP 6137955B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- silicon carbide
- carbide semiconductor
- recess
- electrode
- semiconductor substrate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 185
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims description 181
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 180
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 11
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 11
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 81
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 20
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 12
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003763 carbonization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/872—Schottky diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66053—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having a semiconductor body comprising crystalline silicon carbide
- H01L29/6606—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having a semiconductor body comprising crystalline silicon carbide the devices being controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched, e.g. two-terminal devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/1608—Silicon carbide
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Drying Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Description
本発明は、炭化ケイ素を用いた炭化ケイ素半導体装置及び炭化ケイ素半導体装置の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a silicon carbide semiconductor device using silicon carbide and a method for manufacturing the silicon carbide semiconductor device.
従来から炭化ケイ素(SiC)を用いた炭化ケイ素半導体装置が知られている。このような炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、炭化ケイ素半導体基板の厚みを薄くすることは、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減するのに非常に有効である。 Conventionally, a silicon carbide semiconductor device using silicon carbide (SiC) is known. In such a silicon carbide semiconductor device, reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate is very effective in reducing the ON resistance of the silicon carbide semiconductor device.
この点、従来から半導体装置の基板の下面(裏面)をバックグラインド、メカニカルポリッシュ等によって研削することは知られている。例えば特許文献1では、所定の深さに埋設された複数の埋め込み電極を備えた半導体ウエーハの下面を研削して、全ての埋め込み電極をウエーハの下面に表出させるウエーハの研削方法が開示されている。 In this regard, it is conventionally known that the lower surface (back surface) of a substrate of a semiconductor device is ground by back grinding, mechanical polishing, or the like. For example, Patent Document 1 discloses a wafer grinding method in which the lower surface of a semiconductor wafer having a plurality of embedded electrodes embedded at a predetermined depth is ground so that all embedded electrodes are exposed on the lower surface of the wafer. Yes.
しかしながら、炭化ケイ素は硬くて脆く、バックグラインド、メカニカルポリッシュ等の研削によって炭化ケイ素半導体基板10を薄くすると、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面の縁に非常に破損しやすいナイフ形状のエッジ(以下「ナイフエッジ」という。)が形成されてしまい(図9参照)、このようなナイフエッジが破損されてしまうことがある。また、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10全体を薄くすると、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の反り量が大きくなってしまう。
However, silicon carbide is hard and brittle, and when the silicon
本発明は、このような点を鑑みてなされたものであり、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減しつつ、炭化ケイ素半導体基板の強度を高くし、さらに当該炭化ケイ素半導体基板に反りが発生することも防止することができる炭化ケイ素半導体装置及び炭化ケイ素半導体装置の製造方法を提供する。 The present invention has been made in view of such points, and while reducing the ON resistance of the silicon carbide semiconductor device, the strength of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate is increased, and further, warpage occurs in the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate. The present invention also provides a silicon carbide semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the silicon carbide semiconductor device.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置は、
炭化ケイ素半導体基板と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板上に形成された炭化ケイ素半導体層と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体層上に設けられた電極と、
を備え、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面であって前記電極の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定して、レーザー光を照射することによって形成された複数の凹部を有する凹部郡が設けられている。
A silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention includes:
A silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
A silicon carbide semiconductor layer formed on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
An electrode provided on the silicon carbide semiconductor layer;
With
A recess group having a plurality of recesses formed by irradiating a laser beam is provided only on a lower surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and including a region below the vertical direction of the electrode.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
複数の凹部郡及び複数の電極が設けられ、
各凹部郡は、各電極の鉛直方向下方に設けられていてもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
A plurality of recesses and a plurality of electrodes are provided;
Each recess group may be provided vertically below each electrode.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記凹部郡の各凹部は、水平方向において格子状に設けられていてもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
Each recessed part of the said recessed part group may be provided in the grid | lattice form in the horizontal direction.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記凹部郡の各凹部は、水平方向においてハニカム構造で設けられていてもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
Each recess of the recess group may be provided with a honeycomb structure in the horizontal direction.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置では、
前記凹部郡において、前記電極の中心側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅は、前記電極の周縁側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅よりも大きくなってもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
In the recess group, the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the center side of the electrode may be larger than the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the peripheral side of the electrode.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置では、
前記凹部郡において、前記電極の周縁側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅は、前記電極の中心側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅よりも大きくなってもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
In the recess group, the width in the horizontal direction of the recess positioned on the peripheral side of the electrode may be larger than the width in the horizontal direction of the recess positioned on the center side of the electrode.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記凹部の縦断面形状はU字形状になってもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
The vertical cross-sectional shape of the recess may be U-shaped.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記凹部は、前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板内に形成され、その上端が前記炭化ケイ素半導体層に達していなくてもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
The recess may be formed in the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate, and an upper end thereof may not reach the silicon carbide semiconductor layer.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記レーザー光のエネルギーは、0.5J/cm2以上であってもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
The energy of the laser beam may be 0.5 J / cm 2 or more.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置において、
前記レーザー光によって、前記凹部の露出面に炭素の導電層が形成されてもよい。
In the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention,
A carbon conductive layer may be formed on the exposed surface of the recess by the laser beam.
本発明による炭化ケイ素半導体装置の製造方法は、
炭化ケイ素半導体基板上に炭化ケイ素半導体層を形成する工程と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体層上に電極を設ける工程と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面であって前記電極の鉛直方向下方又は前記電極の配置予定箇所の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定してレーザー光を照射することで複数の凹部を有する凹部郡を形成する工程と、
を備える。
A method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention includes:
Forming a silicon carbide semiconductor layer on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
Providing an electrode on the silicon carbide semiconductor layer;
A recess group having a plurality of recesses is formed by irradiating a laser beam limited to a region on the lower surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and including a region below the electrode in the vertical direction or a region below the electrode in the vertical direction. And a process of
Is provided.
本発明によれば、電極の鉛直方向下方に複数の凹部を有する凹部郡が設けられている。このため、電極の鉛直方向下方における炭化ケイ素半導体基板の厚みを部分的に薄くすることができ、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減することができる。 According to the present invention, a recess group having a plurality of recesses is provided below the electrodes in the vertical direction. For this reason, the thickness of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate below the electrodes in the vertical direction can be partially reduced, and the ON resistance of the silicon carbide semiconductor device can be reduced.
また、本発明では、凹部郡の凹部がレーザー光を用いて形成されるので、バックグラインド、メカニカルポリッシュ等による研削と異なり、炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面にナイフエッジが形成されてしまうことがなく、炭化ケイ素半導体基板の強度を高いものにすることができる。さらに、炭化ケイ素半導体基板全体を薄くすることなく電極の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定して凹部郡を設けるので、炭化ケイ素半導体基板に反りが発生することも防止することができる。 Further, in the present invention, since the recess of the recess group is formed using laser light, unlike the grinding by back grinding, mechanical polishing, etc., the knife edge is not formed on the lower surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate, The strength of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate can be increased. Furthermore, since the recess group is provided only in the region including the lower part in the vertical direction of the electrode without thinning the entire silicon carbide semiconductor substrate, it is possible to prevent the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate from being warped.
第1の実施の形態
《構成》
以下、本発明に係る炭化ケイ素半導体装置(SiC半導体装置)及び炭化ケイ素半導体装置の製造方法の実施の形態について、図面を参照して説明する。ここで、図1乃至図6は本発明の第1の実施の形態を説明するための図である。本発明の炭化ケイ素半導体装置は特に限定されることはないが、例えばショットキーバリアダイオード(SBD)やMOSFET等である。以下では、半導体装置としてショットキーバリアダイオードを用いて説明するが、このショットキーバリアダイオードはあくまでも半導体装置の一例に過ぎない点には留意が必要である。
First Embodiment << Configuration >>
Hereinafter, embodiments of a silicon carbide semiconductor device (SiC semiconductor device) and a method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Here, FIG. 1 to FIG. 6 are diagrams for explaining a first embodiment of the present invention. Although the silicon carbide semiconductor device of this invention is not specifically limited, For example, it is a Schottky barrier diode (SBD), MOSFET, etc. Hereinafter, a Schottky barrier diode will be described as a semiconductor device. However, it should be noted that this Schottky barrier diode is merely an example of a semiconductor device.
図1に示すように、本実施の形態の炭化ケイ素半導体装置は、炭化ケイ素半導体基板(SiC半導体基板)10と、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10上に形成された炭化ケイ素半導体層(SiC半導体層)20と、炭化ケイ素半導体層20上に設けられたショットキー電極(特許請求の範囲で記載された「電極」に対応する。)50と、を備えている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the silicon carbide semiconductor device of the present embodiment includes a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate (SiC semiconductor substrate) 10 and a silicon carbide semiconductor layer (SiC semiconductor layer) 20 formed on the silicon
より具体的には、本実施の形態の半導体装置は、高濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板(第1導電型炭化ケイ素半導体基板)10と、高濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10上に形成された低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層(第1導電型炭化ケイ素半導体層)20と、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20内にリング状で形成されたp型の炭化ケイ素半導体層(第2導電型炭化ケイ素半導体層)30と、を備えている。なお、n型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10は、上面(以下「表面」とも言う。)と、当該上面に背向する下面(以下「裏面」とも言う。)とを有しており、n型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の表面側に上述した低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20が形成されている。また、図2に示すように、n型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の裏面側には、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の裏面の形状に沿ったオーミック電極80が形成される。図示しないが、このオーミック電極80には、はんだ、Al等を介して半導体チップが実装される。なお、図1ではこのオーミック電極80は示されていない。
More specifically, the semiconductor device of the present embodiment includes a high concentration n-type silicon carbide semiconductor substrate (first conductivity type silicon carbide semiconductor substrate) 10 and a high concentration n-type silicon
図2に示すように、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20及びp型の炭化ケイ素半導体層30の上には、これらに跨がってショットキー電極50が設けられている。そして、このショットキー電極50上には引き出し電極55が設けられている。また、ショットキー電極50及び引き出し電極55を取り囲むようにして、リング状で絶縁層60が設けられている。なお、ショットキー電極50の材料としては、例えばTi、Mo、Ni等を挙げることができる。引き出し電極55の材料としては、例えばAl、Ni、Au等を挙げることができる。絶縁層60の材料としては、例えば酸化珪素、窒化珪素、ポリイミド等を挙げることができる。
As shown in FIG. 2, a
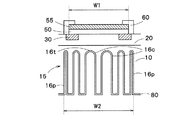
n型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10のうち後述する凹部16が形成されている箇所の厚みは例えば約250μmであり、ショットキー電極50及び引き出し電極55を含んだ炭化ケイ素半導体装置の厚みは例えば約350μmである。このため、この例で言うと、凹部16の深さは約100μmとなっている。
The thickness of the n-type silicon
炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面であってショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定して、レーザー光Lを照射することによって形成された複数の凹部16を有する凹部郡15が設けられている。なお、本実施の形態で用いられるレーザー光Lのエネルギーは、例えば0.5J/cm2以上となっている。また、本実施の形態における凹部16の露出面には、レーザー光Lによってケイ素(Si)が飛び炭素(C)の導電層が形成されている。これは、一般にケイ素の方が炭素よりも飛びやすいことに由来している。すなわち、レーザー光Lを用いて凹部16を形成すると、炭素とケイ素が飛んでいくが、最終的に形成される表面ではケイ素が飛んだ後の炭素によって導体層が形成されることとなる。
A
ちなみに、レーザー光Lは例えば50μmのスポットで照射され、一つのスポットによって又は各スポットを重なり合わせつつずらすことで、凹部16が形成される。また、レーザー光Lの波長は例えば555nm以下となっている。本願発明者による実験によれば、555nmよりもレーザー光Lの波長が長いと炭化ケイ素半導体基板10をレーザー光が透過してしまい炭化ケイ素半導体基板10に凹部16を形成することができなかったが、レーザー光Lの波長が555nm以下となっている場合には、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10に凹部16を形成することができた。なお、このような波長のレーザー光としては、グリーンレーザー(波長は約532nm)やエキシマレーザー等を用いることができる。一般にグリーンレーザー等の波長が長いレーザー光(例えば400nm以上の波長のレーザー光)を照射する機械は低額であることから、このようなレーザー光によって凹部16を形成する場合には低額な機械で処理することができる点で有益である。
Incidentally, the laser beam L is irradiated with a spot of, for example, 50 μm, and the
凹部郡15の各凹部16は様々な配置及び形状で設けることができるが、その一例としては、図4に示すように、各凹部16が水平方向において格子状に設けられているものを挙げることができる。また、このような態様とは異なり、別の例としては、図5に示すように、凹部郡15の各凹部16が水平方向においてハニカム構造(蜂の巣形状)で設けられているものを挙げることができる。
The
上述したように、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の裏面側にはオーミック電極80が形成されている。そして、このオーミック電極80の材料としては、例えばNi、Mo等を挙げることができる。ちなみに、炭化ケイ素は熱伝導性が高く放熱性に優れており、銅等と同程度の熱伝導性を有し、はんだ、Ni、Al等よりも高い熱伝導性を有している。
As described above, the
図2に示すように、凹部郡15の水平方向の幅W2はショットキー電極50の水平方向の幅W1よりも大きくなっている。また、本実施の形態の炭化ケイ素半導体装置には、複数の凹部郡15及び複数のショットキー電極50が設けられている(図1参照)。そして、各凹部郡15は各ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方に設けられており、ショットキー電極50と凹部郡15とが一対一の関係で形成されている。なお、本実施の形態の凹部16は、その縦断面形状がU字形状になっている。ちなみに、本実施の形態では、図2に示すように、凹部郡15において、各凹部16の水平方向における幅が均一となり、同じ長さとなっている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the horizontal width W2 of the
図2に示すように、本実施の形態の凹部16は、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10内に形成されているが、その上端16tはn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20に達していない。すなわち、凹部16の上端16tは、鉛直方向において、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20の下端よりも下方に位置している。
As shown in FIG. 2,
ちなみに、本実施の形態の図面では、各凹部16が同じ深さとなっており態様を用いているが、これに限られることはなく、凹部16の深さは異なっていてもよい。一例としては、電極の中心側に位置する凹部16の深さが、電極の周縁側に位置する凹部16の深さよりも深くなり、電極の中心側に位置する凹部16の上端と炭化ケイ素半導体層20の下端との間の距離が電極の周縁側に位置する凹部16の上端と炭化ケイ素半導体層20の下端との間の距離よりも短くなっていてもよい。また、このような態様と異なり、電極の周縁側に位置する凹部16の深さが、電極の中心側に位置する凹部16の深さよりも深くなり、電極の周縁側に位置する凹部16の上端と炭化ケイ素半導体層20の下端との間の距離が電極の中心側に位置する凹部16の上端と炭化ケイ素半導体層20の下端との間の距離よりも短くなっていてもよい。
Incidentally, in the drawing of the present embodiment, each
《製造工程》
次に、上述した構成からなる本実施の形態の半導体装置の製造工程について、主に図3を用いて説明する。
"Manufacturing process"
Next, the manufacturing process of the semiconductor device of the present embodiment having the above-described configuration will be described mainly with reference to FIG.
まず、高濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10を準備する(図3(a)参照)。
First, a high concentration n-type silicon
次に、高濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体基板10上に、エピタキシャル成長によって低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20を形成する(図3(a)参照)。この低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20は、耐圧を確保するのに必要な不純物濃度及び厚さになっている。
Next, a low-concentration n-type silicon
次に、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20上に、AlやB等をイオン注入し、例えば1500℃以上の加熱処理を施すことでp型の炭化ケイ素半導体層30を形成する(図3(b)参照)。より具体的には、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20の表面にSiO2をCVDによって堆積する。次いで、SiO2上にフォトレジストを形成し、そのフォトレジストのうちp型の炭化ケイ素半導体層30の形成位置に対応する部分を除去する。この状態でエッチング処理を施すことで、p型の炭化ケイ素半導体層30の形成位置に対応する部分のSiO2を除去し、その部分の低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20を露出させる。その後、残りのフォトレジストを除去する。その後、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20の露出部位から例えばAlやB等をイオン注入する。そして、残りのSiO2を除去した後で、1500℃以上の熱処理を施すことで、注入された不純物を活性化する。
Next, Al, B, or the like is ion-implanted on the low-concentration n-type silicon
次に、低濃度のn型の炭化ケイ素半導体層20及びp型の炭化ケイ素半導体層30の上に、これらに跨がってTi、Mo、Ni等からなるショットキー電極50が、例えばスパッタ法によって設けられる(図3(c)参照)。
Next, a
次に、ショットキー電極50上に、Al、Ni、Au等からなる引き出し電極55が設けられる(図3(c)参照)。
Next, an
次に、ショットキー電極50及び引き出し電極55を取り囲むようにして、酸化珪素、窒化珪素、ポリイミド等からなる絶縁層60が設けられる(図3(c)参照)。
Next, an insulating
上述のようにして、ショットキー電極50、引き出し電極55及び絶縁層60が設けられた後又は設けられる前に、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面(すなわち裏面)であってショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方又はショットキー電極50の配置予定箇所の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定してレーザー光Lを照射することで複数の凹部16を有する凹部郡15が形成される(図3(d)参照)。なお、図3に示す態様では、ショットキー電極50、引き出し電極55及び絶縁層60が設けられた後で、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の裏面にレーザー光Lが照射されて、凹部郡15が形成されている。また、照射されるレーザー光Lのエネルギーは例えば0.5J/cm2以上となっている。
As described above, after or before the
このようにして形成される凹部郡15内の凹部16の配置及び形状の一例としては、各凹部16が水平方向において格子状に設けられているものを挙げることができ(図4参照)、また別の例としては、凹部郡15の各凹部16が水平方向においてハニカム構造(蜂の巣形状)で設けられているものを挙げることができる(図5参照)。
As an example of the arrangement and shape of the
このようにして形成される凹部郡15の水平方向の幅W2はショットキー電極50の水平方向の幅W1よりも大きくなっている(図2参照)。また、各凹部16の縦断面形状はU字形状になっている。また、凹部16は、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10内に形成されており、その上端16tが炭化ケイ素半導体層20に達していない(図2参照)。
The horizontal width W2 of the
各凹部郡15は各ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方に対応して形成され、ショットキー電極50と凹部郡15とが一対一の関係で形成される(図1参照)。ちなみに、凹部16の露出面には炭素(C)の導電層が形成されることとなる。
Each
次に、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面(裏面)にオーミック電極80が形成される(図3(e)参照)。より具体的には、Ni、Mo等の金属を炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面(裏面)に蒸着させたり、Ni、Mo等の金属で炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面(裏面)をメッキしたりし、その後、例えば真空中において1000度程度の温度で2分間の加熱処理が行われることで、オーミック電極80が形成される。その後、オーミック電極80に、はんだ等を介して半導体チップが実装される。
Next,
《効果》
次に、上述した構成からなる本実施の形態による効果について説明する。
"effect"
Next, effects of the present embodiment configured as described above will be described.
本実施の形態によれば、ショットキー電極(電極)50の鉛直方向下方に複数の凹部16を有する凹部郡15が設けられている(図1及び図2参照)。このため、ショットキー電極(電極)50の鉛直方向下方における炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みを部分的に薄くすることができ、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減することができる。
According to the present embodiment, the
なお、本実施の形態では、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方に炭化ケイ素半導体基板10が残っている箇所があるため、このように炭化ケイ素半導体基板10が残っている箇所ではオーミック電極80、はんだ等の金属と比較して電気伝導性が小さくなってしまう。しかしながら、炭化ケイ素は熱伝導性が高く放熱性に優れるため、熱を持つことで電気抵抗が上昇することを防止することができる。
In the present embodiment, since there is a portion where silicon
このため、本実施の形態では、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方における炭化ケイ素半導体基板の厚みを部分的に薄くすることと、発生する熱で電気抵抗が上昇することを防止することの組み合わせによって、ON抵抗を低減することができる。
For this reason, in the present embodiment, a combination of partially reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate below the
また、このような凹部郡15の凹部16がレーザー光Lを用いて形成されるので、バックグラインド、メカニカルポリッシュ等による研削と異なり、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面にナイフエッジが形成されてしまうことがなく、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の強度を高いものにすることができる。さらに、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10全体を薄くすることなく、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定して凹部郡15を設けるので、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10に反りが発生することも防止することができる。
In addition, since the
これらの点について説明する。 These points will be described.
炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みを薄くすることは、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減するのに非常に有効である。しかしながら、炭化ケイ素は硬くて脆く、バックグラインド、メカニカルポリッシュ等の研削によって薄くすると、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面の縁に非常に破損しやすいナイフエッジが形成されてしまい、このようなナイフエッジが破損されてしまうことがある(図9参照)。また、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10全体を薄くすると、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の反り量が大きくなってしまう。
Reducing the thickness of the silicon
この点、本実施の形態では、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方を含む領域に限定して炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みを薄くすることから、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10に反りが発生することも防止することができる。
In this regard, in the present embodiment, since the thickness of the silicon
また、凹部16がレーザー光Lを用いて形成されるので、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面にナイフエッジが形成されてしまうことがなく、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の強度を高いものにすることができる。ちなみに、レーザー光を用いずに物理的に研鑽する等して凹部を形成した場合には炭化ケイ素半導体基板10にダメージ層ができてしまうが、本実施の形態では、このようなダメージ層が生成されることを防止することもできる。
Further, since
本実施の形態では、凹部郡15の水平方向の幅W2がショットキー電極50の水平方向の幅W1よりも大きくなっている(図2参照)。このため、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方の全体にわたって断続的に凹部16を形成し、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みを断続的に薄くすることができる。ちなみに、ショットキー電極50等の電極から炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の下面(裏面)に向かって流れる電流は一定の広がりを持つことから、凹部郡15の水平方向の幅W2がショットキー電極50の水平方向の幅W1と等しくなっているのではなく、凹部郡15の水平方向の幅W2がショットキー電極50の水平方向の幅W1よりも大きくなっている方が好ましい。
In the present embodiment, the horizontal width W2 of the
また、本実施の形態では、各凹部郡15が各ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方に設けられており、各ショットキー電極50に対応して各凹部郡15が設けられている(図1参照)。このため、ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方において炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みが断続的に薄くなっていない箇所がなく、各ショットキー電極50の鉛直方向下方で炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みが断続的に薄くなっているので、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗をより確実に低減することができる。また、ショットキー電極50が設けられていない箇所の鉛直下方に凹部16が設けられていないことから、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10の厚みが薄くなる箇所を極力少なくすることができ、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10に反りが発生することを極力防止することができる。
In the present embodiment, each
また、本実施の形態では、凹部16の縦断面形状がU字形状になっており、凹部16が角張った形状となっていない(図1及び図2参照)。この点、凹部が角張った形状となっている場合には、蒸着処理、メッキ処理、ダイボンド処理等を行う際に上端の角に金属がつきにくいこと等で不都合が発生しうるが、本実施の形態のように凹部16の縦断面形状がU字形状になっている場合には、このように金属がつきにくい状況が生じることを防止することができる。
Moreover, in this Embodiment, the longitudinal cross-sectional shape of the recessed
また、本実施の形態では、凹部16が炭化ケイ素半導体基板10内に形成され、その上端16tが炭化ケイ素半導体層20に達していない(図2参照)。このため、耐圧を確保するための炭化ケイ素半導体層20が薄くなることを防止することができ、ひいては、高い耐圧を維持することができる。
Moreover, in this Embodiment, the recessed
ちなみに、凹部16内にはNi等の金属でオーミック電極80が形成された後で、はんだ等が入り込むことになるが、炭化ケイ素は、これらNi及びはんだよりも熱伝導性が高いことから、炭化ケイ素半導体基板10を介して熱を逃がすことができる。
Incidentally, after the
変形例
上述した実施の形態では、凹部16の縦断面形状がU字形状になっている態様を用いて説明した。しかしながら、この態様はあくまでも一例であり、別の態様も用いることができる。別の態様の一例としては、図6に示すように、凹部16’の縦断面形状が矩形状になっているものを挙げることができる。ちなみに、図6において「16’t」は、凹部16’の上端を示している。
Modification In the above-described embodiment, the description has been made using the aspect in which the vertical cross-sectional shape of the
このような変形例による矩形状の凹部16’では、ショットキー電極50(電極)の鉛直方向下方を均一に薄くすることができるので、炭化ケイ素半導体装置のON抵抗を低減することを期待できる。
In the
第2の実施の形態
次に、本発明の第2の実施の形態について説明する。
Second Embodiment Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
第1の実施の形態では、凹部郡15において、各凹部16の水平方向における幅が均一となっている態様であったが、第2の実施の形態では、凹部郡15において、各凹部16の水平方向における幅が異なる態様となっている。
In the first embodiment, the width in the horizontal direction of each
第2の実施の形態において、その他の構成は、第1の実施の形態と略同一の態様となっている。第2の実施の形態において、第1の実施の形態と同一部分には同一符号を付して詳細な説明は省略する。 In the second embodiment, other configurations are substantially the same as those in the first embodiment. In the second embodiment, the same parts as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof is omitted.
本実施の形態でも、第1の実施の形態と同様の効果を奏することができる。第1の実施の形態で詳細に説明したことから、本実施の形態における効果の説明は、本実施の形態において固有な部分についてのみ行う。 Also in this embodiment, the same effects as those of the first embodiment can be obtained. Since it has been described in detail in the first embodiment, the description of the effects in this embodiment will be made only for the parts unique to this embodiment.
本実施の形態の第一の態様としては、図7に示すように、凹部郡15において、ショットキー電極(電極)50の中心側に位置する凹部16cの水平方向における幅が、ショットキー電極50の周縁側に位置する凹部16pの水平方向における幅よりも大きくなっている。より具体的には、ショットキー電極50の中心部の最も近くに位置する凹部16cの水平方向における幅が、ショットキー電極50の周縁部の最も近くに位置する凹部16pの水平方向における幅よりも大きくなっている。なお、図7に示した態様では、ショットキー電極50の中心部から周縁部に向かうにつれて凹部16の幅が段階的に狭くなっている。
As a first aspect of the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7, in the
このような態様によれば、凹部16内に埋設されるオーミック電極80やはんだ等の金属の量をショットキー電極50の鉛直下方の中心部側で多くし、ショットキー電極50の鉛直下方の周縁部側で少なくすることができ、電流を凹部郡15の中心部側に集中させることができる。
According to such an aspect, the amount of metal such as the
本実施の形態の第二の態様としては、図8に示すように、凹部郡15において、ショットキー電極50の周縁側に位置する凹部16pの水平方向における幅が、ショットキー電極50の中心側に位置する凹部16cの水平方向における幅よりも大きくなっている。より具体的には、ショットキー電極50の周縁部の最も近くに位置する凹部16pの水平方向における幅が、ショットキー電極50の中心部の最も近くに位置する凹部16cの水平方向における幅よりも大きくなっている。なお、図8に示した態様では、ショットキー電極50の中心部から周縁部に向かうにつれて凹部16の幅が段階的に広くなっている。
As a second mode of the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 8, in the
このような態様によれば、凹部16内に埋設されるオーミック電極80やはんだ等の金属の量をショットキー電極50の鉛直下方の周縁部側で多くし、ショットキー電極50の鉛直下方の中心部側で少なくすることができ、電流を凹部郡15の周縁部側に集中させることができる。
According to such an aspect, the amount of the metal such as the
なお、上述した第一の態様と第二の態様のいずれを用いるかは、炭化ケイ素半導体装置の設計次第である。一般に、温度が高くなった状態で電流が集中すると炭化ケイ素半導体装置が壊れてしまうことから、温度が高くなった状態において電流を逃がすことができる構造が好ましい。上述したように、第一の態様によれば、電流を凹部郡15の中心部側に集中させることができる。他方、第二の態様によれば、電流を凹部郡15の周縁部側に集中させることができる。この点、温度が高くなった状態で電流を逃がすために、電流を凹部郡15の中心部側に集中させた方がよいか、又は、電流を凹部郡15の周縁部側に集中させた方がよいかは炭化ケイ素半導体装置の設計の仕方によって左右されることから、一概に言えない。このため、炭化ケイ素半導体装置の設計内容に応じて、電流を凹部郡15の中心部側に集中させるか電流を凹部郡15の周縁部側に集中させることを選択し、適宜、温度が高くなった状態において電流を逃がすことで、炭化ケイ素半導体装置が破壊されることを防止することができる。
Note that whether to use the first aspect or the second aspect described above depends on the design of the silicon carbide semiconductor device. In general, a silicon carbide semiconductor device is broken when a current is concentrated in a state where the temperature is high. Therefore, a structure that can release a current in a state where the temperature is high is preferable. As described above, according to the first aspect, the current can be concentrated on the central portion side of the
最後になったが、上述した各実施の形態の記載、変形例の記載及び図面の開示は、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明を説明するための一例に過ぎず、上述した実施の形態の記載又は図面の開示によって特許請求の範囲に記載された発明が限定されることはない。 Lastly, the description of each embodiment described above, the description of modified examples, and the disclosure of the drawings are merely examples for explaining the invention described in the claims, and the description of the embodiment described above. The invention described in the scope of claims is not limited by the disclosure of the description or the drawings.
10 炭化ケイ素半導体基板
15 凹部郡
16 凹部
16’ 凹部
16t 凹部の上端
16’t 凹部の上端
16p 周縁側に位置する凹部
16c 中心側に位置する凹部
20 n型の炭化ケイ素半導体層
30 p型の炭化ケイ素半導体層
50 ショットキー電極(電極)
L レーザー光
W1 ショットキー電極の水平方向の幅
W2 凹部郡の水平方向の幅
DESCRIPTION OF
L Laser light W1 Horizontal width W2 of Schottky electrode Horizontal width of recess group
Claims (10)
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板上に形成された炭化ケイ素半導体層と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体層上に設けられた電極と、
を備え、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面であって前記電極の鉛直方向下方に、複数の凹部を有する凹部郡が設けられており、
前記凹部郡において、前記電極の中心側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅は、前記電極の周縁側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅よりも大きいことを特徴とする炭化ケイ素半導体装置。 A silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
A silicon carbide semiconductor layer formed on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
An electrode provided on the silicon carbide semiconductor layer;
With
A recess group having a plurality of recesses is provided on the lower surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and below the electrodes in the vertical direction ,
In the recess group, the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the center side of the electrode is larger than the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the peripheral side of the electrode .
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板上に形成された炭化ケイ素半導体層と、A silicon carbide semiconductor layer formed on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
前記炭化ケイ素半導体層上に設けられた電極と、An electrode provided on the silicon carbide semiconductor layer;
を備え、With
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面であって前記電極の鉛直方向下方に、複数の凹部を有する凹部郡が設けられており、A recess group having a plurality of recesses is provided on the lower surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and below the electrodes in the vertical direction,
前記凹部郡において、前記電極の周縁側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅は、前記電極の中心側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅よりも大きいことを特徴とする炭化ケイ素半導体装置。In the recess group, the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the peripheral side of the electrode is larger than the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the center side of the electrode.
各凹部郡は、各電極の鉛直方向下方に設けられていることを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の炭化ケイ素半導体装置。 A plurality of recesses and a plurality of electrodes are provided;
3. The silicon carbide semiconductor device according to claim 1 , wherein each of the concave groups is provided vertically below each electrode.
前記炭化ケイ素半導体層上に電極を設ける工程と、
前記炭化ケイ素半導体基板の下面であって前記電極の鉛直方向下方にレーザー光を照射することで複数の凹部を有する凹部郡を形成する工程と、
を備え、
前記凹部郡において、前記電極の中心側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅は、前記電極の周縁側に位置する凹部の水平方向における幅よりも大きいことを特徴とする炭化ケイ素半導体装置の製造方法。 Forming a silicon carbide semiconductor layer on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate;
Providing an electrode on the silicon carbide semiconductor layer;
Forming a recess gun having a plurality of recesses by irradiating vertically below the laser beam of the said electrode is formed on the bottom surface of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate,
Equipped with a,
The method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device characterized in that, in the recess group, the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the center side of the electrode is larger than the width in the horizontal direction of the recess located on the peripheral side of the electrode. .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013125986A JP6137955B2 (en) | 2013-06-14 | 2013-06-14 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013125986A JP6137955B2 (en) | 2013-06-14 | 2013-06-14 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015002259A JP2015002259A (en) | 2015-01-05 |
| JP6137955B2 true JP6137955B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 |
Family
ID=52296601
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013125986A Active JP6137955B2 (en) | 2013-06-14 | 2013-06-14 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6137955B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6812758B2 (en) * | 2016-11-09 | 2021-01-13 | Tdk株式会社 | Schottky barrier diode and electronic circuit equipped with it |
| CN111477545B (en) * | 2020-04-09 | 2021-06-22 | 浙江大学 | GaN device SiC substrate etching method |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6104062A (en) * | 1998-06-30 | 2000-08-15 | Intersil Corporation | Semiconductor device having reduced effective substrate resistivity and associated methods |
| JP2003303966A (en) * | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2010103208A (en) * | 2008-10-22 | 2010-05-06 | Denso Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP5482107B2 (en) * | 2009-10-30 | 2014-04-23 | 株式会社デンソー | Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device |
-
2013
- 2013-06-14 JP JP2013125986A patent/JP6137955B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015002259A (en) | 2015-01-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5724887B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US9240451B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP6540585B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP6566812B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6004561B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor element | |
| JP6477106B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US9384981B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP6261155B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing SiC semiconductor device | |
| JP6705155B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2010205824A (en) | Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP2017011060A (en) | Schottky barrier diode | |
| JP5735077B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| JP2014078660A (en) | Wide gap semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2014229843A (en) | Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device and silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP2011165880A (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| WO2017033216A1 (en) | Wide-gap semiconductor device and method for manufacturing wide-gap semiconductor device | |
| JP2019050362A (en) | Silicon carbide component and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP6137955B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP2014017325A (en) | Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method | |
| JP2015070191A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP6068918B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6309211B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP2011198780A (en) | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2014241345A (en) | Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| US9887086B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing a wide bandgap junction barrier schottky diode |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160108 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20161122 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170110 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170328 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170425 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6137955 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |