JP6025203B2 - Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance - Google Patents
Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6025203B2 JP6025203B2 JP2013034704A JP2013034704A JP6025203B2 JP 6025203 B2 JP6025203 B2 JP 6025203B2 JP 2013034704 A JP2013034704 A JP 2013034704A JP 2013034704 A JP2013034704 A JP 2013034704A JP 6025203 B2 JP6025203 B2 JP 6025203B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- balance
- temperature
- electroforming
- bimetal
- compensated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 51
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 34
- 238000005323 electroforming Methods 0.000 claims description 67
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910000990 Ni alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910001128 Sn alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- GEIAQOFPUVMAGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ZrO Inorganic materials [Zr]=O GEIAQOFPUVMAGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910003465 moissanite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 27
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 27
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 22
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 20
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 17
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 17
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 15
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000708 deep reactive-ion etching Methods 0.000 description 4
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 4
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OPPGAHUCKDKQJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Coelonin Natural products C1CC2=CC(O)=CC=C2C2=C1C=C(O)C=C2OC OPPGAHUCKDKQJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000003423 ankle Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007429 general method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000623 plasma-assisted chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000942 Elinvar Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001374 Invar Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910003271 Ni-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910020888 Sn-Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910019204 Sn—Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002788 crimping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021397 glassy carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002210 silicon-based material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Micromachines (AREA)
Description
本発明は、温度補償型てんぷ、時計用ムーブメント、機械式時計、及び温度補償型てんぷの製造方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a temperature-compensated balance, a timepiece movement, a mechanical timepiece, and a method for producing a temperature-compensated balance.
機械式時計の調速機としては、一般的にてんぷ及びひげぜんまいで構成されている。このうちてんぷは、てん真の回転軸回りに周期的に正逆回転して振動する部材であり、その振動周期は予め決められた規定値内に設定されていることが重要とされている。仮に、振動周期が規定値からずれてしまうと、機械式時計の歩度(時計の遅れ、進みの度合い)が変化するためである。ところが、上記振動周期は各種の原因によって変化し易く、例えば温度変化によっても変化してしまう。
ここで、上記振動周期Tは、次式(1)で表される。
A governor of a mechanical timepiece is generally composed of a balance with a balance and a hairspring. Of these, the balance with hair is a member that vibrates by rotating forward and backward periodically around the true rotation axis, and it is important that the vibration cycle is set within a predetermined value. This is because if the vibration period deviates from the specified value, the rate of the mechanical timepiece (timepiece delay, degree of advancement) changes. However, the vibration cycle is likely to change due to various causes, and for example, changes due to temperature changes.
Here, the vibration period T is expressed by the following equation (1).
上記式(1)において、Iは「てんぷの慣性モーメント」、Kは「ひげぜんまいのばね定数」を示す。従って、てんぷの慣性モーメント、又はひげぜんまいのばね定数が変化すると、振動周期も変化してしまう。
ここで、てんぷに用いられる金属材料としては、一般的に線膨張係数が正の材料とされており、温度上昇によって膨張する。そのため、てん輪が拡径し、慣性モーメントを増加させてしまう。また、ひげぜんまいに一般的に用いられる鋼材料のヤング率は負の温度係数を有しているため、温度上昇によってばね定数を低下させてしまう。
In the above formula (1), I represents “the moment of inertia of the balance”, and K represents “the spring constant of the hairspring”. Therefore, when the moment of inertia of the balance or the spring constant of the hairspring changes, the vibration period also changes.
Here, the metal material used for the balance with hairspring is generally a material having a positive coefficient of linear expansion, and expands as the temperature rises. As a result, the balance wheel expands in diameter and increases the moment of inertia. Moreover, since the Young's modulus of the steel material generally used for the hairspring has a negative temperature coefficient, the spring constant is lowered by the temperature rise.
以上のことにより、温度上昇すると、これに伴って慣性モーメントが増加し且つひげぜんまいのばね定数が低下することとなる。従って、上記式(1)から明らかなように、てんぷの振動周期は、低温で短く、高温で長くなる特性となってしまう。そのため、時計の温度特性としては、低温で進み、高温で遅れるという特性になってしまうものであった。 As described above, when the temperature rises, the moment of inertia increases and the spring constant of the mainspring decreases. Therefore, as apparent from the above formula (1), the vibration period of the balance with hairspring becomes a characteristic that is short at a low temperature and long at a high temperature. For this reason, the time characteristic of the timepiece is such that it proceeds at a low temperature and is delayed at a high temperature.
そこで、てんぷの振動周期の温度特性を改善するための対策として、例えば下記の2つの方法が知られている。
第1の方法としては、てん輪を完全な閉ループをなす円形にする代わりに、てん輪を周方向の二か所で分断して円弧状部とすると共に、各円弧状部を熱膨張率が異なる材料からなる金属板を径方向に接合したバイメタルで形成し、且つ円弧状部の周方向の一端部を固定端、周方向の他端部を自由端とする方法が知られている(特許文献1参照)。
Thus, for example, the following two methods are known as measures for improving the temperature characteristic of the vibration cycle of the balance with hairspring.
As a first method, instead of making the balance wheel into a circular shape that forms a complete closed loop, the balance wheel is divided into two arcuate portions in the circumferential direction, and each arcuate portion has a coefficient of thermal expansion. A method is known in which metal plates made of different materials are formed of bimetals joined in the radial direction, and one end portion in the circumferential direction of the arcuate portion is a fixed end and the other end portion in the circumferential direction is a free end (patent) Reference 1).
通常、上述したように、温度上昇に伴っててん輪は熱膨張により拡径するので、実効的な慣性モーメントを増大させてしまうが、第1の方法によれば、温度上昇時、バイメタルからなる円弧状部は熱膨張率の差により自由端側が径方向の内側に向けて移動するように内向き変形する。これにより、てん輪の平均径を縮径させて、実効的な慣性モーメントを低下させることができ、慣性モーメントの温度特性に負の傾きを持たせることができる。その結果、ひげぜんまいの温度依存性を相殺する程度に慣性モーメントを変化させることができ、てんぷの振動周期の温度依存性を低く抑えることが可能となる。 Normally, as described above, the balance wheel expands due to thermal expansion as the temperature rises, so that the effective moment of inertia increases. However, according to the first method, when the temperature rises, the balance wheel is made of bimetal. The arcuate portion deforms inward so that the free end side moves inward in the radial direction due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficient. As a result, the average diameter of the balance wheel can be reduced, the effective moment of inertia can be reduced, and the temperature characteristic of the moment of inertia can have a negative slope. As a result, the moment of inertia can be changed to such an extent that the temperature dependency of the hairspring can be offset, and the temperature dependency of the vibration cycle of the balance with hairspring can be kept low.
第2の方法としては、ひげぜんまいの材料としてコエリンバー等の恒弾性材料を採用することにより、時計の使用温度範囲(例えば、23℃±15℃)付近でのヤング率の温度係数を正の特性とする方法である。
この第2の方法によれば、上記使用温度範囲内において、てん輪の線膨張係数とひげぜんまいの線膨張係数とを相殺させることで、温度に対するてんぷの慣性モーメントの変化をキャンセルすることができ、てんぷの振動周期の温度依存性を低く抑えることが可能となる。
As a second method, by adopting a constant elastic material such as coelin bar as a material for the hairspring, the temperature coefficient of Young's modulus near the operating temperature range of the watch (for example, 23 ° C. ± 15 ° C.) is positive. It is a method.
According to the second method, the change in the moment of inertia of the balance with respect to the temperature can be canceled by canceling the linear expansion coefficient of the balance wheel and the linear expansion coefficient of the balance spring within the above operating temperature range. The temperature dependency of the vibration cycle of the balance with hairspring can be kept low.
ところで、上記した第1の方法では、熱膨張率が互いに異なる、径方向内側の金属板と径方向外側の金属板とを接合することで、バイメタルの円弧状部を形成するものであるが、その接合方法としてはろう付けや圧着等が挙げられる。ところが、これらの方法では、
そのときの接合条件等によって仕上がりが左右されてしまうので、一定の形状精度を確保することが難しい。しかも、2つの金属板で円弧状部を構成するので、ろう付けや圧着時、又は切断によって各円弧状部を形成する際に、2つの金属板が塑性変形するおそれがあった。
By the way, in the first method described above, the bimetallic arc-shaped portion is formed by joining the radially inner metal plate and the radially outer metal plate having different thermal expansion coefficients. Examples of the joining method include brazing and pressure bonding. However, with these methods,
Since the finish depends on the joining conditions and the like at that time, it is difficult to ensure a certain shape accuracy. In addition, since the arc-shaped portion is constituted by the two metal plates, there is a possibility that the two metal plates are plastically deformed when brazing, pressure bonding, or forming each arc-shaped portion by cutting.
これらのことにより、バイメタルである円弧状部を高精度の形状精度で仕上げることが難しく、慣性モーメントの調整及び温度補償量の設定が不安定になり易かった。加えて、径方向内側に配置される金属板の材料としては、インバー等の鉄系材料(低熱膨張材料)を一般的に採用するが、メッキ工程等を施さないと錆びが発生する問題があった。従って、製造に手間がかかってしまい、改善の余地があった。 For these reasons, it is difficult to finish the arcuate portion that is a bimetal with high accuracy, and adjustment of the moment of inertia and setting of the temperature compensation amount are likely to be unstable. In addition, iron-based materials (low thermal expansion materials) such as invar are generally used as the material for the metal plate disposed on the radially inner side, but there is a problem that rust occurs unless a plating process or the like is performed. It was. Therefore, it takes time to manufacture and there is room for improvement.
また、上記した第2の方法では、コエリンバー等の恒弾性材料でひげぜんまいを作製する際、溶解時における組成や熱処理等の各種加工条件によってヤング率の温度係数が大きく変化する恐れがある。従って、厳密な製造管理工程が必要とされ、ひげぜんまいの製造が容易ではなかった。よって、時計の使用温度範囲付近においてヤング率の温度係数を正にすることが難しい場合があった。 In the second method described above, when the balance spring is made of a constant elastic material such as a coelin bar, the temperature coefficient of Young's modulus may greatly change depending on various processing conditions such as the composition at the time of melting and heat treatment. Therefore, a strict manufacturing control process is required, and it is not easy to manufacture the hairspring. Therefore, it may be difficult to make the temperature coefficient of Young's modulus positive near the operating temperature range of the watch.
本発明は、このような事情に考慮してなされたもので、その目的は、形状精度が優れ、温度補正作業を狙い通りに安定して行うことができると共に、錆び難く、余計な外力(ストレス)が加わることを抑制しながら効率良く製造することができる温度補償型てんぷ、これを具備する時計用ムーブメント、機械式時計、及び温度補償型てんぷの製造方法を提供することである。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and the purpose thereof is excellent in shape accuracy, can be stably performed as intended for temperature correction, and is not easily rusted. Temperature compensation type balance that can be efficiently produced while suppressing the addition of), a timepiece movement having the same, a mechanical timepiece, and a method for producing the temperature compensation type balance.
本発明は、前記課題を解決するために以下の手段を提供する。
(1)本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷは、軸中心に回動するてん真と、前記てん真の回動軸回りに周方向に並んで配置され、該回動軸の周方向に沿って円弧状に延びた複数のバイメタル部、及びこれら複数のバイメタル部と前記てん真とをそれぞれ径方向に連結する連結部材を有するてん輪と、を備え、前記バイメタル部は、第1部材と、該第1部材よりも径方向外側に配置された第2部材とが径方向に重なった積層体とされると共に、周方向の一端部が前記連結部材に連結された固定端とされ、周方向の他端部が自由端とされ、前記第1部材は、セラミックス材料により形成され、前記第2部材は、前記第1部材とは熱膨張率が異なる金属材料により形成されることを特徴とする。
The present invention provides the following means in order to solve the above problems.
(1) A temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention is arranged in a circumferential direction around a rotation shaft of the balance stem rotating around the shaft and around the rotation shaft of the balance, and along the circumferential direction of the rotation shaft. A plurality of bimetal portions extending in an arc shape, and a balance wheel having a connecting member for connecting the plurality of bimetal portions and the balance in the radial direction, the bimetal portion including the first member, The second member disposed radially outward from the first member is a laminated body that overlaps in the radial direction, and one end in the circumferential direction is a fixed end connected to the connecting member, The other end is a free end, the first member is made of a ceramic material, and the second member is made of a metal material having a different coefficient of thermal expansion from the first member.
本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷによれば、温度変化が生じると、第1部材と第2部材との熱膨張率の差によってバイメタル部が固定端を基点として径方向に屈曲変形するので、バイメタル部の自由端を径方向の内側又は外側に向かって移動させることができる。これにより、バイメタル部の自由端の位置を径方向に変化させることができる。そのため、てん輪の平均径を縮径又は拡径させることができ、てん真の回動軸からの距離を変化させててんぷ全体の慣性モーメントを変化させることができる。これにより、慣性モーメントの温度特性の傾きを変化させることができ、温度補正を行うことができる。 According to the temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, when a temperature change occurs, the bimetal portion is bent and deformed in the radial direction from the fixed end as a result of the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the first member and the second member. The free end of the part can be moved radially inward or outward. Thereby, the position of the free end of a bimetal part can be changed to radial direction. Therefore, the average diameter of the balance wheel can be reduced or expanded, and the moment of inertia of the entire balance of the balance can be changed by changing the distance from the rotation axis of the balance. Thereby, the inclination of the temperature characteristic of the moment of inertia can be changed, and temperature correction can be performed.
特に、バイメタル部の第1部材がセラミックス材料で形成されているので、バイメタル部の塑性変形を抑制でき、温度補正により自由端の変形が繰り返されたとしても、経時的に安定した精度のバイメタル部を形成することが可能となる。 In particular, since the first member of the bimetal part is formed of a ceramic material, it is possible to suppress plastic deformation of the bimetal part, and even if the deformation of the free end is repeated due to temperature correction, the bimetal part has stable accuracy over time. Can be formed.
上記したように、塑性変形を防止しながら優れた形状精度でバイメタル部を形成できるので、温度補正作業を狙い通りに安定して行わせることができ、温度変化によって歩度が変化し難い、温度補償性能に優れた高品質なてんぷとすることができる。
また、バイメタル部の形状を規定できるので、バイメタル部の形状自由度を高めることができ、例えば変位量を大きくする等による温度補償量の制御を容易に行い易い。また、第1部材については、セラミックス材料であるのでメッキ等を施さなくても錆び難い。よって、メッキ工程等が不要であり、効率良く製造することが可能となる。
また、径方向に相互に重なる第1部材と第2部材とにより構成されたバイメタル部において内側の第1部材がセラミックス材で形成されているので、温度変化に伴う第1部材の熱変形が抑制されることになり、温度変化に応じたバイメタル部の変形を小さく抑えつつ所望の慣性モーメント調整量を得ることができるようになる。つまり、バイメタル部の内側部材が金属等ではなくセラミックス材であるので、当該内側部材の熱変形量の大きさを考慮しすぎることなく、バイメタル自由端部の変形量を設計することができるようになる。よって、慣性モーメントの温度補正が容易となり、当該補正精度を向上させることができる。
As mentioned above, since the bimetal part can be formed with excellent shape accuracy while preventing plastic deformation, temperature correction work can be performed stably as intended, and the rate is difficult to change due to temperature change, temperature compensation High quality balance with excellent performance can be obtained.
In addition, since the shape of the bimetal portion can be defined, the degree of freedom in shape of the bimetal portion can be increased, and for example, the temperature compensation amount can be easily controlled by increasing the displacement amount. Moreover, since the first member is a ceramic material, it is difficult to rust even if it is not plated. Therefore, a plating process or the like is unnecessary, and it becomes possible to manufacture efficiently.
In addition, since the inner first member is formed of a ceramic material in the bimetal portion formed by the first member and the second member that overlap each other in the radial direction, thermal deformation of the first member due to temperature change is suppressed. As a result, the desired moment of inertia adjustment amount can be obtained while suppressing the deformation of the bimetal portion according to the temperature change. In other words, since the inner member of the bimetal portion is not a metal or the like but a ceramic material, the amount of deformation of the free end portion of the bimetal can be designed without considering the amount of thermal deformation of the inner member too much. Become. Therefore, the temperature correction of the moment of inertia becomes easy and the correction accuracy can be improved.
(2)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記第1部材及び前記連結部材は、セラミックス材料により一体に形成され、前記第2部材は、前記第1部材とは熱膨張率が異なる金属材料からなる電鋳物であることが好ましい。 (2) In the temperature compensated balance according to the present invention, the first member and the connecting member are integrally formed of a ceramic material, and the second member is a metal having a coefficient of thermal expansion different from that of the first member. An electroformed product made of a material is preferable.
この場合には、てん輪のうち連結部材及びバイメタル部を構成する第1部材が、セラミックス材料で一体に形成されているので、半導体製造技術(フォトリソグラフィ技術やエッチング加工技術等を含む技術)を利用して、例えばシリコン基板から優れた形状精度で一体に形成することができる。しかも、半導体製造技術を利用するので、連結部材及び第1部材に対して余計な外力を加えることなく所望する微細な形状で形成することができる。
一方、バイメタル部を構成する第2部材は電鋳物であるので、金属材料を電鋳により成長させるだけの簡便な作業で第1部材に対して接合させることができる。従って、従来のろう付けや圧着等による方法とは異なり、やはり第1部材に対して余計な外力を加えることなく、第2部材を接合することができる。そのため、バイメタル部の塑性変形を防止できるうえ、優れた形状精度でバイメタル部を形成することが可能となる。
In this case, since the first member constituting the connecting member and the bimetal portion of the balance wheel is integrally formed of a ceramic material, semiconductor manufacturing technology (technology including photolithography technology, etching processing technology, etc.) is used. For example, it can be integrally formed from a silicon substrate with excellent shape accuracy. In addition, since the semiconductor manufacturing technique is used, it can be formed in a desired fine shape without applying an extra external force to the connecting member and the first member.
On the other hand, since the 2nd member which comprises a bimetal part is an electroformed product, it can be joined with respect to a 1st member by the simple operation | work only to grow a metal material by electroforming. Therefore, unlike the conventional methods such as brazing and crimping, the second member can be joined without applying an extra external force to the first member. Therefore, it is possible to prevent plastic deformation of the bimetal part and to form the bimetal part with excellent shape accuracy.
(3)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記第2部材は、前記第1部材に形成された第1係合部に係合する第2係合部を備え、該係合を維持したまま前記第1部材に対して接合していることが好ましい。 (3) In the temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, the second member includes a second engagement portion that engages with the first engagement portion formed on the first member, and maintains the engagement. It is preferable that the first member is bonded as it is.
この場合には、第1係合部と第2係合部との係合によって、第1部材と第2部材との接合強度を高めることができるので、バイメタル部としての作動信頼性を向上することができる。また、両係合部の係合によって、第2部材が第1部材に対して周方向に位置決めされるので、第1部材の狙った領域に第2部材を接合できる。この点においても、バイメタル部としての作動信頼性を向上できる。 In this case, since the joint strength between the first member and the second member can be increased by the engagement between the first engagement portion and the second engagement portion, the operation reliability as the bimetal portion is improved. be able to. Further, since the second member is positioned in the circumferential direction with respect to the first member by the engagement of both the engaging portions, the second member can be joined to the region targeted by the first member. Also in this point, the operation reliability as a bimetal part can be improved.
(4)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記第1部材と前記第2部材は、合金層を介して接合されていることが好ましい。 (4) In the temperature compensated balance according to the present invention, it is preferable that the first member and the second member are joined via an alloy layer.
この場合には、第1部材と第2部材とが合金層を介して接合されているので、両部材の接合強度を高めることができ、バイメタル部としての作動信頼性を向上することができる。 In this case, since the 1st member and the 2nd member are joined via the alloy layer, the joint strength of both members can be raised and the operation reliability as a bimetal part can be improved.
(5)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記バイメタル部の自由端には、錘部が設けられていることが好ましい。 (5) In the temperature compensated balance according to the present invention, it is preferable that a weight portion is provided at a free end of the bimetal portion.
この場合には、錘部によってバイメタル部の自由端の重量を増大させることができるので、自由端における径方向の変化量に対して、より効果的に慣性モーメントの温度補正を行うことができる。従って、温度補償性能をより向上させ易い。 In this case, since the weight of the free end of the bimetal portion can be increased by the weight portion, the temperature of the moment of inertia can be more effectively corrected with respect to the amount of change in the radial direction at the free end. Therefore, it is easy to improve the temperature compensation performance.
(6)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記第1部材及び前記連結部材は、Si、SiC、SiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2、又はCのうちのいずれかの材料で形成されていることが好ましい。 (6) In the temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, the first member and the connecting member are made of any material of Si, SiC, SiO 2 , Al 2 O 3 , ZrO 2 , or C. It is preferable that
この場合には、セラミックス材料として、Si、SiC、SiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2、又はCを採用するので、エッチング加工、特にドライエッチング加工を好適に行うことが可能である。従って、連結部材及び第1部材を、より簡便且つ効率良く形成でき、製造効率をさらに高め易い。 In this case, Si, SiC, SiO 2 , Al 2 O 3 , ZrO 2 , or C is employed as the ceramic material, so that it is possible to suitably perform etching processing, particularly dry etching processing. Therefore, the connecting member and the first member can be formed more easily and efficiently, and the manufacturing efficiency can be further increased.
(7)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷにおいて、前記第2部材は、Au、Cu、Ni、Ni合金、Sn、又はSn合金のうちのいずれかの材料で形成されていることが好ましい。 (7) In the temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, the second member is preferably made of any material of Au, Cu, Ni, Ni alloy, Sn, or Sn alloy.
この場合には、金属材料として、Au、Cu、Ni、Ni合金、Sn、又はSn合金を採用するので、電鋳によりスムーズに金属材料を成長させることができ、効率良く第2部材を形成することが可能である。従って、製造効率をさらに高め易い。 In this case, since Au, Cu, Ni, Ni alloy, Sn, or Sn alloy is adopted as the metal material, the metal material can be grown smoothly by electroforming, and the second member is efficiently formed. It is possible. Therefore, it is easy to further improve the manufacturing efficiency.
(8)本発明に係る時計用ムーブメントは、動力源を有する香箱車と、前記香箱車の回転力を伝達する輪列と、前記輪列の回転を制御する脱進機構と、前記脱進機構を調速する上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷと、を備えていることを特徴とする。 (8) A timepiece movement according to the present invention includes a barrel wheel having a power source, a train wheel that transmits the rotational force of the barrel wheel, an escapement mechanism that controls rotation of the train wheel, and the escapement mechanism. And a temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention.
本発明に係る時計用ムーブメントによれば、上述したように温度補償性能が高い温度補償型てんぷを具備しているので、歩度の誤差が少ない高品質な時計用ムーブメントとすることができる。 According to the timepiece movement according to the present invention, the temperature-compensated balance with high temperature compensation performance as described above is provided, so that it is possible to obtain a high-quality timepiece movement with less error in rate.
(9)本発明に係る機械式時計は、上記本発明に係る時計用ムーブメントを備えることを特徴とする。 (9) A mechanical timepiece according to the present invention includes the timepiece movement according to the present invention.
本発明に係る機械式時計によれば、上記した時計用ムーブメントを具備しているので、歩度の誤差の少ない高品質な機械式時計とすることができる。 According to the mechanical timepiece of the invention, since the timepiece movement described above is provided, a high-quality mechanical timepiece with less error in rate can be obtained.
(10)本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷの製造方法は、上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷを製造する方法であって、セラミックス基板を半導体製造技術により加工して、前記連結部材に複数の前記第1部材が一体に連結されると共に、それぞれの前記第1部材との間に電鋳用開放空間を画成させる電鋳用ガイド壁が、それぞれの前記第1部材に一体に連結された前駆体を形成する基板加工工程と、前記前駆体における前記電鋳用開放空間内に前記金属材料を電鋳により成長させることで前記第2部材を形成し、前記第1部材と前記第2部材とが径方向に重なった接合された前記バイメタル部を形成する電鋳工程と、前記電鋳用ガイド壁を前記第1部材から除去する除去工程と、を備えていることを特徴とする。 (10) A method for producing a temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention is a method for producing the temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, wherein a ceramic substrate is processed by a semiconductor manufacturing technique, and a plurality of the connection members are formed on the connecting member. The first member is integrally connected, and an electroforming guide wall that defines an open space for electroforming between the first member and the first member is integrally connected to the first member. A substrate processing step for forming a precursor, and the second member is formed by growing the metal material in the open space for electroforming in the precursor by electroforming, and the first member and the second member And a removing step of removing the electroforming guide wall from the first member. The electroforming step of forming the bimetal portion joined in a radial direction.
本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷの製造方法によれば、上述した温度補償型てんぷと同様の作用効果を奏功することができる。すなわち、塑性変形を防止しながら優れた形状精度でバイメタル部を形成できるので、温度補正作業を狙い通りに安定して行わせることができ、温度変化によって歩度が変化し難い高品質な温度補償性能に優れたてんぷとすることができる。
特に、基板加工工程の際、連結部材及び第1部材に加えて、電鋳用ガイド壁が一体に連結された前駆体を形成している。そのため、この電鋳用ガイド壁と第1部材との間に画成される電鋳用開放空間を優れた形状精度で形成することができる。そして、電鋳工程の際、この電鋳用開放空間内に金属材料を成長させて第2部材を形成するので、優れた形状精度の第2部材を形成することができ、結果として所望の形状を有する高品質なバイメタル部を得ることができる。これにより、上述した作用効果をより顕著に奏功することができる。
According to the method for producing a temperature-compensated balance according to the present invention, the same operational effects as those of the above-described temperature-compensated balance can be achieved. In other words, since the bimetal part can be formed with excellent shape accuracy while preventing plastic deformation, the temperature correction work can be performed stably as intended, and the high-quality temperature compensation performance that does not easily change the rate due to temperature changes It can be an excellent balance with a balance.
In particular, during the substrate processing step, in addition to the connecting member and the first member, a precursor in which electroforming guide walls are integrally connected is formed. Therefore, the electroforming open space defined between the electroforming guide wall and the first member can be formed with excellent shape accuracy. In the electroforming process, the second member is formed by growing a metal material in the open space for electroforming, so that the second member having excellent shape accuracy can be formed. It is possible to obtain a high-quality bimetal part having Thereby, the effect mentioned above can be achieved more remarkably.
(11)上記本発明に係る温度補償型てんぷの製造方法において、前記電鋳工程後、前記バイメタル部が形成された前記前駆体を、所定温度雰囲気下で所定時間の間、熱処理する熱処理工程を行うことが好ましい。 (11) In the method for producing a temperature compensated balance according to the present invention, after the electroforming step, a heat treatment step of heat-treating the precursor on which the bimetal portion is formed in a predetermined temperature atmosphere for a predetermined time. Preferably it is done.
この場合には、電鋳により第1部材に対して第2部材を接合させてバイメタル部を形成した後、熱処理を行うので、電鋳物である第2部材を形成する金属材料を、第1部材との接合界面に沿って拡散させることができ、この拡散を利用して第1部材と第2部材との間に合金層を形成することができる。これにより、第1部材と第2部材とを合金層を介して接合させることができ、両部材の接合強度を高めることができる。従って、バイメタル部としての作動信頼性を向上することができる。 In this case, the second member is joined to the first member by electroforming to form a bimetal portion, and then heat treatment is performed. Therefore, the metal material forming the second member that is an electroformed product is used as the first member. Can be diffused along the interface between the first member and the second member, and an alloy layer can be formed between the first member and the second member. Thereby, a 1st member and a 2nd member can be joined via an alloy layer, and the joint strength of both members can be raised. Therefore, the operation reliability as a bimetal part can be improved.
本発明によれば、形状精度が優れ、温度補正作業を狙い通りに安定して行うことができると共に、錆び難く、余計な外力(ストレス)が加わることを抑制しながら効率良く製造することができ、温度補償性能が高まった温度補償型てんぷを得ることができる。 According to the present invention, shape accuracy is excellent, temperature correction work can be performed stably as intended, and it is difficult to rust and can be efficiently manufactured while suppressing the application of extra external force (stress). A temperature compensated balance with improved temperature compensation performance can be obtained.
以下、本発明に係る実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。
〔機械式時計、時計用ムーブメント、温度補償型てんぷの構成〕
図1に示すように、本実施形態の機械式時計1は、例えば腕時計であって、ムーブメント(時計用ムーブメント)10と、このムーブメント10を収納する図示しないケーシングと、により構成されている。
Hereinafter, embodiments according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[Configuration of mechanical watch, watch movement, temperature compensation balance]
As shown in FIG. 1, the mechanical timepiece 1 of the present embodiment is, for example, a wristwatch, and includes a movement (timepiece movement) 10 and a casing (not shown) that houses the
(ムーブメントの構成)
このムーブメント10は、基板を構成する地板11を有している。この地板11の裏側には図示しない文字板が配されている。なお、ムーブメント10の表側に組み込まれる輪列を表輪列28と称し、ムーブメント10の裏側に組み込まれる輪列を裏輪列と称する。
上記地板11には、巻真案内穴11aが形成されており、ここに巻真12が回転自在に組み込まれている。この巻真12は、おしどり13、かんぬき14、かんぬきばね15及び裏押さえ16を有する切換装置により、軸方向の位置が決められている。また、巻真12の案内軸部には、きち車17が回転自在に設けられている。
(Composition of movement)
This
A winding
このような構成のもと、巻真12が、例えば回転軸方向に沿ってムーブメント10の内側に一番近い方の第1の巻真位置(0段目)にある状態で巻真12を回転させると、図示しないつづみ車の回転を介してきち車17が回転する。そして、このきち車17が回転することにより、これと噛合う丸穴車20が回転する。そして、この丸穴車20が回転することにより、これと噛合う角穴車21が回転する。更に、この角穴車21が回転することにより、香箱車22に収容された図示しないぜんまい(動力源)を巻き上げる。
Under such a configuration, the winding
ムーブメント10の表輪列28は、上記香箱車22の他に、二番車25、三番車26及び四番車27により構成されており、香箱車22の回転力を伝達する機能を果している。また、ムーブメント10の表側には、表輪列28の回転を制御するための脱進機構30及び調速機構31が配置されている。
The
二番車25は、香箱車22に噛合う歯車とされている。三番車26は、二番車25に噛合う歯車とされている。四番車27は、三番車26に噛合う歯車とされている。
脱進機構30は、上記した表輪列28の回転を制御する機構であって、四番車27と噛み合うがんぎ車35と、このがんぎ車35を脱進させて規則正しく回転させるアンクル36と、を備えている。
調速機構31は、上記脱進機構30を調速する機構であって、てんぷ(温度補償型てんぷ)40を具備している。
The
The
The
(てんぷの構成)
てんぷ40は、図2及び図3に示すように、軸線(回動軸)Oを中心に回動する(軸中心に回動する)てん真41と、てん真41に取り付けられたてん輪42と、ひげぜんまい(てんぷばね)43と、を備え、ひげぜんまい43から伝えられた動力によって、軸線O回りに一定の振動周期で正逆回転させられる部材とされている。
なお、本実施形態では、軸線Oに直交する方向を径方向、軸線Oを周回する方向を周方向という。
(Structure of balance)
As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the balance with
In the present embodiment, a direction orthogonal to the axis O is referred to as a radial direction, and a direction around the axis O is referred to as a circumferential direction.
てん真41は、軸線Oに沿って上下に延在した回転軸体であり、上端部及び下端部が上記したムーブメント10を構成する図示しない地板やてんぷ受等の部材によって軸支されている。てん真41における上下方向の略中間部分は、径が最も大きい大径部41aとされている。また、このてん真41には、大径部41aの下方に位置する部分に筒状の振り座45が軸線Oと同軸に外装されている。この振り座45は、径方向の外側に向けて突設された環状の鍔部45aを有しており、該鍔部45aに上記アンクル36を揺動させるための振り石46が固定されている。
The balance stem 41 is a rotating shaft body that extends vertically along the axis O, and the upper end portion and the lower end portion thereof are pivotally supported by members (not shown) such as a base plate and a balance holder that constitute the above-described
ひげぜんまい43は、例えば一平面内で渦巻状に巻かれた平ひげであって、ひげ玉47を介してその内端部がてん真41における大径部41aの上方に位置する部分に固定されている。そして、このひげぜんまい43は、四番車27からがんぎ車35に伝えられた動力を蓄え、上述したように該動力をてん輪42に伝える役割を果たしている。
なお、本実施形態のひげぜんまい43は、ヤング率が負の温度係数を有する一般的な鋼材料で形成されており、温度上昇によってばね定数が低下する特性を有している。
The
In addition, the
てん輪42は、図4及び図5に示すように、てん真41の軸線O回りに周方向に並んで配置された3つのバイメタル部50と、これら3つのバイメタル部50とてん真41とをそれぞれ径方向に連結する連結部材51と、を備えている。
As shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, the
連結部材51は、軸線Oと同軸に配設されており、中心に軸孔55aが形成された連結円板55と、該連結円板55を径方向の外側から間隔をあけて囲繞する連結リング56と、連結円板55の外周部と連結リング56の内周部とを連結する3つ連結ブリッジ57と、を備えている。
そして、この連結部材51は、軸孔55aを介しててん真41の大径部41aに例えば圧入等により固定されることで、てん真41に対して一体に取り付けられる。
The connecting
The connecting
連結リング56の外周部には、径方向の外側に向けて3つの支持突起58が突出している。これら3つの支持突起58は、周方向に一定の間隔をあけて均等配置されている。また、各支持突起58には、連結リング56の外周部から径方向の外側に向かうにしたがって、周方向の一方側(図4に示す矢印T方向)に向けて傾斜した傾斜面58aが形成されている。
Three
連結ブリッジ57は、連結円板55と連結リング56とを径方向に繋ぐ部材であり、周方向に一定の間隔をあけて均等配置されている。図示の例では、3つの連結ブリッジ57と3つの支持突起58とは、互いに周方向に位置がずれた状態で配設されているが、この場合に限定されるものではない。
The
上記バイメタル部50は、径方向の内側に位置する第1部材60と、この第1部材60の径方向の外側に位置する第2部材61とが互いに径方向に重なって接合された積層体であり、周方向に沿って円弧状に延びる帯状に形成されている。そして、このバイメタル部50は、連結リング56の径方向の外側に間隔をあけ、且つ周方向に並んだ状態で配置されており、周方向の一端部が連結部材51に連結された固定端50Aとされている。
The
具体的には、バイメタル部50の固定端50Aは、連結リング56から突出した支持突起58における、傾斜面58aとは周方向の反対の面に連結されている。そして、バイメタル部50は、この支持突起58から周方向に沿いながら矢印T方向に向かって延びている。これにより、3つのバイメタル部50は、周方向に均等配置されている。
Specifically, the
また、バイメタル部50の周方向の他端部は、温度変化に伴う屈曲変形によって径方向に移動可能とされた自由端50Bとされている。この自由端50Bは、主に第1部材60で形成されており、径方向の内側に向けて突出することで、バイメタル部50の他の部分よりも径方向に幅広に形成されている。
これにより、自由端50Bの重量は、バイメタル部50の他の部分よりも重く設計されている。しかも、本実施形態の自由端50Bには錘孔62が形成されており、この錘孔62に錘部65(図2、図3参照)が例えば圧入により取り付けられている。そのため、自由端50Bには錘部65による重量も加わって、バイメタル部50の他の部分よりも十分重く設計されている。
The other end in the circumferential direction of the
Thereby, the weight of the
なお、錘部65は、図2及び図3に示すように、錘孔62に挿入される軸部65aと、自由端50Bの上面に露出するヘッド部65bと、でリベットのごとく形成されている場合を例にしている。
また、図4に示すように、自由端50Bにおける径方向の内側を向いた部分には、支持突起58における傾斜面58aに対向し、該傾斜面58aの傾斜に倣って傾斜した対向傾斜面66とされている。
2 and 3, the
Further, as shown in FIG. 4, a portion of the
ところで、上述したようにバイメタル部50は、図4及び図5に示すように、第1部材60と第2部材61とが径方向に重なって積層されることで形成されているが、これらは熱膨張率の異なる材料で形成されている。
Incidentally, as described above, the
具体的には、径方向の内側に位置する第1部材60は、低熱膨張材料であるセラミックス材料、本実施形態ではシリコン(Si)で形成されている。一方、径方向の外側に位置する第2部材61は、第1部材60よりも熱膨張率が大きい高熱膨張材料であって、且つ電鋳可能な金属材料、本実施形態では金(Au)で形成されている。
従って、温度上昇した場合には、第1部材60よりも第2部材61の方が熱膨張するので、バイメタル部50は、固定端50Aを基点として自由端50Bが径方向の内側に向けて移動するように屈曲変形する。
Specifically, the
Therefore, when the temperature rises, the
また、本実施形態の第1部材60は、連結部材51と一体に形成されている。従って、連結部材51についても、第1部材60と同様にシリコンにより形成されている。つまり、てんぷ40を構成するてん輪42は、連結部材51と第1部材60とがシリコンにより形成され、第2部材61だけが金で形成されている。
Further, the
しかも、この第2部材61は電鋳によって形成された電鋳物とされており、電鋳による金の成長過程で第1部材60に対して密着接合する。加えて、第2部材61における周方向の両端部は、径方向の内側に向かうにしたがって周方向に漸次延びた平面視V字状の楔部(第2係合部)67が形成されており、第1部材60側に形成された平面視V字状の凹部(第1係合部)68に係合した状態で接合されている。
これにより、第2部材61は、第1部材60に対して周方向に位置決めがなされた状態で接合している。
Moreover, the
Thereby, the
〔温度補正方法〕
次に、上記したてんぷ40を利用した、慣性モーメントの温度補正方法について説明する。
本実施形態のてんぷ40によれば、図2に示すように、温度変化が生じると、第1部材60と第2部材61との熱膨張率の差によってバイメタル部50が固定端50Aを基点として径方向に屈曲変形するので、バイメタル部50の自由端50Bを径方向の内側又は外側に向かって移動させることができる。即ち、温度上昇した場合には、バイメタル部50が径方向の内側に屈曲変形するので、自由端50Bを径方向の内側に向けて移動させることができ、温度低下した場合には、その逆に径方向の外側に向けて移動させることができる。
[Temperature correction method]
Next, a method for correcting the temperature of the moment of inertia using the
According to the balance with
そのため、てん輪42の平均径を縮径又は拡径させることができ、てん真41の軸線Oからの距離を変化させててんぷ40全体の慣性モーメントを変化させることができる。つまり、温度上昇した場合には、てん輪42の平均径を縮径させて慣性モーメントを小さくすることができ、温度低下した場合には、てん輪42の平均径を拡径させて慣性モーメントを大きくすることができる。これにより、慣性モーメントの温度特性の傾きを負の傾きに変化させることができ、温度補正を行うことができる。
Therefore, the average diameter of the
すなわち、ヤング率が負の温度係数を有するひげぜんまい43を備えていたとしても、温度上昇時、ひげぜんまい43のヤング率の低下と同時に、慣性モーメントを小さくすることができるので、てんぷ40の振動周期を一定に保つことができ、温度補正を行える。また、温度低下時、ひげぜんまい43のヤング率の増加と同時に、慣性モーメントを大きくすることができるので、やはりてんぷ40の振動周期を一定に保つことができ、温度補正を行える。
That is, even if the
〔てんぷの製造方法〕
次に、上記したてんぷ40の製造方法について、図面を参照して説明する。
てんぷ40の製造方法としては、てん真41を製造する工程と、てん輪42を製造する工程と、ひげぜんまい43を製造する工程と、これらを一体に組み付ける工程と、を備える。ここでは、主にてん輪42を製造する工程を詳細に説明する。
[Method for manufacturing balance]
Next, a method for manufacturing the balance with
The method of manufacturing the balance with
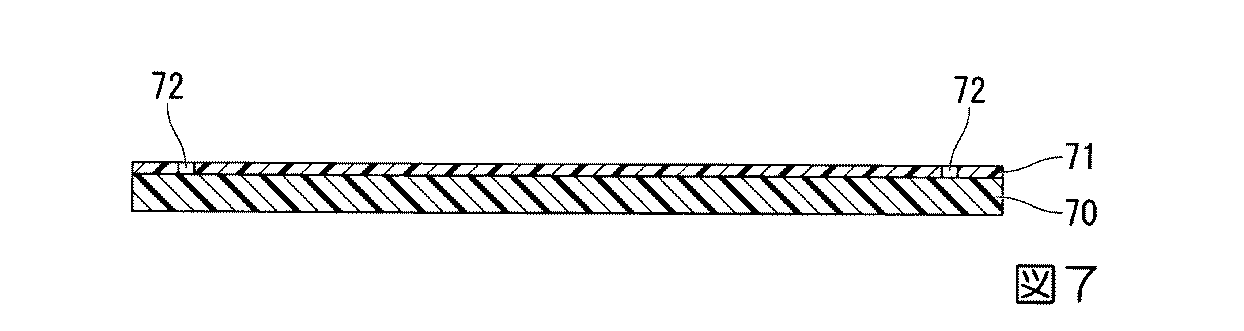
はじめに、図6に示すように、後に連結部材51及び第1部材60となるシリコン基板(セラミックス基板)70を準備した後、その表面にシリコン酸化膜(SiO2)71を形成する。この際、シリコン基板70としては、てん輪42の厚みよりも厚いものを用いる。また、シリコン酸化膜71は、例えばプラズマ化学気相形成法(PCVD)や熱酸化等による方法で形成する。
First, as shown in FIG. 6, after preparing a silicon substrate (ceramic substrate) 70 that will later become the connecting
なお、ここでは説明を簡略化するために、平面視正方形状のシリコン基板70から、てん輪42を1つだけ製造する場合を例に挙げて説明する。但し、ウエハ状のシリコン基板を用意し、てん輪42を一度に複数個同時に製造しても構わない。
Here, in order to simplify the description, a case where only one
続いて、図7及び図8に示すように、シリコン酸化膜71の一部をエッチング等により選択的に除去して、3つの円弧状の溝部72を、周方向に間隔をあけて並ぶように形成する。この溝部72は、後に形成される電鋳用ガイド壁70Aを形成するための溝であり、第2部材61よりも径方向外側に位置するように形成する。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, a part of the
続いて、図9〜図11に示すように、シリコン酸化膜71上における、上記3つの溝部72で囲まれる内側領域にフォトレジストを形成した後、該フォトレジストをパターニングしたレジストパターン73を形成する。このとき、連結部材51及び第1部材60の形状に倣ってパターニングしたレジストパターン本体73Aと、上記した3つの溝部72に入り込むと共に、周方向の両端部がレジストパターン73と連結したガイド壁用パターン73Bと、で構成されるようにレジストパターン73を形成する。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 9 to 11, after forming a photoresist on the inner region surrounded by the three
なお、フォトレジストは、スピンコートやスプレーコート等の一般的な方法により形成すれば良い。また、レジストパターン73は、フォトレジストをフォトリソグラフィ技術等の一般的な方法によりパターニングすることで形成すれば良い。
Note that the photoresist may be formed by a general method such as spin coating or spray coating. The resist
続いて、図12及び図13に示すように、シリコン酸化膜71のうち、上記レジストパターン73でマスクされていない領域を選択的に除去する。具体的には、緩衝フッ酸水溶液を用いたウェットエッチングや、リアクティブイオンエッチング(RIE)等のドライエッチングによるエッチング加工によりシリコン酸化膜71を除去する。
これにより、レジストパターン73の下だけにシリコン酸化膜71を残すことができ、該シリコン酸化膜71をレジストパターン73に倣った形状にパターニングすることができる。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 12 and 13, a region of the
Thereby, the
続いて、図14及び図15に示すように、シリコン基板70のうち、上記レジストパターン73及びシリコン酸化膜71でマスクされていない領域を選択的に除去する。具体的には、ディープリアクティブイオンエッチング(DRIE)等のドライエッチングによるエッチング加工によりシリコン基板70を除去する。
これにより、レジストパターン73及びシリコン酸化膜71の下だけにシリコン基板70を残すことができ、該シリコン基板70をレジストパターン73に倣った形状にパターニングすることができる。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 14 and 15, regions of the
Thereby, the
特に、パターニングされたシリコン基板70のうち、ガイド壁用パターン73Bの下に残された部分は、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aとして機能する。
In particular, the portion of the patterned
続いて、図16及び図17に示すように、マスクとして利用していたレジストパターン73を除去する。この除去方法としては、例えば発煙硝酸によるドライエッチングや、酸素プラズマを用いたドライエッチング等の方法が挙げられる。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 16 and 17, the resist
以上の工程により、シリコン基板70を半導体技術により加工して、連結部材51に3つの第1部材60が一体に連結されると共に、各第1部材60との間に電鋳用開放空間Sを画成させる電鋳用ガイド壁70Aが、各第1部材60に一体に連結された前駆体75を得ることができる。(従って、上述した各工程が本発明における基板加工工程となる。)
Through the above steps, the
上記前駆体75を形成した後、電鋳用開放空間S内に金を電鋳により成長させることで第2部材61を形成し、第1部材60と第2部材61とが接合されたバイメタル部50を形成する電鋳工程を行う。この電鋳工程について、具体的に説明する。
After the
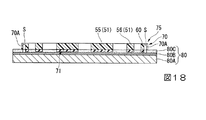
まず、図18及び図19に示すように、基板本体80A上に電極層80Bを介して接着層80Cが例えば貼り合わされた第1支持基板80を用意した後、上記前駆体75を表裏反転させて、パターニングされたシリコン酸化膜71を接着層80Cに張り合わせる。図示の例では、シリコン酸化膜71が接着層80C内に埋め込まれる程度、前駆体75と第1支持基板80とを貼り合わせている。
First, as shown in FIGS. 18 and 19, after preparing the
なお、接着層80Cとしては、特に限定されるものではないが、例えばフォトレジストを用いることが好ましい。この場合には、フォトレジストがペースト状の状態で貼り合わせを行い、その後、フォトレジストがペーストを脱する状態まで硬化させれば良い。
The
そして、上記貼り合わせを行った後、図18に示すように、接着層80Cのうち、前駆体75の電鋳用開放空間Sに連通している部分を選択的に除去する。これにより、電鋳用開放空間S内に、電極層80Bを露出させることができる、
この際、例えば接着層80Cをフォトレジストとしている場合には、フォトリソグラフィ技術によって選択的に除去する作業を容易に行うことが可能である。
And after performing the said bonding, as shown in FIG. 18, the part connected to the open space S for electroforming of the
At this time, for example, when the
続いて、図20及び図21に示すように、電極層80Bを利用して電鋳を行い、電鋳用開放空間S内において電極層80Bから金を徐々に成長させ、電鋳用開放空間S内を満たし、さらに電鋳用開放空間Sを膨出する程度の電鋳物81を生成する。そして、この膨出した電鋳物81を前駆体75と面一となるように研磨する。これにより、この電鋳物81を第2部材61とすることができ、第1部材60と第2部材61とが接合されたバイメタル部50を形成することができる。
なお、上記研磨を行う際、前駆体75のシリコン基板70を同時に研磨しても構わない。
Subsequently, as shown in FIGS. 20 and 21, electroforming is performed using the
In addition, when performing the said grinding | polishing, you may grind | polish the
この段階で、上記した電鋳工程が終了する。なお、図20及び図21では電鋳に必要な一般的な構成部材(電鋳槽等)の図示は省略している。
電鋳が終了した後、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aを第1部材60から除去する除去工程を行う。この除去工程について、具体的に説明する。
At this stage, the above-described electroforming process is completed. In FIGS. 20 and 21, illustration of general components (such as an electroforming tank) necessary for electroforming is omitted.
After the electroforming is completed, a removal step of removing the
まず、図22に示すように、基板本体85A上に接着層85Bが形成された第2支持基板85を用意した後、第1支持基板80から取り外した上記前駆体75を再度表裏反転させて、シリコン基板70のうち、シリコン酸化膜71が形成された側とは反対側の面を接着層85Bに張り合わせる。
First, as shown in FIG. 22, after preparing the
続いて、図23に示すように、前駆体75のうち電鋳用ガイド壁70Aだけを選択的に除去する。具体的には、前駆体75のうち、例えば電鋳用ガイド壁70A以外の領域を図示しないマスクで上方から覆い、ディープリアクティブイオンエッチング(DRIE)等のドライエッチングによるエッチング加工により、マスクされていない電鋳用ガイド壁70Aを除去する。
この段階で、上記除去工程が終了する。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 23, only the
At this stage, the removal process is completed.
続いて、図24に示すように第2支持基板85を取り外した後、図25及び図26に示すように、残ったシリコン酸化膜71を例えばBHFを用いたウェットエッチングにより除去する。
なお、シリコン酸化膜71は必ずしも除去する必要がないが、除去することが好ましい。また、図25及び図26では、シリコン酸化膜71の膜厚を誇張して図示しているため、第1部材60と第2部材61との間に段差が生じているが、この段差量は僅か(例えば1μm程度)であり、実質的には図3に示すように第1部材60と第2部材61との間に段差はないに等しい。
Subsequently, after the
The
そして、最後に、錘孔62に錘部65を圧入等により固定することで、図2に示すてん輪42を製造することができる。
その後、先に説明したように、別途製造されたてん真41及びひげぜんまい43と、てん輪42とを一体に組み付けることで、てんぷ40の製造が終了する。
Finally, the
Thereafter, as described above, the
(作用効果)
上述したように、本実施形態のてんぷ40によれば、バイメタル部50の第1部材60がセラミックス材で形成されるので、バイメタル部50の塑性変形を抑制でき、温度補正により自由端50Bの変形が繰り返されたとしても、経時的に安定した精度のバイメタル部50を形成することが可能となる。
また、径方向に相互に重なる第1部材60と第2部材61とにより構成されたバイメタル部50において内側の第1部材60がセラミックス材で形成されているので、温度変化に伴う第1部材60の熱変形が抑制されることになり、温度変化に応じたバイメタル部50の変形を小さく抑えつつ所望の慣性モーメント調整量を得ることができるようになる。つまり、バイメタル部50の内側部材が金属等ではなくセラミックス材なので、当該内側部材の熱変形量の大きさを考慮しすぎることなく、バイメタル部50の自由端50Bの変形量を設計することができるようになる。よって、慣性モーメントの温度補正が容易となり、当該補正精度を向上させることができる。
(Function and effect)
As described above, according to the balance with
In addition, since the inner
また、所望の慣性モーメント調整幅を確保する際に、バイメタル部50の自由端50Bの変形量を低減できるので、自由端50B周囲の空隙(バイメタル部50と連結部材51とにより挟まれた空間)を小さくすることができ、てんぷ40の高密度形成が可能となる。よって、セラミックス材で形成されるてんぷにおいても所望の剛性を確保できるようになる。
また、密度の高いバイメタル部50が最外周のみに形成されているため、全体の重量を抑えつつ所望の慣性モーメントを得ることができる。つまり、シリコン材(セラミックス材)によりてんぷ40の重量を抑えることによって時計を落下させた時にてん真41に加わる衝撃を少なくすることができる。よって、てん真曲がりやてん真折れの発生頻度を抑えられ、時計としての信頼性を向上させることができるようになる。
In addition, since the amount of deformation of the
Further, since the high-
また、てん輪42のうち、連結部材51及び第1部材60がシリコンで一体に形成されているので、半導体製造技術(フォトリソグラフィ技術やエッチング加工技術等を含む技術)を利用して、シリコン基板70から優れた形状精度で一体に形成することができる。しかも、半導体製造技術を利用するので、連結部材51及び第1部材60に対して余計な外力を加えることなく所望する微細な形状で形成することができる。
In addition, since the connecting
一方、バイメタル部50を構成する第2部材61は電鋳物であるので、金を電鋳により成長させるだけの簡便な作業で第1部材60に対して接合させることができる。従って、従来のろう付けや圧着等による方法とは異なり、やはり第1部材60に対して余計な外力を加えることなく第2部材61を接合することができる。そのため、バイメタル部50の塑性変形を防止できるうえ、優れた形状精度でバイメタル部50を形成することが可能となる。しかも、シリコンをはじめとするセラミックス材は、塑性変形し難い。この点においても、バイメタル部50の塑性変形を防止できる。
On the other hand, since the
上記のように、塑性変形を防止しながら優れた形状精度でバイメタル部50を形成できるので、温度補正作業を狙い通りに安定して行わせることができ、温度変化によって歩度が変化し難い、温度補償性能に優れた高品質なてんぷ40とすることができる。
また、バイメタル部50の形状を規定できるので、バイメタル部50の形状自由度を高めることができ、例えば変位量を大きくする等による温度補償量の制御を容易に行い易い。
As described above, since the
Moreover, since the shape of the
さらに、てん輪42を製造する際、連結部材51及び第1部材60に加えて、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aが一体に形成された前駆体75を形成している。そのため、この電鋳用ガイド壁70Aと第1部材60との間に画成される電鋳用開放空間Sを優れた形状精度で形成することができる。そして、電鋳の際、この電鋳用開放空間S内に金を成長させて第2部材61を形成するので、優れた形状精度の第2部材61を形成することができ、結果として所望の形状を有する高品質なバイメタル部50を得ることができる。
これにより、上述した作用効果をより顕著に奏功することができる。
Further, when the
Thereby, the effect mentioned above can be achieved more remarkably.
また、連結部材51及び第1部材60については、シリコンであるのでメッキ等を施さなくても錆び難い。加えて、第2部材61が金であるので、防錆に優れている。これらのことにより、メッキ工程等が不要であり、効率良く製造することが可能となる。
Further, since the connecting
また、バイメタル部50を構成する第1部材60と第2部材61とは、楔部67と凹部68との係合によっても互いに係合しているので、接合強度を高めることができ、バイメタル部50としての作動信頼性を向上することができる。また、上記係合によって、第2部材61が第1部材60に対して周方向に位置決めされるので、第1部材60の狙った領域に第2部材61を接合できる。この点においても、バイメタル部50としての作動信頼性を向上することができる。
Further, since the
また、本実施形態のムーブメント10によれば、温度補償性能が高い上記した温度補償型てんぷ40を具備しているので、歩度の誤差が少ない高品質なムーブメントとすることができる。
さらに、このムーブメント10を具備する本実施形態の機械式時計1によれば、同様に歩度の誤差の少ない高品質な時計となる。
Further, according to the
Furthermore, according to the mechanical timepiece 1 of this embodiment provided with the
(変形例)
上記実施形態では、バイメタル部50の自由端50Bに錘部65を設けたが、この錘部65は必須ではなく具備しなくても構わない。但し、錘部65を設けることで、自由端50Bの重量を増大させることができるので、自由端50Bにおける径方向の変化量に対して、より効果的に慣性モーメントの温度補正を行うことができ、温度補償性能をより向上させ易い。
なお、錘部65の形状は、錘部65の重量と錘部65に必要とされる慣性モーメントの量から決定すれば良い。
(Modification)
In the above embodiment, the
The shape of the
また、錘部65を設ける場合には、上記実施形態のような錘孔62に圧入等により固定する錘部65に限られるものではなく、自由に変更して構わない。
例えば、図27に示すように、錘孔62内に電鋳により金を成長させた電鋳物を錘部90としても構わない。
この場合には、製造時、接着層85Bの一部を除去して、電極層80Bを電鋳用開放空間Sに露出させる際、同時に、錘孔62に相当する部分の接着層85Bを除去して電極層80Bを露出させる。そして、電鋳により金を成長させて第2部材61を形成する際に、同時に錘孔62内にも金を成長させて錘部90を形成すれば良い。
Moreover, when providing the
For example, as shown in FIG. 27, an electroformed product obtained by growing gold in the
In this case, at the time of manufacturing, when part of the
このようにすることで、1度の電鋳工程で、第2部材61と錘部90とを同時に形成することができるので、製造効率をさらに高めることができる。また、バイメタル部50の自由端50Bに外力を加えることなく錘部90を形成することができるので、より好ましい。
By doing in this way, since the
また、上記実施形態では、第2部材61の周方向の両端部に設けられた楔部67を、第1部材60側の凹部68に係合させた状態で、第1部材60と第2部材61とが接合されている場合を説明したが、楔部67及び凹部68による係合は必須なものではなく、具備しなくても構わない。但し、接合強度を高め、第1部材60からの第2部材61の剥がれや、第1部材60に対する径方向及び周方向への位置ずれを規制することが可能となるので、設けることが好ましい。
さらに、上記楔部67及び凹部68に代えて、別の係合部材を第1部材60と第2部材61に設けても構わないし、上記楔部67及び凹部68に加えて、別の係合部材を第1部材60と第2部材61に追加しても構わない。
Moreover, in the said embodiment, the
Further, instead of the
例えば、図28及び図29に示すように、第1部材60の外周部に径方向の外側に開口する係合凹部(第1係合部)91を周方向に間隔をあけて2つ設け、第2部材61の内周部に径方向の内側に向けて突出し、係合凹部91に係合する係合凸部(第2係合部)92を周方向に間隔をあけて2つ設けても構わない。
このように、係合凹部91及び係合凸部92をさらに加えることで、第1部材60と第2部材61との接合強度をさらに高めることができるので、より好ましい。なお、係合凹部91及び係合凸部92の数は、2つに限定されるものではない。
For example, as shown in FIG. 28 and FIG. 29, two engagement recesses (first engagement portions) 91 that are opened outward in the radial direction are provided on the outer peripheral portion of the
Thus, by further adding the
また、図30及び図31に示すように、第1部材60と第2部材61とを合金層95を介して接合させても構わない。
この合金層95を形成する場合には、電鋳工程によって第2部材61を形成させた後、バイメタル部50が形成された前駆体75を、所定温度雰囲気下で所定時間の間、熱処理する熱処理工程を行う。このように熱処理を行うことで、電鋳物である第2部材61の金を、第1部材60との接合界面に沿って拡散させることができ、この拡散を利用して第1部材60と第2部材61との間に合金層95を形成することができる。
やはり、この場合であっても第1部材60と第2部材61との間の接合強度を高めることができ、バイメタル部50としての作動信頼性を高めることができる。
30 and 31, the
In the case of forming the
Even in this case, the bonding strength between the
なお、上記熱処理を行うタイミングとしては、電鋳工程の後であれば良く、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aを除去する前でも良いし、除去した後でも良い。但し、熱処理によって、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aと第2部材61との間にも合金層95が形成されるので、電鋳用ガイド壁70Aを除去した後に行うことが好ましい。
The timing for performing the heat treatment may be after the electroforming process, and may be before or after the
また、上記実施形態の場合には、第1部材60がシリコン、第2部材61が金であるので、熱処理温度としては1000℃程度で行うことが可能である。また、熱処理は大気中でも可能であるが、酸化を防止するために真空雰囲気中、又はアルゴンガスや窒素ガス雰囲気中でも行うことが好ましい。
Moreover, in the case of the said embodiment, since the
なお、本発明の技術範囲は上記実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の変更を加えることが可能である。 The technical scope of the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
例えば、上記実施形態では、バイメタル部50の数を3つとしたが、2つでも構わないし、4つ以上でも構わない。これらの場合であっても、各バイメタル部50を周方向に均等配置させれば良く、同様の作用効果を奏効することができる。また、連結部材51の形状は一例であり、適宜変更して構わない。
For example, in the above embodiment, the number of the
また、上記実施形態において、ひげぜんまい43の材料としてエリンバー等の恒弾性材料を用い、バイメタル部50における第2部材61を、セラミックス材料からなる第1部材60よりも熱膨張率が低い金属材料で形成しても構わない。この場合であっても、ひげぜんまい43の正の温度係数をキャンセルするように慣性モーメントの温度特性を微調整することが可能である。
In the above embodiment, a constant elastic material such as Elinvar is used as the material of the
また、上記実施形態では、てん輪42を構成する連結部材51及び第1部材60をシリコンとしたが、セラミックス材料で形成されていれば良く、シリコンに限定されるものではない。
例えば、セラミックス材料として、シリコンカーバイト(SiC)、二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)、サファイア、アルミナ(Al2O3)、ジルコニア(ZrO2)や、グラッシーカーボン(C)等を採用しても構わない。これらいずれのものを採用したとしても、エッチング加工、特にドライエッチング加工を好適に行うことが可能であり、連結部材51及び第1部材60を、より簡便且つ効率良く形成でき、製造効率をさらに高め易い。
Moreover, in the said embodiment, although the
For example, silicon carbide (SiC), silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ), sapphire, alumina (Al 2 O 3 ), zirconia (ZrO 2 ), glassy carbon (C), or the like may be employed as the ceramic material. . Even if any of these is adopted, it is possible to suitably perform the etching process, particularly the dry etching process, and the connecting
なお、本実施形態におけるセラミックス材料としては、電気抵抗の高い絶縁性を有していることが好ましい。また、連結部材51及び第1部材60の表面に、例えば酸化膜や窒化膜等のコーティング膜を施しても構わない。
In addition, as a ceramic material in this embodiment, it is preferable to have insulation with high electrical resistance. Further, a coating film such as an oxide film or a nitride film may be provided on the surfaces of the connecting
また、てん輪42を構成する第2部材61を金としたが、第1部材60とは熱膨張率が異なり(好ましくは大きく)、且つ電鋳可能な金属材料であれば良く、金に限定されるものではない。
例えば、Au、Ni、Ni合金(Ni−Fe等)、Sn、Sn合金(Sn−Cu等)等を採用して構わない。これらのいずれのものを採用したとしても、電鋳によりスムーズに金属材料を成長させることができ、効率良く第2部材61を形成することが可能である。
The
For example, Au, Ni, Ni alloy (Ni—Fe, etc.), Sn, Sn alloy (Sn—Cu, etc.) may be employed. Even if any of these is adopted, the metal material can be grown smoothly by electroforming, and the
特に、上記したいずれの金属材料を採用したとしても、熱処理によって合金層95を形成することが可能となる。その場合における、第1部材60側のセラミックス材料の組み合わせとしては、特にシリコン(Si)、シリコンカーバイト(SiC)が好ましい。
なお、これらの組み合わせを行った場合における、熱処理工程時の好ましい熱処理温度を図32に示す。この図32に示す熱処理温度で熱処理を行うことで、接合強度を高めるのに十分な合金層95を形成することが可能である。
In particular, even if any of the above metal materials is adopted, the
Note that FIG. 32 shows a preferable heat treatment temperature in the heat treatment step when these combinations are performed. By performing heat treatment at the heat treatment temperature shown in FIG. 32, it is possible to form an
O…軸線(回動軸)
S…電鋳用開放空間
1…機械式時計
10…ムーブメント(時計用ムーブメント)
22…香箱車
28…表輪列(輪列)
30…脱進機構
40…てんぷ(温度補償型てんぷ)
41…てん真
42…てん輪
50…バイメタル部
50A…固定端
50B…自由端
51…連結部材
60…第1部材
61…第2部材
65、90…錘部
67…楔部(第2係合部)
68…凹部(第1係合部)
70…シリコン基板(セラミックス基板)
70A…電鋳用ガイド壁
75…前駆体
91…係合凹部(第1係合部)
92…係合凸部(第2係合部)
95…合金層
O ... Axis (rotating axis)
S ... Open space for electroforming 1 ...
22 ...
30 ...
41 ... balance 42 ...
68 .. recessed portion (first engaging portion)
70 ... Silicon substrate (ceramic substrate)
70A ...
92 ... engaging convex part (second engaging part)
95 ... Alloy layer
Claims (11)
前記てん真の回動軸回りに周方向に並んで配置され、該回動軸の周方向に沿って円弧状に延びた複数のバイメタル部、及びこれら複数のバイメタル部と前記てん真とをそれぞれ径方向に連結する連結部材を有するてん輪と、を備え、
前記バイメタル部は、第1部材と、該第1部材よりも径方向外側に配置された第2部材とが径方向に重なった積層体とされると共に、周方向の一端部が前記連結部材に連結された固定端とされ、周方向の他端部が自由端とされ、
前記第1部材は、セラミックス材料により形成され、
前記第2部材は、前記第1部材とは熱膨張率が異なる金属材料により形成されることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 With the balance rotating around the axis,
A plurality of bimetal portions arranged in a circumferential direction around the rotation axis of the balance shaft and extending in an arc shape along the circumferential direction of the rotation shaft, and each of the plurality of bimetal portions and the balance stem A balance wheel having a connecting member to be connected in the radial direction,
The bimetal portion is a laminated body in which a first member and a second member arranged radially outside the first member overlap in the radial direction, and one end portion in the circumferential direction is connected to the connecting member. The connected fixed end, the other end in the circumferential direction is the free end,
The first member is formed of a ceramic material,
The temperature-compensated balance balance is characterized in that the second member is made of a metal material having a coefficient of thermal expansion different from that of the first member.
前記第1部材及び前記連結部材は、セラミックス材料により一体に形成され、
前記第2部材は、前記第1部材とは熱膨張率が異なる金属材料からなる電鋳物であることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 In the temperature compensated balance according to claim 1,
The first member and the connecting member are integrally formed of a ceramic material,
The temperature-compensated balance balance, wherein the second member is an electroformed product made of a metal material having a coefficient of thermal expansion different from that of the first member.
前記第2部材は、前記第1部材に形成された第1係合部に係合する第2係合部を備え、該係合を維持したまま前記第1部材に対して接合していることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 In the temperature compensation type balance according to claim 1 or 2,
The second member includes a second engagement portion that engages with a first engagement portion formed on the first member, and is joined to the first member while maintaining the engagement. A temperature-compensated balance that features
前記第1部材と前記第2部材は、合金層を介して接合されていることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 In the temperature compensation type balance according to claim 1 or 2,
The temperature compensation type balance with which the first member and the second member are joined via an alloy layer.
前記バイメタル部の自由端には、錘部が設けられていることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 The temperature-compensated balance according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
A temperature compensated balance with a weight portion provided at a free end of the bimetal portion.
前記第1部材及び前記連結部材は、Si、SiC、SiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2、又はCのうちのいずれかの材料で形成されていることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 In the temperature compensation type balance according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
The temperature-compensated balance balance characterized in that the first member and the connecting member are made of any one material of Si, SiC, SiO 2 , Al 2 O 3 , ZrO 2 , or C.
前記第2部材は、Au、Cu、Ni、Ni合金、Sn、又はSn合金のうちのいずれかの材料で形成されていることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷ。 In the temperature compensation type balance according to any one of claims 1 to 6,
The temperature-compensated balance balance characterized in that the second member is made of any material of Au, Cu, Ni, Ni alloy, Sn, or Sn alloy.
前記香箱車の回転力を伝達する輪列と、
前記輪列の回転を制御する脱進機構と、
前記脱進機構を調速する請求項1に記載の温度補償型てんぷと、を備えていることを特徴とする時計用ムーブメント。 A barrel complete with a power source;
A train wheel for transmitting the rotational force of the barrel wheel,
An escapement mechanism for controlling rotation of the train wheel;
A timepiece movement comprising the temperature compensated balance according to claim 1, wherein the escapement mechanism is controlled.
セラミックス基板を半導体製造技術により加工して、前記連結部材に複数の前記第1部材が一体に連結されると共に、それぞれの前記第1部材との間に電鋳用開放空間を画成させる電鋳用ガイド壁が、それぞれの前記第1部材に一体に連結された前駆体を形成する基板加工工程と、
前記前駆体における前記電鋳用開放空間内に前記金属材料を電鋳により成長させることで前記第2部材を形成し、前記第1部材と前記第2部材とが径方向に重なった接合された前記バイメタル部を形成する電鋳工程と、
前記電鋳用ガイド壁を前記第1部材から除去する除去工程と、を備えていることを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷの製造方法。 A method for producing the temperature-compensated balance according to claim 1,
An electroforming process in which a ceramic substrate is processed by a semiconductor manufacturing technique, and a plurality of the first members are integrally connected to the connecting member, and an open space for electroforming is defined between each of the first members. A substrate processing step in which a guide wall for forming a precursor integrally connected to each of the first members;
The second member is formed by growing the metal material by electroforming in the open space for electroforming in the precursor, and the first member and the second member are joined in a radial direction. An electroforming process for forming the bimetal portion;
And a removing step of removing the electroforming guide wall from the first member.
前記電鋳工程後、前記バイメタル部が形成された前記前駆体を、所定温度雰囲気下で所定時間の間、熱処理する熱処理工程を行うことを特徴とする温度補償型てんぷの製造方法。 In the manufacturing method of the temperature compensation type balance according to claim 10,
A temperature-compensated balance balance manufacturing method characterized by performing a heat treatment step of heat-treating the precursor on which the bimetal portion is formed in a predetermined temperature atmosphere for a predetermined time after the electroforming step.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013034704A JP6025203B2 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2013-02-25 | Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance |
| CN201410055583.8A CN104007650B (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2014-02-19 | Temperature compensating type escapement and its manufacture method, clock machine core, mechanical clock |
| CN201710735064.XA CN107505826B (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2014-02-19 | Temperature compensation type balance wheel and manufacturing method thereof, clock movement and mechanical clock |
| US14/185,131 US9235193B2 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2014-02-20 | Temperature compensation-type balance, timepiece movement, mechanical timepiece and manufacturing method of temperature compensation-type balance |
| CH00272/14A CH707630B1 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2014-02-25 | Balancer of temperature compensating type, movement of a timepiece, mechanical timepiece and method of manufacturing such a balance. |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013034704A JP6025203B2 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2013-02-25 | Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014163785A JP2014163785A (en) | 2014-09-08 |
| JP6025203B2 true JP6025203B2 (en) | 2016-11-16 |
Family
ID=51614527
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013034704A Active JP6025203B2 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2013-02-25 | Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6025203B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6358944B2 (en) * | 2014-12-12 | 2018-07-18 | シチズン時計株式会社 | Method for producing electroformed part, electroformed part, electroformed part for watch and bearing |
| JP6144300B2 (en) | 2015-07-16 | 2017-06-07 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Graphene production method, graphene production apparatus and graphene production system |
| JP6602267B2 (en) * | 2016-06-16 | 2019-11-06 | シチズン時計株式会社 | Ten ring manufacturing method |
| JP2018044835A (en) * | 2016-09-14 | 2018-03-22 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Method for manufacturing machine part, and method for manufacturing watch |
| JP7060988B2 (en) * | 2018-03-16 | 2022-04-27 | セイコーインスツル株式会社 | Temperature-compensated balance, movement and watch |
| EP4187326A1 (en) * | 2021-11-29 | 2023-05-31 | Omega SA | Hairspring for timepiece resonator mechanism provided with a means for adjusting stiffness |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1176527A (en) * | 1914-02-11 | 1916-03-21 | Frederic Ecaubert | Compensating balance-wheel. |
| US2936572A (en) * | 1957-08-12 | 1960-05-17 | Hamilton Watch Co | Balance wheel for electric watch |
| CN101091141B (en) * | 2004-10-26 | 2012-03-21 | Lvmh瑞士制造业股份公司 | Regulating element for wristwatch and mechanical movement comprising one such regulating element |
| EP2062101A2 (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2009-05-27 | Gideon Levingston | Thermally compensating balance wheel |
| CH704016B1 (en) * | 2010-10-15 | 2019-01-31 | Eta Sa Mft Horlogere Suisse | Assembly of a part not having a plastic field. |
-
2013
- 2013-02-25 JP JP2013034704A patent/JP6025203B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014163785A (en) | 2014-09-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107505826B (en) | Temperature compensation type balance wheel and manufacturing method thereof, clock movement and mechanical clock | |
| JP6025203B2 (en) | Temperature-compensated balance, movement for watch, mechanical watch, and method for manufacturing temperature-compensated balance | |
| JP5134137B2 (en) | Integrated adjustment member and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5243324B2 (en) | Monolithic hairspring and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5280903B2 (en) | Monolithic double balance spring and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5243398B2 (en) | Breguet, overcoil and balance spring made of silicon material | |
| US8550699B2 (en) | Composite balance and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP5389999B2 (en) | Speed governor with balance spring and method for manufacturing the same | |
| US8339904B2 (en) | Reinforced micro-mechanical part | |
| US9411314B2 (en) | Integral assembly of a hairspring and a collet | |
| CN104769510B (en) | method for forming flexible multi-stable element | |
| JP4852267B2 (en) | Automatic compensation spring made of two materials | |
| JP7254090B2 (en) | How to make a hairspring | |
| JP2009526215A (en) | Impact ball | |
| JP5366318B2 (en) | Detent escapement and method of manufacturing detent escapement operating lever | |
| JP6025202B2 (en) | Temperature compensated balance, watch movement, and mechanical watch | |
| WO2011030694A1 (en) | Detent escapement and mechanical watch having same | |
| JP2016173241A (en) | Hair spring | |
| CN111610707B (en) | Temperature compensation type balance wheel hairspring mechanism, movement and clock | |
| US11868089B2 (en) | Watch component and watch | |
| US20230136065A1 (en) | Silicon timepiece component for a timepiece | |
| JP2014062783A (en) | Balance wheel, watch movement, watch, and method for manufacturing balance wheel |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20151208 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160920 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160921 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20161006 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20161006 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6025203 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |