JP5538479B2 - LED light source and light emitter using the same - Google Patents
LED light source and light emitter using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5538479B2 JP5538479B2 JP2012137945A JP2012137945A JP5538479B2 JP 5538479 B2 JP5538479 B2 JP 5538479B2 JP 2012137945 A JP2012137945 A JP 2012137945A JP 2012137945 A JP2012137945 A JP 2012137945A JP 5538479 B2 JP5538479 B2 JP 5538479B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- led
- light source
- light
- lens
- led light
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 126
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000002310 reflectometry Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000001579 optical reflectometry Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 36
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 24
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 20
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 18
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 18
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010037660 Pyrexia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000191 radiation effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005562 fading Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
- Non-Portable Lighting Devices Or Systems Thereof (AREA)
- Planar Illumination Modules (AREA)
- Led Device Packages (AREA)
Description
本発明は発光ダイオード(LED; Light Emitting Diode)を用いた多種アプリケーションに適用可能な発光光源と、それを用いた液晶バックライト、照明器具、サイン/広告灯などの発光体に係わるものである。 The present invention relates to a light emitting source applicable to various applications using a light emitting diode (LED) and a light emitting body such as a liquid crystal backlight, a lighting fixture, and a sign / advertisement lamp using the light source.
光学レンズを備え持つLEDパッケージなどのLED光源構造についてはこれまでも数多く発明がなされている。その中で、LED光源の設置面に沿った方向、すなわち光源の側面方向へ強い光(側方放射配光)を発するレンズ及び光源構造についても幾つか提案がなされている。例えば、LED用レンズとレンズキャップ、及びそのレンズを用いた発光装置を対象として、レンズの中心軸に対して傾斜した角度の第一の屈折角、そして底面から第1の屈折面へスムーズな曲面として延びる第2の屈折面を有するレンズ形状により、側面放射を得るようにしたものがある(例えば、特許文献1)。 Many LED light source structures such as an LED package having an optical lens have been invented so far. Among them, some proposals have been made on a lens and a light source structure that emit strong light (side radiation distribution) in a direction along the installation surface of the LED light source, that is, a side surface direction of the light source. For example, for an LED lens, a lens cap, and a light emitting device using the lens, a first refraction angle that is inclined with respect to the central axis of the lens, and a smooth curved surface from the bottom surface to the first refraction surface There is one in which side radiation is obtained by a lens shape having a second refracting surface extending as described above (for example, Patent Document 1).
LEDチップを点光源とみなしてデザインされた上記文献1の発光装置について、大出力光源用(大放射束あるいは大光束)に適した構成とする場合、複数のLEDチップ(例えば近年普及が進んでいる1個あたり1mm×1mmの表面積を持つ1W級のラージLEDチップ)をパッケージ中心部に集中配置する構成が考えられる。しかしながら、上記文献1の特徴的なレンズ形状を用いて配光効果を出すためには、その光源を囲むだけの十分な大きさのレンズ径が必要になり、その光源占用表面積の広さにおよそ比例するように、レンズ厚みを厚くすることが不可欠である。
When the light-emitting device of
薄型化を意図して上記文献1のレンズ形状で、レンズの上下方向を圧縮したようなレンズを用いた場合には、薄型化とともにレンズ表面での全反射を含む反射効果が弱くなり、特徴とする側方放射の配光制御機能(側面放射配光)が大きく失われ、発光装置正面方向(中心軸に沿う方向)の光束比が増大していくこととなる。また、パッケージ中央の集中光源出力が大きくなるほど放熱性と同時に耐熱性確保の必要性が生じてくるため、この部分の厚みを極端に薄くすることが難しい。
In the case of using a lens in which the vertical direction of the lens is compressed with the lens shape of the above-mentioned
また、ラージLEDチップを複数用いる場合、発光効率低下や短寿命化要因となるLEDチップ温度上昇を抑制するために、それぞれのLEDチップの配置間隔を広げた配置を考える。その場合にはLEDチップ占有面積が拡大するため、側面放射特性を維持しようとすると、レンズサイズ(直径、厚み)もそれに比例させるように大きくせねばならず、やはり一つの大光束装置として薄型化を図るのは困難である。さらに、LEDチップ自体がある程度拡散配光特性を有しているため、レンズ体積が増加することでレンズ形状内部の拡散光が増加し、結果としてレンズ表面での屈折/反射制御効果が低減することになってしまう。また、レンズ成形面を考えても側面に凹凸形状を設ける加工は容易なものではなく、量産時の製造コストが高くなることも避けられない。
以上のことから、上記文献1の構成では、LEDチップ総表面積が大きくなる条件において、側方放射配光を維持したまま薄型/コンパクト化に対応させることは非常に困難といえる。
Further, in the case of using a plurality of large LED chips, an arrangement in which the arrangement intervals of the respective LED chips are widened is considered in order to suppress an increase in LED chip temperature that causes a decrease in light emission efficiency and a shortening of the lifetime. In that case, the area occupied by the LED chip will increase, so if you want to maintain the side emission characteristics, the lens size (diameter, thickness) must also be increased proportionally. It is difficult to plan. Furthermore, since the LED chip itself has a certain amount of diffused light distribution characteristics, the diffused light inside the lens shape increases as the lens volume increases, resulting in a reduction in the refraction / reflection control effect on the lens surface. Become. Further, considering the lens molding surface, it is not easy to provide a concavo-convex shape on the side surface, and the production cost during mass production is unavoidable.
From the above, it can be said that with the configuration of the above-mentioned
本発明は、上記のような問題を解決し、大光束(大きな電気入力)かつ薄型で側面放射強度が高く、かつ安価なLED光源を得ること、及びそれを用いた発光効率のよい薄型大光束発光体を得ることにある。 The present invention solves the above problems, obtains a large luminous flux (large electric input), a thin, high side emission intensity, and an inexpensive LED light source, and a thin large luminous flux with good luminous efficiency using the same. It is to obtain a luminous body.
本発明に係るLED光源は、放熱性基板に少なくとも1つのLEDチップが実装され、前記LEDチップが透光性材料で封止されているLEDパッケージ部と、前記LEDパッケージ部上に配置され、前記各LEDチップの直上部で前記LEDチップ側に凹んだ凹部が形成されたレンズと、を備え、前記レンズは、前記凹部の形状が前記LEDチップの中心軸上に頂角を有する逆円錐または逆多角錐形状であるとともに、前記凹部の開始端から前記レンズの外周端に向かって該レンズの厚さが徐々に薄くなる湾曲形状を有し、前記レンズの外周端部が前記LEDパッケージ部の外周端から突出し、突出した部分の背面から光を放射させるように形成されていることを特徴とする。 The LED light source according to the present invention includes an LED package unit in which at least one LED chip is mounted on a heat dissipation substrate, the LED chip is sealed with a light-transmitting material, and the LED package unit is disposed on the LED package unit, and immediately above in the LED chip recess recessed is formed on the side lens of the LED chip, wherein the lens is inverted cone shape of the recess has an apex angle on the mandrel in said LED chip or with an inverted pyramid shape, from the starting end of the concave portion on the outer peripheral edge of the lens have a curved shape in which the thickness is gradually thinned in the lens, peripheral edge of the lens of the LED package portion It protrudes from an outer peripheral end, and is formed so that light may be radiated | emitted from the back surface of the protruded part .
本発明によれば、レンズ上部に形成した凹部によりLEDチップから出た光をレンズの側方に広げ、それを効率よくレンズ周辺まで光伝搬し、レンズ周辺での側方発光成分を増やすことができる。さらにLEDチップを複数用いる場合には、それらを放熱性基板の実装領域に散在させ、互いに間隔を開けて実装配置することで、放熱性が向上しLEDチップの能力劣化も防止される。したがって、大光束または大放射束を目的として複数のラージLEDチップを用いる大投入電力のLED光源においても、LEDチップ温度上昇を抑制し、側面放射強度が高い薄型のLED光源を得ることができる。 According to the present invention, the light emitted from the LED chip is spread to the side of the lens by the recess formed in the upper part of the lens, and the light is efficiently propagated to the periphery of the lens, thereby increasing the side emission component around the lens. it can. Further, when a plurality of LED chips are used, they are scattered in the mounting area of the heat dissipating substrate, and are mounted and arranged at a distance from each other, thereby improving the heat dissipating property and preventing the deterioration of the LED chip performance. Therefore, even in a large input power LED light source using a plurality of large LED chips for the purpose of a large luminous flux or a large radiant flux, a thin LED light source with high side emission intensity can be obtained while suppressing the LED chip temperature rise.
実施の形態1.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図とともに説明する。図1(a)は本発明の実施の形態1に係るLED光源の上面図、図1(b)は図1(a)のA−A断面図である。このLED光源は、LED実装基板である放熱性基板1、ダム材2、LEDチップ3、蛍光材料4、及び透光性の封止樹脂(透光性樹脂)5を有したLEDパッケージ部6と、LEDパッケージ部6の上部に設けられたレンズ7とを備えている。放熱性基板1には少なくとも1個のLEDチップ3が実装され、その上面にLEDチップ3の発光波長により励起発光する波長変換機能を備えた蛍光材料4が設けられている。LEDチップ3の周辺にはダム材2を配置し、ダム材2の内側(ダム材で囲まれた部分)を透光性の封止樹脂5で充填してLEDチップ3を覆い、LEDチップ3の保護と光取出し量向上などを図っている。なお、蛍光材料4は、後述するように、必要に応じて設けられるものである。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1A is a top view of the LED light source according to
放熱性基板1は、薄型化及び高放熱性の特徴を持たせるため、熱伝導性の高い例えば銅やアルミなどの金属材料、あるいはセラミック材料などを用いるとともに、必要に応じLEDチップ3との絶縁を保つ絶縁層や表面反射層を持つように形成する。本実施の形態では、放熱性基板1を薄い銅材を主材としている。なお、図1では複雑化を避けるため、放熱性基板1上におけるLEDチップ3の固着材料である接着層、外部とLEDチップ3との電気回路を形成する配線パタン、さらにそのための金属ワイヤあるいは金属バンプといった部材は省略している。
The
ダム材2は、製造時において封止樹脂5の流動を防ぐもので、樹脂や金属材料などで構成する。また、ダム材2を放熱性基板1と同様の材料で構成してもよい。また、ダム材2にリフレクタとして反射あるいは配光制御機能を与える場合には、その表面を鏡面あるいは拡散性の高反射材料で形成する。ダム材2の内側面及びダム材2で囲まれる放熱性基板1の表面(以下、キャビティ)は高反射率の鏡面とし、ダム材2の他の表面は高反射性拡散部としている。
The
LEDチップ3は、例えば青紫〜青色に発光するLEDチップとし、蛍光材料4をその発光波長を吸収する黄色味を含む光色を発する材料で構成する。そして、蛍光材料4の量の調整により、白色発光光源とすることが可能であり、本実施の形態はそのような構成による大光束白色光源を得る構成例としている。なお、蛍光材料4を用いない場合でも、LEDチップ3の発光色を発する大放射束LED光源として、本発明の効果を得ることができる。
The
図1のLED光源は、大光束のLED光源を得るためにラージLEDチップ3(1個あたり表面約1mm×1mm、1W程度のもの)を4個用いている。そして、これらのLEDチップ3を中央に密集配置させずに、放熱性基板1の実装領域(キャビティ)に散在させ、互いに間隔を開けて実装配置している。すなわち図1では、4個のLEDチップ3を放熱性基板1のキャビティ上に円環状に略等間隔で配置している。これは、LEDチップ3を放熱性基板1の中央に集中配置した場合、LEDチップ相互間での熱影響を受けて温度上昇しやすく、また放熱性基板1直下での発熱量の面積密度が非常に大きくなってしまう。さらに、LEDチップ3はその基本特性として温度上昇により発光効率が低下する性質があり、また封止樹脂5やペースト材をはじめLEDチップ3の周辺構成部材も温度上昇するとともに劣化速度が速まる傾向にある。そのため、LED光源の大きさに制約がある場合でも、大投入電力(大光束化)が必要となる場合には、上述したようにできるだけLEDチップ3の間隔を広くとる構成とすることが温度上昇の抑制に有利となる。
The LED light source of FIG. 1 uses four large LED chips 3 (each having a surface of about 1 mm × 1 mm, about 1 W) to obtain an LED light source with a large luminous flux. Then, these
これに対して、前述した特許文献1のレンズを対象にLEDチップ3を4個集中配置させた場合、特にラージLEDチップの場合、3×3mm程度の集中配置面積が必要になる。したがって、レンズ7の厚みやパッケージベース部6を含めた装置としての厚みは相応に厚い構成となり、本発明で実現しようとする例えば総厚み2mm以下の薄型化を実現することすることは難しい。
On the other hand, when four
レンズ7は、LEDパッケージ部6上に配置し、各LEDチップ3の直上部に向かって徐々に厚みが増す湾曲形状とし、当該直上部にはLEDチップ3側に向かって凹んだ凹部8を有するように構成した。凹部8は、LEDチップ3に向かって凹部内側の空間断面積が徐々に小さくなる形状が好ましく、本実施の形態1ではその形状を逆円錐形状としている。なお、凹部8の形状は、LEDチップ3からの光の側方放射特性が向上するものであれば、円柱、多角柱、逆多角錐などの形状であってもよい。レンズ7に、このような凹部8を設けることで、LEDパッケージ部6の中心軸方向に向かう光を、LEDパッケージ部6の側面方向に効果的に変更させることができる。すなわち、図2に示したように、LEDチップ3からの光線でLEDチップ3の中央上方に進んだものは、凹部8の逆円錐表面8a(凹部8の斜面)でスネルの法則に従って全反射成分を含む反射成分が側方に進むことになる。さらに、レンズ7の湾曲表面での全反射などにより、レンズ周辺部へと光が進み、一部はそのままレンズ7周辺から発光し、また一部はダム材2の表面反射状態により光の進路を変え、レンズ7の表面側へと抜け出る。レンズ7の緩やかな湾曲形状は、それを平面とした場合と比較すると、全反射角を大きく変えることなく導光路を広く確保でき、レンズ7の周辺部までの導光効果を高めることが可能となっている。
The
また、図1のレンズ7では、4個のLEDチップ3にそれぞれ対応する4つの湾曲面を表面に有し、各湾曲面が交差する線をもった表面形状としているが、それによって得られるレンズ7の中央の窪みは、LEDパッケージ6の内部反射を含めキャビティ表面中央部からLED光源の中央方向に放射しようとする光の強度を抑えこむ作用も果たしている。
Further, the
上記のような構成によって、レンズ7の凹部8で光を効果的に側方に広げ、それを効率よくレンズ周辺まで光伝搬し、レンズ周辺での側方発光成分を増やすことができる。したがって、以上のような放熱性に配慮したLEDチップ配置とそれに対応させたレンズ形状により、LEDチップ3の放熱性がよく、しかも側方発光成分の高い大光出力を有するLED光源を得ることができる。
With the configuration as described above, the light can be effectively spread laterally by the
レンズ7は、例えばポリカーボネート、エポキシ、シリコーンなど目的に合わせた樹脂材料で形成することができる。なお近年耐候性改善が進んでいるシリコーン樹脂を用いる場合は、軟質〜硬質材料でn=1.41〜n=1.53程度のもので形成することができる。図1の構成では、例えば封止樹脂5を軟質透光性シリコーンとし、表面レンズ7を光取出し性が良好で外部衝撃に強い、軟質より屈折率が高い硬質シリコーンで形成する。またその際、光取出し効率の面から、封止樹脂5とレンズ7の中間層に空気層が入らないように封止樹脂5とレンズ7を密着させるか、あるいは他の軟質シリコーン材料を介在させるような構成としてもよい。またオーバーモールドのような方法で封止樹脂5とレンズ7を同一の材料で形成してもよい。
The
図2は図1のLED光源のレンズの凹部8の作用を説明する説明図である。図2に示したように、逆円錐凹部の頂角の1/2をθとした場合、θをレンズ屈折率nと周辺媒質n0で定まる全反射角、あるいはそれに近い角度となるようにする。例えば、n0=1(空気)のとき、n=1.41でθ=45°、n=1.53でθ=41°とし、このような構成により、LEDチップ3(蛍光材料4がある場合にはそれも含む)から放射された光で凹部8の逆円錐形状表面へ到達した光のうちで、スネルの法則にしたがってLED光源の側面方向へ光の向きを変えるものが相当量出てくる。なお、その効果を高めるには、逆円錐形状を構成する凹部8がある程度の大きさを持つことが必要になる。そこで凹部8の開始端(切り欠き端)直径が、LEDチップ3の対角寸法以上となるように構成することで、少なくともLEDチップ3からLED光源の垂直方向に進む光に対しては上記逆円錐形状の傾斜面に入射させることが可能となる。
FIG. 2 is an explanatory view for explaining the operation of the
このように構成することで、LEDチップ3から放射した光の凹部8の逆円錐面での全反射成分量を多くすることができ、その結果レンズ7の側面方向に効果的に光を広げることが可能となる。以上の構成の効果は前述した凹部8の形状を逆多角錐とした場合でも得られ、その頂角やレンズ7の表面の逆円錐切り口形状の寸法も逆円錐の場合とほぼ同様に構成すればよい。また、この実施の形態では、レンズ7の湾曲形状表面の逆円錐切り欠き端が角度を持つように構成しているが、この角度の部分を凹部内面から湾曲面へ連続変化するなだらかな曲面になるように構成してもよく、また凹部8の逆円錐の頂点は丸みをおびていても良い。
With this configuration, it is possible to increase the amount of total reflection components on the inverted conical surface of the
図3は本発明の実施の形態1に係るLED光源の変形例を示す側断面図である。図3に示すように、凹部8の表面を反射部材10で形成することで、凹部8から直接放射する光を無くし、凹部8側面方向へ光を制御できる。反射部材10は薄膜や塗料のようなものでもよく、発光効率を高く維持するため高反射性の鏡面、または拡散面として構成するのが好ましい。
FIG. 3 is a side sectional view showing a modification of the LED light source according to
また、図3は、ダム材2よりレンズ7の横幅を広くする、すなわち、レンズ7の外周部がLEDパッケージ部6の外周端から突出する大きさに形成したものである。このように構成することで、意図的にレンズ7のダム材2の端部より突出した部分の背面(ダム材2側)から光を放射させることで、その光を本発明の光源を用いた外部アプリケーション設置空間で有効利用することができる。
さらに、図4のように、ダム材を設けずに封止する加工方法で樹脂封止し、その封止領域よりもレンズ底面積を大きく設定することで、LEDチップ3から側方放射される光を、封止樹脂5を介し直接利用することが可能となる。なお、その封止樹脂5から抜け出る光の一部はレンズを通り上方に向かうものもあるが、その一部はレンズ7表面で反射され、側方あるいは背面方向に向かう光として利用することが可能である。
図3、図4では凹部8に反射部材10を具備する構成で示したが、それを持たない構成においても、光源側方から下部への発光量を高める効果をもつことは変わりない。
Further, FIG. 3 shows that the width of the
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 4, resin sealing is performed by a processing method of sealing without providing a dam material, and the lens bottom area is set larger than the sealing region, so that the
3 and 4 show the configuration in which the
また、図1に示すように、各LEDチップ3に対応するレンズ7の外周縁の接続部がパッケージ部6の中心方向に窪んでいた場合には、パッケージ部6の側方への配光に大きな強弱を生じる場合がある。そこで例えば、図5のように、レンズ7のパッケージ部6の中心からレンズ7の周縁部までの最大長以上の半径を有する円板状の透光部材をレンズ周縁配光対策部9としてレンズ7の背面に備え持つような構造として設けた。本構成によりパッケージ部6の側方への配光強弱を緩和させることが可能になり、適用するアプリケーション側で配光強度の均一性が要求される場合には有用となる。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 1, when the connection portion of the outer peripheral edge of the
以下に、実施の形態1に対応するLED光源を市販の光解析シミュレータでモデリングし、その配光試算を行った結果を示す。図6、図7は本発明が目的とする薄型化を意図し、LED光源総高さ2mmとする条件で作成したモデルの(a)斜視外観図と(b)配光試算結果である。なお、共通条件としてラージLEDチップを4個用い、それらをキャビティ上に集中配置せず、ダム材周縁部に十分間隔をおき配置した。ここで、ダム材及び放熱性基板のキャビティ表面は高反射率面とし、ダム材の内側面及び放熱性基板のキャビティ表面は鏡面反射、その他表面は拡散反射、レンズ屈折率を1.51、封止樹脂屈折率を1.41、LED実装基板である放熱性基板の厚みは0.2mmとした。
Below, the LED light source corresponding to
図6(a)は図1の構成をモデル化したものである。このモデルでは、ダム材2は外径11mm、内径7mm、高さ0.6mm、レンズ7は最大高さ0.8mm、最大径11.5mm、凹部8の斜面角度42°としている。このモデルでは、図6(b)の結果に示すように、配光特性はほぼLED光源を中心とし、中心強度を抑えつつ高い側方発光成分を有していることがわかる。
一方、図7(a)は図3及び図5で説明した構成を合わせ持つモデルである。このモデルでは、ダム材2は外径9mm、内径7mm、高さ0.6mm、レンズ7は最大高さ1.08mm、最大径16.6mm、凹部8の斜面角度42°としている。このモデルでは、図7(b)の結果に示すように、LED光源の中央発光強度はかなり抑えられ、かつ、側面への発光強度が強くなっていることがわかる。本モデルは前述したように、LED光源の下方方向の光の生成を意図したものであるが、図7(a)に示す配光角ηが、およそ60〜90°、及びおよそ−60〜−90°で、大きな発光強度が得られる特徴的光源であることがわかる。よって、ここで示した試算結果からも、本発明の実施の形態に係る放熱性を考慮した薄型大光束LED光源構成は、側方(側下方も含む)の発光強度を高める効果を有する光源構成であるといえる。
FIG. 6A is a model of the configuration of FIG. In this model, the
On the other hand, FIG. 7A is a model having the configuration described in FIGS. In this model, the
本発明の目的は、前述したとおり、放熱性のよい大光束光源を得ることにあり、LEDチップ3の個数を図1よりも多くするようにしてもよい。図8(a)、図8(b)は図1に示した4個のLEDチップよりさらに大光束化する5個のLEDチップ3を用いた場合の構成例である。なお、図8(a)は各LEDチップの温度上昇を抑制するために、LEDチップ5個を放熱性基板1のキャビティ上のダム材2側に周縁配置した例である。LEDチップが6個以上でも同様の配置は可能であり、さらに個数が多くなるような場合にはLEDパッケージ部6外形を必ずしも円形ではなく、楕円状、正方状、長方状などにして、それにあわせて、レンズ7を前述した特徴を備えたものとしてもよい。また、図8(b)は同じくLEDチップが5個の場合であり、1個を中心配置とし、その他4個を周縁配置したものである。図8(b)の場合には、やや光源中心方向への光束が大きくなる。
As described above, an object of the present invention is to obtain a large luminous flux light source with good heat dissipation, and the number of
一方、本発明は、図1ほど光束を必要としない場合にも適用可能である。例えば、図8(c)はLEDチップを3個周縁配置、図8(d)は空間的配光が左右、上下で非対称となるがLEDチップを2個周縁配置、さらに図8(e)はLEDチップを1個中心配置とした例である。なお、前述ではラージLEDチップの使用を前提に説明したが、レギュラーLEDチップ(表面積0.3×0.3mm、0.07W程度)やミドルLEDチップ(ラージチップとレギュラーチップ)を単数または複数個用いる場合でも適用可能である。 On the other hand, the present invention is also applicable to the case where a light beam is not required as in FIG. For example, FIG. 8 (c) shows three LED chips arranged at the periphery, FIG. 8 (d) shows a spatial light distribution that is asymmetrical in the left and right, top and bottom, but two LED chips are arranged at the periphery, and FIG. 8 (e) This is an example in which one LED chip is arranged in the center. Although the above description is based on the assumption that a large LED chip is used, one or more regular LED chips (surface area 0.3 × 0.3 mm, about 0.07 W) and middle LED chips (large chip and regular chip) are used. It is applicable even when used.
実施の形態2.
図9は本発明の実施の形態2に係るLED光源を示すもので、図9(a)は上面図、図9(b)及び図9(c)はその断面図である。ここでは、各LEDチップ3の周りを第一のダム材31で極力小面積となるように囲み、第一のダム材31で囲まれた部分を、蛍光材料4を混入した蛍光材料含有樹脂30で封止した例である。この態様はLEDチップ3の表面にだけ蛍光材料4を設けた図1の態様に比べて、比較的製造が容易で安価となる。第一のダム材31は、各LEDチップ3を囲む穴を設けた円筒状の材料として構成してもよい。さらに第一のダム材31上に別の第二のダム材32を形成し、その内部を透光性樹脂5で樹脂封止する構成としてもよい。このような構成とすることで、図1に示すような広いキャビティ空間に対し、その全空間を、蛍光材料4を含む封止材料で封止すると、キャビティ全体の広い領域が拡散発光領域となってしまいレンズ効果が薄らいでしまうことを抑制できる。
9 shows an LED light source according to
そこで、図9(b)に示すように、LEDチップ3の周辺領域にだけ蛍光材料含有樹脂30を配置し、LEDチップ3周辺の初期発光源が広い面積での拡散光とならないように、拡散光の範囲をLEDチップ3表面付近に制限する構成としてもよい。なお、レンズ7の形状は図1の構成と同様に、LEDチップ3の直上部に向かって厚みが増し、その直上部付近ではLEDチップ3側に凹んだ凹部8が形成されている。この際、凹部8表面を図3に示したような高反射材10で形成することで、さらに側方方向への発光強度の高いLED光源を得ることができる。
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 9B, the fluorescent material-containing
図9(c)は、第一のダム材31で囲まれた蛍光材料含有樹脂30の上部領域を空洞36とした中間導光材料層35を形成し、その空洞36の上面に相当する位置にレンズの凹部頂点が位置する構成である。空洞36の内表面を高反射率材料とすることで、中間導光材料層35の材料によらず蛍光変換光がその空洞36に沿って放射される。本構成においてもレンズ7の凹部8へ効率よく光を放射させることができ、それを凹部8の斜面8aで光の方向を変えることで側面発光強度を高めることができる。
なお、図9(c)の中間導光材料層35を用いる構成は、図1の蛍光材料4をLEDチップ3表面に備えた構成にも適用可能であり、LED発光光が高反射率側面に沿って放射されるとともに、拡散発光面積をおよそLEDチップ3の面積程度に抑えることでレンズ凹部付近への効率よく光が進行するため、側方への光制御を高める効果を有する。
In FIG. 9C, an intermediate light
The configuration using the intermediate light
実施の形態3.
図10は本発明の実施の形態3に係るLED光源を示すもので、図10(a)は上面図、図10(b)は図10(a)の側断面図、図10(c)は図10(b)の変形例を示す側断面図である。ここでは、蛍光材料4として蛍光体を樹脂バインドした蛍光シート33を用いている。図10(b)は図9(b)同様、LEDチップ3ごとに設けた第一のダム材31の内側を透光性のある封止樹脂5で封止し、その封止樹脂5に位置するような蛍光シート33を配置した例である。本構成では、さらにその上部に第二のダム材32を配置し、その内部を透光性のある封止樹脂5で封止した構成している。
また、図10(c)は、第一のダム材31上に複数のLEDチップ3をカバーする蛍光シート34を配置し、その上部を図9(c)と同様に、各LEDチップ3に対応する部分を空洞36とした中間導光材料層35を形成したものである。このような構成としても初期拡散光源の発光面積を小さくすることができ、これまで説明したレンズ構成との協働によりLED光源側方への光制御効果を高めることが可能となる。なお、ここでも凹部8の表面8aに高反射材10を形成することで、さらに側方方向への発光強度の高いLED光源を得ることができる。
FIG. 10 shows an LED light source according to
In FIG. 10C, the
さらに、図11のように、例えば蛍光体を樹脂混合した蛍光材料40をレンズ7に予め付加するような構成としても構わない。この場合、レンズ7背面のLEDチップ3の配置位置に、LEDチップ3と略同等面積の蛍光層(蛍光材料40)を有するように構成する。このような構成でも、蛍光拡散光領域を広げることなく、波長変換された光の凹部8の逆円錐表面の側方への光制御を行いやすい構成となる。図11(b)では、図10の構成と同様チップ3周囲を高反射性材料で囲むような中間導光材料層35を設け、ある程度LED光源の照射方向を制限し、その上部に蛍光層(蛍光材料40)が配置する構成としている。またこの例では封止部(透光性のある封止樹脂5)は光取出しを高めるため、ややドーム状の形状で構成している。図11(c)はレンズ7背面に蛍光層(蛍光材料40)を配置、図11(d)はレンズ7背面に窪みを設けその領域に蛍光層(蛍光材料40)を配置、図11(e)はレンズ7背面のLEDチップ3位置に相当する部分に凸部37を設け、その表面に蛍光層(蛍光材料40)を配置した構成である。なお、(e)は(d)におけるレンズ側面のみ表現した図である。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 11, for example, a
この際、この蛍光材料領域が例えばパッケージ全領域に渡るような大きい領域を仮定すると、レンズ7背面の広い領域から拡散光が入射することになり、レンズ7による光制御効果が大きく失われ、LED光源の配光は本発明で意図しない側方発光成分が少ない完全拡散発光に近づいてしまう。そこで上記のような構成とすることで、およそLEDチップ3の発光領域と同等面積程度に制限した蛍光変換領域を効率よく照射できるとともに、波長変換された拡散光の発光領域をLEDチップ3の面積程度に小さく抑えることができ、側方への光制御効果が高い光源を得ることができる。
At this time, if this fluorescent material region is assumed to be a large region, for example, covering the entire region of the package, diffused light enters from a wide region on the back surface of the
実施の形態4.
次に、本発明に係るLED光源(以下、本LED光源という)を利用した発光体について説明する。本LED光源を組み込む発光体は、例えば導光板方式や、導光板を利用しない直接照明方式や間接照明方式などにより様々な形態が取れるが、ここでは例えば液晶ディスプレイのバックライトなどの面状発光体(導光板)への適用とその発光体の発光効率を高める構成について説明する。
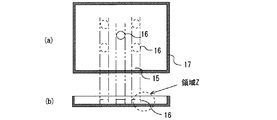
図12は、本LED光源を用いた実施の形態4を示すものであり、本発明のLED光源を組込み可能とした面状導光板の例で、図12(a)はその導光板表面の上面図、図12(b)は12(a)の側面図である。図12において、15は透光性樹脂等からなる導光板、16は本LED光源を配置するLED光源収容部(凹部や開口部等からなる)、17は導光板15の周囲に設けられ側面等に反射材料を有する導光板ケースである。照明面積が比較的小さい場合は、本LED光源を実線のように中央配置し、大面積照明が必要な場合には、例えば点線で示したように複数箇所に配置する構成とする。本LED光源を使用すれば、大面積照明が必要な場合でも、小光束LED光源を用いる場合に比較して、その使用個数を大幅に少なくできる。
Next, a light emitter using the LED light source according to the present invention (hereinafter referred to as the present LED light source) will be described. The light emitter incorporating the LED light source can take various forms such as a light guide plate method, a direct illumination method that does not use a light guide plate, and an indirect illumination method. Here, a planar light emitter such as a backlight of a liquid crystal display is used here. An application to the (light guide plate) and a configuration for increasing the light emission efficiency of the light emitter will be described.
FIG. 12 shows
図13は、図12の導光板15の凹部16を含む側面領域Zに、本LED光源を用いた実施の形態4に係る面状発光体の断面構造図である。導光板15に設けたLED光源収容部16に本LED光源を配置する。本LED光源の背面には放熱性材料18を設けている。また、放熱性材料18の周囲には、パッケージ背面方向に放射した光を反射して導光板15に入射させる高反射材料19を設けている。このようにしたことで、本LED光源の発する熱(LEDチップ発熱)を、LED光源の背面を介して、放熱させやすい構成とすることができる。この際、放熱性材料18の裏側に放熱部材、熱拡散部材、熱搬送部材等を設けて、放熱性をより向上させる構成としてもよい。また、高反射材料19の敷設によって、本LED光源の特に側方から下向き配光成分を反射させて導光板15の内部へ入光させることが可能になる。したがって、図13のような構造にすることで、光源下向き配光を強めるような積極設計を行ったLED光源(図3の構成例)に対して、高い入射効率で導光板15に光を入射させることができる。
FIG. 13 is a cross-sectional structure diagram of a planar light emitter according to
また、導光板15の背面(高反射材料19に接する面)には、背面光制御パタン敷設部20を設けて光伝拡散搬機能を与えている。さらに本発光体では、LED光源収容部16の側面に光源収容部側面光制御部21を、LED光源収容部16のレンズ7との対向面に光源収容部レンズ対向面光制御部22を設けている。これにより、本LED光源の特に上方に放射される光に対して、導光板15表面の輝度均斉化を行っている。これらの制御部21,22には、光制御構造または材料を設けて構成する。例えば、これらの制御部21,22の領域に、薄膜塗料ドット印刷や空間光濃度変調フィルムを配置するなどして導光板表面輝度均斉度を高めるような構成とする。
In addition, a back light control
また、図14のように本LED光源23周囲の光源収容部側面光制御部21として、例えば高さ数十μm程度の導光板背面から縞状に延びる凹凸形状(微細プリズム形状)24を付加するなどして表面積を大きくとり、その表面での光の屈折効果も利用しながら入射効率を高めるような構成としてもよい。
Further, as shown in FIG. 14, as the light source housing side
さらに、図15(a)のように、図13の光源収容部側面光制御部21に相当する部分の導光板15の形状を、本LED光源の表面形状に沿うような緩やかな湾曲面を持つように構成してもよい。その場合は本LED光源と導光板15との間の空気層(光源収容部16)を少なくすることができ、入射効率を高めることができる。あるいはその部分を図15(b)のように、段差状とした階段形状部26として構成することもできる。このようにすることで、配光(たとえば図6(b)や7(b)で示した配光)の側方上向き光成分を屈折、全反射を利用して抑えることができる。
さらに、導光板15の表面上、本LED光源の配光強度の高い方向に位置する領域、あるいはその近傍に、反射性パタンの薄膜印刷や光濃度変調フィルム装着、あるいは微細凹凸形状の直接付加などの光濃度調整部27を設けて、輝度均斉化を行うようにしてもよい。また、上記空気層の隙間に透光性樹脂を充填するような構成とすれば、本LED光源のレンズ7と導光板15との間の層の屈折率差を小さくすることができるため、導光板15への入射効率がさらに高まり発光効率が向上する。
Further, as shown in FIG. 15 (a), the shape of the
Further, on the surface of the
また、上述した実施の形態1〜4では、図1や図3のようにレンズ7の厚み形状がその周端部に向け薄くなる構成、またパッケージ直径に対してレンズ7の外形がやや大きめとなるレンズ7形状の例で効果を説明してきたが、図16に示すようにレンズ7の外径をパッケージ直径と同等とし、レンズ7の側面をほぼ垂直に立ち上がるような平坦面(円柱形状の側面を含む面)として形成するようにしてもよい(図16(b)の断面図参照)。この構成の場合、小径化とともに広い面積を有するレンズ7の側面からの光放射比率が増加するため側方発光の効果方向を有する。
In the first to fourth embodiments described above, the
図17及び図18に、レンズ7の側面を平坦面とした場合のシミュレーションモデル(a)と配光特性試算結果(b)を示す。図17は、図7の構成においてレンズ7の直径と等しくしたものであり、ダム材を外径9mm、内径7mm、高さ0.6mm、レンズを最大高さ0.72mm、最大径9mm、凹部の斜面角度42°とした場合の結果である。図17(a)のモデル角度方向と図17(b)の結果の軸は図6と同様であり、図17(b)図からの側方発光効果を有することがわかる。また図18は図17おいてダム材が無い場合の構成であり、この場合には側方(大きい角度)での光取出し量が増えていることがわかる。
17 and 18 show a simulation model (a) and a light distribution characteristic trial calculation result (b) when the side surface of the
また、他のレンズ表面形状として、例えば図20に示すように、LEDチップ3を4個実装した構成で、図20(b)、(c)のLEDチップ3直上に逆円錐等の凹部8を有する円柱形の構成、図20(d)のレンズ7の中心が薄い凹形状8とした構成などでも側方照射効果を得ることができる。ここでも逆円錐状の凹部8はその頂角の1/2をおよそ全反射角とし、さらに表面と逆円錐の交点が作る円形領域がLEDチップ3を囲むような大きさになるように構成している。何れも各LEDチップ単位に設けた窪み(凹部8に対向する第一のダム材31内)にLEDチップ3を実装し、蛍光体混入した封止材料38で封止した構成例としている。さらに図示したように必要に応じて第二のダム材32を形成し、その内部を透明度の高い封止樹脂で封止する。
これらの構成について、シミュレーションモデルと、キャビティ表面を鏡面反射とした場合の試算結果を図21及び図22に示す。図21は図16(b)のように表面が高反射性のダム材2で各LEDチップ3を囲むように形成(LEDチップ3周囲の4箇所のみ開口した円盤状ダム材)し、さらにその上部に第二のダム材32を形成した0.8mm厚さのパッケージ部に、高さ1.1mm、直径9mm、凹部の斜面角度を42°としたレンズを配置した構成である。また、図22は図20(d)に対応しており、レンズ7の表面を曲率の大きい凹部形状としたものである。図21、図22何れの場合にも正面光度を抑え込み側面発光量を増加させる効果を有する。
In addition, as another lens surface shape, for example, as shown in FIG. 20, a configuration in which four
FIG. 21 and FIG. 22 show simulation models and trial calculation results when the cavity surface is specularly reflected for these configurations. FIG. 21 is formed so that the surface of each
また図23はさらに小径化を図った構成であり、パッケージ部直径6mm、高さ0.4mm、表面平坦レンズの高さ1.1mm、直径径6mm、凹部の斜面角度42°とした場合の結果である。以上の結果からコンパクト化を行っても側方放射効果が保たれることがわかる。
また、かなり大型サイズのLEDチップ(例えば1.5mm×1.5mmサイズ)を1個用いる場合の構成例を図24(e)、(f)に示した。このような構成でもパッケージ基材を放熱性材料とし、これまでの説明と同様の条件で逆円錐凹部8を有するレンズを設けることで、側方強度の高い大光束のLED光源を得ることができる。図25に、そのシミュレーションモデル(厚さ0.8mmのパッケージ部に、高さ1.2mm、直径3.0mm、凹部の斜面角度を42°としたレンズを配置した例)とその配光試算結果を示すが、この場合も側方放射効果を有することがわかる。
Further, FIG. 23 shows a configuration in which the diameter is further reduced, and results when the package part diameter is 6 mm, the height is 0.4 mm, the surface flat lens height is 1.1 mm, the diameter diameter is 6 mm, and the concave slope angle is 42 °. It is. From the above results, it can be seen that the side radiation effect is maintained even when the size is reduced.
In addition, FIGS. 24E and 24F show a configuration example in the case of using one LED chip having a considerably large size (for example, 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm size). Even in such a configuration, an LED light source having a high lateral intensity and a high luminous flux can be obtained by using a heat radiating material as a package base and providing a lens having an inverted
また、図16や図20のようにレンズ7の側面を広く設けた円柱形光源に対しては、図26のように導光板15の開口部を単純に円筒でくり貫いたような面としてその側面にほぼ接するような構成で用いることが可能である。この場合、レンズ7と導光板15の間にできる隙間を非常に少なくすることができ、光進行路における屈折率差を少なくすることができるので界面での反射ロスの少ない、導光板入光効率が高く発光効率の高い発光体を得ることができる。
Further, for a cylindrical light source having a wide side surface of the
また、図27のようにレンズ7の側面(光照射部)のみが導光板15と接するような構成としてもよい。パッケージ部6のダム材2部分より側方発光しない構成で、図26のようにパッケージ側面が導光板開口側面に接していると、その部分から光が入射する機会がなく、さらにパッケージ部高さだけ導光板15の表面に近づくために、導光板15の開口部から直接放射される光の割合が大きくなる。図27の構造ではレンズ7の側面表面積に対して導光板15の開口側面領域を広くとれるので、レンズより放射される光は導光板15に入射する機会が増加する。したがって、本構成により導光板入射効率が高い発光体を得ることが可能になる。この際、パッケージ部分背面の放熱性材料18はパッケージ部分を収納、かつ高反射性材料19を押さえ込むような凹部を有する形状として構成してもよい。以上のような構成でパッケージ放熱効果を保ちながら発光効率向上を実現することが可能となる。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 27, only the side surface (light irradiation unit) of the
図28、図29には、それぞれ図20(c)、図24(f)のLEDパッケージ6を導光板15の凹部に配置する構成例を示した。LEDパッケージ3のパッケージ基板表面を高反射性材料で形成し、およそレンズサイズの導光板15の窪みにほぼレンズ7の側面部と導光板15の窪み側面部が接するように構成した例である。レンズ7部分は薄型小径であるため、薄型導光板15に対しても導光板15のLED光源設置部の開口寸法を小さくでき、LED光源の直上方向の発光強度を抑えつつ、LED光源中央方向の光成分については、必要に応じて光源配置凹部上面光制御部22により光拡散効果あるいは部分的に光減衰効果を持たせ、導光板表面の発光均斉度を高めるように構成する。
また、図27、図28または図29の例では、LED光源のレンズ小径化を図るとともに、熱伝導性パッケージ部分をレンズ直径に対して明らかに大きい構成としている。このような構成により大出力LEDチップの発する大きな熱に対して伝熱面積を広くとることができ、図27、図28、図29のようにその背面をやはり大面積の金属性の導光板ケースに密着させ放熱路を形成することで、LEDチップ温度上昇を抑えた発光効率のよい発光体を得ることができる。
さらに、本構成のような円柱状のLED光源に対しては、図19に示すように、発光効率向上や配光制御の面から、レンズ7の側面の上下方向に例えばプリズムやシリンドリカルストライプなどの凹凸形状7aを加えるように構成してもよい。
FIGS. 28 and 29 show configuration examples in which the
In the example of FIG. 27, FIG. 28, or FIG. 29, the lens diameter of the LED light source is reduced, and the thermally conductive package portion is configured to be clearly larger than the lens diameter. With such a configuration, the heat transfer area can be widened against the large heat generated by the high-power LED chip, and the back surface of the metal light guide plate case having a large area as shown in FIGS. 27, 28, and 29. By forming a heat radiation path in close contact with each other, it is possible to obtain a light-emitting body with good luminous efficiency that suppresses the LED chip temperature rise.
Further, for a columnar LED light source such as this configuration, as shown in FIG. 19, from the surface of luminous efficiency improvement and light distribution control, for example, prisms, cylindrical stripes, etc. in the vertical direction of the side surface of the
以上のような構成により、LED光源23が配置される領域に面する導光板15の側面や、導光板15の表面にLED光源23の配光特性に応じ光制御機能を設けることで、面発光体としての発光効率及び輝度均一性を向上させることが可能となる。なお、本実施の形態では、導光板を対象とした面状発光体を例として本LED光源を用いた発光体の特性向上に係わる構成を説明したが、例えば棒状発光体においても上記と同様の構成により、配光及び熱的な面で特性のよい発光体を得ることができる。
With the configuration described above, surface light emission is achieved by providing a light control function according to the light distribution characteristics of the
以上説明したように、本発明は大光束かつ薄型で側方への発光強度が高いLED光源と、それを用いた発光体に係わるものであり、屋内外設置を問わず、小〜大光束照明用、液晶バックライト用など広い用途に用いることができるものである。 As described above, the present invention relates to an LED light source having a large luminous flux, a thin shape, and a high lateral emission intensity, and a light emitting body using the LED light source. It can be used for a wide range of applications such as LCD and liquid crystal backlights.
1 放熱性基板、2 ダム材、3 LEDチップ、4 蛍光材料、5 封止樹脂(透光性樹脂)、6 LEDパッケージ部、7 レンズ、8 凹部、9 レンズ周縁配光対策部、10 反射部材、15 導光板、16 LED光源収容部、17 導光板ケース、18 放熱性材料、19 高反射性材料、20 背面光制御パタン敷設部、21 光源収容部側面光制御部、22 光源収容部レンズ対向面光制御部、23 LED光源、24 凹凸形状(又は微細プリズム形状)、26 階段形状部、27 光濃度調整部、30 蛍光材料含有樹脂、31 第一のダム材、32 第二のダム材、33 蛍光材料、34 蛍光材料、35 中間導光材料層、36 開口部。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (25)
前記LEDパッケージ部上に配置され、前記各LEDチップの直上部で前記LEDチップ側に凹んだ凹部が形成されたレンズと、を備え、
前記レンズは、
前記凹部の形状が前記LEDチップの中心軸上に頂角を有する逆円錐または逆多角錐形状であるとともに、前記凹部の開始端から前記レンズの外周端に向かって該レンズの厚さが徐々に薄くなる湾曲形状を有し、
前記レンズの外周端部が前記LEDパッケージ部の外周端から突出し、突出した部分の背面から光を放射させるように形成されている
ことを特徴とするLED光源。 An LED package part in which at least one LED chip is mounted on a heat dissipating substrate, and the LED chip is sealed with a translucent material; and
A lens that is disposed on the LED package part and has a concave portion formed on the LED chip side immediately above each LED chip; and
The lens is
The shape of the recess is an inverted cone or inverted polygonal pyramid having an apex angle on the central axis of the LED chip, and the thickness of the lens gradually increases from the start end of the recess toward the outer peripheral end of the lens. It has a curved shape that becomes thinner,
An LED light source, wherein an outer peripheral end portion of the lens protrudes from an outer peripheral end of the LED package portion, and light is emitted from a back surface of the protruding portion.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012137945A JP5538479B2 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2012-06-19 | LED light source and light emitter using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012137945A JP5538479B2 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2012-06-19 | LED light source and light emitter using the same |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008259263A Division JP5025612B2 (en) | 2008-10-06 | 2008-10-06 | LED light source and light emitter using the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012227536A JP2012227536A (en) | 2012-11-15 |
| JP5538479B2 true JP5538479B2 (en) | 2014-07-02 |
Family
ID=47277302
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012137945A Active JP5538479B2 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2012-06-19 | LED light source and light emitter using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5538479B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5612491B2 (en) * | 2011-01-14 | 2014-10-22 | パナソニック株式会社 | Light source for illumination |
| JP6345443B2 (en) * | 2014-03-04 | 2018-06-20 | シチズン時計株式会社 | LED bulb |
| JP6296396B2 (en) * | 2015-09-28 | 2018-03-20 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | lighting equipment |
| CN113641035A (en) * | 2021-03-23 | 2021-11-12 | 达亮电子(滁州)有限公司 | Backlight module and display device |
| TW202413843A (en) * | 2022-08-11 | 2024-04-01 | 美商科銳Led公司 | Solid state light emitting components with unitary lens structures |
| WO2024113880A1 (en) * | 2022-11-29 | 2024-06-06 | 深圳市千岩科技有限公司 | Panel light and panel light apparatus |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6679621B2 (en) * | 2002-06-24 | 2004-01-20 | Lumileds Lighting U.S., Llc | Side emitting LED and lens |
| JP2004349646A (en) * | 2003-05-26 | 2004-12-09 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Light-emitting device |
| KR101080355B1 (en) * | 2004-10-18 | 2011-11-04 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Light emitting diode, lens for the same |
| JP2006186297A (en) * | 2004-12-03 | 2006-07-13 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor light emitting device and its manufacturing method |
| JP4629426B2 (en) * | 2004-12-16 | 2011-02-09 | ライツ・アドバンスト・テクノロジー株式会社 | Light guide and flat illumination device |
| KR101197046B1 (en) * | 2005-01-26 | 2012-11-06 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Two dimensional light source of using light emitting diode and liquid crystal display panel of using the two dimensional light source |
| KR20060135207A (en) * | 2005-06-24 | 2006-12-29 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | Light emitting diode lamp improving luminance and backlight assembly using the same |
| JP2007049019A (en) * | 2005-08-11 | 2007-02-22 | Koha Co Ltd | Light emitting device |
| JP2007067116A (en) * | 2005-08-30 | 2007-03-15 | Toshiba Lighting & Technology Corp | Light-emitting device |
| DE102005061208A1 (en) * | 2005-09-30 | 2007-04-12 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | lighting device |
| JP2007123390A (en) * | 2005-10-26 | 2007-05-17 | Kyocera Corp | Light emitting device |
| JP4844246B2 (en) * | 2006-06-09 | 2011-12-28 | 豊田合成株式会社 | Light emitting device and liquid crystal display backlight device |
| JP2008041290A (en) * | 2006-08-02 | 2008-02-21 | Akita Denshi Systems:Kk | Lighting device and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN101523620B (en) * | 2006-09-29 | 2012-06-06 | 罗姆股份有限公司 | Semiconductor light emitting device |
-
2012
- 2012-06-19 JP JP2012137945A patent/JP5538479B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012227536A (en) | 2012-11-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5025612B2 (en) | LED light source and light emitter using the same | |
| JP4869275B2 (en) | Light source module and light emitting device | |
| TWI426625B (en) | Light emitting unit | |
| JP5097548B2 (en) | Lighting system | |
| KR101203133B1 (en) | Led lighting device | |
| JP4960406B2 (en) | Light emitting diode light source module | |
| JP5538479B2 (en) | LED light source and light emitter using the same | |
| KR102307214B1 (en) | Led module with uniform phosphor illumination | |
| JP2006309242A (en) | Optical lens, light emitting element package using same, and backlight unit | |
| TWI671574B (en) | Light source module and display appartus | |
| JP2013105748A (en) | Illumination apparatus | |
| JP2011114341A (en) | Light emitting element package, and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2009266974A (en) | Light-emitting device and light-emitting apparatus | |
| JP2004191718A (en) | Led light source device | |
| JP5119379B2 (en) | Surface illumination light source device and surface illumination device | |
| JP2012227537A (en) | Led light source and luminous body using the same | |
| JP2005197320A (en) | Luminous light source and optical device using it | |
| KR20180039787A (en) | LED module with lens | |
| TW201506321A (en) | Light emitting diode light source module | |
| JP6127347B2 (en) | lighting equipment | |
| US10312408B2 (en) | Light emitting diode chip scale packaging structure and direct type backlight module | |
| JP2007173133A (en) | Light source unit and surface light emitting device | |
| JP4645240B2 (en) | Planar light emitting device | |
| WO2013175752A1 (en) | Wavelength conversion member, optical element, light-emitting device, and projection device | |
| JP2015035306A (en) | Luminaire |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130709 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130827 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131217 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140124 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140401 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5538479 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140428 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |