JP5453329B2 - Continuous casting mold - Google Patents
Continuous casting mold Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5453329B2 JP5453329B2 JP2011016871A JP2011016871A JP5453329B2 JP 5453329 B2 JP5453329 B2 JP 5453329B2 JP 2011016871 A JP2011016871 A JP 2011016871A JP 2011016871 A JP2011016871 A JP 2011016871A JP 5453329 B2 JP5453329 B2 JP 5453329B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- slab
- short side
- mold
- slab shell
- corner
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000009749 continuous casting Methods 0.000 title claims description 39
- 238000007711 solidification Methods 0.000 claims description 44
- 230000008023 solidification Effects 0.000 claims description 44
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000005499 meniscus Effects 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000015271 coagulation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005345 coagulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000498 cooling water Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007751 thermal spraying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008235 industrial water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Continuous Casting (AREA)
Description
本発明は、凝固収縮に基づく鋳片形状の変化に対応した連続鋳造用鋳型に関する。 The present invention relates to a continuous casting mold corresponding to a change in slab shape based on solidification shrinkage.
図5に示すように、一対の短辺側冷却部材100と一対の長辺側冷却部材101を組み合わせて形成する横断面が矩形状の連続鋳造用鋳型103(例えば、特許文献1参照)を使用した溶鋼の連続鋳造では、溶鋼が短辺側冷却部材100の鋳型壁104及び長辺側冷却部材101の鋳型壁105にそれぞれ接触して冷却され鋳片シェル(凝固シェル)106を形成する場合、凝固前の溶鋼の体積と凝固して鋳片シェル106を形成したときの体積を比べると、溶鋼の凝固収縮により鋳片シェル106の体積は溶鋼であったときの体積に比べて小さくなっている。
As shown in FIG. 5, a
このため、対向する短辺側冷却部材100の鋳型壁104及び長辺側冷却部材101の鋳型壁105に、それぞれ入口側から出口側に向けて(鋳造方向に)鋳片シェル106の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まるように短辺側傾斜部107及び長辺側傾斜部108を形成し、連続鋳造用鋳型103の横断面積を鋳造方向に徐々に減少させて鋳片シェル106の表面が各鋳型壁104、105に常に接触するようにしている。これによって、連続鋳造用鋳型103による鋳片シェル106の冷却を図って、鋳片シェル106の内部に存在する溶鋼109を凝固させて鋳片の厚みが大きくなるようにしている。
For this reason, the amount of solidification shrinkage of the
ここで、鋳片シェル106が形成された際に、連続鋳造用鋳型103の四隅領域で冷却される鋳片角部は、連続鋳造用鋳型103の角部を除いた平坦部で冷却される鋳片平坦部と比較して、短辺側冷却部材100及び長辺側冷却部材101の2面からの冷却の影響を受けるため大きく収縮する。このため、鋳型角部と鋳片角部との間にコーナーエアギャップ110を生じ易い。これによって、鋳片角部の冷却が不十分となり、凝固遅れに伴う鋳片角部の品質異常や、コーナーエアギャップ110から進入するスプレー水(二次冷却水)により鋳型下部の腐食(流電腐食)が発生し易いという問題がある。
また、鋳片角部の冷却が不十分なために鋳片角部の厚みが薄く、鋳片シェル106が連続鋳造用鋳型103内を移動する際に、鋳片角部に応力集中が生じて鋳片角部の品質が劣化したり、最悪の場合には鋳片角部でブレークアウトが発生するという問題が生じる。
Here, when the
In addition, since the corner of the slab corner is not sufficiently cooled, the thickness of the slab corner is thin, and when the
本発明はかかる事情に鑑みてなされたもので、凝固収縮に基づく鋳片形状に対応させて鋳型空間を変化させコーナーエアギャップの発生を防止して鋳片角部の品質異常や鋳型下部の腐食を防止することが可能な連続鋳造用鋳型を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and the mold space is changed corresponding to the slab shape based on the solidification shrinkage to prevent the occurrence of a corner air gap, thereby causing abnormal quality of the slab corner and corrosion of the lower part of the mold. It is an object of the present invention to provide a continuous casting mold capable of preventing the above.
前記目的に沿う本発明に係る連続鋳造用鋳型は、間隔調整が可能な一対の短辺及び該短辺を幅方向の両側から挟む一対の長辺とによって囲繞される鋳型空間部に注入される溶鋼を冷却し鋳片として引き抜く連続鋳造用鋳型において、
前記鋳型空間部を形成する鋳型壁の対向する前記長辺及び該鋳型壁の四隅の領域を除いた対向する前記短辺には、それぞれ前記鋳片が引き抜かれる方向に鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まる長辺側傾斜部及び短辺側傾斜部が形成され、
前記鋳型壁の四隅の領域の前記短辺には、外側に向かって拡大すると共に前記鋳片が引き抜かれる方向では前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小し、しかも、前記鋳型壁の下端から溶鋼の凝固が開始するメニスカス部までの各高さ位置において、前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面に沿って対向する前記短辺間の間隔を、前記鋳型壁の下端部における前記鋳片の広幅サイズWと、前記鋳型壁の下端での前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の形状を基準として算出された前記各高さ位置における平均熱膨張量Cの2倍の値2Cとの和(W+2C)とする短辺側拡大部が形成されている。
The continuous casting mold according to the present invention that meets the above object is injected into a mold space surrounded by a pair of short sides that can be adjusted in distance and a pair of long sides that sandwich the short sides from both sides in the width direction. In a continuous casting mold that cools molten steel and draws it as a slab,
The flat side of the slab shell is formed in the direction in which the slab is pulled out, respectively, on the opposing long side excluding the four corners of the mold wall and the long side of the mold wall that forms the mold space. A long side inclined portion and a short side inclined portion in which the interval gradually narrows following the amount of solidification shrinkage are formed,
The short side of the four corner regions of the mold wall expands outward and gradually decreases in the direction in which the slab is pulled out, following the amount of solidification shrinkage at the short side corner of the slab shell. In addition, at each height position from the lower end of the mold wall to the meniscus portion where solidification of the molten steel starts, an interval between the short sides facing each other along the surface of the short side corner portion of the slab shell is set. The average heat at each height position calculated based on the width W of the slab at the lower end of the mold wall and the shape of the short side corner of the slab shell at the lower end of the mold wall A short-side enlarged portion that is the sum (W + 2C) of the value 2C that is twice the expansion amount C is formed.
本発明に係る連続鋳造用鋳型において、前記鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量及び前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の凝固収縮量は、鋳造条件を基に演算した前記鋳型空間部内での前記鋳片シェルの凝固収縮解析結果に基づいて算出することが好ましい。 In the continuous casting mold according to the present invention, the solidification shrinkage amount of the flat portion of the slab shell and the solidification shrinkage amount of the short side corner of the slab shell are calculated in the mold space portion calculated based on casting conditions. It is preferable to calculate based on the solidification shrinkage analysis result of the slab shell.
請求項1〜3記載の連続鋳造用鋳型においては、鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量及び鋳片シェルの角部の凝固収縮量に基づいて鋳型空間の体積を鋳造方向に変化させることができ、コーナーエアギャップの発生を防止することが可能になる。その結果、鋳片角部の凝固遅れを抑制して鋳片角部の品質異常を防止することが可能になると共に、スプレー水の鋳型下部内への進入を抑制して腐食を防止することが可能になる。
In the continuous casting mold according to
特に、請求項2記載の連続鋳造用鋳型においては、短辺側傾斜部、長辺側傾斜部、及び短辺側拡大部の形状を容易に求めることができ、連続鋳造用鋳型の制作を容易に行なうことが可能になる。
In particular, in the continuous casting mold according to
続いて、添付した図面を参照しつつ、本発明を具体化した実施の形態につき説明し、本発明の理解に供する。
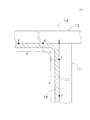
図1に示すように、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る連続鋳造用鋳型10は、間隔を設けて配置される一対の短辺11及び短辺11を幅方向の両側から挟む一対の長辺12とによって囲繞される鋳型空間部13に上方から溶鋼を注入し、鋳型空間部13を形成する鋳型壁14の内面に接触させて冷却し鋳片として鋳型空間部13の下側から引き抜いている。ここで、鋳片とは、例えば、鋳造断面積が固定されるブルームを指す。以下、詳細に説明する。
Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings for understanding of the present invention.
As shown in FIG. 1, the
短辺11(長辺12)は、熱伝導性が良好な金属の一例である銅を主体に形成され、背面側には、冷却水の一例である工業用水が通過する流路が設けられた図示しない冷却部が設けられている。なお、短辺11(長辺12)の表面(溶鋼と接触する面)には、めっきや溶射による被覆層が形成されている。ここで、短辺11(長辺12)の上端(溶鋼の注入側)から下端(鋳片の引抜き側)までの長さは、例えば、700〜1000mmであり、その厚みは、例えば、10〜50mmである。
また、図2に示すように、鋳型壁14の四隅の領域を除いた対向する短辺11及び長辺12には、それぞれ鋳片の引き抜き方向に、鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まる短辺側傾斜部15及び長辺側傾斜部16が形成されている。ここで、鋳片シェルの平坦部とは、鋳型空間部13内で形成される鋳片シェルにおいて、鋳型空間部13を形成する鋳型壁14の短辺11又は長辺12に接触した溶鋼が主に短辺11又は長辺12からの冷却作用のみで凝固すると近似できる領域を指す。
The short side 11 (long side 12) is mainly formed of copper, which is an example of a metal having good thermal conductivity, and a flow path through which industrial water, which is an example of cooling water, is provided on the back side. A cooling unit (not shown) is provided. In addition, the coating layer by plating or thermal spraying is formed in the surface (surface which contacts molten steel) of the short side 11 (long side 12). Here, the length from the upper end (molten steel injection side) to the lower end (slab drawing side) of the short side 11 (long side 12) is, for example, 700 to 1000 mm, and the thickness thereof is, for example, 10 to 10 mm. 50 mm.
Further, as shown in FIG. 2, the opposing
更に、図1に示すように、鋳型壁14の四隅の領域の短辺11及び長辺12には、それぞれ外側に向かって拡大すると共に鋳片が引き抜かれる方向では鋳片シェルの角部の凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小する短辺側拡大部17及び長辺側拡大部18が形成されている。
ここで、鋳片シェルの角部とは、鋳型空間部13内で形成される鋳片において、鋳型空間部13を形成する鋳型壁14の短辺11又は長辺12に接触した溶鋼が短辺11及び長辺12からの冷却作用を同時に受けて凝固すると近似できる領域を指す。そして、鋳型壁14の鋳片引抜き側端部(下端部)における対向する短辺11間距離は鋳造しようとする鋳片の広幅サイズWに実質的に一致し、対向する長辺12の間距離は鋳造しようとする鋳片の狭幅サイズVに実質的に一致している。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1, the
Here, the corner portion of the slab shell is the short side of the slab formed in the
図3に示すように、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの凝固収縮量の算出方法を簡単に説明すると、以下のようになる。
先ず、溶鋼の温度、鋳片の外形サイズ、鋳片の熱膨張係数及び剛性(弾塑性データ)、鋳型空間部13からの鋳片の引く抜き速度、及び鋳型壁14の冷却能力を含む鋳造条件に基づいて、鋳型空間部13内に形成される鋳片シェル19の鋳造方向の温度分布を、例えば、有限要素法により算出する。
鋳片シェル19の鋳造方向の温度分布では、鋳片シェル19の鋳造方向に対して同一位置(例えば、鋳型壁14の下端から同一高さ位置Z)においては、鋳型壁14の短辺11の中央部に接触する鋳片シェル19の表面のP点は短辺11のみから、長辺12の中央部に接触する鋳片シェル19の表面のP点は長辺12のみから冷却されるのに対して、鋳型壁14の四隅の領域に接触して形成される鋳片シェル19の角部の突出点Qは短辺11及び長辺12から同時に冷却されるので、鋳片シェル19の表面のP点の温度が最も高く、鋳片シェル19の角部の突出点Qの温度が最も低くなっている。このため、鋳片シェル19の表面温度で、P点との温度差が、例えば、50℃以内となる鋳片シェル19の表面の領域を鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rとし、その領域における平均温度TR(Z)を鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの温度とする。
As shown in FIG. 3, a method for calculating the amount of solidification shrinkage of the flat portion R of the
First, casting conditions including molten steel temperature, slab outer shape size, thermal expansion coefficient and rigidity of slab (elastic-plastic data), slab pulling speed from
In the temperature distribution in the casting direction of the
また、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの表面温度TR(Z)は、鋳片シェル19の鋳造方向では、凝固が開始するメニスカス近傍の溶鋼温度TMから鋳型壁14の下端Eでの表面温度TR(E)(TR(E)<TR(Z)<TM)まで連続的に変化し、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの厚み方向では、表面温度TR(Z)から背面温度(溶鋼温度)TMまで連続的に変化している。このため、鋳型壁14の下端Eから引き抜かれる鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形が所定形状(狭幅がVで広幅がW)である場合、鋳型壁14の下端から高さ位置Zの鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズは、表面温度の上昇分(TR(Z)−TR(E))及び鋳片シェル19の厚み方向の温度低下分(TM−TR(Z))が組み合わされた平均熱膨張量B(Z)だけ大きくなっている。
実際には、三次元の有限要素解析モデルを用いて凝固収縮解析結果を求めるため、三次元の温度分布(鋳造方向、周方向、及び鋳片シェル19の厚み方向)と鋳片シェル19内の温度分布に依存した線膨張係数及び剛性(弾塑性データ)が考慮された凝固収縮変形量が求まるが、ここでの要点は、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズと角部Sの外形サイズが鋳片の引き抜き方向に変化し、また、その量は鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rと角部Sでそれぞれ異なっているということの説明であるので、ここでは、計算ファクターを少し省略して説明する。
従って、鋳型壁14の高さ位置Zでの鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズを基準にすると、鋳型壁14の下端での鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズは、平均熱膨張量B(Z)に相当する量の凝固収縮の分だけ収縮している。
The surface temperature of the flat portion R of the slab shell 19 T R (Z), in the casting direction of the
Actually, in order to obtain a solidification shrinkage analysis result using a three-dimensional finite element analysis model, the three-dimensional temperature distribution (casting direction, circumferential direction, and thickness direction of the slab shell 19) and the
Therefore, based on the external size of the flat portion R of the
以上のことから、鋳型壁14の下端での鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの所定形状を基準として、鋳型壁14の下端からメニスカス部近傍までの各高さ位置における平均熱膨張量Bをそれぞれ算出し、各高さ位置において、対向する短辺11間の間隔がW+2B、対向する長辺12間の間隔がV+2Bとなるように、短辺11に短辺側傾斜部15を、長辺12に長辺側傾斜部16をそれぞれ形成すると、対向する短辺11(長辺12)間の間隔は、短辺側傾斜部15(長辺側傾斜部16)により、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの平均熱膨張量Bに相当する凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に狭まることになる。
なお、鋳型壁14のメニスカス部から上端までの範囲の短辺11及び長辺12には、メニスカス部近傍における短辺側傾斜部15及び長辺側傾斜部16をそれぞれ延長した傾斜部15a(16a)を設ける。
From the above, based on the predetermined shape of the flat portion R of the
The
同様に、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの凝固収縮量の算出は、以下のようになる。
鋳型壁14の同一高さ位置Zにおける鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面温度TS(Z)は、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って変化し、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面と短辺11側及び長辺12側の各平坦部Rの表面との連結点G、Hにおける温度は、平坦部Rの表面温度TR(Z)に略等しい。また、鋳片シェル19の鋳造方向では、凝固が開始するメニスカス近傍の溶鋼温度TMから鋳型壁14の下端Eでの表面温度TS(E)(TS(E)<TS(Z)<TM)まで連続的に変化し、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの厚み方向では、表面温度TS(Z)から背面温度(溶鋼温度)TMまで連続的に変化している。
このため、鋳型壁14の下端Eから引き抜かれる鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形が所定形状(狭幅がVで広幅がW)である場合、鋳型壁14の下端から高さ位置Zでの鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形サイズは、表面温度の上昇分(TS(Z)−TS(E))及び鋳片シェル19の角部Sの厚み方向の温度低下分(TM−TS(Z))が組み合わされた平均熱膨張量C(Z)だけ鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って大きくなっている。
従って、鋳型壁14の下端から高さ位置Zの鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形サイズを基準にすると、鋳型壁14の下端での鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形サイズでは、角部Sの表面に沿って平均熱膨張量C(Z)に相当する量の凝固収縮の分だけ収縮している。
Similarly, calculation of the amount of solidification shrinkage of the corner S of the
The surface temperature T S (Z) of the corner portion S of the
Therefore, when the outer shape of the corner portion S of the
Therefore, with reference to the outer size of the corner portion S of the
以上のことから、鋳型壁14の下端での鋳片シェル19の角部Sの所定形状を基準として、鋳型壁14の下端からメニスカス近傍までの各高さ位置における平均熱膨張量Cを算出し、各高さ位置において、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って対向する短辺11間の間隔がW+2C、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って対向する長辺12間の間隔がV+2Cとなるように短辺側拡大部17及び長辺側拡大部18をそれぞれ形成すると、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って対向する短辺11(長辺12)間の間隔は、短辺側拡大部17(長辺側拡大部18)により、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの平均熱膨張量Cに相当する凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に狭まることになる。
なお、鋳型壁14のメニスカス部から上端までの範囲の四隅の領域の短辺11及び長辺12には、メニスカス部近傍における短辺側拡大部17及び長辺側拡大部18をそれぞれ延長した拡大部(図示せず)を設ける。
From the above, the average thermal expansion amount C at each height position from the lower end of the
It should be noted that the
続いて、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る連続鋳造用鋳型10の作用について説明する。
連続鋳造鋳型10の鋳型壁14の内側に形成される鋳型空間部13に上側から溶鋼を注入すると、溶鋼は鋳型壁14の内面に接触して冷却され表側に凝固層内側に溶鋼が存在する鋳片シェル19が形成される。
Next, the operation of the
When molten steel is injected from above into the
鋳型壁14の四隅の領域を除いた対向する短辺11及び長辺12に接触し冷却されて形成される鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズは、短辺側傾斜部15及び長辺側傾斜部16により鋳片の引き抜かれる方向に徐々に小さくなっている。更に、鋳型壁14の四隅の領域の短辺11及び長辺12にそれぞれ接触して短辺11及び長辺12から同時に冷却されて形成される鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形サイズは、短辺側拡大部17及び長辺側拡大部18により、鋳型壁14の同一高さ位置では鋳片シェル19の角部Sが平坦部Rよりも外側に拡大している。
The outer size of the flat portion R of the
一方、鋳片が引き抜かれる場合、鋳片シェル19は引抜き速度に応じて鋳型壁14内を上側から下側に向けて移動し、その際に鋳片シェル19の表面温度も徐々に低下する。このとき、鋳片シェル19の角部Sは鋳型壁14の短辺11及び長辺12から同時に冷却され鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rは短辺11又は長辺12のみから冷却されることになる。このため、鋳型壁14の同一高さ位置の鋳片シェル19の表面温度では、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの表面温度に比べて角部Sの方面温度は低くなり、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rに比べて角部Sは大きく凝固収縮する。
On the other hand, when the slab is drawn, the
ここで、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの外形サイズは、引き抜かれる方向に平坦部Rの凝固収縮量Bに伴って徐々に収縮する。これに対して、鋳型壁14の対向する短辺11(長辺12)間の間隔も、短辺側傾斜部15(長辺側傾斜部16)により、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの平均熱膨張量Bに相当する凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に狭まるように変化しているので、鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rは鋳型壁14の四隅の領域を除いた対向する短辺11及び長辺12に対して平坦部Rの表面を常に接触させながら下端側に向けて移動することができる。
また、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの外形サイズは、鋳型壁14の同一高さ位置ではそれぞれ外側に向かって拡大すると共に鋳片シェル19が引き抜かれる方向では鋳片シェル19の角部Sの凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小する。そして、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの表面に沿って対向する短辺11(長辺12)間の間隔は、短辺側拡大部17(長辺側拡大部18)により、鋳片シェル19の角部Sの平均熱膨張量Cに相当する凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に狭まるように変化するので、鋳片シェル19の角部Sは鋳型壁14の四隅の領域の対向する短辺11及び長辺12にそれぞれ角部Sの表面を常に接触させながら、下端側に向けて移動することができる。
Here, the outer size of the flat portion R of the
Further, the outer size of the corner portion S of the
本発明の第2の実施の形態に係る連続鋳造用鋳型20は、図4に示すように、間隔調整が可能な一対の短辺21及び短辺21を幅方向の両側から挟む一対の長辺22とによって囲繞される鋳型空間部23に上方から溶鋼を注入し、鋳型空間部23を形成する鋳型壁24の内面に接触させて冷却し鋳片として鋳型空間部23の下側から引き抜いている。ここで、鋳片とは、例えば、幅が可変のスラブを指す。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
短辺21(長辺22)は、熱伝導性が良好な金属の一例である銅から形成され、背面側には図示しない冷却部が設けられている。なお、短辺21(長辺22)の表面(溶鋼と接触する面)には、めっきや溶射による被覆層が形成されている。ここで、短辺21(長辺22)の上端(溶鋼の注入側)から下端(鋳片の引抜き側)までの長さは、例えば、700〜1100mmであり、その厚みは、例えば、10〜60mmである。
また、第1の実施の形態に係る連続鋳造用鋳型10の短辺11及び長辺12と同様に、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域を除いた対向する短辺21及び長辺22には、それぞれ鋳片の引き抜き方向に、鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まる短辺側傾斜部25及び長辺側傾斜部26が形成されている。ここで、鋳片シェルの平坦部とは、鋳型空間部23内で形成される鋳片シェルにおいて、鋳型壁24の短辺21又は長辺22からの冷却のみの作用で溶鋼が凝固すると近似できる領域を指す。
The short side 21 (long side 22) is formed from copper which is an example of a metal having good thermal conductivity, and a cooling unit (not shown) is provided on the back side. In addition, the coating layer by plating or thermal spraying is formed in the surface (surface which contacts molten steel) of the short side 21 (long side 22). Here, the length from the upper end (molten steel injection side) to the lower end (slab drawing side) of the short side 21 (long side 22) is, for example, 700 to 1100 mm, and the thickness thereof is, for example, 10 to 10 mm. 60 mm.
Further, like the
更に、図4に示すように、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の短辺21には、短辺21の外側に向かって拡大すると共に鋳片が引き抜かれる方向では鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小する短辺側拡大部27が形成されている。
ここで、鋳片シェルの短辺側角部とは、鋳型空間部23内で形成される鋳片シェルにおいて、鋳型壁24の短辺21に接触し短辺21及び長辺22からの冷却の作用を同時に受けて溶鋼が凝固すると近似できる領域を指す。そして、鋳型壁24を形成している対向する短辺21の下端における内幅は、連続鋳造鋳型10の下端から鋳片を排出させる際の設定幅サイズに実質的に一致し、対向する長辺22の下端における内幅は連続鋳造鋳型10の下端から鋳片を排出させる際の設定厚みサイズに実質的に一致している。
Further, as shown in FIG. 4, the
Here, the short side corner of the slab shell is the slab shell formed in the
鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量及び角部の凝固収縮量の算出方法は、それぞれ第1の実施の形態に係る連続鋳造用鋳型10において算出した鋳片シェル19の平坦部Rの凝固収縮量及び角部Sの凝固収縮量と実質的に同一なので詳細な説明は省略する。
なお、鋳型壁24のメニスカス部から上端までの範囲の短辺21及び長辺22には、メニスカス部近傍における短辺側傾斜部25及び長辺側傾斜部26をそれぞれ延長した傾斜部(図示せず)を設けている。更に、鋳型壁24のメニスカス部から上端までの範囲の四隅の領域の短辺21には、メニスカス部近傍における短辺側拡大部27を延長した拡大部(図示せず)を設ける。
連続鋳造用鋳型20の鋳型壁24内に注入した溶鋼が冷却されて形成される鋳片シェルの平坦部の外形サイズは、引き抜かれる方向に平坦部の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まるように変化しているので、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域を除いた対向する短辺21及び長辺22に対して鋳片シェルの平坦部の表面を常に接触させながら下端側に向けて移動することができる。
また、鋳片シェルの角部の外形サイズは、鋳型壁24の下端から同一高さ位置では短辺21の外側に向かって拡大すると共に鋳片が引き抜かれる方向では鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小するように変化しているので、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の対向する短辺21に鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面を常に接触させながら、下端側に向けて移動することができる。
The solidification shrinkage amount of the flat portion of the slab shell and the solidification shrinkage amount of the corner portion are calculated by the solidification shrinkage of the flat portion R of the
Note that the
The outer size of the flat part of the slab shell formed by cooling the molten steel injected into the
Further, the outer size of the corner of the slab shell increases from the lower end of the
このため、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の長辺22と鋳片シェルの長辺側角部との間にはコーナーエアギャップが生じ易いが、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の短辺21には鋳片シェルの短辺側角部が接触しているので、鋳片シェルの長辺側角部の冷却が不十分となることが防止できる。これによって、凝固遅れに伴う鋳片の角部の品質異常の発生を防止できると共に、鋳片の角部の厚みが薄くなるのが防止でき、鋳片の角部の応力集中に伴う鋳片の角部の品質劣化を防止できる。更に、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の短辺21に鋳片シェルの短辺側角部が接触することにより、従来の連続鋳造用鋳型に比べて、コーナーエアギャップを縮小することができ、スプレー水の進入を抑制することができる。
また、鋳型壁24の四隅の領域の短辺21にのみ短辺側拡大部27を設けたので、鋳片の短辺21の間隔を変化させることにより広幅サイズが異なる鋳片を容易に鋳造することができる。
Therefore, a corner air gap is likely to occur between the
Moreover, since the short side
以上、本発明の実施の形態を説明したが、本発明は、この実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、発明の要旨を変更しない範囲での変更は可能であり、前記したそれぞれの実施の形態や変形例の一部又は全部を組み合わせて本発明の連続鋳造用鋳型を構成する場合も本発明の権利範囲に含まれる。
例えば、第1の実施の形態では、鋳型壁の四隅を除く領域の短辺及び長辺にはメニスカス部から上端までの範囲にも傾斜部を、鋳型壁の四隅の領域の短辺及び長辺にはメニスカス部から上端までの範囲にも拡大部をそれぞれ設けたが、メニスカス部から下端までの範囲のみに短辺側傾斜部、長辺側傾斜部、短辺側拡大部、及び長辺側拡大部を設けるようにしてもよい。
また、第2の実施の形態でも、短辺及び長辺でメニスカス部から上端までの範囲に傾斜部を、短辺のメニスカス部から上端までの範囲に拡大部をそれぞれ設けたが、メニスカス部から下端までの範囲のみに短辺側傾斜部、長辺側傾斜部、及び短辺側拡大部を設けるようにしてもよい。
更に、鋳片シェルの平坦部の表面温度を平坦部の平均温度で代表させ、鋳片シェルの平坦部の表面温度及び鋳片シェルの厚み方向の温度分布に基づいて平均熱膨張量を求めたが、算出された平坦部の表面温度及び鋳片シェルの厚み方向の温度分布に基づいて平均熱膨張量を求めてもよい。
As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described, this invention is not limited to this embodiment, The change in the range which does not change the summary of invention is possible, Each above-mentioned embodiment is possible. The case where the mold for continuous casting according to the present invention is configured by combining a part or all of forms and modifications is also included in the scope of the right of the present invention.
For example, in the first embodiment, the short side and the long side of the region excluding the four corners of the mold wall are inclined in the range from the meniscus portion to the upper end, and the short side and the long side of the four corner region of the mold wall. In the range from the meniscus portion to the upper end, an enlarged portion is provided, but only the range from the meniscus portion to the lower end is the short side inclined portion, the long side inclined portion, the short side enlarged portion, and the long side side. You may make it provide an enlarged part.
Also in the second embodiment, an inclined portion is provided in the range from the meniscus portion to the upper end on the short side and the long side, and an enlarged portion is provided in the range from the meniscus portion on the short side to the upper end. You may make it provide a short side inclination part, a long side inclination part, and a short side expansion part only in the range to a lower end.
Further, the surface temperature of the flat part of the slab shell is represented by the average temperature of the flat part, and the average thermal expansion amount was obtained based on the surface temperature of the flat part of the slab shell and the temperature distribution in the thickness direction of the slab shell. However, the average thermal expansion amount may be obtained based on the calculated surface temperature of the flat portion and the temperature distribution in the thickness direction of the slab shell.
10:連続鋳造用鋳型、11:短辺、12:長辺、13:鋳型空間部、14:鋳型壁、15:短辺側傾斜部、15a:傾斜部、16:長辺側傾斜部、16a:傾斜部、17:短辺側拡大部、18:長辺側拡大部、19:鋳片シェル、20:連続鋳造用鋳型、21:短辺、22:長辺、23:鋳型空間部、24:鋳型壁、25:短辺側傾斜部、26:長辺側傾斜部、27:短辺側拡大部 10: Continuous casting mold, 11: Short side, 12: Long side, 13: Mold space, 14: Mold wall, 15: Short side inclined part, 15a: Inclined part, 16: Long side inclined part, 16a : Inclined part, 17: short side enlarged part, 18: long side enlarged part, 19: cast slab shell, 20: continuous casting mold, 21: short side, 22: long side, 23: mold space part, 24 : Mold wall, 25: Short side inclined part, 26: Long side inclined part, 27: Short side enlarged part
Claims (3)
前記鋳型空間部を形成する鋳型壁の対向する前記長辺及び該鋳型壁の四隅の領域を除いた対向する前記短辺には、それぞれ前記鋳片が引き抜かれる方向に鋳片シェルの平坦部の凝固収縮量に追従して間隔が徐々に狭まる長辺側傾斜部及び短辺側傾斜部が形成され、
前記鋳型壁の四隅の領域の前記短辺には、外側に向かって拡大すると共に前記鋳片が引き抜かれる方向では前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の凝固収縮量に追従して徐々に縮小し、しかも、前記鋳型壁の下端から溶鋼の凝固が開始するメニスカス部までの各高さ位置において、前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面に沿って対向する前記短辺間の間隔を、前記鋳型壁の下端部における前記鋳片の広幅サイズWと、前記鋳型壁の下端での前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の形状を基準として算出された前記各高さ位置における平均熱膨張量Cの2倍の値2Cとの和(W+2C)とする短辺側拡大部が形成されていることを特徴とする連続鋳造用鋳型。 In the continuous casting mold for cooling the molten steel injected into the mold space surrounded by the pair of short sides capable of adjusting the interval and the pair of long sides sandwiching the short sides from both sides in the width direction, and drawing it as a slab,
The flat side of the slab shell is formed in the direction in which the slab is pulled out, respectively, on the opposing long side excluding the four corners of the mold wall and the long side of the mold wall that forms the mold space. A long side inclined portion and a short side inclined portion in which the interval gradually narrows following the amount of solidification shrinkage are formed,
The short side of the four corner regions of the mold wall expands outward and gradually decreases in the direction in which the slab is pulled out, following the amount of solidification shrinkage at the short side corner of the slab shell. In addition, at each height position from the lower end of the mold wall to the meniscus portion where solidification of the molten steel starts, an interval between the short sides facing each other along the surface of the short side corner portion of the slab shell is set. The average heat at each height position calculated based on the width W of the slab at the lower end of the mold wall and the shape of the short side corner of the slab shell at the lower end of the mold wall A casting mold for continuous casting, characterized in that a short side enlarged portion having a sum (W + 2C) of a value 2C that is twice the expansion amount C is formed.
前記鋳型壁の下端から同一高さ位置Zにおける前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面温度TS(Z)と、前記鋳型壁の下端での前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面温度TS(E)との差である前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面温度の上昇分(TS(Z)−TS(E))と、
前記メニスカス部の溶鋼温度TMと、前記同一高さ位置Zにおける前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の表面温度TS(Z)との差である前記鋳片シェルの短辺側角部の厚み方向の温度低下分(TM−TS(Z))とを用いて、算出されることを特徴とする連続鋳造用鋳型。 The continuous casting mold according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the average thermal expansion amount C is:
The surface temperature T S (Z) of the short side corner of the slab shell at the same height position Z from the lower end of the mold wall, and the short side corner of the slab shell at the lower end of the mold wall surface temperature T S (E) and the difference between the surface temperature rise of the short side corner of the slab shell component which is the (T S (Z) -T S (E)),
And the molten steel temperature T M of the meniscus portion, the short side corner of the which is the difference between the surface temperature T S (Z) of the short side corner of the slab shell in the same height position Z the slab shell temperature decrease amount of the thickness direction using a (T M -T S (Z) ), the continuous casting mold, characterized in that it is calculated.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011016871A JP5453329B2 (en) | 2011-01-28 | 2011-01-28 | Continuous casting mold |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011016871A JP5453329B2 (en) | 2011-01-28 | 2011-01-28 | Continuous casting mold |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005359261A Division JP2007160346A (en) | 2005-12-13 | 2005-12-13 | Casting mold for continuous casting |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011079062A JP2011079062A (en) | 2011-04-21 |
| JP5453329B2 true JP5453329B2 (en) | 2014-03-26 |
Family
ID=44073671
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011016871A Active JP5453329B2 (en) | 2011-01-28 | 2011-01-28 | Continuous casting mold |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5453329B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106735031A (en) * | 2017-03-08 | 2017-05-31 | 中冶赛迪工程技术股份有限公司 | A kind of hot width adjusting method of continuous cast mold |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017187665A1 (en) * | 2016-04-28 | 2017-11-02 | Mkテクノコンサルティング株式会社 | Continuous casting device for steel |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS57106449A (en) * | 1980-12-25 | 1982-07-02 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Mold for continuous casting of molten metal |
| JPH0444300Y2 (en) * | 1987-04-15 | 1992-10-19 | ||
| JPH01162542A (en) * | 1987-12-18 | 1989-06-27 | Nkk Corp | Mold for continuous casting machine |
| JPH0399762A (en) * | 1989-09-13 | 1991-04-24 | Kobe Steel Ltd | Continuous casting method |
| JPH10249492A (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 1998-09-22 | Nippon Steel Corp | Mold for continuously casting steel |
| JPH11151555A (en) * | 1997-11-19 | 1999-06-08 | Shinko Metal Products Kk | Mold for continuous casting |
| JP2004042080A (en) * | 2002-07-10 | 2004-02-12 | Mishima Kosan Co Ltd | Mold for continuous casting |
| JP4337565B2 (en) * | 2004-01-29 | 2009-09-30 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | Steel slab continuous casting method |
-
2011
- 2011-01-28 JP JP2011016871A patent/JP5453329B2/en active Active
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106735031A (en) * | 2017-03-08 | 2017-05-31 | 中冶赛迪工程技术股份有限公司 | A kind of hot width adjusting method of continuous cast mold |
| CN106735031B (en) * | 2017-03-08 | 2019-03-22 | 中冶赛迪工程技术股份有限公司 | A kind of hot width adjusting method of continuous cast mold |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011079062A (en) | 2011-04-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7234347B2 (en) | Light Reduction Method by Combining Flat Rolls and Convex Rolls for Continuous Bloom Casting | |
| CN112118924B (en) | Die set | |
| US20150231692A1 (en) | Mold designing method and mold | |
| JP2008049385A (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP2007160346A (en) | Casting mold for continuous casting | |
| JP5453329B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP6085571B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| CN110000348B (en) | Hyperbolic funnel-shaped crystallizer wide-surface copper plate and preparation method thereof | |
| JP2010201450A (en) | Mold for continuous casting | |
| JP3930761B2 (en) | Tube type continuous casting mold | |
| JPH02284747A (en) | Mold for continuous casting | |
| WO2011023483A1 (en) | Mould for continuous casting of long or flat products, cooling jacket designed to cooperate with such a mould and assembly comprising such a mould and such a cooling jacket | |
| JP5525966B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP5463189B2 (en) | Method for repairing continuous casting mold and repaired continuous casting mold | |
| JP5006652B2 (en) | Water-cooled metal continuous casting mold | |
| JP6520031B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing center porosity reduction slab | |
| JP5180868B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP6015914B2 (en) | Beam blank casting slab continuous casting mold design method | |
| JP5763584B2 (en) | Chill vent | |
| JP5731831B2 (en) | Mold for casting | |
| KR101660773B1 (en) | Mold for casting | |
| JP5566972B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP4227768B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| JP5525925B2 (en) | Continuous casting mold | |
| CN110125350B (en) | Multilayer composite copper plate for wide surface of slab caster crystallizer and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130425 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130618 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130812 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20131210 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140106 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5453329 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |