JP5419842B2 - Power processing device - Google Patents
Power processing device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5419842B2 JP5419842B2 JP2010226392A JP2010226392A JP5419842B2 JP 5419842 B2 JP5419842 B2 JP 5419842B2 JP 2010226392 A JP2010226392 A JP 2010226392A JP 2010226392 A JP2010226392 A JP 2010226392A JP 5419842 B2 JP5419842 B2 JP 5419842B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- circuit
- main circuit
- power
- inverter circuit
- control circuit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- General Induction Heating (AREA)
- Inverter Devices (AREA)
Description
この発明は、電力を有効的に消費することができる電力処理装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a power processing apparatus that can effectively consume power.
従来の電力処理装置は、スイッチング損失を調整するためスイッチング周波数が一定の条件でゼロ電流スイッチングがなされている。そして、負荷の温度を検出し、インバータ回路のスイッチング周波数を調整する。負荷の温度上昇を検知して、加熱部材の過昇温を未然に回避することができ、電力供給を維持するようスイッチング周波数を制御して負荷をウォームアップ終了温度まで昇温する。そして、スイッチング周波数を共振周波数近傍で調整して出力電力量を調整している(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 In the conventional power processing apparatus, zero current switching is performed under the condition that the switching frequency is constant in order to adjust the switching loss. Then, the temperature of the load is detected, and the switching frequency of the inverter circuit is adjusted. The temperature rise of the load can be detected to avoid overheating of the heating member, and the load is heated to the warm-up end temperature by controlling the switching frequency so as to maintain power supply. Then, the output power is adjusted by adjusting the switching frequency in the vicinity of the resonance frequency (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
従来の電力処理装置は、駆動回路の出力電圧の通電率を調整し出力電力を調整していた。しかし、共振スイッチング状態から外れてしまうため、スイッチングによる損失が発生し、素子の放熱が必要となる。このため、大きな損失が生じ、出力電力のほとんどを誘導加熱により消費するという特徴が失われてしまうという問題点があった。 The conventional power processing apparatus adjusts the output power by adjusting the conduction ratio of the output voltage of the drive circuit. However, since it is out of the resonant switching state, loss due to switching occurs, and heat dissipation of the element is required. For this reason, there is a problem that a large loss occurs and the characteristic that most of the output power is consumed by induction heating is lost.
さらに、常に共振スイッチング状態で操作するために、入力電圧や、入力電力の値に合わせて間欠的に電子抵抗器を動作していた。よって、電子抵抗器の抵抗値と回生電力値とが一致しない場合、外部に雑音など悪影響が生じてしまうという問題点があった。 Further, in order to always operate in the resonant switching state, the electronic resistor is operated intermittently according to the value of the input voltage or input power. Therefore, when the resistance value of the electronic resistor and the regenerative power value do not match, there is a problem that an adverse effect such as noise is generated outside.
この発明は上記のような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、電力を有効的に消費し、雑音を低減することができる電力処理装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a power processing apparatus that can effectively consume power and reduce noise.
この発明は、誘導加熱用コイル部と共振用コンデンサ部とが直列に接続されてなる主回路と、
主回路に交流電流を供給するインバータ回路と、
インバータ回路を制御する制御回路とを備え、
制御回路は、インバータ回路の入力に応じて主回路の回路構成を変更して、主回路の共振周波数を変更しインバータ回路の出力周波数を変更された主回路の共振周波数となるようにし、
上記制御回路は、上記主回路の消費電力が上記インバータ回路の入力電力に近似するように上記主回路の共振周波数を変更するものである。
The present invention includes a main circuit in which an induction heating coil portion and a resonance capacitor portion are connected in series;
An inverter circuit for supplying an alternating current to the main circuit;
A control circuit for controlling the inverter circuit,
The control circuit changes the circuit configuration of the main circuit according to the input of the inverter circuit, changes the resonance frequency of the main circuit so that the output frequency of the inverter circuit becomes the resonance frequency of the changed main circuit ,
The control circuit changes the resonance frequency of the main circuit so that the power consumption of the main circuit approximates the input power of the inverter circuit .
この発明の電力処理装置は、上記のように構成されているため、
電力を有効的に消費し、雑音を低減することができる。
Since the power processing apparatus of the present invention is configured as described above,
Power can be consumed effectively and noise can be reduced.
実施の形態1.
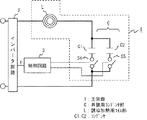
以下、本願発明の実施の形態について説明する。図1はこの発明の実施の形態1における例えばインバータ回路の内部で電圧もしくは出力電力を検出し、外部回路もしくはモーターなどの外部装置から入力される電力(回生電力)を消費するためにインバータ回路に搭載される回生抵抗器としての電力処理装置の構成を示す図、図2は図1に示した電力処理装置における主回路の周波数特性を示した図、図3はこの発明の実施の形態1における他の電力処理装置の構成を示す図である。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below. FIG. 1 shows an inverter circuit for detecting voltage or output power, for example, in an inverter circuit according to
図において、主回路1は共振用コンデンサ部Cと誘導加熱用コイル部Lとが直列に接続されて構成されている。そして、共振用コンデンサ部CはコンデンサC1、コンデンサC2との複数のコンデンサにて構成されている。また、コンデンサC1、C2のそれぞれの容量は異なるものを用いてもよい。ここでは例えば、コンデンサC1>コンデンサC2の容量を有するものとする。そして、各コンデンサC1、C2には、それぞれをオン/オフするためのスイッチS4、スイッチS5がそれぞれ接続されている。そして、主回路1に交流電流を供給するインバータ回路2と、インバータ回路2を制御する制御回路3とを備える。
In the figure, the
そして、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2の入力電力の大きさに応じて主回路1の回路構成を変更して、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量を変更して主回路1の共振周波数を変更し、インバータ回路2の出力周波数f(スイッチング周波数)を、変更させた主回路1の共振周波数に変更するように制御する。この際、制御回路3は、主回路1の消費電力がインバータ回路2の入力電力に近似するように主回路1の共振周波数を変更する。この制御により、主回路1にてインバータ回路2に入力される電力を消費して、インバータ回路2での消費電力を抑制する。また、制御回路3は、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量を変更するために、スイッチS4、S5のオンオフ制御を行うものである。
Then, the
そして、インバータ回路2に、例えば電源または外部からの回生電力の直流電圧を検出する機能も有するものとする。また、インバータ回路2、主回路1、制御回路3を構成する半導体素子は、例えばSiC等のワイドバンドギャップ半導体素子にて形成する。このようにワイドバンドギャップ半導体素子を用いることにより、通常のシリコン半導体素子と比較すると、電流導通時のロスを抑えるものである。尚、このことは以下の実施の形態においても同様であるため、その説明は適宜省略する。
The
また、各コンデンサC1、C2にはそれぞれ並列に接続された放電抵抗(図示せず)を備えるようにしてもよい。各コンデンサC1、C2が充電されている状態で制御回路3によりスイッチS4、S5がオフされた場合、各コンデンサC1、C2は充電された状態になっている。この際、放電抵抗が接続されていれば、スイッチS4、S5がオフしても各コンデンサC1、C2の電荷を消費することができる。尚、このことは以下の実施の形態においても同様であるため、その説明は適宜省略する。
Further, each of the capacitors C1 and C2 may be provided with a discharge resistor (not shown) connected in parallel. When the switches S4 and S5 are turned off by the
次に上記のように構成された実施の形態1の電力処理装置の動作について説明する。まず、コイルの周波数特性を図2に基づいて説明する。図に示すように、コイルの周波数特性は、コイルが周波数f1で駆動したときの抵抗値は抵抗値R1となり、周波数f2で駆動したときの抵抗値は抵抗値R2となる。そして、コイルを駆動する周波数を大きくした場合、そのインダクタンス値は小さくなり、抵抗値は大きくなる傾向がある。よって、主回路1のコイルの駆動周波数を調整することにより、コイルの抵抗値を調整することができ、主回路1の消費電力を調整することが可能であることが判る。尚、このことは以下の実施の形態においても同様であるので、その説明は適宜省略する。
Next, the operation of the power processing apparatus of the first embodiment configured as described above will be described. First, the frequency characteristics of the coil will be described with reference to FIG. As shown in the figure, regarding the frequency characteristics of the coil, the resistance value when the coil is driven at the frequency f1 is the resistance value R1, and the resistance value when the coil is driven at the frequency f2 is the resistance value R2. When the frequency for driving the coil is increased, the inductance value tends to decrease and the resistance value tends to increase. Therefore, it can be seen that by adjusting the drive frequency of the coil of the
このことに基づいて以下の動作を行う。まず、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2に入力される入力電圧が第1の所定値より高いか否かを検出している。そして、この値が第1の所定値より高いことを検出すると、主回路1の抵抗値を小さくして、主回路1の消費電力を大きくする必要があるため、主回路1を駆動するインバータ回路2の出力周波数を低くする。よって、共振周波数を低くするために、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量を大きくする必要があるため、コンデンサC1とコンデンサC2とが並列に接続されるように、スイッチS4、スイッチS5の両方をオンする。そして、制御回路3は、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを変化して駆動を制御する。
Based on this, the following operation is performed. First, the
次に、制御回路3は、入力電圧が第1の所定値より低いことを検出すると、上記の場合より、主回路1の抵抗値を大きくして、主回路1の消費電力を小さくする必要があるため、インバータ回路2の出力周波数を高くする。よって、共振周波数を高くするために、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量を小さくする必要があるため、コンデンサC1のみが接続されるように、スイッチS4はオンしたまま、スイッチS5のみをオフしコンデンサC1のみを接続する。そして、制御回路3は、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを変化して駆動を制御する。
Next, when the
次に、さらに電圧が低くなり、制御回路3は、第2の所定値より低いことを検出すると、上記の場合より主回路1の抵抗値をさらに大きくして、主回路1の消費電力をさらに小さくする必要があるため、インバータ回路2の出力周波数をさらに高くする。よって、共振周波数をさらに高くするために、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量をさらに小さくする必要があるため、コンデンサC2のみが接続されるように、スイッチS5をオンし、スイッチS4をオフしてコンデンサC1を切り離しコンデンサC2のみを接続する。そして、制御回路3は、共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを変化して駆動を制御する。
Next, when the voltage further decreases and the
尚、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2の入力電圧にて制御する例を示したが、制御回路3に外部からの信号により上記に示した場合と同様に制御することも可能である。
また、上記に示した、第1の所定値および第2の所定値とは、第1の所定値>第2の所定値の関係であり、それぞれの値は、電力処理装置の特性、コンデンサの容量などにより適宜設定するものである。また、コンデンサの容量は、コイルとの共振周波数が可聴領域と成らないように選定されている。
In addition, although the
In addition, the first predetermined value and the second predetermined value described above are in a relationship of the first predetermined value> the second predetermined value, and each value represents the characteristics of the power processing device, the capacitor It is appropriately set depending on the capacity. The capacitance of the capacitor is selected so that the resonance frequency with the coil does not become an audible range.
上記のように構成された実施の形態1の電力処理装置によれば、インバータ回路に入力される入力電圧の大きさに応じて、共振用コンデンサ部の容量を変更することにより、主回路の消費電力を調整しているため、主回路によって効率よく電力を消費する。
また、インバータ回路の出力周波数は共振周波数と一致するように制御されているため、インバータ回路はゼロ電流スイッチングがなされ、インバータ回路での消費電力が抑えられる(損失が最小となる)ため、インバータ回路を冷却するための冷却手段(図示せず)などが小さく小型化でき、電力処理装置の特徴を大きくいかすことができる。
According to the power processing device of the first embodiment configured as described above, the consumption of the main circuit is changed by changing the capacitance of the resonance capacitor unit according to the magnitude of the input voltage input to the inverter circuit. Since the power is adjusted, power is efficiently consumed by the main circuit.
In addition, since the output frequency of the inverter circuit is controlled so as to coincide with the resonance frequency, the inverter circuit is zero-current switching, and power consumption in the inverter circuit is suppressed (loss is minimized). A cooling means (not shown) for cooling the battery can be reduced in size and size, and the characteristics of the power processing apparatus can be greatly utilized.
尚、上記実施の形態1においては、共振用コンデンサ部の容量の変更を、2個のコンデンサを備えるようにして、その接続方法を変更することにより対応する方法を示したが、これに限られることはなく、もちろん3個以上のコンデンサを備える場合も考えられる。また、例えば、図3に示すように、共振用コンデンサ部のコンデンサC3として、バリアブルコンデンサを用いるようにすれば、1個でも容量を変更することが可能となる。そして、共振用コンデンサ部の容量を制御するために、制御回路3はスイッチではなく、コンデンサC3の容量を制御することにより行うようにすれば、上記実施の形態1と同様の効果を奏することができる。これにより、本実施の形態では段階的に駆動周波数を変化させたが、共振用コンデンサとしてバリアブルコンデンサを用いることにより共振用コンデンサ容量を連続的に変化させることができるため、駆動周波数も共振用コンデンサの静電容量に合わせて連続的に変化させ、主回路を構成するインダクタの抵抗値を調整し、電力処理装置の消費電力を連続的に調整することができる。これにより回生電力と電力処理装置の電力容量を一致させることができるため、電子抵抗器と入力電力の差異により間欠的に電子抵抗が動作するために発生する騒音をなくすことができる。
In the first embodiment, the method of changing the capacitance of the resonance capacitor unit by providing two capacitors and changing the connection method has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this. Of course, there may be cases where three or more capacitors are provided. Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 3, if a variable capacitor is used as the capacitor C3 of the resonance capacitor unit, the capacitance can be changed even by one. If the
実施の形態2.
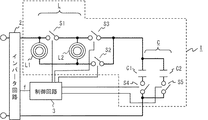
図4はこの発明の実施の形態2における電力処理装置の構成を示す図である。図において、上記実施の形態1と同様の部分は同一符号を付して説明を省略する。誘導加熱用コイル部Lは、複数のコイルL1とコイルL2とにて構成されている。ここでは例えば、コイルL1=コイルL2の抵抗値およびインダクタンス値を有するものとする。そして、本実施の形態において、これらコイルL1、L2の抵抗値およびインダクタンス値は、駆動周波数が倍、半分と変化しても大きく変化しない周波数領域での駆動周波数および回路構成の変更を想定する。これにより回路構成を直列から単体に変更させた場合、回路構成により決まる駆動周波数は高くなりコイル単体の抵抗値は大きくなるが、接続方法を変更することにより誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値は小さくなる場合を想定する。上記条件以外の場合は、2つのコイルL1、L2の特性により回路構成を変更する検出値や、周波数を調整することにより本実施の形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。そして、各コイルL1、L2の接続方法を設定するため、それぞれの回路をオン/オフするためのスイッチS1、スイッチS2、スイッチS3がそれぞれ接続されている。また、制御回路3は、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値を変更するためには、スイッチS1、S2、S3のオンオフ制御を行うものである。
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the configuration of the power processing apparatus according to
次に、上記のように構成された実施の形態2の電力処理装置の動作について説明する。まず、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2に入力される入力電圧(電力)が第1の所定値より高いか否かを検出している。そして、この値が第1の所定値より高いことを検出すると、主回路1の消費電力を大きくする必要があるため、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値を小さくする。そこで、制御回路3はコイルL1とコイルL2とが並列に接続されるように、スイッチS1、スイッチS2をオン、スイッチS3をオフする。よって、主回路1の共振周波数は高くなる。そして、制御回路3は、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを高く変化させ制御する。このため、コイルL1、L2の1つあたりの抵抗値は大きくなるが、主回路1は2つのコイルL1、L2が並列に接続される構成となるため、主回路1の抵抗値は小さくなり、大きな電力を消費することができる。
Next, the operation of the power processing apparatus of the second embodiment configured as described above will be described. First, the
次に、制御回路3は、入力電圧が第1の所定値より低いことを検出すると、上記の場合より主回路1の消費電力を小さくする必要があるため、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値を大きくする。そこで、制御回路3はコイルL1のみが接続されるように、スイッチS2はオンしたまま、スイッチS1およびスイッチS3をオフしコイルL1のみを接続する。よって、共振周波数が低くなる。そして、制御回路3は、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを変化させ制御する。
Next, when the
次に、さらに電圧が低くなり、制御回路3は、第2の所定値より低いことを検出すると、上記の場合より主回路1の消費電力をさらに小さくする必要があるため、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値をさらに大きくする必要がある。そこで、制御回路3コイルL1およびコイルL2を直列に接続されるように、スイッチS3をオンし、スイッチS1およびスイッチS2をオフしてコイルL1およびコイルL2を直列接続する。よって、共振周波数がさらに低くなる。そして、主回路1を駆動するインバータ回路2の出力周波数をさらに低くする。そして、制御回路3は、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの抵抗値の変更によって変更された主回路1の共振周波数の変化に合わせインバータ回路2の出力周波数fを変化して制御する。このため、コイルL1、L2の1つあたりの抵抗値は小さくなるが、主回路1は2つのコイルL1、L2が直列に接続される構成となるため、主回路1の抵抗値は大きくなり、小さな電力しか消費することができなくなる。
Next, when the voltage is further lowered and the
尚、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2の入力電圧にて制御する例を示したが、制御回路3に外部からの信号により上記に示した場合と同様に制御することも可能である。
また、上記に示した、第1の所定値および第2の所定値とは、第1の所定値>第2の所定値の関係であり、それぞれの値は、電力処理装置の特性、コイルの抵抗値などにより適宜設定するものである。また、コイルの抵抗は、コンデンサとの共振周波数が可聴領域と成らないように選定されている。
In addition, although the
In addition, the first predetermined value and the second predetermined value described above are in a relationship of the first predetermined value> the second predetermined value, and the respective values are the characteristics of the power processing apparatus, the coil It is set appropriately depending on the resistance value or the like. Further, the resistance of the coil is selected so that the resonance frequency with the capacitor does not become an audible range.
上記のように構成された実施の形態2の電力処理装置によれば、インバータ回路に入力される入力電圧の大きさに応じて、誘導加熱用コイル部の接続方法を変更することにより主回路の抵抗値を調整し、主回路の消費電力を調整しているため、主回路によって効率よく電力を消費する。
また、共振周波数でインバータ回路の出力周波数は決定されているため、インバータ回路はゼロ電流スイッチングがなされ、インバータ回路での消費電力が抑えられる(損失が最小となる)ため、インバータ回路を冷却するための冷却手段(図示せず)などが小さく小型化でき、電力処理装置の特徴を大きくいかすことができる。
According to the power processing device of the second embodiment configured as described above, the connection method of the induction heating coil unit is changed according to the magnitude of the input voltage input to the inverter circuit, thereby changing the main circuit. Since the resistance value is adjusted and the power consumption of the main circuit is adjusted, power is efficiently consumed by the main circuit.
In addition, since the output frequency of the inverter circuit is determined by the resonance frequency, the inverter circuit is zero-current switching, power consumption in the inverter circuit is suppressed (loss is minimized), and the inverter circuit is cooled. The cooling means (not shown) and the like can be reduced in size, and the characteristics of the power processing apparatus can be greatly utilized.
尚、上記実施の形態2においては、誘導加熱用コイル部の抵抗値の変更を、2個のコイルを備えるようにして、その接続方法を変更することにより対応する方法を示したが、これに限られることはなく、もちろん3個以上のコイルを備える場合も考えられる。 In the second embodiment, the method of changing the resistance value of the induction heating coil portion by providing two coils and changing the connection method has been shown. Of course, there is no limitation, and there may be cases where three or more coils are provided.
実施の形態3.
図5はこの発明の実施の形態3における例えば誘導加熱装置にて成る電力処理装置の構成を示す図、図6は図5に示した電力処理装置の動作を説明するための図である。図において、上記各実施の形態と同様の部分は同一符号を付して説明を省略する。上記実施の形態1では共振用コンデンサ部Cの容量の変更、また、上記実施の形態2では誘導加熱用コイルの抵抗値を変更する場合について示したが、本実施の形態3においては、これらを組み合わせる例について示す。本実施の形態3では、2つのコイルL1、L2の大きさ、インダクタンス値など同じものを用いた場合について説明する。また、2つのコンデンサC1、C2の容量は同容量のものを想定する。
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a configuration of a power processing apparatus including, for example, an induction heating apparatus according to
また、本実施の形態3では、主回路1を切り替える各所定値V1〜V4は、上記想定した動作特性曲線(図2)より電圧値を定め、主回路1の構成を変化させる場合について説明する。しかしながら、回路構成を変化させるための検出電圧の各所定値、及び変化させる主回路1を駆動するインバータ回路2の出力周波数の値は本実施の形態に示したものに限らず、図2に示した実際の周波数特性にあわせ、それぞれの主回路構成を変化させる電圧や周波数を個別に調整、もしくは周波数特性の異なるコイルを用いる場合、切り替える電力値及び主回路1を駆動するインバータ回路2の出力周波数を調整する構成にしてもかまわない。また、主回路1の各所定値V1〜V4にヒステリシスを設け、切り替え時に不安定な動作(チャタリング)を防ぐ構成にしてもかまわない。
Further, in the present third embodiment, a case will be described in which the predetermined values V1 to V4 for switching the
本実施の形態3では2つのコイルL1、L2と2つのコンデンサC1、C2により主回路1が構成され、コイルL1、L2の接続を変更するためのスイッチS1、S2、S3、コンデンサC1、C2の接続を変更するためのスイッチS4、S5から構成されている。制御回路3はインバータ回路2の入力電力もしくは入力電圧に応じ、上記スイッチS1〜S5とインバータ回路2を駆動する出力周波数fとを制御する。
In the third embodiment, the
入力電力(回生電力)Pと入力電圧Vと各スイッチS1からS5の動作状況を図6に基づいて説明する。入力電力PがP1の範囲では、入力電力Pが小さく入力電圧が駆動開始電圧の第4の所定値V4以下となるため、主回路1は動作を停止している。次に、入力電力Pが大きくなりP2の範囲では、入力電圧Vが第4の所定値V4を越え、制御回路3は第4の所定値V4を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS3、S4のみオンさせ2つのコイルL1、L2を直列、1つのコンデンサC1を接続し、その回路構成で指定される共振周波数f2でインバータ回路2のスイッチングを行う。この場合、それぞれのコイルL1、L2の抵抗値はR1、R2となるが、コイルL1、L2が直列に接続されるために誘導加熱装置の抵抗値は上記抵抗値R1、R2が加算された値となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(1)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
The operation status of the input power (regenerative power) P, the input voltage V, and the switches S1 to S5 will be described with reference to FIG. In the range where the input power P is P1, the input power P is small and the input voltage is equal to or lower than the fourth predetermined value V4 of the drive start voltage, so the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP3の範囲では、主回路1の駆動中の入力電圧が第3の所定値V3を越え、制御回路3は第3の所定値V3を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS3、S4、S5をオンさせ、2つのコイルL1、L2を直列、2つのコンデンサC1、C2を並列接続し、その回路構成で指定される共振出力周波数f3でインバータのスイッチングを行う。この場合、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの周波数特性より、主回路1を駆動するインバータ回路2の出力周波数を下げたことにより、それぞれのコイルL1、L2の抵抗値はR3、R4と小さくなるが、コイルが直列に接続されるために主回路1の抵抗値は上記抵抗値R3、R4が加算された値となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(2)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
Further, when the input power P increases and the range of P3, the input voltage during driving of the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP4の範囲では、主回路1の駆動中の入力電圧が第2の所定値V2を越え、制御回路は第2の所定値V2を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS2、S4をオンさせ、1つのコイルL1、1つのコンデンサC1を接続し、その回路構成で指定される共振出力周波数f4でインバータのスイッチングを行う。この場合、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの周波数特性より、ひとつのコイルL1の抵抗値はR4となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(3)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
Further, when the input power P increases and the range of P4, the input voltage during driving of the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP5の範囲では、主回路1の駆動中の入力電圧が第3の所定値V3を越えて、制御回路は第3の所定値V3を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS2、S4、S5をオンさせ、1つのコイルL1、2つのコンデンサC1、C2を接続し、その回路構成の変更に伴い、共振用コンデンサ部Cと誘導加熱用コイル部Lで指定される共振出力周波数f5でインバータ回路2のスイッチングを行う。この場合、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの周波数特性より、ひとつのコイルL1の抵抗値はR5となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(4)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
Further, in the range where the input power P increases and P5, the input voltage during driving of the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP6の範囲では、主回路1の駆動中の入力電圧が第2の所定値V2を越え、制御回路3は第2の所定値V2を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS1、S2、S4をオンさせ、2つのコイルL1、L2を並列、1つのコンデンサC1を接続し、その回路構成で指定される共振出力周波数f6でインバータ回路2のスイッチングを行う。この場合、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの周波数特性より、それぞれのコイルL1、L2の抵抗値は変化しR6,R7となり主回路1の抵抗値はR6、R7が並列に接続された値となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(5)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
Further, when the input power P increases and the range of P6, the input voltage during driving of the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP7の範囲では、主回路1の駆動中の入力電圧が第3の所定値V3を越え、制御回路2は第3の所定値V3を超えたことを検出し、スイッチS1、S2、S4、S5をオンさせ、2つのコイルL1、L2を並列、2つのコンデンサC1、C2を並列接続し、その回路構成で指定される共振出力周波数f7でインバータ回路2のスイッチングを行う。この場合、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの周波数特性より、それぞれのコイルL1、L2の抵抗値は変化しR8、R9となり主回路1の抵抗値はR8、R9が並列に接続された値となる。このため、主回路1は図6の(6)の入力電圧−入力電力Pの特性上で動作する。
Further, in the range where the input power P becomes large and P7, the input voltage during driving of the
さらに、入力電力Pが大きくなりP7の範囲を超え、入力電圧が第1の所定値V1を越えると、主回路1は異常入力電力を検出し、外部に信号を送るなど異常状態を外部回路に連絡し、誘導加熱装置の動作をとめることができる。この際、スイッチS1のみオンし、コイルL1からインバータ回路2や主回路1が接続される入力機器への逆回生を防ぐことができる。これにより、過入力電力による主回路1のインバータ回路2や、誘導加熱用コイル部Lの熱的な故障などを防ぐことができる。
Further, when the input power P increases and exceeds the range of P7, and the input voltage exceeds the first predetermined value V1, the
上記のように構成された実施の形態3の電力処理装置によれば、インバータ回路に入力される入力電力の大きさに応じて、誘導加熱用コイル部の抵抗値および共振コンデンサの容量を変更することを組み合わせることにより、主回路の消費電力を細かく調整しているため、主回路によってより一層柔軟に入力電力の変動に対応することができる。
また、共振周波数でインバータ回路の出力周波数は決定されているため、インバータ回路はゼロ電流スイッチングがなされ、インバータ回路での消費電力が抑えられる(損失が最小となる)ため、インバータ回路を冷却するための冷却手段(図示せず)などが小さく小型化でき、電力処理装置の特徴を大きくいかすことができる。
According to the power processing device of the third embodiment configured as described above, the resistance value of the induction heating coil section and the capacitance of the resonance capacitor are changed according to the magnitude of the input power input to the inverter circuit. By combining the above, since the power consumption of the main circuit is finely adjusted, the main circuit can deal with the fluctuation of the input power more flexibly.
In addition, since the output frequency of the inverter circuit is determined by the resonance frequency, the inverter circuit is zero-current switching, power consumption in the inverter circuit is suppressed (loss is minimized), and the inverter circuit is cooled. The cooling means (not shown) and the like can be reduced in size, and the characteristics of the power processing apparatus can be greatly utilized.
実施の形態4.
図7はこの発明の実施の形態4における電力処理装置の構成を示す図である。図において、上記各実施の形態と同様の部分は同一符号を付して説明を省略する。制御回路3は、検出された入力電圧に応じて駆動通電率を調整し、インバータ回路2を間欠的に動作させ、電力調整を細かく調整する。そして、制御回路3は、インバータ回路2の出力を停止(OFF)している際、スイッチS6をONして、インバータ回路2の出力端子間を短絡する。または、スイッチS7をONして、インバータ回路2の出力端子を地絡する。
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing the configuration of the power processing apparatus according to
例えば、コンデンサC1とコンデンサC2とが同容量であり、2個並列接続していた使用状態から、コンデンサC2を回路から外し、コンデンサC1の1個のみを接続した際、インバータ回路2の出力周波数が倍になるため、主回路1の周波数特性より抵抗値が大きく変化し消費される電力が大きく変化する。よって、このことを調整するために、制御回路3はインバータ回路2を間欠運転となるように通電率を調整することにより消費電力を調整する。たとえば100ms中10ms停止することで、電力処理装置で消費する電力を0.9倍に、100ms中50ms停止することで消費する電力を0.5倍に調整する。このように主回路1の消費電力を調整する。
For example, when the capacitor C1 and the capacitor C2 have the same capacity, and the capacitor C2 is removed from the circuit and only one capacitor C1 is connected from the use state where two capacitors C1 are connected in parallel, the output frequency of the
例えば、入力電力が第2の所定値より小さい場合は、インバータ回路2の出力周波数が一番高く設定されているとする。このように、一番高い出力周波数で駆動されていた場合、さらに入力電力が小さくなり、一番高い周波数で駆動された場合の抵抗値よりも、さらに主回路の抵抗値を大きくして消費電力を小さくする必要がある。この場合、上記に示したような間欠的動作を行うことにより、消費電力の調整を行う。
For example, when the input power is smaller than the second predetermined value, it is assumed that the output frequency of the
また、上記にて示したように、主回路1の共振周波数を変化させた場合、抵抗値は大きく変化している。この、抵抗値の大きな変化を段階的に変化させるよう調整するために、上記に示したような間欠動作を行うことにより、消費電力を調整することもできる。そして、制御回路3はこの間欠動作によりインバータ回路2が停止している間(通電停止中)には、インバータ回路2の出力端子間が短絡もしくは地絡するよう、スイッチS6またはスイッチS7のオンを行い、誘導加熱用コイル部Lからの回生電力がインバータ回路2に入力され回生されるのを防止する。
Further, as described above, when the resonance frequency of the
上記のように構成された実施の形態4の電力処理装置は、上記実施の形態と同様の効果を奏するのはもちろんのこと、インバータ回路を間欠運転させることにより、急激な変化を緩和して対応することができる。尚、制御回路は、間欠運転の出力周波数が可聴領域にならないように主回路を調整し、主回路の抵抗値を調整して消費電力を調整している。 The power processing device according to the fourth embodiment configured as described above has the same effects as those of the above-described embodiment, and can respond to the sudden change by intermittently operating the inverter circuit. can do. Note that the control circuit adjusts the power consumption by adjusting the main circuit so that the output frequency of the intermittent operation does not become an audible range, and adjusting the resistance value of the main circuit.
尚、上記実施の形態4においては、上記実施の形態1と同様の構成を例に示したが、これに限られることはなく、他の実施の形態においても同様に制御することは可能であり、本実施の形態4と同様の効果を奏することができる。 In the fourth embodiment, the same configuration as that of the first embodiment has been described as an example. However, the configuration is not limited to this, and the same control can be performed in other embodiments. The same effects as in the fourth embodiment can be obtained.
1 主回路、2 インバータ回路、3 制御回路、C 共振用コンデンサ部、
C1,C2,C3 コンデンサ、L 誘導加熱コイル部、L1,L2 コイル。
1 main circuit, 2 inverter circuit, 3 control circuit, C resonance capacitor,
C1, C2, C3 capacitor, L induction heating coil part, L1, L2 coil.
Claims (7)
上記主回路に交流電流を供給するインバータ回路と、
上記インバータ回路を制御する制御回路とを備え、
上記制御回路は、上記インバータ回路の入力に応じて上記主回路の回路構成を変更して上記主回路の共振周波数を変更し、上記インバータ回路の出力周波数を変更された上記主回路の共振周波数となるようにし、
上記制御回路は、上記主回路の消費電力が上記インバータ回路の入力電力に近似するように上記主回路の共振周波数を変更することを特徴とする電力処理装置。 A main circuit in which an induction heating coil portion and a resonance capacitor portion are connected in series;
An inverter circuit for supplying an alternating current to the main circuit;
A control circuit for controlling the inverter circuit,
The control circuit changes the circuit configuration of the main circuit according to the input of the inverter circuit to change the resonance frequency of the main circuit, and the output frequency of the inverter circuit is changed. so as to,
The control circuit, the main circuit power consumption characteristics and to that power processing apparatus to change the resonant frequency of the main circuit so as to approximate the input power of the inverter circuit.
上記制御回路は、上記複数個のコンデンサの接続方法を変更することにより、上記主回路の回路構成を変更することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電力処理装置。 The resonance capacitor unit is composed of a plurality of capacitors,
The power processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the control circuit changes a circuit configuration of the main circuit by changing a connection method of the plurality of capacitors.
上記制御回路は、上記複数個のコイルの接続方法を変更することにより、上記主回路の回路構成を変更することを特徴とする請求項1または請求項2に記載の電力処理装置。 The induction heating coil section is composed of a plurality of coils,
The control circuit, by changing the method of connecting the plurality of coils, the power processing apparatus according to claim 1 or claim 2, characterized in that to change the circuit configuration of the main circuit.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010226392A JP5419842B2 (en) | 2010-10-06 | 2010-10-06 | Power processing device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010226392A JP5419842B2 (en) | 2010-10-06 | 2010-10-06 | Power processing device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012080742A JP2012080742A (en) | 2012-04-19 |
| JP5419842B2 true JP5419842B2 (en) | 2014-02-19 |
Family
ID=46240322
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010226392A Expired - Fee Related JP5419842B2 (en) | 2010-10-06 | 2010-10-06 | Power processing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5419842B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6671871B2 (en) * | 2014-07-22 | 2020-03-25 | キヤノン株式会社 | Fixing device |
| JP6143815B2 (en) * | 2015-08-07 | 2017-06-07 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Power converter and induction heating cooker |
| CN112398234A (en) * | 2019-08-19 | 2021-02-23 | 广东美的白色家电技术创新中心有限公司 | Output control device, method and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11121162A (en) * | 1997-10-17 | 1999-04-30 | Toshiba Corp | High frequency heating device |
| JPH11260542A (en) * | 1998-03-11 | 1999-09-24 | Toshiba Corp | Induction heating cooking device |
| JP2003151747A (en) * | 2001-11-12 | 2003-05-23 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Induction heating cooker |
| US20060072931A1 (en) * | 2003-02-20 | 2006-04-06 | Kenji Asakura | Heat-fixing device |
| JP2005038654A (en) * | 2003-07-17 | 2005-02-10 | Hitachi Hometec Ltd | Induction heating cooker |
| JP4310292B2 (en) * | 2005-05-30 | 2009-08-05 | 日立アプライアンス株式会社 | Induction heating device |
| KR101123485B1 (en) * | 2007-08-21 | 2012-03-23 | 미쓰비시덴키 가부시키가이샤 | Induction heating device, electric power converting circuit and electric power processing device |
-
2010
- 2010-10-06 JP JP2010226392A patent/JP5419842B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012080742A (en) | 2012-04-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3773512B2 (en) | Motor power supply device | |
| JP5590268B2 (en) | Electric field coupled wireless power transmission system and power receiving apparatus used therefor | |
| US10734835B2 (en) | Power bypass apparatus with current-sharing function and method of controlling the same | |
| JP5855128B2 (en) | Power converter and control method of power converter | |
| JP5098599B2 (en) | Brushless motor drive device for compressor of air conditioner | |
| JP2009198139A (en) | Brushless motor driving device for compressor of air conditioner | |
| JP2004072832A (en) | Non-contact power feeding method | |
| JP5419842B2 (en) | Power processing device | |
| CN105765838A (en) | Power conversion device | |
| JP2009278794A (en) | Power conversion apparatus | |
| JP6184530B2 (en) | Discharge device | |
| JP2010207010A (en) | Coil switching device of three-phase ac motor drive system | |
| JP6451510B2 (en) | Non-contact power feeding device | |
| JP5927583B2 (en) | Contactless power supply system | |
| JP2013110888A (en) | Power-supply device | |
| JP2013523075A (en) | Motor converter circuit for drive motor and electric drive device having such motor converter circuit | |
| JP2012079648A (en) | Power processing apparatus | |
| JP2004357420A (en) | Electrical appliance controlling unit | |
| JP4446963B2 (en) | Induction heating cooker | |
| JP4494316B2 (en) | Induction heating cooker | |
| JP5842582B2 (en) | Auxiliary power supply and power supply method | |
| JP2010040687A (en) | Peltier drive circuit | |
| JP6854428B2 (en) | Inverter device and its control method | |
| CN106856367B (en) | System for reducing harmonic current content in power circuit and refrigeration compressor | |
| KR102013869B1 (en) | Power converter and operating method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120926 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130830 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130903 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131015 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20131105 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20131119 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5419842 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |