JP5384155B2 - Power generation system - Google Patents
Power generation system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5384155B2 JP5384155B2 JP2009064648A JP2009064648A JP5384155B2 JP 5384155 B2 JP5384155 B2 JP 5384155B2 JP 2009064648 A JP2009064648 A JP 2009064648A JP 2009064648 A JP2009064648 A JP 2009064648A JP 5384155 B2 JP5384155 B2 JP 5384155B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- power
- target value
- charge
- storage device
- output
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
- Supply And Distribution Of Alternating Current (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
Description
本発明は、自然エネルギーを利用した電源装置を備える発電システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a power generation system including a power supply device using natural energy.
近年、変電所から交流電力の供給を受ける各需要家(例えば、住宅や工場など)内に自然エネルギーを利用した電源装置(例えば、太陽光電源装置)が備えられるケースが増えている。電源装置は、変電所の配下に設けられる配電系統に接続されており、電源装置によって出力される電力は、自需要家内に設けられた電力消費装置だけでなく配電系統にも出力される。このように、需要家から配電系統へ向かう電力の流れは「逆潮流」と呼ばれ、需要家から配電系統へ出力される電力は「逆潮流電力」と呼ばれる。 In recent years, there is an increasing number of cases where a power supply device (for example, a solar power supply device) using natural energy is provided in each consumer (for example, a house or a factory) that receives supply of AC power from a substation. The power supply device is connected to a power distribution system provided under the substation, and the power output by the power supply device is output not only to the power consuming device provided in the consumer, but also to the power distribution system. As described above, the flow of power from the consumer to the distribution system is called “reverse power flow”, and the power output from the customer to the power distribution system is called “reverse power flow”.
ところで、自然エネルギーを利用した電源装置の出力は、天候などに応じて変動しうる。そのため、電源装置から配電系統へ逆潮流されている場合、逆潮流電力は、電源装置の出力変動に伴って変動する。その結果、配電系統の系統周波数が変動するおそれがある。このような系統周波数の変動は、自然エネルギーを利用した電源装置を備える需要家が増えるほど顕著となる。 By the way, the output of the power supply device using natural energy can fluctuate according to the weather or the like. Therefore, when a reverse power flow is made from the power supply device to the power distribution system, the reverse power flow varies with the output variation of the power supply device. As a result, the system frequency of the power distribution system may fluctuate. Such fluctuations in the system frequency become more prominent as the number of customers with power supply devices using natural energy increases.
ここで、自然エネルギーを利用した電源装置と蓄電装置とを備え、電源装置の出力変動に応じて蓄電装置の充放電を行う発電システムが提案されている(特許文献1参照)。このような発電システムによれば、逆潮流電力の急激な変動を抑制することができる。 Here, a power generation system that includes a power supply device and a power storage device using natural energy and charges and discharges the power storage device according to output fluctuations of the power supply device has been proposed (see Patent Document 1). According to such a power generation system, rapid fluctuations in reverse power flow can be suppressed.
しかしながら、上記特許文献1に記載の手法では、所定の単位時間毎に頻繁に蓄電装置の充放電が行われるため、蓄電装置の寿命が短くなるという問題があった。
However, the method described in
本発明は、上述した問題を解決するためになされたものであり、蓄電装置の長寿命化を可能とする発電システムを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a power generation system capable of extending the life of a power storage device.
本発明の特徴に係る発電システムは、交流電力が配電される配電系統に接続された発電システムであって、自然エネルギーを利用することによって出力電力を生成する電源装置と、充放電する蓄電装置と、出力電力を検出する検出部と、出力電力の増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間にわたって継続した場合、所定の期間における出力電力の値に基づいて、電源装置及び蓄電装置から配電系統へ逆潮流される電力の目標値を設定する目標値設定部と、目標値に基づいて、電源装置から蓄電装置への充電及び蓄電装置から配電系統への放電の制御である充放電制御を実行する充放電制御部とを備えることを要旨とする。 A power generation system according to a feature of the present invention is a power generation system connected to a distribution system to which AC power is distributed, a power supply device that generates output power by using natural energy, a power storage device that is charged and discharged, and When the output power detection unit and the output power increase trend or decrease trend continue for a predetermined period, reverse power flow from the power supply device and the power storage device to the distribution system based on the value of the output power in the predetermined period A target value setting unit for setting a target value of the generated power, and charge / discharge control for controlling charging from the power supply device to the power storage device and discharging from the power storage device to the distribution system based on the target value The gist is to include a control unit.
本発明の特徴に係る発電システムにおいて、所定の期間は、配電系統におけるガバナフリー運転の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より大きく、配電系統における負荷周波数制御の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より小さくてもよい。 In the power generation system according to the features of the present invention, the predetermined period is greater than ¼ of the load fluctuation period to be governed by the governor-free operation in the distribution system, and the load fluctuation period to be subject to load frequency control in the distribution system. It may be smaller than 1/4.
本発明の特徴に係る発電システムにおいて、目標値設定部は、充放電制御の開始から所定の時間経過後における蓄電装置の蓄電容量に基づいて、新たな目標値を設定し、充放電制御部は、設定された新たな目標値に基づいて、充放電制御を実行してもよい。 In the power generation system according to the features of the present invention, the target value setting unit sets a new target value based on the storage capacity of the power storage device after a predetermined time has elapsed from the start of charge / discharge control, and the charge / discharge control unit The charge / discharge control may be executed based on the set new target value.
本発明の特徴に係る発電システムにおいて、充放電制御部は、充放電制御の終了後において、蓄電装置の蓄電容量を所定の初期容量に調整してもよい。 In the power generation system according to the features of the present invention, the charge / discharge control unit may adjust the storage capacity of the power storage device to a predetermined initial capacity after the end of the charge / discharge control.
本発明によれば、蓄電装置の長寿命化を可能とする発電システムを提供することを目的とすることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a power generation system capable of extending the life of a power storage device.
以下において、本発明の実施形態に係る系統連系システムについて、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、以下の図面の記載において、同一又は類似の部分には、同一又は類似の符号を付している。 Below, the grid connection system which concerns on embodiment of this invention is demonstrated, referring drawings. In the following description of the drawings, the same or similar parts are denoted by the same or similar reference numerals.
ただし、図面は模式的なものであり、各寸法の比率などは現実のものとは異なることに留意すべきである。従って、具体的な寸法などは以下の説明を参酌して判断すべきである。また、図面相互間においても互いの寸法の関係や比率が異なる部分が含まれていることは勿論である。 However, it should be noted that the drawings are schematic and ratios of dimensions and the like are different from actual ones. Therefore, specific dimensions and the like should be determined in consideration of the following description. Moreover, it is a matter of course that portions having different dimensional relationships and ratios are included between the drawings.
また、以下の説明において、配電系統から需要家へ向かう電力の流れを「潮流」といい、配電系統から需要家へ潮流する電力を「潮流電力」という。また、需要家から配電系統へ向かう電力の流れを「逆潮流」といい、需要家から配電系統へ逆潮流する電力を「逆潮流電力」という。 In the following description, the flow of power from the distribution system to the consumer is referred to as “tidal current”, and the power flowing from the distribution system to the consumer is referred to as “tidal power”. In addition, the flow of power from the consumer to the power distribution system is called “reverse power flow”, and the power flowing from the customer to the power distribution system is called “reverse power flow”.
(配電システムの構成)
以下において、実施形態に係る配電システムの構成について、図面を参照しながら説明する。図1は、実施形態に係る配電システム1の構成を示す概略図である。
(Configuration of power distribution system)
Hereinafter, the configuration of the power distribution system according to the embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a configuration of a
図1に示すように、配電システム1は、複数の高圧電力供給源10(高圧電力供給源10A、高圧電力供給源10B)と、変電所20と、複数の需要家30(需要家30A〜30I)とを有する。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
高圧電力供給源10は、高圧送電線40を介して、変電所20に高圧電力を送電する。高圧電力供給源10は、例えば、発電所である。
The high voltage
変電所20は、配電系統50を介して、各需要家30に高圧電力を降圧して生成した交流電力を配電する。配電系統50は、変電所20が各需要家30を管理する単位である。図示しないが、変電所20は、複数の配電系統50を配下に有していてもよい。
The
各需要家30は、発電システム100を備える。発電システム100は、配電系統50を介して変電所20と電気的に接続されている。発電システム100は、配電系統50との間で電力の入出力(潮流及び逆潮流)を行う。
Each
(発電システムの構成)
以下において、実施形態に係る発電システムの構成について、図面を参照しながら説明する。図2は、実施形態に係る発電システム100の構成を示すブロック図である。
(Configuration of power generation system)
Below, the structure of the electric power generation system which concerns on embodiment is demonstrated, referring drawings. FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
図2に示すように、発電システム100は、複数の電力消費装置102(電力消費装置102A〜電力消費装置102C)と、電源装置104と、蓄電装置106と、系統連系装置200とを有する。
As illustrated in FIG. 2, the
電力消費装置102は、配電系統50から配電される潮流電力、及び電源装置104によって出力される出力電力Pを消費する。電力消費装置102は、例えば家電などである。
The power consuming device 102 consumes the tidal power distributed from the
電源装置104は、自然エネルギーを利用することによって出力電力Pを生成する。電源装置104は、例えば太陽光電源装置、風力電源装置などである。このような電源装置104によって生成される出力電力Pは、気象・天候などに応じて変動することに留意すべきである。なお、本実施形態では、電源装置104によって生成される出力電力Pは、系統連系装置200を介して、配電系統50へ逆潮流されうる。
The
蓄電装置106は、所定の定格容量CCAPを有し、充放電可能な装置である。具体的には、蓄電装置106は、電源装置104によって生成される出力電力Pを蓄電する。また、蓄電装置106は、蓄電した電力を配電系統50へ逆潮流する。蓄電装置106は、例えば、リチウムイオン電池やニッケル水素電池などの二次電池、或いは電気二重層キャパシタなどである。
The
本実施形態では、蓄電装置106の初期容量CSTARTは定められており、例えば、定格容量CCAPの50%であるが、これに限られるものではない。
In the present embodiment, the initial capacity C START of the
系統連系装置200は、配電系統50、複数の電力消費装置102、電源装置104及び蓄電装置106の連系を制御する。具体的には、系統連系装置200は、例えば、蓄電装置106から配電系統50への放電や電源装置104から蓄電装置106への充電を制御する。なお、以下の説明において、逆潮流電力PREVには、電源装置104の出力電力Pと蓄電装置106から放電される放電電力Qとが含まれることに留意すべきである。
The
(系統連系装置の構成)
以下において、実施形態に係る系統連系装置の構成について、図面を参照しながら説明する。図3は、実施形態に係る系統連系装置200の構成を示すブロック図である。
(Configuration of grid interconnection device)
Below, the structure of the grid connection apparatus which concerns on embodiment is demonstrated, referring drawings. FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
系統連系装置200は、図3に示すように、検出部201、判定部202、目標値設定部203、充放電制御部204、DC/DC変換部205及びパワーコンディショナー206を備える。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
(検出部)
検出部201は、検出周期TD(例えば、1分)ごとに電源装置104の出力電力Pを検出する。図4は、出力電力Pの推移の一例を示すグラフである。図4に示すグラフにおける検出周期TDは、1分である。なお、検出部201は、出力電力Pが電源装置104の定格出力PCAPの所定割合(例えば、10%)以上である場合に出力電力Pを検出することとしてもよい。
(Detection unit)
The
(判定部)
判定部202は、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続したか否かを判定する。
(Judgment part)
The
具体的には、まず、判定部202は、前回の検出タイミングで検出された出力電力PLASTと、今回の検出タイミングで検出された出力電力PTHISとの差である電力変動幅ΔPを、検出周期TDごとに算出する。判定部202は、電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上か否かを判定する。判定部202は、電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上であると判定されるまで、電力変動幅ΔPの算出を繰り返す。このように、本実施形態では、電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上であることをもって出力電力Pが増加傾向又は減少傾向にあるとみなすが、これに限られるものではない。電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの0%より大きければ、出力電力Pが増加傾向又は減少傾向にあるとみなすことができる。
Specifically, first, the
次に、判定部202は、電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上であると判定された場合、すなわち、出力電力Pが増加傾向又は減少傾向にあると判定された場合に、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続するか否かを判定する。具体的には、判定部202は、出力電力Pが、出力電力PLASTが検出された時刻から所定の期間TT後の時刻まで、出力電力PLAST±10%の範囲外を継続して推移するか否かを判定する。
Next, when the
次に、判定部202は、出力電力Pが出力電力PLAST±10%の範囲外を継続して推移した場合、すなわち、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合に、その旨を目標値設定部203に通知する。
Next, the
ここで、所定の期間TTは、配電系統50におけるガバナフリー(GF:Governor Free)運転の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より大きく、配電系統50における負荷周波数制御(LFC:Load Frequency Control)の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より小さいことに留意すべきである。ガバナフリー運転とは、配電系統50における負荷変動のうち周期が数分程度(例えば、2分)までの微小周期変動を解消するための運転である。ガバナフリー運転は、高圧電力供給源10に設けられた調速機の制限解除による発電出力制御によって行われる。また、LFCとは、配電系統50における負荷変動のうち周期が数分から十数分程度(例えば、2〜20分程度)の短周期変動を解消するための制御である。LFCは、高圧電力供給源10とは別に設けられ、短周期変動に対応可能な周波数制御用の発電所における出力制御によって行なわれる。なお、配電系統50における負荷変動のうち周期が十数分を超える長周期変動は、経済負荷配分制御(EDC:Economic Dispatching Control)により解消されうる。GF運転、LFC及びEDCについては、“横山隆一監修「電力自由化と技術開発−21世紀における電気事業の経営効率と供給信頼性の向上を目指して−」第5章”、及び“電気学会技術報告,第869号”に詳しい。
Here, the predetermined period T T is larger than ¼ of a load fluctuation period to be a target of governor-free (GF) operation in the
ところで、多数の電源装置104から配電系統50に逆潮流されている場合において、配電系統50付近の気象変動によって多数の電源装置104それぞれの出力電力が変動する場合がある。この場合、配電系統50には、微小周期変動、短周期変動、或いは長周期変動のいずれかが発生する。上述の通り、微小周期変動及び長周期変動には、GF運転及びEDCによって対応可能である。従って、微小周期変動及び長周期変動を発生させるような出力電力の変動は、発電システム100内で解消する必要はない。一方で、短周期変動の解消には、配電系統50の規模に応じて、周波数制御用の発電所を増設する必要がある。そのため、短周期変動を発生させるような出力電力の変動は、発電システム100内で解消されることが望ましい。なお、短周期変動の周期は、配電系統50の規模などに応じて異なるものであることに留意すべきである。
By the way, in the case where a reverse power flow is made from a large number of
本実施形態において、所定の期間TTは、GF運転の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より大きく、LFCの対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より小さい。そのため、判定部202は、微小周期変動を発生させるような出力電力Pの変動ではなく、短周期変動を発生させるような出力電力Pの変動に対して、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が継続していると判定する。
In the present embodiment, the predetermined time period T T is larger than 1/4 the period of the load fluctuation to be GF operation, 1/4 smaller than the period of the load fluctuation to be LFC eligible. For this reason, the
(目標値設定部)
目標値設定部203は、判定部202からの通知に応じて、逆潮流電力PREVの目標値を設定する。なお、本発明において、逆潮流電力PREVは、需要家30から配電系統50へ逆潮流する電力であり、電源装置104の出力電力Pと蓄電装置106の放電電力との合成電力であることに留意すべきである。
(Target value setting section)
The target
具体的には、目標値設定部203は、所定の期間TTにおける出力電力Pの値に基づいて、逆潮流電力PREVの目標値である第1目標値PSET1を設定する。また、目標値設定部203は、逆潮流電力PREVが第1目標値PSET1に到達するまでの第1到達時間T1を設定する。
Specifically, the target
具体的には、目標値設定部203は、出力電力PLASTと、出力電力PLASTが検出された時刻から所定の期間TT後の時刻における出力電力PTとの間の値(例えば、出力電力PLASTと出力電力PTとの中間値)を第1目標値PSET1に設定する。また、目標値設定部203は、短周期変動の周期の1/4(例えば、30秒〜5分)以上に第1到達時間T1を設定する。ただし、第1目標値PSET1は、出力電力PLASTと出力電力PTとの間の値であればよく、第1到達時間T1は、出力電力Pの変動を平滑化できる時間であればよい。
Specifically, the target
また、目標値設定部203は、第1到達時間T1経過後における蓄電装置106の蓄電容量CT1に基づいて、逆潮流電力PREVの新たな目標値である第2目標値PSET2を設定する。また、目標値設定部203は、逆潮流電力PREVが第2目標値PSET2に到達するまでの第2到達時間T2を設定する。
Further, the target
具体的には、目標値設定部203は、蓄電容量CT1が初期容量CSTART以上の場合、定格出力PCAPの半分よりも大きな値(例えば、定格出力PCAPの75%)を第2目標値PSET2に設定する。一方で、目標値設定部203は、蓄電容量CT1が初期容量CSTART未満である場合、定格出力PCAPの半分よりも小さな値(例えば、定格出力PCAPの25%)を第2目標値PSET2に設定する。また、目標値設定部203は、短周期変動の周期の1/4(例えば、30秒〜5分)以上に第2到達時間T2を設定する。ただし、第2目標値PSET2は、出力電力PLASTと出力電力PTとの間の値であればよく、第2到達時間T2は、出力電力Pの変動を平滑化できる時間であればよい。
Specifically, when the storage capacity C T1 is equal to or greater than the initial capacity C START , the target
さらに、目標値設定部203は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの間において、第2目標値PSET2が定格出力PCAPの半分以上の値に設定されている場合であって、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART未満となったとき、或いは、第2目標値PSET2が定格出力PCAPの半分よりも小さな値に設定されている場合であって、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上となったとき、逆潮流電力PREVの新たな目標値として第3目標値PSET3を設定する。第3目標値PSET3は、例えば、定格出力PCAPの半分である。
Further, the target
(充放電制御部)
充放電制御部204は、目標値設定部203によって設定された逆潮流電力PREVの目標値に基づいて、電源装置104から蓄電装置106への充電、及び蓄電装置106から配電系統50への放電の制御である充放電制御を実行する。これによって、充放電制御部204は、電源装置104の出力電力Pの変動を平滑化する。
(Charge / Discharge Control Unit)
The charge /
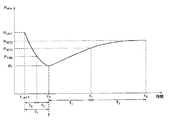
図5は、発電システム100から配電系統50への逆潮流電力PREVの推移を模式的に示すグラフである。図5では、電源装置104の出力電力PLASTが検出された時刻tLASTから所定の期間TT後の時刻tTにおいて、充放電制御部204による充放電制御が開始されている。
FIG. 5 is a graph schematically showing the transition of the reverse power flow PREV from the
充放電制御部204は、逆潮流電力PREVが時刻tTから第1到達時間T1経過後の時刻t1に第1目標値PSET1となるように、充放電制御を実行する。図5に示すように、出力電力Pの減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合には、充放電制御部204は、出力電力Pに放電電力Qを加えて出力する。一方で、図示しないが、出力電力Pの増加傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合には、充放電制御部204は、出力電力Pの一部を蓄電装置106への充電電力Rとする。
具体的には、充放電制御部204は、時刻tTから時刻t1までの間は、次の式(1)に基づいて蓄電装置106からの放電電力Qを算出する。
〔数1〕
放電電力Q1=逆潮流電力PREV−出力電力P(i) …(1)
=(出力電力PT+第1目標値PSET1×i/T1)−出力電力P(i)
ただし、式(1)において、iは、時刻tTからの経過時間であり、出力電力P(i)は、時刻tTからi経過時における出力電力Pである。なお、式(1)に基づいて算出される放電電力Q1が負の値である場合、算出値は充電電力Rを表していることに留意すべきである。充放電制御部204は、算出された放電電力Q1に従って、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
Specifically, charge /
[Equation 1]
Discharge power Q1 = Reverse power flow power P REV −Output power P (i) (1)
= (Output power P T + first target value P SET1 × i / T 1 ) −output power P (i)
However, in the formula (1), i is the elapsed time from the time t T, the output power P (i) is the output power P at the time i has passed since the time t T. It should be noted that when the discharge power Q1 calculated based on the formula (1) is a negative value, the calculated value represents the charge power R. Charging / discharging
次に、充放電制御部204は、逆潮流電力PREVが時刻t1から第2到達時間T2経過後の時刻t2に第2目標値PSET2となるように、充放電制御を実行する。具体的には、充放電制御部204は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの間は、次の式(2)に基づいて蓄電装置106からの放電電力Q2を算出する。
〔数2〕
放電電力Q2=逆潮流電力PREV−出力電力P(j) …(2)
=(第1目標値PSET1+第2目標値PSET2×j/T2)−出力電力P(j)
ただし、式(2)において、jは、時刻t1からの経過時間であり、出力電力P(j)は、時刻t1からj経過時における出力電力Pである。なお、式(1)と同様に、式(2)に基づいて算出される放電電力Q2が負の値である場合、算出値は充電電力Rを表していることに留意すべきである。充放電制御部204は、算出された放電電力Q2に従って、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
Then, the charge and
[Equation 2]
Discharge power Q2 = Reverse power flow power P REV −Output power P (j) (2)
= (First target value P SET1 + second target value P SET2 × j / T 2 ) −output power P (j)
However, in the formula (2), j is the time elapsed from the time t 1, the output power P (j) is the output power P from time t 1 when j elapsed. It should be noted that, similarly to the equation (1), when the discharge power Q2 calculated based on the equation (2) is a negative value, the calculated value represents the charging power R. Charging / discharging
また、充放電制御部204は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの間において、目標値設定部203によって第3目標値PSET3が設定された場合、次の式(3)に基づいて蓄電装置106からの放電電力Q3を算出する。
〔数3〕
放電電力Q3=逆潮流電力PREV(k)−出力電力P(k) …(3)
=逆潮流電力PREV(k)+(第3目標値PSET3−逆潮流電力PREV(k))×l/k)
ただし、式(3)において、kは、時刻t1から第3目標値PSET3設定までに経過した時間であり、逆潮流電力PREV(k)及び出力電力P(k)は、時刻t1からk経過時における逆潮流電力PREV及び出力電力Pである。lは、第3目標値PSET3設定後からの経過時間である。 充放電制御部204は、算出された放電電力Q3に従って、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
Further, the charge and
[Equation 3]
Discharge power Q3 = reverse power flow power P REV (k) −output power P (k) (3)
= Reverse flow power P REV (k) + (third target value P SET3 −reverse flow power P REV (k)) × l / k)
However, in Formula (3), k is the time elapsed from the time t 1 to the third target value P SET3 setting, and the reverse power flow power P REV (k) and the output power P (k) are the time t 1 Are the reverse power flow power PREV and the output power power P after the elapse of k. l is an elapsed time after the third target value P SET3 is set. Charging / discharging
次に、充放電制御部204は、時刻t2経過後、すなわち充放電制御の終了後において、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cを初期容量CSTARTに調整する。充放電制御部204は、蓄電容量Cを初期化するために、逆潮流電力PREVの初期化用目標値PSETSを設定する。
Next, charge /
具体的には、充放電制御部204は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上の場合、定格出力PCAPの半分以上の値(例えば、定格出力PCAPの75%)を初期化用目標値PSETSに設定する。一方で、充放電制御部204は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART未満である場合、定格出力PCAPの半分未満の値(例えば、定格出力PCAPの25%)を初期化用目標値PSETSに設定する。充放電制御部204は、次の式(4)に基づいて蓄電装置106からの放電電力Q4を算出する。
〔数4〕
放電電力Q4=初期化用目標値PSETS−出力電力P(m) …(4)
ただし、式(4)において、mは、時刻t2からの経過時間であり、出力電力P(m)は、時刻t2からm経過時における出力電力Pである。充放電制御部204は、算出された放電電力Q4に従って、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。具体的には、充放電制御部204は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上の場合には放電することによって、また、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART未満である場合には充電することによって、蓄電容量Cを初期化する。
Specifically, when the storage capacity C is equal to or greater than the initial capacity C START , the charge /
[Equation 4]
Discharge power Q4 = initialization target value P SETS −output power P (m) (4)
However, in the formula (4), m is the time elapsed from time t 2, the output power P (m) is the output power P when m elapses from the time t 2. Charging / discharging
(DC/DC変換部とパワーコンディショナー)
DC/DC変換部205は、電源装置104又は配電系統50と蓄電装置106との間での適切な入出力のために電圧の昇降圧を行う。
(DC / DC converter and power conditioner)
The DC /
パワーコンディショナー206は、図3に示すように、最大化制御部206a、電力調整部206b及びDC/AC変換部206cを備える。最大化制御部206aは、電源装置104の出力電力を最大化する。電力調整部206bは、充放電制御部204と協働して逆潮流電力PREVを調整する。DC/AC変換部206cは、出力電力P及び放電電力Qを交流電力に変換する。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
(変動の検出)
以下において、実施形態に係る系統連系装置による変動の検出について、図面を参照しながら説明する。変動検出とは、平滑化を行う必要のある変動(短周期変動を生じさせる変動)を検出することである。図6は、実施形態に係る系統連系装置200の変動検出処理を示すフロー図である。
(Fluctuation detection)
Hereinafter, detection of fluctuations by the grid interconnection device according to the embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. The variation detection is detection of a variation that needs to be smoothed (a variation that causes a short period variation). FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing the fluctuation detection process of the
図6に示すように、ステップS10において、系統連系装置200は、前回の検出タイミングにおける電源装置104の出力電力PLASTと、今回の検出タイミングにおける出力電力PTHISとを検出する。
As shown in FIG. 6, in step S10, the
ステップS11において、系統連系装置200は、出力電力PLASTと出力電力PTHISとの電力変動幅ΔPを算出する。
In step S11, the
ステップS12において、系統連系装置200は、電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上か否かを判定する。電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上である場合、処理はステップS13に進む。電力変動幅ΔPが定格出力PCAPの30%以上でない場合、処理はステップS10に戻る。
In step S12, the
ステップS13において、系統連系装置200は、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続したか否かを判定する。出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合、出力電力Pの変動が感知されたとして処理は後述する平滑化処理に移行する。一方で、出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続しなかった場合、処理はステップS10に戻る。
In step S13, the
(逆潮流電力の平滑化)
以下において、実施形態に係る系統連系装置による平滑化について、図面を参照しながら説明する。図7は、実施形態に係る系統連系装置200の平滑化処理を示すフロー図である。
(Smoothing of reverse power flow)
Hereinafter, smoothing by the grid interconnection device according to the embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the smoothing process of the
図7に示すように、ステップS20において、系統連系装置200は、逆潮流電力PREVの目標値である第1目標値PSET1と、逆潮流電力PREVが第1目標値PSET1に到達するまでの第1到達時間T1とを設定する。
As shown in FIG. 7, in step S20, the
ステップS21において、系統連系装置200は、逆潮流電力PREVが時刻tTから第1到達時間T1経過後の時刻t1に第1目標値PSET1となるように、充放電制御を実行する。具体的には、充放電制御部204は、上記式(1)から算出される放電電力Q1に基づいて、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
In step S21, the
ステップS22において、系統連系装置200は、時刻t1における蓄電装置106の蓄電容量CT1に基づいて、逆潮流電力PREVの第2目標値PSET2と、逆潮流電力PREVが第2目標値PSET2に到達するまでの第2到達時間T2とを設定する。
In step S22, the
ステップS23において、系統連系装置200は、逆潮流電力PREVが時刻t1から第2到達時間T2経過後の時刻t2に第2目標値PSET2となるように、充放電制御を実行する。具体的には、充放電制御部204は、上記式(2)から算出される放電電力Q2に基づいて、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
In step S23, the
ステップS24において、系統連系装置200は、第2目標値PSET2が定格出力PCAPの半分以上の値に設定されており、かつ、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART未満となるか否か、又は、第2目標値PSET2が定格出力PCAPの半分よりも小さな値に設定されており、かつ、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上となるか否かを判定する。いずれかの条件に該当する場合には、処理はステップS25に進む。一方で、いずれの条件にも該当しない場合、処理はステップS27に進む。
In step S24, the
ステップS25において、系統連系装置200は、第2目標値PSET2を破棄して、新たに第3標値PSET3を設定する。
In step S25, the
ステップS26において、系統連系装置200は、逆潮流電力PREVが時刻t2に第3目標値PSET3となるように、充放電制御を実行する。具体的には、充放電制御部204は、上記式(3)から算出される放電電力Q3に基づいて、蓄電装置106の充放電を制御する。
In step S26, the
ステップS27において、系統連系装置200は、時刻t2に到達したか否かを判定する。時刻t2に到達した場合、充放電制御は終了する。一方で、時刻t2に到達していない場合、処理はステップS24に戻る。
In step S27, the
(蓄電装置の初期化)
以下において、実施形態に係る系統連系装置による蓄電装置の初期化について、図面を参照しながら説明する。図8は、実施形態に係る系統連系装置200の初期化処理を示すフロー図である。
(Initialization of power storage device)
Hereinafter, initialization of the power storage device by the grid interconnection device according to the embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing the initialization process of the
図8に示すように、ステップS30において、系統連系装置200は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上か否かを判定する。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上である場合、処理はステップS31に進む。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTART以上でない場合、処理はステップS33に進む。
As shown in FIG. 8, in step S30, the
ステップS31において、系統連系装置200は、定格出力PCAPの半分以上の値を初期化用目標値PSETSに設定する。系統連系装置200は、上記式(4)から算出される放電電力Q4(正の値)に基づいて、蓄電装置106を放電する。
In step S31, the
ステップS32において、系統連系装置200は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなったか否かを判定する。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなった場合、処理は終了する。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなっていない場合、処理はステップS31に戻る。
In step S32, the
ステップS33において、系統連系装置200は、定格出力PCAPの半分未満の値を初期化用目標値PSETSに設定する。系統連系装置200は、上記式(4)から算出される放電電力Q4(負の値)に基づいて、蓄電装置106を充電する。
In step S33, the
ステップS34において、系統連系装置200は、蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなったか否かを判定する。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなった場合、処理は終了する。蓄電容量Cが初期容量CSTARTとなっていない場合、処理はステップS33に戻る。
In step S34, the
(作用及び効果)
実施形態に係る発電システム100において、目標値設定部203は、電源装置104の出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合に、所定の期間TTにおける出力電力Pの値に基づいて、逆潮流電力PREVの第1目標値PSET1を設定する。充放電制御部204は、第1目標値PSET1に基づいて、蓄電装置106の充放電制御を実行する。
(Function and effect)
In the
このように、蓄電装置106の充放電制御は、電源装置104の出力電力Pの増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間TTにわたって継続した場合にのみ実行される。従って、既定の間隔で断続的に充放電制御を実行する場合に比べて、蓄電装置106の充放電回数を減少することができる。そのため、蓄電装置106の長寿命化を図ることができる。
Thus, the charge and discharge control of the
ここで、図9は、2008年4月29日における某太陽電池発電システムの出力電力Pの推移を示すグラフである。所定の期間TTを2分に設定した場合、実施形態に係る発電システム100によれば、図9に示す期間A、B、Cの3回の変動に対してのみ充放電制御が行なわれる。一方で、2分ごとに移動平均法による算出値による充放電制御を行う場合には、10時47分〜11時35分の間に24回の充放電制御が行なわれる。このように、実施形態に係る発電システム100によれば、蓄電装置106の充放電回数を減少することができることは明らかである。
Here, FIG. 9 is a graph showing the transition of the output power P of the solar cell power generation system on April 29, 2008. If you set the predetermined time period T T in 2 minutes, according to the
また、実施形態において、所定の期間TTは、GF運転の対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より大きく、LFCの対象となる負荷変動の周期の1/4より小さい。従って、充放電制御は、微小周期変動を発生させるような出力電力Pの変動ではなく、短周期変動を発生させるような出力電力Pの変動に対して実行される。そのため、GF運転によって解消可能な出力電力Pの変動を解消するために実行される充放電を少なくするとともに、LFCの対象となる短周期変動を発生させるような出力電力Pの変動を解消するために実行される充放電を確保することができる。その結果、各需要家30に設けられた電源装置104の出力変動に起因して、配電系統50に周波数制御用の発電所を増設する必要を小さくすることができる。
Further, in the embodiment, the predetermined period T T is larger than ¼ of the load fluctuation period to be subjected to GF operation and smaller than ¼ of the load fluctuation period to be subjected to LFC. Therefore, the charge / discharge control is executed not with respect to fluctuations in the output power P that cause minute cycle fluctuations but with fluctuations in the output power P that cause short-period fluctuations. Therefore, in order to reduce the amount of charge / discharge that is performed to eliminate the fluctuations in the output power P that can be eliminated by the GF operation, and to eliminate fluctuations in the output power P that cause short-cycle fluctuations that are subject to LFC. It is possible to ensure the charge / discharge performed at the same time. As a result, it is possible to reduce the necessity of adding a power plant for frequency control to the
また、実施形態において、目標値設定部203は、充放電制御の開始から第1到達時間T1経過後における蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cに基づいて、新たに第2目標値PSET2を設定する。従って、第1目標値PSET1設定後における日射変動などによって生じる電源装置104の出力変動に則した目標値を設定できるので、変動の平滑化を効率的に行うことができる。
Further, in the embodiment, the target
また、充放電制御部204は、充放電制御の終了後において、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量Cを初期容量CSTARTに調整する。従って、次回に実行される充放電制御に迅速に対応できるとともに、蓄電装置106の蓄電容量の過不足を生じることなく、毎回同じ条件で充放電制御を実行することができる。
The charge /
[その他の実施形態]
本発明は上述した実施形態によって説明したが、この開示の一部をなす論述及び図面は、この発明を限定するものであると理解すべきではない。この開示から当業者には様々な代替実施形態、実施例及び運用技術が明らかとなろう。
[Other Embodiments]
Although the present invention has been described with reference to the above-described embodiments, it should not be understood that the descriptions and drawings constituting a part of this disclosure limit the present invention. From this disclosure, various alternative embodiments, examples and operational techniques will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
例えば、上述した実施形態において例示した数値は一例であることに留意すべきである。各種閾値などに用いられる数値は、配電システム1及び発電システム100の構成に応じて適宜設定することができる。
For example, it should be noted that the numerical values exemplified in the above-described embodiments are examples. Numerical values used for various thresholds can be appropriately set according to the configurations of the
また、上述した実施形態において、図2及び図3を用いて発電システム100の構成について説明したが、これに限られるものではない。特に、系統連系装置200が備える構成の少なくとも一つは、電源装置104や蓄電装置106などに備えられていてもよいことに留意すべきである。
Moreover, in embodiment mentioned above, although the structure of the electric
なお、上述した系統連系装置200のハードウェア構成は、プログラムモジュールとして実現することができる。したがって、上述した系統連系装置200において実行されるとした処理は、系統連系装置200の機能を有した汎用コンピュータ等によって実行されてもよい。
Note that the hardware configuration of the
以下、本発明に係る太陽電池モジュールの実施例について具体的に説明するが、本発明は、下記の実施例に示したものに限定されるものではなく、その要旨を変更しない範囲において、適宜変更して実施することができるものである。 Hereinafter, examples of the solar cell module according to the present invention will be specifically described. However, the present invention is not limited to those shown in the following examples, and may be appropriately changed within the scope not changing the gist thereof. Can be implemented.
(実施例1)
所定の天候変動が発生した場合の、太陽光発電装置の出力電力P、蓄電装置の放電電力Q、逆潮流電力PREV(P+Q)、蓄電装置の蓄電容量Cの推移についてシミュレーションを行った。図10は、実施例1に係るシミュレーション結果を示すグラフである。
Example 1
A simulation was performed on changes in the output power P of the photovoltaic power generation device, the discharge power Q of the power storage device, the reverse power flow PREV (P + Q), and the storage capacity C of the power storage device when a predetermined weather fluctuation occurred. FIG. 10 is a graph illustrating a simulation result according to the first embodiment.
実施例1では、晴れ(−3分〜−2分)、曇り(−2分〜3分)、晴れ(3分〜13分)の順で天候変動が発生したものとした。また、充放電制御が実行される条件である所定の期間TTを2分に設定とした。また、発電システム全体の容量を4000W、晴れ時の出力電力Pを3500W、曇り時の出力電力Pを700W、蓄電容量Cを1000Wh、蓄電装置の初期容量CSTARTを500Whに設定した。 In Example 1, it was assumed that weather fluctuations occurred in the order of clear (-3 minutes to -2 minutes), cloudy (-2 minutes to 3 minutes), and clear (3 minutes to 13 minutes). Moreover, it was set a predetermined time period T T is a condition that charging and discharging control is executed in two minutes. Further, the capacity of the entire power generation system was set to 4000 W, the output power P in clear weather was set to 3500 W, the output power P in cloudy weather was set to 700 W, the storage capacity C was set to 1000 Wh, and the initial capacity C START of the power storage device was set to 500 Wh.
このような条件では、0分に出力電力Pの変動が検出されて、充放電制御が開始された。その後、10分に蓄電装置の充放電制御が終了して、蓄電容量Cの初期化が開始された。 Under such conditions, a change in the output power P was detected at 0 minutes, and charge / discharge control was started. Thereafter, the charge / discharge control of the power storage device was completed in 10 minutes, and the initialization of the storage capacity C was started.
図10(a)に示すように、出力電力Pは急激に変動しているものの、逆潮流電力PREVは平滑化されることが確認された。また、図10(b)に示すように、蓄電容量Cは、478〜614Wh(47.8〜61.4%)内で推移しているので、蓄電装置の劣化が起こりにくいことが確認された。 As shown in FIG. 10A, it was confirmed that the reverse power flow PREV was smoothed although the output power P fluctuated rapidly. In addition, as shown in FIG. 10 (b), the storage capacity C has changed within a range of 478 to 614 Wh (47.8 to 61.4%), so it has been confirmed that the storage apparatus is unlikely to deteriorate. .
(実施例2)
実施例2では、晴れ(−3分〜−2分)、曇り(−2分〜0分)、晴れ(0分〜10分)、曇り(10分〜17分)の順で天候変動が発生したものとした。その他の条件は、実施例1と同じに設定した。
(Example 2)
In Example 2, weather changes occur in the order of clear (-3 minutes to -2 minutes), cloudy (-2 minutes to 0 minutes), clear (0 minutes to 10 minutes), and cloudy (10 minutes to 17 minutes). It was assumed. Other conditions were set the same as in Example 1.
図11は、実施例2に係るシミュレーション結果を示すグラフである。図11(b)に示すように、蓄電容量Cは、754Wh(75.4%)まで増加し、初期容量CSTARTから254Wh増加している。従って、254Whに対応できるように、蓄電装置の特性、寿命などに基づいて、蓄電装置の種類や容量を決定することができる。 FIG. 11 is a graph illustrating a simulation result according to the second embodiment. As shown in FIG. 11B, the storage capacity C increases to 754 Wh (75.4%), and increases by 254 Wh from the initial capacity C START . Therefore, the type and capacity of the power storage device can be determined based on the characteristics, lifespan, and the like of the power storage device so that 254 Wh can be supported.
(実施例3)
実施例3では、曇り(−3分〜−2分)、晴れ(−2分〜0分)、曇り(0分〜10分)、晴れ(10分〜16分)の順で天候変動が発生したものとした。その他の条件は、実施例1と同じに設定した。
(Example 3)
In Example 3, weather fluctuations occurred in the order of cloudy (-3 minutes to -2 minutes), clear (-2 minutes to 0 minutes), cloudy (0 minutes to 10 minutes), and sunny (10 minutes to 16 minutes). It was assumed. Other conditions were set the same as in Example 1.
図12は、実施例3に係るシミュレーション結果を示すグラフである。図12(b)に示すように、蓄電容量Cは、254Wh(25.4%)まで減少し、初期容量CSTARTから246Wh減少している。従って、254Whに対応できるように、蓄電装置の特性、寿命などに基づいて、蓄電装置の種類や容量を決定することができる。 FIG. 12 is a graph illustrating a simulation result according to the third embodiment. As shown in FIG. 12B, the storage capacity C decreases to 254 Wh (25.4%), and decreases from the initial capacity C START by 246 Wh. Therefore, the type and capacity of the power storage device can be determined based on the characteristics, lifespan, and the like of the power storage device so that 254 Wh can be supported.
ΔP…電力変動幅
C…蓄電容量
CCAP…定格容量
CSTART…初期容量
P…出力電力
PCAP…定格出力
PREV…逆潮流電力
PSETS…初期化用目標値
Q…放電電力
R…充電電力
T1…第1到達時間
T2…第2到達時間
TD…検出周期
TT…所定の期間
1…配電システム
10…高圧電力供給源
20…変電所
30…需要家
40…高圧送電線
50…配電系統
100…発電システム
102…電力消費装置
104…電源装置
106…蓄電装置
200…系統連系装置
201…検出部
202…判定部
203…目標値設定部
204…充放電制御部
205…DC/DC変換部
206…パワーコンディショナー
206a…最大化制御部
206b…電力調整部
206c…DC/AC変換部
ΔP: power fluctuation range C: storage capacity C CAP ... rated capacity C START ... initial capacity P ... output power P CAP ... rated output P REV ... reverse power flow P SETS ... target value for initialization Q ... discharge power R ... charge power T 1 ... First arrival time T 2 ... Second arrival time T D ... Detection period T T ...
Claims (4)
自然エネルギーを利用することによって出力電力を生成する電源装置と、
充放電する蓄電装置と、
前記出力電力を検出する検出部と、
前記出力電力の増加傾向又は減少傾向が所定の期間にわたって継続した場合、前記所定の期間における前記出力電力の値に基づいて、前記電源装置及び前記蓄電装置から前記配電系統へ逆潮流される電力の目標値を設定する目標値設定部と、
前記目標値に基づいて、前記電源装置から前記蓄電装置への充電及び前記蓄電装置から前記配電系統への放電の制御である充放電制御を実行する充放電制御部と
を備えることを特徴とする発電システム。 A power generation system connected to a distribution system to which AC power is distributed,
A power supply device that generates output power by utilizing natural energy;
A power storage device for charging and discharging;
A detection unit for detecting the output power;
When the increasing or decreasing tendency of the output power continues over a predetermined period, based on the value of the output power in the predetermined period, the power that is reversely flowed from the power supply device and the power storage device to the distribution system A target value setting unit for setting a target value;
And a charge / discharge control unit that performs charge / discharge control, which is control of charging from the power supply device to the power storage device and discharging from the power storage device to the power distribution system, based on the target value. Power generation system.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の発電システム。 The predetermined period is greater than ¼ of the load fluctuation period subject to governor-free operation in the distribution system and less than ¼ of the load fluctuation period subject to load frequency control in the distribution system. The power generation system according to claim 1.
前記充放電制御部は、設定された前記新たな目標値に基づいて、前記充放電制御を実行する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の発電システム。 The target value setting unit sets a new target value based on the storage capacity of the power storage device after a predetermined time has elapsed since the start of the charge / discharge control.
The power generation system according to claim 1, wherein the charge / discharge control unit executes the charge / discharge control based on the set new target value.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の発電システム。 The power generation system according to claim 1, wherein the charge / discharge control unit adjusts the storage capacity of the power storage device to a predetermined initial capacity after the end of the charge / discharge control.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009064648A JP5384155B2 (en) | 2009-03-17 | 2009-03-17 | Power generation system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009064648A JP5384155B2 (en) | 2009-03-17 | 2009-03-17 | Power generation system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010220406A JP2010220406A (en) | 2010-09-30 |
| JP5384155B2 true JP5384155B2 (en) | 2014-01-08 |
Family
ID=42978627
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009064648A Active JP5384155B2 (en) | 2009-03-17 | 2009-03-17 | Power generation system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5384155B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011097816A (en) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-05-12 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Power generation system, and charging and discharging controller |
| JP5479182B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2014-04-23 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Power generation system and charge / discharge control device |
| WO2011090096A1 (en) * | 2010-01-20 | 2011-07-28 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Charging and discharging system and charging and discharging control device |
| JP5479499B2 (en) * | 2010-01-20 | 2014-04-23 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Charge / discharge system and charge / discharge control device |
| WO2011122681A1 (en) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-06 | 三洋電機株式会社 | System-stabilizing system, power supply system, method for controlling central management device, and program for central management device |
| JP5580183B2 (en) * | 2010-12-13 | 2014-08-27 | パナソニック株式会社 | Power control apparatus and power control system using the same |
| US8688286B2 (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2014-04-01 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Method for maintaining an optimal amount of energy derived from a power generation system in a storage device |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3108282B2 (en) * | 1994-08-26 | 2000-11-13 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Islanding detection device |
| JP2001157384A (en) * | 1999-11-25 | 2001-06-08 | Nissin Electric Co Ltd | Power storage device |
| JP4189985B2 (en) * | 2000-01-25 | 2008-12-03 | 株式会社パワーシステム | Instantaneous incoming power control system |
| JP2001327080A (en) * | 2000-05-10 | 2001-11-22 | Kansai Electric Power Co Inc:The | Power storage device and control method of distributed power supply system equipped therewith |
| JP4256833B2 (en) * | 2004-11-10 | 2009-04-22 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Power storage device and hybrid distributed power supply system |
| JP4733503B2 (en) * | 2005-11-15 | 2011-07-27 | 大阪瓦斯株式会社 | Control system |
| JP4432938B2 (en) * | 2006-06-07 | 2010-03-17 | 富士電機システムズ株式会社 | Power stabilization system using power storage device and control device thereof |
| JP5006104B2 (en) * | 2007-05-24 | 2012-08-22 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | Power smoothing method, power smoothing device, and design method of the same |
-
2009
- 2009-03-17 JP JP2009064648A patent/JP5384155B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010220406A (en) | 2010-09-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5773368B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for improving burst mode during power conversion | |
| JP5384155B2 (en) | Power generation system | |
| US9343926B2 (en) | Power controller | |
| US9496725B2 (en) | Power control apparatus, method, program, and integrated circuit, and storage battery unit | |
| JP5507582B2 (en) | Power supply method, computer-readable recording medium, and power generation system | |
| US20170093187A1 (en) | Energy storage system | |
| JP5162043B1 (en) | Charger | |
| US20130088900A1 (en) | Energy storage system and controlling method of the same | |
| KR101445738B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controling status of charge of electric energy storage system | |
| JPWO2011162025A1 (en) | DC power distribution system | |
| JP2012095418A (en) | Dc power supply system | |
| US20120228950A1 (en) | Stabilization system, power supply system, control method of the master management device and program for the master management device | |
| RU2568013C2 (en) | Power generation system and method of its operation | |
| JP2016119728A (en) | Storage battery charge/discharge control device and storage battery charge/discharge control method | |
| JPWO2015133136A1 (en) | Power supply system and control method thereof | |
| JP6522901B2 (en) | DC distribution system | |
| KR20150106694A (en) | Energy storage system and method for driving the same | |
| KR20150085227A (en) | The control device and method for Energy Storage System | |
| Nakamura et al. | Green base station using robust solar system and high performance lithium ion battery for next generation wireless network (5G) and against mega disaster | |
| JP2017099235A (en) | Power conversion system and controller | |
| JP2016015864A (en) | Power conditioner and power control method | |
| JP2021083301A (en) | Calculation device and calculation method | |
| JP6207196B2 (en) | DC power supply system | |
| WO2021095645A1 (en) | Calculation device and calculation method | |
| JP2014082915A (en) | Dispersed power supply system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120227 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130826 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130903 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5384155 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |