JP5120696B2 - Polishing equipment - Google Patents
Polishing equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5120696B2 JP5120696B2 JP2007321394A JP2007321394A JP5120696B2 JP 5120696 B2 JP5120696 B2 JP 5120696B2 JP 2007321394 A JP2007321394 A JP 2007321394A JP 2007321394 A JP2007321394 A JP 2007321394A JP 5120696 B2 JP5120696 B2 JP 5120696B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- polishing
- substrate
- polishing pad
- relative
- acceleration
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 title claims description 212
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 101
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 claims description 54
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 22
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 12
- 238000007517 polishing process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 235000012431 wafers Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Finish Polishing, Edge Sharpening, And Grinding By Specific Grinding Devices (AREA)
- Mechanical Treatment Of Semiconductor (AREA)
Description
本発明は、基板を回転させる基板回転機構、基板よりも小径の研磨パッドを回転させるパッド回転機構、基板と研磨パッドとを当接させた状態で基板に対して研磨パッドを相対揺動させる揺動機構、及び基板の回転、研磨パッドの回転及び基板に対する研磨パッドの相対揺動を制御して基板の研磨加工を制御する制御装置とを備えて構成される研磨装置に関するものである。 The present invention includes a substrate rotation mechanism that rotates a substrate, a pad rotation mechanism that rotates a polishing pad having a smaller diameter than the substrate, and a rocking mechanism that swings the polishing pad relative to the substrate while the substrate and the polishing pad are in contact with each other. The present invention relates to a polishing apparatus including a moving mechanism, and a control device that controls the rotation of the substrate, the rotation of the polishing pad, and the relative swing of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate to control the polishing process of the substrate.
基板表面を研磨する研磨装置としてCMP装置が例示される。CMP装置は、化学機械研磨(CMP:Chemical Mechanical Polishing)により基板表面を超精密に研磨加工する技術として、シリコン基板やガラス基板、半導体ウェーハなどの基板の研磨加工に広く利用されている。このような研磨装置では、チャックに保持された基板と研磨ヘッドに装着された研磨パッドとを相対回転させて押接し、基盤と研磨パッドとの当接部に研磨内容に応じたスラリー(Slurry)を供給して化学的・機械的な研磨作用を生じさせ、基板表面を平坦に研磨加工する。 A CMP apparatus is exemplified as a polishing apparatus for polishing the substrate surface. A CMP apparatus is widely used for polishing a substrate such as a silicon substrate, a glass substrate, or a semiconductor wafer as a technique for polishing a substrate surface with high precision by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). In such a polishing apparatus, the substrate held by the chuck and the polishing pad mounted on the polishing head are relatively rotated and pressed, and a slurry (Slurry) corresponding to the polishing content is brought into contact with the substrate and the polishing pad. Is supplied to cause a chemical and mechanical polishing action to polish the substrate surface flatly.
このような研磨装置は、主として基板と研磨パッドの大小関係から、研磨パッドの直径が基板の直径よりも大きなタイプと、研磨パッドの直径が基板の直径よりも小さいタイプの2種類に大別される。研磨パッドの直径が基板の直径よりも小さいタイプの研磨装置では、基板全面を均一に研磨加工するため、一般的に、基板に対して研磨パッドを相対揺動させる揺動機構が設けられている(例えば、特許文献1を参照)。 Such polishing apparatuses are roughly classified into two types, a type in which the diameter of the polishing pad is larger than the diameter of the substrate, and a type in which the diameter of the polishing pad is smaller than the diameter of the substrate, based on the size relationship between the substrate and the polishing pad. The In a polishing apparatus of a type in which the diameter of the polishing pad is smaller than the diameter of the substrate, a swinging mechanism for swinging the polishing pad relative to the substrate is generally provided to uniformly polish the entire surface of the substrate. (For example, see Patent Document 1).
上記のように、研磨パッドの直径が基板の直径よりも小さく揺動機構により基盤と研磨パッドとを相対移動させる研磨装置では、研磨加工中において、研磨パッドと当接して研磨作用を受ける領域と、研磨パッドが離隔して研磨作用を受けない領域とが、(基板の回転角度位置と基板に対する研磨パッドの位置に応じて)瞬時・瞬時に変化する。そのため、研磨加工を行う際に設定する基板の回転速度や研磨パッドの回転速度、基板に対する研磨パッドの相対揺動速度などの加工条件の組み合わせ(研磨レシピと称される)によって、基板表面の研磨レートが領域ごとに異なって研磨量分布に非対称性が生じ、所望の平面度が得られない場合が発生する。 As described above, in the polishing apparatus in which the diameter of the polishing pad is smaller than the diameter of the substrate and the base and the polishing pad are moved relative to each other by the swing mechanism, the polishing pad is in contact with the polishing pad during the polishing process. The region where the polishing pad is separated and not subjected to the polishing action changes instantaneously and instantaneously (depending on the rotation angle position of the substrate and the position of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate). Therefore, the polishing of the substrate surface depends on a combination of processing conditions such as the rotation speed of the substrate, the rotation speed of the polishing pad, and the relative rocking speed of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate (referred to as a polishing recipe). The rate varies from region to region and asymmetry occurs in the polishing amount distribution, so that the desired flatness cannot be obtained.
このような場合に、従来では、研磨レシピのうち、どの条件をどの程度変更すれば良いかを判断することが困難であった。このため、研磨量分布の非対称性が生じた場合に、研磨レシピの各条件値を少しずつ変化させながら、モニター・ウェーハ(Monitor Wafer)を用いたテスト加工を繰り返し行う必要があり、時間的・コスト的に生産性を阻害する要因になるという課題があった。特に、類似する研磨装置を用いて過去に良好な研磨結果を得ていた場合や、基板直径は異なるが加工内容が近似しているような場合には、時間的・コスト的に負荷の大きいテスト加工や、研磨レシピの変更に伴う新たな問題発生を避けるため、できるかぎり実績のある研磨レシピを変更することなく研磨加工を行いたいという要望が強かった。 In such a case, conventionally, it has been difficult to determine how much of the polishing recipe should be changed. For this reason, when asymmetry of the polishing amount distribution occurs, it is necessary to repeatedly perform test processing using a monitor wafer while changing each condition value of the polishing recipe little by little. There was a problem that it became a factor that hinders productivity in terms of cost. In particular, when similar polishing equipment has been used to obtain good polishing results in the past, or when the substrate content is different, but the processing details are similar, this is a time-consuming and costly test. In order to avoid the occurrence of new problems associated with processing and changes in the polishing recipe, there has been a strong demand for polishing without changing the proven polishing recipe as much as possible.
本発明は、上記のような課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、研磨レシピに関する煩雑な作業を解消し生産性を向上できるような研磨装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a polishing apparatus capable of eliminating troublesome work related to a polishing recipe and improving productivity.
上記目的達成のため、請求項1に係る発明の研磨装置は、基板を保持して回転させる基板回転機構と、基板よりも小径に形成され基板と対向姿勢で配設される研磨パッドを回転させるパッド回転機構と、相対回転される基板の被研磨面と研磨パッドの研磨面とを当接させた状態で基板に対して研磨パッドを相対揺動させる揺動機構(例えば、実施形態におけるアーム揺動機構35)と、基板の回転、研磨パッドの回転及び基板に対する研磨パッドの相対揺動を制御して基板の研磨加工を制御する制御装置とを備えて構成される。そのうえで、この研磨装置における制御装置は、研磨加工の加工条件が入力されたときに、入力された加工条件における基板の回転速度、研磨パッドの回転速度、基板に対する研磨パッドの相対揺動範囲及び相対揺動速度、並びに揺動機構の制御条件として予め設定された既定の加減速パターンに基づいて、被研磨面上における研磨面の各部の走行軌跡を積算して被研磨面上における走行軌跡の分布密度を算出し、算出された分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが予め設定された所定の基準値を超えると判断されたときに、既定の加減速パターンを変化させた場合について被研磨面上における走行軌跡の分布密度を算出し、既定の加減速パターンを、分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが基準値以下となる加減速パターンに変更するように構成される。 To achieve the above object, a polishing apparatus according to a first aspect of the present invention rotates a substrate rotating mechanism that holds and rotates a substrate, and a polishing pad that is formed in a smaller diameter than the substrate and is disposed in a posture opposite to the substrate. A pad rotating mechanism and a swinging mechanism that swings the polishing pad relative to the substrate in a state where the surface to be polished of the substrate and the polishing surface of the polishing pad that are relatively rotated are in contact with each other (for example, arm swinging in the embodiment). And a controller for controlling the polishing process of the substrate by controlling the rotation of the substrate, the rotation of the polishing pad, and the relative oscillation of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate. In addition, when a polishing processing condition is input, the control device in the polishing apparatus is configured such that the rotation speed of the substrate, the rotation speed of the polishing pad, the relative swing range of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate, and the relative Based on a predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern set in advance as a swing speed and a swing mechanism control condition, the travel locus of each part of the polishing surface on the surface to be polished is integrated to distribute the travel locus on the surface to be polished. When the density is calculated, and it is determined that the variation in the circumferential direction of the calculated distribution density exceeds a predetermined reference value, a predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern is changed on the surface to be polished. It is configured to calculate the distribution density of the running trajectory and change the default acceleration / deceleration pattern to an acceleration / deceleration pattern in which the variation in the circumferential direction of the distribution density is below the reference value
請求項2に係る発明の研磨装置は、前記制御装置が、前記既定の加減速パターンのうち、基板に対する研磨パッドの相対移動方向が逆転する際に相対揺動速度がゼロとなる揺動停止時間を変化させるように構成される。 A polishing apparatus according to a second aspect of the present invention is the polishing stop time in which the relative swing speed becomes zero when the control device reverses the relative movement direction of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate in the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern. Is configured to change.
請求項3に係る発明の研磨装置は、前記制御装置が、前記既定の加減速パターンのうち、基板に対する研磨パッドの相対移動方向が逆転し相対揺動速度がゼロの状態から加工条件において設定された相対揺動速度に到達するまでの加速時間を変化させるように構成される。請求項4に係る発明の研磨装置は、前記制御装置が、前記既定の加減速パターンのうち、基板に対する研磨パッドの相対移動方向を逆転させるため加工条件において設定された相対揺動速度の状態から相対揺動速度がゼロになるまでの減速時間を変化させるように構成される。 In the polishing apparatus according to a third aspect of the present invention, the control device is set in processing conditions from a state in which the relative movement direction of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate is reversed and the relative rocking speed is zero in the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern. The acceleration time until the relative rocking speed is reached is changed. The polishing apparatus according to a fourth aspect of the present invention is the polishing apparatus according to the fourth aspect of the present invention, wherein the control device is configured to move from a state of relative rocking speed set in a processing condition for reversing a relative movement direction of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate in the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern. The deceleration time until the relative rocking speed becomes zero is changed.
本発明に係る研磨装置によれば、研磨レシピに基づいて、研磨面の各部の走行軌跡が積算されて被研磨面上における走行軌跡の分布密度が算出され、この分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが所定の基準値を超えると判断された場合に、円周方向のばらつきが基準値以下となる加減速パターンに自動変更され、研磨レシピを変更することなく非対称性の問題が生じないように自律制御される。このため、高額なモニター・ウェーハを多数消費したテスト加工を繰り返して非対称性が生じない加工条件を探し出す必要がなく、時間及びコストを低減できるとともに、所望の研磨レシピで研磨加工を実行することができる。 According to the polishing apparatus of the present invention, based on the polishing recipe, the travel locus of each part of the polishing surface is integrated to calculate the distribution density of the travel locus on the surface to be polished, and the distribution density varies in the circumferential direction. Is automatically changed to an acceleration / deceleration pattern in which the variation in the circumferential direction is less than or equal to the reference value, so that asymmetry problems do not occur without changing the polishing recipe. Be controlled. For this reason, it is not necessary to search for processing conditions that do not cause asymmetry by repeating test processing that consumes a large number of expensive monitor wafers, and it is possible to reduce time and cost and perform polishing processing with a desired polishing recipe. it can.
従って、本発明によれば、研磨レシピに関する煩雑な作業を解消し生産性を向上可能な研磨装置を提供することができる。 Therefore, according to this invention, the grinding | polishing apparatus which can eliminate the complicated operation | work regarding a grinding | polishing recipe and can improve productivity can be provided.
以下、本発明を実施するための形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。本発明を適用した研磨装置1の概略構成を図2に示す。研磨装置1は、シリコンウェーハ等の基板Wを保持して回転させる基板回転機構10、研磨パッド23が装着された研磨ヘッド21を回転させるパッド回転機構20、基板Wに対して研磨パッド23を昇降及び相対揺動させるヘッド移動機構30、詳細図示を省略するが、研磨パッド23の中心部にスラリーを供給するスラリー供給機構40、基板Wや研磨パッド23の回転、基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の昇降及び揺動、研磨加工部へのスラリーの供給など、研磨装置の作動を制御して基板Wの研磨加工を制御する制御装置50など備えて構成される。
Hereinafter, embodiments for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. A schematic configuration of a polishing apparatus 1 to which the present invention is applied is shown in FIG. The polishing apparatus 1 includes a
基板回転機構10は、円盤状のチャック11と、このチャック11の下部から鉛直下方に延びるスピンドル14、スピンドル14に回転駆動力を伝達してチャック11を水平面内で回転させるチャック駆動モータ15などから構成される。チャック11は、セラミック等の高剛性材料を用いて平面度の高い円盤状に形成されたチャックプレート12と、このチャックプレート12の上面に貼られた吸着パッド13を有して構成される。チャックプレート11の内部には基板Wの下面を真空吸着する真空チャック構造が設けられて基板Wを着脱可能に構成されるとともに、チャック上部が加工テーブルTから露出して配設されており、チャック11に吸着保持された基板Wの研磨対象面(被研磨面)が上向きの水平姿勢で配設される。
The
チャック駆動モータ15の作動は制御装置50により制御され、チャック11に吸着保持された基板Wの回転・停止、回転方向、回転速度などが、加工プログラムに応じて制御装置50により制御される。基板回転機構10と隣接して、ヘッド移動機構30が設けられており、このヘッド駆動機構30の研磨アーム32の先端にパッド回転機構20が設けられる。
The operation of the
パッド回転機構20は、円盤状の研磨ヘッド21と、研磨ヘッド21の上部から鉛直上方に延びるスピンドル24、スピンドル24に回転駆動力を伝達して研磨ヘッド21を水平面内で回転させるパッド駆動モータ25などから構成される。
The
研磨ヘッド21は、チャック11と同様の高剛性材料を用いて平面度の高い円盤状に形成されたポリッシングプレート22と、このポリッシングプレート22の下面に貼られた研磨パッド23を有して構成される。研磨パッド23は、外径が研磨対象である基板Wの直径よりも幾分小さい(80〜95%程度の)円環状に形成されており、例えば、独立発泡構造を有する硬質ポリウレタンのシートを用いて構成され、ポリッシングプレート22の下面に貼り付けられて研磨面が下向きの水平姿勢で配設される。
The polishing
研磨ヘッド21の中心部に、スラリー供給機構40により供給されるスラリーを研磨パッド23の中央部に供給するためのスラリー供給構造が、ポリッシングプレート22の中心を上下に貫通して設けられている。また、研磨ヘッド21の内部に形成された加圧室にエアの供給を受けてポリッシングプレート22を下向きに加圧する、いわゆるエアバッグ式のパッド加圧機構が設けられており、研磨パッド23を基板Wに当接させた状態で加圧室の圧力を制御することにより基盤Wと研磨パッド23との当接圧力、すなわち研磨圧力を制御可能になっている。
A slurry supply structure for supplying the slurry supplied by the
パッド駆動モータ25の作動及び加圧室の圧力は制御装置50によって制御され、研磨ヘッド21に装着された研磨パッド23の回転・停止、回転方向、回転速度、研磨圧力などが、加工プログラムに基づいて制御装置50により制御される。
The operation of the
ヘッド移動機構30は、加工テーブルTから上方に突出する基部31と、この基部31から水平に延びる研磨アーム32、基部31を通って上下に延びる揺動軸を中心として研磨アーム32を水平揺動させるアーム揺動機構35、および研磨アーム全体を垂直昇降させるアーム昇降機構(不図示)などからなり、上述したパッド回転機構20が研磨アーム32の先端部に設けられている。ヘッド移動機構30は、アーム揺動機構35により研磨アーム32を水平揺動させたときの研磨ヘッド21の揺動軌跡上に基板回転機構10が位置するように構成されており、研磨ヘッド21をチャック11と対向させた状態で研磨アーム全体を昇降させ、研磨パッド23の研磨面を基板Wの被研磨面に当接させた状態で基板Wに対して研磨パッド23を水平揺動可能に構成される。
The
アーム揺動機構35及びアーム昇降機構の作動は、制御装置50によって制御され、チャック11に保持された基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動開始点(研磨アーム32の揺動開始角度位置)、揺動ストローク(研磨アーム32の揺動角度範囲)、揺動速度などが、加工プログラムに基づいて制御装置50により制御される。
The operations of the
制御装置50は、入力された加工プログラムから研磨レシピ(研磨加工の加工条件)を読み出す。加工プログラムには、研磨レシピとして研磨パッド23の回転速度、基板Wの回転速度、基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動開始点及び揺動ストローク、研磨パッド23の揺動速度、研磨圧力、スラリーの種別、スラリーの供給流量などの条件値が含まれている。
The
制御装置50は、研磨レシピから、研磨パッドの走行軌跡を規定するパラメータである研磨パッド23の回転速度、基板Wの回転速度、基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動開始点及び揺動ストローク、研磨パッド23の揺動速度を取得し、これらの条件値に基づいて基板Wの被研磨面上における研磨パッド23の各部の走行軌跡を算出する。具体的に、加工プログラムにおいて設定された研磨パッド23の回転速度Vp=110[rpm]、基板Wの回転速度Vw=−60[rpm]、基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動開始点を基板中心から30[mm]、揺動ストローク90[mm]、揺動速度Vs=60[mm/sec]について、研磨パッドの走行軌跡を算出する。ここで、基板Wに対して研磨パッド23の往復揺動は、平面視において時計廻りの揺動〜停止〜半時計廻りの揺動の繰り返しであり、研磨アーム32の揺動制御は、原則的に制御装置50内のメモリーに予め設定記憶された既定の加減速パターンPV(図4を参照)に基づいて実行される。そこで、この最初の走行軌跡の算出に際しては、研磨アーム32を既定の加減速パターンで往復揺動させた場合について算出される。なお、研磨アーム32の腕の長さは一定であり、研磨アーム32の揺動の加減速パターンと基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の相対揺動の加減速パターンとは同義である。
From the polishing recipe, the
図3は、研磨パッド23の任意点Pについて、上記条件での走行軌跡Lの時間的な変化を示したものであり、(a)(b)(c)の各図は、(a)研磨スタート時:t=0[sec]、(b)研磨スタート後3秒経過時:t=3[sec]、(c)研磨スタート後9秒経過時:t=9[sec]の状態を示している。
FIG. 3 shows the temporal change of the running locus L under the above conditions at an arbitrary point P of the
この図から理解されるように、任意点Pの走行軌跡Lはきわめて複雑であり、基板Wの被研磨面上では、走行軌跡Lの密度が高い領域と低い領域とが見られ、基盤Wの被研磨面から外れた外周領域を走行する軌跡も散見される。基板Wの被研磨面に形成された走行軌跡Lは、研磨パッド23の任意点Pによって研磨される研磨軌跡であることから、走行軌跡Lの密度が高い領域ほど研磨レート(Removal Rate)が高く、走行軌跡Lの密度が低い領域ほど研磨レートが低くなることを表す。
As can be understood from this figure, the traveling locus L of the arbitrary point P is extremely complex, and on the surface to be polished of the substrate W, a region where the density of the traveling locus L is high and a region where the density is low are seen. There are also some trajectories that run in the outer peripheral area outside the surface to be polished. Since the traveling locus L formed on the surface to be polished of the substrate W is a polishing locus that is polished by an arbitrary point P of the
制御装置50は、研磨パッド23の研磨面の各部について走行軌跡を積算し、基板Wの被研磨面上に形成される走行軌跡の密度分布を算出する。例えば、上記任意点Pを、周方向に5度ピッチ、径方向に5mmピッチの多数の走行点P1〜Pnとして設定し、これらP1〜Pnの各点の走行軌跡L1〜Lnを研磨加工時間分について積算して、被研磨面上における研磨面の走行軌跡の密度を算出する。こうして得た走行軌跡の密度分布は、実際に研磨加工を行った基板を形状測定して得た研磨レートの面分布の測定データと高い相関関係を有することが発明者による実験により確認されており、算出された走行軌跡の密度に所定の係数kを乗じたものが、研磨レートの面分布をシミュレートしたものとなる。
The
そして、研磨レートの面分布から、同一半径の円周上に位置する角度0〜360度の角度の研磨レートの分布として展開したものがポーラー研磨レート(Polar Removal Rate)である。横軸に角度をとったポーラー研磨レートのグラフが平坦でなく、研磨量分布の不均一性を表すポーラー・レンジ(Polar Range=(Max-Min)/Average)が大きいことは、基板の中心軸に対して研磨レートの分布が軸対称でないこと、すなわち非対称性の問題が生じることを意味する。 Then, from the surface distribution of the polishing rate, the one developed as the distribution of the polishing rate at an angle of 0 to 360 degrees located on the circumference of the same radius is the polar removal rate. The polar axis (Polar Range = (Max-Min) / Average) representing the non-uniformity of the polishing amount distribution is not flat in the graph of the polar polishing rate with an angle on the horizontal axis. This means that the polishing rate distribution is not axially symmetric, that is, a problem of asymmetry occurs.
本発明は、以上のような走行軌跡の密度分布と研磨レートの面分布との間の高い相関関係、及びポーラー・レンジと被研磨面の非対称性との関係に基づいて成されており、制御装置50は、複数の半径位置について走行軌跡の分布密度を算出し、算出された分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが予め設定された所定の基準値を超えるか否か、換言すれば、シミュレートしたポーラー・レンジの最大値(最大ポーラー・レンジ(Max Polar Range))が所定の基準値を超えるか否かを判断する。走行軌跡の分布密度が予め設定された所定の基準値を超えると判断されたときには、制御装置50内のメモリーに設定された研磨アーム32の既定の加減速パターンを変化させた場合について走行軌跡の密度分布を算出する。そして、既定の加減速パターンを、走行軌跡の密度の円周方向のばらつきが基準値以下となる加減速パターンに変更する。
The present invention is based on the high correlation between the density distribution of the running locus and the surface distribution of the polishing rate as described above, and the relationship between the polar range and the asymmetry of the surface to be polished. The
図4に、研磨アームの加減速パターンPVを示す。図4において横軸が時間t、縦軸が研磨アーム32の揺動速度(基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動速度)の絶対値|V|である。研磨アーム32は、平面視において時計廻りの揺動と半時計廻りの揺動とを交互に繰り返すことから、加減速パターンは、加速〜設定揺動速度Vs(VOscillation)〜減速を繰り返す。揺動方向が逆方向に反転する減速領域と加速領域との間には、アーム揺動機構35に作用するモーメントが無限大になることを防止するため、揺動速度がゼロとなる停止領域が設けられる。
FIG. 4 shows the acceleration / deceleration pattern P V of the polishing arm. In FIG. 4, the horizontal axis represents time t, and the vertical axis represents the absolute value | V | of the swing speed of the polishing arm 32 (the swing speed of the
ここで、加速・減速・停止の各領域にあっても、基板Wと研磨パッド23とはスラリー供給下の押接状態で相対回転しており被研磨面上に走行軌跡が形成される。従って、この加速・減速・停止領域のパターンを変化させれば、研磨レシピにおいて指定された揺動速度Vsを変更することなく、走行軌跡の密度分布を変化させることができ、ポーラー・レンジが所定の基準値以下となる加減速パターンを抽出することができる。
Here, even in each of the acceleration / deceleration / stop regions, the substrate W and the
具体的には、揺動速度がゼロの状態から設定速度Vsに到達するまでの加速時間をtup、設定速度Vsで等速揺動する等速領域の時間をtv、揺動速度が設定速度Vsからゼロになるまでの減速時間をtdown、揺動方向を反転する際に一時停止する揺動停止時間をtstopとしたときに、加速・減速・停止領域の各時間tup,tdown,tstopのうち少なくともいずれかを変化させて、等速領域以外の設定速度Vsに満たない領域の時間(揺動遅れ時間:Oscillation offset Timeという)toffsetを変化させる。ここに、toffset=tup+tdown+tstopである。 Specifically, the acceleration time until the set speed V s is reached from the state where the swing speed is zero is t up , the time in the constant speed region where the constant speed swing is performed at the set speed V s is t v , and the swing speed There set speed V s t a deceleration time until zero the down, the swing stop time to pause when inverting the swing direction when the t stop, each time the acceleration-deceleration and stopping region t At least one of up , t down , and t stop is changed to change the time t offset (oscillation delay time: referred to as Oscillation offset Time) of a region that does not satisfy the set speed V s other than the constant velocity region. Here, t offset = t up + t down + t stop .
いま、加速・減速領域における加速度の絶対値を同一値aとした場合には、
tup=tdown=Vs/a
toffset=tup+tdown+tstop=(2Vs/a)+tstop
If the absolute value of acceleration in the acceleration / deceleration region is the same value a,
t up = t down = V s / a
t offset = t up + t down + t stop = (2V s / a) + t stop
この式から、加速・減速領域の加速度の大きさaを変化させて加速時間tup及び減速時間tdownを変化させ、または揺動折り返しの揺動停止時間tstopを変化させることにより、走行軌跡の密度分布を変化させてポーラー・レンジの値を変化させることができる。 From this equation, by changing the acceleration magnitude a in the acceleration / deceleration region to change the acceleration time t up and the deceleration time t down , or by changing the swing stop time t stop for swing back, The value of the polar range can be changed by changing the density distribution.
上式から加速度aを求めると、
a=2Vs/(toffset−tstop)
揺動停止時間tstopを求めると、
tstop=(2Vs/a)+toffset
When the acceleration a is obtained from the above equation,
a = 2V s / (t offset −t stop )
When the oscillation stop time t stop is obtained,
t stop = (2V s / a) + t offset
制御装置50は、研磨装置の制御プログラムにパラメータとして設定されている加速度a(加速時間tup,減速時間tdown)を所定の加速度範囲内で変化させ、若しくは同様にパラメータ設定されている揺動停止時間tstopを変化させ、またはこれら両方を変化させることによって揺動遅れ時間toffsetを変化させた加減速パターンについて、走行軌跡の密度分布を算出し、これに基づいてシミュレートした研磨レートの面分布から、各条件ごとの最大ポーラー・レンジを算出する。
The
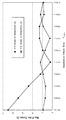
図1は、上記のようにして算出した最大ポーラー・レンジの変化を示すグラフである。図1において、横軸が揺動遅れ時間(Oscillation offset Time)toffset、縦軸が最大ポーラー・レンジ(Max Polar Range)であり、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを0〜0.1[sec]の間で変化させた場合の最大ポーラー・レンジの変化を表している。 FIG. 1 is a graph showing changes in the maximum polar range calculated as described above. In FIG. 1, the horizontal axis is the oscillation offset time t offset , the vertical axis is the maximum polar range, and the oscillation delay time t offset is 0 to 0.1 [sec]. It shows the change of the maximum polar range when changing between.
この図1から、明らかなように、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを変化させることにより最大ポーラー・レンジを変化させることができる。例えば、既定の加減速パターンにおいて揺動遅れ時間toffsetが0.02[sec]であり、このとき算出される最大ポーラー・レンジが17%であった場合に、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを0.04[sec]以上に変更すれば、最大ポーラー・レンジを7%以下に抑制することができ、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを0.05[sec]に変更すれば最大ポーラー・レンジを2%以下とすることができる。 As is apparent from FIG. 1, the maximum polar range can be changed by changing the oscillation delay time t offset . For example, when the oscillation delay time t offset is 0.02 [sec] in the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern and the maximum polar range calculated at this time is 17%, the oscillation delay time t offset is set to 0. If it is changed to .04 [sec] or more, the maximum polar range can be suppressed to 7% or less, and if the oscillation delay time t offset is changed to 0.05 [sec], the maximum polar range is 2%. It can be as follows.
制御装置50は、上記のようなシミュレーション結果に基づき、走行軌跡の密度の円周方向のばらつきが基準値以下となる加減速パターンに変更する。例えば、ポーラー・レンジに換算したときの値が7%以下となる加減速パターンとし、その中の最小値である揺動遅れ時間toffset=0.05[sec]の加減速パターンに変更する。この場合において、変更する具体的なパラメータは、加速度の絶対値a(または加速時間tup,減速時間tdown)及び揺動停止時間tstopの何れであっても良い。
Based on the simulation results as described above, the
制御装置50は、研磨加工の実行操作に応じて研磨加工をスタートさせ、基板回転機構10、パッド回転機構20、ヘッド移動機構30、アーム揺動機構35、及びスラリー供給装置40等の作動を制御し、研磨レシピに基づいた加工条件で研磨加工を実行する。変更された加減速パターンのパラメータは制御装置内のRAMに記憶され、同一の加工プログラムを実行する際に、既定の加減速パターンのパラメータと置換して研磨加工が実行される。
The
なお、研磨レシピにおいて設定された加工条件のままで、走行軌跡の密度分布に偏りが無くポーラー・レンジが比較的小さい場合もある。図5は、基板Wの回転速度Vw=−65[rpm]、基板Wに対する研磨パッド23の揺動速度Vs=62[mm/sec]、他の加工条件を同一とした場合において、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを変化させた場合の最大ポーラー・レンジの変化を三角印でプロットし、丸印でプロットする図1のデータと重ねて表示したグラフである。
In some cases, the processing range set in the polishing recipe remains the same, and the density distribution of the running locus is not biased and the polar range is relatively small. FIG. 5 shows a case where the rotation speed V w of the substrate W = −65 [rpm], the swing speed V s of the
この図5から理解されるように、研磨レシピにおいて設定された加工条件のままで最大ポーラー・レンジが比較的小さい場合であっても、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを変化させることにより最大ポーラー・レンジを最小化することができる。例えば、既定の加減速パターンにおいて揺動遅れ時間toffsetが0.02[sec]の場合、算出される最大ポーラー・レンジは4%弱であり十分に小さい値であるが、揺動遅れ時間toffsetを0.07[sec]に変更すれば、最大ポーラー・レンジをさらに低減して2%以下にすることができる。すなわち、走行軌跡の密度分布の円周方向のばらつきが比較的変化が小さい場合においても、前述同様の処理を行って加減速パターンを変更することにより、研磨レシピを変更することなく非対称性を最小化した条件で研磨加工を実行することができる。 As can be understood from FIG. 5, even when the maximum polar range is relatively small with the processing conditions set in the polishing recipe, the maximum polar range is changed by changing the oscillation delay time t offset. Can be minimized. For example, when the oscillation delay time t offset is 0.02 [sec] in the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern, the calculated maximum polar range is a little less than 4%, which is a sufficiently small value, but the oscillation delay time t If the offset is changed to 0.07 [sec], the maximum polar range can be further reduced to 2% or less. In other words, even when the variation in the circumferential direction of the density distribution of the running trajectory is relatively small, the asymmetry can be minimized without changing the polishing recipe by performing the same process as described above and changing the acceleration / deceleration pattern. Polishing processing can be executed under such conditions.
また、研磨レシピにおいて設定された加工条件のうち、基板の回転速度Vwと基板に対する研磨パッドの揺動速度Vsとを一定範囲で変化させ、これらの加工条件を変更した場合についてそれぞれ前述同様に走行軌跡の密度分布を算出し、研磨レシピを含めて条件の最適化を実行するように構成しても良い。このような構成によれば、例えば図5において丸印でプロットする特性から三角印でプロットする特性に変化させることができ、これにより揺動遅延時間toffsetの変化に対する最大ポーラー・レンジの変化を小さく(揺動遅延時間が変動した場合の対称性に与える影響を小さく)することができる。 Also, among the processing conditions set in the polishing recipe, the substrate rotation speed V w and the polishing pad swing speed V s with respect to the substrate are changed within a certain range, and these processing conditions are changed as described above. Alternatively, the density distribution of the travel locus may be calculated and the conditions may be optimized including the polishing recipe. According to such a configuration, for example, the characteristic plotted with a circle in FIG. 5 can be changed to the characteristic plotted with a triangle, thereby changing the maximum polar range with respect to the change in the oscillation delay time t offset. It can be made smaller (the influence on the symmetry when the oscillation delay time varies) can be reduced.
以上説明したように、本発明の研磨装置では、高額なモニター・ウェーハを多数消費したテスト加工を繰り返して非対称性が生じない加工条件を探し出したり、これに基づいて研磨レシピを変更設定したりする必要がなく、加工プログラムにおいて当初設定した研磨レシピで高品位の研磨加工を実行することができる。従って、本発明によれば、研磨レシピに関する煩雑な作業を解消して生産性を向上可能な研磨装置を提供することができる。 As described above, in the polishing apparatus of the present invention, test processing that consumes a large number of expensive monitor wafers is repeated to find processing conditions that do not cause asymmetry, and the polishing recipe is changed and set based on this. There is no need, and high-quality polishing can be performed with the polishing recipe initially set in the processing program. Therefore, according to this invention, the grinding | polishing apparatus which can eliminate the complicated operation | work regarding a grinding | polishing recipe and can improve productivity can be provided.
1 研磨装置 10 基板回転機構
20 パッド回転機構 23 研磨パッド
30 ヘッド移動機構 35 アーム揺動機構(揺動機構)
50 制御装置 L 走行軌跡
PV 加減速パターン W 基板
tup 加速時間 tdown 減速時間
tstop 揺動停止時間 toffset 揺動遅れ時間
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
50 Control device L Traveling track P V Acceleration / deceleration pattern W Substrate t up acceleration time t down deceleration time t stop oscillation stop time t offset oscillation delay time
Claims (4)
前記制御装置は、研磨加工の加工条件が入力されたときに、入力された前記加工条件における前記基板の回転速度、前記研磨パッドの回転速度、前記基板に対する前記研磨パッドの相対揺動範囲及び相対揺動速度、並びに前記揺動機構の制御条件として予め設定された既定の加減速パターンに基づいて、前記被研磨面上における前記研磨面の各部の走行軌跡を積算して前記被研磨面上における前記走行軌跡の分布密度を算出し、算出された前記分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが予め設定された所定の基準値を超えると判断されたときには、前記既定の加減速パターンを変化させた場合について前記被研磨面上における前記走行軌跡の分布密度を算出し、前記既定の加減速パターンを、前記分布密度の円周方向のばらつきが前記基準値以下となる加減速パターンに変更するように構成したことを特徴とする研磨装置。 A substrate rotating mechanism for holding and rotating the substrate, a pad rotating mechanism for rotating a polishing pad formed in a posture opposite to the substrate and having a smaller diameter than the substrate, and a surface to be polished of the substrate that is relatively rotated A swinging mechanism for swinging the polishing pad relative to the substrate in a state where the polishing pad is in contact with a polishing surface of the polishing pad, rotation of the substrate, rotation of the polishing pad, and the polishing pad with respect to the substrate In a polishing apparatus comprising a control device that controls the relative polishing of the substrate to control the polishing of the substrate,
When a processing condition for polishing is input, the control device is configured to input the rotation speed of the substrate, the rotation speed of the polishing pad, the relative swing range of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate, and the relative Based on a rocking speed and a predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern set in advance as a control condition of the rocking mechanism, the traveling locus of each part of the polishing surface on the surface to be polished is integrated and the surface on the surface to be polished is integrated. When the distribution density of the travel locus is calculated, and it is determined that the variation in the circumferential direction of the calculated distribution density exceeds a predetermined reference value set in advance, the default acceleration / deceleration pattern is changed The distribution density of the travel locus on the surface to be polished is calculated for the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern, and the variation in the circumferential direction of the distribution density is equal to or less than the reference value. Polishing apparatus characterized by being configured to change the acceleration and deceleration patterns.
In the predetermined acceleration / deceleration pattern, the control device reverses the relative movement direction of the polishing pad with respect to the substrate, and the relative rocking speed becomes zero from the state of the relative rocking speed set in the processing conditions. The polishing apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the deceleration time is changed.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321394A JP5120696B2 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2007-12-12 | Polishing equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321394A JP5120696B2 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2007-12-12 | Polishing equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009142924A JP2009142924A (en) | 2009-07-02 |
| JP5120696B2 true JP5120696B2 (en) | 2013-01-16 |
Family
ID=40914167
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321394A Active JP5120696B2 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2007-12-12 | Polishing equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5120696B2 (en) |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001118816A (en) * | 1999-10-19 | 2001-04-27 | Nikon Corp | Chemical/mechanical polishing method |
| JP2001237206A (en) * | 1999-12-15 | 2001-08-31 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Flattening method |
| JP2003205454A (en) * | 2001-12-28 | 2003-07-22 | Nagano Denshi Kogyo Kk | Polishing method and device for thin plate |
| JP2004223636A (en) * | 2003-01-21 | 2004-08-12 | Nikon Corp | Polishing method, polishing device, polishing simulation method, and semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2005254416A (en) * | 2004-03-15 | 2005-09-22 | Okamoto Machine Tool Works Ltd | Polishing method of square work |
-
2007
- 2007-12-12 JP JP2007321394A patent/JP5120696B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009142924A (en) | 2009-07-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4658182B2 (en) | Polishing pad profile measurement method | |
| US8870625B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for dressing polishing pad, profile measuring method, substrate polishing apparatus, and substrate polishing method | |
| TWI681842B (en) | Polishing apparatus, method for controlling the same, and method for outputting a dressing condition | |
| US7357695B2 (en) | Systems and methods for mechanical and/or chemical-mechanical polishing of microfeature workpieces | |
| JP5964262B2 (en) | Method for adjusting profile of polishing member used in polishing apparatus, and polishing apparatus | |
| US20170216991A1 (en) | Polishing-amount simulation method for buffing, and buffing apparatus | |
| JP2011224680A (en) | Polishing method and device | |
| JP2018001325A (en) | Head height adjustment device and substrate processing apparatus including head height adjustment device | |
| JP5120697B2 (en) | Polishing equipment | |
| JP2021065990A (en) | Polishing method and polishing device | |
| JP6121795B2 (en) | Dressing apparatus, polishing apparatus equipped with the dressing apparatus, and polishing method | |
| JP5120696B2 (en) | Polishing equipment | |
| JP2002343753A (en) | Simulation method and apparatus thereof, machining apparatus, machining system, and semiconductor device manufacturing method | |
| JP4384954B2 (en) | Processing method, processing device, and rectangular flat plate processed product processed by this processing method | |
| JPH10217102A (en) | Dressing method for abrasive cloth and its device | |
| JP2010172975A (en) | Polishing apparatus | |
| JP5257752B2 (en) | Polishing pad dressing method | |
| JP2007318041A (en) | Polishing device | |
| JP5234403B2 (en) | Polishing method and polishing apparatus | |
| JP2021142628A (en) | Thickness measurement device for polishing pad | |
| JP2003022992A (en) | Device and method for producing semiconductor | |
| JP5170642B2 (en) | Polishing equipment | |
| JP5294054B2 (en) | Polishing equipment | |
| JP2024129883A (en) | SETUP METHOD, SUBSTRATE PROCESSING METHOD, AND SUBSTRATE PROCESSING APPARAT | |
| JP2011036973A (en) | Polishing method and polishing apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101202 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110215 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120928 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120928 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121011 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151102 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5120696 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151102 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |