JP4832366B2 - Transparent antenna - Google Patents
Transparent antenna Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4832366B2 JP4832366B2 JP2007152761A JP2007152761A JP4832366B2 JP 4832366 B2 JP4832366 B2 JP 4832366B2 JP 2007152761 A JP2007152761 A JP 2007152761A JP 2007152761 A JP2007152761 A JP 2007152761A JP 4832366 B2 JP4832366 B2 JP 4832366B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- transparent
- conductive film
- patch antenna
- transparent conductive
- antenna
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Waveguide Aerials (AREA)
- Details Of Aerials (AREA)
- Support Of Aerials (AREA)
Description
本発明は、光学的に透明なアンテナに関するものである。このアンテナを使用することにより、美観を損なうことなく、アンテナを無線機器や無線端末の表面、あるいはディスプレー窓の上に設置することができる。本発明の透明アンテナは、設置場所が限られる小型無線機器にアンテナが設置できるようになるだけでなく、機器の表面にアンテナを設置することにより、機器内部にある電子部品からアンテナを遠ざけることができ、アンテナに与える影響を小さくすることができるため、アンテナの設計を容易にすることができる。 The present invention relates to an optically transparent antenna. By using this antenna, the antenna can be installed on the surface of the wireless device or the wireless terminal or on the display window without deteriorating the beauty. The transparent antenna of the present invention not only enables the antenna to be installed in a small wireless device having a limited installation location, but also allows the antenna to be kept away from electronic components inside the device by installing the antenna on the surface of the device. Since the influence on the antenna can be reduced, the antenna design can be facilitated.
従来、透明アンテナとしては、色々な方式のものが提案されており、例えば、金属を格子状にしたもの(例えば、非特許文献1参照)、極めて薄い金属を使ったもの(例えば、特許文献1参照)、透明電極を使ったもの(例えば、非特許文献2〜6、特許文献2〜5参照)などが挙げられる。
また、非特許文献2〜6に開示された透明電極としては、スズドープ酸化インジウム(ITO)薄膜が用いられている。
Moreover, as the transparent electrode disclosed in
しかしながら、前述した従来技術には、次のような問題がある。
非特許文献1に開示された格子状金属を用いたアンテナは、部分的にせよ可視光を遮るし、特許文献1に開示された金属膜を使用したアンテナの場合も、金属膜を薄くしても可視光の透過率がかなり低くなるので、いずれの場合も小型無線機器の表面に設置することが外観上難しいという問題がある。
However, the above-described prior art has the following problems.
The antenna using the lattice-shaped metal disclosed in Non-Patent
一方、ITO薄膜は、可視光を透過し透明であるが、抵抗率が高いため、大きな抵抗値をもつ。非特許文献2〜5、特許文献2〜4に開示されているアンテナは、放射素子の抵抗が大きいため、利得が低く、実用的ではない。また、非特許文献2〜5、特許文献2〜4には、透明アンテナにおける抵抗値による利得・放射効率の低下や、透明度と利得・放射効率との関係が明らかにされていない。その上、非特許文献4,5、特許文献2〜4に開示されているアンテナは、給電ラインと直接接続しているため、給電ラインに透明材料を使用した場合、使用された伝送路の損失によって、アンテナの利得が低減する。また、給電ラインに銅などの金属を使用した場合、美観を損なうことになる。さらに、非特許文献6、特許文献5に開示されているアンテナは、ダイポール形状であるため、形状の制限により利得が低い。
On the other hand, the ITO thin film transmits visible light and is transparent, but has a high resistance value because of its high resistivity. The antennas disclosed in
本発明は、前記事情に鑑みてなされ、十分な透明度及び十分な放射特性を有する透明アンテナを提供することを目的とする。 This invention is made | formed in view of the said situation, and it aims at providing the transparent antenna which has sufficient transparency and sufficient radiation | emission characteristic.
前記目的を達成するため、本発明は、誘電体基板および該誘電体基板の一方の面上に成膜され、放射素子をなす透明導電膜からなる透明部材と、基板および該基板の一方の面上に成膜されたマイクロストリップライン、および、前記基板の一方の面とは反対の面上に成膜されたグラウンドからなる給電部材とを備え、前記基板の一方の面に、前記誘電体基板の一方の面とは反対の面が接合されて、前記透明部材が前記給電部材に積層され、前記誘電体基板の一方の面側から見て、前記透明導電膜と前記マイクロストリップラインが対向している透明アンテナであって、前記透明導電膜は、350nm〜780nmの可視光波長領域において光を透過でき、100MHz〜20GHzの周波数帯において電磁波を放射することを特徴とする透明アンテナを提供する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a dielectric substrate and a transparent member formed on one surface of the dielectric substrate and made of a transparent conductive film that forms a radiating element, and the substrate and one surface of the substrate. A microstrip line formed thereon, and a power supply member comprising a ground formed on a surface opposite to the one surface of the substrate, the dielectric substrate on one surface of the substrate The transparent member is laminated on the power feeding member, and the transparent conductive film and the microstrip line face each other when viewed from one surface side of the dielectric substrate. a and are transparent antenna, the transparent conductive film can transmit light in the visible light wavelength region of 350Nm~780nm, transparent, wherein the benzalkonium radiate electromagnetic waves in a frequency band of 100MHz~20GHz To provide a container.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜は、スズドープ酸化インジウム薄膜からなることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is preferably made of a tin-doped indium oxide thin film.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜は、フッ素ドープ酸化スズ薄膜からなることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is preferably made of a fluorine-doped tin oxide thin film.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜が透明な誘電体基板上に成膜されたことが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, it is preferable that the transparent conductive film is formed on a transparent dielectric substrate.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜が透明でない誘電体基板上に成膜されたことが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is preferably formed on a dielectric substrate that is not transparent.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜は、膜厚が100nm以上、前記可視光波長領域における透過率が60%以上、シート抵抗が20Ω/□以下であることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film preferably has a film thickness of 100 nm or more, a transmittance in the visible light wavelength region of 60% or more, and a sheet resistance of 20Ω / □ or less.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜は、膜厚が100nm以上、前記可視光波長領域における透過率が40%以上、シート抵抗が5Ω/□以下であることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film preferably has a film thickness of 100 nm or more, a transmittance in the visible light wavelength region of 40% or more, and a sheet resistance of 5Ω / □ or less.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜はスズドープ酸化インジウム薄膜からなり、前記誘電体基板上に前記透明導電膜が成膜された状態での前記可視光波長領域における透過率が30%であることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is made of a tin-doped indium oxide thin film, and the transmittance in the visible light wavelength region when the transparent conductive film is formed on the dielectric substrate is 30%. It is preferable.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜はフッ素ドープ酸化スズ薄膜からなり、前記誘電体基板上に前記透明導電膜が成膜された状態での前記可視光波長領域における透過率が30%以上であることが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is made of a fluorine-doped tin oxide thin film, and the transmittance in the visible light wavelength region in the state where the transparent conductive film is formed on the dielectric substrate is 30% or more. It is preferable that
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、0.8GHz〜12GHzにおいて、同じ寸法の金属薄膜を用いて作製したアンテナに比べて、利得の低下が6dB以下であり、放射効率が20%以上であることが好ましい。 The transparent antenna of the present invention preferably has a gain reduction of 6 dB or less and a radiation efficiency of 20% or more as compared with an antenna manufactured using a metal thin film of the same size at 0.8 GHz to 12 GHz.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、GPS帯における電圧定在波比が2以下であることが好ましい。
In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the voltage standing wave ratio in the
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記給電部材は、比誘電率ε r 、誘電損失正接tanδが、1<ε r <11、tanδ<0.003の関係を満たす基板を備えたことが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, it is preferable that the feeding member includes a substrate having a relative permittivity ε r and a dielectric loss tangent tan δ satisfying a relationship of 1 <ε r <11 and tan δ <0.003 .
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明部材は、比誘電率ε r 、誘電損失正接tanδが、ε r <5、tanδ<0.006の関係を満たす透明な誘電体基板を備えたことが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, it is preferable that the transparent member includes a transparent dielectric substrate having a relative permittivity ε r and a dielectric loss tangent tan δ satisfying a relationship of ε r <5 and tan δ <0.006 .
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記放射素子の幅w p 、長さL p 、光速を使用周波数で除して算出された波長λ 0 が、0.2w p ≦L p ≦2.0w p 、0.15λ 0 ≦w p ≦0.26λ 0 の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
ここで、使用周波数は、個々のアンテナ特有のパラメータである。
In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the width w p of the radiating elements, the length L p, a wavelength lambda 0 which is calculated by dividing the speed of light to use frequency, 0.2w p ≦ L p ≦ 2.0w p, 0 .15λ 0 ≦ w p ≦ 0.26λ not satisfy the relationship of 0 Rukoto is preferable.
Here, the used frequency is a parameter specific to each antenna.
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜が、誘電体筐体をもつ無線機器の表面、または、表示ディスプレーの内外面の一方または両方に成膜されたことが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, it is preferable that the transparent conductive film is formed on one or both of the surface of a wireless device having a dielectric housing and the inner and outer surfaces of a display display .
本発明の透明アンテナにおいて、前記透明導電膜が、誘電体筐体をもつ無線機器の表面、または、表示ディスプレーの内外面の一方または両方に成膜され、かつ該透明導電膜を挟み込む誘電体基板が積層された構造を有することが好ましい。 In the transparent antenna of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is formed on one or both of the surface of a wireless device having a dielectric casing and the inner and outer surfaces of a display, and sandwiches the transparent conductive film. It is preferable to have a laminated structure .
本発明の透明アンテナは、可視光の領域で透明性を持ち、電磁波を放射することができる。本発明のアンテナは、シート抵抗が低く、透明性が高いITO薄膜を使用し、さらにアンテナの形状を最適に設計することにより、十分な透明度を持ちながら、十分な放射特性を持たせることが可能となる。
また、FTO薄膜を使用すると、希少金属のインジウムの使用を避けることができ、コストを下げることができる。
本発明の透明アンテナは、透明で目立つことがなく、窓ガラスに設置することができ、室内アンテナや車載アンテナとして利用できる。また、年々小型化される無線端末の表面やディスプレー上に装着することができ、アンテナの設置場所を確保できるだけでなく、アンテナの設計を容易にすることができる。
本発明のアンテナを使用することにより、透過率が70%以上を保ちながら、アンテナ利得の低下を1dB以下、放射効率を80%以上にすることができる。
The transparent antenna of the present invention has transparency in the visible light region and can emit electromagnetic waves. The antenna of the present invention can have sufficient radiation characteristics while having sufficient transparency by using an ITO thin film with low sheet resistance and high transparency, and further designing the shape of the antenna optimally. It becomes.
Further, when an FTO thin film is used, the use of rare metal indium can be avoided, and the cost can be reduced.
The transparent antenna of the present invention is transparent and does not stand out, can be installed on a window glass, and can be used as an indoor antenna or a vehicle-mounted antenna. In addition, it can be mounted on the surface or display of a wireless terminal that is becoming smaller year by year, so that not only the location of the antenna can be secured, but also the design of the antenna can be facilitated.
By using the antenna of the present invention, it is possible to reduce the antenna gain to 1 dB or less and the radiation efficiency to 80% or more while maintaining the transmittance of 70% or more.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施形態を説明する。
本発明の透明アンテナは、透明部材を備え、透明部材は、350nm〜780nmの可視光波長領域において光を透過でき、100MHz〜20GHzの周波数帯において電磁波を放射する透明導電膜からなる放射素子を備えたことを特徴とする。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
The transparent antenna of the present invention includes a transparent member, and the transparent member includes a radiating element made of a transparent conductive film that can transmit light in a visible light wavelength region of 350 nm to 780 nm and radiate electromagnetic waves in a frequency band of 100 MHz to 20 GHz. It is characterized by that.
本発明の好ましい実施形態において、前記透明導電膜としては、シート抵抗が1Ω/□〜20Ω/□の範囲であり、かつ透過率(波長550nm)が60%以上となるスズドープ酸化インジウム(ITO)薄膜を使用することが好ましい。
また、コストが安いフッ素ドープ酸化スズ(FTO)薄膜を使用することもできる。この場合、FTO薄膜としては、シート抵抗が1Ω/□〜5Ω/□の範囲であり、かつ透過率(波長550nm)が40%以上のもの、あるいは、シート抵抗が5Ω/□〜20Ω/□の範囲であり、かつ透過率(波長550nm)が80%以上のものを使用することが好ましい。
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the transparent conductive film is a tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) thin film having a sheet resistance in the range of 1Ω / □ to 20Ω / □ and a transmittance (
In addition, a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) thin film can be used at low cost. In this case, the FTO thin film has a sheet resistance in the range of 1Ω / □ to 5Ω / □ and a transmittance (wavelength of 550 nm) of 40% or more, or a sheet resistance of 5Ω / □ to 20Ω / □. It is preferable to use a film having a transmittance within a range of 80% or more (
本実施形態において、放射素子となる透明導電膜に使用するITO薄膜およびFTO薄膜の波長550nmで示す透過率を図1に示す。
ITO薄膜は、シート抵抗が0.6Ω/□からあり、透過率60%以上である。また、FTO薄膜は、シート抵抗が1Ω/□からあり、透過率が40%である。
In this embodiment, the transmittance | permeability shown in wavelength 550nm of the ITO thin film and FTO thin film which are used for the transparent conductive film used as a radiation element is shown in FIG.
The ITO thin film has a sheet resistance of 0.6Ω / □ and a transmittance of 60% or more. The FTO thin film has a sheet resistance of 1Ω / □ and a transmittance of 40%.
また、図2はシート抵抗がそれぞれ1.6Ω/□、15.5Ω/□となるITO薄膜とFTO薄膜の透過率の波長依存性を示すグラフである。透過率の急激な変動は、膜厚の干渉によるものである。 FIG. 2 is a graph showing the wavelength dependence of the transmittance of the ITO thin film and the FTO thin film with sheet resistances of 1.6Ω / □ and 15.5Ω / □, respectively. The sudden change in transmittance is due to film thickness interference.
これらの透明導電膜を用いて、透明アンテナとして、図3、4に示すパッチアンテナを基礎検討用に使用した。アンテナ放射素子の抵抗を考慮し、有限要素法(R.F.Harrington,Field computation by moment methods,IEEE PRESS,1993参照)を用いて解析を行った。
図3、4に示すパッチアンテナでは、アンテナの特性を低減しないように、給電系として電磁結合のマイクロストリップライン結合を使用した。したがって、直接励起用のマイクロストリップラインの損失による利得の低減および不要放射の発生を避けることが可能になる。
Using these transparent conductive films, a patch antenna shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 was used for basic examination as a transparent antenna. In consideration of the resistance of the antenna radiating element, analysis was performed using a finite element method (see RF Harrington, Field calculation by moment methods, IEEE PRESS, 1993).
In the patch antenna shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, electromagnetically coupled microstrip line coupling is used as a feeding system so as not to reduce the antenna characteristics. Accordingly, it is possible to avoid a reduction in gain and generation of unnecessary radiation due to the loss of the microstrip line for direct excitation.
図3に示すパッチアンテナ10は、誘電体基板11、および、その一方の面11a上に成膜され、放射素子をなす透明導電膜12からなる透明部材13と、基板14、その一方の面14a上に成膜されたマイクロストリップライン15、および、基板14の一方の面14aとは反対の面(他方の面)上に成膜されたグラウンド16からなる給電部材17とから構成されている。
また、基板14の一方の面14aに、誘電体基板11の一方の面11aとは反対の面(他方の面)が接合されて、透明部材13が給電部材17に積層されている。
そして、誘電体基板11の一方の面11a側から見て、透明導電膜12とマイクロストリップライン15が対向している。
The
Further, a surface (the other surface) opposite to the one
The transparent
誘電体基板11としては、ガラス基板、樹脂基板、プレキシガラス基板などからなる透明な基板が挙げられる。
基板14としては、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン基板、ガラス基板などからなる透明または不透明な基板が挙げられる。
マイクロストリップライン15としては、銅、アルミニウム、金などの金属からなる金属薄膜が挙げられる。
グラウンド16としては、銅、アルミニウム、金などの金属からなる金属薄膜が挙げられる。
Examples of the
Examples of the
Examples of the
Examples of the
このパッチアンテナ10において、誘電体基板11は、その比誘電率εrと誘電損失正接tanδが、εr<5、tanδ<0.006の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
また、基板14は、その比誘電率εrと誘電損失正接tanδが、1<εr<11、tanδ<0.003の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
さらに、放射素子をなす透明導電膜12の幅wp、長さLp、光速を使用周波数で除して算出された波長λ0が、0.2wp≦Lp≦2.0wp、0.15λ0≦wp≦0.26λ0の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。ここで、使用周波数は、個々のアンテナ特有のパラメータである。
In the
The
Furthermore, the wavelength λ 0 calculated by dividing the width w p , the length L p , and the speed of light of the transparent
このパッチアンテナ10では、透明部材13と給電部材17を結合することにより、マイクロストリップライン15を備えた給電部材17が、誘電法則を含めたMaxwellの方式と一致する電磁結合によって、電磁エネルギーを放つ。
また、マイクロストリップライン15の幅を変えることにより、伝送線路の特性インピーダンスである50Ω整合を取ることができる。また、マイクロストリップライン15の長さを変えることにより、アンテナの整合を調整することができる。
In the
Further, by changing the width of the
一方、透明導電膜12の長さ(主偏波に対して)を変えることにより、アンテナの共振を調整する。
また、透明導電膜12の幅を変えることにより、アンテナの整合を調整する。
On the other hand, the resonance of the antenna is adjusted by changing the length of the transparent conductive film 12 (with respect to the main polarization).
Further, the antenna matching is adjusted by changing the width of the transparent
このパッチアンテナ10は、誘電体基板11上に透明導電膜12が成膜された状態での上記の可視光波長領域における透過率が30%以上であることが好ましい。
また、このパッチアンテナ10は、0.8GHz〜12GHzにおいて、同じ寸法の金属薄膜を用いて作製したアンテナに比べて、利得の低下が6dB以下であり、放射効率が20%以上であることが好ましい。
The
Further, the
図4に示すパッチアンテナ20は、誘電体基板21、および、その一方の面21a上に成膜され、放射素子をなす透明導電膜22からなる透明部材23と、基板24、その他方の面24a上に成膜されたマイクロストリップライン25、基板24の他方の面24aとは反対の面(一方の面)上に成膜されたグラウンド26、および、グラウンド26に設けられたスロット27からなる給電部材28とから構成されている。
また、スロット27は、グラウンド26に設けられた細長い溝状の穴であり、このスロット27において基板24の一方の面が露出している。また、グラウンド26の表面側から見て、このスロット27はマイクロストリップライン25と対向している。
さらに、基板24の一方の面に、誘電体基板21の一方の面21aとは反対の面(他方の面)が接合されて、透明部材23が給電部材28に積層されている。すなわち、透明部材23と給電部材28が、スロット27を設けたグラウンド26を介して接合されている。
そして、誘電体基板21の一方の面21a側から見て、透明導電膜22とスロット27が対向し、結果として、透明導電膜22とマイクロストリップライン25が対向している。
The
The
Further, a surface (the other surface) opposite to the one
Then, when viewed from the one
誘電体基板21としては、上記の誘電体基板11と同様のものが用いられる。
基板24としては、上記の基板14と同様のものが用いられる。
マイクロストリップライン25としては、上記のマイクロストリップライン15と同様のものが挙げられる。
グラウンド26としては、上記のグラウンド16と同様のものが挙げられる。
As the
As the
Examples of the
As the
このパッチアンテナ20において、誘電体基板21は、その比誘電率εrと誘電損失正接tanδが、εr<5、tanδ<0.006の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
また、基板24は、その比誘電率εrと誘電損失正接tanδが、1<εr<11、tanδ<0.003の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
また、放射素子をなす透明導電膜22の幅wp、長さLp、光速を使用周波数で除して算出された波長λ0が、0.2wp≦Lp≦2.0wp、0.15λ0≦wp≦0.26λ0の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
さらに、スロット27の幅wsl、長さLsl、光速を使用周波数で除して算出された波長λ0が、0.0025λ0≦Lsl≦0.15λ0、Lsl/30≦wsl≦Lsl/2の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
In the
Further, the
The wavelength λ 0 calculated by dividing the width w p , the length L p , and the speed of light by the operating frequency of the transparent
Further, the width λ sl of slot 27, the length L sl , and the wavelength λ 0 calculated by dividing the speed of light by the operating frequency are 0.0025 λ 0 ≦ L sl ≦ 0.15λ 0 , L sl / 30 ≦ w sl It is preferable that the relationship of ≦ L sl / 2 is satisfied.
このパッチアンテナ20では、透明部材23と給電部材28を結合することにより、マイクロストリップライン25を備えた給電部材28が、誘電法則を含めたMaxwellの方式と一致する電磁結合によって、電磁エネルギーを放つ。
また、マイクロストリップライン25の幅を変えることにより、伝送線路の特性インピーダンスである50Ω整合を取ることができる。また、マイクロストリップライン25の長さを変えることにより、アンテナの整合を調整することができる。
In the
Further, by changing the width of the
一方、透明導電膜22の長さ(主偏波に対して)を変えることにより、アンテナの共振を調整する。
また、透明導電膜22の幅を変えることにより、アンテナの整合を調整する。
On the other hand, the resonance of the antenna is adjusted by changing the length of the transparent conductive film 22 (with respect to the main polarization).
Also, the antenna matching is adjusted by changing the width of the transparent
また、スロット27の寸法(幅、長さ)を変えることにより、透明導電膜22とマイクロストリップライン25の電磁結合を調整する。
Further, the electromagnetic coupling between the transparent
このパッチアンテナ20は、誘電体基板21上に透明導電膜22が成膜された状態での上記の可視光波長領域における透過率が30%以上であることが好ましい。
また、このパッチアンテナ20は、0.8GHz〜12GHzにおいて、同じ寸法の金属薄膜を用いて作製したアンテナに比べて、利得の低下が6dB以下であり、放射効率が20%以上であることが好ましい。
The
The
「実施例1」
図3に示すように、透明導電膜12の形状を正方形とし、1575.42MHz中心(GPS帯)への応用を目的とするマイクロストリップライン給電を用いたパッチアンテナ10の放射特性を測定した。
表1に測定に用いた各パラメータを示す。
"Example 1"
As shown in FIG. 3, the radiation characteristics of the
Table 1 shows the parameters used for the measurement.
表1に示すパラメータを用いて、パッチアンテナ10の放射特性を算出した。
図5は、Sパラメータを示すグラフである。この図5より、このパッチアンテナ10は、破線で示す目的とするGPS周波数の1575.42MHzに共振することが分かった。
なお、この実施例1では、比較のために、放射素子を銅薄膜で形成したパッチアンテナの特性を示す。
Using the parameters shown in Table 1, the radiation characteristics of the
FIG. 5 is a graph showing the S parameter. From FIG. 5, it was found that the
In addition, in this Example 1, the characteristic of the patch antenna which formed the radiation element with the copper thin film is shown for the comparison.
図6は、アンテナの整合状態を示すグラフである。この図6より、ITO薄膜からなる透明導電膜12は、抵抗Rinが55.7Ω、リアクタンスXinが20.3Ωであることが分かった。
FIG. 6 is a graph showing the matching state of the antenna. From FIG. 6, it was found that the transparent
図7、8は、1.575GHzにおけるパッチアンテナ10の放射特性を示すグラフである。
アンテナの放射特性を、Sパラメータの一番落ちている値の周波数で示す。
図7はφ=0°、θ=90°における垂直面内指向性を表し、図8はφ=90°、θ=90°における水平面内指向性を表す。
また、これら図7、8より、パッチアンテナ10のピーク利得が約4.2dBiであることが分かった。
さらに、ITO薄膜からなる透明導電膜12と、銅薄膜からなる放射素子とを比較すると、透明導電膜12のピーク利得が0.7dB低減することが分かった。
なお、半値幅はそれぞれ、ITO薄膜の半値幅HPBWITO=86°、銅薄膜の半値幅HPBWcopper=85°であった。
また、計算により、透明導電膜12からなる放射素子を備えたパッチアンテナ10の放射効率は62%となり、銅薄膜からなる放射素子を備えたパッチアンテナに比べて、放射効率が27%低減することが分かった。
7 and 8 are graphs showing the radiation characteristics of the
The radiation characteristic of the antenna is indicated by the frequency at which the S parameter is the lowest value.
7 represents the directivity in the vertical plane at φ = 0 ° and θ = 90 °, and FIG. 8 represents the directivity in the horizontal plane at φ = 90 ° and θ = 90 °.
7 and 8, it was found that the peak gain of the
Furthermore, when comparing the transparent
In addition, the half value width of the ITO thin film was HPBW ITO = 86 °, and the half value width of the copper thin film was HPBW copper = 85 °.
Also, the calculation shows that the radiation efficiency of the
「実施例2」
図9は、実施例2のパッチアンテナを示す概略図であり、(a)は斜視図、(b)は平面図である。
図9において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ30では、透明導電膜31の形状を円形とした。
このパッチアンテナ30について、表1に示すパラメータおよび透明導電膜31の半径rp=24.7mmを用いて、放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を算出した。
その結果、実施例1とほぼ同じ結果が得られた。
"Example 2"
FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram illustrating a patch antenna according to the second embodiment, where (a) is a perspective view and (b) is a plan view.
In FIG. 9, the same components as those of the
In the
For the
As a result, almost the same result as in Example 1 was obtained.
「実施例3」
図10は、実施例3のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図10において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ40では、透明導電膜41の形状を長方形とした。
このパッチアンテナ40は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 3"
FIG. 10 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the third embodiment.
10, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例4」
図11は、実施例4のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図11において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ50では、透明導電膜51の形状を楕円形とした。
このパッチアンテナ50は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
Example 4
FIG. 11 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the fourth embodiment.
11, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例5」
図12は、実施例5のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図12において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ60では、透明導電膜61の形状を三角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ60は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 5"
FIG. 12 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the fifth embodiment.
12, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例6」
図13は、実施例6のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図13において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ70では、透明導電膜71の形状を円環形とした。
このパッチアンテナ70は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 6"
FIG. 13 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the sixth embodiment.
13, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例7」
図14は、実施例7のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図14において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ80では、透明導電膜81の形状を五角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ80は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 7"
FIG. 14 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the seventh embodiment.
In FIG. 14, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例8」
図15は、実施例8のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図15において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ90では、透明導電膜91の形状を六角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ90は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 8"
FIG. 15 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the eighth embodiment.
In FIG. 15, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例9」
図16は、実施例9のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図16において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ100では、透明導電膜101の形状をH字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ100は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 9"
FIG. 16 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the ninth embodiment.
In FIG. 16, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例10」
図17は、実施例10のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図17において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ110では、透明導電膜111の形状をU字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ110は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 10"
FIG. 17 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the tenth embodiment.
In FIG. 17, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例11」
図18は、実施例11のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図18において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ120では、透明導電膜121の形状をL字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ120は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 11"
FIG. 18 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the eleventh embodiment.
In FIG. 18, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例12」
図19は、実施例12のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図19において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ130では、透明導電膜131の形状を十字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ130は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 12"
FIG. 19 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twelfth embodiment.
In FIG. 19, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例13」
図20は、実施例13のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図20において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ140では、透明導電膜141の形状をT字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ140は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 13"
FIG. 20 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirteenth embodiment.
20, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例14」
図21は、実施例14のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図21において、図3に示したパッチアンテナ10の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ150では、透明導電膜141の形状を台形とした。
このパッチアンテナ150は、実施例1のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 14"
FIG. 21 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the fourteenth embodiment.
In FIG. 21, the same components as those of the
In this
This
「実施例15」
図4に示すように、透明導電膜22の形状を正方形とし、1575.42MHz中心(GPS帯)への応用を目的とするマイクロストリップライン給電を用いたパッチアンテナ20の放射特性を測定した。
表2に測定に用いた各パラメータを示す。
"Example 15"
As shown in FIG. 4, the radiation characteristics of the
Table 2 shows the parameters used for the measurement.
表2に示すパラメータを用いて、パッチアンテナ20の放射特性を算出した。
図22は、Sパラメータを示すグラフである。この図22より、このパッチアンテナ20は、破線で示す目的とするGPS周波数の1575.42MHzに共振することが分かった。
なお、この実施例15では、比較のために、放射素子を銅薄膜で形成したパッチアンテナの特性を示す。
Using the parameters shown in Table 2, the radiation characteristics of the
FIG. 22 is a graph showing the S parameter. From FIG. 22, it was found that the
For comparison, Example 15 shows characteristics of a patch antenna in which a radiating element is formed of a copper thin film.
図23は、アンテナの整合状態を示すグラフである。この図23より、ITO薄膜からなる透明導電膜22は、抵抗Rinが59.6Ω、リアクタンスXinが2.2Ωであることが分かった。
FIG. 23 is a graph showing an antenna matching state. FIG. 23 shows that the transparent
図24、25は、1.575GHzにおけるパッチアンテナ20の放射特性を示すグラフである。
アンテナの放射特性を、Sパラメータの一番落ちている値の周波数で示す。
図24はφ=0°、θ=90°における垂直面内指向性を表し、図25はφ=90°、θ=90°における水平面内指向性を表す。
また、これら図24、25より、パッチアンテナ20のピーク利得が約2dBiであることが分かった。
さらに、ITO薄膜からなる透明導電膜22と、銅薄膜からなる放射素子とを比較すると、透明導電膜22のピーク利得が1.7dB低減することが分かった。
なお、半値幅はそれぞれ、ITO薄膜の半値幅HPBWITO=90°、銅薄膜の半値幅HPBWcopper=89°であった。
また、計算により、透明導電膜22からなる放射素子を備えたパッチアンテナ20の放射効率は34.6%となり、銅薄膜からなる放射素子を備えたパッチアンテナに比べて、放射効率が16%低減することが分かった。
24 and 25 are graphs showing the radiation characteristics of the
The radiation characteristic of the antenna is indicated by the frequency at which the S parameter is the lowest value.
FIG. 24 shows the directivity in the vertical plane at φ = 0 ° and θ = 90 °, and FIG. 25 shows the directivity in the horizontal plane at φ = 90 ° and θ = 90 °.
24 and 25, the peak gain of the
Furthermore, when comparing the transparent
In addition, the half value width of the ITO thin film was HPBW ITO = 90 °, and the half value width of the copper thin film was HPBW copper = 89 °.
Also, the calculation shows that the radiation efficiency of the
「実施例16」
図26は、実施例16のパッチアンテナを示す概略図であり、(a)は斜視図、(b)は平面図である。
図26において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ160では、透明導電膜161の形状を円形とした。
このパッチアンテナ160について、表2に示すパラメータおよび透明導電膜161の半径rp=24.2mmを用いて、放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を算出した。
その結果、実施例15とほぼ同じ結果が得られた。
"Example 16"
FIG. 26 is a schematic diagram illustrating a patch antenna of Example 16, where (a) is a perspective view and (b) is a plan view.
In FIG. 26, the same components as those of the
In the
With respect to the
As a result, almost the same result as in Example 15 was obtained.
「実施例17」
図27は、実施例17のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図27において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ170では、透明導電膜171の形状を長方形とした。
このパッチアンテナ170は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 17"
FIG. 27 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the seventeenth embodiment.
In FIG. 27, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例18」
図28は、実施例18のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図28において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ180では、透明導電膜181の形状を楕円形とした。
このパッチアンテナ180は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 18"
FIG. 28 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the eighteenth embodiment.
28, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例19」
図29は、実施例19のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図29において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
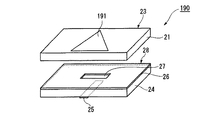
このパッチアンテナ190では、透明導電膜191の形状を三角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ190は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 19"
FIG. 29 is a schematic perspective view showing the patch antenna of the nineteenth embodiment.
29, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例20」
図30は、実施例20のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図30において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ200では、透明導電膜201の形状を円環形とした。
このパッチアンテナ200は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 20"
FIG. 30 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twentieth embodiment.
30, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例21」
図31は、実施例21のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図31において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ210では、透明導電膜211の形状を五角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ210は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 21"
FIG. 31 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-first embodiment.
In FIG. 31, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例22」
図32は、実施例22のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図32において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ220では、透明導電膜221の形状を六角形とした。
このパッチアンテナ220は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 22"
FIG. 32 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-second embodiment.
In FIG. 32, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例23」
図33は、実施例23のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図33において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ230では、透明導電膜231の形状をH字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ230は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 23"
FIG. 33 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-third embodiment.
In FIG. 33, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例24」
図34は、実施例24のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図34において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ240では、透明導電膜241の形状をU字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ240は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 24"
FIG. 34 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-fourth embodiment.
34, the same components as those of the
In this
The
「実施例25」
図35は、実施例25のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図35において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ250では、透明導電膜251の形状をL字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ250は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 25"
FIG. 35 is a schematic perspective view of the patch antenna according to the twenty-fifth embodiment.
35, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例26」
図36は、実施例26のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図36において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ260では、透明導電膜261の形状を十字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ260は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 26"
FIG. 36 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-sixth embodiment.
In FIG. 36, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例27」
図37は、実施例27のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図37において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ270では、透明導電膜271の形状をT字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ270は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 27"
FIG. 37 is a schematic perspective view showing the patch antenna of Example 27.
In FIG. 37, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例28」
図38は、実施例28のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図38において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ280では、透明導電膜281の形状を台形とした。
このパッチアンテナ280は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 28"
FIG. 38 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the twenty-eighth embodiment.
In FIG. 38, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例29」
図39は、実施例29のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図39において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ290では、スロット291の形状を楕円形とした。
このパッチアンテナ290は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 29"
FIG. 39 is a schematic perspective view showing the patch antenna of Example 29.
In FIG. 39, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例30」
図40は、実施例30のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図40において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ300では、スロット301の形状を菱形とした。
このパッチアンテナ300は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 30"
FIG. 40 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirtieth embodiment.
In FIG. 40, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例31」
図41は、実施例31のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図41において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ310では、スロット311の形状を亜鈴形とした。
このパッチアンテナ310は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 31"
FIG. 41 is a schematic perspective view showing the patch antenna of Example 31.
In FIG. 41, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例32」
図42は、実施例32のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図42において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ320では、スロット321の形状をH字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ320は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 32"
FIG. 42 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirty-second embodiment.
In FIG. 42, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例33」
図43は、実施例33のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図43において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ330では、スロット331の形状をボウタイ型とした。
このパッチアンテナ330は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 33"
FIG. 43 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirty-third embodiment.
In FIG. 43, the same components as those of the
In the
The
「実施例34」
図44は、実施例34のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図44において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ340では、スロット341の形状をU字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ340は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 34"
FIG. 44 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirty-fourth embodiment.
44, the same components as those of the
In the
This
「実施例35」
図45は、実施例35のパッチアンテナを示す概略斜視図である。
図45において、図4に示したパッチアンテナ20の構成要素と同じ構成要素には同一符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
このパッチアンテナ350では、スロット351の形状を十時字型とした。
このパッチアンテナ350は、実施例15のパッチアンテナ10とほぼ同等の放射特性(利得減、放射効率)を示した。
"Example 35"
FIG. 45 is a schematic perspective view illustrating the patch antenna according to the thirty-fifth embodiment.
In FIG. 45, the same components as those of the
In the
The
10,20・・・パッチアンテナ、11,21・・・誘電体基板、12,22・・・透明導電膜、13,23・・・透明部材、14,24・・・基板、15,25・・・マイクロストリップライン、16,26・・・グラウンド、17,28・・・給電部材、27・・・スロット。 10, 20 ... patch antenna, 11, 21 ... dielectric substrate, 12, 22 ... transparent conductive film, 13, 23 ... transparent member, 14, 24 ... substrate, 15, 25 ... ..Microstrip line, 16, 26 ... ground, 17,28 ... feed member, 27 ... slot.
Claims (16)
前記透明導電膜は、350nm〜780nmの可視光波長領域において光を透過でき、100MHz〜20GHzの周波数帯において電磁波を放射することを特徴とする透明アンテナ。 A dielectric substrate and a transparent member made of a transparent conductive film forming a radiation element formed on one surface of the dielectric substrate, a microstrip line formed on the substrate and one surface of the substrate, and A power feeding member made of ground formed on a surface opposite to the one surface of the substrate, and a surface opposite to the one surface of the dielectric substrate is bonded to the one surface of the substrate The transparent member is laminated on the power supply member, and the transparent conductive film and the microstrip line are opposed to each other when viewed from one surface side of the dielectric substrate ,
The transparent conductive film can transmit light in the visible light wavelength region of 350Nm~780nm, transparent antenna, wherein the benzalkonium radiate electromagnetic waves in a frequency band of 100MHz~20GHz.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007152761A JP4832366B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2007-06-08 | Transparent antenna |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007152761A JP4832366B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2007-06-08 | Transparent antenna |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008306552A JP2008306552A (en) | 2008-12-18 |
| JP4832366B2 true JP4832366B2 (en) | 2011-12-07 |
Family
ID=40234854
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007152761A Expired - Fee Related JP4832366B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2007-06-08 | Transparent antenna |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4832366B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180099046A (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2018-09-05 | 동우 화인켐 주식회사 | Transparent film antenna |
| US20230352837A1 (en) * | 2022-04-28 | 2023-11-02 | City University Of Hong Kong | Patch antenna |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8766858B2 (en) | 2010-08-27 | 2014-07-01 | Apple Inc. | Antennas mounted under dielectric plates |
| US9455489B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2016-09-27 | Apple Inc. | Cavity antennas |
| JP5692464B2 (en) * | 2011-12-07 | 2015-04-01 | 富士通株式会社 | Delta planar patch antenna device |
| JP5810910B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2015-11-11 | 富士通株式会社 | Antenna design method, antenna design apparatus, antenna design program |
| US8712233B2 (en) | 2012-02-24 | 2014-04-29 | Apple Inc. | Electronic device assemblies |
| US9318793B2 (en) | 2012-05-02 | 2016-04-19 | Apple Inc. | Corner bracket slot antennas |
| US9186828B2 (en) | 2012-06-06 | 2015-11-17 | Apple Inc. | Methods for forming elongated antennas with plastic support structures for electronic devices |
| JP6107012B2 (en) | 2012-09-10 | 2017-04-05 | 富士通株式会社 | Antenna design method |
| US10305163B2 (en) * | 2017-08-14 | 2019-05-28 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Method and apparatus for semitransparent antenna and transmission lines |
| JP2019057831A (en) * | 2017-09-21 | 2019-04-11 | 株式会社フジクラ | Antenna device |
| JP6914301B2 (en) * | 2019-09-13 | 2021-08-04 | 株式会社フジクラ | Antenna device |
| MX2022006745A (en) * | 2019-12-06 | 2022-11-07 | Pittsburgh Glass Works Llc | Multilayer glass patch antenna. |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2833301B2 (en) * | 1991-11-26 | 1998-12-09 | 日立化成工業株式会社 | Dual-polarized planar antenna |
| JP2002076769A (en) * | 2000-08-30 | 2002-03-15 | Shigeo Kawasaki | Active element antenna |
| JP2002146536A (en) * | 2000-11-08 | 2002-05-22 | Japan Science & Technology Corp | Low-temperature deposition method for thin film of tin oxide |
-
2007
- 2007-06-08 JP JP2007152761A patent/JP4832366B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180099046A (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2018-09-05 | 동우 화인켐 주식회사 | Transparent film antenna |
| KR102188997B1 (en) | 2017-02-28 | 2020-12-09 | 동우 화인켐 주식회사 | Transparent film antenna |
| US20230352837A1 (en) * | 2022-04-28 | 2023-11-02 | City University Of Hong Kong | Patch antenna |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2008306552A (en) | 2008-12-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4832366B2 (en) | Transparent antenna | |
| JP2009533888A (en) | Transparent antenna | |
| EP2073308B1 (en) | Antenna device | |
| WO2012154390A2 (en) | Electronic device including a patch antenna and photovoltaic layer and related methods | |
| CN103503236A (en) | Electronic device including electrically conductive mesh layer patch antenna and related methods | |
| Stanley et al. | A transparent dual-polarized antenna array for 5G smartphone applications | |
| WO2012154391A2 (en) | Electronic device including a patch antenna and visual display layer and related methods | |
| Desai et al. | Dual band slotted transparent resonator for wireless local area network applications | |
| Dastranj | Very small planar broadband monopole antenna with hybrid trapezoidal–elliptical radiator | |
| Guan et al. | Antennas made of transparent conductive films | |
| TWI711219B (en) | Antenna system | |
| Xu et al. | Printed multi‐band compound meta‐loop antenna with hybrid‐coupled SRRs | |
| Jizat et al. | Compact size of CPW dual-band meander-line transparent antenna for WLAN applications | |
| Kumar et al. | On the devolvement of fractal antenna for IoT applications | |
| JP2009077072A (en) | Transparent planar inverse f antenna | |
| Zhu et al. | High-performance, transparent and flexible antenna based on conductive nanocomposites | |
| Lee et al. | Optically transparent 1-D EBG antenna using sub-skin depth thin-film alloy in the Ka-band | |
| Li et al. | High-permittivity substrate multiresonant antenna inside metallic cover of laptop computer | |
| El Halaoui et al. | An optically transparent mesh-antenna integrated in OLEDs for WLAN applications | |
| JP2009005155A (en) | Loop antenna | |
| JP2013197987A (en) | Antenna device | |
| Chen et al. | Printed broadband monopole antenna for WLAN/WiMAX applications | |
| Kedze et al. | Silver nanoflake printed flexible composite broadband dipole antenna | |
| Kaim et al. | Dual Band 9-Shaped Graphene-Film Patch Antenna for 5G Applications | |
| Awalludin et al. | Dual-stacked transparent patch antenna using AgHT-8 for wireless application |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20091224 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110526 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110531 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110801 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110823 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110920 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140930 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |