JP4482605B1 - 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ - Google Patents
高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4482605B1 JP4482605B1 JP2009012884A JP2009012884A JP4482605B1 JP 4482605 B1 JP4482605 B1 JP 4482605B1 JP 2009012884 A JP2009012884 A JP 2009012884A JP 2009012884 A JP2009012884 A JP 2009012884A JP 4482605 B1 JP4482605 B1 JP 4482605B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- phosphorus
- copper
- purity
- wire
- copper alloy
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/43—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05599—Material
- H01L2224/056—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/05617—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 400°C and less than 950°C
- H01L2224/05624—Aluminium [Al] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/43—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/4501—Shape
- H01L2224/45012—Cross-sectional shape
- H01L2224/45015—Cross-sectional shape being circular
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45144—Gold (Au) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45147—Copper (Cu) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/485—Material
- H01L2224/48505—Material at the bonding interface
- H01L2224/48599—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Gold (Au)
- H01L2224/486—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Gold (Au) with a principal constituent of the bonding area being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/48638—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Gold (Au) with a principal constituent of the bonding area being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/48639—Silver (Ag) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/485—Material
- H01L2224/48505—Material at the bonding interface
- H01L2224/48799—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Copper (Cu)
- H01L2224/488—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Copper (Cu) with a principal constituent of the bonding area being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/48838—Principal constituent of the connecting portion of the wire connector being Copper (Cu) with a principal constituent of the bonding area being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/48839—Silver (Ag) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/8538—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/85399—Material
- H01L2224/854—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/85438—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/85439—Silver (Ag) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00011—Not relevant to the scope of the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01004—Beryllium [Be]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01007—Nitrogen [N]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01012—Magnesium [Mg]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01014—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01015—Phosphorus [P]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0102—Calcium [Ca]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01022—Titanium [Ti]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01023—Vanadium [V]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01025—Manganese [Mn]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01027—Cobalt [Co]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01028—Nickel [Ni]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01041—Niobium [Nb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01046—Palladium [Pd]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01047—Silver [Ag]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01051—Antimony [Sb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01052—Tellurium [Te]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01072—Hafnium [Hf]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01073—Tantalum [Ta]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01074—Tungsten [W]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01078—Platinum [Pt]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01083—Bismuth [Bi]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/012—Semiconductor purity grades
- H01L2924/01206—6N purity grades, i.e. 99.9999%
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/102—Material of the semiconductor or solid state bodies
- H01L2924/1025—Semiconducting materials
- H01L2924/10251—Elemental semiconductors, i.e. Group IV
- H01L2924/10253—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20752—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 20 microns less than 30 microns
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
Abstract
【解決手段】純度99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅に微量のリン(P)を添加することにより、純度99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅よりも再結晶温度が高く、かつボールボンディングのイニシャルボール硬さが低下する。純度99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅にリン(P)0.5〜15質量ppmを添加し、さらに、その他の含有する不純物の総量をリン(P)の上記含有量より低くすることにより、上記特性を達成する。
【選択図】図1
Description
しかし、銅金属ワイヤの純度が高純度になればなるほど、再結晶温度が低くなり、銅金属ワイヤ自体が軟らかくなる。そのため、あらかじめ加工硬化させておいても時効軟化してしまい、軟らかくなった高純度の銅金属ワイヤの取扱いはきわめて困難となる。特に、ボンディングワイヤ用の銅金属ワイヤは伸線加工によって大量生産されているため、銅金属ワイヤの純度を高くしていくと、伸線加工中に銅金属ワイヤと伸線ダイスとの摩擦熱によって高純度の銅金属ワイヤ自体が軟化してワイヤが切断してしまう。また、手間暇をかければ、このような高純度の銅金属ワイヤも試作することができるが、このような高純度の銅金属ワイヤを用いて前記ICチップの電極上に超音波併用熱圧着しても、ICチップの電極上に接合された銅金属ワイヤから所定のループを形成しようとすると、99.999質量%程度以上の高純度銅金属ワイヤはへたってしまう。
これまでも99.999質量%以上の高純度銅金属ワイヤにいくつかの元素を微量添加していくと、銅合金ワイヤの再結晶温度が上昇し、銅合金ワイヤ自体の室温硬さが増加することは知られていた。すなわち、高純度銅合金ワイヤの室温硬さが増加するという知見は、微量添加元素の添加量とともに増加していくものと考えられていた。事実、リン(P)の場合も、99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅金属ワイヤに0質量ppmから20質量ppm、50質量ppm、100質量ppm、200質量ppmおよび400質量ppmと添加量を増加するにつれ、高純度銅金属ワイヤの結晶粒が微細化していき、一見すると再結晶温度が上昇するとともに材料強度そのものが上がって室温硬さも増加しているようにみえる。このため学術的には、リン(P)を10質量ppm程度添加した銅合金ワイヤの室温硬さは、リン(P)を添加しない高純度銅金属ワイヤのものと大差なく、この程度の硬さの相違は実験による誤差範囲内のものと片付けられていた。
これらの事情について前述の特許文献1によれば、リン(P)含有量40〜400質量ppmの範囲において溶融ボール形成時の酸化物の形成を防止して、ボールの硬さを低減してチップ割れを防止するというものであり、
特許文献2記載のものは、Mg及びPの少なくとも1種を総計で10〜700質量ppm、酸素を6〜20質量ppmの範囲で含有するボンディングワイヤであって、
Mg及びリン(P)の添加は、上記範囲内であればチップ損傷は回避できるというものの、その作用は硬さを向上する元素としている。
また、特許文献3記載のものは、Ti,Hf,V,Nb,Ta,Ni,Pd,Pt,Au,Cd,B,Al,In,Si,Ge,P,Sb,Bi,Se,及びTeから選択された1種又は2種以上の元素を0.001〜2重量%含有し、残部が実質的に銅であるボンディングワイヤが記載されているが、これらの成分元素は硬さを向上すると考えられる。
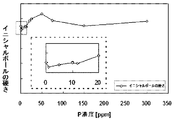
図1は、これらの関係を示すデータをグラフ化したものであって、溶融ボール形成後のP含有量に対する硬さを縦軸に採ったもので、リン(P)含有量が200質量ppm付近からリン(P)含有量の増加につれて硬さが向上することは一般に知られた現象であるが、ここでリン(P)含有量が150ppm近傍より低い領域で硬さが高くなり、一旦上昇してから急激に硬さが低下する領域があることがわかる。
図中で拡大した領域がそれで、P含有量がほぼ0.5〜15質量ppm近傍の間で、その硬さはリン(P)含有量が0の高純度銅金属と同等以下となるのである。
リン(P)の高純度Cu合金に対する室温硬さの低減効果は、次のような現象に基づいているものと考えられる。すなわち、ボンディングワイヤとしての銅合金ワイヤが火花放電によって溶融すると、大気中から酸素を溶融銅(Cu)中に取り込むが、銅合金ワイヤ表面の酸化物の膜はリン(P)によって一部分断され、蒸発されるものと思われる。そうすると、99.998質量%程度以上の高純度銅合金ワイヤの場合は、リン(P)を除く金属元素が10質量ppm程度しかないので酸素と結びつく不純物元素の絶対量が少なくなり、硬質の酸化膜が形成されないため高純度銅合金ワイヤの室温硬さが低くなることとつじつまが合う。
しかも、上記したようにこれらワイヤボンディングにおいて求められる特性と共に、同じ条件下でワイヤの線引き加工に欠かせない銅合金ワイヤの再結晶温度が上昇し、銅合金ワイヤ自体の時効軟化が緩和されて、線引き加工に求められる強度が維持されるのである。
このような知見から本発明者らは本発明を完成するに至ったのである。
(1)リン(P)と銅(Cu)とからなる銅合金のボンディングワイヤにおいて、リン(P)を添加した銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さがリン(P)を添加しない銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低いことを特徴とする高純度ボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤが提供される。
また、本発明によれば、
(2)リン(P)と銅(Cu)とからなる銅合金のボンディングワイヤにおいて、リン(P)を添加した銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さがリン(P)を添加しない銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低く、かつ、銅(Cu)中のリン(P)以外の金属元素の総量がリン(P)の含有量以下であることを特徴とする高純度ボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤが提供される。
また、本発明によれば、
(3)リン(P)と銅(Cu)とからなる銅合金のボンディングワイヤにおいて、リン(P)を0.5〜15質量ppmおよび残部が純度99.9985質量%以上の銅(Cu)からなる銅合金ワイヤであり、かつ、当該銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さがリン(P)を添加しない純度99.9985質量%以上の銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低いことを特徴とする高純度ボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤが提供される。リン(P)を0.5〜10質量ppmおよび残部が純度99.9985質量%以上の銅(Cu)からなる銅合金ワイヤであれば更にイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さが低下するので好ましい。
また、本発明によれば、
(4)リン(P)と銅(Cu)とからなる銅合金のボンディングワイヤにおいて、リン(P)を0.5〜15質量ppmおよび残部が純度99.9985質量%以上の銅(Cu)からなる高純度銅合金ワイヤであり、かつ、銅(Cu)中のリン(P)以外の金属元素の総量がリン(P)の含有量以下で、当該銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さがリン(P)を添加しない純度99.9985質量%以上の銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低いことを特徴とするボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤが提供される。
本発明に係るボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤの製造方法を説明する。99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅(Cu)金属(Cuの地金「A」とする。)および99.999質量%以上の高純度銅(Cu)金属(Cuの地金「B」とする。)を原料として、リン(P)を所定量添加した、表1に示す銅合金ワイヤ組成のものを準備する。これらの組成のものを高純度金ワイヤの製造方法の場合と同様にしてボンディングワイヤに加工する。まず、所定量の原料を真空溶解炉で溶解した後インゴットに鋳造する。このインゴットに溝ロール圧延をした後、アニール処理、防錆処理等を施して直径25μmの高純度銅合金ワイヤを作製した。
99.9999質量%以上の高純度銅およびこの高純度銅にリン(P)を所定量添加した、表1に示す高純度銅ワイヤ(φ200μm)の時効軟化作用を確認した。その結果を表2に示す。
この高純度銅合金ワイヤをボールボンディング装置(株式会社新川製の商品名「UTC-1000」)を用いて、それぞれ200℃程度に加熱したICチップのAl電極上及び200℃程度に加熱した銀(Ag)メッキリードフレームの外部配線上に超音波併用ボールボンディングを連続して3万回行った。この時、ICチップ側のボールボンディングは95%窒素+5%水素の雰囲気中でボールボンディング荷重を0.2N、ボールボンディング時間を10ミリ秒、ボールボンディングパワーを0.30ワットの条件で行った。また、外部配線側の第二ボンディングは荷重を0.3N、ボールボンディング時間を10ミリ秒、ボールボンディングパワーを0.40ワットの条件で行った。
この試験で第一ボンディングのAl膜はがれを起因とする不圧着の回数を数えた。その測定結果を表3右欄に示す。
ワイヤの再結晶温度は伸線加工後の状態から材料が完全に軟化する温度を調べ、その温度を再結晶温度として表2に記した。
第一ボンディングで溶融凝固した銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)ないし溶融ボールの室温硬さに関する評価は、3万回ボンディングした試料から任意に10個のボールボンディングされた資料を選び、株式会社明石製作所製のマイクロヒ゛ッカース硬度計(型式「DMH-1」)で測定し、その平均値を算出した。測定結果を表3に示す。
したがって、本発明のボンディングワイヤは、再結晶温度が高く、時効軟化作用が小さいため、ワイヤ伸線加工特性を維持し、また、ボールボンディングにおいては初期ボールの室温硬さが低いためチップ割れを効果的に防止する。
Claims (3)
- リン(P)の含有量が0.5〜15質量ppm、および残部が純度99.9985質量%以上の銅(Cu)からなる銅合金ワイヤであり、
かつ、その銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さをリン(P)を添加しない純度99.9999質量%以上の銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低下させたことを特徴とするボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤ。 - リン(P)が0.5〜15質量ppm、および残部が純度99.9985質量%以上の銅(Cu)からなる銅合金ワイヤであり、
かつ、銅(Cu)中のリン(P)以外の金属元素の総量がリン(P)の含有量以下であって、当該銅合金ワイヤのイニシャルボール(FAB)の室温硬さをリン(P)を添加しない純度99.9999質量%以上の銅金属ワイヤのものよりも低下させたことを特徴とする高純度ボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤ。 - 銅(Cu)中のリン(P)以外の金属元素がPt,Au,Ag,Pd,Ca,Fe,Mn,Mg,Ni,Al,PbおよびSiの内のいずれか1種または2種以上であることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の高純度ボールボンディング用銅合金ワイヤ。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009012884A JP4482605B1 (ja) | 2009-01-23 | 2009-01-23 | 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009012884A JP4482605B1 (ja) | 2009-01-23 | 2009-01-23 | 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP4482605B1 true JP4482605B1 (ja) | 2010-06-16 |
| JP2010171235A JP2010171235A (ja) | 2010-08-05 |
Family
ID=42351822
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009012884A Expired - Fee Related JP4482605B1 (ja) | 2009-01-23 | 2009-01-23 | 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4482605B1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012120982A1 (ja) * | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | Jx日鉱日石金属株式会社 | α線量が少ない銅又は銅合金及び銅又は銅合金を原料とするボンディングワイヤ |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5219316B1 (ja) * | 2012-09-28 | 2013-06-26 | 田中電子工業株式会社 | 半導体装置接続用銅白金合金細線 |
| JP5213146B1 (ja) * | 2012-10-03 | 2013-06-19 | 田中電子工業株式会社 | 半導体装置接続用銅ロジウム合金細線 |
| JP6098372B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-30 | 2017-03-22 | 住友ベークライト株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6369994B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-02 | 2018-08-08 | 田中電子工業株式会社 | ボールボンディング用銅合金細線 |
| JP6710141B2 (ja) * | 2016-10-14 | 2020-06-17 | 田中電子工業株式会社 | ボールボンディング用銅合金線 |
| WO2018155283A1 (ja) * | 2017-02-22 | 2018-08-30 | 新日鉄住金マテリアルズ株式会社 | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ |
| JP6371932B1 (ja) * | 2017-02-22 | 2018-08-08 | 新日鉄住金マテリアルズ株式会社 | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61251062A (ja) * | 1985-04-30 | 1986-11-08 | Nippon Mining Co Ltd | 半導体装置用ボンデイングワイヤ |
| JPS6280241A (ja) * | 1985-10-01 | 1987-04-13 | Tanaka Denshi Kogyo Kk | 半導体素子のボンデイング用銅線 |
| JPS63266841A (ja) * | 1987-04-24 | 1988-11-02 | Toshiba Corp | 樹脂封止型半導体装置 |
| JPH07122564A (ja) * | 1993-10-22 | 1995-05-12 | Tanaka Denshi Kogyo Kk | バンプ形成方法 |
| JP2003133364A (ja) * | 2001-10-19 | 2003-05-09 | Tanaka Electronics Ind Co Ltd | 銅ボールの熱圧着方法 |
| JP2003197847A (ja) * | 2001-12-25 | 2003-07-11 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
-
2009
- 2009-01-23 JP JP2009012884A patent/JP4482605B1/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61251062A (ja) * | 1985-04-30 | 1986-11-08 | Nippon Mining Co Ltd | 半導体装置用ボンデイングワイヤ |
| JPS6280241A (ja) * | 1985-10-01 | 1987-04-13 | Tanaka Denshi Kogyo Kk | 半導体素子のボンデイング用銅線 |
| JPS63266841A (ja) * | 1987-04-24 | 1988-11-02 | Toshiba Corp | 樹脂封止型半導体装置 |
| JPH07122564A (ja) * | 1993-10-22 | 1995-05-12 | Tanaka Denshi Kogyo Kk | バンプ形成方法 |
| JP2003133364A (ja) * | 2001-10-19 | 2003-05-09 | Tanaka Electronics Ind Co Ltd | 銅ボールの熱圧着方法 |
| JP2003197847A (ja) * | 2001-12-25 | 2003-07-11 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012120982A1 (ja) * | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | Jx日鉱日石金属株式会社 | α線量が少ない銅又は銅合金及び銅又は銅合金を原料とするボンディングワイヤ |
| CN103415633A (zh) * | 2011-03-07 | 2013-11-27 | 吉坤日矿日石金属株式会社 | α射线量少的铜或铜合金及以铜或铜合金作为原料的接合线 |
| CN103415633B (zh) * | 2011-03-07 | 2015-09-09 | 吉坤日矿日石金属株式会社 | 铜或铜合金、接合线、铜的制造方法、铜合金的制造方法及接合线的制造方法 |
| KR101623629B1 (ko) | 2011-03-07 | 2016-05-23 | 제이엑스 킨조쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 구리 또는 구리 합금, 본딩 와이어, 구리의 제조 방법, 구리 합금의 제조 방법 및 본딩 와이어의 제조 방법 |
| PH12017501498A1 (en) * | 2011-03-07 | 2019-01-14 | Jx Nippon Mining & Metals Corp | COPPER OR COPPER ALLOY REDUCED IN a-RAY EMISSION, AND BONDING WIRE OBTAINED FROM COPPER OR COPPER ALLOY AS RAW MATERIAL |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010171235A (ja) | 2010-08-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4482605B1 (ja) | 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5246314B2 (ja) | 半導体用銅合金ボンディングワイヤ | |
| WO2011118009A1 (ja) | 高純度Cuボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5343069B2 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤの接合構造 | |
| WO2012169067A1 (ja) | 高強度、高伸び率金合金ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5213146B1 (ja) | 半導体装置接続用銅ロジウム合金細線 | |
| JP2008085320A (ja) | 半導体装置用銅合金ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP6710141B2 (ja) | ボールボンディング用銅合金線 | |
| TWI714562B (zh) | 銅合金接合線 | |
| JP5403702B2 (ja) | 銅ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JPH10326803A (ja) | 半導体素子用金銀合金細線 | |
| JP6369994B2 (ja) | ボールボンディング用銅合金細線 | |
| JPS6365036A (ja) | 銅細線とその製造方法 | |
| JP4195495B1 (ja) | ボールボンディング用金合金線 | |
| JPH1167811A (ja) | 半導体素子用金銀合金細線 | |
| JPH0726167B2 (ja) | 半導体装置のボンデイングワイヤ用Au合金極細線 | |
| JPH0464121B2 (ja) | ||
| JP6898705B2 (ja) | ボールボンディング用銅合金細線 | |
| JP4134261B1 (ja) | ボールボンディング用金合金線 | |
| CN111656501A (zh) | 接合线 | |
| JP3907534B2 (ja) | ボンディング用金合金線 | |
| JP4947670B2 (ja) | 半導体素子用ボンディングワイヤの熱処理方法 | |
| CN102859672B (zh) | 高纯度铜焊接引线 | |
| JPS6365034A (ja) | 銅細線とその製造方法 | |
| JP4713149B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100316 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100319 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130326 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4482605 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140326 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |