JP4200884B2 - Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system - Google Patents
Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4200884B2 JP4200884B2 JP2003384191A JP2003384191A JP4200884B2 JP 4200884 B2 JP4200884 B2 JP 4200884B2 JP 2003384191 A JP2003384191 A JP 2003384191A JP 2003384191 A JP2003384191 A JP 2003384191A JP 4200884 B2 JP4200884 B2 JP 4200884B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- data
- image
- compressed data
- partial area
- processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Compression Of Band Width Or Redundancy In Fax (AREA)
- Record Information Processing For Printing (AREA)
Description
本発明は、複数のプロセッサを用いて並列に画像処理(特に画像伸長処理)を行うための技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for performing image processing (particularly image decompression processing) in parallel using a plurality of processors.
一般に、レーザプリンタシステムでは、RIP(ラスターイメージプロセッサ)により、PDL(ページ記述言語)で記述された印刷対象を印刷イメージに展開し、順次に走査ライン(ラスター)ごとに印刷エンジンに送り出して、印刷を実行する。 Generally, in a laser printer system, a print object described in PDL (page description language) is developed into a print image by a RIP (raster image processor), and sequentially sent to a print engine for each scan line (raster) for printing. Execute.
このとき、印刷イメージを1ページ分全部展開して記憶しておこうとすると、大変多くのメモリ領域が必要となってしまう。そのため、1ページを複数の走査ラインから構成されるバンドに分割し、その単位で印刷イメージを展開するのが普通である。 At this time, if all the print images are developed and stored for one page, a very large memory area is required. Therefore, it is common to divide one page into bands composed of a plurality of scanning lines and develop a print image in that unit.
このようなバンド単位の展開処理を高速に行うために、複数のプロセッサそれぞれに各バンドを割り当てて並列に展開処理を行う構成が提案されている(特許文献1)。
RIPをホスト装置が備える場合、展開した印刷イメージをプリンタ側に送信する必要がある。この場合、印刷イメージはデータ量が多いことから、ホスト装置において送信する前に圧縮処理を施し、プリンタ側で伸長するという枠組みを取るのが普通である。 When the RIP is provided in the host device, the developed print image needs to be transmitted to the printer side. In this case, since the print image has a large amount of data, it is usual to adopt a framework in which compression processing is performed before transmission by the host device and decompression is performed on the printer side.
ここで、ホスト装置やプリンタが複数のプロセッサを備えている場合、特許文献1のように、複数のプロセッサそれぞれに各バンドを割り当てて並列に圧縮処理や伸長処理を行うという構成が考えられる。
Here, when the host device or the printer includes a plurality of processors, a configuration in which each band is assigned to each of the plurality of processors and compression processing or decompression processing is performed in parallel as in
しかし、このようなバンド単位に並列化する手法では、個々の走査ライン(個々のバンド)のデータに対しては並列化がなされていない。そのため、最初の1走査ライン(1バンド)について処理結果が得られるまでに必要な時間が単一のプロセッサで処理を行う場合と変わらないといった問題が残る。別言すれば、複数のプロセッサで並列化しているにもかかわらず、実際に印刷が実行されるまでの立ち上がりについてはアドバンテージが得られていない。 However, in such a method of parallelizing in units of bands, data of individual scanning lines (individual bands) is not parallelized. Therefore, there remains a problem that the time required for obtaining the processing result for the first one scanning line (one band) is the same as when processing is performed by a single processor. In other words, despite the parallelization by a plurality of processors, no advantage is obtained with respect to the rise until the actual printing is executed.
また、バンド単位に並列化する手法の場合、スループットを向上させるためには、各プロセッサが自己に割り当てられたバンドについて並列に処理を実行できるように、プロセッサ数分の処理結果を格納するメモリ領域が必要となる。そのため、プロセッサ数を増やして並列度を上げていくと、それに応じて処理に必要なメモリ領域も増加してしまうという問題が生じる。 In addition, in the case of the method of parallelization in units of bands, in order to improve the throughput, a memory area for storing the processing results for the number of processors so that each processor can execute processing in parallel for the band allocated to itself. Is required. Therefore, if the number of processors is increased to increase the degree of parallelism, there arises a problem that the memory area necessary for processing increases accordingly.
本願の発明者らは、上記問題を検討した結果、個々の走査ライン(個々のバンド)について、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域(以下、「チャンネル」と呼ぶ)に分割した場合の、前記チャンネルのそれぞれに前記複数のプロセッサのうち少なくとも1つを割り当てて並列に画像処理(圧縮処理、伸長処理)を行うことで、上記目的を達成できると考えるに至った。 The inventors of the present application have studied the above problem, and as a result, the individual scanning lines (individual bands) are divided into a plurality of partial regions (hereinafter referred to as “channels”) perpendicular to the direction of the scanning lines. It has been considered that the above object can be achieved by assigning at least one of the plurality of processors to each of the channels and performing image processing (compression processing and decompression processing) in parallel.
ここで、ホスト装置からプリンタ側へ各チャンネルの圧縮データを転送する場合、高速にデータ転送すべく、各チャンネルについて同容量(例えばnバイト)の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送を行う構成とすることが望ましい。特に、ホスト装置側で並列圧縮データをSDRAM(Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)に格納しておくことで、より高速にバースト転送を行うことが可能である。 Here, when the compressed data of each channel is transferred from the host device to the printer side, burst transfer is performed in units of data sets including compressed data of the same capacity (for example, n bytes) for each channel in order to transfer data at high speed. It is desirable to have a configuration. In particular, by storing parallel compressed data in SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) on the host device side, burst transfer can be performed at higher speed.
一方、プリンタ側で複数のプロセッサを用いて並列伸長する際、各プロセッサの処理を単純化すべく、FIFO(First In First out)メモリを利用して各プロセッサが常に同じ場所から圧縮データを読み出せる構成とすることが望ましい。 On the other hand, when performing parallel decompression using a plurality of processors on the printer side, each processor can always read compressed data from the same location using a FIFO (First In First Out) memory in order to simplify the processing of each processor. Is desirable.
しかし、バースト転送とFIFOメモリとを単純に組み合せようとすると、すなわちバースト転送された圧縮データを単一のFIFOメモリに格納して伸長処理を行おうとすると、次のような問題が発生する。 However, if the burst transfer and the FIFO memory are simply combined, that is, if the compressed data subjected to the burst transfer is stored in a single FIFO memory and decompression processing is performed, the following problem occurs.
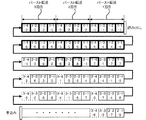
通常、1チャンネル分の圧縮データのサイズは圧縮状況に応じて異なっているため、各チャンネルについて同容量のデータセットを単位としてバースト転送を行うと、1回のバースト転送で転送されるデータセットの中にチャンネルによって異なる走査ライン(異なるバンド)の圧縮データが含まれる状況が生じうる。 Normally, the size of compressed data for one channel differs depending on the compression status. Therefore, when burst transfer is performed for each channel in units of data sets having the same capacity, the data set transferred in one burst transfer A situation may occur in which compressed data of different scan lines (different bands) is included in each channel.
かかる状況を、図16〜図18を参照して、走査ラインが4つのチャンネルに分割される場合を例に説明する。今、図16に示すように、ホスト装置において圧縮データが格納されており、図17に示すように、1チャンネルについて1バイトの圧縮データを含む計4バイトのデータセットを単位としてバースト転送を行うものとする。この場合、1回目〜6回目までのバースト転送されるデータセットの中には、各チャンネルともに第1走査ラインに関する圧縮データが含まれている。しかし、7回目にバースト転送されるデータセットでは、第1、2、4チャンネルは第1走査ラインに関する圧縮データ、第3チャンネルは第2走査ラインに関する圧縮データとなっており、チャンネルによって異なる走査ラインの圧縮データが含まれてしまう状況が生じている。 Such a situation will be described with reference to FIGS. 16 to 18 as an example in which the scanning line is divided into four channels. As shown in FIG. 16, compressed data is stored in the host device. As shown in FIG. 17, burst transfer is performed in units of a 4-byte data set including 1-byte compressed data for one channel. Shall. In this case, the first to sixth burst-set data sets include compressed data related to the first scan line for each channel. However, in the data set that is burst transferred at the seventh time, the first, second, and fourth channels are compressed data related to the first scan line, and the third channel is compressed data related to the second scan line. There is a situation where the compressed data is included.
このようにバースト転送された結果をそのままFIFOメモリに格納すると、図18に示すように、走査ラインの並びが維持されずに(すなわち、部分的に走査ラインの並びに関して逆転が生じた状態で)格納されることになる。このような状態のFIFOメモリからデータを読み出しつつ、各プロセッサの動作について走査ライン単位で同期させようとする場合、第3チャンネル担当プロセッサは、第1走査ライン第3チャンネル第6バイト目のデータ(符号1−3−6)を読み出して伸長処理を行った時点で、第1走査ラインに関する伸長処理を終了して停止し、第2走査ラインに関する伸長処理の開始を待つことになる。この場合、FIFOメモリには第2走査ライン第3チャンネル第1バイト目のデータ(符号2−3−1)が読み出されずに残るため、第4チャンネル担当プロセッサは、第1走査ライン第4チャンネル第7バイト目のデータ(符号1−4−7)を読み出すことができなくなってしまう。 When the result of burst transfer is stored in the FIFO memory as it is, the scan line sequence is not maintained as shown in FIG. 18 (that is, in a state where a partial inversion occurs with respect to the scan line sequence). Will be stored. When reading data from the FIFO memory in such a state and trying to synchronize the operation of each processor in units of scan lines, the processor in charge of the third channel reads the data in the sixth byte of the first scan line, third channel ( At the time when the code 1-3-6) is read and the expansion process is performed, the expansion process for the first scan line is terminated and stopped, and the start of the expansion process for the second scan line is awaited. In this case, since the data (reference numeral 2-3-1) of the second byte of the second scan line and third channel remains unread in the FIFO memory, the processor in charge of the fourth channel performs the first scan line and the fourth channel of the first channel. The 7th byte data (reference numeral 1-4-7) cannot be read out.
このように、バースト転送された圧縮データをそのままFIFOメモリに格納して伸長処理を行う構成では、走査ライン単位(又はバンド単位)で同期させながら並列に伸長処理を行うことができないという問題が発生することがわかった。 As described above, in the configuration in which compressed data transferred in bursts is stored in the FIFO memory as it is and decompression processing is performed, there is a problem that decompression processing cannot be performed in parallel while synchronizing in units of scan lines (or bands). I found out that
そこで、本発明は、複数のプロセッサを用いて圧縮データを並列に伸長する場合に、バースト転送された圧縮データを受け取る構成と、FIFOメモリから圧縮データを読み出して並列に伸長する構成とを両立させた上で、各プロセッサの動作を走査ライン単位又はバンド単位で同期させつつ高速に並列処理を実行できる枠組みを提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention achieves both a configuration for receiving burst-transferred compressed data and a configuration for reading compressed data from a FIFO memory and decompressing in parallel when decompressing compressed data in parallel using a plurality of processors. In addition, an object of the present invention is to provide a framework capable of executing parallel processing at high speed while synchronizing the operation of each processor in units of scan lines or bands.
上記課題を解決するために本発明の画像処理装置は、イメージを構成する走査ライン(又はバンド)について、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域に分割した場合の、前記部分領域ごとに圧縮されたデータを対象として並列に伸張処理を行う画像処理装置であって、各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプの複数のメモリと、各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されたデータを前記各部分領域の圧縮データに振り分けてそれぞれ対応するメモリに格納する格納手段と、各プロセッサが、それぞれに割り当てられた部分領域に対応するメモリから前記各部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長処理を実行する並列プロセッサユニットと、を備えることを特徴とする。 In order to solve the above-described problem, the image processing apparatus of the present invention compresses each partial area when the scan line (or band) constituting the image is divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scan line. An image processing apparatus that performs parallel decompression processing on processed data, and includes a plurality of FIFO type memories provided corresponding to each partial area, and compressed data of the same capacity for each partial area A storage means for distributing the burst-transferred data in units of sets to the compressed data of each partial area and storing it in the corresponding memory, and each processor from the memory corresponding to the allocated partial area A parallel processor that reads compressed data in a region and executes decompression processing in parallel in synchronization with each scan line (or band). Characterized in that it comprises a unit.
また、本発明のプリンタ装置は、上記画像伸長装置を備えることを特徴とする。 According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a printer apparatus comprising the image expansion apparatus.
また、本発明の画像処理システムは、イメージ圧縮部及びイメージ伸長部を含んで構成され、それぞれが複数のプロセッサを用いて並列に画像処理を行う機能を備える画像処理システムであって、イメージ圧縮部は、イメージを構成する走査ライン(又はバンド)について、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域に分割した場合の、前記部分領域のそれぞれに複数のプロセッサのうち少なくとも1つを割り当てて並列に画像圧縮処理を行い、各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてイメージ伸長部へバースト送信し、イメージ伸長部は、イメージ圧縮部からバースト転送されたデータを受信し、この受信したデータを部分領域ごとの圧縮データに振り分けて、各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプのメモリに格納し、各プロセッサは、それぞれに割り当てられた各メモリから部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に画像伸長処理を行うように制御することを特徴とする。 The image processing system of the present invention is an image processing system that includes an image compression unit and an image decompression unit, each having a function of performing image processing in parallel using a plurality of processors, and the image compression unit In a case where a scan line (or band) constituting an image is divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scan line, at least one of a plurality of processors is assigned to each of the partial areas in parallel. Image compression processing is performed, and a burst is transmitted to the image decompression unit in units of data sets containing the same amount of compressed data for each partial area. The image decompression unit receives the data burst-transferred from the image compression unit, and receives this data. The FIs provided for each partial area are allocated to the compressed data for each partial area. Each processor stores the compressed data of the partial area from each memory allocated to the O-type memory, and controls to perform image decompression processing in parallel in units of scan lines (or bands). It is characterized by that.
また、本発明の画像処理方法は、イメージを構成する走査ライン(又はバンド)について、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域に分割した場合の、前記部分領域ごとに圧縮されたデータを対象として、複数のプロセッサを用いて並列に伸長する画像伸長方法であって、各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されたデータを受信し、この受信したデータを部分領域ごとの圧縮データに振り分けて、各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプのモリに格納する工程と、各プロセッサが、それぞれに割り当てられたメモリから部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に画像伸長処理を行うように制御する工程と、を備えることを特徴とする。 Further, the image processing method of the present invention targets the compressed data for each partial area when the scan line (or band) constituting the image is divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scan line. An image decompression method for decompressing in parallel using a plurality of processors, receiving data burst-transferred in units of data sets including compressed data of the same capacity for each partial area, The process of allocating the compressed data for each area and storing it in a FIFO type memory provided corresponding to each partial area, and each processor reading and scanning the compressed data of the partial area from the memory allocated to each area And a step of performing control so that image expansion processing is performed in parallel in synchronization in units of lines (or bands). .
また、本発明の画像伸長方法は、コンピュータにより実施することができるが、そのためのコンピュータプログラムは、CD−ROM、磁気ディスク、半導体メモリ及び通信ネットワークなどの各種の媒体を通じてコンピュータにインストールまたはロードすることができる。また、コンピュータプログラムが、プリンタ用カードやプリンタ用オプションボードに記録されて流通する場合も含む。 In addition, the image decompression method of the present invention can be implemented by a computer, and a computer program therefor is installed or loaded on the computer through various media such as a CD-ROM, a magnetic disk, a semiconductor memory, and a communication network. Can do. It also includes the case where a computer program is recorded and distributed on a printer card or printer option board.
本発明によれば、複数のプロセッサを用いて圧縮データを並列に伸長する場合に、バースト転送された圧縮データを受け取る構成と、FIFOメモリから圧縮データを読み出して並列に伸長する構成とを両立させた上で、各プロセッサの動作を走査ライン単位又はバンド単位で同期させつつ高速に並列処理を実行することができる。 According to the present invention, when a plurality of processors are used to decompress compressed data in parallel, a configuration for receiving burst-transferred compressed data and a configuration for reading compressed data from a FIFO memory and decompressing in parallel are made compatible. In addition, it is possible to execute parallel processing at high speed while synchronizing the operations of the processors in units of scan lines or bands.
(第1の実施形態)
図1は、本発明の実施形態のプリンタシステム1のハードウェア構成を示すブロック図である。図1に示すように、プリンタシステム1は、ホスト装置10と、通信ネットワーク(LAN、インターネット、専用線、パケット通信網、それらの組み合わせ等のいずれであってもよく、有線、無線の両方を含む)を介して該ホスト装置10と通信可能に構成されるプリンタ装置(画像形成装置)20とを含んでいる。
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a
ホスト装置10は、メインCPU、並列処理プロセッサ11〜14を備える並列処理ユニット15、ROM、RAM、ユーザインタフェース、通信インタフェース等のハードウェアを備えている。本実施形態では、並列処理ユニット15が4つのプロセッサ11〜14を備える構成としているが、プロセッサ数は設計に応じて2以上の任意の数(例えば8)とすることができる。
The
ホスト装置10は、プリンタ装置20に印刷を実行させるため必要な通常の制御機能として、プリンタドライバ手段16を備えている。
The
プリンタドライバ手段16は、通常のプリンタドライバと同様の機能構成であり、例えば、ホスト装置10上で動作するアプリケーションプログラムからの印刷要求に応じて、ポストスクリプト等の所定のプリンタ制御言語により記述された印刷対象データに基づいてラスタイメージを生成するRIP手段、ラスタイメージに対して所定の画像処理(スクリーン処理など)を施して印刷イメージを作成する画像処理手段などを備える。
The
ただし、本実施形態のプリンタドライバ手段16は、後述するように、並列処理ユニット15を用いて個々の走査ライン(又は個々のバンド)に対して並列に画像圧縮処理を実行する圧縮制御手段17、並列処理ユニット15によって圧縮されたデータをプリンタ装置20へバースト転送する転送手段18などを備えている点で、従来の構成と異なっている(図2参照)。
However, as will be described later, the
なお、これらの各手段は、ホスト装置10内のROMやRAM、外部の記憶媒体等に格納されるプログラムをメインCPUが実行することにより機能的に実現される。
Each of these means is functionally realized by the main CPU executing a program stored in a ROM or RAM in the
プリンタ装置20は、動力機構部とプリンタコントローラ26を備えている。
The
動力機構部は、用紙をプリンタ内に供給する給紙機構、印字を行う印刷エンジン、及び用紙をプリンタ機外に排出する排紙機構等により構成される。印刷エンジンは、例えば、インクジェットプリンタや熱転写プリンタのように1文字単位で印刷するシリアルプリンタ、1行単位で印刷するラインプリンタ、ページ単位で印刷するページプリンタ等に対応する各種印刷エンジンを用いることができる。 The power mechanism unit includes a paper feed mechanism that supplies paper into the printer, a print engine that performs printing, and a paper discharge mechanism that discharges paper outside the printer. As the print engine, for example, a serial printer that prints in units of characters, such as an inkjet printer or a thermal transfer printer, a line printer that prints in units of lines, a page printer that prints in units of pages, and the like are used. it can.
プリンタコントローラ26は、メインCPU、プロセッサ21〜24を備える並列処理ユニット25、ROM、RAM、ユーザインタフェース、通信インタフェース等を備えている。なお、本実施形態では、並列処理ユニット25が4つのプロセッサ21〜24を備える構成としているが、プロセッサ数は設計に応じて2以上の任意の数(例えば8)とすることができる。また、動力機構部が独立してCPUを備えていてもよく、その場合は、動力機構部のCPUが、所定の通信路を介して情報処理部のメインCPUと通信を行い、印刷エンジンを制御して印刷動作を行わせることになる。
The
プリンタコントローラ26は、通常のプリンタにおけるプリンタコントローラと同様の機能構成であり、例えば、動力機構部を制御して印刷を実行させるエンジン制御手段やホスト装置10からコマンドやデータを受信して受信バッファに格納する受信手段27などを備える。
The
ただし、本実施形態の受信手段27は、バースト転送されたデータを受信すると、この受信したデータを部分領域ごとの圧縮データに振り分けて、各部分領域にそれぞれ対応して設けられた複数のFIFOタイプの受信バッファ(入力バッファ)にそれぞれ格納する。 However, when the receiving means 27 of this embodiment receives burst-transferred data, the receiving means 27 sorts the received data into compressed data for each partial area, and a plurality of FIFO types provided corresponding to the respective partial areas. Stored in the receiving buffer (input buffer).
また、本実施形態のプリンタコントローラ26は、各受信バッファに格納される圧縮データに基づいて、並列処理ユニット25を用いて個々の走査ライン(又は個々のバンド)に対して並列に伸長処理を実行する伸長制御手段28、並列処理ユニット25による伸長処理結果を印刷に用いられる順序で印刷エンジンへ転送する転送手段29などを備えている点で、従来の構成と異なっている(図2参照)。
Further, the
なお、これらの各手段は、プリンタ装置20内のROMやRAM、外部の記憶媒体等に格納されるプログラムをメインCPUが実行することにより実現される。
Each of these means is realized by the main CPU executing a program stored in a ROM or RAM in the
以下、図3〜図12に示すフローチャート等を参照して、プリンタシステム1における印刷処理について説明する。各工程(符号が付与されていない部分的な工程を含む)は処理内容に矛盾を生じない範囲で任意に順番を変更して又は並列に実行することができる。
Hereinafter, the printing process in the
(ホスト装置10における処理)
プリンタドライバ手段16は、外部又はホスト装置10上で動作しているアプリケーションプログラムから印刷要求を受け付けると、プリンタ装置20(プリンタコントローラ26)に対して印刷指示コマンドを送信するとともに、RIP手段などに対して処理の開始を指示する。
(Processing in the host device 10)
When the
RIP手段は、処理開始の指示を受け付けると、アプリケーションプログラムから受け取った、ポストスクリプト等の所定のプリンタ制御言語により記述された印刷対象データに基づいて、ラスタイメージを生成する。なお、アプリケーションプログラム等からラスタイメージの形式で印刷対象データを受け取ることができる場合は、RIP手段による処理は省略できる。 When the RIP unit receives an instruction to start processing, the RIP unit generates a raster image based on print target data described in a predetermined printer control language such as a postscript received from the application program. If the print target data can be received in the form of a raster image from an application program or the like, the processing by the RIP unit can be omitted.
画像処理手段は、前記生成されたラスタイメージに対して所定の画像処理(スクリーン処理など)を施し、印刷イメージを生成して、RAMの所定領域に格納する。 The image processing means performs predetermined image processing (screen processing or the like) on the generated raster image, generates a print image, and stores it in a predetermined area of the RAM.
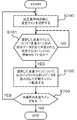
圧縮制御手段17は、前記生成された印刷イメージを構成する主走査方向のライン(以下、単に「走査ライン」と呼ぶ)を副走査方向の順に選択する(図3:ステップS100)。なお、主走査方向、副走査方向は、プリンタ装置20における走査を基準として定めるものとする。
The compression control means 17 selects lines in the main scanning direction (hereinafter simply referred to as “scanning lines”) constituting the generated print image in the order of the sub-scanning direction (FIG. 3: step S100). The main scanning direction and the sub-scanning direction are determined based on scanning in the
次に、圧縮制御手段17は、前記選択した走査ラインを、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域に分割する(図3:ステップS101)。以下では、かかる部分領域を「チャンネル」と呼び、走査ライン方向における並び順、すなわち左から順にチャンネル番号を付加して各チャンネルを識別するものとする(図4参照)。なお、本実施形態では、走査ラインが左から右へ水平に走査されることを前提として、左右という概念を用いている。 Next, the compression control means 17 divides the selected scanning line into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scanning line (FIG. 3: step S101). Hereinafter, such a partial area is referred to as a “channel”, and channel numbers are added in order of arrangement in the scanning line direction, that is, from the left to identify each channel (see FIG. 4). In the present embodiment, the concept of right and left is used on the assumption that the scanning line is scanned horizontally from left to right.
次に、圧縮制御手段17は、前記選択した走査ラインにおいて各チャンネルに含まれる印刷イメージ(以下、「部分データ」と呼ぶ)の先頭位置を特定する(図3:ステップS102)。例えば、1走査ラインが2048画素である場合、1つの走査ラインをプロセッサ数に応じて均等に4つの部分領域に分割し、第1画素、第512画素、第1024画素、第1536画素をそれぞれ部分データの先頭位置として特定することが考えられる。 Next, the compression control means 17 specifies the head position of the print image (hereinafter referred to as “partial data”) included in each channel in the selected scanning line (FIG. 3: step S102). For example, when one scan line is 2048 pixels, one scan line is equally divided into four partial areas according to the number of processors, and the first pixel, the 512th pixel, the 1024th pixel, and the 1536th pixel are respectively partial. It may be possible to specify the head position of data.
なお、全走査ラインに共通してチャンネルを定め、予め各チャンネルの部分データの先頭位置を特定しておけば、ステップS101〜102は省略することができる。 Note that steps S101 to S102 can be omitted if channels are defined in common for all scanning lines and the head position of partial data of each channel is specified in advance.
次に、圧縮制御手段17は、前記複数のチャンネルのそれぞれにプロセッサ11〜14のうち少なくとも1つを割り当てる(図3:ステップS103)。具体的には、チャンネル1にはプロセッサ11、チャンネル2にはプロセッサ12というように、チャンネルとプロセッサの組み合わせを固定して割り当てるものとする。
Next, the compression control means 17 assigns at least one of the
次に、圧縮制御手段17は、前記割り当てたプロセッサが新たなデータを処理できるかどうかを判断し、処理できる場合には、対応する部分データの先頭位置を前記割り当てたプロセッサに渡し、該部分データの読み出しを指示する(図3:ステップS104)。 Next, the compression control means 17 determines whether or not the allocated processor can process new data. If the allocated data can be processed, the compression control means 17 passes the head position of the corresponding partial data to the allocated processor, and the partial data Is read (FIG. 3: Step S104).
ここで、プロセッサが新たなデータを処理できる場合とは、該プロセッサが次の処理結果を新たに書き込むことができる場合である。例えば、処理結果を書き込む領域として、プロセッサ11〜14(チャンネル1〜4)に対して図16に示すように出力バッファの一部領域をそれぞれ割り当てる場合、該出力バッファの割当領域に空きがあるか、又は割当領域に既に書き込まれた処理結果について転送手段18による転送が終了し上書きすることができるかどうかに基づいて、新たなデータを処理できるかどうかを判断すればよい。
Here, the case where the processor can process new data is a case where the processor can newly write the next processing result. For example, when a partial area of the output buffer is assigned to each of the
なお、出力バッファは、高速にバースト転送を行うことができるSDRAMにより構成することが望ましい。後述するように、出力バッファに書き込まれた処理結果(圧縮データ)は転送手段18によってバースト転送されるからである。 Note that the output buffer is preferably constituted by an SDRAM capable of performing burst transfer at high speed. This is because the processing result (compressed data) written in the output buffer is burst transferred by the transfer means 18 as will be described later.
次に、圧縮制御手段17は、前記生成された印刷イメージを構成する走査ラインのうち未選択の走査ラインがある場合は、ステップS100に戻る(図3:ステップS105)。 Next, when there is an unselected scan line among the scan lines constituting the generated print image, the compression control means 17 returns to Step S100 (FIG. 3: Step S105).
並列処理ユニット15の各プロセッサ11〜14は、圧縮制御手段17から部分データの先頭位置及び読み出し指示を受け付けると(図5:ステップS200:YES)、前記生成した印刷イメージを格納したRAMの所定領域から該先頭位置に基づいて部分データを読み出す(図5:ステップS201)。
When each of the
次に、前記読み出した部分データに対して所定の圧縮処理を実行して部分圧縮データを生成する(図5:ステップS202)。このとき、部分圧縮データの境界が検出できるように、部分圧縮データの終端に(又は最初に)所定の境界情報を追加しておく。なお、所定の圧縮処理としては、設計に応じて従来の種々の圧縮アルゴリズムを採用することができ、例えば印刷イメージが2値データの場合であれば、JBIG(Joint Bi−level Image Experts Group)のアルゴリズムを採用することが考えられる。 Next, a predetermined compression process is performed on the read partial data to generate partial compressed data (FIG. 5: step S202). At this time, predetermined boundary information is added to the end (or first) of the partially compressed data so that the boundary of the partially compressed data can be detected. As the predetermined compression processing, various conventional compression algorithms can be adopted depending on the design. For example, if the print image is binary data, JBIG (Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group). It is conceivable to adopt an algorithm.
そして、前記生成した部分圧縮データを出力バッファの割り当てられた一部領域に書き込む(図5:ステップS203)。なお、図16に示すように各プロセッサに出力バッファの一部領域を割り当てる場合、各プロセッサが次に書き込みを行うアドレス(カレントアドレス)を参照できるように、例えばプロセッサごとにカレントアドレスを格納するカウンタを設け、書き込んだ容量(バイト数)に応じてカウンタを加算する構成を採用することが考えられる。 Then, the generated partial compressed data is written in a partial area assigned to the output buffer (FIG. 5: step S203). When assigning a partial area of the output buffer to each processor as shown in FIG. 16, for example, a counter that stores the current address for each processor so that each processor can refer to the address (current address) to be written next. It is conceivable to adopt a configuration in which a counter is added according to the written capacity (number of bytes).
転送手段18は、前記生成された印刷イメージについて、出力バッファに未転送のデータがあるかどうかを判断する(図6:ステップS300)。そして、未転送のデータがない(転送が終了している)場合は、処理を終了する。
The
一方、未転送のデータがある場合、転送手段18は、例えばプリンタ装置20(プリンタコントローラ26)との通信結果に基づいて、プリンタ装置20(プリンタコントローラ26)が部分圧縮データを受信可能であるかどうかを判断する(図6:ステップS301)。
On the other hand, if there is untransferred data, the
そして、受信可能である場合、各チャンネルにつき同容量の部分圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送を行うように、出力バッファからプリンタ装置20(プリンタコントローラ26)へのデータ転送を制御する(図6:ステップS302)。 If reception is possible, data transfer from the output buffer to the printer device 20 (printer controller 26) is controlled so that burst transfer is performed in units of data sets including partially compressed data of the same capacity for each channel ( FIG. 6: Step S302).
なお、バースト転送を行うデータセットのサイズは設計に応じて定めることができるが、本実施形態では、図7に示すように、各チャンネルにつき8バイト分の部分圧縮データを含む計32バイト(4チャンネル×8バイト)のデータセットを単位として、バースト転送を行うものとする。このようにバースト転送を行う場合、バースト転送されるデータセットには複数の走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データが含まれる可能性がある。図7を参照すると、1回目のバースト転送では、第1走査ラインと第2走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データが含まれていることがわかる。 Although the size of the data set for burst transfer can be determined according to the design, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7, a total of 32 bytes (4 bytes including partial compressed data for 8 bytes for each channel). It is assumed that burst transfer is performed in units of a data set of (channel × 8 bytes). When burst transfer is performed in this way, there is a possibility that partially compressed data relating to a plurality of scan lines is included in the data set to be burst transferred. Referring to FIG. 7, it can be seen that the first burst transfer includes partially compressed data relating to the first scan line and the second scan line.
(プリンタ装置20における処理)
プリンタコントローラ26は、ホスト装置10から印刷指示コマンドが送られると、受信手段27を介してこれを受信するとともに、エンジン制御手段により動力機構部を制御して印刷の準備を整える。
(Processing in the printer device 20)
When a print instruction command is sent from the
受信手段27は、印刷指示コマンドの受信後、バースト転送されたデータセットを受信すると(図8:ステップS400のYes)、受信バッファへの格納処理を実行する。
When receiving the print instruction command and receiving the burst-transferred data set (FIG. 8: Yes in step S400), the receiving
ここで、受信バッファは、上述したようにホスト装置10から各チャンネルの部分圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されてくるデータを、チャンネル毎の部分圧縮データに振り分けて格納するためのバッファとなることから、例えばRAM上に図9に示すようなFIFOタイプのバッファをチャンネル毎に構成することが考えられる(又はFIFOタイプメモリをチャンネル毎に複数設けるように構成することも可能である)。図9(A)に示す例では、バースト転送されたデータをチャンネル毎に振り分けて格納できるように、チャンネルの数に応じた4つの受信バッファが構成されている。
Here, as described above, the reception buffer is a buffer for allocating and storing data that is burst-transferred from the
受信手段27は、バースト転送を行うデータセットの設定に従って(Nチャンネル×Mバイト)、バースト転送されたデータをチャンネル毎の部分圧縮データに振り分ける。具体的には、受信手段27は、チャンネルの並び順に受信バッファを選択する(図8:ステップS401)。そして、受信したデータから1チャンネル容量分のデータ(1チャンネル分の部分圧縮データ)を取り出して、選択した受信バッファへ格納する(図8:ステップS402)例えば、本実施形態では、ホスト装置10から各チャンネルにつき8バイトの部分圧縮データを含む計32バイトのデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されてくる構成であるので、受信手段27は、チャンネル1に対応する受信バッファ1を選択すると、受信したデータから8バイト分のデータを取り出して受信バッファ1に格納する。
The receiving means 27 distributes the burst-transferred data to the partial compressed data for each channel according to the setting of the data set for burst transfer (N channels × M bytes). Specifically, the receiving means 27 selects a receiving buffer in the order of channel arrangement (FIG. 8: step S401). Then, data for one channel capacity (partially compressed data for one channel) is extracted from the received data and stored in the selected reception buffer (FIG. 8: step S402). For example, in this embodiment, from the
受信手段27は、全てのチャンネルのデータについて受信バッファへの格納処理を終えたか否か判断し(図8:ステップS403)、格納処理を終えていないと判断した場合は(図8:ステップS403のNo)、残りのチャンネルのデータを処理するためにS401に戻る。一方、全てのチャンネルのデータについて格納処理を終えたと判断した場合は(図8:ステップS403のYes)、処理を終了し、伸張制御手段28へ伸張処理の開始を指示する。これにより、1回目のバースト転送により受信したデータの各受信バッファへの格納処理が終了する。
The receiving means 27 determines whether or not the storage process for the data of all channels has been completed (FIG. 8: step S403), and if it is determined that the storage process has not been completed (FIG. 8: step S403). No), the process returns to S401 to process the remaining channel data. On the other hand, if it is determined that the storage process has been completed for all the channel data (FIG. 8: Yes in step S403), the process ends, and the
このように受信バッファをチャンネルの数に応じて複数構成した場合、チャンネル1の部分圧縮データは受信バッファ1に連続して格納され、チャンネル2の部分圧縮データは受信バッファ2に連続して格納され、チャンネルNの部分圧縮データは受信バッファNに連続して格納されることとなる。つまり、各チャンネルの部分圧縮データは、図9(B)に示すように各チャンネルに対応する受信バッファに格納されるので、並列処理ユニット25の各プロセッサは、常に同じ場所(受信バッファ)を特定して、各プロセッサに割り当てられたチャンネルの部分圧縮データを読み出すことができる。
When a plurality of reception buffers are configured in accordance with the number of channels in this way, the partial compressed data of
伸張制御手段28は、伸張処理開始の指示を受け付けると、チャンネルごとに用意される伸張フラグに初期値として”未終了”をセットする(図10:ステップS500)。かかる伸張フラグは、後述するように、各チャンネルにおいて1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸張が終了した場合に”終了”に変更されることになる。
When the
次に、伸張制御手段28は、並列処理ユニット25の各プロセッサ21〜24に対して、それぞれ割り当てられたチャンネルに対応する受信バッファからの部分圧縮データの読み出しを指示する(図10:ステップS501)。そして、全てのチャンネルの伸張フラグが”終了”となっているか否かを判断し(図10:ステップS502)、全ての伸張フラグが”終了”となっている場合には、1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸張が終了したとみなし、受信バッファに部分圧縮データが未だ格納されているか否かを判断する(図10:ステップS503)。そして、受信バッファに部分圧縮データが格納されている場合には、次の走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸張処理を行うために、S500に戻る。
Next, the decompression control means 28 instructs each of the
一方、伸張制御手段28は、S502にて全ての伸張フラグが”終了”となっていないと判断した場合には、1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸張が未だ終了していないとみなして、伸張フラグをチェックする(図10:ステップS502)。 On the other hand, if the decompression control means 28 determines in S502 that all the decompression flags are not “finished”, it regards that the decompression of the partial compressed data related to one scanning line has not yet been finished, The decompression flag is checked (FIG. 10: Step S502).
次に、並列処理ユニット25の各プロセッサ21〜24の伸張処理について説明する。本実施形態では、各プロセッサ21〜24には、あらかじめ処理すべきチャンネルと部分圧縮データを読み出すべき受信バッファが割り当てられているが、伸張制御手段28が、処理を開始する際に、各プロセッサ21〜24に対して処理すべきチャンネルを割り当てる構成としてもよい。
Next, decompression processing of each of the
各プロセッサ21〜24は、伸張制御手段28から部分圧縮データの読み出し指示を受け付けると(図11:S600)、それぞれが割り当てられている受信バッファから部分圧縮データを1バイトずつ読み出す(図11:ステップS601)。
When each
次に、各プロセッサ21〜24は、この読み出した1バイトデータに対して所定の伸長処理を実行して、対応する部分データの一部を生成し(図11:ステップS602)、プリンタコントローラ26の出力バッファに格納する(図11:ステップS603)。なお、伸長処理は、ホスト装置10の並列処理ユニット15において採用した圧縮アルゴリズムに対応する伸長処理を採用する必要がある。
Next, each of the
次に、各プロセッサ21〜24は、前記読み出した1バイトデータが部分圧縮データの終端を示す情報を含んでいるか否かを判断する(図11:ステップS604)。そして、読み出した1バイトデータが部分圧縮データの終端を示す情報を含んでいない場合は(図11:ステップS604のYes)、続けて伸張処理を実行すべくS601に戻る。
Next, each of the
一方、終端を示す情報を含んでいる場合は(図11:ステップS604のNo)、自己の伸張フラグを”終了”に変更するとともに(図11:ステップS605)、走査ラインでの同期を実現すべく、処理を停止する。 On the other hand, when the information indicating the end is included (FIG. 11: No in step S604), the expansion flag is changed to “end” (FIG. 11: step S605), and synchronization on the scanning line is realized. Therefore, the process is stopped.
このように、本実施形態では、各チャンネルつまりプロセッサごとに受信バッファを設ける構成としたので、各プロセッサが1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸長処理が終わったところで処理を停止する構成(すなわち走査ライン単位で同期して動作する構成)としても、並列に伸長処理を行うことが可能となる。 As described above, in this embodiment, since a reception buffer is provided for each channel, that is, for each processor, each processor stops processing when decompression processing of partial compressed data for one scan line is completed (that is, scanning). Even in a configuration that operates synchronously in line units, it is possible to perform decompression processing in parallel.
転送手段29は、印刷に用いられる順序でデータを送信すべく、副走査方向の順に走査ラインを選択する(図12:ステップS700)。
The
次に、転送手段29は、前記選択した走査ラインについて、1走査ライン分の部分データが全て伸長された状態で出力バッファに格納されているかどうかを判断する(図12:ステップS701)。
Next, the
そして、全て伸長された状態で格納されていると判断した場合に、印刷に用いられる順序でデータを送信すべく、前記選択した走査ラインについて出力バッファから部分データを読み出して印刷エンジンへ転送する(図12:ステップS702)。 If it is determined that the data is stored in an expanded state, partial data is read from the output buffer for the selected scan line and transferred to the print engine in order to transmit the data in the order used for printing. FIG. 12: Step S702).
その後、転送手段29は、前記生成された印刷イメージについて未選択の走査ラインがある場合は、S700に戻る(図12:ステップS703)。
Thereafter, when there is an unselected scan line for the generated print image, the
本実施形態の構成によれば、1つの走査ラインを構成する各チャンネルに対して(すなわち、各部分データに対して)並列に圧縮処理が実行されるため、個々の走査ラインについての圧縮処理時間を短縮することができる。特に、最初の1走査ラインの圧縮処理時間が短縮されることで、印刷イメージの圧縮処理を開始してから最初の走査ラインの圧縮処理が終了し、その処理結果がプリンタ装置20(プリンタコントローラ26)へ転送されるまでの時間を短縮すること可能となり、立ち上がりの早い圧縮処理(ひいては印刷処理)を実現することができる。 According to the configuration of the present embodiment, the compression processing is performed in parallel for each channel constituting one scan line (that is, for each partial data), so the compression processing time for each scan line Can be shortened. In particular, since the compression processing time for the first scan line is shortened, the compression processing for the first scan line is completed after the compression processing for the print image is started, and the processing result is the printer device 20 (printer controller 26). It is possible to shorten the time until the data is transferred to (), and it is possible to realize a compression process (and thus a print process) that starts quickly.
同様に、1つの走査ラインを構成する各チャンネルに対して(すなわち、各部分圧縮データに対して)並列に伸長処理が実行されるため、個々の走査ラインについての伸長処理時間を短縮することができる。特に、最初の1走査ラインの伸長処理時間が短縮されることで、圧縮された印刷イメージの伸長処理を開始してから最初の走査ラインについて伸長処理が終了し、その処理結果が印刷エンジンへ転送されるまでの時間を短縮すること可能となり、立ち上がりの早い伸長処理(ひいては印刷処理)を実現することができる。 Similarly, since decompression processing is executed in parallel for each channel constituting one scan line (that is, for each partial compressed data), the decompression processing time for each scan line can be shortened. it can. In particular, since the decompression time of the first scan line is shortened, the decompression process is completed for the first scan line after the decompression process of the compressed print image is started, and the processing result is transferred to the print engine. It is possible to shorten the time until the image is processed, and it is possible to realize a decompression process (and thus a print process) that starts quickly.
更に、プリンタコントローラ26において、バースト転送された部分圧縮データを格納する受信バッファを、各チャンネルにそれぞれ対応する複数のFIFOタイプの受信バッファとして構成しているため、バースト転送された部分圧縮データを受け取る構成と、FIFOタイプの受信バッファから部分圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長する構成とを両立させた上で、高速に並列処理を実行できる枠組みを提供することができる。その結果、一定速度で走査ライン単位の印刷データをエンジンに供給し続ける必要があるレーザプリンタ等に対してもリアルタイムに対応することができる。
Further, in the
(第2の実施形態)
第1の実施形態は、各プロセッサが1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの伸長処理が終わったところで処理を停止する構成(すなわち走査ライン単位で同期して動作する構成)について説明したが、第2の実施形態は、各プロセッサは走査ライン単位で同期をとることなく伸張処理を実行することで、各プロセッサの処理の高速化を図ろうとするものである。
(Second Embodiment)
In the first embodiment, the configuration in which each processor stops processing when the partial compressed data decompression processing for one scan line is completed (that is, the configuration that operates synchronously in units of scan lines) has been described. In this embodiment, each processor performs expansion processing without synchronizing in units of scan lines, thereby increasing the processing speed of each processor.
ただし、各プロセッサが同期をとることなく伸張処理をする構成とすると、出力バッファには、チャンネルによって異なる走査ラインの部分伸張データが含まれてしまうという状況が生じする
そこで、第2の実施形態は、各プロセッサの部分伸張データをそれぞれ格納するための中間出力バッファをチャンネルごとに設けるとともに、この中間出力バッファに格納された部分伸張データを、走査ライン単位で出力バッファに格納するように制御することとした。以下に、図13〜図15を用いて第2の実施形態にかかる伸張処理について詳細に説明する。なお、ホスト装置10における処理は、第1の実施形態における処理と同様の構成であるので、ここでは説明を省略する。
However, if each processor is configured to perform decompression processing without synchronization, a situation occurs in which the output buffer includes partial decompression data for different scan lines depending on the channel. Therefore, in the second embodiment, In addition, an intermediate output buffer for storing the partial decompression data of each processor is provided for each channel, and the partial decompression data stored in the intermediate output buffer is controlled to be stored in the output buffer in units of scanning lines. It was. Hereinafter, the decompression processing according to the second embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. Note that the processing in the
まず、本実施形態にかかるプリンタコントローラ26は、第1の実施形態にて説明した各機能に加えて、各プロセッサが伸張した部分伸張データをチャンネルごとに格納する中間出力バッファから、1走査ライン分の部分伸張データを読み出して出力バッファに転送するデータ順序調整手段30を備える(図13を参照)。
First, in addition to the functions described in the first embodiment, the
次に、本実施形態におけるプリンタ装置20における処理について説明する。第1の実施形態と同様に、受信手段27は、バースト転送された部分圧縮データをチャンネル毎の部分圧縮データに振り分けて、それぞれの受信バッファへ格納する(図8のフローチャートを参照)。そして、受信手段27は、全てのチャンネルのデータについて格納処理を終えたと判断した場合は、処理を終了し、並列処理ユニット25の各プロセッサ21〜24に対して、それぞれに割り当てられた受信バッファからの部分圧縮データの読み出しを指示する。
Next, processing in the
各プロセッサ21〜24は、受信手段27から部分圧縮データの読み出し指示を受け付けると、それぞれが割り当てられている受信バッファから部分圧縮データを1バイトずつ読み出す。そして、各プロセッサ21〜24は、この読み出した1バイトデータに対して所定の伸長処理を実行して対応する部分データの一部を生成し、図14に示すように、それぞれ対応する中間出力バッファ1〜4に格納する。図14は、チャンネル毎に設けられた中間出力バッファを説明するための図である。
When each of the
このとき、各プロセッサ21〜24は、前記読み出した1バイトデータが部分圧縮データの終端を示す情報を含んでいるか否かを判断する。そして、読み出した1バイトデータが部分圧縮データの終端を示す情報を含んでいる場合は、伸張した部分データの境界が検出できるように、伸張した部分データの終端に(又は最初に)所定の境界情報を追加しておく。
At this time, each of the
次に、データ順序調整手段30は、チャンネルごとに用意される転送フラグに初期値として”未終了”をセットする(図15:ステップS800)。かかる転送フラグは、後述するように、各チャンネルにおいて1つの走査ラインに関する部分圧縮データの転送(中間出力バッファから出力バッファへの転送)が終了した場合に”終了”に変更されることになる。
Next, the data
次に、データ順序調整手段30は、チャンネルの並び順にチャンネルを選択する(図15:ステップS801)。そして、前記選択したチャンネルの転送フラグをチェックし、転送フラグが”終了”となっている場合は、S801に戻る(図15:ステップS802)。 Next, the data order adjusting means 30 selects the channels in the order of the channels (FIG. 15: Step S801). Then, the transfer flag of the selected channel is checked, and if the transfer flag is “end”, the process returns to S801 (FIG. 15: step S802).
一方、転送フラグが”未終了”となっている場合は、データ順序調整手段30は、中間出力バッファ1〜4のうち前記選択したチャンネルに対応する中間出力バッファを特定し、この特定した中間出力バッファに格納された未転送の部分伸張データから1バイト分のデータを選択する(図15:ステップS803)。
On the other hand, when the transfer flag is “unfinished”, the data
次に、データ順序調整手段30は、前記選択した1バイトデータを出力バッファに転送するとともに(図15:ステップS804)、前記選択した1バイトデータが部分伸張データの終端を示す情報を含んでいるか否か判断する(図15:ステップS805)。
Next, the data
前記選択した1バイトデータが部分伸張データの終端を示す情報を含んでいない場合には、データ順序調整手段30は、ステップS803に戻り、次の1バイト分のデータについて転送処理を実行する。一方、前記選択した1バイトデータが部分伸張データの終端を示す情報を含んでいる場合は、前記選択したチャンネルの転送フラグを”終了”に変更する(図15:ステップS806)。
If the selected 1-byte data does not include information indicating the end of the partial decompression data, the data
次に、データ順序調整手段30は、転送フラグが”未終了”となっているチャンネルがある場合(図15:ステップS807のYes)、すなわち1つの走査ラインについて全チャンネルの部分伸張データの転送が終了していない場合、次のチャンネルを選択すべく、S801に戻る。
Next, when there is a channel whose transfer flag is “incomplete” (FIG. 15: Yes in step S807), the data
一方、全てのチャンネルの転送フラグが”終了”となっている場合(図15:ステップS807のNo)、データ順序調整手段30は、中間出力バッファ1〜4に転送すべきデータ(未転送の走査ライン伸張データ)が残っているかどうかを判断する(図15:ステップS808)。そして、残っている場合は、次の走査ラインについて転送処理をすべく、S800に戻る。
On the other hand, when the transfer flags of all the channels are “end” (FIG. 15: No in step S807), the data
次に、転送手段29は、第1の実施形態と同様に、印刷に用いられる順序でデータを送信すべく副走査方向の順に走査ラインを選択し、この選択した走査ラインについて1走査ライン分の部分データが全て伸長された状態で出力バッファに格納されているかどうかを判断する。そして、全て伸長された状態で格納されていると判断した場合に、印刷に用いられる順序でデータを送信すべく、前記選択した走査ラインについて出力バッファから部分データを読み出して印刷エンジンへ転送する(図12のフローチャートを参照)。
Next, as in the first embodiment, the
このように処理を構成した場合、各プロセッサは、各チャンネルのデータを個別に伸張処理することができるとともに、全チャンネルの転送フラグが”終了”となるまでに転送される一連のデータは、1つの走査ラインに関する部分データに属することとなるので、出力バッファには、走査ラインの並び順が維持された状態で、1つの走査ラインに属する部分データが連続して、格納されることになる。その結果、走査ライン単位で同期をとりつつ印刷エンジンへ転送するとともに、各プロセッサの伸張処理を高速に実行することができるようになる。 When the processing is configured in this way, each processor can individually decompress the data of each channel, and a series of data transferred until the transfer flag of all the channels is “finished” is 1 Since it belongs to partial data relating to one scanning line, partial data belonging to one scanning line is continuously stored in the output buffer in a state where the arrangement order of the scanning lines is maintained. As a result, the image data is transferred to the print engine while being synchronized in units of scan lines, and the decompression process of each processor can be executed at high speed.
(その他の実施形態)
本発明は上記実施形態に限定されることなく、種々に変形して適用することが可能である。例えば、本発明は、イメージを圧縮/伸長するシステムであれば、プリンタシステム以外に対しても適用することができる。
(Other embodiments)
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and can be variously modified and applied. For example, the present invention can be applied to a system other than a printer system as long as the system compresses / decompresses an image.
また例えば、上記実施形態では、プリンタ装置20が並列処理ユニット25、プリンタコントローラ26を備える構成としているが、本発明は必ずしもこのような構成に限られない。例えば並列処理ユニット25やプリンタコントローラ26をプリンタ装置20に接続可能な外部装置として構成することも考えられる。更には、並列処理ユニット25やプリンタコントローラ26を例えばPCIバス等の規格によりホスト装置10に接続可能な装置として構成してもよい。並列処理ユニット25をホスト装置10に接続する構成の場合、ホスト装置10のメインCPU等によってプリンタコントローラ26の各機能を実現する構成としてもよい。
For example, in the above-described embodiment, the
また例えば、上記実施形態では、1走査ラインをプロセッサ数に応じて均等に部分領域に分割する構成について説明したが、例えばプロセッサのスペック等に応じて割り当てる部分領域の大小を変えるなど、必ずしも均等に分割しなくてもよい。また、部分領域の分割数(チャンネル数)は、必ずしもプロセッサ数と等しくなくてもよい。 For example, in the above-described embodiment, the configuration in which one scan line is equally divided into partial areas according to the number of processors has been described. However, for example, the size of the partial area to be allocated is changed according to the processor specifications and the like. It is not necessary to divide. Further, the number of divisions (number of channels) of the partial area is not necessarily equal to the number of processors.
また例えば、上記実施形態では、チャンネルとプロセッサの組み合わせを固定して割り当てる構成について説明したが、例えば、処理が終了したプロセッサを次のチャンネルに割り当てるように構成してもよい。この場合、走査ラインごとにプロセッサとチャンネルの対応関係が異なる可能性がある。なお、並列処理ユニット15、25のプロセッサのみならず、メインCPUに対してもチャンネルを割り当てて、並列処理を実行する構成としてもよい。
Further, for example, in the above-described embodiment, the configuration in which the combination of the channel and the processor is fixedly described has been described. However, for example, the processor that has completed the processing may be allocated to the next channel. In this case, the correspondence between the processor and the channel may be different for each scan line. Note that not only the processors of the
また例えば、上記実施形態では、プロセッサ11〜14がRAMから部分データを読み出す構成について説明としたが、例えばホスト装置10がRAMからプロセッサ11〜14へ部分データを転送する手段(例えば、DMA転送手段)を備える場合は、圧縮制御手段は該手段に対して指示を行えばよい。この場合、プロセッサ11〜14は該手段からの転送を受けて処理を実行することになる。同様に、例えばプリンタ装置20がデータ受信バッファからプロセッサ21〜24へ部分圧縮データを転送する手段(例えば、DMA転送手段)を備える場合は、伸長制御手段は該手段に対して指示を行えばよく、プロセッサ21〜24は該手段からの転送を受けて処理を実行することになる。
Further, for example, in the above embodiment, the configuration in which the
また例えば、上記実施形態では、印刷イメージの全走査ラインについて並列処理を行う構成について説明したが、印刷イメージを構成する少なくとも1つの走査ラインについて本発明を適用すれば、該走査ラインについて圧縮処理時間/伸長処理時間の短縮という効果を得ることができる。 Further, for example, in the above-described embodiment, the configuration in which the parallel processing is performed for all the scan lines of the print image has been described. However, if the present invention is applied to at least one scan line constituting the print image, the compression processing time for the scan line is determined. / An effect of shortening the extension processing time can be obtained.
また例えば、上記実施形態では、転送手段29が1走査ライン分のデータが揃ったところで印刷エンジンへデータを転送する構成について説明しているが、印刷エンジンのタイプによっては、1走査ライン分のデータが揃うのを待つことなく、又は複数走査ライン分のデータが揃ったところで、印刷エンジンへデータを転送する構成としてもよい。
Further, for example, in the above-described embodiment, a configuration has been described in which the
また例えば、上記実施形態では、圧縮処理、伸長処理、同期させる単位について、いずれも走査ラインを基準として構成しているが、本発明は必ずしもこのような構成に限られるものではない。例えば、所定数の走査ラインを含んで構成されるバンドを基準として処理を構成してもよい。この場合、原則として上記実施形態において「走査ライン」を「バンド」に置き換えて処理を構成すればよいが、いくつかの工程については当業者に自明な範囲での変更が必要となる。例えば、ステップS102については、圧縮制御手段17は、選択したバンドにおける各チャンネルの部分データの先頭位置として、バンドに含まれる走査ラインごとに先頭アドレスを特定する必要がある。なお、バンドを基準にする構成を前提とすると、上記実施形態は1走査ライン=1バンドとした場合の態様と考えることもできる。 For example, in the above embodiment, the compression processing, the decompression processing, and the unit to be synchronized are all configured based on the scanning line, but the present invention is not necessarily limited to such a configuration. For example, the processing may be configured on the basis of a band including a predetermined number of scanning lines. In this case, in principle, the processing may be configured by replacing “scan lines” with “bands” in the above-described embodiment, but some steps need to be changed within a range obvious to those skilled in the art. For example, for step S102, the compression control means 17 needs to specify the head address for each scanning line included in the band as the head position of the partial data of each channel in the selected band. Assuming a configuration with a band as a reference, the above embodiment can be considered as an aspect in which one scanning line = 1 band.
1 プリンタシステム、10 ホスト装置、 11〜14 並列処理用プロセッサ、 15 並列処理ユニット、 16 プリンタドライバ手段、 17 圧縮制御手段、 18 転送手段、 20 プリンタ装置、 21〜24 並列処理用プロセッサ、 25 並列処理ユニット、 26 プリンタコントローラ、 27 受信手段、 28 伸長制御手段、 29 転送手段
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプの複数のメモリと、
各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されたデータを、前記各部分領域の圧縮データに振り分けてそれぞれ対応するメモリに格納する格納手段と、
各プロセッサが、それぞれに割り当てられた部分領域に対応するメモリから前記各部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長処理を実行する並列プロセッサユニットと、を備え、
前記各部分領域の圧縮データは、当該圧縮データの終端に当該圧縮データが生成される際に追加された所定の境界情報を含んでおり、
前記バースト転送されるデータセットは、前記部分領域によって異なる走査ライン(又はバンド)の圧縮データを含んでおり、
前記各プロセッサは、前記メモリから読み出した前記各部分領域の圧縮データが前記所定の境界情報を含んでいるか否かを判断し、前記所定の境界情報を含んでいる場合は、自己の伸長処理を停止することにより、前記走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長処理を実行することを特徴とする画像伸長装置。 An image processing device that performs decompression processing in parallel on data compressed for each partial area when the scanning line (or band) constituting the image is divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scanning line Because
A plurality of FIFO type memories provided corresponding to the respective partial areas;
Storage means for allocating the data burst-transferred in units of data sets including the same amount of compressed data for each partial area, and storing the data in the corresponding memory by allocating the compressed data of each partial area;
Each processor, and a parallel processor unit for executing expansion processing in parallel in synchronization with the scan line (or band) unit compressed data reads of each partial area from the memory corresponding to the allocated portion region, respectively, the Prepared,
The compressed data of each partial area includes predetermined boundary information added when the compressed data is generated at the end of the compressed data,
The burst transferred data set includes compressed data of scan lines (or bands) that vary depending on the partial area.
Each of the processors determines whether or not the compressed data of each partial area read from the memory includes the predetermined boundary information. When the predetermined boundary information is included, the processor performs its own decompression process. An image decompression apparatus that performs decompression processing in parallel in synchronization with each scanning line (or band) by stopping .
イメージ圧縮部は、
イメージを構成する走査ライン(又はバンド)について、走査ラインの方向と垂直に複数の部分領域に分割した場合の、前記部分領域のそれぞれに複数のプロセッサのうち少なくとも1つを割り当てて並列に画像圧縮処理を行い、各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてイメージ伸長部へバースト送信し、
イメージ伸長部は、
イメージ圧縮部からバースト転送されたデータを受信し、この受信したデータを部分領域ごとの圧縮データに振り分けて、各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプのメモリに格納し、各プロセッサは、それぞれに割り当てられた各メモリから部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に画像伸長処理を行うように制御し、
前記イメージ圧縮部は、前記各部分領域の圧縮データの終端に所定の境界情報を追加し、前記部分領域によって異なる走査ライン(又はバンド)の圧縮データを含むデータセットを前記イメージ伸長部へバースト送信し、
前記イメージ伸長部は、
前記各プロセッサが、前記メモリから読み出した前記各部分領域の圧縮データが前記所定の境界情報を含んでいるか否かを判断し、前記所定の境界情報を含んでいる場合は、自己の伸長処理を停止することにより、前記走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長処理を実行することを特徴とする画像処理システム。 An image processing system including an image compression unit and an image expansion unit, each having a function of performing image processing in parallel using a plurality of processors,
The image compression unit
When scanning lines (or bands) constituting an image are divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scanning lines, at least one of a plurality of processors is assigned to each of the partial areas and image compression is performed in parallel. Perform processing, burst transmission to the image expansion unit in units of data sets containing the same amount of compressed data for each partial area,
Image decompression section
The data transferred in burst from the image compression unit is received, the received data is distributed into compressed data for each partial area, and stored in a FIFO type memory provided for each partial area. The compressed data of the partial area is read from each memory allocated to each , and controlled so as to perform image expansion processing in parallel in synchronization with each scanning line (or band) ,
The image compression unit adds predetermined boundary information to the end of the compressed data of each partial area, and burst-transmits a data set including compressed data of scan lines (or bands) that differ depending on the partial area to the image expansion unit. And
The image decompression unit
Each processor determines whether or not the compressed data of each partial area read from the memory includes the predetermined boundary information. If the processor includes the predetermined boundary information, the processor performs its own decompression process. by stopping the image processing system characterized that you execute the decompression processing in parallel in synchronization with the scan line (or band) units.
各部分領域につき同容量の圧縮データを含むデータセットを単位としてバースト転送されたデータを受信し、この受信したデータを部分領域ごとの圧縮データに振り分けて、各部分領域それぞれに対応して設けられたFIFOタイプのメモリに格納する工程と、
各プロセッサが、それぞれに割り当てられたメモリから部分領域の圧縮データを読み出して走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に画像伸長処理を行うように制御する工程と、を備え、
前記メモリに格納する工程は、前記各部分領域の圧縮データの終端に所定の境界情報を追加し、前記部分領域によって異なる走査ライン(又はバンド)の圧縮データを含むデータセットを前記イメージ伸長部へバースト送信する工程を含み、
前記制御する工程は、前記各プロセッサが、前記メモリから読み出した前記各部分領域の圧縮データが前記所定の境界情報を含んでいるか否かを判断し、前記所定の境界情報を含んでいる場合は、自己の伸長処理を停止することにより、前記走査ライン(又はバンド)単位で同期して並列に伸長処理を実行するように制御することを特徴とする画像伸長方法。 A scan line (or band) constituting an image is divided into a plurality of partial areas perpendicular to the direction of the scan line, and the compressed data compressed for each partial area is used as a target in parallel using a plurality of processors. An image decompression method that decompresses
Receives data transferred in bursts in units of data sets containing the same amount of compressed data for each partial area, and distributes the received data to compressed data for each partial area. and the step of storing the FIFO type of memory was,
Each processor reads out the compressed data of the partial area from the memory allocated to each processor, and controls to perform image expansion processing in parallel in synchronization with each scan line (or band) ,
In the step of storing in the memory, predetermined boundary information is added to the end of the compressed data of each partial area, and a data set including compressed data of different scanning lines (or bands) depending on the partial area is sent to the image decompression unit. Including burst transmission,
In the controlling step, each processor determines whether or not the compressed data of each partial area read from the memory includes the predetermined boundary information, and when the predetermined boundary information is included An image decompression method comprising: controlling the decompression process in parallel in synchronization with each scanning line (or band) by stopping the self decompression process.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003384191A JP4200884B2 (en) | 2003-11-13 | 2003-11-13 | Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system |
| US10/953,415 US7580151B2 (en) | 2003-10-01 | 2004-09-30 | Image processing system and method, printing system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003384191A JP4200884B2 (en) | 2003-11-13 | 2003-11-13 | Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005151054A JP2005151054A (en) | 2005-06-09 |
| JP4200884B2 true JP4200884B2 (en) | 2008-12-24 |
Family
ID=34692700
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003384191A Expired - Fee Related JP4200884B2 (en) | 2003-10-01 | 2003-11-13 | Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4200884B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7957025B2 (en) * | 2006-06-30 | 2011-06-07 | Konica Minolta Systems Laboratory, Inc. | Systems and methods for processing pixel data for a printer |
| JP5105970B2 (en) * | 2007-06-26 | 2012-12-26 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image forming apparatus and control method |
| KR101576560B1 (en) * | 2009-12-21 | 2015-12-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Image processing apparatus for reading compressed data from memory via data bus and image processing method thereof |
-
2003
- 2003-11-13 JP JP2003384191A patent/JP4200884B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005151054A (en) | 2005-06-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2009146251A (en) | Image processing device, and image forming system and program | |
| JP2003312068A (en) | Method and apparatus for processing image | |
| US7580151B2 (en) | Image processing system and method, printing system | |
| JP4136292B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JP3660154B2 (en) | Image processing device for printing | |
| JP6904697B2 (en) | Information processing device and communication control method | |
| JP4200884B2 (en) | Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system | |
| JP6655963B2 (en) | An image processing apparatus and a control method for the image processing apparatus. | |
| JP6772020B2 (en) | Image processing device, control method of image processing device, and program | |
| JP6544905B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, program | |
| JP4182428B2 (en) | Image decompression apparatus and method, and image processing system | |
| JP3757587B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image output system, and image processing method | |
| JP4389199B2 (en) | Printer system | |
| JP4345055B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and method, and printer system | |
| JP3655457B2 (en) | Printer control device | |
| JP5093576B2 (en) | Printing control apparatus and image forming system | |
| JP2002067399A (en) | Printer controller | |
| JPH10202962A (en) | Apparatus for processing printing data and apparatus for forming input data | |
| JP2000137587A (en) | Printing controller and its method | |
| JP2001096854A (en) | Apparatus and method for printing processing | |
| JP4369137B2 (en) | Image processing device for printing | |
| JPH11187261A (en) | Image processor | |
| JPH11179975A (en) | Color printer control device | |
| JP2004268553A (en) | Printing device | |
| JPH11232050A (en) | Device and method for controlling print |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20061019 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080624 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080627 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080826 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080916 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080929 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111017 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121017 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121017 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131017 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |