JP3772929B2 - Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array - Google Patents
Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3772929B2 JP3772929B2 JP00960297A JP960297A JP3772929B2 JP 3772929 B2 JP3772929 B2 JP 3772929B2 JP 00960297 A JP00960297 A JP 00960297A JP 960297 A JP960297 A JP 960297A JP 3772929 B2 JP3772929 B2 JP 3772929B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- optical fiber
- temporary positioning
- groove
- holding component
- positioning member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mechanical Coupling Of Light Guides (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、導波路と光ファイバを接続するために用いられる光ファイバ保持部品および、光ファイバ保持部品に固定されて形成されが光ファイバアレイに関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
複数本の光ファイバ素線を光ファイバ保持部品に固定して光ファイバや光部品と接続を行なうようにした光ファイバアレイが用いられている。
【0003】
特開平4−73607号公報に記載された光ファイバアレイで、基板部材に設けられたV溝部に光ファイバ素線を配列させて接着剤で固定したものである。また、特開平7−151929号公報に記載された光ファイバアレイは、基板部材に設けられたV溝部に光ファイバ素線を配列させ、その上から蓋部材で押圧して接着剤で固定したものである。特開平8−110441号公報に記載された光ファイバアレイでも、同様に、基板部材に設けられたV溝部に光ファイバ素線を配列させ、その上から蓋部材で押圧して接着剤で固定しているが、基板部材は後方まで延長され、テープ状光ファイバの外被を載置して、外被も基板部材に接着剤で固定している。
【0004】
このような従来の光ファイバアレイでは、基板部材のV溝部に光ファイバ素線を配列して接着剤を流し込んで固定するまでに、光ファイバ素線が動いてしまうことがあり、精度よく配列させるのが困難であるという問題がある。また、光ファイバ固定部品の基板部材を厚くしないと、強度が十分でなく、クラックが生じることもあった。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
本発明は、上述した事情に鑑みてなされたもので、光ファイバ固定部品に光ファイバを仮位置決めする機構を設けたことによって、光ファイバを精度よく配列固定することができ、基板部材の強度も大きくできる光ファイバ固定部品、および、この光ファイバ固定部品に光ファイバを固定した光ファイバアレイを提供することを目的とするものである。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1に記載の発明は、少なくとも2本以上の光ファイバ素線を配列させて固定するための光ファイバ保持部品であって、前方に光ファイバ素線を配列させるためのV溝部を有し後方に光ファイバケーブルの外被部分を載置するための外被載置部を有する基板部材と、前記基板に接合され、前記V溝部を所定の間隔をもって跨ぐようにして光ファイバ素線を前記V溝部に仮位置決めするための仮位置決め用部分が設けられた仮位置決め用部材と、前記V溝部に仮位置決めされた光ファイバ素線を押圧するための蓋部材を有する光ファイバ保持部品において、前記基板部材は、V溝部と外被載置部の両側において長手方向に沿う梁状の部分が設けられ、前記仮位置決め用部材は、前記梁状の部分の上に長手方向に沿って接合される接合部分を有することを特徴とするものである。
【0009】
請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材は、ほぼH字形状であることを特徴とするものである。
【0010】
請求項3に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材は、ほぼU字形状であることを特徴とするものである。
【0011】
請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし3のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材の前記仮位置決め用部分と前記接合部分とが交わる部分に円弧状の繋ぎ部分が設けられたことを特徴とするものである。
【0012】
請求項5に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし4のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材の前記仮位置決め用部分の光ファイバ素線の導入側に傾斜部分が形成されたことを特徴とするものである。
【0013】
請求項6に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし5のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記V溝部の後端部に傾斜部分が形成されたことを特徴とするものである。
【0014】
請求項7に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし6のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記V溝部は、前記仮位置決め用部材の前記仮位置決め用部分によって光ファイバ素線を仮位置決めする位置よりも後方まで延びるように形成されていることを特徴とするものである。
【0015】
請求項8に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし7のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材の線膨張係数と前記基板部材の線膨張係数がほぼ同じであることを特徴とするものである。
【0017】
請求項9に記載の発明は、請求項1ないし8のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品において、前記仮位置決め用部材と前記蓋部材とが紫外線透過性の材料で形成され、前記基板部材と紫外線硬化型接着剤で固定されたことを特徴とするものである。
【0018】
請求項10に記載の発明は、光ファイバアレイにおいて、請求項1ないし9のいずれか1項に記載の光ファイバ保持部品を用い、光ファイバケーブルの外被部分が前記外被載置部に載置され、光ファイバ素線が前記V溝部に配列されて前記蓋部材で押圧されて、接着剤で固定されたことを特徴とするものである。
【0019】
請求項11に記載の発明は、請求項10に記載の光ファイバアレイにおいて、前記光ファイバケーブルがテープ状光ファイバであることを特徴とするものである。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
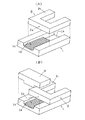
図1は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の参考例を説明するためのもので、図1(A)は組立図、図1(B)は斜視図である。図中、1は基板部材、1aはV溝部、1bは外被載置部、2は仮位置決め用部材、2aは仮位置決め用部分、2bは固定部、3は蓋部材である。基板部材1は、光ファイバ素線を配列するためのV溝部1aと、光ファイバケーブルの外被部分を載置するための外被載置部1bが形成されている。仮位置決め用部材2は、両側に基板部材1に固定される固定部2bが突出されており、固定部2bの間に仮位置決め用部分2aが位置している。
【0022】
仮位置決め用部材2の固定部2bを、図1(A)の破線で降ろした位置に接着剤等によって固定すると、仮位置決め用部分2aはV溝部1aを跨ぐように位置される。図1(B)では、仮位置決め用部材2は基板部材1に固定されている。固定位置では、V溝部1aは、仮位置決め用部分2aの位置よりも後方まで延びるようにするのが、光ファイバ素線の挿入に都合がよい。後述するが、外被載置部1b側から光ファイバケーブルを差し込んで、光ファイバ素線をV溝部1a上に配列し、蓋部材3により光ファイバ素線を押圧した状態で、基板部材1に蓋部材3と光ファイバケーブルの外被部分とを接着剤で固定する。
【0023】
図2は、光ファイバ素線の固定方法を説明するための説明図で、図2(A)は光ファイバアレイの斜視図、図2(B)は仮位置決め用部材の位置における断面図、図2(C)は先端部分の正面図、図2(D)はV溝部の底部の線に沿う断面図である。図中、図1と同様な部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。4aは光ファイバ素線、4bは外被部分、5は接着剤である。光ファイバケーブルは、この例ではテープ状光ファイバを用いたが、これに限られるものではない。したがって、本明細書でいう光ファイバケーブルは、テープ状光ファイバのほか、複数本の光ファイバを撚り合わせなどによって集合したケーブルや、単心の光コードなども含むものである。単心の光ファイバの場合には、複数本を用いて、参考例の光ファイバ保持部品に固定することができる。
【0024】
図2(A)は、8心のテープ状光ファイバを図1で説明した光ファイバ保持部品に固定した状態の斜視図である。テープ状光ファイバを光ファイバ保持部品に固定するにあたっては、テープ状光ファイバの先端部分の外被であるテープ被覆を剥がし、露出した心線の被覆を除去して光ファイバ素線を露出させる。この光ファイバ素線を外被載置部1b側からV溝部1aに沿って挿入する。挿入に伴って、光ファイバ素線が仮位置決め用部分2aとV溝部1aとの間隙を通って前進させ、テープ状光ファイバの外被部分4bを外被載置部1bに載置する。図2(B)に示すように、仮位置決め用部分2aとV溝部1aの頂点との間隙dは、光ファイバ素線4aの直径より小さくされている。したがって、仮位置決め用部分2aの下では、光ファイバ素線4aが隣のV溝部に移動することはできず、各光ファイバ素線4aは、それぞれのV溝部1aに位置決めされる。しかし、仮位置決め用部分2aは、光ファイバ素線4aをV溝部1aの底部に押し付けるものではなく、最終的な位置決めは蓋部材によって行なわれるから、仮位置決め用部分2aによる位置決めは、仮位置決めということができる。
【0025】
V溝部1aに仮位置決めされた光ファイバ素線は、図2(C)に示すように、蓋部材で3で押圧され、V溝部1aに位置決めされる。なお、V溝部1aの間隔は、この例では、テープ状光ファイバにおける心線のピッチ間隔とした。したがって、テープ状光ファイバにおける各心線の中心線と各V溝の中心線とはほぼ一致し、光ファイバ保持部品に保持されて形成された光ファイバアレイにおける各光ファイバ素線には、不要な曲げが加えられることはない。
【0026】
図2(D)に示すように、光ファイバ素線4aが蓋部材3で押圧された状態で接着剤5で全体が接着される。その後、端面が研磨されるが、傾斜面となるように研磨される場合もある。この場合の傾斜面の角度θは、例えば約8度である。傾斜面とすることによって、光ファイバアレイを突き合わせて接続する場合の、接合面での反射による戻り光を防止できる。
【0027】
図3は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第1の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図3(A)は組立図、図3(B)は斜視図である。図中、図1と同様な部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。1cは梁状部分である。この実施の形態では、基板1の両側に長手方向に梁状部分1cを形成した。梁状部分を1cを形成したことによって、基板1の強度を増し、基板1にクラックが生じるのを防止することが可能となる。梁状部分1cの高さは、図2(B)で説明した間隔dとするのがよい。そうすれば、仮位置決め用部材2の基板への固定部2bを、図1に示すように脚状としたり、あるいは、切り欠いたりする必要がないという利点がある。蓋部材3は、図3(B)に示すように、V溝部1aへの押圧部分を凸状にするのがよい。
【0028】
図4は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第2の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図4(A)は組立図、図4(B)は斜視図である。図中、図1,図3と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。2cは延長部である。この実施の形態では、仮位置決め用部材2をU字形状として、その延長部2cを基板1の両側に乗るように、後方に向けて延長した。本発明でいうU字形状は、U字の下の部分が曲線状であることに限られるものではなく、ほぼ直角な形状で曲げられたものも含むものである。図4では、直角に曲げられたU字形状のものとした。この仮位置決め用部材2を基板1に設けられた梁状部分1cの上に接合することによって、基板1の強度はさらに向上する。
【0029】
図5は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第3の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図5(A)は組立図、図5(B)は斜視図である。図中、図1,図3,図4と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。2dは延長部である。この実施の形態では、仮位置決め用部材2をH字形状として、その延長部2c,2dを基板1の両側に乗るように、前方および後方に向けて延長した。この仮位置決め用部材2を基板1に設けられた梁状部分1cの上に接合することによって、基板1の強度はさらに向上する。
【0030】
図6は、2枚のテープ状光ファイバを重ねて光ファイバ保持部品に固定して光ファイバアレイを構成した実施の形態のを説明するためのもので、図6(A)は光ファイバアレイの斜視図、図6(B)は仮位置決め用部材の位置における断面図、図6(C)は先端部分の正面図である。図中、図2,図5と同様な部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。なお、図6(B),(C)において光ファイバ素線が二重丸で図示したものがあるが、これは、2枚のテープ状光ファイバの光ファイバ素線の区別をするために、一方の光ファイバ素線を二重丸で図示したのであり、例えば、二重丸で図示した光ファイバ素線が上方のテープ状光ファイバのものであることを示している。
【0031】
この実施の形態では、V溝の間隔は、テープ状光ファイバの心線間隔のほぼ半分である。そして、2枚のテープ状光ファイバは、外被載置部において心線間隔のほぼ半分だけ横方向にずらせて載置される。したがって、下側のテープ状光ファイバの光ファイバ素線の間に上側の光ファイバ素線が入り込むことになる。例えば、光ファイバ素線の外径を125μm、保護被覆に厚さを62.5μmとした心線を配列して外被で被覆した8心のテープ状光ファイバを2枚重ねて光ファイバ保持部品に固定して光ファイバアレイを構成する場合、V溝は、127μm間隔で16列形成されており、2枚のテープ状光ファイバをほぼ125μm横方向にずらせて外被載置部に載置して固定すれば、テープ状光ファイバにおける各心線の中心線とV溝部の各V溝の中心線とをほぼ一致させることができ、光ファイバ素線に加えられる曲げを最小にすることができる。なお、この数値例では、V溝の間隔は、理想的には125μmであるが、光ファイバ素線の外径のばらつきを考慮して、余裕を与えて127μmとしたものである。
【0032】
光ファイバ素線のV溝への挿入は、図6(B)に示すように、V溝の頂部と仮位置決め用部材2の仮位置決め用部分2aとの間隔dを光ファイバ素線の外径より小さくすることにより仮位置決めが確実にできる。また、図6(C)に示すように、各光ファイバ素線は蓋部材で3で押圧され、V溝部1aに位置決めされる。上述したように、上下のテープ状光ファイバの光ファイバ素線が、互いに入り込むように配列されているから、端面においても、2枚のテープ状光ファイバの光ファイバ素線が交互に配列され、高密度の光ファイバアレイを提供できる。
【0033】
図7は、光ファイバアレイの別の実施の形態の斜視図である。図中、図6と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。この実施の形態では、2枚のテープ状光ファイバを横方向に並べるようにして、光ファイバアレイを構成した。この場合、左右のテープ状光ファイバに対するV溝部は、連続して形成したが、V溝部に配列される光ファイバ素線は、図6(C)で説明したように交互に配列されるのではなく、左右に分けてそれぞれ配列される。したがって、左右のテープ状光ファイバの外被部分を隣接させて外被載置部に載置しても、両方のテープ状光ファイバの内側の光ファイバ素線の間隔は、テープ状光ファイバ内の心線間隔に比べて外被部分の厚さの2倍の間隔だけ大きくなり、V溝部に挿入される光ファイバ素線に曲がりが生じる。この曲がりを小さくするためには、外被部分の先端部とV溝部の後端部との距離を大きくすればよい。また、V溝の間隔をテープ状光ファイバ内の心線間隔より大きい間隔としてもよい。また、光ファイバ左右のテープ状光ファイバからの光ファイバ素線が配列されるV溝部の境界部分に、上述した外被部分の厚さの2倍の間隔だけ離すようにしてもよい。
【0034】
図8は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第4の実施の形態を説明するための平面図である。図中、図5と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。2e,2fは繋ぎ部分である。この実施の形態では、図5で説明した第3の実施の形態における延長部2c,2dと仮位置決め用部分2bとの強度の向上を図ったものである。図8(A)の例では、延長部2cと仮位置決め用部分2bとの接合部分に円弧状の繋ぎ部分2eを形成した。この繋ぎ部分2eの形成は、図4で説明した第2の実施の形態にも適用できるものである。図8(B)の例では、延長部2dと仮位置決め用部分2bとの接合部分にも円弧状の繋ぎ部分2fを形成した。延長部2c,2dと仮位置決め用部分2bとの強度をより向上させることができる。
【0035】
図9は、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第5の実施の形態を説明するための断面図である。この断面は、図2(D)と同様に、V溝の底部を通る断面である。図中、図2と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。1d,2gは傾斜部である。この実施の形態では、仮位置決め用部材の仮位置決め用部分2aの光ファイバ素線の導入側に傾斜部2gが形成されている。傾斜部2gは曲面で形成したが、平面で形成してもよい。仮位置決め用部分2aの光ファイバ素線の導入側に傾斜部2gが形成されたことによって、光ファイバ素線をV溝に沿って仮位置決め用部分2aの下を貫通させる際に、光ファイバ素線の挿入を容易にし、光ファイバを傷つけることを防止できる。
【0036】
また、V溝の後端側に傾斜部1dを形成するようにしてもよい。図では傾斜部1dを平面で形成したが、曲面で形成してもよい。V溝の光ファイバ素線の導入側に傾斜部2gが形成されたことによって、外被載置部1bからV溝への光ファイバ素線の挿入を容易にし、光ファイバを傷つけることを防止できる。
【0037】
図10は、テープ状光ファイバを用いた多心の光ファイバアレイの実施の形態の一例を説明するためのもので、図10(A)は平面図、図10(B)は正面図、図10(C)は側面図、図10(D)は断面図である。図中、図2,図5と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。この実施の形態では、4枚のテープ状光ファイバを用いて、2枚のテープ状光ファイバを横方向に並べ、その上に2枚のテープ状光ファイバを重なるように横方向に並べた。1枚のテープ状光ファイバを8心とすれば、32心の光ファイバアレイが得られる。この実施の形態では、光ファイバ素線に与える曲げを小さくするために、V溝の後端部とテープ状光ファイバの外被部分4bの先端部との間隔を大きくするようにした。上下のテープ状光ファイバは、図6で説明したように、心線の中心線間隔のほぼ半分だけ横方向にずらせて重ねるのがよい。また、V溝は、間隔をおいた2群とした。この間隔は、テープ被覆の側部の厚さの2倍とするのがよい。もちろん、多心の光ファイバアレイがここで説明した4枚のテープ状光ファイバを用いるものに限られるものではなく。さらに多数枚のテープ状光ファイバを複数枚横方向に、また、複数段重ねるようにしてもよい。
【0038】
図11は、図5で説明した第3の実施の形態の光ファイバ保持部品の作成方法の一例の説明図である。図中、6,7はシリコンウェハである。この例では、2枚のシリコンウェハを6,7を用いた。1枚のシリコンウェハ6に、図5(A)の基板部材1を縦横方向に並べた状態のパターンでV溝部と外被載置部をザグリ加工やエッチング加工によって形成し、他の一枚のシリコンウェハ7に、図5(A)の仮位置決め用部材2を縦横方向に並べた状態のパターンとなるよう、長方形の貫通孔を形成した。この2枚のシリコンウェハ6,7を位置合わせをして貼り付け、破線で図示した部分で切断することによって、図5(B)に示す基板部材と仮位置決め用部材が接合された光ファイバ保持部品を製造することができる。この製造方法によれば、多数の光ファイバ保持部品を一度に加工できるので、量産に優れ、コストの低下の面から有利である。
【0039】
図12は、光ファイバアレイを製造する過程における接着方法の一例の説明図である。図中、図7と同様の部分には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。8は導光部材、9は紫外線である。この実施の形態では、少なくとも、仮位置決め用部材2および蓋部材3に紫外線を透過できる材料、例えば、ガラスやシリコンウェハを用いた。図示されていない接着剤として、紫外線硬化型接着剤を塗布し、蓋部材3を押圧しながら、導光部材8を通して、紫外線を接着剤に照射し、硬化させる。蓋部材3の押圧は、導光部材8で行なうようにしてもよい。また、外被部分等への紫外線の照射は、導光部材を通すことなく、直接照射をするようにしてもよい。
【0040】
なお、仮位置決め用部材と基板部材の材料には、適宜のものを用いることができるが、両者の線膨張係数がほぼ同じであるのがよい。上述した図11に示す例では、両者ともシリコンウェハを用いたが、その一方または双方をガラスとしてもよい。もちろん、シリカ粒子を充填させたエポキシ樹脂等、適宜の材料を選択することができる。
【0041】
仮位置決め用部材と基板部材との接合には、接着剤を用いた接合や、陽極接合によって接合する方法も採用できる。陽極接合による接合方法は、接合強度を大きくできる利点がある。
【0042】
【発明の効果】
以上の説明から明らかなように、請求項1に記載の発明によれば、光ファイバ保持部品の光ファイバを取り付けて光ファイバアレイを構成する際の作業性を改善し、かつ高精度な位置決めを維持することができる。また、基板部材の両側において長手方向に沿う梁状の部分が設けられたことにより、基板部材の強度を増し、基板にクラックが生じるのを防止することができる。さらに、仮位置決め用部材が、前記梁状の部分の上に沿って接合される長手方向の接合部分を有することにより、基板部材と仮位置決め用部材との接着強度を増大でき、光ファイバ保持部品分の強度を向上させることができる。
【0044】
請求項2,3に記載の発明によれば、仮位置決め用部材が、前記梁状の部分の上に沿って接合される長手方向の接合部分を有し、ほぼH字形状であることにより、または、ほぼU字形状であることにより、基板部材と仮位置決め用部材との接着強度を増大でき、光ファイバ保持部品分の強度を向上させることができる。
【0045】
請求項4に記載の発明によれば、仮位置決め用部材の仮位置決め用部分と接合部分とが交わる部分に円弧状の繋ぎ部分が設けられたことにより、仮位置決め用部材における仮位置決め用部分の強度を増大できる。
【0046】
請求項5,6に記載の発明によれば、仮位置決め用部材の仮位置決め用部分の光ファイバ素線の導入側に面取りがされたことにより、または、V溝部の後端部に面取りがされたことにより、光ファイバ素線の挿入を容易にし、光ファイバを傷つけることを防止できる。
【0047】
請求項7に記載の発明によれば、V溝部は、光ファイバ素線を前記仮位置決め用部材の前記仮位置決め用部分によって仮位置決めする部分よりも後方にまで延長して形成されていることにより、光ファイバ素線のV溝部への挿入が容易となる効果がある。
【0048】
請求項8に記載の発明によれば、仮位置決め用部材の線膨張係数と基板部材の線膨張係数がほぼ同じであることにより、温度変化時に発生する熱応力が緩和される効果がある。
【0050】
請求項9に記載の発明によれば、仮位置決め用部材と蓋部材が紫外線透過性の材料で形成され、仮位置決め用部材と基板部材とが紫外線硬化型接着剤で固定されたことにより、信頼性に優れた紫外線硬化型接着剤を適用可能にすることができる。
【0051】
請求項10に記載の発明によれば、本発明の光ファイバ保持部品を用い、光ファイバケーブルの外被部分が外被載置部に載置され、光ファイバ素線がV溝部に配列されて蓋部材で押圧されて、接着剤で固定されて、光ファイバアレイを構成することができる。
【0052】
請求項11に記載の発明によれば、光ファイバケーブルとしてテープ状光ファイバを用いたことを可能にしたことにより、テープ状光ファイバを用いた光配線網において、光ファイバアレイを容易に構成することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の参考例を説明するためのもので、図1(A)は組立図、図1(B)は斜視図である。
【図2】 光ファイバ素線の固定方法を説明するための説明図で、図2(A)は光ファイバアレイの斜視図、図2(B)は仮位置決め用部材の位置における断面図、図2(C)は先端部分の正面図、図2(D)はV溝部の底部の線に沿う断面図である。
【図3】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第1の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図3(A)は組立図、図3(B)は斜視図である。
【図4】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第2の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図4(A)は組立図、図4(B)は斜視図である。
【図5】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第3の実施の形態を説明するためのもので、図5(A)は組立図、図5(B)は斜視図である。
【図6】 2枚のテープ状光ファイバを重ねて光ファイバ保持部品に固定して光ファイバアレイを構成した実施の形態のを説明するためのもので、図6(A)は光ファイバアレイの斜視図、図6(B)は仮位置決め用部材の位置における断面図、図6(C)は先端部分の正面図である。
【図7】 光ファイバアレイの別の実施の形態の斜視図である。
【図8】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第4の実施の形態を説明するための平面図である。
【図9】 本発明の光ファイバ保持部品の第5の実施の形態を説明するための断面図である。
【図10】 テープ状光ファイバを用いた多心の光ファイバアレイの実施の形態の一例を説明するためのもので、図10(A)は平面図、図10(B)は正面図、図10(C)は側面図、図10(D)は断面図である。
【図11】 図5で説明した第3の実施の形態の光ファイバ保持部品の作成方法の一例の説明図である。
【図12】 光ファイバアレイを製造する過程における接着方法の一例の説明図である。
【符号の説明】
1…基板部材、1a…V溝部、1b…外被載置部、1c…梁状部分、1d…傾斜部、2…仮位置決め用部材、2a…仮位置決め用部分、2b…固定部、2c,2d…延長部、2e,2f…繋ぎ部分、2g…傾斜部、3…蓋部材、4a…光ファイバ素線、4b…外被部分、5…接着剤、6,7…シリコンウェハ、8…導光部材、9…紫外線。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an optical fiber holding component used for connecting a waveguide and an optical fiber, and an optical fiber array formed by being fixed to the optical fiber holding component.
[0002]
[Prior art]
An optical fiber array is used in which a plurality of optical fiber strands are fixed to an optical fiber holding component and are connected to an optical fiber or an optical component.
[0003]
In the optical fiber array described in JP-A-4-73607, optical fiber strands are arranged in a V-groove portion provided on a substrate member and fixed with an adhesive. In addition, the optical fiber array described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 7-151929 is an optical fiber array in which optical fiber strands are arranged in a V-groove portion provided on a substrate member and pressed with a lid member from above and fixed with an adhesive. It is. Similarly, in the optical fiber array described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 8-110441, optical fiber strands are arranged in a V-groove portion provided on the substrate member, and are pressed with a lid member from above and fixed with an adhesive. However, the substrate member is extended to the rear, and the outer cover of the tape-like optical fiber is placed thereon, and the outer cover is also fixed to the substrate member with an adhesive.
[0004]
In such a conventional optical fiber array, the optical fiber strands may move until the optical fiber strands are arranged in the V-groove portion of the substrate member and the adhesive is poured and fixed, so that the optical fiber strands are arranged accurately. There is a problem that it is difficult. Further, unless the substrate member of the optical fiber fixing component is made thick, the strength is not sufficient and a crack may occur.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described circumstances. By providing a mechanism for temporarily positioning the optical fiber in the optical fiber fixing component, the optical fiber can be arranged and fixed with high accuracy, and the strength of the substrate member can also be improved. It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber fixing part that can be enlarged and an optical fiber array in which an optical fiber is fixed to the optical fiber fixing part.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The invention according to
[0009]
Claim2The invention described in claim1In the optical fiber holding component described in the
[0010]
Claim3The invention described in claim1In the optical fiber holding component described in the
[0011]
Claim4The invention described in claim1Or3In the optical fiber holding component according to any one of the above, an arc-shaped connecting portion is provided at a portion where the temporary positioning portion and the joining portion of the temporary positioning member intersect. is there.
[0012]
Claim5The invention described in
[0013]
Claim6The invention described in
[0014]
Claim7The invention described in
[0015]
Claim8The invention described in
[0017]
Claim9The invention described in
[0018]
Claim10The invention described in
[0019]
Claim11The invention described in claim10In the optical fiber array described in (1), the optical fiber cable is a tape-shaped optical fiber.
[0021]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 shows an optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.Reference exampleFIG. 1 (A) is an assembly view, and FIG. 1 (B) is a perspective view. In the figure, 1 is a substrate member, 1a is a V-groove portion, 1b is a jacket placement portion, 2 is a temporary positioning member, 2a is a temporary positioning portion, 2b is a fixing portion, and 3 is a lid member. The
[0022]
When the
[0023]
2A and 2B are explanatory views for explaining a method of fixing the optical fiber, FIG. 2A is a perspective view of the optical fiber array, FIG. 2B is a cross-sectional view at the position of the temporary positioning member, and FIG. 2 (C) is a front view of the tip portion, and FIG. 2 (D) is a cross-sectional view taken along the bottom line of the V-groove portion. In the figure, parts similar to those in FIG. 4a is an optical fiber, 4b is a jacket portion, and 5 is an adhesive. In this example, a tape-like optical fiber is used as the optical fiber cable, but the optical fiber cable is not limited to this. So bookSpecificationThe optical fiber cable includes a tape-like optical fiber, a cable in which a plurality of optical fibers are gathered together by twisting, a single-core optical cord, and the like. In the case of a single-core optical fiber,Reference exampleIt can be fixed to the optical fiber holding part.
[0024]
FIG. 2A is a perspective view of a state in which an eight-core tape-like optical fiber is fixed to the optical fiber holding component described in FIG. In fixing the tape-shaped optical fiber to the optical fiber holding component, the tape coating that is the outer cover of the tip portion of the tape-shaped optical fiber is peeled off, and the exposed coating of the core wire is removed to expose the optical fiber strand. This optical fiber is inserted along the V-groove portion 1a from the
[0025]
As shown in FIG. 2C, the optical fiber strand temporarily positioned in the V-groove portion 1a is pressed by 3 with a lid member and positioned in the V-groove portion 1a. In addition, the space | interval of the V groove part 1a was made into the pitch space | interval of the core wire in a tape-shaped optical fiber in this example. Therefore, the center line of each core wire in the tape-like optical fiber and the center line of each V-groove are substantially coincident and are not necessary for each optical fiber strand in the optical fiber array formed by being held by the optical fiber holding component. No bending is added.
[0026]
As shown in FIG. 2 (D), the optical fiber 4 a is bonded by the adhesive 5 in a state where the optical fiber 4 a is pressed by the
[0027]
FIG. 3 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component of the present invention.1FIG. 3A is an assembly view, and FIG. 3B is a perspective view. In the figure, parts similar to those in FIG. 1c is a beam-shaped part. In this embodiment, beam-like portions 1c are formed on both sides of the
[0028]
FIG. 4 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component of the present invention.24A is an assembly view, and FIG. 4B is a perspective view. In the figure, the same parts as those in FIGS. 2c is an extension part. In this embodiment, the
[0029]
FIG. 5 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component of the present invention.3FIG. 5 (A) is an assembly view, and FIG. 5 (B) is a perspective view. In the figure, the same parts as those in FIGS. 1, 3 and 4 are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted. 2d is an extension part. In this embodiment, the
[0030]
FIG. 6 is a view for explaining an embodiment in which an optical fiber array is configured by superposing two tape-like optical fibers and fixing them to an optical fiber holding part. FIG. FIG. 6B is a sectional view at the position of the temporary positioning member, and FIG. 6C is a front view of the tip portion. In the figure, the same parts as those in FIG. 2 and FIG. 6 (B) and 6 (C), there are optical fiber strands that are illustrated as double circles, but this is to distinguish the optical fiber strands of two tape-shaped optical fibers. One of the optical fiber strands is illustrated with a double circle, and for example, the optical fiber strand illustrated with a double circle indicates that it is that of an upper tape-shaped optical fiber.
[0031]
In this embodiment, the interval between the V grooves is approximately half of the interval between the cores of the tape-like optical fiber. Then, the two tape-like optical fibers are placed in the outer placement portion while being shifted in the lateral direction by approximately half of the interval between the core wires. Accordingly, the upper optical fiber strand enters between the optical fiber strands of the lower tape-shaped optical fiber. For example, an optical fiber holding component is formed by stacking two optical fiber ribbons each having an outer diameter of 125 .mu.m and a protective coating having a thickness of 62.5 .mu.m. When an optical fiber array is formed by fixing to the optical fiber array, 16 rows of V-grooves are formed at 127 μm intervals, and two tape-like optical fibers are shifted in the lateral direction by about 125 μm and placed on the outer placement portion. If fixed, the center line of each core wire in the tape-like optical fiber and the center line of each V groove of the V groove portion can be made substantially coincident, and the bending applied to the optical fiber can be minimized. . In this numerical example, the V-groove interval is ideally 125 μm, but it is 127 μm with a margin in consideration of variations in the outer diameter of the optical fiber.
[0032]
As shown in FIG. 6 (B), the optical fiber strand is inserted into the V-groove by setting the distance d between the top of the V-groove and the
[0033]
FIG. 7 is a perspective view of another embodiment of an optical fiber array. In the figure, the same parts as those in FIG. In this embodiment, the optical fiber array is configured by arranging two tape-like optical fibers in the horizontal direction. In this case, the V-groove portions for the left and right tape-shaped optical fibers are formed continuously, but the optical fiber strands arranged in the V-groove portions are not alternately arranged as described with reference to FIG. Rather, they are arranged separately on the left and right. Therefore, even if the jacket portions of the left and right tape-shaped optical fibers are adjacent to each other and placed on the jacket placement portion, the distance between the optical fiber strands inside the both tape-shaped optical fibers is within the tape-shaped optical fiber. Compared to the distance between the core wires, the distance is twice as large as the thickness of the jacket portion, and the optical fiber inserted into the V-groove is bent. In order to reduce this bending, the distance between the front end portion of the jacket portion and the rear end portion of the V groove portion may be increased. Moreover, it is good also as a space | interval larger than the space | interval of a core wire in a tape-shaped optical fiber for the space | interval of V groove | channel. Moreover, you may make it leave | separate the space | interval part of the V-groove part in which the optical fiber from the tape-shaped optical fiber on either side of an optical fiber is arranged by the space | interval of twice the thickness of the above-mentioned jacket part.
[0034]
FIG. 8 is a diagram of the optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.4It is a top view for demonstrating this embodiment. In the figure5The same parts as those in FIG. 2e and 2f are connecting portions. In this embodiment, the first described in FIG.3In this embodiment, the strength of the
[0035]
FIG. 9 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component of the present invention.5It is sectional drawing for demonstrating embodiment of this. This cross section is a cross section passing through the bottom of the V groove, as in FIG. In the figure, parts similar to those in FIG. Reference numerals 1d and 2g denote inclined portions. In this embodiment, the inclined portion 2g is formed on the optical fiber strand introduction side of the
[0036]
Further, the inclined portion 1d may be formed on the rear end side of the V groove. Although the inclined portion 1d is formed as a flat surface in the figure, it may be formed as a curved surface. By forming the inclined portion 2g on the optical fiber strand introduction side of the V-groove, the insertion of the optical fiber strand from the
[0037]
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining an example of an embodiment of a multi-core optical fiber array using tape-like optical fibers, FIG. 10 (A) is a plan view, FIG. 10 (B) is a front view, FIG. 10 (C) is a side view and FIG. 10 (D) is a cross-sectional view. In the figure, the same parts as those in FIGS. In this embodiment, four tape-shaped optical fibers are used, two tape-shaped optical fibers are arranged in the horizontal direction, and two tape-shaped optical fibers are arranged in the horizontal direction so as to overlap therewith. If one tape-like optical fiber is 8 cores, a 32-fiber optical fiber array can be obtained. In this embodiment, in order to reduce the bending applied to the optical fiber, the distance between the rear end portion of the V-groove and the front end portion of the
[0038]
11 is the same as that shown in FIG.3It is explanatory drawing of an example of the preparation method of the optical fiber holding component of embodiment. In the figure, 6 and 7 are silicon wafers. In this example, two silicon wafers 6 and 7 were used. A V-groove part and an outer placement part are formed on a single silicon wafer 6 by counterboring or etching in a pattern in which the
[0039]
FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram of an example of a bonding method in the process of manufacturing the optical fiber array. In the figure, parts similar to those in FIG. 8 is a light guide member, and 9 is an ultraviolet ray. In this embodiment, at least the
[0040]
In addition, although an appropriate thing can be used for the material for temporary positioning member and a board | substrate member, both should have the substantially same linear expansion coefficient. In FIG. 11 mentioned aboveShowIn the examples, both use silicon wafers, but one or both of them may be glass. Of course, an appropriate material such as an epoxy resin filled with silica particles can be selected.
[0041]
For joining the temporary positioning member and the substrate member, joining using an adhesive or anodic joining may be employed. The bonding method by anodic bonding has the advantage that the bonding strength can be increased.
[0042]
【The invention's effect】
As is apparent from the above description, according to the invention described in
[0044]
Claim2, 3According to the invention described in (1), the temporary positioning member has a joint portion in the longitudinal direction joined along the beam-like portion.AndBy being substantially H-shaped or being substantially U-shaped, the adhesive strength between the substrate member and the temporary positioning member can be increased, and the strength of the optical fiber holding component can be improved.
[0045]
Claim4According to the invention described in the above, the strength of the temporary positioning portion in the temporary positioning member is increased by providing the arc-shaped connecting portion at the portion where the temporary positioning portion and the joining portion of the temporary positioning member intersect. it can.
[0046]
Claim5, 6According to the invention described in the above, the chamfering of the temporary positioning portion of the temporary positioning member to the optical fiber strand introduction side, or the chamfering of the rear end portion of the V-groove portion, The fiber strand can be easily inserted and the optical fiber can be prevented from being damaged.
[0047]
Claim7According to the invention described in V, the V-groove is, Behind the portion where the optical fiber is temporarily positioned by the temporary positioning portion of the temporary positioning memberAs a result, the optical fiber strand can be easily inserted into the V-groove portion.
[0048]
Claim8According to the invention described in (4), since the linear expansion coefficient of the temporary positioning member and the linear expansion coefficient of the substrate member are substantially the same, there is an effect that the thermal stress generated when the temperature changes is reduced.
[0050]
Claim9According to the invention described in the above, the temporary positioning member and the lid member are made of an ultraviolet light transmissive material, and the temporary positioning member and the substrate member are fixed with the ultraviolet curable adhesive, so that the reliability is excellent. An ultraviolet curable adhesive can be applied.
[0051]
Claim10According to the invention described in the above, using the optical fiber holding component of the present invention, the jacket portion of the optical fiber cable is placed on the sheath placement portion, and the optical fiber strands are arranged in the V-groove portion and are covered with the lid member. The optical fiber array can be configured by being pressed and fixed with an adhesive.
[0052]
Claim11According to the invention described in, the optical fiber array can be easily configured in the optical wiring network using the tape-shaped optical fiber by enabling the use of the tape-shaped optical fiber as the optical fiber cable. .
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 shows an optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.Reference exampleFIG. 1 (A) is an assembly view, and FIG. 1 (B) is a perspective view.
2A and 2B are explanatory diagrams for explaining a method of fixing an optical fiber, in which FIG. 2A is a perspective view of the optical fiber array, FIG. 2B is a cross-sectional view at the position of a temporary positioning member, and FIG. 2 (C) is a front view of the tip portion, and FIG. 2 (D) is a cross-sectional view taken along the bottom line of the V groove.
FIG. 3 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component of the present invention.1FIG. 3A is an assembly view, and FIG. 3B is a perspective view.
FIG. 4 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.24A is an assembly view, and FIG. 4B is a perspective view.
FIG. 5 shows a first embodiment of the optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.3FIG. 5 (A) is an assembly view, and FIG. 5 (B) is a perspective view.
6A and 6B are diagrams for explaining an embodiment in which an optical fiber array is configured by stacking two tape-shaped optical fibers and fixing them to an optical fiber holding part. FIG. FIG. 6B is a sectional view at the position of the temporary positioning member, and FIG. 6C is a front view of the tip portion.
FIG. 7 is a perspective view of another embodiment of an optical fiber array.
FIG. 8 is a first view of an optical fiber holding component according to the present invention.4It is a top view for demonstrating this embodiment.
FIG. 9 shows an optical fiber holding component of the present invention.5It is sectional drawing for demonstrating embodiment of this.
10A and 10B are diagrams for explaining an example of an embodiment of a multi-core optical fiber array using tape-like optical fibers, FIG. 10A is a plan view, FIG. 10B is a front view, FIG. 10 (C) is a side view and FIG. 10 (D) is a cross-sectional view.
FIG. 11 shows the first described in FIG.3It is explanatory drawing of an example of the preparation method of the optical fiber holding component of embodiment.
FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram of an example of an adhesion method in the process of manufacturing an optical fiber array.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP00960297A JP3772929B2 (en) | 1997-01-22 | 1997-01-22 | Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP00960297A JP3772929B2 (en) | 1997-01-22 | 1997-01-22 | Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10206697A JPH10206697A (en) | 1998-08-07 |
| JP3772929B2 true JP3772929B2 (en) | 2006-05-10 |
Family
ID=11724869
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP00960297A Expired - Fee Related JP3772929B2 (en) | 1997-01-22 | 1997-01-22 | Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3772929B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3321042B2 (en) * | 1997-08-27 | 2002-09-03 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Optical switch and optical fiber alignment unit |
| JP4090597B2 (en) * | 1998-10-30 | 2008-05-28 | 株式会社フジクラ | Optical fiber array and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2000221364A (en) * | 1999-02-03 | 2000-08-11 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | Multi-fiber optical connector |
| JP2001074975A (en) * | 1999-09-07 | 2001-03-23 | Totoku Electric Co Ltd | High density multiple core optical ferrule assembly body |
| KR20030037285A (en) * | 2001-11-01 | 2003-05-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Glass cover of optical fiber block for minimizing stress concentration and contacting device therewith |
| JP4094273B2 (en) * | 2001-11-02 | 2008-06-04 | イビデン株式会社 | Optical fiber array |
| JP2004078028A (en) * | 2002-08-21 | 2004-03-11 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Optical fiber guide part and its manufacturing method |
| KR20040048581A (en) * | 2002-12-04 | 2004-06-10 | 우리로광통신주식회사 | Optical fiber array |
| JP4074563B2 (en) * | 2003-07-04 | 2008-04-09 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Manufacturing method of optical fiber guide parts |
| JP7051073B2 (en) * | 2017-01-27 | 2022-04-11 | アダマンド並木精密宝石株式会社 | Manufacturing method of optical fiber array and optical fiber array |
-
1997
- 1997-01-22 JP JP00960297A patent/JP3772929B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH10206697A (en) | 1998-08-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5995920B2 (en) | Multi-core fiber connector for multi-core optical fiber cable | |
| US5611017A (en) | Fiber optic ribbon cable with pre-installed locations for subsequent connectorization | |
| WO1998005989A1 (en) | Multicore optical connector and method of producing the connector | |
| JP3772929B2 (en) | Optical fiber holding component and optical fiber array | |
| JP3821971B2 (en) | Fiber optic array | |
| JPH11174274A (en) | Optical fiber array and manufacture of die | |
| EP0200414B1 (en) | Optical fibre terminating device and a method of terminating optical fibres | |
| JPH10246838A (en) | Optical fiber array device | |
| JP3374508B2 (en) | Optical fiber array | |
| JP3813318B2 (en) | Multi-fiber optical connector and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP3191797B2 (en) | Optical fiber connector and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP3966835B2 (en) | Multi-fiber optical connector and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP3441206B2 (en) | Optical fiber alignment board | |
| JP2819954B2 (en) | Connection method and connection structure between multi-core tape fiber and ferrule | |
| JP2000066057A (en) | Optical fiber array | |
| JP3968543B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of optical fiber array | |
| JPS6343111A (en) | Optical fiber branching device | |
| JPH095576A (en) | Multi-fiber optical transmission body terminal part | |
| JP2003344731A (en) | Polarization maintaining optical fiber transmission member and manufacturing method therefor | |
| KR20020052988A (en) | Ribbon fiber and manufacturing method therefor, and optical fiber array using the same | |
| TWI771467B (en) | Optical connection part, manufacturing method of optical connection part | |
| JP2003294971A (en) | Method of incorporating tape-like optical fiber in optical fiber array fabrication process | |
| JPS61252508A (en) | Formation of multicore optical fiber core terminal and forming part of multicore optical fiber core terminal | |
| KR100424459B1 (en) | Alignment method for optical fiber block | |
| JP4301245B2 (en) | Optical fiber array |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20041021 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20041102 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041222 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050803 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050906 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060125 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060207 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090224 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100224 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110224 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110224 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120224 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |