JP3676757B2 - Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device - Google Patents
Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3676757B2 JP3676757B2 JP2002162969A JP2002162969A JP3676757B2 JP 3676757 B2 JP3676757 B2 JP 3676757B2 JP 2002162969 A JP2002162969 A JP 2002162969A JP 2002162969 A JP2002162969 A JP 2002162969A JP 3676757 B2 JP3676757 B2 JP 3676757B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- object detection
- casing
- detection axis
- axis
- detection means
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、外面に基準面を有するケーシングの内部に、所定の検知方向が設定された対象物検知手段を固定した対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
ACCシステム(アダプティブ・クルーズ・コントロール・システム)、Stop&Goシステム(渋滞追従システム)、車間警報システム等に使用されるレーダー装置を車両に取り付ける場合、そのレーダー装置の対象物検知軸の方向が予め設定した目標とする対象物検知軸の方向を正しく指向していないと、隣車線の対向車を誤検知してシステムが誤作動したり、路面、陸橋、看板だけを検知して先行車を検知しないためにシステムが作動しないという問題が発生する。そこで、レーダー装置の対象物検知軸の方向を目標とする対象物検知軸の方向に一致させるエイミングを行う必要がある。
【0003】
特開平11−326495号公報には、レーダー装置の対象物検知軸の上下方向のエイミングを行うべく、車体に取り付けたアンテナの角度を水準器で測定し、その上下角度が正しい角度となるように調整するものが開示されている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、レーダー装置のケーシングの車体に対する取付角を水準器等で測定してエイミングを行う場合、ケーシングに内蔵されたレーダー機構部の対象物検知軸が該ケーシングに対して一定の関係にあることが必要である。しかしながら、実際には組立上の誤差により個々のレーダー装置の対象物検知軸の方向にばらつきが発生することが避けられず、ケーシングの車体に対する取付角を正しく調整しても、前記ばらつきによって対象物検知軸の方向が目標とする対象物検知軸の方向からずれてしまう問題がある。
【0005】
本発明は前述の事情に鑑みてなされたもので、レーダー装置のケーシングに対する対象物検知軸の方向のばらつきを補償し、正しいエイミングが行えるようにすることを目的とする。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するために、請求項1に記載された発明によれば、外面に基準面を有するケーシングの内部に、所定の検知方向が設定された対象物検知手段を固定した対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法において、ケーシングに対する対象物検知手段の初期固定状態における該対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸と前記所定の検知方向との角度差を検出する第1工程と、ケーシングに対象物検知手段を固定する際に、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の固定部間に調整部材を挟持することで、ケーシングの基準面と対象物検知軸とが平行となるようにケーシングに対する対象物検知手段の取付角度を前記角度差に応じて調整する第2工程と、ケーシングの基準面が前記所定の検知方向に対して所定の関係となるように、該ケーシングの車体に対する取付角度を調整する第3工程とを含み、前記第1及び第2工程は、対象物検知装置を車体に取付ける前に実行され、また前記第3工程は、対象物検知装置を車体に取付けた後に実行されることを特徴とする対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法が提案される。
【0007】
上記構成によれば、対象物検知装置を車体に取付ける前に、先ず第1工程で、ケーシングの内部に対象物検知手段を固定したときの、対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差を検出し、続いて第2工程で、ケーシングに対象物検知手段を固定する際に、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の固定部間に調整部材を挟持することで、ケーシングの基準面と対象物検知軸とが平行となるようにケーシングに対する対象物検知手段の取付角度を前記角度差に応じて調整する。そして、対象物検知装置を車体に取付けた後、第3工程で、ケーシングの基準面の方向が前記所定の検知方向に対して所定の関係となるように該ケーシングの車体に対する取付角度を調整することで、対象物検知軸の方向を所定の検知方向に一致させることができる。従って、組立上の誤差により個々の対象物検知装置の対象物検知軸の方向にばらつきが発生して該対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差が種々に変化しても、調整部材の厚さを変化させることで前記角度差を補償して対象物検知軸の軸調整を行うことができる。
【0008】
また請求項2に記載された発明によれば、請求項1の構成に加えて、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の固定部は環状であり、調整部材はケーシングに当接する第1底面が対象物検知手段に当接する第2底面に対して楔状に傾斜した環状部材であり、かつ調整部材はケーシングおよび対象物検知手段に対する回転方向位置が調整可能であることを特徴とする対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法が提案される。
【0009】
上記構成によれば、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の環状の固定部に挟持される調整部材が、ケーシングに当接する第1底面と対象物検知手段に当接する第2底面とが楔状に傾斜した環状部材であるため、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段に対する調整部材の回転方向位置を調整することにより、ケーシングの基準面の方向を対象物検知軸に一致させて軸調整の精度を高めることができる。
【0010】
また請求項3に記載された発明によれば、請求項2の構成に加えて、調整部材の第1底面および第2底面の傾斜角度は、前記初期固定状態において発生する前記角度差の最大値以上の所定角度であることを特徴とする対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法が提案される。 上記構成によれば、調整部材の第1底面および第2底面の傾斜角度を、初期固定状態における対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差の最大値以上としたので、前記角度差が最大値となった場合でも対象物検知軸を所定の検知方向に支障なく調整することができる。
【0011】
また請求項4に記載された発明によれば、請求項1〜請求項3の何れか1項の構成に加えて、前記所定の検知方向が水平方向であり、前記所定の関係がケーシングの基準面の方向を水平方向に一致させるものであることを特徴とする対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法が提案される。
【0012】
上記構成によれば、ケーシングの角度を調整して基準面の方向を所定の検知方向である水平方向に一致させるので、対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸を水平方向に調整することができる。
【0013】
尚、実施例のレーダー機構部33は本発明の対象物検知手段に対応し、実施例の目標とする対象物検知軸Ar0は本発明の所定の検知方向に対応する。
【0014】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、添付図面に示した本発明の実施例に基づいて説明する。 図1〜図19は本発明の第1実施例を示すもので、図1はレーダー装置を備えた車両の平面図、図2は図1の2方向矢視図、図3はレーダー装置の斜視図、図4は図3の4方向矢視図、図5は図3の5方向矢視図、図6は図3の6方向矢視図、図7は図5の7部拡大断面図、図8は図5の8部拡大断面図、図9はレーダー装置の縦断面図、図10はレーダー機構部の正面図、平面図および側面図、図11はレドームの正面図、平面図および側面図、図12はケーシングの正面図、平面図及び側面図、図13は調整部材の正面図、平面図および側面図、図14はレーダー装置の分解図、図15はレーダー装置の構成を示すブロック図、図16はレーダー装置に対して物体が接近移動しているときの送受信波の波形およびピーク周波数を示すグラフ、図17はレーダー機構部支持治具及びターゲット治具を示す図、図18は図17の18部拡大図、図19は図18の19方向矢視図である。
【0015】
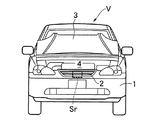
図1および図2に示すように、車両Vの進行方向に存在する前走車等の対象物を検知するレーダー装置Srは、フロントバンパー1の中央上部に固定されたフロントグリル2の後方であって、ボンネット3で開閉されるエンジンルーム4の前端部に配置される。尚、本明細書中で使用される前後左右の用語はシートに着座した乗員を基準とするもので、その定義は図3に示される。
【0016】
図3〜図8から明らかなように、レーダー装置Srを支持板12に支持するためのブラケット13は、金属板をL字状断面に折り曲げた左右のブラケット本体13a,13bと、両ブラケット本体13a,13bの上端間および下端間を接続する上下の連結部材13c,13dとで構成されており、その四隅が4本のボルト14…で支持板12に固定される。レーダー装置Srはレドーム31およびケーシング32を備えており、ケーシング32から突出する3個のステー32g,32h,32iに合成樹脂製のナット部材16,17,18が支持される。
【0017】
各々のステー32g,32h,32iの後方に位置するように、左右のブラケット本体13a,13bに3個のボルト支持部材22,23,24が固定される。図7に示すように、右上のステー32gの後方に位置するボルト支持部材22を貫通するボルト部材19の基端はプッシュナット25により軸方向に固定され、雄ねじ部19aはナット部材16に螺合する。
【0018】
図8に示すように、右下および左上のステー32h,32iの後方に位置するボルト支持部材23,24を貫通するボルト部材20,21に基端はプッシュナット26,27により軸方向に固定され、雄ねじ部20a,21aはナット部材17,18に螺合する。ボルト部材20,21の頭部20b,21bの前面にはギヤ歯20c,21cが形成されており、このギヤ歯20c,21cに対向するガイド突起23a,24aがボルト支持部材23,24の後面に突出する。支持部材23,24の上面には、後述する調整ビット28を挿入するための開口23b,24bが形成される。
【0019】
図4に示すように、右上のボルト支持部材22は右下のボルト支持部材23に対して前方にずれており、従って上方から見たときに、右下のボルト支持部材23の上面の開口23bは右上のボルト支持部材22に遮られることなく露出する。
【0020】
図9〜図14から明らかなように、レーダー装置Srは、後面が開放したカップ状のレドーム31と、前面が開放したカップ状のケーシング32と、レドーム31およびケーシング32の内部空間に収納されたレーダー機構部33と、レーダー機構部33の角度を調整するための調整部材52とを備える。
【0021】
図10に示すように、レーダー機構部33は板状のフレーム34を備えており、その中央部に形成された開口34aに平面アンテナ35が嵌合する。平面アンテナ35の後部に固定された支軸36の上端は軸受け37を介してフレーム34に支持され、その下端はフレーム34に固定したモータ38に接続される。従って、モータ38を往復回転駆動することにより、平面アンテナ35は支軸36まわりに往復回動する。フレーム34の後面には3枚の回路基板39…が積層状態で支持される。フレーム34には90°間隔で4個のボルト孔34b…が形成される。
【0022】
図11に示すように、レーダー機構部33の前面を覆うレドーム31は、正20角柱よりなるレドーム本体31aと、レドーム本体31aの前面を閉塞する底板31bと、レドーム本体31aの後面から半径方向外側に張り出す正20角形のフランジ31cとを備えており、フランジ31cには90°間隔で4個のボルト孔31d…が形成される。正20角柱よりなるレドーム本体31aの中心線はフランジ31cに対して直交しており、レドーム31はその中心線に対して回転対称な構造を有している。尚、レドーム本体31aは必ずしも多角柱である必要はなく、レーダー機構部33の前面を覆うことができれば、円柱のような単純な形状であっても良い。
【0023】
図12に示すように、レーダー機構部33の後面を覆うケーシング32は、正20角柱よりなるケーシング本体32aと、ケーシング本体32aの後面を閉塞する底板32bと、ケーシング本体32aの前面から半径方向外側に張り出す正20角形のフランジ32cとを備えており、フランジ32cには90°間隔で4個のボルト孔32d…が形成される。またフランジ32cの内側には正20角形の段部32eが一段低く形成されており、そこに90°間隔で4個のボルト孔32f…が形成される。更に、フランジ32cから前記3個のステー32g,32h,32iが一体に突出する。尚、ケーシング本体31aは必ずしも多角柱である必要はなく、その上面に水平な基準面Pを備えていれば任意の形状であっても良い。
【0024】
図13に示すように、調整部材52は正20角形の環状部材であって、ケーシング32の段部32eに当接する第1底面52aと、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34の後面に当接する第2底面52bとを備えており、第1底面52aおよび第2底面52bは1.0°の角度を有して楔状に形成される。そして調整部材52には円周方向に18°間隔で20個のボルト孔52c…が形成される。
【0025】
図9および図14に示すように、ケーシング32の段部32eに調整部材52を嵌合させ、更にその前面にレーダー機構部33のフレーム34を嵌合させた状態で、4本のボルト53…を用いてレーダー機構部33および調整部材52をケーシング32に共締めする。このとき、正20角形の調整部材52は20通りの回転方向位置の何れかを選択することができ、その回転方向位置に応じてケーシング32に対するレーダー機構部33の取付角度が調整される。そしてケーシング32のフランジ32cにレドーム31のフランジ31cを当接させて4本のボルト40…で締結することで、レーダー装置Srの組立が完了する。
【0026】
図15に示すように、FM−CW波を用いたミリ波レーダー装置Srは、タイミング信号生成回路41から入力されるタイミング信号に基づいて発振器43の発信作動がFM変調制御回路42により変調制御され、図16(A)に実線で示すように、周波数が三角波状に変調された送信波がアンプ44およびサーキュレータ45を介して平面アンテナ35から、自車の前方の所定の検知範囲の水平方向に異なる方向に向けて例えば9チャンネルに別れて送信される。このFM−CW波が先行車等の物体に反射された反射波が平面アンテナ35に受信されると、この受信波は、例えば物体が自車に接近してくる場合には、図16(A)に破線で示すように、送信波の周波数が直線的に増加する上昇側では送信波よりも低い周波数で送信波から遅れて出現し、また送信波の周波数が直線的に減少する下降側では送信波よりも高い周波数で送信波から遅れて出現する。
【0027】
平面アンテナ35で受信した受信波はサーキュレータ45を介してミキサ46に入力される。ミキサ46には、サーキュレータ45からの受信波の他に発振器43から出力される送信波から分配された走信波がアンプ47を介して入力されており、ミキサ46で送信波および受信波が混合されることにより、図16(B)に示すように、送信波の周波数が直線的に増加する上昇側でピーク周波数Fupを有し、送信波の周波数が直線的に減少する下降側でピーク周波数Fdnを有するビート信号が生成される。
【0028】
ミキサ46で得られたビート信号はアンプ48で必要なレベルの振幅に増幅され、A/Dコンバータ49によりサンプリングタイム毎にA/D変換され、デジタル化された増幅データがメモリ50に時系列的に記憶保持される。このメモリ50には、タイミング信号生成回路41からタイミング信号が入力されており、そのタイミング信号に応じてメモリ50は、送受信波の周波数が増加する上昇側および前記周波数が減少する下降側毎にデータを記憶保持することになる。
【0029】
メモリ50に記憶されたデータに基づいて中央演算処理装置(CPU)51は、ピーク周波数Fup,Fdnに基き周知の方法により物体との相対距離および相対速度を算出するとともに、車両制御用の電子制御ユニットUに通信する。
【0030】
ところで、レーダー装置Srのレーダー機構部33は、そのフレーム34に対して対象物検知軸Arが直交するように設計されており、レーダー機構部33をケーシング32に固定したときに対象物検知軸Arが基準面Pと平行になるはずである。しかしながら、製造上の誤差により対象物検知軸Arの角度がフレーム34に対して上下にずれている場合があり、この場合にはレーダー機構部33をケーシング32に固定したときに対象物検知軸Arが基準面Pと非平行になってしまう。
【0031】
図17〜図19には、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34に対する対象物検知軸Arの上下方向のずれを検知するためのレーダー機構部支持治具61およびターゲット治具62が示される。
【0032】
レーダー機構部支持治具61は、台座63に鉛直に立設した2本の支柱64,64を備えており、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34がボルト65…で支柱64,64に固定される。従って、レーダー機構部支持治具61に固定されたレーダー機構部33のフレーム34は鉛直姿勢となる。ターゲット治具62は、台座66に鉛直に立設した1本の支柱67を備えており、支柱67に上下位置調整自在に支持されたスライダ68に基準反射体Rが固定される。基準反射体Rは相互に直交する3個の平坦な反射面69…を有しており、その頂点に設けたボルト70でスライダ68に固定される。基準反射体Rの反射面69…はミリ波を反射することが必要であり、金属製でも良いし、簡易なものとしてはボール紙にアルミ箔を貼ったものでも良い。
【0033】
次に、上記構成を備えた本発明の第1実施例の作用について説明する。
【0034】
先ず、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34に対する対象物検知軸Arの上下方向のずれ、つまり目標とする対象物検知軸Ar0に対する実際の対象物検知軸Arのずれを検知する。図17に示すように、レーダー機構部33の平面アンテナ35の中心が床面から1000mmの高さになるように、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34をレーダー機構部支持治具61にボルト65…で固定する。レーダー機構部33の正面の前方5000mmの位置に、ターゲット治具62のスライダ68に固定した基準反射体Rを設置し、基準反射体Rの位置を上下に移動させながら、レーダー機構部33からミリ波を照射して基準反射体Rを検知する。そして反射波の受信強度が閾値を越える基準反射体Rの上限位置と下限位置とを検知する。
【0035】
図17の例では、基準反射体Rの上限位置の高さが1150mmであり、下限位置の高さが800mmであるから、その中央位置の高さは975mmとなる。レーダー機構部33のフレーム34に対して対象物検知軸Arの角度が上下方向にずれていなければ、前記中央位置の高さは平面アンテナ35の中心の高さと同じ1000mmになるはずであるが、それが975mmであるということから、対象物検知軸Arの角度が下向きに0.286°ずれていることが分かる。
【0036】
以上のようにして、レーダー機構部33のフレーム34に対する対象物検知軸Arの上下方向の角度のずれが検知されると、レーダー機構部33をレーダー機構部支持治具61から取り外し、ケーシング32の段部32eに調整部材52を介在させた状態で4本のボルト53…で共締めする。このとき、ケーシング32の上面の基準面Pの方向が対象物検知軸Arの方向に一致するように、調整部材52の回転方向位置が選択される。
【0037】
【表1】
【0038】
即ち、図13および表1を参照すると明らかなように、調整部材52の最も薄い部分、つまりNo.1のボルト孔52cが上になるように調整部材52を回転させると、ケーシング32の基準面Pに対してレーダー機構部33のフレーム34が1.0°上向きになり、調整部材52の最も厚い部分、つまりNo.11のボルト孔52cが上になるように調整部材52を回転させると、ケーシング32の基準面Pに対してレーダー機構部33のフレーム34が1.0°下向きになり、調整部材52の厚さが中間の部分、つまりNo.6あるいはNo.16のボルト孔52cが上になるように調整部材52を回転させると、ケーシング32の基準面Pに対してレーダー機構部33のフレーム34が直角になる。このようにして、調整部材52を1ピッチ(18°)回転させる毎にケーシング32の基準面Pに対するレーダー機構部33のフレーム34の角度を0.2°ずつ変化させ、1.0°上向きの状態から1.0°下向きの状態まで調整することができる。
【0039】
尚、製造上の誤差による対象物検知軸Arのずれ量よりも調整部材52による調整範囲を大きくすれば全ての場合に対応することができるため、本実施例では±1.0°の範囲とした。勿論、調整部材52のよる調整範囲は±1.0°に限定されず、対象物検知軸Arのずれの大きさに応じて適宜変更可能である。
【0040】
図17の例では、対象物検知軸Arがフレーム34に対して(つまりケーシング32の基準面Pに対して)下向きに0.286°ずれているため、No.5(あるいはNo.17)のボルト孔52cが上になるように調整部材52を回転させる。その結果、対象物検知軸Arが0.2°上向きに調整されるため、ケーシング32の基準面Pとの角度差は0.286°−0.2°=0.086°となり、対象物検知軸Arとケーシング32の基準面Pとを略平行にすることができる。
【0041】
続いて、組立を終えたレーダー装置Srを車体の支持板12にブラケット13を介して取り付け、図3に示すように、ケーシング32の基準面Pに水準器29を載置した状態で、その基準面Pが水平になるようにレーダー装置Srの上下角度を調整する。前述したように、基準面Pと対象物検知軸Arとが平行であることが保証されているため、基準面Pを水平に調整すれば対象物検知軸Arも水平になってレーダー装置Srのエイミングが完了することになる。
【0042】
尚、レーダー装置Srの対象物検知軸Arの左右方向のずれの検知は、本発明の要旨と直接関係ないので説明を省略するが、公知の任意の方法を採用することができる。表1に示すように、調整部材52を回転させると対象物検知軸Arの方向が左右方向に変化するが、そのずれは左右方向のエイミングによって吸収されるので支障はない。
【0043】
レーダー装置Srの対象物検知軸Arの調整は以下のようにして行われる。即ち、レーダー装置Srの実際の対象物検知軸Arが目標とする対象物検知軸Ar0に対して上下方向にずれている場合には、調整ビット28の先端の凹凸部28aを右下のボルト部材20の頭部20bのギヤ歯20cに係合させて回転させる。このとき調整ビット28の凹凸部28aとボルト部材20のギヤ歯20cとの係合が外れないように、ボルト支持部材23のガイド突起23aによって調整ビット28の凹凸部28aの背面が支持される(図8参照)。
【0044】
右下のボルト部材20を回転させてフランジ32のステー32hを前方に押し出すと、上側の2本のボルト部材19,21を支点としてレーダー装置Srが上向きに揺動し、対象物検知軸Arが上向きに調整される。逆に、フランジ21のステー32hを後方に引き戻すと、上側の2本のボルト部材19,21を支点としてレーダー装置Srが下向きに揺動し、対象物検知軸Arが下向きに調整される。
【0045】
同様にして、調整ビット28を用いて左上のボルト部材21を回転させてフランジ32のステー32iを前方に押し出すと、右側の2本のボルト部材19,20を支点としてレーダー装置Srが右向きに揺動し、対象物検知軸Arが右向きに調整される。逆にフランジ32のステー32iを後方に引き戻すと、右側の2本のボルト部材19,20を支点としてレーダー装置Srのが左向きに揺動し、対象物検知軸Arが左向きに調整される。
【0046】
以上のように、個々のレーダー装置Srの組立上の誤差によりレーダー機構部33に対して対象物検知軸Arの方向がずれていても、ずれた対象物検知軸Arとケーシング2の基準面Pとが平行になるように調整部材52を用いて調整することで、前記ケーシング32の基準面Pを水準器29を用いて水平に調整するだけで、対象物検知軸Arを目標とする対象物検知軸Ar0に簡単かつ精密に一致させることが可能となる。このとき、ケーシング32の上面になる基準面Pに水準器29を載置して水平に調整するので、水平を検知する一般的な水準器を使用することができるだけでなく、ケーシング32の上面に水準器29を設置できるので作業が容易であり、水準器29を設置する場所を間違えることがない。
【0047】
次に、図20に基づいて本発明の第2実施例を説明する。
【0048】
第1実施例の調整部材52はNo.1のボルト孔52cおよびNo.11のボルト孔52cを結ぶ直線に対して左右対称な形状であるため、20個のボルト孔52c…を備えているにも拘わらず、11通りの角度調整しかできなかった。第2実施例は、20個のボルト孔52c…によって20通りの角度調整を可能にして、対象物検知軸Arの調整精度を更に高めたものである。
【0049】
即ち、No.1のボルト孔52cは調整部材52の最も薄い部分から時計方向に4.5°ずれた位置にあり、No.11のボルト孔52cは調整部材52の最も厚い部分から時計方向に4.5°ずれた位置にある。従って、調整部材52の最も薄い部分および最も薄い部分を通る断面の楔角度が1.0°であるのに対し、No.1のボルト孔52cおよびNo.11のボルト孔52cを通る断面の楔角度は0.95°になる。
【0050】
【表2】
【0051】
その結果、表2から明らかなように、No.1〜No.20の20個のボルト孔52c…が上になるように調整部材52を回転させると、対象物検知軸Arの方向を重複することなく20通りに調整することが可能になる。尚、この場合には対象物検知軸Arの方向を水平方向(±0°)に調整することができなくなるが、図20に52c′…で示す追加のボルト孔を設け、No.6′あるいはNo.16′のボルト孔52c′を上になるように調整部材52を回転させることで、対象物検知軸Arの方向を水平方向に調整することができる。
【0052】
以上、本発明の実施例を詳述したが、本発明はその要旨を逸脱しない範囲で種々の設計変更を行うことが可能である。
【0053】
例えば、実施例ではレーダー装置Srの対象物検知軸Arの上下方向の角度を水平方向に調整しているが、水平方向よりも上向きや下向きに調整することもできる。
【0054】
またレーダー装置Srで検知する対象物は車両に限定されず、人、道路の設置物、道路の白線等を含むものとし、本発明の対象物検知装置はミリ波レーダー装置Srに限定されず、レーザーレーダー装置、ソナー、カメラ等を含むものとする。尚、対象物検知装置としてレーザーレーダー装置を用いる場合には、基準反射体Rは、自動車の車体後部に設けられるリフレクタと同じ構造のものが適切である。
【0055】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明によれば、対象物検知装置を車体に取付ける前に、先ず第1工程で、ケーシングの内部に対象物検知手段を固定したときの、対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差を検出し、続いて第2工程で、ケーシングに対象物検知手段を固定する際に、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の固定部間に調整部材を挟持することで、ケーシングの基準面と対象物検知軸とが平行となるようにケーシングに対する対象物検知手段の取付角度を前記角度差に応じて調整することができる。そして、対象物検知装置を車体に取付けた後、第3工程で、ケーシングの基準面の方向が前記所定の検知方向に対して所定の関係となるように該ケーシングの車体に対する取付角度を調整することで、対象物検知軸の方向を所定の検知方向に一致させることができる。従って、組立上の誤差により個々の対象物検知装置の対象物検知軸の方向にばらつきが発生して該対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差が種々に変化しても、調整部材の厚さを変化させることで前記角度差を補償して対象物検知軸の軸調整を行うことができる。
【0056】
また請求項2に記載された発明によれば、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段の環状の固定部に挟持される調整部材が、ケーシングに当接する第1底面と対象物検知手段に当接する第2底面とが楔状に傾斜した環状部材であるため、ケーシングおよび対象物検知手段に対する調整部材の回転方向位置を調整することにより、ケーシングの基準面の方向を対象物検知軸に一致させて軸調整の精度を高めることができる。
【0057】
また請求項3に記載された発明によれば、調整部材の第1底面および第2底面の傾斜角度を、初期固定状態における対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸と所定の検知方向との角度差の最大値以上としたので、前記角度差が最大値となった場合でも対象物検知軸を所定の検知方向に支障なく調整することができる。
【0058】
また請求項4に記載された発明によれば、ケーシングの角度を調整して基準面の方向を所定の検知方向である水平方向に一致させるので、対象物検知手段の対象物検知軸を水平方向に調整することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 レーダー装置を備えた車両の平面図
【図2】 図1の2方向矢視図
【図3】 レーダー装置の斜視図
【図4】 図3の4方向矢視図
【図5】 図3の5方向矢視図
【図6】 図3の6方向矢視図
【図7】 図5の7部拡大断面図
【図8】 図5の8部拡大断面図
【図9】 レーダー装置の縦断面図
【図10】 レーダー機構部の正面図、平面図および側面図
【図11】 レドームの正面図、平面図および側面図
【図12】 ケーシングの正面図、平面図および側面図
【図13】 調整部材の正面図、平面図および側面図
【図14】 レーダー装置の分解図
【図15】 レーダー装置の構成を示すブロック図
【図16】 レーダー装置に対して物体が接近移動しているときの送受信波の波形およびピーク周波数を示すグラフ
【図17】 レーダー機構部支持治具およびターゲット治具を示す図
【図18】 図17の18部拡大図
【図19】 図18の19方向矢視図
【図20】 本発明の第2実施例に係る調整部材の5面図
【符号の説明】
32 ケーシング
33 レーダー機構部(対象物検知手段)
52 調整部材
52a 第1底面
52b 第2底面
Ar 対象物検知軸
Ar0 目標とする対象物検知軸(所定の検知方向)
P 基準面[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a detection axis adjusting method for an object detection device in which an object detection means having a predetermined detection direction is fixed inside a casing having a reference surface on the outer surface.
[0002]
[Prior art]
When a radar device used in an ACC system (adaptive cruise control system), Stop & Go system (traffic jam tracking system), inter-vehicle warning system, etc. is mounted on a vehicle, the direction of the object detection axis of the radar device is preset. If the direction of the target object detection axis is not correctly oriented, the oncoming vehicle on the adjacent lane will be detected incorrectly, and the system will malfunction, or only the road surface, overpass and signboard will be detected and the preceding vehicle will not be detected. The problem occurs that the system does not work. Therefore, it is necessary to perform aiming to match the direction of the object detection axis of the radar device with the direction of the target object detection axis.
[0003]
In Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 11-326495, in order to aim the vertical direction of the object detection axis of the radar device, the angle of the antenna attached to the vehicle body is measured with a level and the vertical angle is set to the correct angle. What to adjust is disclosed.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, when the aiming is performed by measuring the mounting angle of the casing of the radar device with respect to the vehicle body with a level or the like, the object detection axis of the radar mechanism part built in the casing may have a certain relationship with the casing. is necessary. However, in actuality, it is inevitable that variations in the direction of the object detection axis of each radar device occur due to assembly errors, and even if the mounting angle of the casing to the vehicle body is adjusted correctly, There is a problem that the direction of the detection axis is deviated from the direction of the target object detection axis.
[0005]
The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to compensate for variations in the direction of an object detection axis with respect to a casing of a radar device so that correct aiming can be performed.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, according to the invention described in
[0007]
According to the above configuration, the object detection shaft of the object detection unit and the predetermined detection when the object detection unit is fixed inside the casing in the first step before the object detection device is attached to the vehicle body. When the angle difference from the direction is detected and then the object detection means is fixed to the casing in the second step, the adjustment member is sandwiched between the casing and the fixing portion of the object detection means. The attachment angle of the object detection means with respect to the casing is adjusted according to the angle difference so that the surface and the object detection axis are parallel . Then, after attaching the object detecting apparatus to the vehicle body, in a third step, adjusting the mounting angle to the vehicle body of the casing so that the direction of the reference surface of the casing has a predetermined relationship with said predetermined detection direction Thus, the direction of the object detection axis can be matched with a predetermined detection direction. Therefore, even if a variation occurs in the direction of the object detection axis of each object detection device due to an assembly error, and the angle difference between the object detection axis and the predetermined detection direction changes variously, the adjustment member By changing the thickness of the object, the angle difference can be compensated and the axis of the object detection axis can be adjusted.
[0008]
According to the second aspect of the present invention, in addition to the structure of the first aspect, the fixed portion of the casing and the object detection means is annular, and the adjustment member has the first bottom surface that contacts the casing as the object detection. A detection shaft of an object detection device, wherein the detection member is an annular member inclined in a wedge shape with respect to a second bottom surface abutting on the means, and the adjustment member is capable of adjusting a rotational direction position relative to the casing and the object detection means. An adjustment method is proposed.
[0009]
According to the above configuration, the adjustment member sandwiched between the annular fixed portion of the casing and the object detection means has an annular shape in which the first bottom surface contacting the casing and the second bottom surface contacting the object detection means are inclined in a wedge shape. Since it is a member, by adjusting the rotational direction position of the adjustment member with respect to the casing and the object detection means, the direction of the reference surface of the casing can be made to coincide with the object detection axis, and the accuracy of axis adjustment can be improved.
[0010]
According to the invention described in
[0011]
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in addition to the configuration of any one of the first to third aspects, the predetermined detection direction is a horizontal direction, and the predetermined relationship is a casing reference. A detection axis adjustment method for an object detection device is proposed, characterized in that the direction of the surface is made to coincide with the horizontal direction.
[0012]
According to the configuration described above, the angle of the casing is adjusted so that the direction of the reference plane coincides with the horizontal direction that is the predetermined detection direction, so that the object detection axis of the object detection means can be adjusted in the horizontal direction.
[0013]
The
[0014]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described based on examples of the present invention shown in the accompanying drawings. 1 to 19 show a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 1 is a plan view of a vehicle equipped with a radar device, FIG. 2 is a two-way arrow view of FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is a perspective view of the radar device. 4 is a view in the direction of the
[0015]
As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the radar device Sr for detecting an object such as a preceding vehicle existing in the traveling direction of the vehicle V is behind a
[0016]
As apparent from FIGS. 3 to 8, the
[0017]
Three
[0018]
As shown in FIG. 8, the base ends of the
[0019]
As shown in FIG. 4, the upper right
[0020]
As is apparent from FIGS. 9 to 14, the radar device Sr is housed in the inner space of the
[0021]
As shown in FIG. 10, the
[0022]
As shown in FIG. 11, the
[0023]
As shown in FIG. 12, the
[0024]
As shown in FIG. 13, the
[0025]
As shown in FIGS. 9 and 14, in the state where the
[0026]
As shown in FIG. 15, in the millimeter wave radar device Sr using the FM-CW wave, the transmission operation of the
[0027]
The received wave received by the
[0028]
The beat signal obtained by the
[0029]
Based on the data stored in the
[0030]
By the way, the
[0031]
17 to 19 show a radar
[0032]
The radar mechanism
[0033]
Next, the operation of the first embodiment of the present invention having the above configuration will be described.
[0034]
First, the vertical deviation of the object detection axis Ar with respect to the
[0035]
In the example of FIG. 17, since the height of the upper limit position of the reference reflector R is 1150 mm and the height of the lower limit position is 800 mm, the height of the center position is 975 mm. If the angle of the object detection axis Ar is not vertically shifted with respect to the
[0036]
As described above, when the vertical deviation of the object detection axis Ar with respect to the
[0037]
[Table 1]
[0038]
That is, as is clear from FIG. 13 and Table 1, the thinnest portion of the
[0039]
It should be noted that all cases can be dealt with if the adjustment range by the
[0040]
In the example of FIG. 17, the object detection axis Ar is shifted by 0.286 ° downward with respect to the frame 34 (that is, with respect to the reference plane P of the casing 32). The
[0041]
Subsequently, the assembled radar device Sr is attached to the
[0042]
In addition, since detection of the shift | offset | difference of the left-right direction of the target object detection axis Ar of the radar apparatus Sr is not directly related to the summary of this invention, description is abbreviate | omitted, However, Well-known arbitrary methods are employable. As shown in Table 1, when the
[0043]
Adjustment of the object detection axis Ar of the radar device Sr is performed as follows. That is, when the actual object detection axis Ar of the radar device Sr is displaced in the vertical direction with respect to the target object detection axis Ar0, the concave and
[0044]
When the lower
[0045]
Similarly, when the upper
[0046]
As described above, even if the direction of the object detection axis Ar deviates with respect to the
[0047]
Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
[0048]
The
[0049]
That is, no. No. 1
[0050]
[Table 2]
[0051]
As a result, as is apparent from Table 2, No. 1-No. When the adjusting
[0052]
As mentioned above, although the Example of this invention was explained in full detail, this invention can perform a various design change in the range which does not deviate from the summary.
[0053]
For example, although the vertical angle of the object detection axis Ar of the radar device Sr is adjusted in the horizontal direction in the embodiment, it can be adjusted upward or downward from the horizontal direction.
[0054]
The objects detected by the radar device Sr are not limited to vehicles, but include persons, road installations, road white lines, and the like, and the object detection device of the present invention is not limited to the millimeter wave radar device Sr, but a laser. Includes radar equipment, sonar, camera, etc. In addition, when using a laser radar apparatus as a target object detection apparatus, the thing with the same structure as the reflector provided in the vehicle body rear part of a motor vehicle is suitable for the reference | standard reflector R. FIG.
[0055]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the object detection shaft of the object detection means when the object detection means is first fixed in the casing in the first step before the object detection device is attached to the vehicle body. And the predetermined detection direction is detected , and then, in the second step, when the object detection means is fixed to the casing, an adjustment member is sandwiched between the fixing portion of the casing and the object detection means. The mounting angle of the object detection means with respect to the casing can be adjusted according to the angle difference so that the reference plane of the casing and the object detection axis are parallel to each other . Then, after attaching the object detecting apparatus to the vehicle body, in a third step, adjusting the mounting angle to the vehicle body of the casing so that the direction of the reference surface of the casing has a predetermined relationship with said predetermined detection direction Thus, the direction of the object detection axis can be matched with a predetermined detection direction. Therefore, even if a variation occurs in the direction of the object detection axis of each object detection device due to an assembly error, and the angle difference between the object detection axis and the predetermined detection direction changes variously, the adjustment member By changing the thickness of the object, the angle difference can be compensated and the axis of the object detection axis can be adjusted.
[0056]
According to the second aspect of the present invention, the adjusting member sandwiched between the casing and the annular fixing portion of the object detection means includes the first bottom surface that contacts the casing and the second bottom surface that contacts the object detection means. Is an annular member inclined in a wedge shape, and by adjusting the rotational direction position of the adjustment member with respect to the casing and the object detection means, the direction of the reference plane of the casing is made to coincide with the object detection axis, and the axis adjustment accuracy Can be increased.
[0057]
According to the invention described in
[0058]
According to the invention described in
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a plan view of a vehicle equipped with a radar device. FIG. 2 is a perspective view of the radar device in FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a perspective view of the radar device. FIG. 6 is a view taken in the direction of the
32
52
P Reference plane
Claims (4)
ケーシング(32)に対する対象物検知手段(33)の初期固定状態における該対象物検知手段(33)の対象物検知軸(Ar)と前記所定の検知方向(Ar0)との角度差を検出する第1工程と、
ケーシング(32)に対象物検知手段(33)を固定する際に、ケーシング(32)および対象物検知手段(33)の固定部間に調整部材(52)を挟持することで、ケーシング(32)の基準面(P)と対象物検知軸(Ar)とが平行となるようにケーシング(32)に対する対象物検知手段(33)の取付角度を前記角度差に応じて調整する第2工程と、
ケーシング(32)の基準面(P)が前記所定の検知方向(Ar0)に対して所定の関係となるように、該ケーシング(32)の車体に対する取付角度を調整する第3工程とを含み、
前記第1及び第2工程は、対象物検知装置(Sr)を車体に取付ける前に実行され、また前記第3工程は、対象物検知装置(Sr)を車体に取付けた後に実行されることを特徴とする、対象物検知装置の検知軸調整方法。In the detection axis adjustment method of the object detection device, in which the object detection means (33) having a predetermined detection direction (Ar0) is fixed inside the casing (32) having the reference surface (P) on the outer surface,
Detecting an angular difference between the object detection axis (Ar) of the object detection means (33) and the predetermined detection direction (Ar0) in the initial fixed state of the object detection means (33) with respect to the casing (32). 1 process,
When the object detection means (33) is fixed to the casing (32), the adjustment member (52) is sandwiched between the fixing portions of the casing (32) and the object detection means (33), whereby the casing (32). A second step of adjusting the attachment angle of the object detection means (33) with respect to the casing (32) according to the angle difference so that the reference plane (P) of the object and the object detection axis (Ar) are parallel to each other ;
As the reference surface of the casing (32) (P) becomes a predetermined relationship to said predetermined detection direction (Ar0), seen including a third step of adjusting the mounting angle to the vehicle body of the casing (32) ,
The first and second steps are executed before attaching the object detection device (Sr) to the vehicle body, and the third step is executed after attaching the object detection device (Sr) to the vehicle body. A method for adjusting a detection axis of a target object detection device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002162969A JP3676757B2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2002-06-04 | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002162969A JP3676757B2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2002-06-04 | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004012184A JP2004012184A (en) | 2004-01-15 |
| JP3676757B2 true JP3676757B2 (en) | 2005-07-27 |
Family
ID=30431564
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002162969A Expired - Fee Related JP3676757B2 (en) | 2002-06-04 | 2002-06-04 | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3676757B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4313089B2 (en) * | 2003-05-23 | 2009-08-12 | 富士通テン株式会社 | Radar apparatus for automobile and its mounting direction adjusting method |
| JP4444265B2 (en) | 2006-11-27 | 2010-03-31 | 富士通テン株式会社 | Vehicular radar apparatus and method for manufacturing the same, reference section, and adjustment method of beam emitting direction |
| JP6952677B2 (en) * | 2018-12-04 | 2021-10-20 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Detector and vehicle |
-
2002
- 2002-06-04 JP JP2002162969A patent/JP3676757B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004012184A (en) | 2004-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3632013B2 (en) | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device | |
| Abou-Jaoude | ACC radar sensor technology, test requirements, and test solutions | |
| US9523769B2 (en) | Alignment method and system for radar of vehicle | |
| US8593333B2 (en) | Radar sensor with frontal and lateral emission | |
| CN101788659B (en) | Apparatus and sensor for adjusting sensor vertical alignment | |
| US6556166B1 (en) | Method of measuring elevational mis-alignment of an automotive radar sensor | |
| EP1257843B1 (en) | Automotive radar elevation alignment | |
| EP1480055B1 (en) | Radar apparatus for automobile, attachment direction adjuster and attachment direction adjusting method for radar apparatus | |
| JP4232570B2 (en) | Radar equipment for vehicles | |
| US6246357B1 (en) | Radar apparatus | |
| US20080186223A1 (en) | Radar Sensor for Motor Vehicles | |
| KR102179784B1 (en) | Method for calibrating sensors in automobiles for angle measurement, calculation devices, driver assistance systems, and automobiles | |
| US20080091380A1 (en) | Velocity sensor and ground vehicle velocity sensor using the same | |
| US20120169525A1 (en) | Fmcw radar sensor for motor vehicles | |
| JP3958970B2 (en) | Mobile radar system | |
| JP6957820B2 (en) | Radio sensor, adjustment method and adjustment program | |
| JP4331152B2 (en) | Object detection device mounting structure | |
| US20110095937A1 (en) | Monostatic multi-beam radar sensor for motor vehicles | |
| JP3676757B2 (en) | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device | |
| JP3511606B2 (en) | Position adjustment device and position adjustment method for vehicle-mounted radar device | |
| JP3838632B2 (en) | Method for adjusting detection axis of object detection device | |
| JP2006047140A (en) | Method and detector for detecting axial shift in radar system | |
| US20040066325A1 (en) | Sensor alignment method and system | |
| JP2003035768A (en) | Radio wave radar device and vehicle loaded therewith | |
| JP2005172824A (en) | Method for adjusting setting angle of vehicular radar installation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20041101 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20041208 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050207 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20050420 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20050428 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20080513 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090513 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090513 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100513 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110513 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110513 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |