JP2024120453A - Construction Machinery - Google Patents
Construction Machinery Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2024120453A JP2024120453A JP2023027261A JP2023027261A JP2024120453A JP 2024120453 A JP2024120453 A JP 2024120453A JP 2023027261 A JP2023027261 A JP 2023027261A JP 2023027261 A JP2023027261 A JP 2023027261A JP 2024120453 A JP2024120453 A JP 2024120453A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- bucket
- claw
- excavation
- length dimension
- camera
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 210000000078 claw Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 157
- 238000009412 basement excavation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 124
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000036544 posture Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000002689 soil Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010191 image analysis Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Operation Control Of Excavators (AREA)
- Component Parts Of Construction Machinery (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】 掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化を容易に、かつ正確に把握することにより、マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを用いた作業の信頼性を向上する。【解決手段】 油圧ショベル1は、作業装置7のバケット10を撮影するカメラを備えている。この上で、コントローラ19は、カメラ18が撮影したバケット10の画像を解析して掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1(L0)を算出し、算出した掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1(L0)の変化量を爪先位置演算に反映させる。【選択図】 図1[Problem] To improve the reliability of work using machine guidance or machine control by easily and accurately grasping changes in the length dimension of an excavation claw. [Solution] A hydraulic excavator 1 is equipped with a camera that photographs a bucket 10 of a working device 7. A controller 19 then analyzes an image of the bucket 10 photographed by a camera 18 to calculate the length dimension L1 (L0) of the excavation claw 12, and reflects the calculated amount of change in the length dimension L1 (L0) of the excavation claw 12 in the claw tip position calculation. [Selected Figure] Figure 1
Description
本発明は、マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを利用して作業を行う油圧ショベル等の建設機械に関する。 The present invention relates to construction machinery such as hydraulic excavators that use machine guidance and machine control to carry out work.
一般に、建設機械の代表例である油圧ショベルは、自走可能な下部走行体と、下部走行体に旋回可能に搭載された上部旋回体と、を備えている。上部旋回体の前側には、バケットを有する作業装置が回動可能に設けられ、この作業装置を用いて土砂の掘削作業等の土木作業が行われる。 Generally, hydraulic excavators, which are a typical example of construction machinery, are equipped with a self-propelled lower traveling body and an upper rotating body that is rotatably mounted on the lower traveling body. A working device with a bucket is rotatably mounted on the front side of the upper rotating body, and this working device is used to perform civil engineering work such as excavating soil and sand.
近年では、ICT(Information and Communication Technology)を用いた情報化施工が土木作業にも導入されている。この情報化施工には、トータルステーション(TS)や全地球航法衛星システム(GNSS)を利用したマシンガイダンス(MG)、マシンコントロール(MC)がある。マシンガイダンス(MG)は、油圧ショベルのバケットの掘削爪の先端位置を演算し、演算したバケットの掘削爪の先端位置や、演算したバケットの掘削爪の先端位置と施工情報から設計値(三次元設計データ)との差分を算出してオペレータに提供し、油圧ショベルの操作をサポートするものである。マシンコントロール(MC)は、油圧ショベルのバケットの掘削爪の先端位置を演算し、バケットの掘削爪の先端位置が設計値(三次元設計データ)に沿うように機械をリアルタイムに自動制御し施工を行うものである。 In recent years, information-based construction using ICT (Information and Communication Technology) has been introduced into civil engineering work. This information-based construction includes machine guidance (MG) and machine control (MC) that use total stations (TS) and global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). Machine guidance (MG) calculates the tip position of the digging claws of the hydraulic excavator bucket, calculates the calculated tip position of the digging claws of the bucket, and calculates the difference between the calculated tip position of the digging claws of the bucket and the design value (three-dimensional design data) from the construction information, and provides this to the operator, thereby supporting the operation of the hydraulic excavator. Machine control (MC) calculates the tip position of the digging claws of the hydraulic excavator bucket, and automatically controls the machine in real time to perform construction so that the tip position of the digging claws of the bucket is in line with the design value (three-dimensional design data).
マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを行う油圧ショベルは、作業装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出センサと、姿勢検出センサによって検出された作業装置の姿勢に基づいて、バケットの掘削爪の先端位置を演算する爪先位置演算を実行するコントローラと、を備えている(特許文献1)。 A hydraulic excavator that performs machine guidance and machine control is equipped with a posture detection sensor that detects the posture of the work equipment, and a controller that performs a toe position calculation that calculates the tip position of the bucket's excavation claws based on the posture of the work equipment detected by the posture detection sensor (Patent Document 1).
しかし、バケットに設けられた掘削爪は、掘削時の衝撃や摩擦によって摩耗や欠損を生じて長さ寸法が短くなることがある。また、掘削爪を交換する場合、新品の掘削爪を取付けた場合と、中古の掘削爪を取付けた場合でも、長さ寸法が変化する。このように掘削爪の長さ寸法が変化すると、爪先位置演算を用いて作業を行う場合に、作業精度が低下する虞がある。 However, the digging claws on the bucket can become worn or damaged due to impacts and friction during digging, shortening their length. Furthermore, when replacing the digging claws, the length changes whether a new digging claw is installed or a used digging claw is installed. If the length of the digging claws changes in this way, there is a risk that the accuracy of work will decrease when work is performed using claw tip position calculations.
そこで、爪先位置演算を用いて作業を行う油圧ショベルには、掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化、例えば、掘削爪の摩耗量を算出する機能を備えたものがある。この油圧ショベルは、掘削爪の先端を地面に位置決めした状態でバケットを回動させることにより、任意の座標の移動寸法を検出して掘削爪の摩耗量を算出している(特許文献2)。 Some hydraulic excavators that use toe position calculations to carry out work are equipped with a function to calculate changes in the length dimension of the excavation claw, for example, the amount of wear on the excavation claw. This hydraulic excavator detects the movement dimension of any coordinate by rotating the bucket with the tip of the excavation claw positioned on the ground, and calculates the amount of wear on the excavation claw (Patent Document 2).
しかし、掘削爪の摩耗量による座標の変化は僅かであるから、掘削爪の先端の位置がずれないようにバケットを回動させる必要がある。これには、掘削爪を押付けることができる強固な地面が必要になる上に、熟練した作業装置の操作技術も必要になる。従って、掘削爪の正確な摩耗量を得るのが難しくなり、マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを用いた作業の信頼性が低下するという問題がある。 However, because the change in coordinates due to wear on the excavation claws is slight, it is necessary to rotate the bucket so that the position of the tip of the excavation claw does not shift. This requires a solid ground against which the excavation claws can be pressed, as well as skilled techniques for operating the work equipment. This makes it difficult to obtain an accurate measurement of the wear on the excavation claws, which reduces the reliability of work using machine guidance and machine control.
本発明の目的は、掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化を容易に、かつ正確に把握することにより、マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを用いた作業の信頼性を向上できるようにした建設機械を提供することにある。 The object of the present invention is to provide a construction machine that can easily and accurately grasp changes in the length dimension of the excavation claws, thereby improving the reliability of work using machine guidance and machine control.
本発明は、車体と、前記車体に設けられ、先端にバケットを有する作業装置と、前記作業装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出センサと、前記姿勢検出センサによって検出された前記作業装置の姿勢に基づいて、前記バケットの掘削爪の先端位置を演算する爪先位置演算を実行するコントローラと、を備えた建設機械において、前記バケットを撮影するカメラを備え、前記コントローラは、前記カメラが撮影した前記バケットの画像を解析して前記掘削爪の長さ寸法を算出し、算出した前記掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化量を前記爪先位置演算に反映させる。 The present invention relates to a construction machine including a vehicle body, a working device provided on the vehicle body and having a bucket at its tip, an attitude detection sensor for detecting the attitude of the working device, and a controller for executing a toe position calculation for calculating the tip position of the excavation claw of the bucket based on the attitude of the working device detected by the attitude detection sensor. The construction machine is equipped with a camera for photographing the bucket, and the controller analyzes an image of the bucket photographed by the camera to calculate the length dimension of the excavation claw, and reflects the calculated amount of change in the length dimension of the excavation claw in the toe position calculation.
本発明によれば、掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化を容易に、かつ正確に把握することができ、マシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを用いた作業の信頼性を向上することができる。 According to the present invention, changes in the length dimension of the excavation claws can be easily and accurately grasped, improving the reliability of work using machine guidance and machine control.
以下、本発明に係る建設機械の実施形態を、クローラ式の油圧ショベルに適用した場合を例に挙げ、添付図面を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。なお、実施形態では、作業装置の伸長方向を前後方向とし、作業装置の伸長方向と直交する作業装置の幅方向を左右方向として説明する。 Below, an embodiment of the construction machine according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the attached drawings, taking as an example a case where it is applied to a crawler-type hydraulic excavator. Note that in the embodiment, the extension direction of the working device will be described as the front-rear direction, and the width direction of the working device, which is perpendicular to the extension direction of the working device, will be described as the left-right direction.
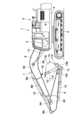
図1ないし図8は第1の実施形態を示している。図1において、建設機械の代表例である油圧ショベル1は、自走可能なクローラ式の下部走行体2と、下部走行体2に旋回可能に搭載され、下部走行体2と共に車体を構成する上部旋回体3と、上部旋回体3の前側に回動可能に取付けられた後述の作業装置7と、を備えている。油圧ショベル1は、下部走行体2によって作業の現場を走行し、上部旋回体3を旋回させつつ作業装置7を回動させることにより、土砂の掘削作業等を行う。
Figures 1 to 8 show the first embodiment. In Figure 1, a hydraulic excavator 1, which is a representative example of a construction machine, is equipped with a self-propelled crawler-type lower traveling
上部旋回体3は、ベースとなる旋回フレーム4を有し、旋回フレーム4の前側の左右方向の中間部には、作業装置7のブーム8等が回動可能に取付けられている。上部旋回体3は、旋回フレーム4の左前部にキャブ5を備えている。
The upper rotating body 3 has a rotating frame 4 as a base, and a
キャブ5は、運転室を画成するボックス状に形成され、その内部には、オペレータが座る運転席(図示せず)が設けられている。また、運転席の前側には、油圧ショベル1の走行動作を制御する走行用レバー・ペダル装置(図示せず)が設けられている。運転席の左右両側には、上部旋回体3の旋回動作および作業装置7の回動動作を制御する作業用レバー装置(図示せず)が設けられている。さらに、キャブ5内には、油圧ショベル1に搭載された機器(エンジン、アクチュエータ、センサ等)の状態、作業の状態、作業の指示等の情報を表示するモニタ6(本発明の表示装置)、後述のコントローラ18が設けられている。
The cab 5 is formed in a box shape that defines the driver's compartment, and inside it is provided a driver's seat (not shown) where the operator sits. In addition, in front of the driver's seat is provided a travel lever and pedal device (not shown) that controls the travel operation of the hydraulic excavator 1. On both the left and right sides of the driver's seat are provided work lever devices (not shown) that control the rotation operation of the upper rotating body 3 and the rotation operation of the work device 7. Furthermore, inside the cab 5 are provided a monitor 6 (the display device of the present invention) that displays information such as the status of the equipment (engine, actuators, sensors, etc.) installed on the hydraulic excavator 1, the status of the work, and work instructions, and a
図1、図2に示すように、作業装置7は、上部旋回体3の前側に回動可能に取付けられている。作業装置7は、後述するブーム8、アーム9、バケット10、バケットリンク13、ブームシリンダ14、アームシリンダ15、バケットシリンダ16を含んで構成されている。作業装置7は、ブームシリンダ14、アームシリンダ15、バケットシリンダ16を適宜に伸長、縮小させることにより、ブーム8、アーム9、バケット10等を回動して土砂の掘削作業等を行う。また、作業装置7には、ブーム8、アーム9、バケット10の姿勢を検出する後述の姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cが設けられている。
As shown in Figures 1 and 2, the working device 7 is rotatably attached to the front side of the upper rotating body 3. The working device 7 is composed of a
ブーム8は、上部旋回体3の旋回フレーム4に回動可能に取付けられている。ブーム8は、前側に倒した状態で下側に位置する下面8A、上側に位置する上面8Bおよび左右両側に位置する側面8C(左側のみ図示)を有している。ブーム8は、長さ方向の中間部が逆V字状に折り曲げられた角筒構造体として形成されている。
The
ブーム8は、一端側の端部が連結ピン(図示せず)を用いて旋回フレーム4に回動可能に取付けられている。ブーム8の他端側の端部には、アーム9の一端側の端部が取付けられている。ブーム8の下面8Aには、アーム9とバケット10を折り畳んだときに、バケット10の他端側と対面する位置(長さ方向の中間部付近)に、後述のカメラ18が取付けられている。さらに、上面8Bには、長さ方向の中間部付近に位置してアームシリンダブラケット8Dが設けられている。
One end of the
アーム9は、ブーム8の他端側の端部に回動可能に取付けられている。アーム9は、直線的な角筒構造体として形成されている。アーム9は、一端側の端部が左右方向に延びた連結ピン9Aを用いてブーム8の他端側の端部に回動可能に取付けられている。アーム9の一端側の端部には、アームシリンダブラケット9Bが設けられている。また、アーム9の一端側には、バケットシリンダブラケット9Cが設けられている。アーム9の他端側の端部には、バケット10の一端側の端部が取付けられている。
The
バケット10は、アーム9の他端側の端部に回動可能に取付けられている。バケット10は、内部が土砂の収容空間となったバケット本体11と、バケット本体11の他端側に設けられた複数の掘削爪12とを有している。
The
バケット本体11は、掘削した土砂等を収容する。バケット本体11は、凹湾曲状をなす底板11Aと、底板11Aの左右両側に固着された左側板11Bおよび右側板11C(図7参照)とを有し、これら底板11A、左側板11B、右側板11Cによって土砂の収容空間が形成されている。底板11Aの一端側には、左右方向に間隔をもって一対のブラケット11Dが設けられている。また、底板11Aの他端側には、底板11Aよりも厚肉な平板状のカッティングエッジ11Eが設けられている。そして、バケット本体11は、一対のブラケット11Dが左右方向に延びた連結ピン11Fを用いてアーム9の他端側の端部に回動可能に取付けられている。また、一対のブラケット11Dには、バケットリンク13の前リンク13Bが回動可能に取付けられている。
The
掘削爪12は、バケット本体11の他端側に位置するカッティングエッジ11Eの他端から突出して設けられている。掘削爪12は、カッティングエッジ11Eに左右方向に並んで複数本、例えば本実施形態においては5本配置されている。掘削爪12は、後述のアダプタ12A、ポイント12Bおよび固定ピン12Cによって構成されている。
The digging
5本のアダプタ12Aは、バケット本体11のカッティングエッジ11Eに左右方向に一定の間隔をもって配置されている。アダプタ12Aは、カッティングエッジ11Eを挟んだ状態で、カッティングエッジ11Eに溶接によって固着されている。また、カッティングエッジ11Eから突出したアダプタ12Aの先端部(他端部)には、ポイント12Bが着脱可能に取付けられる。
The five
5本のポイント12Bは、交換式の爪部として形成されている。ポイント12Bは、長さ方向の基端側が厚肉となり、先端側が薄肉となっている。ポイント12Bの基端側は、アダプタ12Aの先端部に被さる凹部となっている。
The five
そして、ポイント12Bは、基端側の凹部をアダプタ12Aの先端部に被せた(嵌合した)状態で、ポイント12Bの凹部とアダプタ12Aの先端部とに亘り、カッティングエッジ11Eの厚さ方向に固定ピン12Cを打ち込むことにより、アダプタ12Aに固定的に取付けることができる。また、固定ピン12Cを打ち込み方向と反対に打ち抜くことにより、アダプタ12Aからポイント12Bを取外すことができる。これにより、ポイント12Bは、大きく摩耗した場合や欠損した場合に交換することができる。
The
ここで、図7に示すように、5本の掘削爪12は、ポイント12Bと反対側となるアダプタ12Aの基端部12A1からポイント12Bの先端部12B1までが全体の長さ寸法(全長寸法)となる。掘削爪12の全長寸法は、新品の掘削爪12の全長寸法となる後述の基準長さ寸法L2から摩耗や欠損を経て後述の算出長さ寸法L1へと短く変化する。アダプタ12Aの基端部12A1は、図7に示すカメラ18が撮影した画像における固定点(摩耗や欠損が生じても変化しない点)となっている。摩耗や欠損による掘削爪12の全長寸法の変化、具体的には、新品のポイント12Bの先端部12B2と比較して現状のポイント12Bの先端部12B1がどれだけ短くなったのかを計測する場合には、掘削爪12の長さ方向において基準となる任意の点(本実施形態ではアダプタ12Aの基端部12A1)を設定し、その任意の点からポイント12Bの先端部12B1までの寸法を計測している。前述した基準となる任意の点は、摩耗や欠損が生じても変化しない点であればよく、固定ピン12Cやポイント12Bの基端部でもよい。
Here, as shown in FIG. 7, the five
摩耗や欠損によって変化する掘削爪12(ポイント12B)の長さ寸法、即ち、算出長さ寸法L1を計測する場合、カメラ18で撮影した画像を解析して掘削爪12の外縁(輪郭)を明確にし、画像データから掘削爪12を抽出する。このときに、アダプタ12Aの基端部12A1は、平坦なカッティングエッジ11Eから突出しているから当該カッティングエッジ11Eとの境界部分が明確であり、掘削爪12の外縁を正確に抽出する(見分ける)ことができる。
When measuring the length dimension of the digging claw 12 (
バケットリンク13は、アーム9の他端側とバケット10との間に設けられている。バケットリンク13は、一端がアーム9の先端側に連結された後リンク13Aと、一端が後リンク13Aの他端に連結され、他端がバケット本体11のブラケット11Dに連結された前リンク13Bとにより構成されている。
The
ブームシリンダ14は、ブーム8を挟んで左右に1本ずつ設けられている(左側のみ図示)。ブームシリンダ14は、長さ方向の一端が旋回フレーム4に回動可能に取付けられ、他端がブーム8の側面8Cに回動可能に取付けられている。2本のブームシリンダ14は、伸縮することにより、ブーム8を上部旋回体3(旋回フレーム4)に対して前後方向ないし上下方向に回動させる。
The
アームシリンダ15は、ブーム8とアーム9との間に設けられている。アームシリンダ15は、長さ方向の一端がブーム8のアームシリンダブラケット8Dに回動可能に取付けられ、他端がアーム9のアームシリンダブラケット9Bに回動可能に取付けられている。アームシリンダ15は、伸縮することにより、アーム9をブーム8に対して前後方向ないし上下方向に回動させる。
The
バケットシリンダ16は、アーム9とバケットリンク13との間に設けられている。バケットシリンダ16は、長さ方向の一端がアーム9のバケットシリンダブラケット9Cに回動可能に取付けられ、他端が後リンク13Aと前リンク13Bとの連結部に回動可能に取付けられている。バケットシリンダ16は、伸縮することにより、バケット10をアーム9に対して前後方向ないし上下方向に回動させる。
The
姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cは、作業装置7に設けられ、作業装置7の姿勢を検出する。姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cは、後述のコントローラ19の入力部に接続されている。姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cは、ブーム8、アーム9、バケット10の角度を検出し、その検出データをコントローラ19に出力する。姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cには、旋回フレーム4とブーム8との間、ブーム8とアーム9との間、アーム9とバケット10との間に設けられた角度センサ、ブームシリンダ14、アームシリンダ15、バケットシリンダ16の伸縮状態(長さ寸法)を検出するストロークセンサ等が用いられる。
The
このように構成された作業装置7は、アームシリンダ15とバケットシリンダ16を大きく伸長させ、姿勢検出センサ17B,17Cを用いてアーム9とバケット10とを所定の姿勢に配置する。これにより、バケット10がブーム8の下面8Aに対面した位置に配置される。以降の説明では、バケット10がブーム8の下面8Aに対面した姿勢を「特定位置」と呼称する。
The work device 7 configured in this manner greatly extends the
カメラ18は、ブーム8の下面8Aに設けられている。カメラ18は、ブーム8の下面8Aに対して前後方向に回動可能に取付けられている。カメラ18は、バケット10がブーム8の下面8Aに対面した特定位置(図1ないし図3に示す位置)に配置された状態で、掘削爪12を含むバケット10の他端側を撮影する。このときに、カメラ18は、2本以上となる5本の掘削爪12を含む範囲を撮影する。具体的には、カメラ18は、図7に示す範囲を撮影する。
The
図4、図5に示すように、カメラ18は、ブーム8の下面8Aに取付けられた固定部材18Aと、固定部材18Aにボルト18Bを介して前後方向に回動可能に連結された回動部材18Cと、回動部材18Cに設けられたカメラ本体18Dと、により構成されている。カメラ本体18Dは、有線または無線で後述のコントローラ19に接続されている。カメラ18は、ボルト18Bを緩めて回動部材18Cを回動させることにより、カメラ本体18Dをバケット10の他端側(カッティングエッジ11E、掘削爪12等)に対面させることができ、この位置でボルト18Bを締付けることで固定することができる。従って、アーム9やバケット10が交換された場合でも、回動部材18Cを回動させて対応することができる。カメラ本体18Dがバケット10の他端側に対面した位置とは、カメラ本体18Dの光軸がカッティングエッジ11Eに直交した位置または凡そ直交した位置である。
As shown in Figures 4 and 5, the
図6に示すように、コントローラ19は、例えば上部旋回体3のキャブ5内に設けられている。コントローラ19は、例えば、マイクロコンピュータからなる演算部(図示せず)、ROM、RAM等の半導体メモリからなる記憶部19A、信号を受信する入力部、信号を発信する出力部(いずれも図示せず)等を備えている。コントローラ19の入力部には、姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17C、カメラ18のカメラ本体18D、エンジンスイッチ、各種センサ類(いずれも図示せず)が接続されている。一方、コントローラ19の出力部には、キャブ5内のモニタ6等が接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
コントローラ19の記憶部19Aは、事前に入力した設計データの座標と全地球航法衛星システム(GNSS:Global Navigation Satellite System)、トータルステーション(TS:Total Station)等を利用して算出した現状の座標との差を報知するマシンガイダンス、カメラ18から送信された画像の解析(掘削爪12の抽出)、解析した画像に基づく掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1の算出、摩耗等による掘削爪12の寸法変化を反映したマシンガイダンスの数値補正、等の処理プログラムを有している。また、記憶部19Aには、掘削爪12の長さ寸法の基準値、本実施形態では、新品のポイント12Bを取付けたときの掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2が記憶されている。この掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2は、マシンガイダンスの数値補正を行うときに使用される。
The
コントローラ19は、カメラ18が撮影したバケット10の掘削爪12の画像を解析してバケット10の掘削爪12の長さ寸法を算出し、算出したバケット10の掘削爪12の長さ寸法の変化量を爪先位置演算に反映させる。また、コントローラ19は、カメラ18が撮影した掘削爪12の画像を解析することにより算出した掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1に基づき基準値となる基準長さ寸法L2を補正し、その補正した基準値長さ寸法L2により爪先位置演算を行うと共に、演算した掘削爪12の爪先位置(先端部12B1)の情報をモニタ6に表示させる。
The
摩耗や欠損による掘削爪12の全長寸法の変化、具体的には、新品のポイント12Bと比較して現状のポイント12Bがどれだけ短くなったのかを計測する手段について、その一例を説明する。カメラ18の画像を解析して掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1を算出し、この算出長さ寸法L1を、新品のポイント12Bが取付けられた掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2と比較し、摩耗等によって短くなった差分の寸法ΔLを算出する(L2-L1=ΔL)。
An example of a means for measuring the change in the overall length of the
本実施形態による油圧ショベル1は上述の如き構成を有するもので、油圧ショベル1を用いて掘削作業を行う場合には、オペレータは、キャブ5内に乗込み、走行用レバー・ペダル装置(図示せず)を操作することにより、油圧ショベル1を所望の作業場所まで自走させる。そして、オペレータは、作業用レバー装置(図示せず)を操作することにより、上部旋回体3を旋回させつつ、作業装置7のブーム8、アーム9、バケット10を回動させて土砂の掘削作業を行う。この掘削作業を含む各種作業を行うときに、例えば、全地球航法衛星システム、トータルステーション等にリンクしたマシンガイダンスを利用し、モニタ6に表示された指示に沿って作業を行うことで、簡単かつ正確に設計データ通りに作業することができる。
The hydraulic excavator 1 according to this embodiment has the above-mentioned configuration, and when performing excavation work using the hydraulic excavator 1, the operator gets into the cab 5 and operates the travel lever/pedal device (not shown) to drive the hydraulic excavator 1 to the desired work site. The operator then operates the work lever device (not shown) to rotate the upper rotating body 3 while rotating the
ここで、バケット10に設けられた掘削爪12(ポイント12B)は、掘削時の衝撃や摩擦によって摩耗や欠損を生じて全長寸法が短くなることがある。また、掘削爪12のポイント12Bを交換する場合、新品のポイント12Bを取付けた場合と、中古のポイント12Bを取付けた場合でも、掘削爪12の全長寸法が変化する。このように掘削爪12の全長寸法が変化すると、マシンガイダンスに沿って作業を行う場合に、作業精度が低下することが考えられる。
The excavation claw 12 (
これに対し、特許文献1の発明の油圧ショベルは、掘削爪の先端を地面に位置決めした状態でバケットを回動させることにより、任意の座標の移動寸法を検出して掘削爪の摩耗量(長さ寸法)を算出している。 In contrast, the hydraulic excavator disclosed in Patent Document 1 rotates the bucket while the tip of the digging claw is positioned on the ground, and detects the movement dimension of any coordinate to calculate the wear (length dimension) of the digging claw.
しかし、掘削爪の摩耗量による座標の変化は僅かであるから、掘削爪の先端の位置がずれないようにバケットを回動させる必要がある。これには、掘削爪を押付けることができる強固な地面が必要になる上に、熟練した作業装置の操作技術も必要になる。従って、掘削爪の正確な摩耗量を把握するのが難しくなり、マシンガイダンスを用いた作業の信頼性が低下してしまう。そこで、本実施形態では、マシンガイダンスを利用して油圧ショベル1を操作するときに、マシンガイダンスの寸法表示(作業指示)をコントローラ19によって補正している。
However, because the change in coordinates due to wear on the excavation claws is slight, it is necessary to rotate the bucket so that the position of the tip of the excavation claw does not shift. This requires a solid ground against which the excavation claws can be pressed, as well as skilled techniques for operating the work equipment. This makes it difficult to grasp the exact amount of wear on the excavation claws, reducing the reliability of work using machine guidance. Therefore, in this embodiment, when operating the hydraulic excavator 1 using machine guidance, the dimensional display (work instructions) of the machine guidance is corrected by the
次に、マシンガイダンスを利用して油圧ショベル1で作業するときのコントローラ19の制御処理およびマシンガイダンスに用いる寸法表示の補正処理について、図8を参照して説明する。
Next, the control process of the
図8のステップS1では、作業装置7の掘削爪12を特定位置に配置する。具体的には、図1、図2に示すように、アームシリンダ15とバケットシリンダ16を大きく伸長させてアーム9とバケット10を折り畳むことにより、バケット10の他端側に位置する掘削爪12がブーム8の下面8Aに対面するように、姿勢検出センサ17B,17Cを用いてアーム9とバケット10とを所定の姿勢、即ち、特定位置に配置する。これにより、掘削爪12を含むバケット10の他端側は、カメラ18のカメラ本体18Dに対し、所定の距離寸法および所定の角度位置に配置されている。
In step S1 of FIG. 8, the
この場合、所定の距離寸法は、カメラ18がバケット10の他端側を撮影したときに、2本以上の掘削爪12を撮影できる距離寸法である。本実施形態では、図7に示すように、5本の掘削爪12を撮影できる距離寸法に設定している。
In this case, the predetermined distance is a distance that allows two or
また、所定の角度位置とは、アダプタ12Aの基端部12A1とポイント12Bの先端部12B1とを明確に撮影できる角度であり、望ましくは、カメラ本体18Dの光軸がカッティングエッジ11Eに直交する角度位置または凡そ直交した角度位置となる。これにより、カメラ18は、複数本の掘削爪12の全体を掘削爪12の正面から明確に撮影することができる。
The predetermined angular position is an angle at which the base end 12A1 of the
続いて、作業装置7の掘削爪12を特定位置に配置したら、ステップS2に移り、カメラ18で複数本(5本)の掘削爪12(バケット10の他端側)を撮影し、ステップS3では、撮影した画像データをコントローラ19に送信する。
Next, once the
ステップS4では、画像データを画像解析して個々の掘削爪12を抽出する。例えば、コントローラ19は、カメラ18で撮影した画像を解析して5本の掘削爪12の外縁(輪郭)を明確にすることで、画像データから5本の掘削爪12の全体像を抽出する。
In step S4, the image data is subjected to image analysis to extract the
続くステップS5では、コントローラ19は、5本の掘削爪12について、アダプタ12Aの基端部12A1からポイント12Bの先端部12B1までの直線距離で使用している画素の個数を数える。そして、カメラ本体18Dの画素の間隔寸法(画素数)と計数した画素の個数との関係から個々の掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1を算出する。ここで、5本の掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1にばらつきがある場合には、各算出長さ寸法L1の平均値L0を用いる。
In the next step S5, the
掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L0を算出したら、ステップS6に移行して、予め記憶されていた摩耗していない(新品の)ポイント12Bが取付けられた掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法(基準値)L2と掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L0との変化量を爪先位置演算に反映させて差分の寸法ΔLを算出する。続く、ステップS7では、算出した差分の長さ寸法ΔLをマシンガイダンスに用いる数値に加算する補正を行う。即ち、掘削爪12が摩耗した分(長さ寸法ΔL)だけバケット10を掘削面の近くまで移動できるように指示する。ステップS8では、補正された爪先位置の情報(補正値)をモニタ6に表示する。そして、オペレータは、モニタ6に表示された爪先位置の情報を参照して作業を行うことにより、正確な作業を行うことができる。
After calculating the calculated length dimension L0 of the
かくして、本実施形態による油圧ショベル1は、作業装置7のバケット10を撮影するカメラを備え、コントローラ19は、カメラ18が撮影したバケット10の画像を解析して掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1(L0)を算出し、算出した掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1(L0)の変化量を爪先位置演算に反映させる。
Thus, the hydraulic excavator 1 according to this embodiment is equipped with a camera that photographs the
従って、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1(L0)は、熟練した作業装置7の操作技術を必要とせず、容易かつ正確に計測される。この結果、油圧ショベル1でマシンガイダンスやマシンコントロールを用いた作業を行うときの信頼性を向上することができる。
Therefore, the calculated length dimension L1 (L0) of the
また、カメラ18は、ブーム8の下面8Aに対して回動可能に取付けられている。これにより、アーム9やバケット10が交換された場合でも、カメラ18(カメラ本体18D)をバケット10の他端側に対面させることができる。また、カメラ18の撮影範囲も調整可能である。
The
また、バケット10の掘削爪12は、左右方向に並んで複数本、例えば5本設けられ、カメラ18は、5本の掘削爪12のうち、2本以上の掘削爪12(本実施形態では5本)を含む範囲を撮影する構成としている。これにより、複数本の掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1を平均長さ寸法L0として求めることができ、マシンガイダンスの補正に対する信頼性(正確性)を向上することができる。
The
さらに、表示装置としてのモニタ6を備えている。コントローラ19は、カメラ18が撮影した掘削爪12の画像を解析することにより算出した掘削爪12の長さ寸法L1(L0)に基づき基準値を補正し、その補正した基準値により爪先位置演算を行うと共に、演算した掘削爪12の爪先位置となるポイント12Bの先端部12B1の情報をモニタ6に表示させる。これにより、モニタ6を目視することによってマシンガイダンスに沿って正確な作業を容易に行うことができる。
The device further includes a
次に、図9および図10は本発明の第2の実施形態を示している。本実施形態の特徴は、コントローラは、姿勢検出センサにより検出された作業装置の姿勢と爪先位置演算により算出した掘削爪の先端位置とに基づいて、掘削爪の先端位置が予め指定された経路に沿って動作するように作業装置を制御することにある。以下、このような掘削爪の制御手法を「マシンコントロール」と呼称する。なお、第2の実施形態では、前述した第1の実施形態と同一の構成要素に同一の符号を付し、その説明を省略するものとする。 Next, Figures 9 and 10 show a second embodiment of the present invention. The feature of this embodiment is that the controller controls the working device so that the tip position of the digging claw moves along a pre-specified path based on the attitude of the working device detected by the attitude detection sensor and the tip position of the digging claw calculated by the tip position calculation. Hereinafter, this type of control method for the digging claw is referred to as "machine control." Note that in the second embodiment, the same components as those in the first embodiment described above are given the same reference numerals, and their explanation will be omitted.
走行操作装置21は、キャブ5内に位置して運転席の前側に設けられた走行用レバー・ペダル装置、走行用レバー・ペダル装置の操作に応じて下部走行体2の駆動輪(走行モータ)を動作させる走行制御弁(いずれも図示せず)を含んで構成されている。また、作業操作装置22は、キャブ5内に位置して運転席の左右両側に設けられた作業用レバー装置、作業用レバー装置の操作に応じて作業装置7、旋回装置を動作させる作業制御弁(いずれも図示せず)を含んで構成されている。そして、走行操作装置21と作業操作装置22は、コントローラ23の出力部に接続されている。
The
第2の実施形態のコントローラ23には、第1の実施形態のコントローラ19と同様に、記憶部23Aに、画像解析、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1の算出、等の処理プログラムと、新品のポイント12Bを取付けたときの掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2とが保存されている。第2の実施形態によるコントローラ23は、作業制御部23Bと、マシンコントロールの数値を補正する機能とを有している点で、第1の実施形態のコントローラ19と相違している。第2の実施形態のコントローラ23は、マシンコントロールを行うとき、摩耗、欠損等による掘削爪12の全長寸法の変化を反映して数値を補正する。
In the
作業制御部23Bは、姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cにより検出された作業装置7の姿勢と爪先位置演算により算出した掘削爪12の先端部12B1とに基づいて、掘削爪12の先端部12B1が予め指定された経路に沿って動作するように作業装置7を制御する。また、作業制御部23Bは、事前に入力した設計データの座標と全地球航法衛星システム、トータルステーション等を利用して算出した現状の座標とを比較し、例えば、作業装置7が設計データよりも過剰に掘削するように操作されたときに、掘り過ぎないように作業装置7の動きを制限する。
The
次に、マシンコントロールを利用して油圧ショベル1で作業するときのコントローラ23の制御処理およびマシンコントロールの数値補正について、図10を参照して説明する。
Next, the control process of the
図10のステップS11からステップS16は、第1の実施形態のステップS1からステップS6と同様である。ステップS18では、算出した差分に対応する長さ寸法ΔLをマシンコントロールに用いる数値に加算する補正を行う。即ち、掘削爪12が摩耗した分(長さ寸法ΔL)だけバケット10を掘削面の近くまで移動できるように動作制限を変更する。ステップS19では、補正された数値(補正値)を用いてマシンコントロールを実行する。具体的には、コントローラ23は、記憶部23Aに記憶した掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2と算出長さ寸法L1との差分の寸法ΔLを加味し、作業制御部23Bによるマシンコントロールによって掘削爪12(バケット10)を指定された経路に沿って動かすことにより、正確な作業を簡単に行うことができる。
Steps S11 to S16 in FIG. 10 are the same as steps S1 to S6 in the first embodiment. In step S18, a correction is made by adding the length dimension ΔL corresponding to the calculated difference to the numerical value used for machine control. That is, the operation limit is changed so that the
かくして、このように構成された第2の実施形態においても、前述した第1の実施形態と同様の作用および効果を得ることができる。特に、第2の実施形態によれば、作業装置7は、当該作業装置7の姿勢を特定するための姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cを備え、コントローラ23は、掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2を記憶する記憶部23Aと、新品の掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2と姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cからの情報とを基にして掘削爪12を予め指定された経路に沿って動かす作業制御部23Bと、を備え、コントローラ23は、記憶部23Aに記憶した掘削爪12の基準長さ寸法L2と算出長さ寸法L1との差分の寸法ΔLを加味し、作業制御部23Bのマシンコントロールによって掘削爪12を指定された経路に沿って動かすことができる。これにより、掘削爪12が摩耗して算出長さ寸法L1が変化しても、正確な作業を簡単に行うことができる。
Thus, in the second embodiment configured as described above, the same action and effect as in the first embodiment can be obtained. In particular, according to the second embodiment, the working device 7 is provided with
次に、図11および図12は本発明の第3の実施形態を示している。本実施形態の特徴は、コントローラは、掘削爪の算出長さ寸法と姿勢検出センサからの情報とを基にして掘削爪を予め指定された経路に沿って動かす作業制御部を備えている。なお、第3の実施形態では、前述した第2の実施形態と同一の構成要素に同一の符号を付し、その説明を省略するものとする。 Next, Figures 11 and 12 show a third embodiment of the present invention. The feature of this embodiment is that the controller is equipped with a work control unit that moves the excavation claw along a pre-specified path based on the calculated length dimension of the excavation claw and information from the attitude detection sensor. Note that in the third embodiment, the same components as those in the second embodiment described above are given the same reference numerals, and their explanation will be omitted.
図11において、第3の実施形態のコントローラ31は、第2の実施形態のコントローラ23と同様に、記憶部23Aに、画像解析、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1の算出、等の処理プログラムを有している。しかし、第3の実施形態のコントローラ31は、マシンコントロールの数値補正に代えてマシンコントロールの数値更新の機能を有している点で、第2の実施形態のコントローラ23と相違している。マシンコントロールの数値更新は、摩耗、欠損等による掘削爪12の寸法変化を反映してマシンコントロールを行うときの数値を更新する。
In FIG. 11, the
作業制御部31Bは、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1と姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cからの情報とを基にして掘削爪12(バケット10)を予め指定された経路に沿って動かす。作業制御部31Bは、事前に入力した設計データの座標と全地球航法衛星システム、トータルステーション等を利用して算出した現状の座標とを比較し、例えば、作業装置7が設計データよりも過剰に掘削するように操作されたときに、掘り過ぎないように作業装置7の動きを制限するマシンコントロールを行う。
The
次に、マシンコントロールを利用して油圧ショベル1で作業するときのコントローラ31の制御処理およびマシンコントロールの数値更新について、図12を参照して説明する。
Next, the control process of the
図12のステップS21からステップS25は、第2の実施形態のステップS11からステップS15と同様である。ステップS26では、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1に従ってマシンコントロールに用いる数値を更新する。すなわち、第3の実施形態においては、掘削爪12の長さは固定された値として取り扱うのではなく、直前に実行されたステップS25で計測された長さに都度更新される。ステップS27では、更新された数値を用いてマシンコントロールを実行する。具体的には、コントローラ31は、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1と姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cからの情報とを基にし、作業制御部31Bによるマシンコントロールによって掘削爪12(バケット10)を指定された経路に沿って動かすことにより、正確な作業を簡単に行うことができる。なお、この掘削爪12の長さの更新頻度は任意で設定することができ、例えばエンジン始動時にだけ更新を行い、一連の作業中は更新しないと設定したり、一定の回数の掘削作業を行うたびに更新すると設定したりすることが可能である。
Steps S21 to S25 in FIG. 12 are the same as steps S11 to S15 in the second embodiment. In step S26, the numerical value used for machine control is updated according to the calculated length dimension L1 of the
第3の実施形態によれば、作業装置7は、当該作業装置7の姿勢を特定するための姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cを備え、コントローラ31は、掘削爪12の算出長さ寸法L1と姿勢検出センサ17A,17B,17Cからの情報とを基にして掘削爪12を予め指定された経路に沿って動かす作業制御部31Bを備えている。そして、マシンコントロールを行うたびに計測される掘削爪12の長さを基にして爪先が制御されるので、常に正確に制御される。また第3の実施形態では、掘削爪12が他の掘削爪(平爪等)に交換されて長さが変化した場合でも、その都度算出する掘削爪の算出長さ寸法に従ってマシンコントロールに用いる数値を更新するので、容易に対応することができる。
According to the third embodiment, the working device 7 is equipped with
なお、実施形態では、5本の掘削爪12のうち、全部の掘削爪12をカメラ18で撮影した場合を例示している。しかし、本発明はこれに限らず、例えば、1本~4本の掘削爪12を撮影する構成としてもよい。また、掘削爪は、バケットに1本~4本または6本以上設ける構成としてもよい。
In the embodiment, an example is shown in which all of the five
また、実施形態では、掘削爪12を、バケット本体11に固定されたアダプタ12Aと、アダプタ12Aに着脱可能に取付けられたポイント12Bと、の2部材によって形成した場合を例示している。しかし、本発明はこれに限らず、例えば、1部材からなる掘削爪をバケット本体にボルトを用いて着脱可能に取付ける構成としてもよい。
In the embodiment, the
さらに、実施形態では、クローラ式の下部走行体2を備えた油圧ショベル1を例に挙げて説明した。しかし、本発明はこれに限らず、ホイール式の下部走行体を備えた油圧ショベルに適用してもよい。本発明における表示装置は上述したモニタに限られず、各種情報を表示できる媒体であればよく、例えばヘッドマウントディスプレイや空中ディスプレイも可能である。
Furthermore, in the embodiment, a hydraulic excavator 1 equipped with a crawler-type
1 油圧ショベル
2 下部走行体(車体)
3 上部旋回体(車体)
6 モニタ(表示装置)
7 作業装置
8 ブーム
8A 下面
10 バケット
12 掘削爪
12B ポイント
12B1 先端部(先端位置)
18 カメラ
19,23,31 コントローラ
19A,23A,31A 記憶部
23B,31B 作業制御部
L1(L0) 掘削爪の算出長さ寸法
L2 掘削爪の基準長さ寸法(基準値)
1
3. Upper rotating body (car body)
6 Monitor (display device)
7 Working
18
Claims (5)
前記車体に設けられ、先端にバケットを有する作業装置と、
前記作業装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出センサと、
前記姿勢検出センサによって検出された前記作業装置の姿勢に基づいて、前記バケットの掘削爪の先端位置を演算する爪先位置演算を実行するコントローラと、
を備えた建設機械において、
前記バケットを撮影するカメラを備え、
前記コントローラは、前記カメラが撮影した前記バケットの画像を解析して前記掘削爪の長さ寸法を算出し、算出した前記掘削爪の長さ寸法の変化量を前記爪先位置演算に反映させることを特徴とする建設機械。 The car body and
a working device provided on the vehicle body and having a bucket at its tip;
a posture detection sensor for detecting a posture of the working device;
a controller that executes a tip position calculation to calculate a tip position of an excavation claw of the bucket based on the attitude of the working device detected by the attitude detection sensor;
In a construction machine equipped with
A camera is provided to photograph the bucket,
The controller analyzes the image of the bucket taken by the camera to calculate the length dimension of the digging claw, and reflects the calculated change in the length dimension of the digging claw in the tip position calculation.
前記カメラは、前記ブームの前記下面に対して回動可能に取付けられていることを特徴とする建設機械。 2. The construction machine according to claim 1,
A construction machine characterized in that the camera is rotatably attached to the underside of the boom.
前記掘削爪は、前記バケットの左右方向に並んで複数本設けられ、
前記カメラは、複数本の前記掘削爪のうち、2本以上の前記掘削爪を含む範囲を撮影することを特徴とする建設機械。 2. The construction machine according to claim 1,
The excavation claws are provided in a plurality of pieces aligned in the left-right direction of the bucket,
The construction machine is characterized in that the camera photographs an area including two or more of the plurality of digging claws.
表示装置をさらに備え、
前記コントローラには、前記掘削爪の長さ寸法の基準値が記憶されており、
前記コントローラは、前記カメラが撮影した前記掘削爪の画像を解析することにより算出した前記掘削爪の長さ寸法に基づき前記基準値を補正し、その補正した基準値により前記爪先位置演算を行うと共に、演算した前記掘削爪の爪先位置の情報を前記表示装置に表示させることを特徴とする建設機械。 2. The construction machine according to claim 1,
Further comprising a display device,
The controller stores a reference value for the length dimension of the excavation claw,
The controller corrects the reference value based on the length dimension of the digging claw calculated by analyzing the image of the digging claw taken by the camera, calculates the tip position using the corrected reference value, and displays information on the calculated tip position of the digging claw on the display device.
前記コントローラは、前記姿勢検出センサにより検出された前記作業装置の姿勢と前記爪先位置演算により算出した前記掘削爪の先端位置とに基づいて、前記掘削爪の先端位置が予め指定された経路に沿って動作するように前記作業装置を制御することを特徴とする建設機械。 2. The construction machine according to claim 1,
The controller controls the working device so that the tip position of the digging claw moves along a pre-specified path based on the attitude of the working device detected by the attitude detection sensor and the tip position of the digging claw calculated by the tip position calculation.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023027261A JP2024120453A (en) | 2023-02-24 | 2023-02-24 | Construction Machinery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023027261A JP2024120453A (en) | 2023-02-24 | 2023-02-24 | Construction Machinery |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2024120453A true JP2024120453A (en) | 2024-09-05 |
Family
ID=92593801
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023027261A Pending JP2024120453A (en) | 2023-02-24 | 2023-02-24 | Construction Machinery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2024120453A (en) |
-
2023
- 2023-02-24 JP JP2023027261A patent/JP2024120453A/en active Pending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111441401B (en) | Excavator | |
| JP6068730B2 (en) | Work machine and work machine parameter correction method for work machine | |
| KR101833603B1 (en) | Control system of work machine and work machine | |
| KR101759409B1 (en) | Work vehicle and method of controlling work vehicle | |
| JP6322612B2 (en) | Construction management system and shape measurement method | |
| JP6872945B2 (en) | Construction machinery | |
| JP6585697B2 (en) | Construction management system | |
| AU2017282197A1 (en) | Construction system and construction method | |
| CN106460363A (en) | Work Machinery Control System, Work Machinery, And Work Machinery Control Method | |
| JP2024052764A (en) | Display control device and display method | |
| CN115667636A (en) | Excavation plan creation device, work machine, and excavation plan creation method | |
| WO2019225133A1 (en) | Hydraulic shovel and system | |
| CN115698434A (en) | Information acquisition system and information acquisition method | |
| JP2024120453A (en) | Construction Machinery | |
| US20230392353A1 (en) | Work machine, method for controlling work machine, and execution management device | |
| JP6606230B2 (en) | Shape measurement system | |
| JP7536580B2 (en) | Display control device and display method | |
| JP7324100B2 (en) | working machine | |
| WO2023063038A1 (en) | Bucket information acquisition device and construction machine provided with same | |
| JP7065002B2 (en) | Work machine | |
| KR20230136210A (en) | Position estimation systems, position estimation units, working machines, and extension units | |
| WO2023202796A1 (en) | Work machine comprising a grade control system and method of grading terrain using a work implement of a work machine with continuous calibration of the grade control system | |
| JP2022128423A (en) | System and method for acquiring shape data indicating shape of work device in work machine having work device |