JP2024030174A - Compound and metal extractant - Google Patents
Compound and metal extractant Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2024030174A JP2024030174A JP2022132781A JP2022132781A JP2024030174A JP 2024030174 A JP2024030174 A JP 2024030174A JP 2022132781 A JP2022132781 A JP 2022132781A JP 2022132781 A JP2022132781 A JP 2022132781A JP 2024030174 A JP2024030174 A JP 2024030174A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- compound
- represented
- monovalent group
- group represented
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 137
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims abstract description 81
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 81
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 125000000732 arylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 21
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001183 hydrocarbyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 2
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 abstract description 36
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 23
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 19
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 18
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 16
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 15
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 14
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 11
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 238000000638 solvent extraction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 8
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- 230000018044 dehydration Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012153 distilled water Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 6
- VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-ylamino)-N-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound C1C(CC2=CC=CC=C12)NC1=NC=C(C=N1)C(=O)NCCC(N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2)=O VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 125000000101 thioether group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- KZVBBTZJMSWGTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethoxy]butane Chemical compound CCCCOCCOCCOCCCC KZVBBTZJMSWGTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LHNRHYOMDUJLLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-hexylsulfanylhexane Chemical compound CCCCCCSCCCCCC LHNRHYOMDUJLLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LOXRGHGHQYWXJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-octylsulfanyloctane Chemical compound CCCCCCCCSCCCCCCCC LOXRGHGHQYWXJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004809 thin layer chromatography Methods 0.000 description 4
- XFVMALALJWFNST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chloro-1-methylsulfanylethane Chemical compound CSC(C)Cl XFVMALALJWFNST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MYFKLQFBFSHBPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chloro-2-methylsulfanylethane Chemical compound CSCCCl MYFKLQFBFSHBPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000005033 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 3
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphide Chemical compound [S-2] UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000000862 absorption spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000655 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- JRNVQLOKVMWBFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-benzenedithiol Chemical compound SC1=CC=CC=C1S JRNVQLOKVMWBFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YLZOPXRUQYQQID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)-1-[4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methylamino]pyrimidin-5-yl]piperazin-1-yl]propan-1-one Chemical compound N1N=NC=2CN(CCC=21)CCC(=O)N1CCN(CC1)C=1C=NC(=NC=1)NCC1=CC(=CC=C1)OC(F)(F)F YLZOPXRUQYQQID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IMNFDUFMRHMDMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Heptane Chemical compound CCCCCCC IMNFDUFMRHMDMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZWOASCVFHSYHOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,3-dithiol Chemical compound SC1=CC=CC(S)=C1 ZWOASCVFHSYHOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrachloromethane Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)Cl VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- STCOOQWBFONSKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N tributyl phosphate Chemical compound CCCCOP(=O)(OCCCC)OCCCC STCOOQWBFONSKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 2
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [NH4+].[OH-] VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIPNSKYNPDTRPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[2-oxo-2-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)ethyl]-2-[[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methylamino]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound O=C(CNC(=O)C=1C=NC(=NC=1)NCC1=CC(=CC=C1)OC(F)(F)F)N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2 NIPNSKYNPDTRPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]-2-[[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methylamino]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound O=C(CCNC(=O)C=1C=NC(=NC=1)NCC1=CC(=CC=C1)OC(F)(F)F)N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2 AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001338 aliphatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- WYLQRHZSKIDFEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,4-dithiol Chemical compound SC1=CC=C(S)C=C1 WYLQRHZSKIDFEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003350 kerosene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- TVMXDCGIABBOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N octane Chemical compound CCCCCCCC TVMXDCGIABBOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 platinum group metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003568 thioethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003799 water insoluble solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/64—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and sulfur atoms, not being part of thio groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K3/00—Materials not provided for elsewhere
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P10/00—Technologies related to metal processing
- Y02P10/20—Recycling
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本開示は、化合物および金属抽出剤に関する。 The present disclosure relates to compounds and metal extractants.
パラジウムや白金などの金属は、自動車排ガス触媒に使用されている。近年では、排ガス規制の強化が世界的に広がり、こうした有用な金属の需要が高まっていることから、金属資源の安定確保は難しくなっている。このような金属は、高価であり、資源として貴重であることから、使用後に回収してリユースすることが行われている。 Metals such as palladium and platinum are used in automobile exhaust gas catalysts. In recent years, stricter exhaust gas regulations have spread worldwide and demand for these useful metals has increased, making it difficult to secure a stable supply of metal resources. Since such metals are expensive and valuable as resources, they are collected and reused after use.
白金族金属の分離工程における精製には、電解析出法、イオン交換法、沈殿法、溶媒抽出法などが提案されているが、経済性や操作性に優れている理由から、溶媒抽出法が広く採用されている。そして、溶媒抽出法に使用される様々な金属抽出剤が開発されている。例えば、パラジウムおよび白金の金属抽出剤としてジアルキルスルフィドやトリブチルホスフェイトが用いられており(例えば、特許文献1~2)、前者ではアンモニア水溶液による逆抽出、後者では水による逆抽出が行われる。 Electrolytic deposition, ion exchange, precipitation, and solvent extraction methods have been proposed for purification in the separation process of platinum group metals, but solvent extraction is preferred due to its superior economy and operability. Widely adopted. Various metal extractants have been developed for use in solvent extraction methods. For example, dialkyl sulfide and tributyl phosphate are used as metal extractants for palladium and platinum (for example, Patent Documents 1 and 2), and the former is used for back extraction with an ammonia aqueous solution, and the latter is used for back extraction with water.
しかしながら、上記の方法では、ジアルキルスルフィドと酸性水溶液とが長時間接触するため、ジアルキルスルフィドのスルフィド部位が酸化され、パラジウムの抽出能力が低下してしまい、再利用性に乏しい。さらには、ジアルキルスルフィドはパラジウムの抽出速度が遅い。また、トリブチルホスフェイトを使用する場合、白金に対する選択性が低いという問題がある。こうした状況から、金属抽出剤に有用な化合物が求められている。 However, in the above method, since the dialkyl sulfide and the acidic aqueous solution are in contact for a long time, the sulfide moiety of the dialkyl sulfide is oxidized, and the ability to extract palladium is reduced, resulting in poor reusability. Additionally, dialkyl sulfides have a slow palladium extraction rate. Furthermore, when tributyl phosphate is used, there is a problem in that the selectivity to platinum is low. Under these circumstances, there is a need for compounds useful as metal extractants.
本開示の目的は、金属抽出能に優れた化合物、およびこの化合物を含む金属抽出剤を提供することである。 An object of the present disclosure is to provide a compound with excellent metal extraction ability and a metal extractant containing this compound.
[1] 下記式(1)で表される化合物。
[2] 前記式(1)で表される化合物が下記式(4)で表される化合物である、上記[1]に記載の化合物。
[3] 前記式(4)で表される化合物は、R5が前記式(2)で表される1価の基であり、R7が前記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、R3~R4、R6およびR8~R10が水素原子であり、mおよびnが2である化合物を除く、上記[2]に記載の化合物。
[4] 前記式(1)で表される化合物が下記式(4)~(7)のいずれかで表される化合物である、上記[1]に記載の化合物。
[5] 前記式(1)で表される化合物が下記式(1-1)で表される化合物である、上記[1]に記載の化合物。
[9] 前記金属抽出剤は、Pd、Au、Pt、Ru、Ag、Cu、Rh、NiおよびCoからなる群より選択される1種以上の金属を抽出する抽出剤である、上記[8]に記載の金属抽出剤。
[1] A compound represented by the following formula (1).
[2] The compound according to the above [1], wherein the compound represented by the formula (1) is a compound represented by the following formula (4).
[3] In the compound represented by the above formula (4), R 5 is a monovalent group represented by the above formula (2), and R 7 is a monovalent group represented by the above formula (3). The compound according to [2] above, excluding compounds in which R 3 to R 4 , R 6 and R 8 to R 10 are hydrogen atoms, and m and n are 2.
[4] The compound according to the above [1], wherein the compound represented by the formula (1) is a compound represented by any of the following formulas (4) to (7).
[5] The compound according to the above [1], wherein the compound represented by the formula (1) is a compound represented by the following formula (1-1).
[9] [8] above, wherein the metal extractant is an extractant that extracts one or more metals selected from the group consisting of Pd, Au, Pt, Ru, Ag, Cu, Rh, Ni, and Co. Metal extractants as described in .
本開示によれば、金属抽出能に優れた化合物、およびこの化合物を含む金属抽出剤を提供することができる。 According to the present disclosure, it is possible to provide a compound with excellent metal extraction ability and a metal extractant containing this compound.
以下、実施形態に基づき詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, it will be explained in detail based on the embodiment.
本発明者らは、鋭意研究を重ねた結果、化合物を新たに合成し、この化合物が金属抽出能に優れていることを見出し、かかる知見に基づき本発明を完成させるに至った。 As a result of intensive research, the present inventors newly synthesized a compound, discovered that this compound has excellent metal extraction ability, and completed the present invention based on this knowledge.
実施形態の化合物は、下記式(1)で表される化合物である。 The compound of the embodiment is a compound represented by the following formula (1).
上記式(1)中、Arは、アリーレン基であり、R1は、下記式(2)で表される1価の基であり、R2は、下記式(3)で表される1価の基である。 In the above formula (1), Ar is an arylene group, R 1 is a monovalent group represented by the following formula (2), and R 2 is a monovalent group represented by the following formula (3). It is the basis of
上記式(2)中、R3は、水素原子または分岐していてもよいアルキル基であり、mは1以上の整数であり、*は、Arとの結合位置を表す。 In the above formula (2), R 3 is a hydrogen atom or an optionally branched alkyl group, m is an integer of 1 or more, and * represents the bonding position with Ar.
上記式(3)中、R4は、水素原子または分岐していてもよいアルキル基であり、nは1以上の整数であり、*は、Arとの結合位置を表す。 In the above formula (3), R 4 is a hydrogen atom or an optionally branched alkyl group, n is an integer of 1 or more, and * represents the bonding position with Ar.
上記式(1)において、アリーレン基であるArは、1つ以上の芳香環を有する。Arが複数の芳香環を有する場合、上記式(2)で表される1価の基と上記式(3)で表される1価の基とは、同じ芳香環に結合されてもよいし、異なる芳香環に結合されてもよい。 In the above formula (1), Ar, which is an arylene group, has one or more aromatic rings. When Ar has multiple aromatic rings, the monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and the monovalent group represented by the above formula (3) may be bonded to the same aromatic ring. , may be bonded to different aromatic rings.
式(1)で表される化合物がArに結合する上記式(2)の基および上記式(3)の基を有すると、化合物は優れた金属抽出能を有する。 When the compound represented by the formula (1) has the group of the above formula (2) and the group of the above formula (3) that bond to Ar, the compound has an excellent metal extraction ability.
また、式(1)で表される化合物が下記式(4)で表される化合物であると、化合物の金属抽出能がさらに向上する。 Furthermore, when the compound represented by formula (1) is a compound represented by formula (4) below, the metal extraction ability of the compound is further improved.
上記式(4)中、R5~R10のうち、2つは、上記式(2)で表される1価の基および上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、残り4つは、それぞれ独立して、OR、NR2、R、ハロゲン原子、COOH、SO3H、COR、NO2もしくはCH3CORまたはこれらの塩であり、Rは、水素原子または分岐していてもよい炭化水素基であり、当該残り4つのうちの隣接する2つがベンゼン環または複素環を形成してもよい。隣接する2つとは、例えば、R9とR10である。 In the above formula (4), two of R 5 to R 10 are the monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and the monovalent group represented by the above formula (3), and the remaining The four are each independently OR, NR 2 , R, a halogen atom, COOH, SO 3 H, COR, NO 2 or CH 3 COR, or a salt thereof, and R is a hydrogen atom or a branched Two of the remaining four groups may form a benzene ring or a heterocycle. The two adjacent ones are, for example, R 9 and R 10 .
なかでも、金属抽出能を向上する観点から、式(4)で表される化合物は、R5が上記式(2)で表される1価の基であり、R7が上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、R3~R4、R6およびR8~R10が水素原子であり、mおよびnが2である化合物を除く、すなわち式(4)で表される化合物は、上記化合物以外であることが好ましい。 Among them, from the viewpoint of improving metal extraction ability, the compound represented by formula (4) is such that R 5 is a monovalent group represented by the above formula (2), and R 7 is the monovalent group represented by the above formula (3). A monovalent group represented by formula (4), except for compounds in which R 3 to R 4 , R 6 and R 8 to R 10 are hydrogen atoms, and m and n are 2, that is, a monovalent group represented by formula (4). It is preferable that the compound used is other than the above-mentioned compounds.
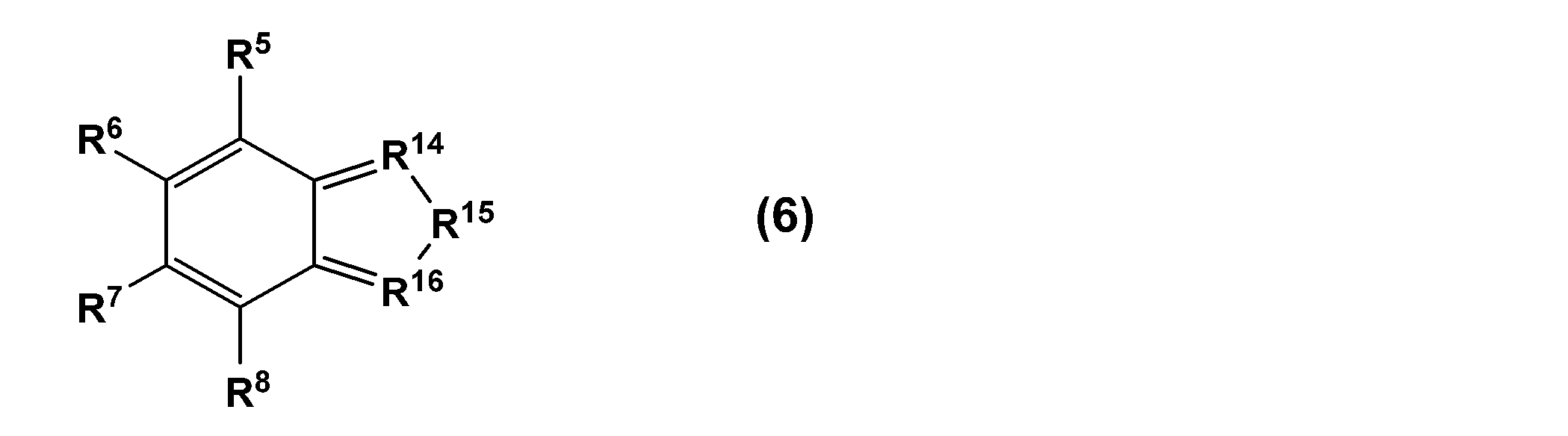
また、上記式(1)で表される化合物が下記式(4)~下記式(7)のいずれかで表される化合物であると、化合物の金属抽出能がさらに向上する。 Furthermore, when the compound represented by the above formula (1) is a compound represented by any of the following formulas (4) to (7), the metal extraction ability of the compound is further improved.
上記式(4)中、R5~R10のうち、2つは、上記式(2)で表される1価の基および上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、残り4つは、水素原子である。また、上記式(5)中、R5~R8のうち、2つは、上記式(2)で表される1価の基および上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、残り2つは、それぞれ独立して、OR、NR2、R、ハロゲン原子、COOH、SO3H、COR、NO2もしくはCH3CORまたはこれらの塩であり、Rは、水素原子または分岐していてもよい炭化水素基であり、R11は、CH2、NH、O、SまたはPHであり、R12~R13は、それぞれ独立して、CHまたはNである。また、上記式(6)中、R5~R8のうち、2つは、上記式(2)で表される1価の基および上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、残り2つは、それぞれ独立して、OR、NR2、R、ハロゲン原子、COOH、SO3H、COR、NO2もしくはCH3CORまたはこれらの塩であり、Rは、水素原子または分岐していてもよい炭化水素基であり、R14およびR16は、それぞれ独立して、CHまたはNであり、R15は、NH、OまたはSである。また、上記式(7)中、R5~R8のうち、2つは、上記式(2)で表される1価の基および上記式(3)で表される1価の基であり、残り2つは、それぞれ独立して、OR、NR2、R、ハロゲン原子、COOH、SO3H、COR、NO2もしくはCH3CORまたはこれらの塩であり、Rは、水素原子または分岐していてもよい炭化水素基であり、R17~R20は、それぞれ独立して、CHまたはNである。 In the above formula (4), two of R 5 to R 10 are the monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and the monovalent group represented by the above formula (3), and the remaining Four are hydrogen atoms. Furthermore, in the above formula (5), two of R 5 to R 8 are a monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and a monovalent group represented by the above formula (3). , the remaining two are each independently OR, NR 2 , R, a halogen atom, COOH, SO 3 H, COR, NO 2 or CH 3 COR, or a salt thereof, and R is a hydrogen atom or a branched R 11 is CH 2 , NH, O, S or PH, and R 12 to R 13 are each independently CH or N. Furthermore, in the above formula (6), two of R 5 to R 8 are a monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and a monovalent group represented by the above formula (3). , the remaining two are each independently OR, NR 2 , R, a halogen atom, COOH, SO 3 H, COR, NO 2 or CH 3 COR, or a salt thereof, and R is a hydrogen atom or a branched R 14 and R 16 are each independently CH or N, and R 15 is NH, O or S. Furthermore, in the above formula (7), two of R 5 to R 8 are a monovalent group represented by the above formula (2) and a monovalent group represented by the above formula (3). , the remaining two are each independently OR, NR 2 , R, a halogen atom, COOH, SO 3 H, COR, NO 2 or CH 3 COR, or a salt thereof, and R is a hydrogen atom or a branched R 17 to R 20 are each independently CH or N.
また、上記で説明した式において、化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、式(2)のmは、1以上9以下の奇数であることが好ましく、1であることがより好ましい。また、同様の観点から、式(2)のR3は、直鎖状または分岐状のアルキル基であることが好ましく、メチル基であることがより好ましい。 Furthermore, in the formula explained above, from the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound, m in formula (2) is preferably an odd number of 1 or more and 9 or less, and more preferably 1. Further, from the same viewpoint, R 3 in formula (2) is preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, and more preferably a methyl group.
また、上記で説明した式において、化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、式(3)のnは、1以上9以下の奇数であることが好ましく、1であることがより好ましい。また、同様の観点から、式(3)のR4は、直鎖状または分岐状のアルキル基であることが好ましく、メチル基であることがより好ましい。 Further, in the formula explained above, n in formula (3) is preferably an odd number of 1 or more and 9 or less, and more preferably 1, from the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound. Further, from the same viewpoint, R 4 in formula (3) is preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, and more preferably a methyl group.
mまたはnが奇数である場合、式(2)または式(3)で表される1価の基を構成するスルフィド基の数は偶数になるため、このスルフィド基の硫黄原子が金属に効率よく二座配位でき、化合物の金属抽出能が向上すると考えられる。特にmまたはnが1である場合、式(2)または式(3)で表される1価の基を構成する2つのスルフィド基の硫黄原子は二座で配位しつつ、さらに、同一分子内の他方の1価の基、または他の分子中の式(2)もしくは式(3)で表される1価の基を構成するスルフィド基の硫黄原子が配位しやすいため、化合物の金属抽出能がさらに向上すると考えられる。 When m or n is an odd number, the number of sulfide groups constituting the monovalent group represented by formula (2) or formula (3) will be an even number, so the sulfur atom of this sulfide group will efficiently attach to the metal. It is believed that the bidentate coordination improves the metal extraction ability of the compound. In particular, when m or n is 1, the sulfur atoms of the two sulfide groups constituting the monovalent group represented by formula (2) or formula (3) are coordinated bidentately, and Since the sulfur atom of the sulfide group constituting the other monovalent group in the compound or the monovalent group represented by formula (2) or formula (3) in another molecule is likely to coordinate, the metal of the compound It is thought that the extraction ability will be further improved.
化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、上記式(5)で表される化合物の好適例を以下に列挙する。 From the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound, preferred examples of the compound represented by the above formula (5) are listed below.
また、化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、上記式(6)で表される化合物の好適例を以下に列挙する。 Further, from the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound, preferred examples of the compound represented by the above formula (6) are listed below.
また、化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、上記式(7)で表される化合物の好適例を以下に列挙する。 Further, from the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound, preferred examples of the compound represented by the above formula (7) are listed below.
また、化合物の金属抽出能を向上する観点から、上記式(4)~(7)で表される化合物以外の好適例を以下に列挙する。 Further, from the viewpoint of improving the metal extraction ability of the compound, preferred examples other than the compounds represented by the above formulas (4) to (7) are listed below.
なかでも、金属抽出能を向上する観点から、式(1)の化合物は、下記式(1-1)で表される化合物、下記式(1-2)で表される化合物または下記式(1-3)で表される化合物であることが好ましい。 Among them, from the viewpoint of improving metal extraction ability, the compound of formula (1) is a compound represented by the following formula (1-1), a compound represented by the following formula (1-2), or a compound represented by the following formula (1). A compound represented by -3) is preferable.
上記式(1-1)~式(1-3)の化合物は、金の抽出剤であるジブチルカルビトール(DBC)に比べて、例えば0.1mM程度の低濃度の金属抽出剤で、金の抽出率を大幅に向上できる。また、上記式(1-1)~式(1-3)の化合物は、パラジウムの抽出剤であるジヘキシルスルフィド(DHS)やジオクチルスルフィド(DOS)に比べて、例えば0.1mM程度の低濃度の金属抽出剤で、パラジウムの抽出率を大幅に向上できる。 The compounds of formulas (1-1) to (1-3) above are metal extractants with a lower concentration of, for example, about 0.1mM than dibutyl carbitol (DBC), which is a gold extractant. The extraction rate can be greatly improved. In addition, the compounds of formulas (1-1) to (1-3) above can be used at a low concentration of, for example, about 0.1mM, compared to dihexyl sulfide (DHS) and dioctyl sulfide (DOS), which are extractants for palladium. Metal extractants can significantly improve the palladium extraction rate.
上記式(1-1)で表される化合物は、下記反応式で表される反応によって合成することができる。 The compound represented by the above formula (1-1) can be synthesized by a reaction represented by the following reaction formula.
o-Benzenedithiol、2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfideおよびKOHを反応容器内のエタノールに投入する。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流する。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留する物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のためHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いてNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウム(Na2SO4)により脱水を行う。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、目的物である式(1-1)の化合物を得ることができる。 o-Benzenedithiol, 2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide and KOH are added to ethanol in a reaction vessel. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, once with HCl to treat excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase, followed by aqueous NaOH solution. After contacting with water five times, dehydration is performed using sodium sulfate (Na 2 SO 4 ). After the solvent is distilled off, it is dried under reduced pressure at 100° C. to obtain the target compound of formula (1-1).
また、上記式(1-2)で表される化合物は、下記反応式で表される反応によって合成することができる。 Further, the compound represented by the above formula (1-2) can be synthesized by a reaction represented by the following reaction formula.
m-Benzenedithiol、2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfideおよびKOHを反応容器内のエタノールに投入する。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流する。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留する物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のためHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いてNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウム(Na2SO4)により脱水を行う。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、目的物である式(1-2)の化合物を得ることができる。 m-Benzenedithiol, 2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide and KOH are added to ethanol in a reaction vessel. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, once with HCl to treat excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase, followed by aqueous NaOH solution. After contacting with water five times, dehydration is performed using sodium sulfate (Na 2 SO 4 ). After the solvent is distilled off, the product is dried under reduced pressure at 100° C. to obtain the target compound of formula (1-2).
また、上記式(1-3)で表される化合物は、下記反応式で表される反応によって合成することができる。 Further, the compound represented by the above formula (1-3) can be synthesized by a reaction represented by the following reaction formula.
p-Benzenedithiol、2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfideおよびKOHを反応容器内のエタノールに投入する。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流する。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留する物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のためHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いてNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウム(Na2SO4)により脱水を行う。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、目的物である式(1-3)の化合物を得ることができる。 P-Benzenedithiol, 2-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide and KOH are added to ethanol in a reaction vessel. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, once with HCl to treat excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase, followed by aqueous NaOH solution. After contacting with water five times, dehydration is performed using sodium sulfate (Na 2 SO 4 ). After the solvent is distilled off, it is dried under reduced pressure at 100° C. to obtain the target compound of formula (1-3).
上記式(1)で表される化合物について、溶媒抽出における金属の抽出能が高い。さらに、この化合物は、複数種の金属に対する抽出能を有する。特に、従来の金属抽出剤に比べて、式(1)で表される化合物を少量で、換言すると、金属抽出剤中の化合物濃度を低濃度で、溶媒抽出における1種以上の金属の抽出量を増加できる。そのため、式(1)で表される化合物は、金属抽出剤に好適に用いられる。また、式(1)で表される化合物は、白金族金属を含む溶液から抽出対象物の金属を抽出できる。 The compound represented by the above formula (1) has a high ability to extract metals in solvent extraction. Furthermore, this compound has the ability to extract multiple types of metals. In particular, compared to conventional metal extractants, the amount of one or more metals extracted in solvent extraction can be reduced by using a small amount of the compound represented by formula (1), in other words, by lowering the concentration of the compound in the metal extractant. can be increased. Therefore, the compound represented by formula (1) is suitably used as a metal extractant. Further, the compound represented by formula (1) can extract the metal to be extracted from a solution containing a platinum group metal.
次に、実施形態の金属抽出剤について説明する。 Next, the metal extractant of the embodiment will be explained.
実施形態の金属抽出剤は、上記実施形態の化合物、すなわち上記式(1)で表される化合物を含む。金属抽出剤は、溶媒抽出に好適に用いられる。 The metal extractant of the embodiment includes the compound of the above embodiment, that is, the compound represented by the above formula (1). Metal extractants are preferably used for solvent extraction.
金属抽出剤は、1種の金属のみならず、複数種の金属に対する高い抽出能を有する。なかでも、金属抽出剤は、Pd、Au、Pt、Ru、Ag、Cu、Rh、NiおよびCoからなる群より選択される1種以上の金属に対する抽出能に優れており、なかでもPd、Au、Pt、Ru、AgおよびCuからなる群より選択される1種以上の金属に対する抽出能にさらに優れている。 A metal extractant has a high extraction ability not only for one type of metal but also for multiple types of metals. Among these, the metal extractant has excellent extraction ability for one or more metals selected from the group consisting of Pd, Au, Pt, Ru, Ag, Cu, Rh, Ni, and Co. , Pt, Ru, Ag, and Cu.
金属抽出剤の形態は、溶媒抽出のプロセスに応じて、適宜選択できる。金属抽出剤は、上記化合物のみから構成されてもよいし、金属抽出能を低下しなければ、上記化合物に加えて各種機能性物質を含んでもよい。 The form of the metal extractant can be appropriately selected depending on the solvent extraction process. The metal extractant may be composed only of the above-mentioned compounds, or may contain various functional substances in addition to the above-mentioned compounds as long as the metal extraction ability is not reduced.
次に、実施形態の金属抽出剤を用いた金属の抽出方法の一例について説明する。 Next, an example of a metal extraction method using the metal extractant of the embodiment will be described.
金属の抽出方法は、上記実施形態の化合物を含む有機相と金属を含む酸性水溶液とを接触させる接触工程を有する。接触工程で有機相と酸性水溶液とを接触させることで、抽出対象物である金属を有機相に抽出できる。 The metal extraction method includes a contacting step of bringing an organic phase containing the compound of the above embodiment into contact with an acidic aqueous solution containing the metal. By bringing the organic phase into contact with the acidic aqueous solution in the contacting step, the metal to be extracted can be extracted into the organic phase.
酸性水溶液に接触する前の有機相では、上記化合物が溶媒中に溶解されている。有機相の溶媒は、非水溶性の溶媒であり、上記化合物を溶解できれば特に限定されるものではない。 In the organic phase before contacting the acidic aqueous solution, the above compound is dissolved in the solvent. The solvent for the organic phase is a water-insoluble solvent and is not particularly limited as long as it can dissolve the above compound.
有機相の溶媒としては、石油、ケロシンなどの鉱油、ヘキサン、ヘプタン、オクタンなどの脂肪族炭化水素、トルエン、キシレンなどの芳香族炭化水素、四塩化炭素、塩化メチレン、クロロホルム、塩化エチレンなどのハロゲン化溶媒が好適である。また、溶媒は、1種の溶媒を単独で用いてもよいし、2種以上の溶媒を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 Examples of organic phase solvents include petroleum, mineral oils such as kerosene, aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane, aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene, and halogens such as carbon tetrachloride, methylene chloride, chloroform, and ethylene chloride. solvents are preferred. Moreover, one type of solvent may be used alone, or two or more types of solvents may be used in combination.
有機相における上記化合物の濃度は、従来の金属抽出剤中の抽出剤濃度に比べて低いことが好ましい。特に、パラジウムの溶媒抽出では、有機相における上記化合物の濃度は、0.05mM以上0.50mM以下であることが好ましく、0.05mM以上0.40mM以下であることがより好ましい。また、金の溶媒抽出では、有機相における上記化合物の濃度は、0.05mM以上0.50mM以下であることが好ましく、0.05mM以上0.25mM以下であることがより好ましい。 Preferably, the concentration of the compound in the organic phase is low compared to the extractant concentration in conventional metal extractants. In particular, in solvent extraction of palladium, the concentration of the above compound in the organic phase is preferably 0.05 mM or more and 0.50 mM or less, more preferably 0.05 mM or more and 0.40 mM or less. Further, in the solvent extraction of gold, the concentration of the above compound in the organic phase is preferably 0.05 mM or more and 0.50 mM or less, more preferably 0.05 mM or more and 0.25 mM or less.
また、有機相に接触する前の酸性水溶液は、抽出対象物である金属が塩酸中に溶解されている。塩酸の濃度は、例えば0.01M以上8.00M以下であり、抽出率を高くする観点から、好ましくは0.01M以上2.00M以下、より好ましくは0.01M以上1.00M以下、さらに好ましくは0.05M以上0.50M以下、特に好ましくは0.05M以上0.15M以下である。 Further, in the acidic aqueous solution before contacting the organic phase, the metal to be extracted is dissolved in hydrochloric acid. The concentration of hydrochloric acid is, for example, 0.01 M or more and 8.00 M or less, and from the viewpoint of increasing the extraction rate, it is preferably 0.01 M or more and 2.00 M or less, more preferably 0.01 M or more and 1.00 M or less, and even more preferably is 0.05M or more and 0.50M or less, particularly preferably 0.05M or more and 0.15M or less.
酸性水溶液における金属の濃度は、特に限定されるものではなく、例えば1ppm以上1000ppm以下である。 The concentration of metal in the acidic aqueous solution is not particularly limited, and is, for example, 1 ppm or more and 1000 ppm or less.
また、金属抽出剤の金属抽出能が損なわれなければ、酸性水溶液には、抽出対象物の金属以外の金属などが含まれてもよい。 Further, the acidic aqueous solution may contain metals other than the metal to be extracted, as long as the metal extraction ability of the metal extractant is not impaired.
例えば、酸性水溶液は、少なくとも抽出対象物の金属を含む廃棄物を塩酸処理して水溶液化した酸浸出液である。このような廃棄物としては、好ましくは自動車排ガス触媒である。 For example, the acidic aqueous solution is an acid leachate obtained by treating waste containing at least the metal to be extracted with hydrochloric acid to form an aqueous solution. Such waste is preferably an automobile exhaust gas catalyst.
接触工程において、接触させる有機相および酸性水溶液の温度は、有機相の溶媒の沸点以下であり、例えば25℃程度である。接触工程では、有機相と酸性水溶液とを振とうや撹拌などによって互いに接触させる。例えば、振とうの振とう数は、100回/分以上500回/分以下である。 In the contacting step, the temperature of the organic phase and the acidic aqueous solution to be brought into contact is below the boiling point of the solvent of the organic phase, for example, about 25°C. In the contacting step, the organic phase and the acidic aqueous solution are brought into contact with each other by shaking, stirring, or the like. For example, the number of shaking is 100 times/min or more and 500 times/min or less.
以上説明した実施形態によれば、上記化合物を新たに合成し、この新規の化合物を金属抽出剤に用いることによって、1種の金属のみならず、複数種の金属に対する金属抽出能を向上することができる。 According to the embodiment described above, by newly synthesizing the above compound and using this new compound as a metal extractant, the metal extraction ability for not only one type of metal but also multiple types of metals can be improved. Can be done.
以上、実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上記実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本開示の概念および特許請求の範囲に含まれるあらゆる態様を含み、本開示の範囲内で種々に改変することができる。 Although the embodiments have been described above, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, but includes all aspects included in the concept of the present disclosure and the scope of the claims, and may be variously modified within the scope of the present disclosure. be able to.
次に、実施例および比較例について説明するが、本開示はこれら実施例に限定されるものではない。 Next, Examples and Comparative Examples will be described, but the present disclosure is not limited to these Examples.
以下の化合物を合成した後、各化合物を含む金属抽出剤を用いて、各実施例を行った。 After synthesizing the following compounds, each example was carried out using a metal extractant containing each compound.
(式(1-1)の化合物の合成)
o-Benzenedithiol(0.5g、3.52mmol、ALDRICH)、1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide(1.98g、17.6mmol、東京化成工業)およびKOH(1.578g、28.0mmol、関東化学)を反応容器内のエタノール(20mL、関東化学)に投入した。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流した。この間、薄層クロマトグラフィー(TLC)によって反応の追跡を行った(展開溶媒 n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1)。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留した物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のため2MのHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いて0.1MのNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウムにより脱水を行った。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、式(1-1)の化合物を得た。この化合物は、薄黄色溶液であった。収率は87.4%であった。この化合物の構造は、核磁気共鳴スペクトルと赤外吸収スペクトルにて確認した。
(Synthesis of compound of formula (1-1))
o-Benzenedithiol (0.5 g, 3.52 mmol, ALDRICH), 1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide (1.98 g, 17.6 mmol, Tokyo Kasei Kogyo) and KOH (1.578 g, 28.0 mmol, Kanto Kagaku) were placed in a reaction vessel. ethanol (20 mL, Kanto Kagaku). Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. During this time, the reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) (developing solvent: n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1). The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, followed by once with 2M HCl to dispose of excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase. After contacting with 0.1M NaOH aqueous solution five times, dehydration was performed using sodium sulfate. After distilling off the solvent, it was dried under reduced pressure at 100°C to obtain a compound of formula (1-1). This compound was a pale yellow solution. The yield was 87.4%. The structure of this compound was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and infrared absorption spectrum.
分析結果は以下の通りであった。
1H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl3): 7.32 (2H, d), 7.18 (2H, d), 3.12 (4H, t), 2.73 (4H, t), 2.14 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm-1): 2965, 2927, 1479, 1422
The analysis results were as follows.
1 H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl 3 ): 7.32 (2H, d), 7.18 (2H, d), 3.12 (4H, t), 2.73 (4H, t), 2.14 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm -1 ): 2965, 2927, 1479, 1422
(式(1-2)の化合物の合成)
m-Benzenedithiol(0.5g、3.52mmol、東京化成工業)、1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide(1.98g、17.6mmol、東京化成工業)およびKOH(1.578g、28.0mmol、関東化学)を反応容器内のエタノール(20mL、関東化学)に投入した。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流した。この間、薄層クロマトグラフィーによって反応の追跡を行った(展開溶媒 n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1)。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留した物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のため2MのHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いて0.1MのNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウムにより脱水を行った。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、式(1-2)の化合物を得た。この化合物は、薄黄色溶液であった。収率は92.5%であった。この化合物の構造は、核磁気共鳴スペクトルと赤外吸収スペクトルにて確認した。
(Synthesis of compound of formula (1-2))
m-Benzenedithiol (0.5g, 3.52mmol, Tokyo Kasei Kogyo), 1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide (1.98g, 17.6mmol, Tokyo Kasei Kogyo) and KOH (1.578g, 28.0mmol, Kanto Kagaku). The mixture was poured into ethanol (20 mL, Kanto Kagaku) in a reaction container. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. During this time, the reaction was followed by thin layer chromatography (developing solvent: n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1). The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, followed by once with 2M HCl to dispose of excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase. After contacting with 0.1M NaOH aqueous solution five times, dehydration was performed using sodium sulfate. After distilling off the solvent, it was dried under reduced pressure at 100°C to obtain a compound of formula (1-2). This compound was a pale yellow solution. The yield was 92.5%. The structure of this compound was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and infrared absorption spectrum.
分析結果は以下の通りであった。
1H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl3): 7.38 (1H, s), 7.21 (1H, t), 7.18 (2H, d), 3.12 (4H, t), 2.72 (4H, t), 2.14 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm-1): 2968, 2913, 1570, 1463, 1427
The analysis results were as follows.
1 H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl 3 ): 7.38 (1H, s), 7.21 (1H, t), 7.18 (2H, d), 3.12 (4H, t), 2.72 (4H, t), 2.14 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm -1 ): 2968, 2913, 1570, 1463, 1427
(式(1-3)の化合物の合成)
p-Benzenedithiol(0.5g、3.52mmol、東京化成工業)、1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide(1.98g、17.6mmol、東京化成工業)およびKOH(1.578g、28.0mmol、関東化学)を反応容器内のエタノール(20mL、関東化学)に投入した。その後、窒素雰囲気下において4時間攪拌し、加熱還流した。この間、薄層クロマトグラフィーによって反応の追跡を行った(展開溶媒 n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1)。その後、クロロホルムを用いて反応容器内に残留した物質を分液漏斗に移動させ、余剰KOHの処理のため2MのHClを1回、続いて有機相の洗浄のため蒸留水を2回、続いて0.1MのNaOH水溶液を5回接触させた後、硫酸ナトリウムにより脱水を行った。溶媒留去の後、100℃で減圧乾燥させて、式(1-3)の化合物を得た。この化合物は、無色透明結晶であった。収率は82.2%であった。この化合物の構造は、核磁気共鳴スペクトルと赤外吸収スペクトルにて確認した。
(Synthesis of compound of formula (1-3))
p-Benzenedithiol (0.5g, 3.52mmol, Tokyo Kasei Kogyo), 1-Chloroethyl methyl sulfide (1.98g, 17.6mmol, Tokyo Kasei Kogyo) and KOH (1.578g, 28.0mmol, Kanto Kagaku). The mixture was poured into ethanol (20 mL, Kanto Kagaku) in a reaction container. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to reflux. During this time, the reaction was followed by thin layer chromatography (developing solvent: n-Hexane:Acetone=4:1). The remaining material in the reaction vessel was then transferred to a separatory funnel using chloroform, followed by once with 2M HCl to dispose of excess KOH, followed by twice with distilled water to wash the organic phase. After contacting with 0.1M NaOH aqueous solution five times, dehydration was performed using sodium sulfate. After distilling off the solvent, the residue was dried under reduced pressure at 100°C to obtain a compound of formula (1-3). This compound was colorless and transparent crystal. The yield was 82.2%. The structure of this compound was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and infrared absorption spectrum.
分析結果は以下の通りであった。
1H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl3): 7.28 (4H, s), 3.10 (4H, t), 2.70 (4H, t), 2.13 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm-1): 2965, 2927, 1480, 1422
The analysis results were as follows.
1 H NMR (500 MHz, δ from TMS, CDCl 3 ): 7.28 (4H, s), 3.10 (4H, t), 2.70 (4H, t), 2.13 (6H, s)
FT-IR (ATR, ν/cm -1 ): 2965, 2927, 1480, 1422
(実施例1-1)
クロロホルムを用いて、式(1-1)の化合物の濃度が0.10mMの有機相を調製した。また、0.02Mの塩酸を用いて、抽出対象物であるAuの濃度が0.1mMの酸性水溶液を調製した。そして、常温下、有機相と酸性水溶液とを24時間振とうして互いに接触させて、Auの抽出を行った。その結果、表1に示すように、Auの抽出率は95.0%であった。
(Example 1-1)
An organic phase containing the compound of formula (1-1) at a concentration of 0.10 mM was prepared using chloroform. Further, using 0.02M hydrochloric acid, an acidic aqueous solution having a concentration of 0.1mM of Au, which is an object to be extracted, was prepared. Then, the organic phase and the acidic aqueous solution were shaken for 24 hours at room temperature and brought into contact with each other to extract Au. As a result, as shown in Table 1, the extraction rate of Au was 95.0%.
(実施例1-2)
式(1-1)の化合物を式(1-2)の化合物に変更した以外は実施例1-1と同様にして、Auの抽出を行った。Auの抽出率を表1に示す。
(Example 1-2)
Au was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1-1 except that the compound of formula (1-1) was changed to the compound of formula (1-2). Table 1 shows the extraction rate of Au.
(実施例1-3)
式(1-1)の化合物を式(1-3)の化合物に変更した以外は実施例1-1と同様にして、Auの抽出を行った。
(Example 1-3)
Au was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1-1 except that the compound of formula (1-1) was changed to the compound of formula (1-3).
(比較例1-1)
式(1-1)の化合物をジブチルカルビトール(DBC)に変更した以外は実施例1-1と同様にして、Auの抽出を行った。
(Comparative example 1-1)
Au was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1-1 except that the compound of formula (1-1) was changed to dibutyl carbitol (DBC).
(実施例2-1)
クロロホルムを用いて、式(1-2)の化合物の濃度が0.10mMの有機相を調製した。また、0.01Mの塩酸を用いて、抽出対象物であるPdの濃度が0.1mMの酸性水溶液を調製した。そして、常温下、有機相と酸性水溶液とを24時間振とうして互いに接触させて、Pdの抽出を行った。その結果、表2に示すように、Pdの抽出率は98.8%であった。
(Example 2-1)
An organic phase containing the compound of formula (1-2) at a concentration of 0.10 mM was prepared using chloroform. Further, using 0.01M hydrochloric acid, an acidic aqueous solution having a concentration of 0.1mM of Pd, which is an object to be extracted, was prepared. Then, the organic phase and the acidic aqueous solution were shaken for 24 hours at room temperature and brought into contact with each other to extract Pd. As a result, as shown in Table 2, the extraction rate of Pd was 98.8%.
(実施例2-2)
式(1-2)の化合物を式(1-3)の化合物に変更した以外は実施例2-1と同様にして、Pdの抽出を行った。Pdの抽出率を表2に示す。
(Example 2-2)
Pd was extracted in the same manner as in Example 2-1 except that the compound of formula (1-2) was changed to the compound of formula (1-3). Table 2 shows the extraction rate of Pd.
(比較例2-1)
式(1-2)の化合物をジヘキシルスルフィド(DHS)に変更した以外は実施例2-1と同様にして、Pdの抽出を行った。
(Comparative example 2-1)
Pd was extracted in the same manner as in Example 2-1 except that the compound of formula (1-2) was changed to dihexyl sulfide (DHS).
(比較例2-2)
式(1-2)の化合物をジオクチルスルフィド(DOS)に変更した以外は実施例2-1と同様にして、Pdの抽出を行った。
(Comparative example 2-2)
Pd was extracted in the same manner as in Example 2-1 except that the compound of formula (1-2) was changed to dioctyl sulfide (DOS).
表1~2に示すように、式(1)で表される化合物は、既存の抽出剤に比べて金属の抽出率が高かった。このように、式(1)で表される化合物は、金属抽出能に優れているため、少量で効率的に金属を回収できた。
As shown in Tables 1 and 2, the compound represented by formula (1) had a higher metal extraction rate than existing extractants. As described above, since the compound represented by formula (1) has excellent metal extraction ability, metals could be efficiently recovered in a small amount.
Claims (9)
The metal according to claim 8, wherein the metal extractant is an extractant that extracts one or more metals selected from the group consisting of Pd, Au, Pt, Ru, Ag, Cu, Rh, Ni, and Co. extractant.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022132781A JP2024030174A (en) | 2022-08-23 | 2022-08-23 | Compound and metal extractant |
| PCT/JP2023/028161 WO2024043020A1 (en) | 2022-08-23 | 2023-08-01 | Compound and metal extractant |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022132781A JP2024030174A (en) | 2022-08-23 | 2022-08-23 | Compound and metal extractant |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2024030174A true JP2024030174A (en) | 2024-03-07 |
Family
ID=90013042
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022132781A Pending JP2024030174A (en) | 2022-08-23 | 2022-08-23 | Compound and metal extractant |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2024030174A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2024043020A1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104892656A (en) * | 2015-06-16 | 2015-09-09 | 广东工业大学 | Metal-organic framework material and synthetic method thereof |
| FR3039765B1 (en) * | 2015-08-07 | 2018-08-24 | Oreal | COSMETIC PROCESS FOR TREATING KERATINIC MATERIALS |
| EP3730478A1 (en) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-10-28 | Basf Se | Process for the preparation of compounds with at least one alkylene group and at least one thiol or thiolate group |
| CN112500577B (en) * | 2020-11-18 | 2023-02-03 | 广东工业大学 | Functionalized metal-organic framework material and preparation method and application thereof |
-
2022
- 2022-08-23 JP JP2022132781A patent/JP2024030174A/en active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-08-01 WO PCT/JP2023/028161 patent/WO2024043020A1/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2024043020A1 (en) | 2024-02-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5299962B2 (en) | Palladium extractant and rapid separation and recovery method using the same | |
| CN113481391B (en) | Method for separating rare earth elements | |
| JP2024030174A (en) | Compound and metal extractant | |
| EP2894143A1 (en) | Method for producing optically active 2,3-dihydrofarnesal | |
| WO2001012586A1 (en) | Calixarene acetamido derivatives, preparation and use thereof for extracting strontium | |
| CN113234001B (en) | High-value utilization method of 2-sodium thioglycollate in tail liquid of thiourethane production | |
| JPS585700B2 (en) | Oyoekikarajiyukinzoku Oyobi Hakukin Igaino | |
| KR100346749B1 (en) | Oxylan, aziridine or cyclopropane production method | |
| JP6948698B2 (en) | Palladium / Platinum Extractor, Palladium / Platinum Separation Method | |
| JP6708341B2 (en) | Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic carbene-gold(I) complex with immobilized magnetic nanoparticles | |
| Amosova et al. | Terminal Organylchalcogenoethyl-and-propylamines and Their Schiff Base Derivatives | |
| JP2022125712A (en) | Palladium extractant and palladium separation method | |
| WO2015067448A1 (en) | Catalytic hydrogenation for the preparation of amines from amide acetals, ketene n,o-acetals or ester imides | |
| JP4102052B2 (en) | Noble metal extractant comprising thioaniline derivative and method for separating noble metal using the same | |
| JP7079978B2 (en) | Palladium extractant, palladium extraction method, palladium recovery method, palladium extractor regeneration method, and palladium recovery method repeatedly. | |
| JP5008063B2 (en) | Diphosphine core type amphiphilic dendrimer, process for producing the same, bidentate phosphine ligand and palladium-containing complex compound having a coordination structure thereof | |
| CN113429312B (en) | N, N-dialkyl amide carboxylic acid compound and preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP4822410B2 (en) | Phosphine-encapsulated amphiphilic dendrimer, process for producing the same, phosphine ligand and palladium-containing complex catalyst having a coordination structure thereof | |
| RU2661635C1 (en) | Method for preparing low dosage hydrate inhibitors with anti-corrosion and bactericidal action | |
| CN117069602A (en) | Synthetic method of gamma-amino alcohol compound | |
| JP2008155201A (en) | New ruthenium-based catalyst and method for producing 1,1-dithio-1-alkene using the same | |
| JP4359440B2 (en) | Method for producing nitriles | |
| CN113480475A (en) | Synthesis method of 4- (2-pyridyl) benzonitrile | |
| CN117756749A (en) | Method for preparing vortioxetine prodrug by catalyzing C-S coupling reaction through mechanical grinding method | |
| CN108069872A (en) | A kind of conjugation γ-diimine compounds and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220909 |