JP2023094188A - Lens and electronic apparatus - Google Patents
Lens and electronic apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2023094188A JP2023094188A JP2021209512A JP2021209512A JP2023094188A JP 2023094188 A JP2023094188 A JP 2023094188A JP 2021209512 A JP2021209512 A JP 2021209512A JP 2021209512 A JP2021209512 A JP 2021209512A JP 2023094188 A JP2023094188 A JP 2023094188A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- lens
- lens group
- present application
- optical axis
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 38
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 30
- 201000009310 astigmatism Diseases 0.000 description 24
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 21
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004984 smart glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Lenses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本願は、撮影機器の技術分野に属し、特に、レンズ及び電子機器に関する。 The present application belongs to the technical field of photographic equipment, and more particularly relates to lenses and electronic equipment.
近年、携帯情報端末に搭載される撮像装置は、より高画質な画像を得るために、大型の撮像素子が用いられるようになってきている。このため、撮像レンズの小型、軽量化が大きな課題となっている。 2. Description of the Related Art In recent years, an imaging device mounted on a mobile information terminal has come to use a large-sized imaging element in order to obtain a higher quality image. Therefore, miniaturization and weight reduction of the imaging lens have become major issues.
しかしながら、従来の提案では、センサの大型化に伴い、撮像装置におけるレンズも大型化する。即ち、従来の提案では、大型のセンサに対応する場合には、光学系の小型、軽量化を図ることが困難であった。 However, according to the conventional proposal, the size of the lens in the imaging device increases as the size of the sensor increases. That is, in the conventional proposals, it was difficult to reduce the size and weight of the optical system when dealing with a large sensor.
本願の実施例の目的は、大型のセンサに対応する場合に光学系の小型、軽量化を図ることが困難であるという問題を解決するレンズ及び電子機器を提供することにある。 An object of the embodiments of the present application is to provide a lens and an electronic device that solve the problem that it is difficult to reduce the size and weight of an optical system when dealing with a large sensor.
本願の実施例の第1態様は、レンズを提供する。該レンズは、物体側から像側へ光軸方向に沿って順に配列されている絞りと、全体として正の屈折力を有し、1枚以上の正の屈折力を有する第1レンズと1枚以上の負の屈折力を有する第2レンズを含む第1レンズ群と、全体として負の屈折力を有する第2レンズ群とを含み、前記第1レンズ群と前記第2レンズ群の光軸上の距離を所定範囲内に制御する沈胴機構を更に含む。 A first aspect of embodiments of the present application provides a lens. The lens includes a diaphragm arranged in order along the optical axis direction from the object side to the image side, and a first lens having positive refractive power as a whole and one or more first lenses having positive refractive power. A first lens group including a second lens having a negative refractive power and a second lens group having a negative refractive power as a whole, and on the optical axis of the first lens group and the second lens group It further includes a collapsible mechanism for controlling the distance of the to within a predetermined range.
本願の実施例の第2態様は、第1態様に記載のレンズを含む電子機器を提供する。 A second aspect of the embodiments of the present application provides an electronic device comprising a lens according to the first aspect.
本願の実施例において、全体として正の屈折力を有する第1レンズ群と、全体として負の屈折力を有する第2レンズ群とを設け、該第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群との間隔を沈胴機構により所定範囲内に制御して主光線入射角CRA(Chief Ray Angle)を変化させることにより、大型センサに対応しつつ、第1レンズ群の径を小さくして、光学系の小型軽量化を実現している。 In the embodiments of the present application, a first lens group having positive refractive power as a whole and a second lens group having negative refractive power as a whole are provided, and the distance between the first lens group and the second lens group is set to By changing the chief ray incident angle CRA (Chief Ray Angle) by controlling it within a predetermined range with a collapsible mechanism, the diameter of the first lens group can be reduced while supporting a large sensor, thereby reducing the size and weight of the optical system. is realized.
本願の実施例における技術的解決策は、本願の実施例における図面と併せて明確かつ完全に説明される。説明される実施例は、本願の一部の実施例であり、全ての実施例ではないことが明らかである。本願における実施例に基づいて、当業者が創造的な労働をすることなく得られる全ての他の実施例は、全て本願の保護範囲に属する。 The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application are clearly and completely described together with the drawings in the embodiments of the present application. Apparently, the described embodiments are some but not all embodiments of the present application. Based on the embodiments in the present application, all other embodiments obtained by persons skilled in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present application.
本願の明細書及び特許請求の範囲における「第1」、「第2」などの用語は、特定の順序又は前後順序を記述するために使用されるのではなく、類似の対象を区別するために使用される。このように使用されるデータは、ここで図示又は説明されるもの以外の順序でも本願の実施例が実施できるように、適切な場合には交換できることや、「第1」、「第2」などで区別される対象は、一般的に同類であり、対象の数が限定されず、例えば、第1対象は、1つであっても、複数であってもよいことを理解されたい。また、明細書及び特許請求の範囲における「及び/又は」は、接続される対象の少なくとも1つを示し、「/」は、通常、前後の関連対象の「又は」の関係を示す。 The terms "first", "second", etc. in the specification and claims of this application are not used to describe a particular order or order, but to distinguish between similar objects. used. The data used in this manner may be interchanged, where appropriate, and the terms "first", "second", etc. may be used to allow embodiments of the present application to be practiced in orders other than that illustrated or described herein. It should be understood that the objects distinguished by are generally cognate and the number of objects is not limited, for example, the first object may be one or more. Also, "and/or" in the specification and claims indicates at least one connected object, and "/" usually indicates an "or" relationship between related objects before and after.
以下、図面を参照しながら、具体的な実施例及びその応用シナリオを通して、本願の実施例によるレンズを詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, the lenses according to the embodiments of the present application will be described in detail through specific embodiments and their application scenarios with reference to the drawings.
本願の実施例によるレンズは、図1に示すように、物体側(図1の左側)から像側(図1の右側)へ光軸方向に沿って順に配列されている絞り1と、第1レンズ群2と、第2レンズ群3とを含む。ここで、絞りは、光学系において光束に対する制限作用をなす実物を意味し、その作用は、光束を制限するか、視野(若しくは結像範囲)の大きさを制限する。絞りは、光学レンズの縁部、光学レンズのフレーム、鏡筒、又は開口絞りなどである。絞りは、光通過領域を有する。これは、絞り自体が有する性質であり、いずれの絞りも光通過領域を有する。
As shown in FIG. 1, the lens according to the embodiment of the present application includes a
第1レンズ群2は、1枚以上の正の屈折力を有する第1レンズ21と、1枚以上の負の屈折力を有する第2レンズを含む。第1レンズ群2は、全体として正の屈折力を有し、第2レンズ群3は、全体として負の屈折力を有する。
The first lens group 2 includes at least one
なお、第2レンズ群3は、特定の組み立て方式により機器における光学センサ4と位置が固定されている。それに対応して、レンズの沈胴制御の際に、実際には第1レンズ群2が移動するように制御し、第1レンズ群2と第2レンズ群3との間の距離を変更する。本願の実施例は、第2レンズ群3の組み立て方式を限定しない。 The position of the second lens group 3 is fixed to that of the optical sensor 4 in the equipment by a specific assembly method. Correspondingly, the first lens group 2 is controlled to actually move when the lens is retracted, and the distance between the first lens group 2 and the second lens group 3 is changed. The embodiments of the present application do not limit the method of assembling the second lens group 3 .
レンズは、第1レンズ群2と第2レンズ群3の光軸上の距離を所定範囲内に制御する沈胴機構(図示せず)を更に含む。本願の実施例は、沈胴機構の具体的な構成を限定しない。 The lens further includes a retraction mechanism (not shown) that controls the distance on the optical axis between the first lens group 2 and the second lens group 3 within a predetermined range. The embodiments of the present application do not limit the specific configuration of the collapsible mechanism.
本願の実施例において、全体として正の屈折力を有する第1レンズ群と、全体として負の屈折力を有する第2レンズ群とを設け、該第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群との間隔を沈胴機構により所定範囲内に制御して主光線入射角CRAを変化させることにより、大型センサに対応しつつ、第1レンズ群の径を小さくして、光学系の小型軽量化を実現している。 In the embodiments of the present application, a first lens group having positive refractive power as a whole and a second lens group having negative refractive power as a whole are provided, and the distance between the first lens group and the second lens group is set to By changing the principal ray incident angle CRA by controlling it within a predetermined range using a collapsible mechanism, the diameter of the first lens group can be reduced while supporting a large sensor, and the size and weight of the optical system can be reduced. .
具体的に、図2a及び図2bを参照する。図2aは、従来のレンズにおいて主光線がレンズによって屈折されるシナリオを示し、図2bは、本願の実施例によるレンズにおいて主光線がレンズによって屈折されるシナリオを示す。図2aと図2bを比較すると、本願の実施例によるレンズを用いることで、CRAを大きくすることができ、同じサイズのレンズに対してより大きなサイズのセンサを適用することができ、その分、同じサイズのセンサに対して本願の実施例によるレンズの方が、よりレンズのサイズを小さくすることができ、これにより、大型のセンサに対応しつつ、レンズの小型、軽量化を実現することができることが分かる。 Specifically, refer to FIGS. 2a and 2b. FIG. 2a shows a scenario in which the chief ray is refracted by the lens in a conventional lens, and FIG. 2b shows a scenario in which the chief ray is refracted by the lens in a lens according to embodiments of the present application. Comparing FIG. 2a and FIG. 2b, it can be seen that by using the lens according to the embodiments of the present application, the CRA can be increased, and a larger size sensor can be applied for the same size lens. With respect to sensors of the same size, the lenses according to the embodiments of the present application can be made smaller in size, so that the size and weight of the lenses can be reduced while supporting large sensors. I know you can.
引き続き図1を参照すると、可能な実施形態において、第2レンズ群3は、赤外線IR(Infrared Radiation)カット機能を有する平面基板31と、平面基板31に設けられ、物体側に凹面を向けた凹面レンズ32とを含む。このように、IRカットフィルタの配置を省略することができるので、機器の内部空間を節約することができる。
Continuing to refer to FIG. 1, in a possible embodiment, the second lens group 3 includes a
第1レンズ群が持つ像面湾曲を第2レンズ群で効果的に補正するためには、第2レンズ群における軸外の主光線の高さをできるだけ高くする必要がある。そこで、本願では、第2レンズ群をセンサ面の近傍に固定している。この場合、センサが大型化すると、第2レンズ群のレンズ径が大きくなり、一般的な射出成形が困難となる。この対策として、平行平板であるガラス基板上にレンズ部が形成された光学素子を実施例として挙げる。例えば、平板状のレンズ基板の表面に複数のレンズ部を形成し、レンズ基板の裏面をそのまま残す、又は、裏面にも同様の方法でレンズ部を形成した状態でレンズ部毎に切り出せば、複数のレンズブロックを一括して得ることができる。特に、レンズ基板の片面をそのまま残す場合には、レンズ基板の高い平面性を利用することができ、製造難易度を低減することができる。 In order for the second lens group to effectively correct the curvature of field of the first lens group, the height of the off-axis principal ray in the second lens group must be as high as possible. Therefore, in the present application, the second lens group is fixed near the sensor surface. In this case, if the size of the sensor increases, the lens diameter of the second lens group increases, making general injection molding difficult. As a countermeasure against this, an optical element in which a lens portion is formed on a glass substrate, which is a parallel flat plate, will be described as an example. For example, by forming a plurality of lens portions on the front surface of a flat lens substrate and leaving the rear surface of the lens substrate as it is, or by cutting out the lens portions after forming the lens portions on the rear surface in a similar manner, a plurality of lens portions can be obtained. of lens blocks can be obtained at once. In particular, when one side of the lens substrate is left as it is, the high flatness of the lens substrate can be utilized, and the manufacturing difficulty can be reduced.
また、この平面部分に赤外線IR(Infrared Radiation)カット機能を持たせることで、小型化にも寄与する。 In addition, providing the flat portion with an infrared IR (Infrared Radiation) cut function contributes to miniaturization.
更に、第2レンズ群にガラス基板を使うことで温度変化に強くなり、基板上に形成されるプラスチックレンズについても、センサ面に近くに配置されることで、近軸光線高さが小さくなるため、温度変化による第2レンズ群のパワー変動に対する収差やバックフォーカス(Back focus)への影響は小さい。 Furthermore, the use of a glass substrate for the second lens group makes it resistant to temperature changes, and the plastic lens formed on the substrate is also placed close to the sensor surface, which reduces the height of paraxial rays. , the power fluctuation of the second lens group due to temperature change has little effect on aberration and back focus.
第2レンズ群は、諸収差の補正だけでなくCRAの調整、周辺光量の改善など、さまざまな補正レンズとして使用可能である。 The second lens group can be used not only for correction of various aberrations, but also as a correction lens for various purposes such as CRA adjustment and peripheral light amount improvement.
可能な実施形態において、所定範囲は、0.14<DG12/OAL<0.60(以下、条件(1)とする)を満たす。ただし、DG12は、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群の光軸上の距離であり、OALは、第1レンズ群の物体側面から第2レンズ群の像側面までの光軸上の距離である。 In a possible embodiment, the predetermined range satisfies 0.14<DG12/OAL<0.60 (hereinafter referred to as condition (1)). However, DG12 is the distance on the optical axis between the first lens group and the second lens group, and OAL is the distance on the optical axis from the object side surface of the first lens group to the image side surface of the second lens group. .
可能な実施形態において、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群は、0.6<(TL1+TL2)/MIH<1.65(以下、条件(2)とする)を満たす。ただし、TL1は、第1レンズ群の有効径内で物体側面から像側面までの光軸と平行な方向の厚さであり、TL2は、第2レンズ群の有効径内で物体側面から像側面までの光軸と平行な方向の厚さであり、MIHは、最大像高である。 In a possible embodiment, the first lens group and the second lens group satisfy 0.6<(TL1+TL2)/MIH<1.65 (hereinafter referred to as condition (2)). However, TL1 is the thickness in the direction parallel to the optical axis from the object side surface to the image side surface within the effective diameter of the first lens group, and TL2 is the thickness from the object side surface to the image side surface within the effective diameter of the second lens group. is the thickness in the direction parallel to the optical axis, and MIH is the maximum image height.
可能な実施形態において、第1レンズ群は、0.13<(MIH-MSDG1)/f<0.70(以下、条件(3)とする)を満たす。ただし、MIHは、最大像高であり、MSDG1は、上記第1レンズ群の最大有効半径であり、fは、レンズ全系の焦点距離である。 In a possible embodiment, the first lens group satisfies 0.13<(MIH-MSDG1)/f<0.70 (hereinafter referred to as condition (3)). However, MIH is the maximum image height, MSDG1 is the maximum effective radius of the first lens group, and f is the focal length of the entire lens system.
条件(1)~(3)は、センサ大型化に伴う光学サイズの増大に対する対策である。 Conditions (1) to (3) are countermeasures against an increase in optical size due to an increase in sensor size.
条件(1)の範囲内で第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群の間隔(DG12)を適切に保つことにより、性能を確保しながらAF(Automatic Focus)・OIS(Optical image stabilization)時に駆動する第1レンズ群の小型(小径化)・軽量化が可能となる。 By maintaining an appropriate distance (DG12) between the first lens group and the second lens group within the range of condition (1), it is possible to drive the first lens group during AF (automatic focus) and OIS (optical image stabilization) while ensuring performance. It is possible to reduce the size (reduction in diameter) and weight of one lens group.
また、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群の間隔を広げることによる光学全長の増加に対しては、レンズ使用時には第1レンズ群がpop-upし、レンズ収納時には第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群の間隔を縮める沈胴機構を付けることで厚み方向の小型化を図る。この時、条件(2)の範囲を満たすことで、センササイズが大きくなっても、性能を維持しながら撮像装置全体の薄型化が実現できる。 In addition, in response to the increase in the total optical length due to the widening of the distance between the first lens group and the second lens group, the first lens group pops up when the lens is in use, and the first lens group and the second lens group when the lens is retracted. Compactness in the thickness direction is achieved by attaching a collapsible mechanism that shortens the distance between groups. At this time, by satisfying the range of condition (2), even if the sensor size increases, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the entire imaging device while maintaining performance.
条件(3)は、第1レンズ群の小径化に関する。この範囲を満たすことで、センササイズが大きくなっても、駆動する第1レンズ群が大型化することがなく、小径化と軽量化が同時に実現できる。 Condition (3) relates to reducing the diameter of the first lens group. By satisfying this range, even if the sensor size increases, the first lens group to be driven does not increase in size, and a reduction in diameter and weight can be achieved at the same time.
このように第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群に分割することで、撮像装置全体の小型化が可能となるが、さらなる利点として、AF・OIS時に、駆動する正の第1レンズ群と、センサに固定される負の第2レンズ群に分割することで、AF移動量、OIS駆動量が従来のレンズに比べて小さくなる。よって、センサの大型化に伴うAFや、OISの駆動量の増加を抑制できる。 By dividing the first lens group and the second lens group in this way, it is possible to reduce the overall size of the imaging apparatus. By dividing into the negative second lens group fixed to , the AF movement amount and the OIS driving amount become smaller than those of the conventional lens. Therefore, it is possible to suppress an increase in the driving amount of AF and OIS due to the enlargement of the sensor.
第2レンズ群は、像面補正の役割をするため、センサの大型化に伴う近距離性能の低下(像面の倒れ)を防ぐことができる。 Since the second lens group plays a role of correcting the image plane, it is possible to prevent deterioration of close-range performance (tilt of the image plane) due to an increase in size of the sensor.
可能な実施形態において、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群は、-2.8<FG2/FG1<-0.7(以下、条件(4)とする)を満たす。ただし、FG1は、第1レンズ群の焦点距離であり、FG2は、第2レンズ群の焦点距離である。 In a possible embodiment, the first lens group and the second lens group satisfy −2.8<FG2/FG1<−0.7 (hereinafter referred to as condition (4)). However, FG1 is the focal length of the first lens group, and FG2 is the focal length of the second lens group.
可能な実施形態において、第1レンズと第2レンズ群は、-3.0<FG2/f1<-0.6(以下、条件(5)とする)を満たす。ただし、f1は、第1レンズの焦点距離であり、FG2は、第2レンズ群の焦点距離である。 In a possible embodiment, the first lens and the second lens group satisfy −3.0<FG2/f1<−0.6 (hereinafter referred to as condition (5)). However, f1 is the focal length of the first lens, and FG2 is the focal length of the second lens group.
条件(4)、(5)は、大型センサに対応した高性能レンズを得るための条件である。 Conditions (4) and (5) are conditions for obtaining a high-performance lens compatible with a large sensor.
第1レンズ群は、主として結像作用を、第2レンズ群は、像面補正の役割を果たす。条件(4)を満たすことで、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群の焦点距離のバランスが適切に保たれ、良好な性能を確保できる。 The first lens group mainly functions for image formation, and the second lens group functions for image plane correction. By satisfying the condition (4), the balance between the focal lengths of the first lens group and the second lens group can be appropriately maintained, and good performance can be ensured.
大型センサ用のレンズでは、軸上色収差と倍率色収差のバランスが崩れやすく、色収差を適切に補正することが求められる。第1レンズ群の第1レンズは、色収差の補正に深く関わっており、誤差感度も高くなりやすい。条件(5)を満たすことで、大型センサに対応した軸外と軸上の性能をバランス良く補正でき、誤差感度の抑制にもつながる。 In lenses for large sensors, the balance between axial chromatic aberration and chromatic aberration of magnification tends to be lost, and it is required to correct chromatic aberration appropriately. The first lens in the first lens group is deeply involved in correction of chromatic aberration, and tends to have high error sensitivity. By satisfying condition (5), off-axis and on-axis performances corresponding to large sensors can be corrected in a well-balanced manner, leading to suppression of error sensitivity.
可能な実施形態において、第1レンズ群と第2レンズ群は、3.5<|CRAG2-CRAS|max<19.5(以下、条件(6)とする)を満たす。ただし、CRAG2は、第2レンズ群に入射する主光線の角度であり、CRASは、光学センサに入射する主光線の角度であり、|CRAG2-CRAS|maxは、各像高でCRAG2とCRASの差の絶対値をとり、その中で最大となる値である。 In a possible embodiment, the first lens group and the second lens group satisfy 3.5<|CRAG2-CRAS|max<19.5 (hereinafter referred to as condition (6)). where CRAG2 is the angle of the principal ray incident on the second lens group, CRAS is the angle of the principal ray incident on the optical sensor, and |CRAG2-CRAS|max is the angle of CRAGS2 and CRAS at each image height. It is the maximum value among the absolute values of the differences.
条件(6)は、CRAの調整に関するもので、この範囲を満たすことで、センサ面への入射角を適切に保ちながら、第1レンズ群の小径化が可能となる。つまり、第1レンズ群から第2レンズ群へ入射する光線の角度を適度に大きくすることで、第1レンズ群の有効径を小さく保つことができる。この場合、第2レンズ群の非球面を使ってセンサへのCRAを適切に補正する。 Condition (6) relates to the adjustment of CRA. By satisfying this range, it is possible to reduce the diameter of the first lens group while appropriately maintaining the angle of incidence on the sensor surface. In other words, the effective diameter of the first lens group can be kept small by appropriately increasing the angle of light rays incident on the second lens group from the first lens group. In this case, the aspheric surface of the second lens group is used to properly correct the CRA to the sensor.
本願の実施例は、上記の本願の実施例によるレンズを含む電子機器を更に提供する。前記電子機器は、携帯電話、タブレット(Tablet Personal Computer)、ラップトップ(Laptop Computer)又はノートブックコンピュータ、パーソナルデジタルアシスタントPDA(Personal Digital Assistant)、パームトップコンピュータ、ネットブック、ウルトラモバイルパーソナルコンピュータUMPC(ultra-mobile personal computer)、モバイルネット装置MID(Mobile Internet Device)、ロボット、車載機器(VUE)、歩行者端末(PUE)、ウェアラブル機器(Wearable Device)ゲーム機などである。ウェアラブル機器は、スマートウォッチ、スマートリング、スマートイヤホン、スマートグラス、スマートアクセサリ(スマートハンドブレスレット、スマートハンドチェーンブレスレット、スマートリング、スマートネックレス、スマートフットブレスレット、スマートフットチェーンブレスレットなど)、スマートリストバンド、スマート衣類を含む。本願の実施例は、電子機器の具体的なカテゴリーを限定しない。 Embodiments of the present application further provide an electronic device including a lens according to the embodiments of the present application above. Said electronic devices include mobile phones, Tablet Personal Computers, Laptop Computers or Notebook Computers, Personal Digital Assistants PDA, Palmtop Computers, Netbooks, Ultra Mobile Personal Computers UMPCs (ultra -mobile personal computer), mobile internet device MID (Mobile Internet Device), robot, in-vehicle equipment (VUE), pedestrian terminal (PUE), wearable device (Wearable Device) game machine, and the like. Wearable devices include smart watches, smart rings, smart earbuds, smart glasses, smart accessories (smart hand bracelets, smart hand chain bracelets, smart rings, smart necklaces, smart foot bracelets, smart foot chain bracelets, etc.), smart wristbands, smart Including clothing. Embodiments of the present application do not limit specific categories of electronic devices.
以下、本願のレンズの具体的な実施例について説明する。非球面の形状は、面の頂点を原点とし、光軸方向にX軸をとり、光軸と垂直方向の高さをhとして以下の式で表す。
なお、以下の各実施例に係る面番号は、図3に示す態様を参照して番号付けを行う。以下の各実施例に係る各アルファベットは、以下の意味を有する。
f:撮像レンズ全系の焦点距離
Fno:Fナンバー
HFOV:半画角
MIH:撮像レンズの最大像高
R:曲率半径
D:軸上面間隔
Nd:レンズ材料のd線に対する屈折率
νd:レンズ材料のアッベ数。
It should be noted that surface numbers according to the following examples are assigned with reference to the aspect shown in FIG. Each alphabet according to the following examples has the following meaning.
f: Focal length of the entire imaging lens system Fno: F-number HFOV: Half angle of view MIH: Maximum image height of the imaging lens R: Radius of curvature D: Distance between upper surfaces of the axis Nd: Refractive index of the lens material for the d-line νd: Lens material Abbe number.
実施例1
レンズデータを、表1に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 1.
非球面係数は、表2に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図4aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図4bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 4a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 4b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例2
レンズデータを、表3に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 3.
非球面係数は、表4に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図5aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図5bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 5a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 5b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例3
レンズデータを、表5に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 5.
非球面係数は、表6に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図6aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図6bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 6a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 6b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例4
レンズデータを、表7に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 7.
非球面係数は、表8に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図7aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図7bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 7a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 7b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例5
レンズデータを、表9に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 9.
非球面係数は、表10に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図8aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図8bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 8a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 8b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例6
レンズデータを、表11に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 11.
非球面係数は、表12に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図9aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図9bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 9a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 9b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例7
レンズデータを、表13に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 13.
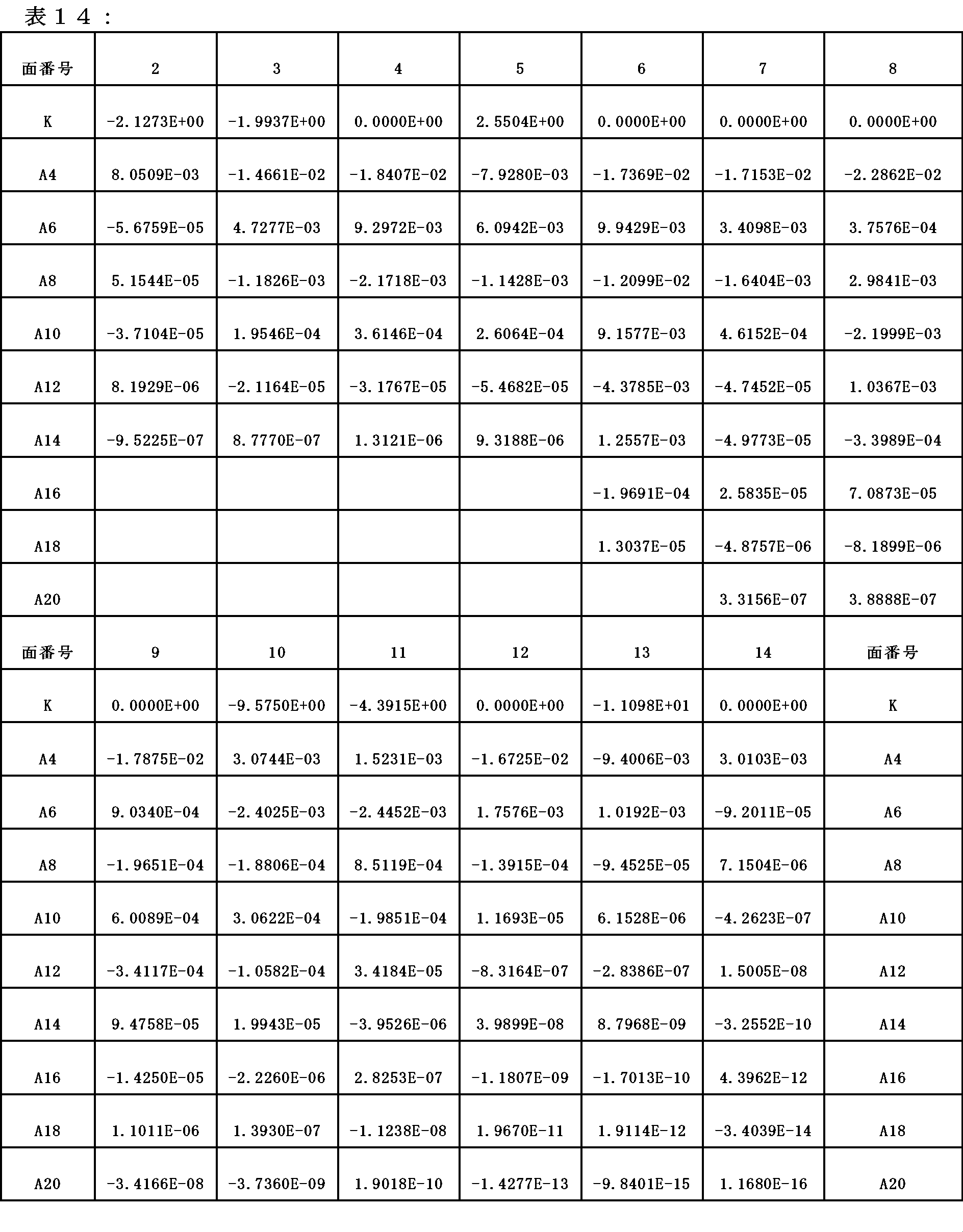
非球面係数は、表14に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図10aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図10bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 10a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 10b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例8
レンズデータを、表15に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 15.
非球面係数は、表16に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図11aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図11bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 11a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 11b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
なお、IRカット機能を有する基板にレンズを形成する製造技術が難しいであることを考慮し、実施例9、10、11は、IRカットフィルタを省略しない実施例である。 Considering the difficulty of manufacturing technology for forming lenses on a substrate having an IR cut function, Examples 9, 10, and 11 are examples in which the IR cut filter is not omitted.
実施例9
レンズデータを、表17に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 17.
非球面係数は、表18に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図12aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図12bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 12a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 12b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例10
レンズデータを、表19に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 19.
非球面係数は、表20に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図13aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図13bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 13a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 13b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例11
レンズデータを、表21に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 21.
非球面係数は、表22に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図14aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図14bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 14a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 14b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例12
レンズデータを、表23に示す。
Lens data are shown in Table 23.
非球面係数は、表24に示す。
本実施例のレンズ断面図を図15aに示し、非点収差(mm)と歪曲収差(%)は、図15bに示す。非点収差図では、実線がサジタル像面を表し、点線がタンジェンシャル像面を表す。各収差図から、諸収差が良好に補正され、優れた結像性能を有していることが明らかである。 A cross-sectional view of the lens of this example is shown in FIG. 15a, and astigmatism (mm) and distortion (%) are shown in FIG. 15b. In the astigmatism diagram, the solid line represents the sagittal image plane, and the dotted line represents the tangential image plane. From each aberration chart, it is clear that various aberrations are well corrected and that the lens has excellent imaging performance.
実施例のまとめ:
各実施例の全体諸元
Overall specifications of each embodiment
実施例に示した通り、センササイズが1/1.5(最大像高5.34mm)以上の大型センサにおいて、Fナンバー1.95以下の明るい高性能レンズの小型、軽量化を達成することができた。 As shown in the examples, it is possible to achieve a compact and lightweight bright high-performance lens with an F number of 1.95 or less in a large sensor with a sensor size of 1/1.5 or more (maximum image height of 5.34 mm). did it.
以上、本願の実施例を、図面を参照して説明したが、本願は、前記具体的な実施形態に限定されるものではない。上記の具体的な実施形態は、例示的なものに過ぎず、限定的なものではない。当業者であれば、本願からヒントを受け、本願の思想及び特許請求の範囲から逸脱することなく、本願の保護範囲に属する多くの形態をなすことができる。 Although the examples of the present application have been described above with reference to the drawings, the present application is not limited to the specific embodiments described above. The specific embodiments described above are exemplary only and are not limiting. A person skilled in the art can take inspiration from this application and make many configurations that fall within the scope of protection of this application without departing from the spirit and scope of the claims of this application.
Claims (9)
前記第1レンズ群と前記第2レンズ群の光軸上の距離を所定範囲内に制御する沈胴機構を更に含むことを特徴とするレンズ。 A diaphragm arranged in order along the optical axis direction from the object side to the image side; A first lens group including a second lens having refractive power, and a second lens group having negative refractive power as a whole,
The lens, further comprising a collapsible mechanism for controlling the distance on the optical axis between the first lens group and the second lens group within a predetermined range.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021209512A JP2023094188A (en) | 2021-12-23 | 2021-12-23 | Lens and electronic apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021209512A JP2023094188A (en) | 2021-12-23 | 2021-12-23 | Lens and electronic apparatus |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2023094188A true JP2023094188A (en) | 2023-07-05 |
Family
ID=87001502
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021209512A Pending JP2023094188A (en) | 2021-12-23 | 2021-12-23 | Lens and electronic apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2023094188A (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015040867A1 (en) * | 2013-09-20 | 2015-03-26 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Image pickup optical system |
| JP2019213151A (en) * | 2018-06-08 | 2019-12-12 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Imaging apparatus |
| WO2021059097A2 (en) * | 2019-09-24 | 2021-04-01 | Corephotonics Ltd. | Slim pop-out cameras and lenses for such cameras |
-
2021
- 2021-12-23 JP JP2021209512A patent/JP2023094188A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015040867A1 (en) * | 2013-09-20 | 2015-03-26 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Image pickup optical system |
| JP2019213151A (en) * | 2018-06-08 | 2019-12-12 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Imaging apparatus |
| WO2021059097A2 (en) * | 2019-09-24 | 2021-04-01 | Corephotonics Ltd. | Slim pop-out cameras and lenses for such cameras |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11579419B2 (en) | Optical imaging lens | |
| US10578833B2 (en) | Photographing optical lens assembly | |
| JP6490115B2 (en) | Imaging lens | |
| JP5063434B2 (en) | Imaging lens | |
| US11906711B2 (en) | Optical imaging system | |
| JP2020064179A (en) | Imaging lens | |
| JP2012177852A (en) | Imaging lens | |
| JP2006162829A (en) | Wide angle imaging lens and imaging apparatus | |
| WO2022033326A1 (en) | Optical system, lens module, and electronic device | |
| US7933072B2 (en) | Zoom lens and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2015141384A (en) | Imaging lens and imaging device | |
| JP2008096621A (en) | Imaging lens | |
| CN114488477A (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| KR102268263B1 (en) | Small lens system | |
| US6775072B2 (en) | Single-focus lens | |
| TWI688785B (en) | Imaging lens, imaging device and electronic device having the same | |
| CN105190393B (en) | Wide-angle lens and camera device | |
| CN114114617B (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| JP2023094188A (en) | Lens and electronic apparatus | |
| WO2022133651A1 (en) | Optical system, photographing module, and electronic device | |
| WO2021142620A1 (en) | Optical system, lens module, and electronic device | |
| CN114002832A (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114185161A (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| TWI745462B (en) | Photographing lens | |
| TWI740493B (en) | Optical camera lens |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20211223 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220920 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20221220 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20230307 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20230707 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20230829 |
|
| A912 | Re-examination (zenchi) completed and case transferred to appeal board |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20231102 |