JP2021074646A - Coated substrate manufacturing method - Google Patents
Coated substrate manufacturing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2021074646A JP2021074646A JP2019200760A JP2019200760A JP2021074646A JP 2021074646 A JP2021074646 A JP 2021074646A JP 2019200760 A JP2019200760 A JP 2019200760A JP 2019200760 A JP2019200760 A JP 2019200760A JP 2021074646 A JP2021074646 A JP 2021074646A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- aqueous solution
- base material
- alkali metal
- metal silicate
- layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 24
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 title abstract description 12
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 102
- 229910052910 alkali metal silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 69
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 41
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 96
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 claims description 78
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium silicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000004115 Sodium Silicate Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 229910052911 sodium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- PAZHGORSDKKUPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N lithium metasilicate Chemical compound [Li+].[Li+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O PAZHGORSDKKUPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052912 lithium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 41
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 7
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 235000019353 potassium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 5
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 240000005109 Cryptomeria japonica Species 0.000 description 4
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000005350 fused silica glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl acrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C=C BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004111 Potassium silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011259 mixed solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052913 potassium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- NNHHDJVEYQHLHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium silicate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NNHHDJVEYQHLHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002803 thermoplastic polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- OEPOKWHJYJXUGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carbaldehyde Chemical compound O=CC1=CSC(C=2C=C(OCC=3C=CC=CC=3)C=CC=2)=N1 OEPOKWHJYJXUGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910000975 Carbon steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920002943 EPDM rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 244000043261 Hevea brasiliensis Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000877 Melamine resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Vinyl chloride Chemical compound ClC=C BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000122 acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004676 acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004840 adhesive resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006223 adhesive resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000180 alkyd Polymers 0.000 description 1
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000004760 aramid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006231 aramid fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010962 carbon steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004568 cement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006026 co-polymeric resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004567 concrete Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011094 fiberboard Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007602 hot air drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000000347 magnesium hydroxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001862 magnesium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N melamine Chemical compound NC1=NC(N)=NC(N)=N1 JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052914 metal silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004570 mortar (masonry) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003052 natural elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001194 natural rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011505 plaster Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011120 plywood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001084 poly(chloroprene) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001567 vinyl ester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Fireproofing Substances (AREA)
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
- Chemical And Physical Treatments For Wood And The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、被覆基材の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a method for producing a coated substrate.
従来より、基材に防火性能を付与すべく、基材の表面にアルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液を塗布してアルカリ金属珪酸塩層を形成することが知られている。 Conventionally, it has been known to apply an aqueous alkali metal silicate solution to the surface of a base material to form an alkali metal silicate layer in order to impart fire protection performance to the base material.
アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液を基材の垂直表面等の傾斜面に塗布する際には、アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液の液だれが発生し、塗布/乾燥を何回も繰り返さないと厚いアルカリ珪酸金属塩層の形成が困難な場合が多い。したがって、従来の方法では、液だれの防止の点で改善の余地がある。 When the alkali metal silicate aqueous solution is applied to an inclined surface such as the vertical surface of the base material, dripping of the alkali metal silicate aqueous solution occurs, and the thick alkali metal silicate metal salt layer must be repeatedly applied / dried. Is often difficult to form. Therefore, there is room for improvement in the conventional method in terms of preventing dripping.
更に従来の方法では、形成されるアルカリ金属珪酸塩層の透明性が低いため、基材の表面の木目などの模様を外部から視認しにくい。 Further, in the conventional method, since the alkali metal silicate layer formed has low transparency, it is difficult to visually recognize the pattern such as the grain of wood on the surface of the base material from the outside.
本発明は上記課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、垂直面等の傾斜面に塗布する場合の液だれを抑制でき、且つ、得られる被覆基材が透明性に優れる、被覆基材の製造方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and is a method for producing a coated base material, which can suppress dripping when applied to an inclined surface such as a vertical surface, and the obtained coated base material has excellent transparency. The purpose is to provide.
本発明にかかる被覆基材の製造方法は、基材の表面に非晶質シリカ及びアルカリ金属珪酸塩を含む水溶液を塗布する工程と、塗布された水溶液を乾燥させてアルカリ金属珪酸塩層を形成する工程、を備え、水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6が1500mPa・s以上である。 The method for producing a coated base material according to the present invention includes a step of applying an aqueous solution containing amorphous silica and an alkali metal silicate on the surface of the base material, and drying the applied aqueous solution to form an alkali metal silicate layer. The B-type viscosity μ 6 under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. of the aqueous solution is 1500 mPa · s or more.
本発明によれば、水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6が1500mPa・s以上であるため、垂直面等の傾斜面に塗布する場合の液だれを抑制することができる。そのため、塗布/乾燥を何回も繰り返さずに、厚いアルカリ珪酸金属塩層を形成することができる。また、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層の厚みの均一性を高くすることができる。更に、形成されたアルカリ金属珪酸塩層は、透明性に優れる。 According to the present invention, since the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. is 1500 mPa · s or more, it is possible to suppress dripping when applied to an inclined surface such as a vertical surface. Therefore, a thick alkali silicate metal salt layer can be formed without repeating coating / drying many times. In addition, the uniformity of the thickness of the alkali metal silicate layer can be increased. Further, the formed alkali metal silicate layer is excellent in transparency.
また、上記水溶液の60rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度をμ60としたときに、μ6/μ60が3以上であってよい。水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6が1500mPa・s以上であり、且つ、μ6/μ60が3以上であることで、液だれを抑制しつつ、水溶液を塗布する際の水溶液の伸びが優れたものとなる。そして、水溶液の伸びが優れたものとなることで、得られる被覆基材は、表面の平滑性が優れたものとなる。 Further, when the B-type viscosity of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 60 rpm and 20 ° C. is μ 60 , μ 6 / μ 60 may be 3 or more. When the aqueous solution is applied while suppressing dripping , the B-type viscosity μ 6 under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. is 1500 mPa · s or more and μ 6 / μ 60 is 3 or more. The elongation of the aqueous solution of is excellent. Then, the elongation of the aqueous solution becomes excellent, so that the obtained coating base material has excellent surface smoothness.
また、上記基材は、可燃性基材であることができる。 Further, the base material can be a flammable base material.
また、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩が珪酸ナトリウムを含んでいてもよい。 Further, the alkali metal silicate may contain sodium silicate.
また、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩が珪酸ナトリウムを含む場合、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩が、さらに珪酸リチウムを含んでいてもよい。 When the alkali metal silicate contains sodium silicate, the alkali metal silicate may further contain lithium silicate.
また、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩が珪酸ナトリウム及び珪酸リチウムを含む場合、アルカリ金属珪酸塩に含まれる上記珪酸ナトリウムの質量に対する、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩に含まれる上記珪酸リチウムの質量の質量比が0.01〜1.5であってよい。 When the alkali metal silicate contains sodium silicate and lithium silicate, the mass ratio of the mass of the lithium silicate contained in the alkali metal silicate to the mass of the sodium silicate contained in the alkali metal silicate is 0. It may be 01 to 1.5.
また、上記水溶液に含まれる上記非晶質シリカの含有量が、上記アルカリ金属珪酸塩の全量に対して、3.0〜160質量%であってよい。 Further, the content of the amorphous silica contained in the aqueous solution may be 3.0 to 160% by mass with respect to the total amount of the alkali metal silicate.
本発明によれば、垂直面等の傾斜面に塗布する場合の液だれを抑制でき、且つ、得られる被覆基材が透明性に優れる、被覆基材の製造方法が提供される。 According to the present invention, there is provided a method for producing a coated base material, which can suppress dripping when applied to an inclined surface such as a vertical surface, and the obtained coated base material has excellent transparency.
以下、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明する。ただし、本発明は以下の実施形態に限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described. However, the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
(被覆基材の製造方法)
[第一実施形態]
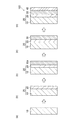
本発明の第一実施形態に係る被覆基材100の製造方法について、図1を参照して説明する。
(Manufacturing method of coating base material)
[First Embodiment]
A method for producing the coated
(基材の準備)
まず、図1の(a)に示すように、基材本体10を用意する。基材本体10は、可燃性基材であってよく、不燃性基材であってよい。
(Preparation of base material)
First, as shown in FIG. 1A, the base material
可燃性基材の例は、木材製材品、製材品、合板、LVL(Laminated Veneer Lumber)、集成材、CLT(Cross Laminated Timber)、構造用パネル(配向性ストランドボード(OSB))、パーティクルボード、ファイバーボード等の木質材料である。 Examples of flammable substrates include wood-based materials, lumber products, plywood, LVL (Laminated Veneer Lumber), laminated lumber, CLT (Cross Laminated Timmer), structural panels (oriented strand boards (OSB)), particle boards, etc. It is a wood material such as fiber board.
可燃性基材の他の例は、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ABS、ポリカーボネート、アクリル酸メチル、ポリメタクリル酸メチル、ポリウレタン、天然ゴム、クロロプレンゴム、EPDM、ふっ素樹脂、ポリエステル、メラミン、ポリアミド等の樹脂材料であり、これらはバルク、発泡体、その他の形態とすることができる。 Other examples of flammable substrates include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, ABS, polycarbonate, methyl acrylate, polymethyl methacrylate, polyurethane, natural rubber, chloroprene rubber, EPDM, fluororesin, polyester, melamine, It is a resin material such as polyamide, which can be in bulk, foam or other form.
不燃性基材の例は、コンクリート、モルタル、セメント、しっくい、石、金属、ガラス、及びセラミック等である。 Examples of nonflammable substrates are concrete, mortar, cement, plaster, stone, metal, glass, ceramic and the like.
基材本体10の厚みに特に制限は無い。たとえば、3μm〜3.5mとすることができる。
The thickness of the
続いて、図1の(b)に示すように、基材本体10の表面に公知の方法でプライマー層20を形成し、基材25を得る。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 1B, a
プライマー層20は、基材本体10とアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30との密着性を向上させる層であるが、必須では無い。プライマー層20は、例えば、変性エポキシ樹脂、ウレタン樹脂などの接着性樹脂であることができる。プライマー層として、シリカ、アルミナ等の無機系材料を使用することも可能である。このようなプライマー層は、プライマー層の原料を基材本体10の表面に塗布することにより形成できる。
The
プライマー層20の厚みに限定は無いが、透明性を高める観点から150μm以下(塗布量500g/m2以下相当)、より好ましくは90μm以下(塗布量300g/m2以下相当)とすることが好適であり、密着性向上効果、目止め効果を得る観点から15μm以上(塗布量50g/m2以上相当)とすることが好適であり、30μm以上(塗布量100g/m2以上相当)とすることがより好適である。
The thickness of the
本実施形態では、基材25(基材本体10)の表面が、水平面に対して90°傾斜している。 In the present embodiment, the surface of the base material 25 (base material body 10) is inclined by 90 ° with respect to the horizontal plane.
続いて、図1の(c)に示すように、基材25の表面に、非晶質シリカ及びアルカリ金属珪酸塩を含む水溶液(以下、「水溶液」ともいう)を塗布し、水溶液層30aを形成する。塗布する水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6は、1500mPa・s以上である。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 1 (c), an aqueous solution containing amorphous silica and an alkali metal silicate (hereinafter, also referred to as “aqueous solution”) is applied to the surface of the
ここで水溶液について詳しく説明する。
<アルカリ金属珪酸塩>
アルカリ金属珪酸塩は、M2O・nSiO2で表される。ここで、Mは、Na、K、Li、又は、これらのうちの任意の組合せである。nは、M2Oのモル数に対するSiO2のモル数を示すモル比であり、Naの場合には2.0〜3.8、Liの場合には、3.5〜7.5、Kの場合には1.8(1号珪酸カリ)〜3.7(2号珪酸カリ)とすることができる。また、nは、Naの場合には好ましくは2.0〜3.3であることができる。
Here, the aqueous solution will be described in detail.
<Alkali metal silicate>
The alkali metal silicate is represented by M 2 O · nSiO 2. Here, M is Na, K, Li, or any combination thereof. n is a molar ratio indicating the number of moles of SiO 2 with respect to the number of moles of M 2 O. In the case of Na, it is 2.0 to 3.8, and in the case of Li, it is 3.5 to 7.5, K. In the case of, it can be 1.8 (No. 1 potassium silicate) to 3.7 (No. 2 potassium silicate). Further, n can be preferably 2.0 to 3.3 in the case of Na.
なかでも、アルカリ金属珪酸塩は、MがNaであるもの、すなわち、珪酸ナトリウムを含むことが好適である。 Among them, the alkali metal silicate preferably contains Na in M, that is, sodium silicate.
珪酸ナトリウムとしては、珪酸ナトリウム水溶液である、JIS K1408に規定された、水ガラス1号〜3号を好適に利用できる。また、水ガラス1号から3号ではnは2.0〜3.3であるが、nが2.0〜3.8の水ガラスも好適に利用できる。 As the sodium silicate, water glasses No. 1 to No. 3 specified in JIS K1408, which is an aqueous solution of sodium silicate, can be preferably used. Further, in water glass Nos. 1 to 3, n is 2.0 to 3.3, but water glass having n of 2.0 to 3.8 can also be preferably used.
水溶液に含まれる全アルカリ金属珪酸塩の含有量は、防火性能の付与の観点から、水溶液の全量に対して、10〜90質量%であることが好ましく、20〜80質量%であることがより好ましく、25〜70質量%であることが更に好ましい。 The content of the total alkali metal silicate contained in the aqueous solution is preferably 10 to 90% by mass and more preferably 20 to 80% by mass with respect to the total amount of the aqueous solution from the viewpoint of imparting fire protection performance. It is preferably 25 to 70% by mass, more preferably 25 to 70% by mass.
全アルカリ金属珪酸塩に占める珪酸ナトリウムの質量割合は、成膜性の向上及び防火性能の付与の観点から、40質量%以上であることが好ましく、50質量%以上であることがより好ましく、60質量%以上であることが更に好ましい。 The mass ratio of sodium silicate to the total alkali metal silicate is preferably 40% by mass or more, more preferably 50% by mass or more, and more preferably 60% by mass, from the viewpoint of improving film forming property and imparting fire protection performance. It is more preferably mass% or more.
アルカリ金属珪酸塩は、耐水性を向上させる観点から、珪酸ナトリウムに加えて、珪酸リチウムを含むことが好ましい。 The alkali metal silicate preferably contains lithium silicate in addition to sodium silicate from the viewpoint of improving water resistance.
アルカリ金属珪酸塩が珪酸リチウムを含む場合、珪酸ナトリウムの質量に対する、珪酸リチウムの質量の質量比は、光沢を高め耐水性を向上させる観点から、0.01〜1.5であることが好ましく、0.2〜1.4であることがより好ましく、0.3〜1.2であることが更に好ましい。 When the alkali metal silicate contains lithium silicate, the mass ratio of the mass of lithium silicate to the mass of sodium silicate is preferably 0.01 to 1.5 from the viewpoint of enhancing gloss and improving water resistance. It is more preferably 0.2 to 1.4, and even more preferably 0.3 to 1.2.
<非晶質シリカ>
非晶質シリカは、溶融石英ガラスであってもよく、合成シリカガラスであってもよい。溶融石英ガラスは、電気溶融により製造されたものでも、火炎溶融により製造されたものでもよい。合成シリカガラスは、乾式シリカでもよく、湿式シリカでもよい。
<Amorphous silica>
The amorphous silica may be fused silica glass or synthetic silica glass. The fused silica glass may be produced by electromelting or flame melting. The synthetic silica glass may be dry silica or wet silica.
非晶質シリカの粒径は、透明性を高める観点から、1〜15μmであることが好ましい。非晶質シリカの粒径は、レーザ回折式粒度分布測定における体積基準の粒度分布のD50を指す。 The particle size of the amorphous silica is preferably 1 to 15 μm from the viewpoint of enhancing transparency. The particle size of amorphous silica refers to D50 of the volume-based particle size distribution in the laser diffraction type particle size distribution measurement.
非晶質シリカの比表面積は、粘性を付与する観点から、6〜500m2/gであってよい。 The specific surface area of the amorphous silica may be 6 to 500 m 2 / g from the viewpoint of imparting viscosity.
非晶質シリカの5質量%水溶液のpHは、4〜7であってよい。 The pH of the 5% by mass aqueous solution of amorphous silica may be 4-7.
非晶質シリカの吸油量(ISO 787−5)は、100〜500g/100gであってよい。 The oil absorption of amorphous silica (ISO 787-5) may be 100 to 500 g / 100 g.
水溶液に含まれる非晶質シリカの含有量は、水溶液のB型粘度μ6が上記の要件を満たすように調節すればよい。非晶質シリカの量を増やすと水溶液のB型粘度μ6が高くなり、非晶質シリカの量を減らすと水溶液のB型粘度μ6が低くなる。非晶質シリカの種類によって、好適な非晶質シリカの添加量は異なるが、水溶液に含まれる非晶質シリカの含有量は、例えば、アルカリ金属珪酸塩の全量に対して、3.0〜160質量%であってよく、6.8〜90質量%であってよい。 The content of amorphous silica contained in the aqueous solution may be adjusted so that the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution satisfies the above requirements. Increasing the amount of amorphous silica increases the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution, and decreasing the amount of amorphous silica decreases the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution. The suitable amount of amorphous silica added differs depending on the type of amorphous silica, but the content of amorphous silica contained in the aqueous solution is, for example, 3.0 to 3.0 to the total amount of alkali metal silicate. It may be 160% by mass, and may be 6.8 to 90% by mass.
上述のように、水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6は、1500mPa・s以上であるが、垂直面等の傾斜面に塗布した場合の液だれを一層抑制する観点から、3000mPa・s以上であることが好ましく、4500mPa・s以上であることがより好ましい。水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6は、100000mPa・s以下であってよい。 As described above, the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. is 1500 mPa · s or more, but from the viewpoint of further suppressing dripping when applied to an inclined surface such as a vertical surface. It is preferably 3000 mPa · s or more, and more preferably 4500 mPa · s or more. The B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. may be 100,000 mPa · s or less.
B型粘度は、B型粘度計(単一円筒形回転粘度計)を用いて測定される。測定は、JIS K7117‐1を参照して行うことができる。 The B-type viscosity is measured using a B-type viscometer (single cylindrical rotational viscometer). The measurement can be performed with reference to JIS K7117-1.
水溶液を塗布する際の水溶液の伸びをよくすべく、水溶液の60rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度をμ60としたときに、μ6/μ60は、3以上であることが好ましく、4以上であることが好ましく、5以上であることがより好ましい。μ6/μ60は、20以下であってよい。 In order to improve the elongation of the aqueous solution when applying the aqueous solution, when the B-type viscosity of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 60 rpm and 20 ° C. is set to μ 60 , μ 6 / μ 60 is preferably 3 or more. It is preferably 4 or more, and more preferably 5 or more. μ 6 / μ 60 may be 20 or less.
水溶液の60rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度をμ60は、水溶液の水の割合等により調整できる。 60 a B-type viscosity at the conditions of 60 rpm, 20 ° C. of an aqueous solution μ can be adjusted by the proportion of water such as an aqueous solution.
水溶液の塗布量は、適宜調整できる。例えば、100g/m2以上とすることができ、3000g/m2以下とすることができる。 The amount of the aqueous solution applied can be adjusted as appropriate. For example, it can be 100 g / m 2 or more, and can be 3000 g / m 2 or less.
続いて、図1の(d)に示すように、乾燥前の水溶液層30a上に、織布35などのシート状の繊維を貼りつける。水溶液は高い粘度を有するので、貼りつけるだけでシート状の繊維の基材25の表面上への仮固定が可能である。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 1D, a sheet-like fiber such as a
<シート状の繊維>
シート状の繊維の例は、織布(平織りなど)、及び、不織布である。図1では、シート状の繊維の1例として、織布35を図示している。織布35は、縦糸及び横糸を有する。
<Sheet-shaped fiber>
Examples of sheet-like fibers are woven fabrics (plain weave, etc.) and non-woven fabrics. In FIG. 1, a
繊維の材料の例は、ガラス繊維;炭素繊維;アルミナ繊維、シリカ繊維などのセラミック繊維;アラミド繊維、ポリプロピレン繊維等の樹脂繊維;炭素鋼繊維、ステンレス繊維、めっき鋼繊維等の金属繊維等が挙げられる。 Examples of fiber materials include glass fibers; carbon fibers; ceramic fibers such as alumina fibers and silica fibers; resin fibers such as aramid fibers and polypropylene fibers; metal fibers such as carbon steel fibers, stainless fibers and plated steel fibers. Be done.
特に、ガラス繊維の織布(ガラスクロス)及び不織布(ガラスマットなど)は、本実施形態において特に好適なシート状の繊維である。 In particular, a glass fiber woven fabric (glass cloth) and a non-woven fabric (glass mat, etc.) are sheet-shaped fibers that are particularly suitable in the present embodiment.
シート状の繊維の厚みは、0.003〜2mmとすることができる。 The thickness of the sheet-shaped fiber can be 0.003 to 2 mm.
シート状の繊維がガラス繊維の織布又は不織布の場合、シート状の繊維の単位面積あたりの重量は、1〜1000g/m2とすることができる。 When the sheet-shaped fiber is a woven fabric or a non-woven fabric of glass fiber, the weight of the sheet-shaped fiber per unit area can be 1 to 1000 g / m 2.
続いて、図1の(e)に示すように、繊維のシート(たとえば織布35)の上に、さらに、上述の水溶液を塗布して水溶液層30aの厚みを大きくする。二回目に塗布する水溶液の塗布量も適宜調節でき、好適な範囲は1回目と同様である。必要に応じて、水溶液層30aに対する別のシート状の繊維(たとえば織布35)の貼り付け、及び、さらなる水溶液の塗布をさらに繰り返してもよい。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 1 (e), the above-mentioned aqueous solution is further applied onto the fiber sheet (for example, woven fabric 35) to increase the thickness of the
水溶液層30aの合計の塗布量はたとえば、100g/m2以上、300g/m2以上、500g/m2以上とすることができ、3000g/m2以下、2000g/m2以下、1500g/m2以下とすることができる。
The total coating amount of the
複数回の塗布により形成される水溶液層30aの合計厚みはたとえば30〜900μmとすることができる。
The total thickness of the
次に、水溶液層30aを乾燥させて固体状態のアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30を得る。乾燥は、自然乾燥、熱風乾燥等により行うことができる。
Next, the
シート状の繊維は完全にアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30内に埋め込まれていることが好適であるが、一部がアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30から突出していることもできる。
It is preferable that the sheet-like fiber is completely embedded in the alkali
(アルカリ金属珪酸塩層)
得られるアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30は、シート状の繊維、アルカリ金属珪酸塩、及び、非晶質シリカを含む。
(Alkali metal silicate layer)
The obtained alkali
アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30の厚みは、防火性能付与の観点から、30μm以上、好ましくは90μm以上、より好ましくは150μm以上とすることができる。厚みは、透明性及び施工性の観点から900μm以下、好ましくは600μm以下、より好ましくは450μm以下とすることができる。
The thickness of the alkali
アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30の単位面積あたりのアルカリ金属珪酸塩の重量は、防火性能付与の観点から、乾燥重量50g/m2以上(水溶液塗布量100g/m2以上に相当)、好ましくは乾燥重量150g/m2以上(水溶液塗布量300g/m2以上に相当)、より好ましくは乾燥重量250g/m2以上(水溶液塗布量500g/m2以上に相当)とすることができる。重量は、透明性及び施工性の観点から乾燥重量1500g/m2以下(水溶液塗布量3000g/m2以下に相当)、好ましくは乾燥重量1000g/m2以下(水溶液塗布量2000g/m2以下に相当)、より好ましくは乾燥重量750g/m2以下(水溶液塗布量1500g/m2以下に相当)とすることができる。
The weight of the alkali metal silicate per unit area of the alkali
次に、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30の上に、公知の方法で図1の(f)に示すように、トップ層40を形成する。
Next, the
(トップ層)
トップ層は、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30を水等から保護するための層である。トップ層40の材料の例は、アルキド樹脂、アクリル樹脂、ウレタン樹脂、アクリルシリコン樹脂、フッ素樹脂、シリコーン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、塩化ビニリデン共重合樹脂、塩化ビニル系樹脂等(水系、溶剤系を問わない)である。トップ層40は、トップ層の成膜材料を塗液として塗布するか、予め成膜したフィルムとして粘着剤等を介して貼り合わせることで積層できる。これにより、被覆基材100が完成する。なお、本実施形態は、トップ層40を形成しなくても実施できる。
(Top layer)
The top layer is a layer for protecting the alkali
本実施形態に係る製造方法によれば、6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6が1500mPa・s以上である水溶液を基材25上に塗布するため、基材25が水平方向に対して垂直に立てられているなど、基材の表面が傾斜する場合であっても、水溶液の液だれを抑制することができる。そのため、塗布/乾燥を何回も繰り返さずに、厚いアルカリ珪酸金属塩層を形成することができる。また、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層の厚みの均一性を高くすることができる。
According to the manufacturing method according to the present embodiment , since an aqueous solution having a B-type viscosity μ 6 of 1500 mPa · s or more under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. is applied onto the
更に、形成されたアルカリ金属珪酸塩層は、透明性に優れるため、木質材料などの基材本体の表面の模様(木目など)を外部から視認できて好ましい。 Further, since the formed alkali metal silicate layer is excellent in transparency, it is preferable that the pattern (wood grain, etc.) on the surface of the base material body such as a wood material can be visually recognized from the outside.
さらに、μ6/μ60が3以上である場合には、液だれを防ぎつつ、水溶液を塗布する際の水溶液の伸びが確保され、塗装作業性が向上する。水溶液の伸びが確保されることにより、得られる被覆基材は、表面の平滑性が優れたものとなる。 Further, when μ 6 / μ 60 is 3 or more, the elongation of the aqueous solution at the time of applying the aqueous solution is ensured while preventing dripping, and the coating workability is improved. By ensuring the elongation of the aqueous solution, the obtained coating base material has excellent surface smoothness.
[第二実施形態]
本発明の第二実施形態に係る被覆基材100の製造方法について、図2を参照して説明する。
[Second Embodiment]
A method for producing the
まず、図2の(a)及び図2の(b)に示すように、第一実施形態に係る被覆基材100の製造方法と同様にして、基材本体10を用意し、基材本体10の表面に公知の方法でプライマー層20を形成し、基材25を得る。
First, as shown in (a) of FIG. 2 and (b) of FIG. 2, the base material
続いて、図2の(c)に示すように、基材25の表面上に、シート状の繊維(たとえば織布35)を仮固定する。仮固定の方法は特に限定されず、たとえば、ステープル、ピン、ビス留め等による機械式固定、接着剤による固定等とすることができる。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 2C, sheet-shaped fibers (for example, woven fabric 35) are temporarily fixed on the surface of the
続いて、図2の(d)に示すように、基材25上のシート状の繊維(たとえば織布35)に、上述の水溶液を塗布して、シート状の繊維(たとえば織布35)を埋設した上述の水溶液層30aを形成する。水溶液の塗布量及び厚みは第1実施形態と同様とすることができる。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 2D, the above-mentioned aqueous solution is applied to the sheet-shaped fibers (for example, woven fabric 35) on the
その後、水溶液層30aを乾燥させてシート状の繊維(たとえば織布35)を埋設した固体状態のアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30を得る。アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30の厚みは第1実施形態と同様とすることができる。その後、第1実施形態と同様にして、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30上にトップ層40を形成することができる。
Then, the
[第三実施形態]
本発明の第三実施形態に係る被覆基材100の製造方法について、図3を参照して説明する。
[Third Embodiment]
A method for producing the
まず、図3の(a)及び図3の(b)に示すように、第一実施形態に係る被覆基材100の製造方法と同様にして、基材本体10を用意し、基材本体10の表面に公知の方法でプライマー層20を形成し、基材25を得る。
First, as shown in (a) of FIG. 3 and (b) of FIG. 3, the base material
続いて、図3の(c)に示すように、基材25上に、水溶液を塗布して水溶液層30aを形成する。水溶液の塗布量は、第2実施形態と同様とすることができる。本実施形態においては、シート状繊維を基材25上に配置しない。そのかわり、水溶液に対して、あらかじめ、繊維を分散させておく。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 3C, an aqueous solution is applied onto the
(分散された繊維)
繊維の材料の例は、第1実施形態と同様である。好適な繊維の径は0.003〜1mmであり、好適な繊維の長さは0.1〜100mmである。水溶液における繊維の量は、水溶液の全量に対して、0.1〜20重量%であることができる。繊維としては、長繊維であってもよく、短繊維であってもよいが、水溶液の混練性を向上させる観点から、短繊維であることが好ましい。短繊維とは50mm以下の繊維である。短繊維の長さは、15mm以下が好ましく、10mm以下とすることもできる。
(Dispersed fiber)
Examples of fiber materials are the same as in the first embodiment. Suitable fiber diameters are 0.003 to 1 mm and suitable fiber lengths are 0.1 to 100 mm. The amount of fibers in the aqueous solution can be 0.1 to 20% by weight based on the total amount of the aqueous solution. The fiber may be a long fiber or a short fiber, but is preferably a short fiber from the viewpoint of improving the kneadability of the aqueous solution. Short fibers are fibers of 50 mm or less. The length of the short fibers is preferably 15 mm or less, and may be 10 mm or less.
その後、図3の(d)に示すように、水溶液層30aを乾燥させてアルカリ金属珪酸塩層30を得た後、公知の方法で図3の(e)に示すように、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30上にトップ層40を形成する。
Then, as shown in FIG. 3 (d), the
上述した各製造方法により得られる被覆基材100は、防火性能を有することができ、たとえば、柱、梁、床、壁、屋根材等の建築物の構造体、天井材、内壁材、外装材、階段、建具等の建築物の仕上げ材料、その他、自動車、鉄道、船舶等の内装材料、家具の材料として利用できる。
The
なお、本実施形態において、水溶液に対して、一般的な難燃剤、例えばリン系、フォスファゼン系、窒素系、臭素系、無機系(水酸化マグネシウム、水酸化アルミニウム等)の各種難燃剤を添加する事を否定しない。 In this embodiment, general flame retardants such as phosphorus-based, phosphazen-based, nitrogen-based, bromine-based, and inorganic-based (magnesium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, etc.) are added to the aqueous solution. I do not deny the matter.
本発明は上記実施形態に限定されず、様々な変形態様をとることが出来る。
例えば、上記製造方法では、基材25(基材本体10)の表面が、水平面に対して90°傾斜しているが、水平面に対して斜めに傾斜していてもよいし、水平面と平行であってもよい。基材25の表面が水平面に対して10〜90°傾斜していることが好適であり、25〜90°傾斜していることがより好適である。
The present invention is not limited to the above embodiment, and various modifications can be taken.
For example, in the above manufacturing method, the surface of the base material 25 (base material body 10) is inclined by 90 ° with respect to the horizontal plane, but it may be inclined with respect to the horizontal plane or parallel to the horizontal plane. There may be. It is preferable that the surface of the
また、上述した製造方法では、プライマー層20を含む基材25を用いたが、プライマー層20は必須ではない。アルカリ金属珪酸塩層30は、基材25の表面の少なくとも一部に形成されていればよい。上述した製造方法では、トップ層40を設けたが、トップ層40は必須ではない。
Further, in the above-mentioned production method, the
また、第3実施形態において、上述の水溶液が、分散された繊維を含んでいなくても実施は可能である。 Further, in the third embodiment, the above-mentioned aqueous solution can be carried out even if it does not contain dispersed fibers.
[水溶液の調整]
(実施例1〜11及び比較例1)
珪酸ナトリウム水溶液(水ガラス3号:n=3.1〜3.3、珪酸ナトリウム濃度:38.5〜40.0質量%)及び珪酸リチウム水溶液(商品名:リチウムシリケート45、SiO2/Li2Oモル比4.5、珪酸ナトリウム濃度:22質量%)を、珪酸ナトリウム水溶液と珪酸リチウム水溶液の質量比が珪酸ナトリウム水溶液:珪酸リチウム水溶液=2:1となるように混合し、混合液を得た。
さらに、混合液100質量部に対して、非晶質シリカ(商品名:ACMATT TS−100、デグサAG製、乾式シリカ、比表面積250m2/g、平均粒径9.5μm、5%水分散液のpH6.5、吸油量380g/100g)を、表1に記載の量で添加し、600〜800rpmの攪拌速度で30分間攪拌し、水溶液を調製した。水溶液における非晶質シリカの濃度を表1に示す。また、水溶液に含まれる珪酸ナトリウムの含有量は25.6質量%、珪酸リチウムの含有量は7.3質量%であった。珪酸ナトリウムの質量に対する、珪酸リチウムの質量の質量比は、0.3であった。アルカリ金属珪酸塩の全量に対する、非晶質シリカの含有量(質量%)を表1に示す。
[Adjustment of aqueous solution]
(Examples 1 to 11 and Comparative Example 1)
Aqueous solution of sodium silicate (water glass No. 3: n = 3.1 to 3.3, sodium silicate concentration: 38.5 to 40.0% by mass) and an aqueous solution of lithium silicate (trade name: lithium silicate 45, SiO 2 / Li 2). Omolar ratio 4.5, sodium silicate concentration: 22% by mass) was mixed so that the mass ratio of the sodium silicate aqueous solution and the lithium silicate aqueous solution was 2: 1 of the sodium silicate aqueous solution: lithium silicate aqueous solution = 2: 1 to obtain a mixed solution. It was.
Further, with respect to 100 parts by mass of the mixed solution, amorphous silica (trade name: ACMATT TS-100, manufactured by Degusa AG, dry silica, specific surface area 250 m 2 / g, average particle size 9.5 μm, 5% aqueous dispersion) The pH of 6.5 and the oil absorption amount (380 g / 100 g) were added in the amounts shown in Table 1 and stirred at a stirring speed of 600 to 800 rpm for 30 minutes to prepare an aqueous solution. Table 1 shows the concentration of amorphous silica in the aqueous solution. The content of sodium silicate contained in the aqueous solution was 25.6% by mass, and the content of lithium silicate was 7.3% by mass. The mass ratio of the mass of lithium silicate to the mass of sodium silicate was 0.3. Table 1 shows the content (mass%) of amorphous silica with respect to the total amount of alkali metal silicate.
(実施例12及び13並びに比較例3〜5)
非晶質シリカ(商品名:ACMATT TS−100、デグサAG製)に代えて、非晶質シリカ(商品名:F−205、フミテック株式会社製、溶融シリカ、粒径5.5μm、比表面積6m2/g、5%水分散液のpH4.0〜6.0)を用いたこと以外は、実施例1と同様にして水溶液を調整した。非晶質シリカの添加量、水溶液における非晶質シリカ濃度、アルカリ金属珪酸塩の全量に対する、非晶質シリカの含有量(質量%)を表1に示す。
(Examples 12 and 13 and Comparative Examples 3 to 5)
Amorphous silica (trade name: F-205, manufactured by Fumitech Co., Ltd., fused silica, particle size 5.5 μm, specific surface area 6 m) instead of amorphous silica (trade name: ACMATT TS-100, manufactured by Degusa AG) The aqueous solution was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the pH of the 2 / g, 5% aqueous dispersion was 4.0 to 6.0). Table 1 shows the content (% by mass) of amorphous silica with respect to the amount of amorphous silica added, the concentration of amorphous silica in the aqueous solution, and the total amount of alkali metal silicate.
[粘度の測定]
B型粘度計(東機産業株式会社製、商品名:BM型)を用いて、水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6と、水溶液の60rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度をμ60とを測定した。結果を表1に示した。
[Measurement of viscosity]
Using a B-type viscometer (manufactured by Toki Sangyo Co., Ltd., trade name: BM type), B-type viscosity μ 6 under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C for the aqueous solution and B under the conditions of 60 rpm and 20 ° C for the aqueous solution. The mold viscosity was measured as μ 60. The results are shown in Table 1.
[被覆基材の製造]
(実施例1〜13及び比較例2〜5)
基材本体としてスギ材を用意した。スギ材の水平な表面に、バーサチック酸−ビニルエステル系樹脂を含有する塗料を塗布してプライマー層を形成し、スギ材の表面にプライマー層が形成された基材を得た。得られた基材におけるプライマー層が形成された表面に、シート状のガラス繊維(セントラルグラスファイバー サーフェイスマット FC−30S)を置き、その上からアルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液を1000g/m2塗布し、その後、水溶液層が形成された基材を、該水溶液層が形成された面が水平方向に対して垂直になるように立て、水溶液層を乾燥させた。乾燥は、温度23℃、湿度50%(相対湿度)の環境下で24時間行った。アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液層を乾燥させることで、アルカリ金属珪酸塩層(アルカリ金属珪酸塩の単位面積あたりの乾燥重量600g/m2)を形成し、被覆基材を得た。
[Manufacturing of coating base material]
(Examples 1 to 13 and Comparative Examples 2 to 5)
Sugi material was prepared as the main body of the base material. A paint containing a versatic acid-vinyl ester resin was applied to the horizontal surface of the Sugi material to form a primer layer, and a substrate having a primer layer formed on the surface of the Sugi material was obtained. A sheet-shaped glass fiber (central glass fiber surface mat FC-30S) is placed on the surface of the obtained base material on which the primer layer is formed, and 1000 g / m 2 of an aqueous alkali metal silicate solution is applied thereto. The base material on which the aqueous solution layer was formed was erected so that the surface on which the aqueous solution layer was formed was perpendicular to the horizontal direction, and the aqueous solution layer was dried. Drying was carried out for 24 hours in an environment of a temperature of 23 ° C. and a humidity of 50% (relative humidity). By drying the alkali metal silicate aqueous solution layer, an alkali metal silicate layer (dry weight 600 g / m 2 per unit area of alkali metal silicate) was formed, and a coating base material was obtained.
(比較例1)
アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液の塗布量を700g/m2としたこと以外は、実施例1と同様にして被覆基材を得た。
(Comparative Example 1)
A coating base material was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the coating amount of the alkali metal silicate aqueous solution was 700 g / m 2.
[評価:液だれ]
被覆基材の製造において、水溶液を乾燥させる際に、該水溶液層が形成された基材表面における水溶液の液だれの有無を確認した。液だれの有無は、下記の基準に従い評価した。結果を表1に示した。
○:乾燥するまで30分経過しても液だれが発生しなかった
△:垂直に立てた直後には液だれが発生しないが、30分経過後には、垂直に立てられた基材の底部に水溶液がたまる様子が確認された
×:垂直に立てた直後にしずくとなって液だれが発生した
[Evaluation: Dripping]
In the production of the coated substrate, when the aqueous solution was dried, the presence or absence of dripping of the aqueous solution on the surface of the substrate on which the aqueous solution layer was formed was confirmed. The presence or absence of dripping was evaluated according to the following criteria. The results are shown in Table 1.
◯: No dripping occurred even after 30 minutes had passed until it dried. Δ: No dripping occurred immediately after standing vertically, but after 30 minutes, it was placed on the bottom of the vertically erected base material. It was confirmed that the aqueous solution accumulated. ×: Immediately after standing vertically, it became a drop and dripping occurred.
[評価:平滑性(伸び)]
得られた被覆基材に対して、目視にて被覆基材におけるアルカリ金属珪酸塩層が設けられた表面の平滑性を下記の基準に従い評価した。結果を表1に示した。被覆基材の表面が平滑性に優れることは、水溶液の伸びが良好であることを意味する。
○:被覆基材の表面に凹凸が観察されない
○−:被覆基材の表面に僅かに凹凸が観察される
△:被覆基材の表面に若干の凹凸が観察される
×:アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液の粘度が高すぎるため、アルカリ金属珪酸塩水溶液の塗布ができなかった
[Evaluation: Smoothness (elongation)]
With respect to the obtained coated base material, the smoothness of the surface of the coated base material provided with the alkali metal silicate layer was visually evaluated according to the following criteria. The results are shown in Table 1. The excellent smoothness of the surface of the coating base material means that the aqueous solution has good elongation.
◯: No unevenness is observed on the surface of the coated base material ○ −: Slight unevenness is observed on the surface of the coated base material Δ: Some unevenness is observed on the surface of the coated base material ×: Alkali metal silicate aqueous solution The alkali metal silicate aqueous solution could not be applied because the viscosity of the metal silicate was too high.
[評価:透明性]
得られた被覆基材に対して、目視にてアルカリ金属珪酸塩層の透明性の評価を行った。結果を表1に示す。○はスギ材表面の木目がはっきり視認できたことを意味する。
[Evaluation: Transparency]
The transparency of the alkali metal silicate layer was visually evaluated for the obtained coated base material. The results are shown in Table 1. ○ means that the grain on the surface of the sugi wood was clearly visible.
10…基材本体、20…プライマー層、25…基材、30…アルカリ金属珪酸塩層、100…被覆基材。 10 ... Base material body, 20 ... Primer layer, 25 ... Base material, 30 ... Alkali metal silicate layer, 100 ... Coating base material.
Claims (7)
塗布された水溶液を乾燥させてアルカリ金属珪酸塩層を形成する工程、を備え、
前記水溶液の6rpm、20℃の条件でのB型粘度μ6が1500mPa・s以上である、被覆基材の製造方法。 The process of applying an aqueous solution containing amorphous silica and alkali metal silicate to the surface of the base material,
It comprises a step of drying the applied aqueous solution to form an alkali metal silicate layer.
A method for producing a coating base material, wherein the B-type viscosity μ 6 of the aqueous solution under the conditions of 6 rpm and 20 ° C. is 1500 mPa · s or more.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019200760A JP7397436B2 (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Manufacturing method of coated base material |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019200760A JP7397436B2 (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Manufacturing method of coated base material |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021074646A true JP2021074646A (en) | 2021-05-20 |
| JP7397436B2 JP7397436B2 (en) | 2023-12-13 |
Family
ID=75899891
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019200760A Active JP7397436B2 (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Manufacturing method of coated base material |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7397436B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022270360A1 (en) * | 2021-06-24 | 2022-12-29 | デンカ株式会社 | Fire spread prevention material, method for producing same, laminate, assembled battery, and automobile |
| WO2022270359A1 (en) * | 2021-06-24 | 2022-12-29 | デンカ株式会社 | Fire spread prevention material, battery pack and automobile |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1193296A (en) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-04-06 | Nippon Zeri Kk | Foaming inorganic fire resistant covering material, and fire resistant covering construction method of steel frame |
| JP2003155426A (en) * | 2001-11-20 | 2003-05-30 | Osaka Yushi Kogyo Kk | Fire-resistant coating agent and fire-resistant structure |
| JP2004035377A (en) * | 2002-07-08 | 2004-02-05 | Kawaguchi Makku Kogyo:Kk | Heat-insulation refractory material composition and heat-insulation refractory material using the same |
| JP2005048142A (en) * | 2003-07-31 | 2005-02-24 | Nippon Sheet Glass Co Ltd | Solution for forming colored film and method for producing glass base having colored film formed by using the same |
| US20100178519A1 (en) * | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Keimfarben Gmbh & Co. Kg | Compound coating for wood |
| JP2014152269A (en) * | 2013-02-08 | 2014-08-25 | Tsubakimoto Chain Co | Paint, painted article, and method for manufacturing paint |
-
2019
- 2019-11-05 JP JP2019200760A patent/JP7397436B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1193296A (en) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-04-06 | Nippon Zeri Kk | Foaming inorganic fire resistant covering material, and fire resistant covering construction method of steel frame |
| JP2003155426A (en) * | 2001-11-20 | 2003-05-30 | Osaka Yushi Kogyo Kk | Fire-resistant coating agent and fire-resistant structure |
| JP2004035377A (en) * | 2002-07-08 | 2004-02-05 | Kawaguchi Makku Kogyo:Kk | Heat-insulation refractory material composition and heat-insulation refractory material using the same |
| JP2005048142A (en) * | 2003-07-31 | 2005-02-24 | Nippon Sheet Glass Co Ltd | Solution for forming colored film and method for producing glass base having colored film formed by using the same |
| US20100178519A1 (en) * | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Keimfarben Gmbh & Co. Kg | Compound coating for wood |
| JP2014152269A (en) * | 2013-02-08 | 2014-08-25 | Tsubakimoto Chain Co | Paint, painted article, and method for manufacturing paint |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022270360A1 (en) * | 2021-06-24 | 2022-12-29 | デンカ株式会社 | Fire spread prevention material, method for producing same, laminate, assembled battery, and automobile |
| WO2022270359A1 (en) * | 2021-06-24 | 2022-12-29 | デンカ株式会社 | Fire spread prevention material, battery pack and automobile |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7397436B2 (en) | 2023-12-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI491682B (en) | Formaldehyde free coatings for panels | |
| KR102479244B1 (en) | Silicate Coatings for Improved Acoustic Panel Performance and Methods of Making The Same | |
| JP7397436B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of coated base material | |
| KR20190030148A (en) | Panels Formed with Nonflammable Coated Layer for Buildings and Method of Forming Nonflammable Coated Layer on Panels | |
| CN112189038A (en) | Borate and silicate coatings for improved acoustical panel performance and method of making same | |
| JP5051028B2 (en) | Incombustible decorative board | |
| CN103216047A (en) | Fire-resistant bituminous cellulose cover plate and manufacturing method | |
| JP6794278B2 (en) | Coating base material and its manufacturing method | |
| JPH10265722A (en) | Thick film-form elastic heat-insulating coating material and coating heat-insulating technique using the same | |
| ITTO930608A1 (en) | FINE PLASTER FOR INTERIORS AND PROCEDURE FOR ITS MANUFACTURE | |
| US20220297156A1 (en) | Hybrid Coating Process | |
| JP2008044139A (en) | Interior finish material | |
| JP6581123B2 (en) | Coated substrate and method for producing the same | |
| JP7436979B2 (en) | Coated base material and its manufacturing method | |
| JP7426645B2 (en) | Coated base material and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2006328235A (en) | Emulsion composition for producing oil-resistant moistureproof film and its utilization | |
| US20230130177A1 (en) | Stable high temperature coating compositions and methods of preparing and using the same | |
| JP2669011B2 (en) | Flame retardant coating film waterproofing composition | |
| JP6850943B2 (en) | Non-combustible veneer | |
| JP6759561B2 (en) | Non-combustible decorative board | |
| JP6917225B2 (en) | Veneer | |
| JP2023163185A (en) | Product attached with film and laminate | |
| JP6850942B2 (en) | Non-combustible veneer | |
| JP2000229368A (en) | Method for forming insulating laminate having fire proof property | |
| JP2002115366A (en) | Membrane ceiling or membrane wall structure with sound absorbing function |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20221013 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20230727 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230808 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20231010 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20231024 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20231122 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7397436 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |