JP2020044844A - Joint structure - Google Patents
Joint structure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2020044844A JP2020044844A JP2019219020A JP2019219020A JP2020044844A JP 2020044844 A JP2020044844 A JP 2020044844A JP 2019219020 A JP2019219020 A JP 2019219020A JP 2019219020 A JP2019219020 A JP 2019219020A JP 2020044844 A JP2020044844 A JP 2020044844A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light
- opening
- absorbing member
- welded portion
- transmitting member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 65
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 93
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 claims description 34
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000010926 purge Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 abstract description 55
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 abstract description 28
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 56
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 56
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 32
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 24
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 20
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 description 20
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 16
- -1 for example Polymers 0.000 description 14
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 12
- RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,4,4,6,6-hexaphenoxy-1,3,5-triaza-2$l^{5},4$l^{5},6$l^{5}-triphosphacyclohexa-1,3,5-triene Chemical compound N=1P(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP=1(OC=1C=CC=CC=1)OC1=CC=CC=C1 RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000004071 soot Substances 0.000 description 10
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229920005990 polystyrene resin Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 230000006837 decompression Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000003763 carbonization Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000013011 mating Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 4
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M Methacrylate Chemical compound CC(=C)C([O-])=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 239000004734 Polyphenylene sulfide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000002845 discoloration Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005187 foaming Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920005669 high impact polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000004797 high-impact polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 4
- JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N olefin Natural products CCCCCCCC=C JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920006122 polyamide resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920005668 polycarbonate resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000004431 polycarbonate resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920013716 polyethylene resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920013636 polyphenyl ether polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920000069 polyphenylene sulfide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000012779 reinforcing material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 3
- 241000219122 Cucurbita Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000009852 Cucurbita pepo Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910009372 YVO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920000122 acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000006229 carbon black Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000032798 delamination Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004880 explosion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009776 industrial production Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009834 vaporization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008016 vaporization Effects 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012463 white pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Lining Or Joining Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、相互に重ね合わされ、その境界面または境界面近傍に形成された溶着部を介して互いに接合された光吸収性部材及び光透過性部材を備える接合構造体、及びその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a joint structure including a light-absorbing member and a light-transmitting member that are overlapped with each other and joined to each other via a welded portion formed at or near a boundary surface thereof, and a method of manufacturing the same.
従来、複数の部材を接合する方法として、レーザ光の照射による接合方法があり、その中でも最近では、局所的な加熱であり製品への熱ダメージが少ないとともに、溶着部の、外観への影響が少ないレーザ透過溶着法(Laser Transmission Welding)が注目されている。この接合方法は、接合部材の一方にレーザ光に対して透過性を有する部材(光透過性部材)を用い、他方にレーザ光に対して吸収性を有する部材(光吸収性部材)を用い、これらを互いに重ね合わせて加圧した状態で、レーザ光を光透過性部材側から照射することで、照射されたレーザ光のエネルギが光吸収性部材の境界面付近で吸収されて発熱し、その熱が光透過性部材にも伝達して両部材が溶融し、最後にその溶融部が冷却、固化されることで両部材が接合される方法である。 Conventionally, as a method of joining a plurality of members, there is a joining method by laser beam irradiation, and recently, among these, local heating is performed, so that heat damage to the product is small, and the effect of the welded portion on the appearance is reduced. Attention has been paid to a small number of laser transmission welding methods (Laser Transmission Welding). In this bonding method, a member having a property of transmitting laser light (a light transmitting member) is used as one of the bonding members, and a material having a property of absorbing the laser light (a light absorbing member) is used as the other of the bonding members. By irradiating the laser light from the light transmitting member side in a state where these are superimposed on each other and pressurized, the energy of the irradiated laser light is absorbed near the boundary surface of the light absorbing member and generates heat. In this method, both members are melted by transmitting heat to the light transmissive member, and finally, the melted portion is cooled and solidified to join the two members.
このレーザ透過溶着法には、いくつかの重要なポイントがあるが、とりわけ重要なのが接合される部材同士を加圧して確実に密着させることである。接合される部材間に隙間が存在すると、レーザ照射によって光吸収性部材で発生した熱が相手側である光透過性部材にうまく伝達されず、局所的な温度上昇によって隆起、膨張、爆発といった溶着不良となるからである。 The laser transmission welding method has several important points, and particularly important is to press the members to be bonded to each other to ensure close contact. If there is a gap between the members to be joined, the heat generated by the light absorbing member due to the laser irradiation will not be transmitted well to the opposing light transmitting member, and welding such as bulging, expansion and explosion will occur due to local temperature rise. This is because it becomes defective.
この加圧は、一般的には、レーザ光に対して透過性を有するガラス板を光透過性部材上に配置し、このガラス板を介して両部材に押し圧を加える方法によって実現される(下記特許文献1参照)。しかし、この方法の場合、接合部材の加熱、溶融時に発生する煤や難燃剤の気化成分によってガラス板が汚れ、レーザ光に対するガラス板の吸収率が上がってガラス板自体が加熱されて割れに至るという問題がある。また、汚れたガラス板は、レーザ光を遮り、光吸収性部材に十分な光が届かなくなる結果、溶着強度の低下をも引き起こす。 This pressurization is generally realized by a method in which a glass plate having transparency to laser light is disposed on a light-transmitting member, and a pressing force is applied to both members via the glass plate ( See Patent Document 1 below). However, in the case of this method, the glass plate is contaminated by soot and a vaporization component of the flame retardant generated when the joining member is heated and melted, and the absorption rate of the glass plate with respect to laser light is increased, and the glass plate itself is heated and cracked. There is a problem. In addition, the dirty glass plate blocks the laser beam and prevents sufficient light from reaching the light-absorbing member, resulting in a decrease in welding strength.
これに対して、下記特許文献2では、ガラス板を用いず、接合される部材同士を吸引により密着させる方法が提案されている。具体的には、特許文献2に記載の方法は、接合される部材の一方に溝部を形成しておき、この溝部の空間を減圧することで両部材同士を密着させるものである。しかし、レーザ照射により溶着する際に接合される部材の一方又は双方に熱変形が生じたり、成形時に接合される部材に反りが生じたりする結果、接合される部材間に隙間が発生し、これにより吸引密着性が低下する場合がある。
On the other hand,
それ故本発明の目的は、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させるのに適した接合構造体を提供するとともに、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させることができる接合構造体の製造方法を提供することにある。 Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide a joint structure suitable for uniformly and surely adhering members to be joined to each other without using a glass plate, and without using a glass plate. It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for manufacturing a joined structure in which members to be joined can be uniformly and surely brought into close contact with each other.
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材と、開口部を覆うように光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、を備え、開口部を囲繞するとともに光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する環状の溶着部が形成され、光透過性部材は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成されていることを特徴とするものである。 A joint structure of the present invention for solving the above-mentioned problem, a light-absorbing member having at least one opening, a light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening, An annular welded portion surrounding the opening and joining the light absorbing member and the light transmissive member is formed, and the light transmissive member is located inside the opening before the annular welded portion is formed. Are deformed when depressurized, and are formed in a thin plate shape closely adhering to the light absorbing member.
この場合、光透過性部材は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。 In this case, the light transmissive member is deformed when the inside of the opening is reduced to a gauge pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less before the annular welded portion is formed, and the light transmissive member adheres to the light absorbing member. Preferably, it is formed to a thickness.
また、本発明の接合構造体にあっては、環状の溶着部に隣接して位置し、光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する点状の溶着部を備えることが好ましい。 Further, the joint structure of the present invention preferably includes a point-like welded portion located adjacent to the annular welded portion and joining the light-absorbing member and the light-transmitting member.
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材と、開口部を覆うように光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、を備え、開口部を囲繞するとともに光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する環状の溶着部が形成され、光透過性部材は、環状の溶着部よりも外側に、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を有することを特徴とするものである。 A joint structure of the present invention for solving the above-mentioned problem, a light-absorbing member having at least one opening, a light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening, And an annular welded portion surrounding the opening and joining the light absorbing member and the light transmissive member is formed, and the light transmissive member has an annular welded portion outside the annular welded portion. It is characterized in that it has a thin piece that deforms when the inside of the opening is decompressed in a state before it is formed and adheres to the light absorbing member.
この場合、薄肉片は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。 In this case, the thin piece is deformed when the inside of the opening is reduced to a gauge pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less before the annular welded portion is formed, and the thin piece is formed to have a thickness that is in close contact with the light absorbing member. It is preferred that
また、本発明の接合構造体にあっては、薄肉片は、光吸収性部材の周縁部に沿って形成されていることが好ましい。 In the joint structure of the present invention, it is preferable that the thin piece is formed along the peripheral edge of the light absorbing member.
さらに、本発明の接合構造体にあっては、環状の溶着部に隣接して位置し、光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する点状の溶着部を備えることが好ましい。 Further, the joint structure of the present invention preferably includes a point-like welded portion that is located adjacent to the annular welded portion and joins the light-absorbing member and the light-transmitting member.
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体の製造方法は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材に、開口部を覆うように光透過性部材を重ね合わせ、光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することにより開口部を囲繞するよう環状の溶着部を形成して光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する接合構造体の製造方法であって、光透過性部材を、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成しておき、環状の溶着部を形成するにあたり、開口部内を減圧することにより光透過性部材を変形させ光吸収性部材に密着させた状態で光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することを特徴とするものである。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, a method of manufacturing a bonded structure according to the present invention includes a step of superimposing a light-transmitting member on a light-absorbing member having at least one opening so as to cover the opening. A method of manufacturing a joining structure for joining a light absorbing member and a light transmitting member by forming an annular welded portion so as to surround an opening by irradiating a laser beam from a side, comprising: Is deformed when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed, and is formed in a thin plate shape that is in close contact with the light absorbing member, and the annular welded portion is formed. In this case, the light transmitting member is deformed by depressurizing the inside of the opening, and the laser light is irradiated from the light transmitting member side in a state in which the light transmitting member is in close contact with the light absorbing member.
この場合、光透過性部材を、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成しておくことが好ましい。 In this case, the light transmissive member is deformed when the inside of the opening is reduced to a pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less with a gauge pressure before the annular welded portion is formed, and the light transmissive member adheres to the light absorbing member. It is preferable to form it to a thickness.
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体の製造方法は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材に、開口部を覆うように光透過性部材を重ね合わせ、光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することにより開口部を囲繞するよう環状の溶着部を形成して光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する接合構造体の製造方法であって、光透過性部材の、環状の溶着部よりも外側に、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を形成しておき、環状の溶着部を形成するにあたり、開口部内を減圧することにより薄肉片を変形させ光吸収性部材に密着させた状態で光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することを特徴とするものである。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, a method of manufacturing a bonded structure according to the present invention includes a step of superimposing a light-transmitting member on a light-absorbing member having at least one opening so as to cover the opening. A method of manufacturing a joining structure for joining a light absorbing member and a light transmitting member by forming an annular welded portion so as to surround an opening by irradiating a laser beam from a side, comprising: Outside the annular welded portion, a thin piece that is deformed and adheres to the light absorbing member when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed is formed. In forming an annular welded portion, a laser beam is irradiated from the light transmitting member side in a state in which the thin piece is deformed by reducing the pressure in the opening and brought into close contact with the light absorbing member. is there.
この場合、薄肉片を、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成しておくことが好ましい。 In this case, the thin piece is deformed when the inside of the opening is reduced to a gauge pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less before the annular welded portion is formed, and the thin piece is formed to have a thickness that is in close contact with the light absorbing member. It is preferable to keep it.
また、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、薄肉片を、光吸収性部材の周縁部に沿って形成しておくことが好ましい。 In the method for manufacturing a joined structure according to the present invention, it is preferable that the thin piece is formed along the peripheral edge of the light-absorbing member.
また、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、光透過性部材を光吸収性部材に重ね合わせた後であってかつ環状の溶着部を形成する前に、光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射して光吸収性部材と光透過性部材とを接合する点状の溶着部を形成することが好ましい。 Further, in the method for manufacturing a joined structure according to the present invention, after the light-transmitting member is overlapped with the light-absorbing member and before forming the annular welded portion, from the light-transmitting member side. It is preferable to form a point-like welded portion for joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member by irradiating the laser beam.
さらに、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、光吸収性部材に、開口部につながるとともに外部の減圧装置に連通する吸引開口を形成しておくことが好ましい。 Furthermore, in the method for manufacturing a joined structure according to the present invention, it is preferable that a suction opening connected to the opening and communicating with an external decompression device is formed in the light absorbing member.
さらに、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、環状の溶着部の形成後に、開口部内の減圧を維持したまま光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することによって吸引開口を溶融、閉塞させることが好ましい。 Furthermore, in the method for manufacturing a joint structure of the present invention, after forming the annular welded portion, the suction opening is melted by irradiating laser light from the light transmitting member side while maintaining the reduced pressure in the opening, It is preferred to occlude.
さらに、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、開口部内の減圧を、該開口部内にパージガスを供給しながら行うことが好ましい。 Further, in the method for manufacturing a joined structure according to the present invention, it is preferable that the pressure in the opening is reduced while supplying a purge gas into the opening.
この場合、開口部内の減圧と該開口部内へのパージガスの供給とを、二重配管を用いて吸引開口を通じて行うことが好ましい。 In this case, it is preferable that the pressure reduction in the opening and the supply of the purge gas into the opening are performed through the suction opening using a double pipe.
また、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、環状の溶着部を形成した後に引き続き開口部内の減圧を保持し、または開口部内を加圧し、あるいは減圧と加圧を交互に行い、その際の単位時間当たりの圧力の変化を測定することによって環状の溶着部の気密性試験を行うことが好ましい。 Further, in the method for manufacturing a joined structure of the present invention, after forming the annular welded portion, continuously holding the reduced pressure in the opening, or pressurizing the inside of the opening, or alternately performing reduced pressure and pressurized, At that time, it is preferable to conduct an airtightness test of the annular welded portion by measuring a change in pressure per unit time.
さらに、本発明の接合構造体の製造方法にあっては、開口部内の圧力を常時検出し、その圧力の変化に基づき、光吸収性部材と光透過性部材との間の密着、環状の溶着部の形成開始、及び環状の溶着部の形成完了の判別を行うことが好ましい。 Further, in the method for manufacturing a joined structure according to the present invention, the pressure in the opening is constantly detected, and based on the change in the pressure, the close contact between the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member and the annular welding are performed. It is preferable to determine the start of the formation of the portion and the completion of the formation of the annular welded portion.
本発明にあっては、接合構造体の製造において、互いに接合される光吸収性部材と光透過性部材を、開口部内を減圧することによって薄板状に形成された光透過性部材又は光透過性部材に設けられた薄肉片を変形させ、光吸収性部材に密着させることができるので、光吸収性部材及び光透過性部材同士の優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。 According to the present invention, in the production of the joined structure, the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member that are joined to each other are formed in a thin plate shape by reducing the pressure in the opening. Since the thin piece provided on the member can be deformed and brought into close contact with the light absorbing member, excellent suction adhesion between the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member can be obtained.
しがたって本発明によれば、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させるのに適した接合構造体を提供することができるとともに、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させることができる接合構造体の製造方法を提供することができる。 Therefore, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a joint structure suitable for uniformly and surely adhering members joined to each other without using a glass plate, and to use a glass plate. Without this, it is possible to provide a method of manufacturing a joined structure in which members joined to each other can be uniformly and surely brought into close contact with each other.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づき詳細に説明する。なお、各図において同様の
部材または部分には、符号に「100」又は「200」のいずれかを加えた符号を付し、
重複する説明は省略する。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In each drawing, similar members or portions are denoted by reference numerals obtained by adding either “100” or “200” to the reference numerals,
Duplicate description will be omitted.
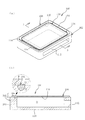
図1は、本発明の一実施形態の接合構造体100を示しており、(a)は斜視図、(b)は(a)中のA−A線に沿う断面図である。この図に示すように、本実施形態の接合構造体100は、開口部Oを有する光吸収性部材102と、該開口部Oを覆うように光吸収性部材102に重ねられ、開口部Oを囲繞する環状の溶着部104を介して該光吸収性部材102に接合された光透過性部材106とを備えている。なお、「環状」とは、輪のような円い形だけを意味するのではなく、連続的に閉じた形状(無端形状)を意味する。よって、「環状」には、円形や楕円形だけではなく、矩形、多角形、その他の閉鎖形状が含まれる。溶着部104は、光透過性部材106と光吸収性部材102の境界面F上に形成されており、後で詳細に説明するが、このような溶着部104は、光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102へ向けてレーザ光を照射し、光吸収性部材102をまず発熱させて溶融し、その熱で光透過性部材106をも溶融させ、その後溶融部を固化させることで形成することができる。
1A and 1B show a
光吸収性部材102は、レーザ光に対する吸収率が光透過性部材106の同レーザ光に対する吸収率よりも高い部材であり、主として熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーからなり、射出成形等により形成することができる。具体的には、波長193〜10600nmの範囲内に発振波長の中心を有するレーザ光から選択されたレーザ光に対して10%以上の吸収率を有するものが好ましい。レーザとしては、例えば、炭酸ガスレーザ(波長約10600nm)、Nd:YAGレーザ(波長約1064nm)、Nd:YVO4レーザの第2次高調波であるグリーンレーザ(波長約532nm)、ダイオードレーザ(波長約800nm,840nm,または950nm)、エキシマレーザ(波長約193nm)等が挙げられる。光吸収性部材102の吸収率を調整するため、熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーにカーボンブラック等の黒色着色剤や顔料、染料等を混練することができる。
The light
熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、ポリアミド樹脂、ポリエチレン樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリブチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリフェニルエーテル樹脂、ポリスチレン樹脂、ハイインパクトポリスチレン樹脂、水添ポリスチレン樹脂、ポリアクリルスチレン樹脂、ABS樹脂、AS樹脂、AES樹脂、ASA樹脂、SMA樹脂、ポリアルキルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリメチルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリフェニレンスルファイド、液晶ポリマー等が挙られる。熱可塑性エラストマーとしては、例えばスチレン系熱可塑性エラストマー、オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリエステル系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリウレタン系熱可塑性エラストマー、PVC系熱可塑性エラストマー等が挙げられる。熱可塑性樹脂には、強化材としてガラスファイバやミネラル等を混練してもよい。 As the thermoplastic resin, for example, polyamide resin, polyethylene resin, polypropylene resin, polyethylene terephthalate resin, polybutylene terephthalate resin, polyphenyl ether resin, polystyrene resin, high impact polystyrene resin, hydrogenated polystyrene resin, polyacrylstyrene resin, ABS Resin, AS resin, AES resin, ASA resin, SMA resin, polyalkyl methacrylate resin, polymethyl methacrylate resin, polycarbonate resin, polyester resin, polyphenylene sulfide, liquid crystal polymer and the like. Examples of the thermoplastic elastomer include a styrene-based thermoplastic elastomer, an olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer, a polyester-based thermoplastic elastomer, a polyurethane-based thermoplastic elastomer, and a PVC-based thermoplastic elastomer. Glass fiber, mineral, or the like may be kneaded with the thermoplastic resin as a reinforcing material.
図示例において光吸収性部材102は主として、開口部Oを区画する周壁108と、周壁108の下端部を閉塞する底壁110とからなる。周壁108の横断面形状は略矩形であるが、これに限らず、円形、楕円形、台形、多角形、ひょうたん形状等如何なる形状としてもよい。周壁108には、後述するように開口部Oに繋がり該開口部O内を減圧状態とするのに適した吸引開口112が形成されている。吸引開口112は、底壁110に形成してもよい。あるいは、底壁110を設けずに周壁109の下端を開放し、該下端開口を吸引開口112として用いてもよい。
In the illustrated example, the
光透過性部材106はレーザ光に対する吸収率が同レーザ光に対する光吸収性部材102の吸収率よりも低い部材であり、主として熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーからなり、射出成形等により形成することができる。具体的には、波長193〜10600nmの範囲内に発振波長の中心を有するレーザ光から選択されたレーザ光に対して、光吸収性部材102の吸収率よりも低い吸収率を有するものが好ましい。
The
光透過性部材106を構成する熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、ポリアミド樹脂、ポリエチレン樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリブチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリフェニルエーテル樹脂、ポリスチレン樹脂、ハイインパクトポリスチレン樹脂、水添ポリスチレン樹脂、ポリアクリルスチレン樹脂、ABS樹脂、AS樹脂、AES樹脂、ASA樹脂、SMA樹脂、ポリアルキルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリメチルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリフェニレンスルファイド、液晶ポリマー等が挙られる。熱可塑性エラストマーとしては、例えばスチレン系熱可塑性エラストマー、オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリエステル系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリウレタン系熱可塑性エラストマー、PVC系熱可塑性エラストマー等が挙げられる。なお、熱可塑性樹脂には、強化材としてガラスファイバやミネラル等を混練させてもよい。熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーには、光吸収性部材の吸収率よりも低い吸収率を得られる限り、例えば、白色顔料や黄色、緑色、赤色等の有彩色着色剤を混練してもよい。
As the thermoplastic resin constituting the
そして、光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、その周縁部が光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に密着する薄板状に形成されている。これにより、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際に、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面と光透過性部材106との間に隙間が生じている場合でも、吸引開口112を通じて開口部O内を減圧した際に光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に密着させることができるため、真空漏れを防止し光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102の相互間で優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
The
これをより確実にするため、光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材102に密着する易変形性を発揮する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。具体的には、十分な変形による密着性を確保するため、光透過性部材106の厚みは、0.005mm〜0.2mmとすることが好ましく、成形性を考慮すると0.01mm〜0.1mmとすることがより好ましい。
In order to ensure this, the
光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材102に密着するよう引張弾性係数(ヤング率)を0.01〜18GPaの範囲内の材料を選定又は調整するのが好ましい。光透過性部材106の引張弾性係数(ヤング率)を18GPaよりも大きくした場合には、開口部O内を減圧したときに変形し易くするために極めて薄く形成する必要があり、設計どおりに成形することが難しくなり、例えば、射出成形により光透過性部材106を形成する場合には、薄い部分に樹脂が流れず成形不良の原因となる。一方、光透過性部材106の引張弾性係数(ヤング率)が0.01GPaを下回ると、材料自体の剛性が低くなるため、自身の形状を保持することが難しくなり、目的の位置に目的の形状で位置決めすることが難しくなる。光透過性部材106の易変形性、成形性、位置決め性をより高次元でバランスさせるため、光透過性部材106の材料は、引張弾性係数(ヤング率)が6〜10GPaの範囲内となるよう選定又は調整することがより好ましい。この引張弾性係数(ヤング率)は、JIS K7161の規定に準拠し、JIS K7162に記載の試験片を引張試験機に装着し応力とひずみ(変形量)から応力―ひずみ曲線を作図し、その傾きから求めることができる。この際、応力―ひずみ曲線が直線状にならず傾きを求め難い場合には、ヤング率の代替係数としてセカント係数(応力―ひずみ曲線上の点と原点とを結ぶ直線の傾き)などを用いることができる。
The
また、本実施形態の接合構造体100では、図1(a)に示すように、環状の溶着部104に隣接した位置に、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106とを接合する点状の溶着部114が設けられている。これにより、光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106同士の接合強度はより一層高められている。
In addition, in the
点状の溶着部114は、環状の溶着部104と同様、レーザ光を光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102へ向けて照射することにより形成することができる。点状の溶着部114は、光透過性部材106が略矩形の場合にはコーナー部に隣接して形成することが好ましく、これによれば、点状の溶着部114が、環状の溶着部104を形成する際の光透過性部材106の熱変形による反りを効果的に抑制して、開口部O内の減圧時に、薄板状の光透過性部材106の易変形による密着効果と相俟って、光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102同士のより一層優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
As in the case of the annular welded
また、本実施形態の接合構造体100では、図1(b)中の拡大図で示すように、環状の溶着部104の延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、溶着部104の光透過性部材106側の部分(当該図において境界面Fよりも上の部分であり、以下「第1部分」ともいう。)の面積S1に対する、光吸収性部材102側の部分(当該図において境界面Fよりも下の部分であり、以下、「第2部分」ともいう。)の面積S2の比は、12〜35の範囲内としている。当該比が12未満の場合には、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102から引き剥がすような力が加わった際に環状の溶着部104の境界を起点とした剥離(界面剥離)や溶着部104の光吸収性部材102側の部分の少なくとも一部が光透過性部材106に一体化した状態での剥離が発生する虞がある。また、この種の剥離は工業生産において非破壊で検査することは困難である。面積S1に対する面積S2の比率が12以上では、溶着部104に剥離は生じ難く、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102から引き剥がすような力が加わった場合には、光透過性部材106又は光吸収性部材102自体が破壊する「部材破壊」となるため、溶着強度を設計(設定)するにあたり、部材102,106の強さを管理すればよく、安定して生産することができる。一方、上記比率が35を超えると光吸収性部材102の深くまでレーザ光を届かせるために、パワーを上げるかあるいは照射時間を長くする必要があるため、光透過性部材106への熱影響(隆起や気泡、表面上の溶け、焼けに伴う炭化や変色の発生)や光吸収性部材102への熱影響(焼けに伴う炭化、気泡の発生)が顕在化する虞がある。これらの熱影響の回避と溶着部104における剥離の抑制、防止をより高次元で実現するためには、面積S1に対する面積S2の比率は19〜26の範囲内とすることがより好ましい。
Further, in the
このように溶着部104の光透過性部材側部分の面積S1に対する、光吸収性部材側部分の面積S2の比を上記範囲内とすることで、接合強度を確保しつつ、環状の溶着部104の形成に伴う光透過性部材106への熱影響を小さくし光透過性部材106の熱歪みを抑制することができるため、開口部O内の減圧時に、薄板状の光透過性部材106の易変形による密着効果と相俟って光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102同士のより一層優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
As described above, by setting the ratio of the area S2 of the light absorbing member side portion to the area S1 of the light transmitting member side portion of the
なお、上記比率下の面積S1,S2を有する溶着部104は、図8を参照して後述する接合構造体の製造方法により形成することができる。また、面積S1及びS2を算出するにあたり、溶着部104の範囲(境界)は、接合構造体100を溶着部104の延在方向に対する直交方向にカットして試験片を作成し、その断面を光学顕微鏡または電子顕微鏡で観察することや、X線CTを用いた断層画像を確認することで判断することができる。
Note that the welded
ところで、光透過性部材106を射出成形により製造する場合、ゲートの位置や溶融樹脂の流れ方、金型から取り出した後の冷却不均一等を起因として、光透過性部材106に下面側へ凸となる反り又は上面側へ凸となる反りが発生することがある。下面側へ凸となる反りは、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際に光透過性部材106の周縁部と光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面との間に隙間を生じさせることになるため好ましくない。そこで、本実施形態では、光透過性部材106の下面(光吸収性部材102側の面)に板厚を減じた凹部116を環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%以上に亘って形成し、これにより反りの方向を上面側へ凸となる方向に誘導している。凹部116の形成領域が、環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%未満の場合には、反りの原因である樹脂材料の収縮に関して、光透過性部材106全体の反りを誘導するほどの十分な力を得ることができない虞がある。また、反りの量が過大となるのを防ぐため、凹部116の深さは板厚の50%以下とすることが好ましい。凹部116の深さが板厚の50%を超える場合には、反りの原因である樹脂材料の収縮に関して、光透過性部材106の剛性が低下してねじれが発生するため、吸引密着させる際に光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102間に隙間が生じて密着が不十分な状態となり、位置ずれや溶着不具合(熱が伝わらないことによる過度な温度上昇や未溶融)が発生する虞がある。
When the light-transmitting
図2を参照し、本発明に従う他の実施形態の接合構造体200について説明する。この
実施形態の接合構造体200は、光吸収性部材202に複数の開口部Oが形成されている
点で先の実施形態の接合構造体100とは異なる。
With reference to FIG. 2, a description will be given of a
具体的には、光吸収性部材202は、周壁208の上端部に繋がる天壁218を有し、該天壁218には同一方向へ延在する複数のスリット220が穿設されて開口部Oが区画されている。天壁218は、光透過性部材206の上面に外部から衝撃や荷重が加わった場合において光透過性部材206の撓み変形を規制するため、光透過性部材206や溶着部204,214が破損されるのを防ぐことができる。さらに天壁218は梁のように作用するため、光吸収性部材202の周壁208を補強することができる。
Specifically, the
また、光透過性部材206の凹部216は、上述のように光透過性部材206の反りの方向及び量を制御する効果をもたらすが、これに加えて、光透過性部材206と天壁218の間に隙間を維持し、開口部Oを減圧した際に光透過性部材206が天壁218に接触して陰圧の受圧面積が減少するのを防止することができる。陰圧の受圧面積が減少すると、光透過性部材206を真空圧で十分に変形させることができなくなり、光透過性部材206及び光吸収性部材202間の吸引密着性が損なわれる虞がある。これを防止する観点においても、光透過性部材206に形成する凹部216の形成領域は、環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%以上とすることが好ましい。
The
本実施形態の接合構造体200においても、先の実施形態の接合構造体100と同様、環状の溶着部204は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、光透過性部材206側の部分の面積S1に対する光吸収性部材202側の部分の面積S2の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。
Also in the
図3を参照し、本発明に従う他の実施形態の接合構造体300について説明する。この実施形態の接合構造体300は、光透過性部材300の、環状の溶着部304よりも外側位置に、環状の溶着部304が形成される前の状態で開口部O内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に密着する薄肉片324を設けた点で先の実施形態の接合構造体100,200とは異なる。これにより、光透過性部材306を光吸収性部材302に重ね合わせた際に、光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面と光透過性部材306との間に隙間が生じている場合でも、吸引開口312を通じて開口部O内を減圧した際に光透過性部材306の薄肉片324を光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に引き寄せて密着させることができるため、空気漏れによる真空破壊を防止し光透過性部材306及び光吸収性部材302同士で優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
Referring to FIG. 3, a description will be given of a
これをより確実にするため、薄肉片324は、環状の溶着部304が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材302に密着する易変形性を発揮する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。具体的には、十分な変形による密着性を確保するため、薄肉片の厚みは、0.005mm〜0.2mmとすることが好ましく、成形性を考慮すると0.01mm〜0.1mmとすることがより好ましい。
In order to ensure this, the
図3に示す例では、薄肉片324は、光透過性部材306の周縁部下端から光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に沿うように水平に形成されているが、これに限らず、図4(a)に示すように周壁308の外周面に沿うように光透過性部材306の周縁部下端から垂下させてもよく、あるいは図4(b)に示すように、光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に環状溝326を形成するとともに、光透過性部材306の下面から薄肉片324を垂下させ環状溝326内に挿入するようにしてもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 3, the
本実施形態の接合構造体300においても、先の実施形態の接合構造体100,200と同様、環状の溶着部304は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、光透過性部材306側の部分の面積S1に対する光吸収性部材302側の部分の面積S2の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。
Also in the
次に、図5〜図9を参照して、本発明に従う一実施形態の接合構造体の製造方法について説明する。なお、ここでは図1に示した接合構造体100を製造する方法を例にとり説明するが、この製造方法は、図2〜図4に示した接合構造体200,300を製造する場合にも適用することができる。
Next, with reference to FIGS. 5 to 9, a description will be given of a method for manufacturing a joint structure according to an embodiment of the present invention. Here, a method for manufacturing the
まず、第1の工程は部材準備工程であり、この工程では光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106を準備する。光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106の材料及び基本的な構造については、接合構造体100について図1を参照して説明したとおりであるため、重複する説明は省略する。
First, the first step is a member preparing step, in which the
図5は、光透過性部材106との接合前の光吸収性部材102を示し、(a)は平面図であり、(b)は(a)中のD−D線に沿う断面図である。この図に示すように、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面(光透過性部材106と当接する面)であって、環状の溶着部104の形成予定部位には環状溝130を予め形成しておく。環状溝130の幅は、そこに照射されるレーザ光の径よりも大きくしておくことが好ましく、例えば、0.1mm〜3mmとすることが好ましい。環状溝130の幅が0.1mm未満の場合には、そこに形成される環状の溶着部104の幅を十分に確保できず、溶着強度が低下するため、外力や圧力変動によって空気や水、埃が浸透し気密性能等を維持できなくなる虞がある。一方、環状溝130の幅が3mmを超えると、溶着時の熱によって環状の溶着部104以外の部分が熱の影響を受けて変形したり、環状の溶着部104が固化する際の熱収縮によって部品に過度のひずみが残り、変形したりする虞がある。また、環状溝130の深さ(境界面Fから溝底までの距離)は、環状溝130の幅をL(mm)として、L/20(mm)以上L(mm)以下とすることが好ましく、このようにすれば、図8を参照して後述するように、環状溝130へのレーザ光照射により溝底に発生した溶融池を十分に膨張させることができとともに、その熱を過不足なく光透過性部材106へ伝達させることができ、良好な溶着部104を形成することができる。さらに、環状溝130の深さは、L/10(mm)以上L/3(mm)以下とすることが、溶着部104の強度及び気密性を確保する点で好ましい。例えば、環状溝130は、溝幅Lを0.3mm、溝深さを0.05(=L/6)mmとすることができる。溶着部130の深さがL/20(mm)未満であり浅すぎると、環状溝130の溝底へのレーザ光の照射後直ぐに、膨張した溶融池が光透過性部材106に接触するとともに熱が拡散し、溶融池を十分に横方向へ広げることができず、溶着不良となる(環状溝130の一部が残ったままとなる)虞がある。溶着部130の深さがL(mm)を超え深すぎると、環状溝130の溝底で発生した溶融池が膨張するものの光透過性部材106まで到達できず、その場で焼けに伴う炭化や変色が発生し、溶着不良となる虞がある。なお、図示例において環状溝130の断面形状は矩形であるが、半円形状または半楕円形状であってもよい。また、周壁108の上端面には、環状溝130と開口部O内とを連通する少なくとも1つ(図示例では各辺に対応して4つ)の連通溝132を予め形成しておく。
5A and 5B show the
第2の工程は、図6(a)に示すように、光吸収性部材102の上に光透過性部材106を開口部Oを覆うように配置する配置工程である。
The second step is an arrangement step of disposing a
第3の工程は、互いに重ね合わされた光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を吸引密着させる吸引密着工程であり、かかる吸引密着は開口部O内を減圧することにより行う。図6(b)の左図に光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ねた後の様子を示すように、光透過性部材106と光吸収性部材102との間には、光透過性部材106の成形時の反りや後述するレーザ光による溶着時の熱変形等に起因して隙間が生じる場合があるが、光透過性部材106を薄板状に形成したことから、図6(b)の右図に示すように、開口部O内を減圧することにより光透過性部材106の周縁部を周壁108の上端面に引き寄せるように変形させ、該上端面に密着させることができる。
The third step is a suction and adhesion step in which the light-absorbing
開口部O内の減圧は、具体的には、図7に示すような外部の圧力調整装置Dを用い、光吸収性部材102に予め形成した吸引開口112を通じて行うことができる。
Specifically, the pressure in the opening O can be reduced through the
圧力調整装置Dは主として、減圧装置D1と、加圧装置D2と、制御器D3と、吸引開口112に接続される二重配管Pとからなる。
The pressure adjusting device D mainly includes a pressure reducing device D1, a pressurizing device D2, a controller D3, and a double pipe P connected to the
減圧装置D1は、開口部O内の空気を吸引排気するための真空ポンプと電動のリークバルブとを有している(図示省略)。減圧装置D1の吸引ラインL1には、圧力センサPG1が設けられており、これにより減圧時の開口部O内の圧力を検出することができる。 The pressure reducing device D1 has a vacuum pump for sucking and discharging air in the opening O and an electric leak valve (not shown). A pressure sensor PG1 is provided on the suction line L1 of the decompression device D1, so that the pressure in the opening O at the time of decompression can be detected.
加圧装置D2は、空気又は窒素やアルゴン等の不活性ガスからなるパージガスを供給するための加圧タンクと供給バルブとを有している(図示省略)。加圧装置D2の供給ラインL2には、圧力センサPG2が設けられており、これにより加圧時において開口部O内の圧力を検出することができる。 The pressurizing device D2 has a pressurizing tank for supplying a purge gas composed of air or an inert gas such as nitrogen or argon, and a supply valve (not shown). The supply line L2 of the pressurizing device D2 is provided with a pressure sensor PG2, which can detect the pressure in the opening O during pressurization.
制御器D3は、PLC(プログラマブルロジックコントローラ)やパーソナルコンピュータ等によって構成され、供給バルブ及びリークバルブの開度を調整する。また、圧力センサPG1,PG2も制御器D3に接続し、圧力センサPG1,PG2の検出信号に基づき上記供給バルブ及びリークバルブを制御することもできる。 The controller D3 is configured by a PLC (programmable logic controller), a personal computer, or the like, and adjusts the opening of the supply valve and the leak valve. Further, the pressure sensors PG1 and PG2 can also be connected to the controller D3 to control the supply valve and the leak valve based on the detection signals of the pressure sensors PG1 and PG2.
二重配管Pは、外側に配置された吸引配管p1と内側に配置された供給配管p2からなる。吸引配管p1は開口部O内と減圧装置D1とを連通し、開口部O内の空気を吸引する。供給配管p2は、開口部O内と加圧装置D2とを連通し、開口部O内にパージガスを供給する。図示は省略するが、二重配管Pの外側の配管を供給配管とし、内側の配管を吸引配管とすることもできるが、図示例のように、外側に吸引配管p1を配置する方が、溶着時に発生するガスを効率的に除去できる点で好ましい。 The double pipe P includes a suction pipe p1 arranged outside and a supply pipe p2 arranged inside. The suction pipe p1 communicates the inside of the opening O with the decompression device D1, and sucks the air in the opening O. The supply pipe p2 communicates the inside of the opening O with the pressurizing device D2, and supplies the purge gas into the opening O. Although illustration is omitted, the outer pipe of the double pipe P can be used as a supply pipe, and the inner pipe can be used as a suction pipe. This is preferable in that the gas generated sometimes can be efficiently removed.
第4の工程は、図7に示すように、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106とを吸引密着した状態で、レーザ光LBを光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面へ向けて照射し、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106の境界面Fまたはその近傍に環状の溶着部104及び点状の溶着部114(図1参照)を形成して光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106同士を接合する接合工程である。
In the fourth step, as shown in FIG. 7, in a state where the
この接合工程においても引き続き開口部O内の減圧状態は維持するが、少なくとも環状の溶着部104を形成する間は、供給配管p2を介して開口部O内にパージガスを供給することが好ましい。このようにすれば、開口部O内に空気の流れを発生させることができ、溶着時に生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを吸引配管p1を通じて効率的に外部に排出、除去することができる。
In this joining step, the pressure-reduced state in the opening O is maintained, but it is preferable to supply a purge gas into the opening O via the supply pipe p2 at least while the annular welded
そして、溶着部104,114を形成するにあたっては、まず点状の溶着部114を形成し、その後に、環状の溶着部104を形成する。これは、光透過性部材106への熱負荷が比較的小さい点状の溶着部114により光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に仮接合することで、その後に熱負荷の比較的大きい環状の溶着部104を形成した際の光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制し、該熱変形に起因した空気漏れによる真空破壊を防止するためである。環状の溶着部104の溶着が進むにつれて、真空の受圧面積が減るため、その陰圧分を補う点では点状の溶着部114は平面を形成できる3点以上設けることが好ましい。この例では、点状の溶着部114は、光透過性部材106のコーナー部に隣接して4箇所に形成する。
Then, in forming the welded
点状の溶着部114は、光学ヘッドH(図7)を光透過性部材106の上方で停止させた状態でレーザ光LBを光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に照射することで形成される。点状の溶着部114の径は、約0.3〜0.7mmとすることが好ましく、約0.5mmとすることがより好ましい。環状の溶着部104は、光学ヘッドHを光透過性部材106の上方において光吸収性部材102の周壁108に沿って移動させながらレーザ光LBを周壁108上端面に照射することで形成される。環状の溶着部104の幅は、約0.3〜0.7mmとすることが好ましく、約0.5mmとすることがより好ましい。なお、レーザ光LBの発信器としては、例えば、ファイバレーザ(波長:1070nm)やYAGレーザ(波長:1064nm)、半導体レーザ(波長:808nm,840nmまたは940nm)、CO2レーザ(波長:10600nm)などを用いることができる。
The point-like welded
ここで図8(a)〜(d)を参照し、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に予め形成した環状溝130にレーザ光LBを照射することにより、図1で説明した第1部分の面積S1に対する第2部分の面積S2の比率が12〜35となる環状の溶着部104を形成するプロセスについて説明する。
Here, with reference to FIGS. 8A to 8D, by irradiating the
図8(a)に示すように、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を互いに吸引密着させた状態で、光透過性部材106側から環状溝130の溝底にレーザ光を照射すると、図8(b)に示すように環状溝130の溝底が発熱して溶融し、溶融池内で発泡が開始される。引き続きレーザ光を照射すると、図8(c)に示すように発泡が成長して溶融池が成長する。このとき、環状溝130の存在により、光吸収性部材102の溶融池は直ぐには光透過性部材106に接触せず、溶融池は十分な幅及び深さとなるまで成長させることができる。図8(d)には、溶融池が光透過性部材106に到達した後にレーザ光の照射を停止し、環状の溶着部104の形成が完了した状態を示している。
As shown in FIG. 8A, when the light-absorbing
また、本実施形態では、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130と開口部Oとを連通する連通溝132を設けているため、環状の溶着部104の形成過程で生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vは、環状溝130及び連通溝132を通って開口部O内に吸引、排出され、最終的には、吸引配管p1により外部に排出される。
In the present embodiment, since the
第5の工程は、環状の溶着部104を形成した後に引き続き開口部O内の減圧を保持し、または開口部O内を加圧し、あるいは減圧と加圧を交互に行い、その際の単位時間当たり圧力の変化を測定することによって環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行う気密性検査工程である。開口部O内の圧力は、図7に示した圧力センサPG1,PG2で測定し、その単位時間当たりの圧力の変化は制御部D3で演算し、必要に応じて外部に出力ないし表示させることができる。あるいは、図示しない流量センサを吸引ラインL1又は供給ラインL2に設けておき、単位時間当たりの流量の変化を測定することにより、環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行うこともできる。
The fifth step is to maintain the reduced pressure in the opening O after forming the annular welded
図示しない第6の工程は、環状の溶着部104の形成後に、開口部O内の減圧を維持したまま、光透過性部材106側からレーザ光LBを吸引開口112の内部又はその周囲に照射することによって吸引開口112を閉塞させる吸引開口閉鎖工程である。これにより、開口部O内の真空を保ったまま開口部O内を密閉することができる。勿論、吸引開口112は開放したままでもよい。
In a sixth step (not shown), after the formation of the annular welded
本実施形態の接合構造体の製造方法によれば、光吸収性部材102に開口部Oを設けておき、この開口部O内を減圧することによって光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を吸引密着させる構成としたので、両部材102,106を加圧密着するための従来のガラス板を不要とすることができ、上述したようなガラス板に起因する種々の問題を解消することができる。
According to the method for manufacturing a joint structure of the present embodiment, the
また、開口部Oの減圧に伴い光透過性部材106を容易に変形可能に構成したことから、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際にこれらの間に隙間が生じる場合でも開口部O内を減圧することにより光透過性部材106でこの隙間を閉鎖することができ、優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
In addition, since the
さらに、環状の溶着部104を形成するのに先立って、点状の溶着部114を形成して仮接合する構成としたことから、環状の溶着部104の形成途中での光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制することができ、当該熱変形に起因した吸引密着性の低下を防止することができる。
Further, prior to the formation of the annular welded
さらに、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130を形成し、この環状溝130にレーザ光LBを照射して環状の溶着部104を形成する構成としたことから、十分な幅及び深さの溶着部104を形成して高い接合強度を得ることができるのに加えて、光透過性部材106への熱影響を小さくし、溶着過程における光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制することができ、当該熱変形に起因した吸引密着性の低下を防止することができる。
Further, an
さらに、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130と開口部Oを連通する連通溝132を設ける構成としたことから、環状の溶着部104の形成過程で生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを、環状溝130及び連通溝132と介して開口部O内に吸引し、最終的には、吸引配管p1を介して外部に排出することができる。
Further, since the
さらに、開口部O内の減圧を該開口部O内にパージガスを供給しながら行う構成としたことにより、開口部O内に空気の流れを発生させ、煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを効率的に排出、除去することができる。 Further, by employing a configuration in which the pressure in the opening O is reduced while supplying the purge gas into the opening O, a flow of air is generated in the opening O, and the vaporized component v of soot and a flame retardant is efficiently removed. Can be discharged and removed.
さらに、環状の溶着部104を形成した後に引き続き開口部O内の減圧を保持し、または開口部O内を加圧し、あるいは減圧と加圧を交互に行い、その際の単位時間当たりの圧力又は流量の変化を測定することによって環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行う場合には、製造設備を簡略化することができるのに加えて、製造時間を大幅に短縮することができる。
Further, after the annular welded
さらに、開口部O内の圧力を圧力センサPG1で常時検出し、その圧力の変化に基づき、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106との密着、環状の溶着部104の形成開始、及び環状の溶着部104の形成完了の判別を行うようにした場合には、通常生産時の加工時間の短縮と、異常発生時の早期対応が可能となる。
Further, the pressure in the opening O is constantly detected by the pressure sensor PG1, and based on the change in the pressure, the
以上、図示例に基づき本発明について説明したが、本発明は上述の実施形態に限定されず、特許請求の範囲の記載内で種々の変更、追加等を行うことが可能である。例えば、上述の実施形態の接合構造体の製造方法においては、溝底が平坦な環状溝130を図示したが、これに限らず、図9(a)に示すように、環状溝の溝底に隆起部134を設けてもよい。また、環状溝130は一つに限らず、図9(b)に示すように隣接して2つ設け、溶着時に合体して一つの幅広の溶着部104を形成するようにしてもよく、図9(c)に示すように、光透過性部材106側にも環状溝136を設けてもよい。
As described above, the present invention has been described based on the illustrated examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various changes, additions, and the like can be made within the scope of the claims. For example, in the method of manufacturing the joint structure according to the above-described embodiment, the
(第1実施例)
本発明をコネクタに適用した例について説明する。図10は、図2に示した実施形態の接合構造体200の一実施例としてのコネクタを示し、(a)は斜視図であり、(b)は嵌合方向Xに沿った断面図である。図中、対応する部材又は部分には符号に「’」を加えて示し、重複した説明は省略する。
(First embodiment)
An example in which the present invention is applied to a connector will be described. 10A and 10B show a connector as one example of the
このコネクタ200’は、携帯機器や情報機器などの電子機器内の基板に固定され、嵌合方向Xに沿って挿入される図示しない相手方のコネクタに接続されるレセプタクルコネクタであり、主として、光吸収性部材202としてのハウジング202’と、それぞれ嵌合方向Xに延在しかつ嵌合方向Xに対して直交する方向に配列される複数のコンタクト203と、ハウジング202’の開口部O’を覆うとともに封止する、光透過性部材206としての薄板状のカバー206’とを備えるものである。
The
ハウジング202’は、光吸収性かつ絶縁性の熱可塑性樹脂から形成されており、前方に相手方のコネクタが挿入される嵌合口212’を有する周壁208’と、底壁210’と、天壁218’とを有している。
The
ハウジング202’の天壁218’には、嵌合方向Xに沿って形成された複数のスリット220’が形成されており、該スリット220’により開口部O’が区画されている。各スリット220’内にはコンタクト203が配置されている。各コンタクト203の前方端部は相手方のコネクタとの接続のため天壁218’の内面より下方に突出し、その後方端部が電子機器の基板または他の配線板との接続のためハウジング202’から露出している。
A plurality of slits 220 'are formed in the top wall 218' of the housing 202 'along the fitting direction X, and the slits 220' define openings O '. A
カバー206’は、ハウジング202’の開口部O’を覆うようにハウジング202’に重ね合わされ、すべてのスリット220’をまとめて囲繞するように形成された環状の溶着部204’を介して周壁208’の上端面に全周に亘って接合されている。これにより、嵌合口212’から電子機器内部へのスリット220’を介した空気や埃、水の浸水ルートは、カバー206’及び環状の溶着部204’によって遮断されている。また、環状の溶着部204’の外側には、カバー206’のコーナー部に隣接して4つの点状の溶着部214’が形成されている。
The
コネクタ200’において、環状の溶着部204’は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、カバー206’側の部分の面積S1’に対するハウジング202’側の部分の面積S2’の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。 In the connector 200 ', the ratio of the area S2' of the portion on the housing 202 'side to the area S1' of the portion on the side of the cover 206 'is 12 to 35 when viewed in a cross section perpendicular to the extending direction of the annular welded portion 204'. And more preferably in the range of 19 to 26.
このようなコネクタ200’は、嵌合口212’を吸引開口212として、図5〜図8を参照して説明した実施形態の製造方法に従って製造することができる。
Such a connector 200 'can be manufactured according to the manufacturing method of the embodiment described with reference to FIGS. 5 to 8 using the fitting opening 212' as the
(第2実施例)
本発明をセンサに適用した例について説明する。図11は、図4(a)に示した実施形態の接合構造体300の一実施例としてのセンサを示し、(a)は斜視図であり、(b)は断面図である。
(Second embodiment)
An example in which the present invention is applied to a sensor will be described. FIGS. 11A and 11B show a sensor as one example of the
このセンサ300’は、加速度センサ、振動センサ、角速度センサ、距離センサ、位置センサなど如何なる形式のセンサとすることができる。センサ300’は、主として、光吸収性部材302としての筐体302’と、筐体302’の開口部O’を覆うとともに封止する光透過性部材306としてのカバー306’とを備えるものであり、筐体302’内部に図示しない検出器本体(センサチップ)を収容する。
The sensor 300 'can be any type of sensor, such as an acceleration sensor, a vibration sensor, an angular velocity sensor, a distance sensor, a position sensor, and the like. The
筐体302’は、光吸収性の熱可塑性樹脂から形成されており、開口部O’を区画するとともに前方に向けて吸引筒312’を突設する周壁308’と、底壁310’とを有している。
The
カバー306’は、筐体302’の開口部O’を覆うように筐体302’の周壁308’に被せられ、点状の溶着部314’及び環状の溶着部304’を介して全周に亘って接合されている。カバー306’の周縁部には、周壁308’の外面に沿って薄肉片324’が垂設されている。この薄肉片324’は吸引筒312’を通じて開口部O’内を減圧した際に周壁308’側に引き寄せられて密着するよう形成されている。
The
センサ300’において、環状の溶着部304’は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、カバー306’側の部分の面積S1’に対する筐体302’側の部分の面積S2’の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。 In the sensor 300 ', the annular welded portion 304' has a ratio of the area S2 'of the portion on the housing 302' side to the area S1 'of the portion on the cover 306' side as viewed in a cross section perpendicular to the extending direction thereof of 12 to 12. It is in the range of 35, more preferably in the range of 19-26.
このようなセンサ300’は、吸引筒312’を吸引開口312として、図5〜図8を参照して説明した実施形態の製造方法に従って製造することができる。
Such a sensor 300 'can be manufactured according to the manufacturing method of the embodiment described with reference to FIGS. 5 to 8 using the suction tube 312' as the
なお、吸引筒312’の基端部は開口したままであるが、上述した製造方法の第6工程に従い、環状の溶着部304’の形成後に、開口部O’内の減圧を維持したままの状態でカバー306’側からレーザ光を吸引筒312’の基端部の開口周辺に照射することにより、吸引筒312’の基端部の開口を閉塞してもよい。これにより、センサ300’の内部空間を真空に保ったまま密閉することができる。 Although the base end of the suction tube 312 'remains open, the reduced pressure in the opening O' is maintained after the formation of the annular welded portion 304 'according to the sixth step of the above-described manufacturing method. The opening at the base end of the suction tube 312 'may be closed by irradiating the laser beam from the cover 306' side to the vicinity of the opening at the base end of the suction tube 312 'in this state. Thus, the sensor 300 'can be hermetically sealed while keeping the internal space at a vacuum.
かくして本発明によれば、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させるのに適した接合構造体を提供するとともに、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させることができる接合構造体の製造方法を提供することができる。 Thus, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a joint structure suitable for uniformly and surely adhering members to be joined to each other without using a glass plate, and to join each other without using a glass plate. It is possible to provide a method for manufacturing a joined structure in which members to be bonded can be uniformly and surely brought into close contact with each other.
100,200,300 接合構造体
102,202,302 光吸収性部材
104,204,304 環状の溶着部
106,206,306 光透過性部材
108,208,308 周壁
112,212,312 吸引開口
114,214,314 点状の溶着部
130 環状溝
132 連通溝
324 薄肉片
D 圧力調整装置
D1 減圧装置
D2 加圧装置
D3 制御器
F 境界面
H 光学ヘッド
L1 吸引ライン
L2 供給ライン
O 開口部
PG1,PG2 圧力センサ
S1 環状の溶着部の第1部分(光透過性部材側)の面積
S2 環状の溶着部の第2部分(光吸収性部材側)の面積
100, 200, 300
本発明は、相互に重ね合わされ、その境界面または境界面近傍に形成された溶着部を介して互いに接合された光吸収性部材及び光透過性部材を備える接合構造体に関する。 The present invention is superimposed on each other, about the joined structure comprising a light-absorbing member and the light transmitting member that are joined together via a weld portion formed near the boundary surface or interface.
従来、複数の部材を接合する方法として、レーザ光の照射による接合方法があり、その中でも最近では、局所的な加熱であり製品への熱ダメージが少ないとともに、溶着部の、外観への影響が少ないレーザ透過溶着法(Laser Transmission Welding)が注目されている。この接合方法は、接合部材の一方にレーザ光に対して透過性を有する部材(光透過性部材)を用い、他方にレーザ光に対して吸収性を有する部材(光吸収性部材)を用い、これらを互いに重ね合わせて加圧した状態で、レーザ光を光透過性部材側から照射することで、照射されたレーザ光のエネルギが光吸収性部材の境界面付近で吸収されて発熱し、その熱が光透過性部材にも伝達して両部材が溶融し、最後にその溶融部が冷却、固化されることで両部材が接合される方法である。 Conventionally, as a method of joining a plurality of members, there is a joining method by laser beam irradiation, and recently, among these, local heating is performed, so that heat damage to the product is small, and the effect of the welded portion on the appearance is reduced. Attention has been paid to a small number of laser transmission welding methods (Laser Transmission Welding). In this bonding method, a member having a property of transmitting laser light (a light transmitting member) is used as one of the bonding members, and a material having a property of absorbing the laser light (a light absorbing member) is used as the other of the bonding members. By irradiating the laser light from the light transmitting member side in a state where these are superimposed on each other and pressurized, the energy of the irradiated laser light is absorbed near the boundary surface of the light absorbing member and generates heat. In this method, both members are melted by transmitting heat to the light transmissive member, and finally, the melted portion is cooled and solidified to join the two members.
このレーザ透過溶着法には、いくつかの重要なポイントがあるが、とりわけ重要なのが接合される部材同士を加圧して確実に密着させることである。接合される部材間に隙間が存在すると、レーザ照射によって光吸収性部材で発生した熱が相手側である光透過性部材にうまく伝達されず、局所的な温度上昇によって隆起、膨張、爆発といった溶着不良となるからである。 The laser transmission welding method has several important points, and particularly important is to press the members to be bonded to each other to ensure close contact. If there is a gap between the members to be joined, the heat generated by the light absorbing member due to the laser irradiation will not be transmitted well to the opposing light transmitting member, and welding such as bulging, expansion and explosion will occur due to local temperature rise. This is because it becomes defective.
この加圧は、一般的には、レーザ光に対して透過性を有するガラス板を光透過性部材上に配置し、このガラス板を介して両部材に押し圧を加える方法によって実現される(下記特許文献1参照)。しかし、この方法の場合、接合部材の加熱、溶融時に発生する煤や難燃剤の気化成分によってガラス板が汚れ、レーザ光に対するガラス板の吸収率が上がってガラス板自体が加熱されて割れに至るという問題がある。また、汚れたガラス板は、レーザ光を遮り、光吸収性部材に十分な光が届かなくなる結果、溶着強度の低下をも引き起こす。 This pressurization is generally realized by a method in which a glass plate having transparency to laser light is disposed on a light-transmitting member, and a pressing force is applied to both members via the glass plate ( See Patent Document 1 below). However, in the case of this method, the glass plate is contaminated by soot and a vaporization component of the flame retardant generated when the joining member is heated and melted, and the absorption rate of the glass plate with respect to laser light is increased, and the glass plate itself is heated and cracked. There is a problem. In addition, the dirty glass plate blocks the laser beam and prevents sufficient light from reaching the light-absorbing member, resulting in a decrease in welding strength.
これに対して、下記特許文献2では、ガラス板を用いず、接合される部材同士を吸引により密着させる方法が提案されている。具体的には、特許文献2に記載の方法は、接合される部材の一方に溝部を形成しておき、この溝部の空間を減圧することで両部材同士を密着させるものである。しかし、レーザ照射により溶着する際に接合される部材の一方又は双方に熱変形が生じたり、成形時に接合される部材に反りが生じたりする結果、接合される部材間に隙間が発生し、これにより吸引密着性が低下する場合がある。
On the other hand,
それ故本発明の目的は、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させた接合構造体を提供することにある。 It is therefore an object of the present invention, without the use of the glass plate is to provide a joined structure obtained by uniformly and reliably contact the members to each other to be joined together.
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材と、開口部を覆うように光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、開口部を囲繞するように延在するとともに、光吸収性部材およびそれに密着した光透過性部材を相互に接合する環状の溶着部と、を備え、光透過性部材は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して周縁部が光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成されていることを特徴とするものである。 A joint structure of the present invention for solving the above-mentioned problem, a light-absorbing member having at least one opening, a light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening , with extending so as to surround the opening portion, comprises an annular weld portion for joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member in close contact therewith mutually, the light transmitting member, the welding portion of the annular formation When the inside of the opening is decompressed in a state before being performed, the opening is deformed and the peripheral portion is formed in a thin plate shape closely contacting the light absorbing member.
この場合、光透過性部材は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して周縁部が光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。 In this case, the light transmissive member deforms when the inside of the opening is reduced to a gauge pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less before the annular welded portion is formed, and the peripheral portion becomes a light absorbing member. It is preferable that it is formed to a thickness that allows close contact.
また、本発明の接合構造体にあっては、環状の溶着部に隣接して位置し、光吸収性部材および光透過性部材を相互に接合する点状の溶着部を備えることが好ましい。 Further, the joint structure of the present invention preferably includes a point-like welded portion located adjacent to the annular welded portion and joining the light-absorbing member and the light-transmitting member to each other .
上述した課題を解決するための本発明の接合構造体は、少なくとも1つの開口部を有する光吸収性部材と、開口部を覆うように光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、開口部を囲繞するように延在するとともに、光吸収性部材およびそれに密着した光透過性部材を相互に接合する環状の溶着部と、を備え、光透過性部材は、光吸収性部材の周縁部に沿って形成され、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を有することを特徴とするものである。 A joint structure of the present invention for solving the above-mentioned problem, a light-absorbing member having at least one opening, a light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening , with extending so as to surround the opening portion includes a welded portion of the annular joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member in close contact therewith mutually, the light transmitting member, the periphery of the light-absorbing member Formed along the portion, having a thin piece that is deformed and closely adheres to the light absorbing member when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed. is there.
この場合、薄肉片は、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。 In this case, the thin piece is deformed when the inside of the opening is reduced to a gauge pressure of −80 kPa or more and −20 kPa or less before the annular welded portion is formed, and the thin piece is formed to have a thickness that is in close contact with the light absorbing member. It is preferred that
さらに、本発明の接合構造体にあっては、環状の溶着部に隣接して位置し、光吸収性部材および光透過性部材を相互に接合する点状の溶着部を備えることが好ましい。 Further, the joint structure of the present invention preferably includes a point-like welded portion located adjacent to the annular welded portion and joining the light-absorbing member and the light-transmitting member to each other .
本発明の接合構造体にあっては、光透過性部材が、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して周縁部が光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成され、または光吸収性部材の周縁部に沿って形成され、環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を有することから、接合構造体の製造工程において、開口部内を減圧することによって、薄板状に形成された光透過性部材又は光吸収性部材の周縁部に沿って形成された薄肉片を変形させて光透過性部材の周縁部又は薄肉片を光吸収性部材に密着させることができるので、光吸収性部材及び光透過性部材の相互の優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。 In the joint structure of the present invention, the light transmissive member is deformed when the inside of the opening is decompressed before the annular welded portion is formed, and the peripheral portion becomes a light absorbing member. It is formed in the shape of a thin plate that adheres, or is formed along the periphery of the light-absorbing member, and deforms when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed, and absorbs light. Because it has a thin piece that adheres to the member, in the manufacturing process of the joint structure, by reducing the pressure in the opening , it is formed along the peripheral edge of the light transmitting member or the light absorbing member formed in a thin plate shape. Deforming the thin-walled piece so that the peripheral portion of the light-transmitting member or the thin- walled piece can be in close contact with the light-absorbing member, thereby obtaining excellent mutual suction adhesion between the light-absorbing member and the light-transmitting member. Can be.
したがって本発明の接合構造体によれば、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させた接合構造体を提供することができる。 According to the but I the bonding structure of the present invention, it is possible without using a glass plate, to provide a joined structure obtained by uniformly and reliably contact the members to each other to be joined together.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づき詳細に説明する。なお、各図において同様の部材または部分には、符号に「100」又は「200」のいずれかを加えた符号を付し、重複する説明は省略する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. Incidentally, the same members or portions in the respective drawings, denoted by reference numerals obtained by adding either "100" or "200" to the code, without redundant description.
図1は、本発明の一実施形態の接合構造体100を示しており、(a)は斜視図、(b)は(a)中のA−A線に沿う断面図である。この図に示すように、本実施形態の接合構造体100は、開口部Oを有する光吸収性部材102と、該開口部Oを覆うように光吸収性部材102に重ねられ、開口部Oを囲繞する環状の溶着部104を介して該光吸収性部材102に接合された光透過性部材106とを備えている。なお、「環状」とは、輪のような円い形だけを意味するのではなく、連続的に閉じた形状(無端形状)を意味する。よって、「環状」には、円形や楕円形だけではなく、矩形、多角形、その他の閉鎖形状が含まれる。溶着部104は、光透過性部材106と光吸収性部材102の境界面F上に形成されており、後で詳細に説明するが、このような溶着部104は、光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102へ向けてレーザ光を照射し、光吸収性部材102をまず発熱させて溶融し、その熱で光透過性部材106をも溶融させ、その後溶融部を固化させることで形成することができる。
1A and 1B show a
光吸収性部材102は、レーザ光に対する吸収率が光透過性部材106の同レーザ光に対する吸収率よりも高い部材であり、主として熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーからなり、射出成形等により形成することができる。具体的には、波長193〜10600nmの範囲内に発振波長の中心を有するレーザ光から選択されたレーザ光に対して10%以上の吸収率を有するものが好ましい。レーザとしては、例えば、炭酸ガスレーザ(波長約10600nm)、Nd:YAGレーザ(波長約1064nm)、Nd:YVO4レーザの第2次高調波であるグリーンレーザ(波長約532nm)、ダイオードレーザ(波長約800nm,840nm,または950nm)、エキシマレーザ(波長約193nm)等が挙げられる。光吸収性部材102の吸収率を調整するため、熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーにカーボンブラック等の黒色着色剤や顔料、染料等を混練することができる。
The light
熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、ポリアミド樹脂、ポリエチレン樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリブチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリフェニルエーテル樹脂、ポリスチレン樹脂、ハイインパクトポリスチレン樹脂、水添ポリスチレン樹脂、ポリアクリルスチレン樹脂、ABS樹脂、AS樹脂、AES樹脂、ASA樹脂、SMA樹脂、ポリアルキルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリメチルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリフェニレンスルファイド、液晶ポリマー等が挙られる。熱可塑性エラストマーとしては、例えばスチレン系熱可塑性エラストマー、オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリエステル系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリウレタン系熱可塑性エラストマー、PVC系熱可塑性エラストマー等が挙げられる。熱可塑性樹脂には、強化材としてガラスファイバやミネラル等を混練してもよい。 As the thermoplastic resin, for example, polyamide resin, polyethylene resin, polypropylene resin, polyethylene terephthalate resin, polybutylene terephthalate resin, polyphenyl ether resin, polystyrene resin, high impact polystyrene resin, hydrogenated polystyrene resin, polyacrylstyrene resin, ABS Resin, AS resin, AES resin, ASA resin, SMA resin, polyalkyl methacrylate resin, polymethyl methacrylate resin, polycarbonate resin, polyester resin, polyphenylene sulfide, liquid crystal polymer and the like. Examples of the thermoplastic elastomer include a styrene-based thermoplastic elastomer, an olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer, a polyester-based thermoplastic elastomer, a polyurethane-based thermoplastic elastomer, and a PVC-based thermoplastic elastomer. Glass fiber, mineral, or the like may be kneaded with the thermoplastic resin as a reinforcing material.
図示例において光吸収性部材102は主として、開口部Oを区画する周壁108と、周壁108の下端部を閉塞する底壁110とからなる。周壁108の横断面形状は略矩形であるが、これに限らず、円形、楕円形、台形、多角形、ひょうたん形状等如何なる形状としてもよい。周壁108には、後述するように開口部Oに繋がり該開口部O内を減圧状態とするのに適した吸引開口112が形成されている。吸引開口112は、底壁110に形成してもよい。あるいは、底壁110を設けずに周壁109の下端を開放し、該下端開口を吸引開口112として用いてもよい。
In the illustrated example, the
光透過性部材106はレーザ光に対する吸収率が同レーザ光に対する光吸収性部材102の吸収率よりも低い部材であり、主として熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーからなり、射出成形等により形成することができる。具体的には、波長193〜10600nmの範囲内に発振波長の中心を有するレーザ光から選択されたレーザ光に対して、光吸収性部材102の吸収率よりも低い吸収率を有するものが好ましい。
The
光透過性部材106を構成する熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、ポリアミド樹脂、ポリエチレン樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリブチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリフェニルエーテル樹脂、ポリスチレン樹脂、ハイインパクトポリスチレン樹脂、水添ポリスチレン樹脂、ポリアクリルスチレン樹脂、ABS樹脂、AS樹脂、AES樹脂、ASA樹脂、SMA樹脂、ポリアルキルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリメチルメタクリレート樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリフェニレンスルファイド、液晶ポリマー等が挙られる。熱可塑性エラストマーとしては、例えばスチレン系熱可塑性エラストマー、オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリエステル系熱可塑性エラストマー、ポリウレタン系熱可塑性エラストマー、PVC系熱可塑性エラストマー等が挙げられる。なお、熱可塑性樹脂には、強化材としてガラスファイバやミネラル等を混練させてもよい。熱可塑性樹脂又は熱可塑性エラストマーには、光吸収性部材の吸収率よりも低い吸収率を得られる限り、例えば、白色顔料や黄色、緑色、赤色等の有彩色着色剤を混練してもよい。
As the thermoplastic resin constituting the
そして、光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、その周縁部が光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に密着する薄板状に形成されている。これにより、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際に、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面と光透過性部材106との間に隙間が生じている場合でも、吸引開口112を通じて開口部O内を減圧した際に光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に密着させることができるため、真空漏れを防止し光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102の相互間で優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
The
これをより確実にするため、光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材102に密着する易変形性を発揮する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。具体的には、十分な変形による密着性を確保するため、光透過性部材106の厚みは、0.005mm〜0.2mmとすることが好ましく、成形性を考慮すると0.01mm〜0.1mmとすることがより好ましい。
In order to ensure this, the
光透過性部材106は、環状の溶着部104が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材102に密着するよう引張弾性係数(ヤング率)を0.01〜18GPaの範囲内の材料を選定又は調整するのが好ましい。光透過性部材106の引張弾性係数(ヤング率)を18GPaよりも大きくした場合には、開口部O内を減圧したときに変形し易くするために極めて薄く形成する必要があり、設計どおりに成形することが難しくなり、例えば、射出成形により光透過性部材106を形成する場合には、薄い部分に樹脂が流れず成形不良の原因となる。一方、光透過性部材106の引張弾性係数(ヤング率)が0.01GPaを下回ると、材料自体の剛性が低くなるため、自身の形状を保持することが難しくなり、目的の位置に目的の形状で位置決めすることが難しくなる。
The
光透過性部材106の易変形性、成形性、位置決め性をより高次元でバランスさせるため、光透過性部材106の材料は、引張弾性係数(ヤング率)が6〜10GPaの範囲内となるよう選定又は調整することがより好ましい。この引張弾性係数(ヤング率)は、JIS K7161の規定に準拠し、JIS K7162に記載の試験片を引張試験機に装着し応力とひずみ(変形量)から応力―ひずみ曲線を作図し、その傾きから求めることができる。この際、応力―ひずみ曲線が直線状にならず傾きを求め難い場合には、ヤング率の代替係数としてセカント係数(応力―ひずみ曲線上の点と原点とを結ぶ直線の傾き)などを用いることができる。
The material of the light-transmitting
また、本実施形態の接合構造体100では、図1(a)に示すように、環状の溶着部104に隣接した位置に、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106とを接合する点状の溶着部114が設けられている。これにより、光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106同士の接合強度はより一層高められている。
In addition, in the
点状の溶着部114は、環状の溶着部104と同様、レーザ光を光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102へ向けて照射することにより形成することができる。点状の溶着部114は、光透過性部材106が略矩形の場合にはコーナー部に隣接して形成することが好ましく、これによれば、点状の溶着部114が、環状の溶着部104を形成する際の光透過性部材106の熱変形による反りを効果的に抑制して、開口部O内の減圧時に、薄板状の光透過性部材106の易変形による密着効果と相俟って、光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102同士のより一層優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
As in the case of the annular welded
また、本実施形態の接合構造体100では、図1(b)中の拡大図で示すように、環状の溶着部104の延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、溶着部104の光透過性部材106側の部分(当該図において境界面Fよりも上の部分であり、以下「第1部分」ともいう。)の面積S1に対する、光吸収性部材102側の部分(当該図において境界面Fよりも下の部分であり、以下、「第2部分」ともいう。)の面積S2の比は、12〜35の範囲内としている。当該比が12未満の場合には、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102から引き剥がすような力が加わった際に環状の溶着部104の境界を起点とした剥離(界面剥離)や溶着部104の光吸収性部材102側の部分の少なくとも一部が光透過性部材106に一体化した状態での剥離が発生する虞がある。また、この種の剥離は工業生産において非破壊で検査することは困難である。面積S1に対する面積S2の比率が12以上では、溶着部104に剥離は生じ難く、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102から引き剥がすような力が加わった場合には、光透過性部材106又は光吸収性部材102自体が破壊する「部材破壊」となるため、溶着強度を設計(設定)するにあたり、部材102,106の強さを管理すればよく、安定して生産することができる。一方、上記比率が35を超えると光吸収性部材102の深くまでレーザ光を届かせるために、パワーを上げるかあるいは照射時間を長くする必要があるため、光透過性部材106への熱影響(隆起や気泡、表面上の溶け、焼けに伴う炭化や変色の発生)や光吸収性部材102への熱影響(焼けに伴う炭化、気泡の発生)が顕在化する虞がある。これらの熱影響の回避と溶着部104における剥離の抑制、防止をより高次元で実現するためには、面積S1に対する面積S2の比率は19〜26の範囲内とすることがより好ましい。
Further, in the
このように溶着部104の光透過性部材側部分の面積S1に対する、光吸収性部材側部分の面積S2の比を上記範囲内とすることで、接合強度を確保しつつ、環状の溶着部104の形成に伴う光透過性部材106への熱影響を小さくし光透過性部材106の熱歪みを抑制することができるため、開口部O内の減圧時に、薄板状の光透過性部材106の易変形による密着効果と相俟って光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102同士のより一層優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
As described above, by setting the ratio of the area S2 of the light absorbing member side portion to the area S1 of the light transmitting member side portion of the
なお、上記比率下の面積S1,S2を有する溶着部104は、図8を参照して後述する接合構造体の製造方法により形成することができる。また、面積S1及びS2を算出するにあたり、溶着部104の範囲(境界)は、接合構造体100を溶着部104の延在方向に対する直交方向にカットして試験片を作成し、その断面を光学顕微鏡または電子顕微鏡で観察することや、X線CTを用いた断層画像を確認することで判断することができる。
Note that the welded
ところで、光透過性部材106を射出成形により製造する場合、ゲートの位置や溶融樹脂の流れ方、金型から取り出した後の冷却不均一等を起因として、光透過性部材106に下面側へ凸となる反り又は上面側へ凸となる反りが発生することがある。下面側へ凸となる反りは、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際に光透過性部材106の周縁部と光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面との間に隙間を生じさせることになるため好ましくない。そこで、本実施形態では、光透過性部材106の下面(光吸収性部材102側の面)に、板厚を減じた凹部116を、環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%以上に亘って形成し、これにより反りの方向を上面側へ凸となる方向に誘導している。凹部116の形成領域が、環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%未満の場合には、反りの原因である樹脂材料の収縮に関して、光透過性部材106全体の反りを誘導するほどの十分な力を得ることができない虞がある。また、反りの量が過大となるのを防ぐため、凹部116の深さは板厚の50%以下とすることが好ましい。凹部116の深さが板厚の50%を超える場合には、反りの原因である樹脂材料の収縮に関して、光透過性部材106の剛性が低下してねじれが発生するため、吸引密着させる際に光透過性部材106及び光吸収性部材102間に隙間が生じて密着が不十分な状態となり、位置ずれや溶着不具合(熱が伝わらないことによる過度な温度上昇や未溶融)が発生する虞がある。
When the light-transmitting
図2を参照し、本発明に従う他の実施形態の接合構造体200について説明する。この実施形態の接合構造体200は、光吸収性部材202に複数の開口部Oが形成されている点で先の実施形態の接合構造体100とは異なる。
With reference to FIG. 2, a description will be given of a
具体的には、光吸収性部材202は、周壁208の上端部に繋がる天壁218を有し、該天壁218には同一方向へ延在する複数のスリット220が穿設されて開口部Oが区画されている。天壁218は、光透過性部材206の上面に外部から衝撃や荷重が加わった場合において光透過性部材206の撓み変形を規制するため、光透過性部材206や溶着部204,214が破損されるのを防ぐことができる。さらに天壁218は梁のように作用するため、光吸収性部材202の周壁208を補強することができる。
Specifically, the
また、光透過性部材206の凹部216は、上述のように光透過性部材206の反りの方向及び量を制御する効果をもたらすが、これに加えて、光透過性部材206と天壁218の間に隙間を維持し、開口部Oを減圧した際に光透過性部材206が天壁218に接触して陰圧の受圧面積が減少するのを防止することができる。陰圧の受圧面積が減少すると、光透過性部材206を真空圧で十分に変形させることができなくなり、光透過性部材206及び光吸収性部材202間の吸引密着性が損なわれる虞がある。これを防止する観点においても、光透過性部材206に形成する凹部216の形成領域は、環状の溶着部104の内側領域の50%以上とすることが好ましい。
The
本実施形態の接合構造体200においても、先の実施形態の接合構造体100と同様、環状の溶着部204は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、光透過性部材206側の部分の面積S1に対する光吸収性部材202側の部分の面積S2の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。
Also in the
図3を参照し、本発明に従う他の実施形態の接合構造体300について説明する。この実施形態の接合構造体300は、光透過性部材300の、環状の溶着部304よりも外側位置に、環状の溶着部304が形成される前の状態で開口部O内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に密着する薄肉片324を設けた点で先の実施形態の接合構造体100,200とは異なる。これにより、光透過性部材306を光吸収性部材302に重ね合わせた際に、光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面と光透過性部材306との間に隙間が生じている場合でも、吸引開口312を通じて開口部O内を減圧した際に光透過性部材306の薄肉片324を光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に引き寄せて密着させることができるため、空気漏れによる真空破壊を防止し光透過性部材306及び光吸収性部材302同士で優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
Referring to FIG. 3, a description will be given of a
これをより確実にするため、薄肉片324は、環状の溶着部304が形成される前の状態で開口部O内がゲージ圧で−80kPa以上−20kPa以下に減圧された場合に変形して、光吸収性部材302に密着する易変形性を発揮する厚みに形成されていることが好ましい。具体的には、十分な変形による密着性を確保するため、薄肉片の厚みは、0.005mm〜0.2mmとすることが好ましく、成形性を考慮すると0.01mm〜0.1mmとすることがより好ましい。
In order to ensure this, the
図3に示す例では、薄肉片324は、光透過性部材306の周縁部下端から光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に沿うように水平に形成されているが、これに限らず、図4(a)に示すように周壁308の外周面に沿うように光透過性部材306の周縁部下端から垂下させてもよく、あるいは図4(b)に示すように、光吸収性部材302の周壁308の上端面に環状溝326を形成するとともに、光透過性部材306の下面から薄肉片324を垂下させ環状溝326内に挿入するようにしてもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 3, the
本実施形態の接合構造体300においても、先の実施形態の接合構造体100,200と同様、環状の溶着部304は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、光透過性部材306側の部分の面積S1に対する光吸収性部材302側の部分の面積S2の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。
Also in the
次に、図5〜図9を参照して、上記実施形態の接合構造体を製造するための製造方法について説明する。なお、ここでは図1に示した接合構造体100を製造する方法を例にとり説明するが、この製造方法は、図2〜図4に示した接合構造体200,300を製造する場合にも適用することができる。
Next, a manufacturing method for manufacturing the joint structure of the above embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. Here, a method for manufacturing the
まず、第1の工程は部材準備工程であり、この工程では光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106を準備する。光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106の材料及び基本的な構造については、接合構造体100について図1を参照して説明したとおりであるため、重複する説明は省略する。
First, the first step is a member preparing step, in which the
図5は、光透過性部材106との接合前の光吸収性部材102を示し、(a)は平面図であり、(b)は(a)中のD−D線に沿う断面図である。この図に示すように、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面(光透過性部材106と当接する面)であって、環状の溶着部104の形成予定部位には環状溝130を予め形成しておく。環状溝130の幅は、そこに照射されるレーザ光の径よりも大きくしておくことが好ましく、例えば、0.1mm〜3mmとすることが好ましい。環状溝130の幅が0.1mm未満の場合には、そこに形成される環状の溶着部104の幅を十分に確保できず、溶着強度が低下するため、外力や圧力変動によって空気や水、埃が浸透し気密性能等を維持できなくなる虞がある。一方、環状溝130の幅が3mmを超えると、溶着時の熱によって環状の溶着部104以外の部分が熱の影響を受けて変形したり、環状の溶着部104が固化する際の熱収縮によって部品に過度のひずみが残り、変形したりする虞がある。
5A and 5B show the
また、環状溝130の深さ(境界面Fから溝底までの距離)は、環状溝130の幅をL(mm)として、L/20(mm)以上L(mm)以下とすることが好ましく、このようにすれば、図8を参照して後述するように、環状溝130へのレーザ光照射により溝底に発生した溶融池を十分に膨張させることができとともに、その熱を過不足なく光透過性部材106へ伝達させることができ、良好な溶着部104を形成することができる。
Further, it is preferable that the depth of the annular groove 130 (the distance from the boundary surface F to the groove bottom) is L / 20 (mm) or more and L (mm) or less, where L is the width of the annular groove 130 (mm). In this way, as described later with reference to FIG. 8, the molten pool generated at the bottom of the
さらに、環状溝130の深さは、L/10(mm)以上L/3(mm)以下とすることが、溶着部104の強度及び気密性を確保する点で好ましい。例えば、環状溝130は、溝幅Lを0.3mm、溝深さを0.05(=L/6)mmとすることができる。溶着部130の深さがL/20(mm)未満であり浅すぎると、環状溝130の溝底へのレーザ光の照射後直ぐに、膨張した溶融池が光透過性部材106に接触するとともに熱が拡散し、溶融池を十分に横方向へ広げることができず、溶着不良となる(環状溝130の一部が残ったままとなる)虞がある。溶着部130の深さがL(mm)を超え深すぎると、環状溝130の溝底で発生した溶融池が膨張するものの光透過性部材106まで到達できず、その場で焼けに伴う炭化や変色が発生し、溶着不良となる虞がある。なお、図示例において環状溝130の断面形状は矩形であるが、半円形状または半楕円形状であってもよい。また、周壁108の上端面には、環状溝130と開口部O内とを連通する少なくとも1つ(図示例では各辺に対応して4つ)の連通溝132を予め形成しておく。
Further, it is preferable that the depth of the
第2の工程は、図6(a)に示すように、光吸収性部材102の上に光透過性部材106を、開口部Oを覆うように配置する配置工程である。
The second step is an arrangement step of disposing a light-transmitting
第3の工程は、互いに重ね合わされた光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を吸引密着させる吸引密着工程であり、かかる吸引密着は開口部O内を減圧することにより行う。図6(b)の左図に光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ねた後の様子を示すように、光透過性部材106と光吸収性部材102との間には、光透過性部材106の成形時の反りや後述するレーザ光による溶着時の熱変形等に起因して隙間が生じる場合があるが、光透過性部材106を薄板状に形成したことから、図6(b)の右図に示すように、開口部O内を減圧することにより光透過性部材106の周縁部を周壁108の上端面に引き寄せるように変形させ、該上端面に密着させることができる。
The third step is a suction and adhesion step in which the light-absorbing
開口部O内の減圧は、具体的には、図7に示すような外部の圧力調整装置Dを用い、光吸収性部材102に予め形成した吸引開口112を通じて行うことができる。
Specifically, the pressure in the opening O can be reduced through the
圧力調整装置Dは主として、減圧装置D1と、加圧装置D2と、制御器D3と、吸引開口112に接続される二重配管Pとからなる。
The pressure adjusting device D mainly includes a pressure reducing device D1, a pressurizing device D2, a controller D3, and a double pipe P connected to the
減圧装置D1は、開口部O内の空気を吸引排気するための真空ポンプと電動のリークバルブとを有している(図示省略)。減圧装置D1の吸引ラインL1には、圧力センサPG1が設けられており、これにより減圧時の開口部O内の圧力を検出することができる。 The pressure reducing device D1 has a vacuum pump for sucking and discharging air in the opening O and an electric leak valve (not shown). A pressure sensor PG1 is provided on the suction line L1 of the decompression device D1, so that the pressure in the opening O at the time of decompression can be detected.
加圧装置D2は、空気又は窒素やアルゴン等の不活性ガスからなるパージガスを供給するための加圧タンクと供給バルブとを有している(図示省略)。加圧装置D2の供給ラインL2には、圧力センサPG2が設けられており、これにより加圧時において開口部O内の圧力を検出することができる。 The pressurizing device D2 has a pressurizing tank for supplying a purge gas composed of air or an inert gas such as nitrogen or argon, and a supply valve (not shown). The supply line L2 of the pressurizing device D2 is provided with a pressure sensor PG2, which can detect the pressure in the opening O during pressurization.
制御器D3は、PLC(プログラマブルロジックコントローラ)やパーソナルコンピュータ等によって構成され、供給バルブ及びリークバルブの開度を調整する。また、圧力センサPG1,PG2も制御器D3に接続し、圧力センサPG1,PG2の検出信号に基づき上記供給バルブ及びリークバルブを制御することもできる。 The controller D3 is configured by a PLC (programmable logic controller), a personal computer, or the like, and adjusts the opening of the supply valve and the leak valve. Further, the pressure sensors PG1 and PG2 can also be connected to the controller D3 to control the supply valve and the leak valve based on the detection signals of the pressure sensors PG1 and PG2.
二重配管Pは、外側に配置された吸引配管p1と内側に配置された供給配管p2からなる。吸引配管p1は開口部O内と減圧装置D1とを連通し、開口部O内の空気を吸引する。供給配管p2は、開口部O内と加圧装置D2とを連通し、開口部O内にパージガスを供給する。図示は省略するが、二重配管Pの外側の配管を供給配管とし、内側の配管を吸引配管とすることもできるが、図示例のように、外側に吸引配管p1を配置する方が、溶着時に発生するガスを効率的に除去できる点で好ましい。 The double pipe P includes a suction pipe p1 arranged outside and a supply pipe p2 arranged inside. The suction pipe p1 communicates the inside of the opening O with the decompression device D1, and sucks the air in the opening O. The supply pipe p2 communicates the inside of the opening O with the pressurizing device D2, and supplies the purge gas into the opening O. Although illustration is omitted, the outer pipe of the double pipe P can be used as a supply pipe, and the inner pipe can be used as a suction pipe. This is preferable in that the gas generated sometimes can be efficiently removed.
第4の工程は、図7に示すように、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106とを吸引密着した状態で、レーザ光LBを光透過性部材106側から光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面へ向けて照射し、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106の境界面Fまたはその近傍に環状の溶着部104及び点状の溶着部114(図1参照)を形成して光吸収性部材102及び光透過性部材106同士を接合する接合工程である。
In the fourth step, as shown in FIG. 7, in a state where the
この接合工程においても引き続き開口部O内の減圧状態は維持するが、少なくとも環状の溶着部104を形成する間は、供給配管p2を介して開口部O内にパージガスを供給することが好ましい。このようにすれば、開口部O内に空気の流れを発生させることができ、溶着時に生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを吸引配管p1を通じて効率的に外部に排出、除去することができる。
In this joining step, the pressure-reduced state in the opening O is maintained, but it is preferable to supply a purge gas into the opening O via the supply pipe p2 at least while the annular welded
そして、溶着部104,114を形成するにあたっては、まず点状の溶着部114を形成し、その後に、環状の溶着部104を形成する。これは、光透過性部材106への熱負荷が比較的小さい点状の溶着部114により光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に仮接合することで、その後に熱負荷の比較的大きい環状の溶着部104を形成した際の光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制し、該熱変形に起因した空気漏れによる真空破壊を防止するためである。環状の溶着部104の溶着が進むにつれて、真空の受圧面積が減るため、その陰圧分を補う点では点状の溶着部114は平面を形成できる3点以上設けることが好ましい。この例では、点状の溶着部114は、光透過性部材106のコーナー部に隣接して4箇所に形成する。
Then, in forming the welded
点状の溶着部114は、光学ヘッドH(図7)を光透過性部材106の上方で停止させた状態でレーザ光LBを光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に照射することで形成される。点状の溶着部114の径は、約0.3〜0.7mmとすることが好ましく、約0.5mmとすることがより好ましい。環状の溶着部104は、光学ヘッドHを光透過性部材106の上方において光吸収性部材102の周壁108に沿って移動させながらレーザ光LBを周壁108上端面に照射することで形成される。環状の溶着部104の幅は、約0.3〜0.7mmとすることが好ましく、約0.5mmとすることがより好ましい。なお、レーザ光LBの発信器としては、例えば、ファイバレーザ(波長:1070nm)やYAGレーザ(波長:1064nm)、半導体レーザ(波長:808nm,840nmまたは940nm)、CO2レーザ(波長:10600nm)などを用いることができる。
The point-like welded
ここで図8(a)〜(d)を参照し、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に予め形成した環状溝130にレーザ光LBを照射することにより、図1で説明した第1部分の面積S1に対する第2部分の面積S2の比率が12〜35となる環状の溶着部104を形成するプロセスについて説明する。
Here, with reference to FIGS. 8A to 8D, by irradiating the
図8(a)に示すように、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を互いに吸引密着させた状態で、光透過性部材106側から環状溝130の溝底にレーザ光を照射すると、図8(b)に示すように環状溝130の溝底が発熱して溶融し、溶融池内で発泡が開始される。引き続きレーザ光を照射すると、図8(c)に示すように発泡が成長して溶融池が成長する。このとき、環状溝130の存在により、光吸収性部材102の溶融池は直ぐには光透過性部材106に接触せず、溶融池は十分な幅及び深さとなるまで成長させることができる。図8(d)には、溶融池が光透過性部材106に到達した後にレーザ光の照射を停止し、環状の溶着部104の形成が完了した状態を示している。
As shown in FIG. 8A, when the light-absorbing
また、図5に示した製造方法では、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130と開口部Oとを連通する連通溝132を設けているため、環状の溶着部104の形成過程で生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vは、環状溝130及び連通溝132を通って開口部O内に吸引、排出され、最終的には、吸引配管p1により外部に排出される。
Further, in the manufacturing method shown in FIG. 5, since the
第5の工程は、環状の溶着部104を形成した後に引き続き開口部O内の減圧を保持し、または開口部O内を加圧し、あるいは減圧と加圧を交互に行い、その際の単位時間当たり圧力の変化を測定することによって環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行う気密性検査工程である。開口部O内の圧力は、図7に示した圧力センサPG1,PG2で測定し、その単位時間当たりの圧力の変化は制御部D3で演算し、必要に応じて外部に出力ないし表示させることができる。あるいは、図示しない流量センサを吸引ラインL1又は供給ラインL2に設けておき、単位時間当たりの流量の変化を測定することにより、環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行うこともできる。
The fifth step is to maintain the reduced pressure in the opening O after forming the annular welded
図示しない第6の工程は、環状の溶着部104の形成後に、開口部O内の減圧を維持したまま、光透過性部材106側からレーザ光LBを吸引開口112の内部又はその周囲に照射することによって吸引開口112を閉塞させる吸引開口閉鎖工程である。これにより、開口部O内の真空を保ったまま開口部O内を密閉することができる。勿論、吸引開口112は開放したままでもよい。
In a sixth step (not shown), after the formation of the annular welded
上記の接合構造体の製造方法によれば、光吸収性部材102に開口部Oを設けておき、この開口部O内を減圧することによって光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106を吸引密着させる構成としたので、両部材102,106を加圧密着するための従来のガラス板を不要とすることができ、上述したようなガラス板に起因する種々の問題を解消することができる。
According to the above-described method for manufacturing a joint structure, the
また、開口部Oの減圧に伴い光透過性部材106を容易に変形可能に構成したことから、光透過性部材106を光吸収性部材102に重ね合わせた際にこれらの間に隙間が生じる場合でも開口部O内を減圧することにより光透過性部材106でこの隙間を閉鎖することができ、優れた吸引密着性を得ることができる。
In addition, since the
さらに、環状の溶着部104を形成するのに先立って、点状の溶着部114を形成して仮接合する構成としたことから、環状の溶着部104の形成途中での光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制することができ、当該熱変形に起因した吸引密着性の低下を防止することができる。
Further, prior to the formation of the annular welded
さらに、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130を形成し、この環状溝130にレーザ光LBを照射して環状の溶着部104を形成する構成としたことから、十分な幅及び深さの溶着部104を形成して高い接合強度を得ることができるのに加えて、光透過性部材106への熱影響を小さくし、溶着過程における光透過性部材106の熱変形を抑制することができ、当該熱変形に起因した吸引密着性の低下を防止することができる。
Further, an
さらに、光吸収性部材102の周壁108の上端面に環状溝130と開口部Oを連通する連通溝132を設ける構成としたことから、環状の溶着部104の形成過程で生じる煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを、環状溝130及び連通溝132と介して開口部O内に吸引し、最終的には、吸引配管p1を介して外部に排出することができる。
Further, since the
さらに、開口部O内の減圧を該開口部O内にパージガスを供給しながら行う構成としたことにより、開口部O内に空気の流れを発生させ、煤や難燃剤の気化成分vを効率的に排出、除去することができる。 Further, by employing a configuration in which the pressure in the opening O is reduced while supplying the purge gas into the opening O, a flow of air is generated in the opening O, and the vaporized component v of soot and a flame retardant is efficiently removed. Can be discharged and removed.
さらに、環状の溶着部104を形成した後に引き続き開口部O内の減圧を保持し、または開口部O内を加圧し、あるいは減圧と加圧を交互に行い、その際の単位時間当たりの圧力又は流量の変化を測定することによって環状の溶着部104の気密性試験を行う場合には、製造設備を簡略化することができるのに加えて、製造時間を大幅に短縮することができる。
Further, after the annular welded
さらに、開口部O内の圧力を圧力センサPG1で常時検出し、その圧力の変化に基づき、光吸収性部材102と光透過性部材106との密着、環状の溶着部104の形成開始、及び環状の溶着部104の形成完了の判別を行うようにした場合には、通常生産時の加工時間の短縮と、異常発生時の早期対応が可能となる。
Further, the pressure in the opening O is constantly detected by the pressure sensor PG1, and based on the change in the pressure, the
以上、図示例に基づき本発明について説明したが、本発明は上述の実施形態に限定されず、特許請求の範囲の記載内で種々の変更、追加等を行うことが可能である。例えば、上述の実施形態の接合構造体においては、溝底が平坦な環状溝130を図示したが、これに限らず、図9(a)に示すように、環状溝の溝底に隆起部134を設けてもよい。また、環状溝130は一つに限らず、図9(b)に示すように隣接して2つ設け、溶着時に合体して一つの幅広の溶着部104を形成するようにしてもよく、図9(c)に示すように、光透過性部材106側にも環状溝136を設けてもよい。
As described above, the present invention has been described based on the illustrated examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various changes, additions, and the like can be made within the scope of the claims. For example, Oite the connection structure of the embodiment described above, although the groove bottom is shown a flat
(第1実施例)
本発明をコネクタに適用した例について説明する。図10は、図2に示した実施形態の接合構造体200の一実施例としてのコネクタを示し、(a)は斜視図であり、(b)は嵌合方向Xに沿った断面図である。図中、対応する部材又は部分には符号に「’」を加えて示し、重複した説明は省略する。
(First embodiment)
An example in which the present invention is applied to a connector will be described. 10A and 10B show a connector as one example of the
このコネクタ200’は、携帯機器や情報機器などの電子機器内の基板に固定され、嵌合方向Xに沿って挿入される図示しない相手方のコネクタに接続されるレセプタクルコネクタであり、主として、光吸収性部材202としてのハウジング202’と、それぞれ嵌合方向Xに延在しかつ嵌合方向Xに対して直交する方向に配列される複数のコンタクト203と、ハウジング202’の開口部O’を覆うとともに封止する、光透過性部材206としての薄板状のカバー206’とを備えるものである。
The
ハウジング202’は、光吸収性かつ絶縁性の熱可塑性樹脂から形成されており、前方に相手方のコネクタが挿入される嵌合口212’を有する周壁208’と、底壁210’と、天壁218’とを有している。
The
ハウジング202’の天壁218’には、嵌合方向Xに沿って形成された複数のスリット220’が形成されており、該スリット220’により開口部O’が区画されている。各スリット220’内にはコンタクト203が配置されている。各コンタクト203の前方端部は相手方のコネクタとの接続のため天壁218’の内面より下方に突出し、その後方端部が電子機器の基板または他の配線板との接続のためハウジング202’から露出している。
A plurality of slits 220 'are formed in the top wall 218' of the housing 202 'along the fitting direction X, and the slits 220' define openings O '. A
カバー206’は、ハウジング202’の開口部O’を覆うようにハウジング202’に重ね合わされ、すべてのスリット220’をまとめて囲繞するように形成された環状の溶着部204’を介して周壁208’の上端面に全周に亘って接合されている。これにより、嵌合口212’から電子機器内部へのスリット220’を介した空気や埃、水の浸水ルートは、カバー206’及び環状の溶着部204’によって遮断されている。また、環状の溶着部204’の外側には、カバー206’のコーナー部に隣接して4つの点状の溶着部214’が形成されている。
The
コネクタ200’において、環状の溶着部204’は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、カバー206’側の部分の面積S1’に対するハウジング202’側の部分の面積S2’の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。 In the connector 200 ', the ratio of the area S2' of the portion on the housing 202 'side to the area S1' of the portion on the side of the cover 206 'is 12 to 35 when viewed in a cross section perpendicular to the extending direction of the annular welded portion 204'. And more preferably in the range of 19 to 26.
このようなコネクタ200’は、嵌合口212’を吸引開口212として、図5〜図8を参照して説明した製造方法に従って製造することができる。
Such a connector 200 'can be manufactured according to the manufacturing method described with reference to FIGS. 5 to 8 using the fitting opening 212' as the
(第2実施例)
本発明をセンサに適用した例について説明する。図11は、図4(a)に示した実施形態の接合構造体300の一実施例としてのセンサを示し、(a)は斜視図であり、(b)は断面図である。
(Second embodiment)
An example in which the present invention is applied to a sensor will be described. FIGS. 11A and 11B show a sensor as one example of the
このセンサ300’は、加速度センサ、振動センサ、角速度センサ、距離センサ、位置センサなど如何なる形式のセンサとすることができる。センサ300’は、主として、光吸収性部材302としての筐体302’と、筐体302’の開口部O’を覆うとともに封止する光透過性部材306としてのカバー306’とを備えるものであり、筐体302’内部に図示しない検出器本体(センサチップ)を収容する。
The sensor 300 'can be any type of sensor, such as an acceleration sensor, a vibration sensor, an angular velocity sensor, a distance sensor, a position sensor, and the like. The
筐体302’は、光吸収性の熱可塑性樹脂から形成されており、開口部O’を区画するとともに前方に向けて吸引筒312’を突設する周壁308’と、底壁310’とを有している。
The
カバー306’は、筐体302’の開口部O’を覆うように筐体302’の周壁308’に被せられ、点状の溶着部314’及び環状の溶着部304’を介して全周に亘って接合されている。カバー306’の周縁部には、周壁308’の外面に沿って薄肉片324’が垂設されている。この薄肉片324’は吸引筒312’を通じて開口部O’内を減圧した際に周壁308’側に引き寄せられて密着するよう形成されている。
The
センサ300’において、環状の溶着部304’は、その延在方向に対する垂直断面でみて、カバー306’側の部分の面積S1’に対する筐体302’側の部分の面積S2’の比が12〜35の範囲内にあり、19〜26の範囲内にあることがより好ましい。 In the sensor 300 ', the annular welded portion 304' has a ratio of the area S2 'of the portion on the housing 302' side to the area S1 'of the portion on the cover 306' side as viewed in a cross section perpendicular to the extending direction thereof of 12 to 12. It is in the range of 35, more preferably in the range of 19-26.
このようなセンサ300’は、吸引筒312’を吸引開口312として、図5〜図8を参照して説明した製造方法に従って製造することができる。
Such a sensor 300 'can be manufactured according to the manufacturing method described with reference to FIGS. 5 to 8 using the suction tube 312' as the
なお、吸引筒312’の基端部は開口したままであるが、上述した製造方法の第6工程に従い、環状の溶着部304’の形成後に、開口部O’内の減圧を維持したままの状態でカバー306’側からレーザ光を吸引筒312’の基端部の開口周辺に照射することにより、吸引筒312’の基端部の開口を閉塞してもよい。これにより、センサ300’の内部空間を真空に保ったまま密閉することができる。 Although the base end of the suction tube 312 'remains open, the reduced pressure in the opening O' is maintained after the formation of the annular welded portion 304 'according to the sixth step of the above-described manufacturing method. The opening at the base end of the suction tube 312 'may be closed by irradiating the laser beam from the cover 306' side to the vicinity of the opening at the base end of the suction tube 312 'in this state. Thus, the sensor 300 'can be hermetically sealed while keeping the internal space at a vacuum.
かくして本発明によれば、ガラス板を用いることなしに、互いに接合される部材同士を均一かつ確実に密着させた接合構造体を提供することができる。 Thus, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a joint structure in which members to be joined to each other are uniformly and surely adhered to each other without using a glass plate.
100,200,300 接合構造体
102,202,302 光吸収性部材
104,204,304 環状の溶着部
106,206,306 光透過性部材
108,208,308 周壁
112,212,312 吸引開口
114,214,314 点状の溶着部
130 環状溝
132 連通溝
324 薄肉片
D 圧力調整装置
D1 減圧装置
D2 加圧装置
D3 制御器
F 境界面
H 光学ヘッド
L1 吸引ライン
L2 供給ライン
O 開口部
PG1,PG2 圧力センサ
S1 環状の溶着部の第1部分(光透過性部材側)の面積
S2 環状の溶着部の第2部分(光吸収性部材側)の面積
100, 200, 300
Claims (16)
前記開口部を覆うように前記光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、を備え、
前記開口部を囲繞するように延在するとともに前記光吸収性部材と前記光透過性部材とを接合する環状の溶着部が形成され、
前記光透過性部材は、前記環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で前記開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、前記光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成されていることを特徴とする接合構造体。 A light absorbing member having at least one opening;
A light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening,
An annular welded portion extending to surround the opening and joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member is formed,
The light transmissive member is formed in a thin plate shape that is deformed when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed, and is in close contact with the light absorbing member. A joint structure characterized by the above-mentioned.
前記開口部を覆うように前記光吸収性部材上に配置された光透過性部材と、を備え、
前記開口部を囲繞するとともに前記光吸収性部材と前記光透過性部材とを接合する環状の溶着部が形成され、
前記光透過性部材は、前記環状の溶着部よりも外側に、前記環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で前記開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して前記光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を有することを特徴とする接合構造体。 A light absorbing member having at least one opening;
A light-transmitting member disposed on the light-absorbing member so as to cover the opening,
An annular welded portion surrounding the opening and joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member is formed,
The light transmissive member is deformed when the inside of the opening is decompressed in a state before the annular welded portion is formed outside the annular welded portion, and the light transmissive member is deformed to the light absorbing member. A bonded structure having a thin piece that is in close contact.
前記光透過性部材を、前記環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で前記開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して、前記光吸収性部材に密着する薄板状に形成しておき、
前記環状の溶着部を形成するにあたり、前記開口部内を減圧することにより前記光透過性部材を変形させ光吸収性部材に密着させた状態で前記光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することを特徴とする接合構造体の製造方法。 A light transmitting member is superimposed on the light absorbing member having at least one opening so as to cover the opening, and a laser beam is irradiated from the light transmitting member side so as to surround the opening. A method of manufacturing a joining structure for joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member by forming a welded portion of
The light transmissive member is formed in a thin plate shape that is deformed when the inside of the opening is depressurized before the annular welded portion is formed, and is in close contact with the light absorbing member. ,
In forming the annular welded portion, the laser light is irradiated from the light transmitting member side in a state in which the light transmitting member is deformed by reducing the pressure in the opening and is brought into close contact with the light absorbing member. A method of manufacturing a joint structure, which is characterized by the following.
前記光透過性部材の、前記環状の溶着部よりも外側に、前記環状の溶着部が形成される前の状態で前記開口部内が減圧状態とされた場合に変形して前記光吸収性部材に密着する薄肉片を形成しておき、
前記環状の溶着部を形成するにあたり、前記開口部内を減圧することにより前記薄肉片を変形させ前記光吸収性部材に密着させた状態で前記光透過性部材側からレーザ光を照射することを特徴とする接合構造体の製造方法。 A light transmitting member is superimposed on the light absorbing member having at least one opening so as to cover the opening, and a laser beam is irradiated from the light transmitting member side so as to surround the opening. A method of manufacturing a joining structure for joining the light absorbing member and the light transmitting member by forming a welded portion of
The light transmissive member, outside the annular welded portion, deforms when the inside of the opening is depressurized in a state before the annular welded portion is formed, and is deformed by the light absorbing member. Form a thin piece that adheres,
In forming the annular welded portion, a laser beam is irradiated from the light transmitting member side in a state in which the thin piece is deformed by reducing the pressure in the opening portion and is brought into close contact with the light absorbing member. A method for manufacturing a joined structure.
The method according to claim 15, wherein the pressure reduction in the opening and the supply of the purge gas into the opening are performed through the suction opening using a double pipe.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019219020A JP6857705B2 (en) | 2019-12-03 | 2019-12-03 | Joint structure |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019219020A JP6857705B2 (en) | 2019-12-03 | 2019-12-03 | Joint structure |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016193992A Division JP6670215B2 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2016-09-30 | Manufacturing method of joint structure |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020044844A true JP2020044844A (en) | 2020-03-26 |
| JP6857705B2 JP6857705B2 (en) | 2021-04-14 |
Family
ID=69900479
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019219020A Active JP6857705B2 (en) | 2019-12-03 | 2019-12-03 | Joint structure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6857705B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022097253A1 (en) * | 2020-11-06 | 2022-05-12 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Motor and method for manufacturing motor |
| WO2022118621A1 (en) * | 2020-12-04 | 2022-06-09 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Sensor module |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002283457A (en) * | 2001-03-26 | 2002-10-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | Laser fusing method for resin parts |
| JP2006242247A (en) * | 2005-03-02 | 2006-09-14 | Toyota Motor Corp | Gas vessel and its manufacturing method |
| JP2010005913A (en) * | 2008-06-26 | 2010-01-14 | Akebono Brake Ind Co Ltd | Laser beam welding method and apparatus |
| JP2017007218A (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2017-01-12 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Manufacturing method for valve unit and valve unit |
-
2019
- 2019-12-03 JP JP2019219020A patent/JP6857705B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002283457A (en) * | 2001-03-26 | 2002-10-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | Laser fusing method for resin parts |
| JP2006242247A (en) * | 2005-03-02 | 2006-09-14 | Toyota Motor Corp | Gas vessel and its manufacturing method |
| JP2010005913A (en) * | 2008-06-26 | 2010-01-14 | Akebono Brake Ind Co Ltd | Laser beam welding method and apparatus |
| JP2017007218A (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2017-01-12 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Manufacturing method for valve unit and valve unit |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022097253A1 (en) * | 2020-11-06 | 2022-05-12 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Motor and method for manufacturing motor |
| JPWO2022097253A1 (en) * | 2020-11-06 | 2022-05-12 | ||
| WO2022118621A1 (en) * | 2020-12-04 | 2022-06-09 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Sensor module |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6857705B2 (en) | 2021-04-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6437976B2 (en) | Junction structure and method for manufacturing the junction structure | |
| JP6857705B2 (en) | Joint structure | |
| CA2739517C (en) | Composite material manufacturing device and composite material manufacturing method | |
| JP5078774B2 (en) | Laser light welding method and apparatus | |
| JP6670215B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of joint structure | |
| JP6670216B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of joint structure | |
| JP5479758B2 (en) | Laser welding method and housing | |
| EP2184784A2 (en) | Photoelectric sensor housing assembling method and photoelectric sensor | |
| JP6861265B2 (en) | Joint structure | |
| JP2002283457A (en) | Laser fusing method for resin parts | |
| JP6574881B2 (en) | Bonding structure | |
| JP5595454B2 (en) | Resin welded body and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2019001150A (en) | Laser welding method and laser welding device for welding workpieces | |
| JP2009234070A (en) | Welding method using laser beam and laser beam welded body | |
| JP2010214730A (en) | Method for laser-welding resin material | |
| JP2011005705A (en) | Laser welding method of resin material | |
| JP5677786B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of detection sensor | |
| KR101846929B1 (en) | MOC actuator coupled by ultrasonic welding method | |
| KR102298986B1 (en) | Welding method of plate type heat exchangers | |
| JP2010253742A (en) | Injection molding equipment, method of manufacturing molded object and the molded object | |
| JP6896526B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of liquid flow path member | |
| JP2006100312A (en) | Optical semiconductor device and range finding module | |
| JP2023156008A (en) | Battery and manufacturing method for the same | |
| JPH01149030A (en) | Production of lcd cell | |
| JP2007040750A (en) | Microchip substrate sticking device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200106 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200106 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20201202 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210122 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210316 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210322 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6857705 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |