JP2018169238A - Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program - Google Patents
Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2018169238A JP2018169238A JP2017065545A JP2017065545A JP2018169238A JP 2018169238 A JP2018169238 A JP 2018169238A JP 2017065545 A JP2017065545 A JP 2017065545A JP 2017065545 A JP2017065545 A JP 2017065545A JP 2018169238 A JP2018169238 A JP 2018169238A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- capacity
- storage battery
- circuit voltage
- measurement timing
- calculated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Tests Of Electric Status Of Batteries (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、蓄電制御装置、蓄電制御システム、サーバ、蓄電制御方法及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a power storage control device, a power storage control system, a server, a power storage control method, and a program.
家庭用や産業用の蓄電池(二次電池)は、充電及び放電すなわち充放電の繰り返しに伴い、満容量(満充電容量)が減少するという問題がある。そのため、蓄電池の満容量を見積もる技術が用いられている。 Storage batteries (secondary batteries) for home use and industrial use have a problem that the full capacity (full charge capacity) decreases with repeated charging and discharging, that is, charging and discharging. Therefore, a technique for estimating the full capacity of the storage battery is used.
特許文献1に開示された手法では、第1及び第2の無負荷タイミングにおいて検出された開放電圧からそれぞれ求めた第1及び第2の残容量SOC1[%]、SOC2[%]の差に基づいて、満容量Ahfを検出している。具体的には、第1及び第2の残容量SOC1[%]、SOC2[%]の差に基づく変化率δS[%]と、第1及び第2の無負荷タイミング間の容量変化値δAhとを求め、式「Ahf=δAh/(δS/100)」に代入することによって、満容量Ahfを算出している。 In the method disclosed in Patent Document 1, based on the difference between the first and second remaining capacities SOC1 [%] and SOC2 [%] obtained from the open-circuit voltages detected at the first and second no-load timings, respectively. Thus, the full capacity Ahf is detected. Specifically, a change rate δS [%] based on the difference between the first and second remaining capacities SOC1 [%] and SOC2 [%], and a capacity change value δAh between the first and second no-load timings, And the full capacity Ahf is calculated by substituting it into the formula “Ahf = δAh / (δS / 100)”.
特許文献1に開示された手法では、開放電圧と残容量との関係を予め記憶しておき、検出した開放電圧から残容量を求めている。発明者らは、残容量を求めるために利用する開放電圧と残容量との関係が、蓄電池の劣化度合に応じて変化することを見出した。特許文献1に開示された手法では、このようなことが考慮されていないため、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合に、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出できない虞があった。 In the method disclosed in Patent Document 1, the relationship between the open circuit voltage and the remaining capacity is stored in advance, and the remaining capacity is obtained from the detected open circuit voltage. The inventors have found that the relationship between the open-circuit voltage used for obtaining the remaining capacity and the remaining capacity varies depending on the deterioration degree of the storage battery. In the method disclosed in Patent Document 1, since this is not taken into consideration, there is a possibility that the full capacity of the storage battery cannot be accurately calculated when the deterioration of the storage battery progresses.
本発明は、このような課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出可能な蓄電制御装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a power storage control device that can accurately calculate the full capacity of a storage battery even when the storage battery has deteriorated.
本発明にかかる蓄電制御装置は、
蓄電池の電圧に基づいて前記蓄電池の開放電圧を推定する開放電圧推定部と、
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する容量算出部と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する制御部と、を含み、
前記制御部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するものである。
The power storage control device according to the present invention includes:
An open-circuit voltage estimation unit for estimating an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery;
A capacity calculator that calculates an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A controller that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The controller is
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
The full capacity is calculated based on the held capacity maintenance rate.
また、本発明にかかる蓄電制御システムは、
蓄電池と、
前記蓄電池の電圧を測定する電圧測定部と、
前記蓄電池の電流を測定する電流測定部と、
前記電圧測定部によって測定された前記電圧に基づいて前記蓄電池の開放電圧を推定する開放電圧推定部と、
前記電流測定部によって測定された前記電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する容量算出部と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する制御部と、を含み、
前記制御部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するものである。
Further, the power storage control system according to the present invention includes:
A storage battery,
A voltage measuring unit for measuring the voltage of the storage battery;
A current measuring unit for measuring the current of the storage battery;
An open-circuit voltage estimation unit that estimates an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage measured by the voltage measurement unit;
A capacity calculation unit that calculates an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current measured by the current measurement unit;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A controller that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The controller is
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
The full capacity is calculated based on the held capacity maintenance rate.
また、本発明にかかるサーバは、
蓄電池の電圧に基づいて推定された前記蓄電池の開放電圧と、前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて算出された前記蓄電池の積算容量とを取得する取得部と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する算出部と、を含み、
前記算出部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するである。
The server according to the present invention is
An acquisition unit that acquires an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery estimated based on a voltage of the storage battery and an integrated capacity of the storage battery calculated based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A calculation unit that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the integrated capacity and the integrated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The calculation unit includes:
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
The full capacity is calculated on the basis of the capacity maintenance rate being held.
また、本発明にかかる蓄電制御方法は、
蓄電池の電圧に基づいて前記蓄電池の開放電圧を推定する工程と、
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する工程と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する工程と、を含み、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するものである。
The power storage control method according to the present invention includes:
Estimating the open voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery;
Calculating an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing Calculating the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing,
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
The full capacity is calculated based on the held capacity maintenance rate.
また、本発明にかかるプログラムは、
蓄電池の電圧に基づいて前記蓄電池の開放電圧を推定し、
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出し、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出し、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するように、
コンピュータを機能させるものである。
The program according to the present invention is
Estimating the open voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery,
Calculate the accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery,
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing Based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing, the full capacity of the storage battery is calculated,
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Based on the capacity maintenance rate that is held, the full capacity is calculated,
It is what makes a computer function.
本発明によれば、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出可能な蓄電制御装置を提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, even when deterioration of a storage battery progresses, the electrical storage control apparatus which can calculate the full capacity of a storage battery accurately can be provided.
以下、本発明を適用した具体的な実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。ただし、本発明が以下の実施の形態に限定される訳ではない。また、説明を明確にするため、以下の記載及び図面は、適宜、簡略化されている。 Hereinafter, specific embodiments to which the present invention is applied will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the following embodiment. In addition, for clarity of explanation, the following description and drawings are simplified as appropriate.
ここで、以下の説明において用いる用語の定義をまとめて示す。
開放電圧(OCV:Open Circuit Voltage)とは、蓄電池に負荷を接続しない状態での蓄電池両端の電圧である。
残容量(SOC:State Of Charge)とは、蓄電池の充電率であり、蓄電池の満容量に対する現在の充電容量の比率である。SOCは、通常、パーセンテージで示されるため、SOC[%]と表現される場合もある。
容量維持率(SOH:State Of Health)とは、蓄電池の初期の満容量に対する現在の満容量の比率である。SOHは、通常、パーセンテージで示されるため、SOH[%]と表現される場合もある。
Here, definitions of terms used in the following explanation are shown together.
The open circuit voltage (OCV) is the voltage across the storage battery when no load is connected to the storage battery.
The remaining capacity (SOC: State Of Charge) is the charging rate of the storage battery, and is the ratio of the current charging capacity to the full capacity of the storage battery. Since the SOC is normally indicated as a percentage, it may be expressed as SOC [%].
The capacity maintenance rate (SOH: State Of Health) is the ratio of the current full capacity to the initial full capacity of the storage battery. Since SOH is usually expressed as a percentage, it may be expressed as SOH [%].
(第1の実施形態)
<蓄電制御装置の構成>
まず、図1を参照して、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御装置について説明する。図1は、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御装置の一例を示すブロック図である。図1に示すように、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御装置40は、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、制御部43を備えている。
(First embodiment)
<Configuration of power storage control device>
First, the power storage control device according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a power storage control device according to the first embodiment. As illustrated in FIG. 1, the power
開放電圧推定部41は、蓄電池の電圧Vmに基づいて蓄電池の開放電圧OCVcを推定する。
容量算出部42は、蓄電池の電流Imに基づいて蓄電池の積算容量Qcを算出する。
The open circuit
The
制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングにおける開放電圧OCV1に基づいて算出した第1の残容量SOC1と、第2の測定タイミングにおける開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量SOC2と、第1の測定タイミングにおける積算容量Q1と、第2の測定タイミングにおける積算容量Q2とに基づいて、蓄電池の満容量Qfullを算出する。
さらに、制御部43は、算出した満容量Qfullと初期の満容量とから容量維持率(SOH)を算出して保持する。そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに基づいて、次回の満容量Qfullを算出する。
The
Further, the
第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御装置では、算出した満容量Qfullと初期の満容量とからSOHを算出して保持し、保持しているSOHに基づいて、次回の満容量Qfullを算出する。
このように、劣化の指標となるSOHに基づいて満容量Qfullを算出するため、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量Qfullを精度よく算出することができる。
In the power storage control device according to the first embodiment, the SOH is calculated and held from the calculated full capacity Qfull and the initial full capacity, and the next full capacity Qfull is calculated based on the held SOH.
Thus, since the full capacity Qfull is calculated based on the SOH that is an indicator of deterioration, the full capacity Qfull of the storage battery can be accurately calculated even when the deterioration of the storage battery progresses.
<蓄電制御システムの構成>
次に、図2、図3を参照して、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムについて説明する。図2、図3は、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの一例を示すブロック図である。図2は、蓄電制御システムにおけるブロック間の接続関係を示している。図3は、蓄電制御システムにおけるブロック間の信号(情報)の流れを示している。図2、図3に示すように、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムは、蓄電池10、電圧測定部20、電流測定部30、蓄電制御装置40、電力変換部50を備えている。ここで、蓄電制御装置40は、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、制御部43を備えている。
<Configuration of power storage control system>
Next, the power storage control system according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 2 and 3. 2 and 3 are block diagrams illustrating an example of the power storage control system according to the first embodiment. FIG. 2 shows a connection relationship between blocks in the power storage control system. FIG. 3 shows a flow of signals (information) between blocks in the power storage control system. As illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3, the power storage control system according to the first embodiment includes a
まず、図2、図3を参照して、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムを構成する各ブロックについて順に説明する。
蓄電池10は、複数の電池セル11を含む。ここで、電池セル11は、代表的にはリチウムイオン二次電池であるが、これに限定されない。図2、図3では、蓄電池10に含まれる複数の電池セル11が直列に接続されているが、これに限定されない。例えば、蓄電池10は、直列又は並列に接続された複数の電池セル11を含んでもよい。また、蓄電池10は、直列又は並列に接続された複数の電池セル11からなる組電池が、さらに直列又は並列に接続された構成でもよい。蓄電池10は、蓄電制御システムの外部負荷と電気的に接続するための負極端子60A及び正極端子60Bに接続されている。
First, with reference to FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, each block which comprises the electrical storage control system which concerns on 1st Embodiment is demonstrated in order.
The
蓄電池10には、電力変換部50を介して、負極端子60A及び正極端子60Bから供給される電力が充電される。また、蓄電池10に蓄積された電力は、電力変換部50を介して、負極端子60A及び正極端子60Bから放電される。詳細には後述するように、電力変換部50は、蓄電制御装置40によって制御される。
The
電圧測定部20は、図2に示すように、蓄電池10が含む各電池セル11の正極及び負極に接続され、各電池セル11の正極及び負極間の電圧を測定する。また、電圧測定部20は、開放電圧推定部41及び制御部43に接続されている。
電圧測定部20は、図3に示すように、測定した電圧Vmを開放電圧推定部41及び制御部43に送信する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
As shown in FIG. 3, the
電流測定部30は、図2に示すように、蓄電池10と直列に接続され、蓄電池10に充電される電流や蓄電池10から放電される流れる電流を測定する。図2の例では、電流測定部30は、蓄電池10の負極と負極端子60Aとの間に設けられている。また、電流測定部30は、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、及び制御部43に接続されている。
電流測定部30は、図3に示すように、測定した電流Imを開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、及び制御部43に送信する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
The
電流測定部30における電流の測定手段として、例えば、検流計、シャント抵抗を用いた検流器、又は、クランプメータを用いてもよい。ただし、本実施形態は、これらの検出機器に限定されない。本実施形態の電流測定部30では、電流を測定する手段であれば、どのような手段を用いてもよい。
For example, a galvanometer, a galvanometer using a shunt resistor, or a clamp meter may be used as a current measurement unit in the
開放電圧推定部41は、図2に示すように、電圧測定部20、電流測定部30、及び制御部43に接続されている。
開放電圧推定部41は、図3に示すように、電圧測定部20が測定した電圧Vmと、電流測定部30が測定した電流Imとに基づいて、蓄電池10の開放電圧(OCV)を推定する。開放電圧推定部41は、推定した開放電圧OCVcを制御部43に送信する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the open circuit
As shown in FIG. 3, the open-circuit
容量算出部42は、図2に示すように、電流測定部30及び制御部43に接続されている。
容量算出部42は、図3に示すように、電流測定部30が測定した電流Imに基づいて、蓄電池10の積算容量を算出する。容量算出部42は、算出した積算容量Qcを制御部43に送信する。
The
As shown in FIG. 3, the
制御部43は、図2に示すように、蓄電池10と電圧測定部20、電流測定部30、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、及び電力変換部50に接続されている。
制御部43は、図3に示すように、電圧測定部20が測定した電圧Vm、電流測定部30が測定した電流Im、開放電圧推定部41が推定した開放電圧OCVc、容量算出部42が算出した積算容量Qcに基づいて、電力変換部50に制御信号CTLfを送信し、蓄電池10の充電及び放電を制御する。そして、制御部43は、蓄電池10の満容量を算出する。さらに、制御部43は、予め記憶された初期の満容量と算出した満容量とから容量維持率(SOH)を算出し、保持する。制御部43の動作の詳細については後述する。
なお、制御部43は、図示しない外部装置から制御信号を受信し、その制御信号に基づいて動作してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
As shown in FIG. 3, the
The
電力変換部50は、図2に示すように、蓄電制御システムの外部負荷と電気的に接続するための負極端子60A及び正極端子60B間に設けられている。電力変換部50は、例えば、双方向のDC(Direct Current)/DCコンバータやAC(Alternating Current)/DCコンバータである。また、電力変換部50は、制御部43に接続されている。
電力変換部50は、図3に示すように、蓄電池10を制御するために制御部43から出力された制御信号CTLfに基づいて、蓄電池10の充電及び放電の動作を切り換える。より具体的には、電力変換部50の動作を制御部43が制御することによって、蓄電池10の充電及び放電における電流や電圧や電力を制御する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
As shown in FIG. 3, the
次に、図3を参照して、本実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムにおけるブロック間の信号(情報)の流れについて説明する。
電圧測定部20は、所定の測定タイミング(例えば、一定間隔)で各電池セル11の端子間の電圧を測定する。
そして、電圧測定部20は、測定した電圧Vmを電圧情報として開放電圧推定部41及び制御部43に送信する。
Next, a flow of signals (information) between blocks in the power storage control system according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
The
Then, the
なお、電圧測定部20は、電流測定部30と同期して、開放電圧推定部41及び制御部43に電圧情報(電圧Vm)を送信することが望ましい。ただし、電圧測定部20は、電流測定部30により送信される電流情報(電流Im)と異なるタイミングで電圧情報(電圧Vm)を送信してもよい。
The
また、電圧測定部20は、開放電圧推定部41又は制御部43からの要求に基づいて、電圧情報(電圧Vm)を送信してもよい。
あるいは、電圧測定部20は、開放電圧推定部41又は制御部43からの要求に基づいて、電圧の測定を開始してもよい。この場合、電圧測定部20は、測定完了後に、電圧情報(電圧Vm)を送信する。
Further, the
Alternatively, the
電流測定部30は、所定の測定タイミング(例えば、一定間隔)で蓄電池10の充電電流及び放電電流(以下、まとめて「充放電電流」と呼ぶ)の値を測定する。そして、電流測定部30は、測定した電流Imを電流情報として開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42、及び制御部43に送信する。
電流測定部30は、測定した電流の値をそのまま電流情報(電流Im)として送信してもよい。あるいは、電流測定部30は、所定の回数測定した電流の平均値を電流情報(電流Im)として送信してもよい。
The
The
なお、電流測定部30は、電圧測定部20と同期して、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42及び制御部43に電流情報(電流Im)を送信することが望ましい。ただし、電流測定部30は、電圧測定部20により送信される電圧情報(電圧Vm)と異なるタイミングで電流情報を送信してもよい。
The
また、電流測定部30は、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42又は制御部43からの要求に基づいて、電流情報(電流Im)を送信してもよい。
あるいは、電流測定部30は、開放電圧推定部41、容量算出部42又は制御部43からの要求に基づいて、電流の測定を開始してもよい。この場合、電流測定部30は、測定完了後に、電流情報(電流Im)を送信する。
In addition, the
Alternatively, the
開放電圧推定部41は、電圧測定部20から、蓄電池10を構成する電池セル11の電圧情報(電圧Vm)を受信する。
また、開放電圧推定部41は、電流測定部30から、蓄電池10の充電又は放電時の電流情報(電流Im)を受信する。
なお、繰り返しとなるが、開放電圧推定部41は、同期した同じ時刻で、電圧情報(電圧Vm)と電流情報(電流Im)とを受信することが望ましい。
The open-circuit
Further, the open-circuit
In addition, although it repeats, it is desirable for the open circuit
そして、開放電圧推定部41は、電圧情報(電圧Vm)と、電流情報(電流Im)とに基づき、電池セル11の開放電圧(OCV)を推定する。開放電圧推定部41は、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2を推定する。第1の測定タイミングT1及び第2の測定タイミングT2の定義は後述する。そして、開放電圧推定部41は、推定した開放電圧OCVc(開放電圧OCV1、OCV2)をOCV情報として制御部43に送信する。
なお、開放電圧推定部41は、すべての測定タイミングに対応して、開放電圧を推定してもよい。
And the open circuit
In addition, the open circuit
ここで、開放電圧推定部41による開放電圧(OCV)の推定手法は、特に制限はない。例えば、開放電圧推定部41は、電池セル11の等価回路モデルに基づき、開放電圧を推定してもよい。あるいは、開放電圧推定部41は、電池セル11の内部抵抗に基づき、開放電圧を推定してもよい。また、開放電圧推定部41は、電池セル11の等価回路モデルにおけるパラメータ又は電池セル11の内部抵抗を、蓄電池10の使用に伴って動的に算出し、算出された値を用いて開放電圧を推定してもよい。また、充放電電流が0の場合の電池セル11の電圧から開放電圧を推定してもよい。
Here, the open-circuit voltage (OCV) estimation method by the open-circuit
容量算出部42は、電流測定部30から、蓄電池10の充電又は放電時の電流情報(電流Im)を受信する。
容量算出部42は、ある時点を0として、電流情報(電流Im)に基づき、電流の積分値として容量を算出し、算出した容量を積算して積算容量を算出し、算出した積算容量Qcを積算容量情報として制御部43に送信する。容量算出部42は、例えば、積算容量を、現在時刻での電流値に、現在時刻と1つ前の算出時刻との差分時間を掛け合わせたものを、1つ前の算出時刻の積算容量に加えたものとして算出する。つまり、容量算出部42は、電流情報(電流Im)の時間積分することによって、積算容量を算出する。積分容量の単位は、通常、[Ah]を用いる。例えば、容量算出部42は、充電方向の電流をプラス、放電方向の電流をマイナスとして、算出した容量を積算して積算容量を算出する。
The
The
制御部43は、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCVc)を受信する。
ここで、本実施形態の制御部43は、SOHの低下に対応した電池セル11の開放電圧(OCV)に対する残容量SOC[%](以下、「OCV−SOC[%]」とする)の関係を示した情報を参照して残容量SOCを算出する。例えば、制御部43の内部メモリ(不図示)や制御部43に接続されたメモリ(不図示)が、関数又はルックアップテーブルとしてSOHの低下に対応した複数のOCV−SOC[%]の関係を予め記憶している。
The
Here, the
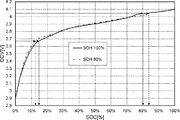
図4は、SOHの低下に対応した開放電圧OCVに対する残容量SOC[%]の関係の一例を表すグラフである。図4には、SOH100%、SOH90%、SOH80%、SOH70%のそれぞれにおけるOCV−SOC[%]の関係を表す4つの曲線が示されている。
制御部43は、保持しているSOHを参照すると共に、そのSOHに対応するOCV−SOC[%]の関係を示す関数又はルックアップテーブルを参照し、受信したOCV情報(開放電圧OCVc)に対する残容量SOCを算出する。
具体的には、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1に基づき残容量SOC1を算出するとともに、第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2に基づき残容量SOC2を算出する。
FIG. 4 is a graph showing an example of the relationship of the remaining capacity SOC [%] with respect to the open circuit voltage OCV corresponding to a decrease in SOH. FIG. 4 shows four curves representing the OCV-SOC [%] relationship in
The
Specifically, the
なお、SOHに対応するOCV−SOC[%]の関係は、代表的なSOHにおけるOCV−SOC[%]の関係を記憶しておき、適宜補完して算出してもよい。例えば、図4に示すように、SOH100%、SOH90%、SOH80%、SOH70%等の代表的なSOHにおけるOCV−SOC[%]の関係を記憶しておく。その他のSOHについては、前後の代表的なSOHにおけるOCV−SOC[%]の関係から算出することができる。例えば、SOH85%については、SOH90%及びSOH80%におけるOCV−SOC[%]の関係から算出することができる。
Note that the OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the SOH may be calculated by storing the OCV-SOC [%] relationship in a typical SOH and appropriately complementing it. For example, as shown in FIG. 4, the relationship of OCV-SOC [%] in typical SOH such as
また、制御部43は、容量算出部42から積算容量情報(積算容量Qc)を受信する。
また、制御部43は、電力変換部50に、制御信号CTLfを送信する。制御信号CTLfは、電力変換部50が蓄電池10を放電する放電モード又は充電する充電モードといった、電力変換部50の動作モードの設定を含む。あるいは、制御信号CTLfは、電力変換部50の放電時の放電設定又は充電時の充電設定を含む。
なお、制御部43は、電力変換部50が蓄電池10を充放電させる際に取得する電流や電圧等の計測情報を電力変換部50から受信してもよい。
Further, the
In addition, the
The
制御部43は、予め、蓄電池10を構成する電池セル11の充放電可能な電圧範囲(以下、「適正電圧範囲」と呼ぶ)を保持する。電池セル11がリチウムイオン二次電池の単電池の場合、適正電圧範囲は、例えば2.5V〜4.2Vである。そして、制御部43は、電圧測定部20から受信した電池セル11の電圧情報(電圧Vm)が、適正電圧範囲内か否かを判定する。
The
電池セル11の電圧情報(電圧Vm)が適正電圧範囲外の場合、制御部43は、電力変換部50に制御信号CTLfを送信し、蓄電池10の充電又は放電を停止する。この動作によって、制御部43は、充電中及び放電中の過放電及び過充電を防止する。
例えば、充電時には、電池セル11の少なくとも1つの電圧が適正電圧範囲の上限を超えた場合、制御部43は、充電を停止することができる。放電時には、電池セル11の少なくとも1つの電圧が適正電圧範囲の下限を下回った場合、制御部43は、放電を停止することができる。
When the voltage information (voltage Vm) of the
For example, at the time of charging, when at least one voltage of the
さらに、制御部43は、予め、蓄電池10の充電時及び放電時に許容される電流範囲(以下、「許容電圧範囲」と呼ぶ)を保持する。そして、制御部43は、電流測定部30から受信した蓄電池10の電流情報(電流Im)が、許容電流範囲外か否かを判定する。蓄電池10の電流情報(電流Im)が許容電流範囲外の場合、制御部43は、電力変換部50に制御信号CTLfを送信し、蓄電池10への充電又は放電を停止する。この動作によって、制御部43は、蓄電池10に含まれる電池セル11に対する過電流を防止する。
Furthermore, the
<蓄電制御システムの動作>
次に、図5を参照して、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの動作について説明する。また、蓄電制御システムの動作の説明に当たっては、図3を適宜参照する。
図5は、第1の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムにおいて、充電動作時に開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOC[%]の時間変化を示すグラフである。図5において、開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOCを「SOC(@OCV)」と表す。図5には、第1の測定タイミングT1における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV1から算出される残容量SOC1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV2から算出される残容量SOC2が示されている。充電動作時であるため、図5に示すように、時間の経過と共に残容量SOC[%]が上昇する。
<Operation of power storage control system>
Next, the operation of the power storage control system according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. In describing the operation of the power storage control system, FIG. 3 will be referred to as appropriate.
FIG. 5 is a graph showing the time change of the remaining capacity SOC [%] calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV during the charging operation in the power storage control system according to the first embodiment. In FIG. 5, the remaining capacity SOC calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV is represented as “SOC (@OCV)”. FIG. 5 shows the remaining capacity SOC1 calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV1 of the
まず、制御部43は、図3に示す制御信号CTLfによって電力変換部50に充電モードを指示する。充電モード中の電力変換部50は、蓄電池10からの放電を行わず、蓄電池10に充電を行う。
制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV1)受信する。
First, the
The
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1に対応した第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1を算出する。
上述の通り、制御部43は、容量算出部42から積算容量情報(積算容量Qc)を受信する。第1の測定タイミングT1では、積算容量情報(積算容量Q1)を受信する。
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
As described above, the
引き続き、制御部43は、充電を継続する。そして、制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV2)受信する。
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2に対応した第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2を算出する。
さらに、制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2における積算容量情報(積算容量Q2)を受信する。
Subsequently, the
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
Furthermore, the
そして、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1[%]、第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2[%]、第1の測定タイミングT1における積算容量Q1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における積算容量Q2に基づいて、満容量Qfullを算出する。例えば、制御部43は、次式(1)を用いて、満容量Qfullを算出する。
Qfull=(Q2−Q1)/{(SOC2−SOC1)/100}・・・式(1)
The
Qfull = (Q2-Q1) / {(SOC2-SOC1) / 100} Expression (1)
さらに、制御部43は、算出した満容量Qfullと予め記憶された初期の満容量とからSOHを算出し、保持する。保持されたSOHは、次回の満容量Qfullの算出に用いられる。
なお、初期の満容量として、初期の満容量の代表値を設定してもよいし、初回に算出した満容量Qfullを設定してもよい。また、満容量Qfullを算出する度にSOHを更新する必要はない。例えば、満容量Qfullを所定の回数算出する度にSOHを更新するようにしてもよい。
Furthermore, the
As the initial full capacity, a representative value of the initial full capacity may be set, or the full capacity Qfull calculated for the first time may be set. Further, it is not necessary to update the SOH every time the full capacity Qfull is calculated. For example, the SOH may be updated every time the full capacity Qfull is calculated a predetermined number of times.
第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1と第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2は、残容量SOC[%]の0〜100[%]に対応する開放電圧OCVの範囲内の電圧である。例えば、電池セル11が2.9V〜4.1Vを使用範囲とするリチウムイオン二次電池の場合、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1と第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2は、その使用範囲内の電圧である。
The open circuit voltage OCV1 at the first measurement timing T1 and the open circuit voltage OCV2 at the second measurement timing T2 are voltages within the range of the open circuit voltage OCV corresponding to 0 to 100 [%] of the remaining capacity SOC [%]. For example, when the
第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2の条件は、例えば、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応した第1及び第2の開放電圧OCV1、OCV2によって設定することができる。具体的には、制御部43は、開放電圧推定部41から取得したOCV情報(開放電圧OCVc)がSOHに対応して予め設定された第1及び第2の開放電圧OCV1、OCV2に達した時点を、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2とする。なお、第2の開放電圧OCV2>第1の開放電圧OCV1となる。保持しているSOHを参照して、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応した第1及び第2の開放電圧OCV1、OCV2を設定してもよい。
The conditions of the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2 can be set by the first and second open-circuit voltages OCV1 and OCV2 corresponding to the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2, for example. Specifically, the
他方、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2の条件は、例えば、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応した第1及び第2の残容量SOC1、SOC2によって設定することもできる。具体的には、制御部43は、開放電圧推定部41から取得したOCV情報(開放電圧OCVc)と、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、残容量SOCを算出する。そして、残容量SOCが予め設定した第1及び第2の残容量SOC1、SOC2に達した時点を、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2とする。なお、第2の残容量SOC2>第1の残容量SOC1となる。
On the other hand, the conditions of the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2 can be set by the first and second remaining capacities SOC1 and SOC2 corresponding to the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2, for example. . Specifically, the
さらに、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2は、例えば、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応した電池セル11の端子間の電圧(第1及び第2の電圧)V1、V2によって設定することもできる。具体的には、制御部43は、電圧測定部20から取得した電圧情報(電圧Vm)がSOHに対応して予め設定した第1及び第2の電圧V1、V2に達した時点、もしくはその時点から一定時間経過した時点を、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2とする。保持しているSOHを参照して、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応した第1及び第2の電圧V1、V2を設定してもよい。
Furthermore, the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2 are, for example, voltages (first and second voltages) V1 between the terminals of the
本実施形態では、第1の測定タイミングT1を完全放電状態(残容量SOC=0[%])とし、第2の測定タイミングT2を満充電状態(残容量SOC=100[%])とする必要がない。すなわち、本実施形態では、完全放電状態と異なる状態の時を第1の測定タイミングT1とし、満充電状態と異なるタイミングの時を第2の測定タイミングT2とすることができる。
なお、第1の測定タイミングT1を完全放電状態とし、第2の測定タイミングT2を満充電状態と異なるタイミングの時としてもよい。また、第1の測定タイミングT1を完全放電状態と異なる状態の時とし、第2の測定タイミングT2を満充電状態としてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the first measurement timing T1 needs to be in a fully discharged state (remaining capacity SOC = 0 [%]), and the second measurement timing T2 must be in a fully charged state (remaining capacity SOC = 100 [%]). There is no. That is, in the present embodiment, a time different from the fully discharged state can be set as the first measurement timing T1, and a time different from the fully charged state can be set as the second measurement timing T2.
Note that the first measurement timing T1 may be a fully discharged state, and the second measurement timing T2 may be a timing different from the fully charged state. Alternatively, the first measurement timing T1 may be set to a state different from the fully discharged state, and the second measurement timing T2 may be set to a fully charged state.
第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2の条件を、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2に対応する第1及び第2の残容量SOC1、SOC2によって設定する場合、上述のように予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係を用いるのではなく、算出した満容量Qfullを用いることもできる。
この場合、制御部43は、算出した満容量Qfullと、容量算出部42から取得した積算容量Qcとから残容量SOCを算出する。そして、制御部43は、算出した残容量SOCが第1及び第2の残容量SOC1、SOC2に達した時点を第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2とする。
When the conditions of the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2 are set by the first and second remaining capacities SOC1 and SOC2 corresponding to the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2, as described above, Instead of using the stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship, the calculated full capacity Qfull can also be used.
In this case, the
この際、単純に式「SOC=Qc/Qfull」を用いるのではなく、積算容量Qcの補正量Qadjを導入することが好ましい。
具体的には、制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2においてOCV−SOC[%]の関係から算出した第2の残容量SOC2、積算容量Q2、及び満容量Qfullを用いた式「SOC2=(Q2+Qadj)/Qfull」から補正量Qadjを決定する。それ以降、制御部43は、その時点の積算容量Qcを式「SOC=(Qc+Qadj)/Qfull」に代入することによって残容量SOCを算出する。そして、制御部43は、算出した残容量SOCが予め設定した第1及び第2の残容量SOC1、SOC2に達した時点を、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2とする。
At this time, it is preferable to introduce the correction amount Qadj of the integrated capacity Qc, instead of simply using the expression “SOC = Qc / Qfull”.
Specifically, the
また、第1と第2の測定タイミングを、SOHの低下すなわち蓄電池10の劣化によるOCV−SOC[%]の関係の変化が少ない残容量SOCの範囲に設定してもよい。例えば、図4の例では、残容量SOCが25[%]付近、70[%]付近において、SOHの低下によるOCV−SOC[%]の関係の変化が小さい。そこで、例えば、第1の測定タイミングT1の条件を残容量SOC=25[%]、第2の測定タイミングT2の条件を残容量SOC=70[%]と設定する。ここで、残容量SOCに対応する開放電圧OCVで条件を設定しても同義である。すなわち、第1の測定タイミングT1の条件を開放電圧OCV=3.772V、第1の測定タイミングT1の条件を開放電圧OCV=3.984Vと設定してもよい。
Further, the first and second measurement timings may be set in the range of the remaining capacity SOC in which the change in the OCV-SOC [%] relationship due to the SOH decrease, that is, the deterioration of the
<効果の説明>
次に、本実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの効果について説明する。
図6は、SOH100%及びSOH80%の場合のOCV−SOC[%]の関係の一例を表すグラフである。
まず、図6に実線矢印で示すように、SOH100%におけるSOC15%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第1の測定タイミングT1に設定すると共に、SOH100%におけるSOC80%に対応するOCVを第2の測定タイミングT2に設定した場合について考える。
<Description of effects>
Next, effects of the power storage control system according to the present embodiment will be described.
FIG. 6 is a graph showing an example of the relationship of OCV-SOC [%] when SOH is 100% and SOH is 80%.
First, as indicated by a solid arrow in FIG. 6, the open circuit voltage OCV corresponding to SOC 15% at
図6に破線矢印で示すように、SOHが100%から80%まで低下すると、SOH100%において第1の測定タイミングT1として設定した開放電圧OCVに対応する残容量SOCは、15%から13%程度まで低下している。また、SOH100%において第2の測定タイミングT2として設定した開放電圧OCVに対応する残容量SOCは、80%から84%程度まで上昇している。
従って、SOHが100%から80%まで低下すると、式(1)で算出される蓄電池の満容量Qfullは、実際の容量より大きく算出されてしまう。このように、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出することができない。
As indicated by a broken line arrow in FIG. 6, when the SOH decreases from 100% to 80%, the remaining capacity SOC corresponding to the open circuit voltage OCV set as the first measurement timing T1 in the
Accordingly, when the SOH decreases from 100% to 80%, the full capacity Qfull of the storage battery calculated by the equation (1) is calculated to be larger than the actual capacity. Thus, when the deterioration of the storage battery progresses, the full capacity of the storage battery cannot be calculated with high accuracy.
本実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムでは、満容量Qfullを算出すると共にSOHを算出し、保持する。そして、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第1及び第2の測定タイミングT1、T2における開放電圧OCV1、OCV2に対応した残容量SOC1、SOC2を算出する。 In the power storage control system according to the present embodiment, the full capacity Qfull is calculated and the SOH is calculated and held. Based on the OCV-SOC [%] relationship stored in advance corresponding to the held SOH, the remaining capacity SOC1 corresponding to the open-circuit voltages OCV1 and OCV2 at the first and second measurement timings T1 and T2, Calculate SOC2.
そのため、図7に実線矢印で示すように、当初SOH100%におけるSOC15%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第1の測定タイミングT1に設定した場合にも、保持しているSOHを参照し、そのSOHにおけるSOC15%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第1の測定タイミングT1として再設定することができる。そのため、図7に破線矢印で示すように、SOHが100%から80%まで低下しても、SOH80%におけるSOC15%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第1の測定タイミングT1に設定することができる。従って、SOHが100%から80%まで低下しても、第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1を15%近傍に維持することができる。
Therefore, as shown by the solid line arrow in FIG. 7, even when the open circuit voltage OCV corresponding to SOC 15% in the
同様に、図7に実線矢印で示すように、当初SOH100%におけるSOC80%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第2の測定タイミングT2に設定した場合にも、保持しているSOHを参照し、そのSOHにおけるSOC80%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第2の測定タイミングT2として再設定することができる。そのため、図7に破線矢印で示すように、SOHが100%から80%まで低下しても、SOH80%におけるSOC80%に対応する開放電圧OCVを第2の測定タイミングT2に設定することができる。従って、SOHが100%から80%まで低下しても、第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2を80%近傍に維持することができる。
Similarly, as shown by the solid line arrow in FIG. 7, even when the open circuit voltage OCV corresponding to the
従って、SOHが100%から80%まで低下しても、式(1)で算出される蓄電池の満容量Qfullを、精度よく算出することができる。このように、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出することができる。 Therefore, even when the SOH decreases from 100% to 80%, the full capacity Qfull of the storage battery calculated by the equation (1) can be calculated with high accuracy. Thus, even when the deterioration of the storage battery progresses, the full capacity of the storage battery can be calculated with high accuracy.
ところで、蓄電池を完全放電状態まで放電させた後、満充電状態まで充電し、完全放電状態から満充電状態までの充電容量から満容量を求める方法が知られている。当該方法では、蓄電池を完全放電状態まで放電させた後、満充電状態まで充電するため、満容量を求める際に長時間を要する。また、蓄電池を完全放電状態まで放電する際、放電電流は蓄電池に接続される負荷に応じて変動する。そのため、放電電流が小さいと、完全放電状態までの放電に長時間を要する。
これに対し、本実施形態の蓄電制御システムでは、上述の通り、第1の測定タイミングT1を完全放電状態とし、第2の測定タイミングT2を満充電状態とする必要がない。そのため、短時間で蓄電池の満容量を求めることができる。
By the way, after discharging a storage battery to a complete discharge state, it charges to a full charge state, and the method of calculating | requiring a full capacity from the charge capacity from a complete discharge state to a full charge state is known. In this method, since the storage battery is discharged to the fully discharged state and then charged to the fully charged state, it takes a long time to obtain the full capacity. Further, when discharging the storage battery to a fully discharged state, the discharge current varies depending on the load connected to the storage battery. Therefore, if the discharge current is small, it takes a long time to discharge to the complete discharge state.
On the other hand, in the power storage control system of the present embodiment, as described above, it is not necessary to set the first measurement timing T1 to the fully discharged state and the second measurement timing T2 to the fully charged state. Therefore, the full capacity of the storage battery can be obtained in a short time.
<第1の実施形態の変形例>
蓄電池10が、直列に接続した複数の電池セル11を含む場合、電池セル11の開放電圧OCVの平均値を算出し、算出した平均値を開放電圧OCVとして、残容量SOC[%]を算出してもよい。
<Modification of First Embodiment>
When the
あるいは、第1の測定タイミングT1では、電池セル11各々の開放電圧の中の最小の開放電圧によりSOC1を算出してもよい。さらに、最小の開放電圧に代えて、複数の電池セル11各々の開放電圧の中の大きい方から順に定めた順位が下位x%に含まれる開放電圧の統計値(平均値、中間値、最頻値等)に基づき、SOC1[%]を算出してもよい。なお、xは、0より大100より小である。
Alternatively, at the first measurement timing T1, SOC1 may be calculated from the minimum open circuit voltage among the open circuits of each
同様に、第2の測定タイミングT2では、電池セル11各々の開放電圧の中の最大の開放電圧によりSOC2を算出してもよい。さらに、最大の開放電圧に代えて、複数の電池セル11各々の開放電圧の中の大きい方から順に定めた順位が上位x%に含まれる開放電圧の統計値(平均値、中間値、最頻値等)に基づき、SOC2[%]を算出してもよい。
Similarly, at the second measurement timing T2, SOC2 may be calculated from the maximum open voltage among the open voltages of the
なお、制御部43は、電圧測定部20と、電流測定部30と、開放電圧推定部41と、容量算出部42と、電力変換部50とネットワークを介して接続されていてもよい。
The
(第2の実施形態)
次に、第2の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムについて説明する。本実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの構成は、第1の実施形態の蓄電制御システムと同様のため、構成の詳細な説明を省略する。また、説明中の変数は、第1の実施形態と同様である。
(Second Embodiment)
Next, a power storage control system according to the second embodiment will be described. Since the configuration of the power storage control system according to the present embodiment is the same as that of the power storage control system according to the first embodiment, detailed description of the configuration is omitted. Moreover, the variables in the description are the same as those in the first embodiment.
<蓄電制御システムの動作>
図8を参照して、第2の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの動作について説明する。また、蓄電制御システムの動作の説明に当たっては、図3を適宜参照する。
図8は、第2の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムにおいて、放電動作時に開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOC[%]の時間変化を示すグラフである。図8において、開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOCを「SOC(@OCV)」と表す。図8には、第1の測定タイミングT1における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV1から算出される残容量SOC1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV2から算出される残容量SOC2が示されている。放電動作時であるため、図8に示すように、時間の経過と共に残容量SOC[%]が低下する。
<Operation of power storage control system>
With reference to FIG. 8, the operation of the power storage control system according to the second embodiment will be described. In describing the operation of the power storage control system, FIG. 3 will be referred to as appropriate.
FIG. 8 is a graph showing the time change of the remaining capacity SOC [%] calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV during the discharging operation in the power storage control system according to the second embodiment. In FIG. 8, the remaining capacity SOC calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV is represented as “SOC (@OCV)”. FIG. 8 shows the remaining capacity SOC1 calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV1 of the
まず、制御部43は、図3に示す制御信号CTLfによって電力変換部50に放電モードを指示する。放電モード中の電力変換部50は、蓄電池10に充電を行わず、蓄電池10から放電を行う。
制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV2)受信する。
First, the
The
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2に対応した第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2を算出する。
上述の通り、制御部43は、容量算出部42から積算容量情報(積算容量Qc)を受信する。第2の測定タイミングT2では、積算容量情報(積算容量Q2)を受信する。
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
As described above, the
引き続き、制御部43は、放電を継続する。そして、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV1)受信する。
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1に対応した第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1を算出する。
さらに、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1における積算容量情報(積算容量Q1)を受信する。
Subsequently, the
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
Furthermore, the
そして、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1[%]、第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2[%]、第1の測定タイミングT1における積算容量Q1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における積算容量Q2に基づいて、満容量Qfullを算出する。例えば、制御部43は、上記式(1)を用いて、満容量Qfullを算出する。
The
さらに、制御部43は、算出した満容量Qfullと予め記憶された初期の満容量とからSOHを算出し、保持する。保持されたSOHは、次回の満容量Qfullの算出に用いられる。
以上のように、算出したSOHを満容量Qfullの算出に用いることにより、放電中であっても、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出することができる。
Furthermore, the
As described above, by using the calculated SOH for calculating the full capacity Qfull, the full capacity of the storage battery can be accurately calculated even when the storage battery is deteriorated even during discharging.
(第3の実施形態)
次に、第3の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムについて説明する。本実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの構成は、第1の実施形態の蓄電制御システムと同様のため、構成の詳細な説明を省略する。また、説明中の変数は、第1の実施形態と同様である。
(Third embodiment)
Next, a power storage control system according to the third embodiment will be described. Since the configuration of the power storage control system according to the present embodiment is the same as that of the power storage control system according to the first embodiment, detailed description of the configuration is omitted. Moreover, the variables in the description are the same as those in the first embodiment.
<蓄電制御システムの動作>
図9を参照して、第3の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムの動作について説明する。また、蓄電制御システムの動作の説明に当たっては、図3を適宜参照する。
図9は、第3の実施形態に係る蓄電制御システムにおいて、充放電動作時に開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOC[%]の時間変化を示すグラフである。図9において、開放電圧OCVから算出される残容量SOCを「SOC(@OCV)」と表す。図9には、第1の測定タイミングT1における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV1から算出される残容量SOC1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における電池セル11の開放電圧OCV2から算出される残容量SOC2が示されている。充放電動作時であるため、図9に示すように、時間の経過と共に残容量SOC[%]が上昇した後、低下し、再度上昇している。
<Operation of power storage control system>
With reference to FIG. 9, the operation of the power storage control system according to the third embodiment will be described. In describing the operation of the power storage control system, FIG. 3 will be referred to as appropriate.
FIG. 9 is a graph showing the time change of the remaining capacity SOC [%] calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV during the charge / discharge operation in the power storage control system according to the third embodiment. In FIG. 9, the remaining capacity SOC calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV is represented as “SOC (@OCV)”. FIG. 9 shows the remaining capacity SOC1 calculated from the open circuit voltage OCV1 of the
まず、制御部43は、図3に示す制御信号CTLfによって電力変換部50に充放電モード(充電及び放電を行うモード)を指示する。充放電モード中の電力変換部50は、制御部43からの指示、もしくは、電力変換部50に接続される電源や負荷の状況に応じて充電及び放電を切り換えて充放電を行う。
制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV1)受信する。
First, the
The
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第1の測定タイミングT1における開放電圧OCV1に対応した第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1を算出する。
上述の通り、制御部43は、容量算出部42から積算容量情報(積算容量Qc)を受信する。第1の測定タイミングT1では、積算容量情報(積算容量Q1)を受信する。
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
As described above, the
その後、制御部43は、充電から放電に切り換え、さらに放電から充電に切り換える。そして、制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2において、開放電圧推定部41からOCV情報(開放電圧OCV2)受信する。
そして、制御部43は、保持しているSOHに対応する予め記憶されたOCV−SOC[%]の関係に基づいて、第2の測定タイミングT2における開放電圧OCV2に対応した第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2を算出する。
さらに、制御部43は、第2の測定タイミングT2における積算容量情報(積算容量Q2)を受信する。
Thereafter, the
Then, based on the previously stored OCV-SOC [%] relationship corresponding to the held SOH, the
Furthermore, the
そして、制御部43は、第1の測定タイミングT1における残容量SOC1[%]、第2の測定タイミングT2における残容量SOC2[%]、第1の測定タイミングT1における積算容量Q1、及び、第2の測定タイミングT2における積算容量Q2に基づいて、満容量Qfullを算出する。例えば、制御部43は、上記式(1)を用いて、満容量Qfullを算出する。
The
さらに、制御部43は、算出した満容量Qfullと予め記憶された初期の満容量とからSOHを算出し、保持する。保持されたSOHは、次回の満容量Qfullの算出に用いられる。
以上のように、算出したSOHを満容量Qfullの算出に用いることにより、放電中であっても、蓄電池の劣化が進んだ場合にも、蓄電池の満容量を精度よく算出することができる。
Furthermore, the
As described above, by using the calculated SOH for calculating the full capacity Qfull, the full capacity of the storage battery can be accurately calculated even when the storage battery is deteriorated even during discharging.
なお、本実施形態では、第1の測定タイミングT1と第2の測定タイミングT2の間の制御内容が充電及び放電の一方に制限されない。すなわち、充電と放電とを自由に切り換えることができる。本実施形態によれば、第1の測定タイミングT1と第2の測定タイミングT2の間の蓄電池10の利用形態の自由度が高まり好ましい。
In the present embodiment, the control content between the first measurement timing T1 and the second measurement timing T2 is not limited to one of charging and discharging. That is, charging and discharging can be switched freely. According to this embodiment, the degree of freedom of the usage form of the
<変形例>
次に、図10を参照して、図1〜図3に示した蓄電制御装置40のハードウエア構成の一例について説明する。
蓄電制御装置40が備える機能の一部または全部は、コンピュータにプログラムを実行させることにより実現することも可能である。
<Modification>
Next, an example of the hardware configuration of the power
Part or all of the functions of the power
プログラムは、様々なタイプの非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体(non-transitory computer readable medium)を用いて格納され、コンピュータに供給することができる。非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体は、様々なタイプの実体のある記録媒体(tangible storage medium)を含む。非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体の例は、磁気記録媒体(例えばフレキシブルディスク、磁気テープ、ハードディスクドライブ)、光磁気記録媒体(例えば光磁気ディスク)、CD−ROM(Read Only Memory)、CD−R、CD−R/W、半導体メモリ(例えば、マスクROM、PROM(Programmable ROM)、EPROM(Erasable PROM)、フラッシュROM、RAM(Random Access Memory))を含む。また、プログラムは、様々なタイプの一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体(transitory computer readable medium)によってコンピュータに供給されてもよい。一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体の例は、電気信号、光信号、及び電磁波を含む。一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体は、電線及び光ファイバ等の有線通信路、又は無線通信路を介して、プログラムをコンピュータに供給できる。 The program may be stored using various types of non-transitory computer readable media and supplied to a computer. Non-transitory computer readable media include various types of tangible storage media. Examples of non-transitory computer-readable media include magnetic recording media (for example, flexible disks, magnetic tapes, hard disk drives), magneto-optical recording media (for example, magneto-optical disks), CD-ROMs (Read Only Memory), CD-Rs, CD-R / W, semiconductor memory (for example, mask ROM, PROM (Programmable ROM), EPROM (Erasable PROM), flash ROM, RAM (Random Access Memory)) are included. The program may also be supplied to the computer by various types of transitory computer readable media. Examples of transitory computer readable media include electrical signals, optical signals, and electromagnetic waves. The temporary computer-readable medium can supply the program to the computer via a wired communication path such as an electric wire and an optical fiber, or a wireless communication path.
図10は、蓄電制御装置40のハードウエア構成を例示するブロック図である。図10に示すように、蓄電制御システムは、プロセッサ1、メモリ2、入出力インターフェイス3、周辺回路4、バス5を有する。周辺回路4には、様々なモジュールが含まれる。
FIG. 10 is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of the power
バス5は、プロセッサ1、メモリ2、周辺回路4及び入出力インターフェイス3が相互にデータを送受信するためのデータ伝送路である。プロセッサ1は、例えばCPU(Central Processing Unit)やGPU(Graphics Processing Unit)などの演算処理装置である。メモリ2は、例えばRAM(Random Access Memory)やROM(Read Only Memory)などのメモリである。入出力インターフェイス3は、入力装置(例:キーボード、マウス、マイク、物理キー、タッチパネルディスプレイ、コードリーダ等)、外部装置、外部サーバ、外部センサ等から情報を取得するためのインターフェイスや、出力装置(例:ディスプレイ、スピーカ、プリンター、メーラ等)、外部装置、外部サーバ等に情報を出力するためのインターフェイスなどを含む。プロセッサ1は、各モジュールに指令を出し、それらの演算結果をもとに演算を行うことができる。
The bus 5 is a data transmission path through which the processor 1, the
また、第1〜第3の実施形態では、蓄電池10と物理的及び/又は論理的に一体となった蓄電制御システムにおいて、満容量Qfullを算出するためのデータの取得及び演算を行った。変形例では、物理的及び/又は論理的に互いに分かれた複数の装置により、満容量Qfullを算出するためのデータの取得及び演算を行ってもよい。
In the first to third embodiments, in the power storage control system physically and / or logically integrated with the
例えば、各蓄電池10に対応して設置された端末装置と、サーバ(例:クラウドサーバ)とにより、満容量Qfullを算出するためのデータの取得及び演算を行ってもよい。端末装置とサーバは、任意の通信手段で互いに情報の送受信ができるよう構成される。
For example, data acquisition and calculation for calculating the full capacity Qfull may be performed by a terminal device installed corresponding to each
この場合、図2に示す電圧測定部20、電流測定部30及び電力変換部50は、端末装置に備えられてもよい。開放電圧推定部41は、端末装置又はサーバに備えられてもよい。容量算出部42は、端末装置又はサーバに備えられてもよい。制御部43は、サーバに備えられてもよい。当該条件を満たすあらゆる組合せを採用できる。
In this case, the
以上、実施形態を参照して本願発明を説明したが、本願発明は上記実施形態に限定されるものではない。本願発明の構成及び詳細には、本願発明のスコープ内で当業者が理解し得る様々に変更をすることができる。 While the present invention has been described with reference to the embodiments, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments. Various changes that can be understood by those skilled in the art can be made to the configuration and details of the present invention within the scope of the present invention.
1 プロセッサ
2 メモリ
3 入出力インターフェイス
4 周辺回路
5 バス
10 蓄電池
11 電池セル
20 電圧測定部
30 電流測定部
40 蓄電制御装置
41 開放電圧推定部
42 容量算出部
43 制御部
50 電力変換部
60A 負極端子
60B 正極端子
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (10)
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する容量算出部と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する制御部と、を含み、
前記制御部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出する、
蓄電制御装置。 An open-circuit voltage estimation unit for estimating an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery;
A capacity calculator that calculates an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A controller that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The controller is
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Calculate the full capacity based on the capacity retention rate that is held,
Power storage control device.
当該関係と、保持している前記容量維持率とに基づいて、前記第1及び第2の残容量を算出する、
請求項1に記載の蓄電制御装置。 Obtain in advance the relationship between the open circuit voltage and the remaining capacity corresponding to the capacity maintenance rate,
Calculating the first and second remaining capacities on the basis of the relationship and the capacity retention rate held;
The power storage control device according to claim 1.
当該関係と、保持している前記容量維持率とに基づいて、前記第1及び第2の測定タイミングを設定する、
請求項1又は2に記載の蓄電制御装置。 Obtain in advance the relationship between the open circuit voltage and the remaining capacity corresponding to the capacity maintenance rate,
Setting the first and second measurement timings based on the relationship and the capacity retention rate being held;
The power storage control device according to claim 1 or 2.
請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の蓄電制御装置。 The controller calculates a full capacity of the storage battery based on a difference between the accumulated capacities at the first and second measurement timings;
The power storage control device according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
請求項1〜4のいずれか一項に記載の蓄電制御装置。 The control unit calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on a difference between the first and second remaining capacity;
The power storage control device according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
以下の式(1)に基づいて、前記制御部が前記蓄電池の前記満容量を算出する、
請求項1〜5のいずれか一項に記載の蓄電制御装置。
Qfull=(Q2−Q1)/{(SOC2−SOC1)/100}・・・式(1) The first remaining capacity is SOC1, the second remaining capacity is SOC2, the accumulated capacity at the first measurement timing is Q1, the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing is Q2, and the full capacity of the storage battery is If Qfull,
Based on the following formula (1), the control unit calculates the full capacity of the storage battery,
The power storage control device according to any one of claims 1 to 5.
Qfull = (Q2-Q1) / {(SOC2-SOC1) / 100} Expression (1)
前記蓄電池の電圧を測定する電圧測定部と、
前記蓄電池の電流を測定する電流測定部と、
前記電圧測定部によって測定された前記電圧に基づいて前記蓄電池の開放電圧を推定する開放電圧推定部と、
前記電流測定部によって測定された前記電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する容量算出部と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する制御部と、を含み、
前記制御部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出する、
蓄電制御システム。 A storage battery,
A voltage measuring unit for measuring the voltage of the storage battery;
A current measuring unit for measuring the current of the storage battery;
An open-circuit voltage estimation unit that estimates an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage measured by the voltage measurement unit;
A capacity calculation unit that calculates an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current measured by the current measurement unit;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A controller that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The controller is
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Calculate the full capacity based on the capacity retention rate that is held,
Power storage control system.
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する算出部と、を含み、
前記算出部は、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出する、
サーバ。 An acquisition unit that acquires an open-circuit voltage of the storage battery estimated based on a voltage of the storage battery and an integrated capacity of the storage battery calculated based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing A calculation unit that calculates the full capacity of the storage battery based on the integrated capacity and the integrated capacity at the second measurement timing;
The calculation unit includes:
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Calculate the full capacity based on the capacity retention rate that is held,
server.
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出する工程と、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出する工程と、を含み、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出する、
蓄電制御方法。 Estimating the open voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery;
Calculating an accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery;
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing Calculating the full capacity of the storage battery based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing,
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Calculate the full capacity based on the capacity retention rate that is held,
Power storage control method.
前記蓄電池の電流に基づいて前記蓄電池の積算容量を算出し、
第1の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第1の残容量と、第2の測定タイミングにおける前記開放電圧に基づいて算出した第2の残容量と、前記第1の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量と、前記第2の測定タイミングにおける前記積算容量とに基づいて、前記蓄電池の満容量を算出し、
算出した前記満容量と初期満容量とから容量維持率を算出して保持し、
保持している前記容量維持率に基づいて、前記満容量を算出するように、
コンピュータを機能させる、
プログラム。 Estimating the open voltage of the storage battery based on the voltage of the storage battery,
Calculate the accumulated capacity of the storage battery based on the current of the storage battery,
The first remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the first measurement timing, the second remaining capacity calculated based on the open circuit voltage at the second measurement timing, and the first remaining capacity calculated at the first measurement timing Based on the accumulated capacity and the accumulated capacity at the second measurement timing, the full capacity of the storage battery is calculated,
Calculate and hold a capacity maintenance rate from the calculated full capacity and initial full capacity,
Based on the capacity maintenance rate that is held, the full capacity is calculated,
Make the computer work,
program.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017065545A JP2018169238A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2017-03-29 | Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017065545A JP2018169238A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2017-03-29 | Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018169238A true JP2018169238A (en) | 2018-11-01 |
Family
ID=64019489
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017065545A Pending JP2018169238A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2017-03-29 | Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2018169238A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111009698A (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2020-04-14 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Information processing method and electronic equipment |
| WO2020262655A1 (en) * | 2019-06-27 | 2020-12-30 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Secondary battery control device |
| WO2023181612A1 (en) | 2022-03-23 | 2023-09-28 | パナソニックエナジー株式会社 | Backup power supply |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011090020A1 (en) * | 2010-01-19 | 2011-07-28 | 株式会社Gsユアサ | Device for measuring state of charge of secondary battery and method for measuring state of charge of secondary battery |
| JP2013044734A (en) * | 2011-08-26 | 2013-03-04 | Gs Yuasa Corp | Capacity computing device, capacity computing method, device to be charged and charge rate reference range determination method |
| WO2014083856A1 (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-05 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Battery management device, power supply, and soc estimation method |
| US20160103185A1 (en) * | 2014-10-14 | 2016-04-14 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Electrified vehicle battery state-of-charge monitoring with aging compensation |
-
2017
- 2017-03-29 JP JP2017065545A patent/JP2018169238A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011090020A1 (en) * | 2010-01-19 | 2011-07-28 | 株式会社Gsユアサ | Device for measuring state of charge of secondary battery and method for measuring state of charge of secondary battery |
| JP2013044734A (en) * | 2011-08-26 | 2013-03-04 | Gs Yuasa Corp | Capacity computing device, capacity computing method, device to be charged and charge rate reference range determination method |
| WO2014083856A1 (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-05 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Battery management device, power supply, and soc estimation method |
| US20160103185A1 (en) * | 2014-10-14 | 2016-04-14 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Electrified vehicle battery state-of-charge monitoring with aging compensation |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020262655A1 (en) * | 2019-06-27 | 2020-12-30 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Secondary battery control device |
| JP7466155B2 (en) | 2019-06-27 | 2024-04-12 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Secondary battery control device |
| CN111009698A (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2020-04-14 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Information processing method and electronic equipment |
| CN111009698B (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2021-04-13 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Information processing method and electronic equipment |
| WO2023181612A1 (en) | 2022-03-23 | 2023-09-28 | パナソニックエナジー株式会社 | Backup power supply |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6686166B2 (en) | Device and method for detecting battery health status | |
| JP5541112B2 (en) | Battery monitoring device and battery monitoring method | |
| US9291682B2 (en) | Degradation state estimating method and degradation state estimating apparatus | |
| US10444296B2 (en) | Control device, control method, and recording medium | |
| EP2851700B1 (en) | Method and terminal for displaying capacity of battery | |
| JP6763376B2 (en) | Battery control device, power storage system, control method and computer-readable medium | |
| JP5843051B2 (en) | Pack battery and secondary battery discharge control method | |
| JP5618393B2 (en) | Power storage system and secondary battery control method | |
| JP6848475B2 (en) | Storage control device, server, storage control method and program | |
| WO2016009757A1 (en) | Battery state detection device, secondary battery system, program product, and battery state detection method | |
| KR20130039681A (en) | Battery status measuring method and battery status measuring apparatus | |
| JP2017511104A (en) | Apparatus and method for controlling a plurality of cells of a battery | |
| JPWO2016051722A1 (en) | Power storage device, control device, power storage system, power storage device control method and control program | |
| JP2016170034A (en) | Remaining battery life prediction device and battery pack | |
| JP2012185124A (en) | State-of-charge estimation device, state-of-charge estimation method, and program | |
| JP2016171716A (en) | Battery residual amount prediction device and battery pack | |
| US20180278064A1 (en) | Storage battery management device, method, and computer program product | |
| JP2017054692A (en) | Power storage system, secondary battery control system, and secondary battery control method | |
| JP2018169238A (en) | Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program | |
| JPWO2018155270A1 (en) | Charging system, battery pack, and protection device | |
| JP5851514B2 (en) | Battery control device, secondary battery system | |
| JP2016024170A (en) | Battery control device | |
| JP2018169237A (en) | Power storage controller, power storage control system, server, power storage control method, and program | |
| JP6478661B2 (en) | Battery cell voltage correction method, battery monitoring device, semiconductor chip, and vehicle | |
| KR20220149428A (en) | Semiconductor device and method of monitoring battery remaining capacity |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200205 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20210119 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210126 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20210803 |