JP2016100352A - Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same - Google Patents
Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2016100352A JP2016100352A JP2014233625A JP2014233625A JP2016100352A JP 2016100352 A JP2016100352 A JP 2016100352A JP 2014233625 A JP2014233625 A JP 2014233625A JP 2014233625 A JP2014233625 A JP 2014233625A JP 2016100352 A JP2016100352 A JP 2016100352A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- film
- wiring board
- printed wiring
- pad
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Production Of Multi-Layered Print Wiring Board (AREA)
- Electric Connection Of Electric Components To Printed Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、プリント配線板およびその製造方法に関する。さらに詳しくは、表面に半導体素子などが搭載される際に、半導体素子の電極端子と接続されるパッドの構造が改善されたプリント配線板およびその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a printed wiring board and a manufacturing method thereof. More particularly, the present invention relates to a printed wiring board having an improved structure of a pad connected to an electrode terminal of a semiconductor element when a semiconductor element or the like is mounted on the surface, and a method for manufacturing the same.
特許文献1には、その一面側に半導体素子がハンダバンプを介して搭載される多層基板が示されている。しかし、この特許文献1に記載される多層基板では、半導体素子が接続されるパッドの表面が平坦で、パッド周囲の最外層の表面と同一の高さか、または、最外層の表面に対して凹んでいる。 Patent Document 1 discloses a multilayer substrate on which a semiconductor element is mounted via a solder bump on one surface side. However, in the multilayer substrate described in Patent Document 1, the surface of the pad to which the semiconductor element is connected is flat and has the same height as the surface of the outermost layer around the pad, or is recessed with respect to the surface of the outermost layer. It is out.
特許文献1に示されるような、表面が平坦なパッドで、その表面が、パッド周囲の表面と同一または凹んでいると、ハンダバンプの高さを高くすることが難しいと考えられる。このため、半導体素子と多層基板との熱膨張係数の差に起因する応力を高さの高いハンダバンプにより吸収し難くなったり、多層基板と半導体素子間にアンダーフィル樹脂を充填し難くなったりすると考えられる。また、パッドとハンダバンプとの接触面積が平坦部だけで小さいので、ハンダ付けの信頼性も低下すると考えられる。 If the surface of the pad is flat as shown in Patent Document 1 and the surface is the same as or recessed from the surface around the pad, it is considered difficult to increase the height of the solder bump. For this reason, it is difficult to absorb the stress caused by the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the semiconductor element and the multilayer substrate with a high solder bump, and it is difficult to fill the underfill resin between the multilayer substrate and the semiconductor element. It is done. Further, since the contact area between the pad and the solder bump is small only at the flat portion, it is considered that the reliability of soldering also decreases.
本発明の目的は、パッドとハンダバンプとの接続の信頼性を向上させると共に、半導体素子とプリント配線板との熱膨張係数の差に基づく応力を緩和しやすい、すなわち高さの高いバンプを形成することができるプリント配線板およびその製造方法を提供することである。 An object of the present invention is to improve the reliability of connection between a pad and a solder bump and to form a bump that is easy to relieve stress based on a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between a semiconductor element and a printed wiring board, that is, has a high height. It is providing the printed wiring board which can be manufactured, and its manufacturing method.
本発明のプリント配線板は、第1面、および該第1面と反対側の第2面を有する樹脂絶縁層と、前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第1面側に形成されている、電子部品を搭載するためのパッドおよび配線パターンを含む第1導体層と、前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面に形成される第2導体層と、前記樹脂絶縁層を貫通して形成され、前記第1導体層と前記第2導体層とを接続するビア導体と、を有している。そして、前記パッドは、前記樹脂絶縁層内に埋め込まれるベース部と前記樹脂絶縁層から突出しているポスト部とからなると共に、前記ポスト部の幅は前記ベース部の幅より小さく、かつ、前記ベース部の前記ポスト側の面が前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第1面と面一であり、前記パッドは、前記ベース部と前記ポスト部とが一体に形成された電気めっき膜である。 The printed wiring board of the present invention includes a resin insulating layer having a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface, and an electronic component formed on the first surface side of the resin insulating layer. A first conductor layer including a pad and a wiring pattern for mounting; a second conductor layer formed on the second surface of the resin insulating layer; and the first conductor formed through the resin insulating layer. And a via conductor connecting the layer and the second conductor layer. The pad includes a base portion embedded in the resin insulating layer and a post portion protruding from the resin insulating layer, and the width of the post portion is smaller than the width of the base portion, and the base The post-side surface of the portion is flush with the first surface of the resin insulating layer, and the pad is an electroplated film in which the base portion and the post portion are integrally formed.
本発明のプリント配線板の製造方法は、金属膜上に第1のめっきレジスト膜のパターンを形成することと、前記第1のめっきレジスト膜のパターンから露出する前記金属膜の表面に電気めっき膜を形成することと、前記第1のめっきレジスト膜を除去することと、前記第1のめっきレジスト膜の除去により露出する前記金属膜および前記電気めっき膜の表面にバリア層を形成することと、前記バリア層上に第2のめっきレジスト膜のパターンを形成することと、前記第2のめっきレジスト膜のパターンから露出する前記バリア層上に電気めっき膜を形成することにより、パッドのパターンを含む第1導体層を形成することと、前記第2のめっきレジスト膜を除去することと、前記第1導体層のパターンの間隙部および表面に形成され、前記第1導体層側を第1面、該第1面と反対面を第2面とする樹脂絶縁層を形成することと、前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面側から開口を形成し、該開口内にビア導体を形成すると共に、前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面に、前記ビア導体を介して前記第1導体層と接続される第2導体層を形成することと、前記金属膜および該金属膜上に形成された前記電気めっき膜を除去することと、前記バリア層を全面に亘って除去することと、を含む。 The method for manufacturing a printed wiring board according to the present invention includes forming a pattern of a first plating resist film on a metal film, and forming an electroplating film on the surface of the metal film exposed from the pattern of the first plating resist film. Forming a barrier layer on the surface of the metal film and the electroplating film exposed by removing the first plating resist film, and removing the first plating resist film; A pattern of a pad is included by forming a pattern of a second plating resist film on the barrier layer and forming an electroplating film on the barrier layer exposed from the pattern of the second plating resist film. Forming the first conductor layer; removing the second plating resist film; and forming the first conductor layer in a gap portion and a surface of the pattern; Forming a resin insulating layer having a conductor layer side as a first surface and a surface opposite to the first surface as a second surface; and forming an opening from the second surface side of the resin insulating layer; Forming a via conductor and forming a second conductor layer connected to the first conductor layer via the via conductor on the second surface of the resin insulation layer; and the metal film and the metal film Removing the electroplated film formed thereon, and removing the barrier layer over the entire surface.
本発明の一実施形態のプリント配線板およびその製造方法が、図面を参照して説明される。図1は、本実施形態のプリント配線板1の断面説明図である。本実施形態のプリント配線板1は、第1面11a、およびその第1面11aと反対側の第2面11bを有する樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11a側に電子部品を搭載するためのパッド12c、第1パターン12a、および配線パターン12bを含む第1導体層12が形成されている。そして、樹脂絶縁層11の第2面11bに第2導体層14が形成され、さらに、樹脂絶縁層11を貫通して、第1導体層12と第2導体層14とを接続するビア導体15が形成されている。そして、パッド12cは、樹脂絶縁層11内に埋め込まれるベース部12c1と樹脂絶縁層11から突出しているポスト部12c2とからなると共に、ポスト部12c2の幅dはベース部12c1の幅wより小さく、かつ、ベース部12c1のポスト12c2側の面が樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと面一であり、パッド12cは、ベース部12c1とポスト部12c2とが一体に形成された電気めっき膜である。
A printed wiring board and a manufacturing method thereof according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional explanatory view of a printed wiring board 1 of the present embodiment. The printed wiring board 1 of the present embodiment is a pad for mounting electronic components on the
ここにポスト部12c2およびベース部12c1の「幅」とは、ポスト部12c2およびベース部12c1の樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと略平行な面での断面形状で端から端までの一番長い部分の距離を意味し、断面が円形であれば直径を、矩形であれば対角線の長さ、楕円形状であれば長径の長さを意味する。
Here, the “width” of the post portion 12c2 and the base portion 12c1 is the cross-sectional shape of the post portion 12c2 and the base portion 12c1 in the plane substantially parallel to the
すなわち、本実施形態のプリント配線板1は、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面側の図示しない半導体素子が搭載される第1導体層12のパッド12cが、ベース部12c1とポスト部12c2とを有する構造に形成され、しかも電気めっきにより一体に形成されている。さらに、このベース部12c1は、第1パターン12aおよび配線パターン12bと同様に、樹脂絶縁層11内に埋め込まれ、その一面のみが樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと面一で露出し、ポスト部12c2は、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aから突出していることに特徴がある。
That is, in the printed wiring board 1 of the present embodiment, the
このような構造に形成されることにより、このパッドに図示しない半導体素子の電極端子がハンダバンプにより接続される場合に、ポスト部12c2の上面との間でハンダ付けされるため、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと半導体素子の電極端子が設けられる面との間の距離を大きくすることができる。その結果、プリント配線板1と半導体素子との間での熱膨張係数の違いにより生じる応力が吸収されやすくなる。また、その間の隙間にアンダーフィルとする樹脂層が流れ込みやすくなる。しかも、本実施形態によれば、パッド12cのベース部12c1とポスト部12c2とが一体に形成されているため、例えば銅めっきなどにより形成されれば、非常に電気抵抗を小さくすることができ、表面にニッケルメッキなどが施された場合と比べて、電気特性の優れたプリント配線板が得られる。
By forming in this structure, when the electrode terminal of the semiconductor element (not shown) is connected to the pad by a solder bump, it is soldered between the upper surface of the post portion 12c2, and therefore the
さらに、パッドがベース部12c1とポスト部12c2とで形成されており、ポスト部12c2が樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aよりも突出しているので、ハンダ付けがされた場合に、ポスト部12c2の側面およびベース部12c1の露出面にもハンダが濡れやすく、広い面積で接着されるため、ハンダ付けの信頼性が向上する。しかも、パッド12cの表面には、パッド12cが、たとえば銅で形成された場合に、銅よりも電気抵抗が高いニッケルメッキやスズめっきのような膜が設けられないので、ハンダバンプなどと、電気抵抗の低い銅からなるパッド12cとが直接接合されることが可能となり、図示しない半導体素子などとの接続部の電気抵抗が小さくなることがある。
Further, since the pad is formed by the base portion 12c1 and the post portion 12c2, and the post portion 12c2 protrudes from the
さらに、本実施形態のプリント配線板1は、後述する製造方法の実施形態で示されるように、バリア層23(図2D参照)としてニッケルめっき膜も使用されるが、そのニッケルめっき膜は、エッチングの際のバリア層として用いられるもので、パッドの部分だけに形成されるのではなく、全面に形成され、後に全てエッチングにより除去されるものである。そのため、パッド12cにバリア層として形成されたものが後にエッチング除去された場合と異なり、ベース部12c1の表面が樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aよりも凹むことがなく、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと面一に形成され得る。すなわち、パッド12cの部分だけに、たとえばニッケルめっき膜が施されて製造され、最終的にそのニッケルめっき膜がエッチングにより除去されると、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aからそのニッケルめっき膜の厚さ分だけ凹むことになる。その凹み分だけバンプが下がることになるため、樹脂絶縁層11と半導体素子との間隙が小さくなる。しかし、本実施形態のプリント配線板では、ニッケルめっき膜は全面に形成され、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aとパッド12cのベース部12c1の表面とは同じニッケルめっき膜に面しているため、ニッケルめっき膜がエッチング除去されても、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aとパッド12cのベース部12c1の表面とは面一になる。その結果、ハンダバンプはたとえベース部12c1の露出面までハンダが濡れ広がっても、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aよりも下がることはない。そのため、ハンダバンプの高さを高くすることができる。
Furthermore, the printed wiring board 1 of the present embodiment uses a nickel plating film as the barrier layer 23 (see FIG. 2D) as shown in an embodiment of the manufacturing method described later, but the nickel plating film is etched. In this case, it is used as a barrier layer and is not formed only on the pad portion, but is formed on the entire surface, and is later removed by etching. Therefore, unlike the case where what is formed as a barrier layer on the
樹脂絶縁層11は、第1面11aと、第1面11aの反対側の第2面11bとを有する絶縁層である。樹脂絶縁層11は、たとえばガラス繊維のような芯材にフィラーを含む樹脂組成物を含浸させたものでもよく、芯材を含まないで、フィラーを含む樹脂組成物だけで形成されたものでもよい。また、1層であってもよく、複数の絶縁層から形成されていてもよい。樹脂絶縁層11は、複数の絶縁層から形成されるならば、たとえば熱膨張率、柔軟性、厚さが容易に調整され得る。樹脂としては、エポキシ等が例示される。樹脂絶縁層11の厚さとしては、25〜100μmが例示される。第1面11a側には、第1導体層12が一面だけ露出するように、樹脂絶縁層11内に埋め込まれて形成され、樹脂絶縁層11の第2面11bには、第2導体層14が形成されている。
The
第1導体層12は、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11a側の樹脂絶縁層11内に埋め込まれて形成されるパターンである。パターンとしては、第2導体層14と接続するためのビア導体15と接続される第1パターン12a、配線パターン12b、前述の半導体素子と接続するためのパッド12cなどが形成されている。第1導体層12を形成する方法は、特に限定されない。好ましくは、第1導体層12は、電気めっきにより形成される。しかし、他の金属箔などを含んでもよい。第1導体層12が主として電気めっき膜であるならば、純粋な金属膜として形成されるという利点がある。第1導体層12を構成する材料は、銅が例示される。銅は、電気めっきが容易でありながら、電気抵抗が小さく腐食の問題も生じにくい。この第1導体層12の厚さは、10〜20μmが例示される。
The
この第1導体層12は、後述する製造方法の例で明らかになるように、樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11a側に埋め込んで形成されながら、パッド12cのポスト部12c2だけが樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aから突出している。後述されるように、ベース部12c1とポスト部12c2の凹凸部と逆パターンの金属膜19と電気めっき膜22(図2C参照)により形成された凹凸の表面にニッケルなどのめっき膜が形成され、その凹部内に銅などの電気めっき膜が埋め込まれることにより形成される。従って、ベース部12c1とその中心部に立ち上がっているポスト部12c2とからなる逆T字型のパッド12cが電気めっきにより一体に形成されている。
The
第2導体層14は、樹脂絶縁層11の第2面11b上に形成されている。すなわち、この第2導体層14は樹脂絶縁層11内には埋め込まれないで、第2面11b上に形成されている。第2導体層14を形成する方法は、特に限定されない。第2導体層14を構成する材料は、銅が例示される。しかし、これには限定されない。第2導体層14の構成は、たとえば金属箔14aと、無電解めっきなどからなる金属被膜14b(図2J参照)と、電気めっき膜14c(図2K参照)などとにより形成されてもよいし、金属箔がなくて、金属被膜14aと電気めっき膜14cとで構成されてもよい。本実施形態では、銅箔14aと無電解銅めっきからなる金属被膜14bと電気めっき膜14cとで構成されている。第2導体層14の厚さは、10〜20μmが例示される。第2導体層14は、図1では、これらの合成層として1層で示されている。この電気めっき膜により形成される場合、予め不要な部分にレジスト膜が形成されて電気めっきが行われるアディティブ法でもよいし、全面に電気めっき膜が形成された後に、不要部分がエッチングにより除去されるサブトラクト法で形成されてもよい。しかし、ファインピッチの配線層を形成するには、パターニングの点で、アディティブ法の方が好ましい。いずれにしても所望の回路パターンが形成されることにより、第2導体層14が形成される。
The
ビア導体15は、樹脂絶縁層11を貫通し、第1導体層12と第2導体層14とを電気的に接続している。ビア導体15は、後述する製造方法で説明されるように、樹脂絶縁層11の第2面11bに設けられる金属箔14aの上からレーザ光照射による加工により第1導体層12が底面となるような開口11dが形成され、その開口11d内に導体を埋めることにより形成されている。ビア導体15としては、たとえば銅が例示され、本実施形態では、第2導体層14の形成と同時に銅の電気めっきにより埋め込まれているので、銅めっき膜により形成される。
The via
第1導体層12の図示しない電子部品が搭載されるパッド12cには、OSPなどの保護膜が形成される。後述するハンダバンプなどとの接続性を向上させる。保護膜は、Ni/Au、Ni/Pd/Au、Sn等の表面処理でもよいが、たとえばパッド12cが銅で形成される場合に、前述のように、電気抵抗の良好なパッド12cの銅とハンダバンプなどとが直接接合されることにより接合部の電気抵抗が低くなるという観点から、前述のOSPが好ましい。
A protective film such as OSP is formed on the
次に、図1に示されるプリント配線板の製造方法が図2A〜2Oを参照しながら説明される。 Next, a method for manufacturing the printed wiring board shown in FIG. 1 will be described with reference to FIGS.
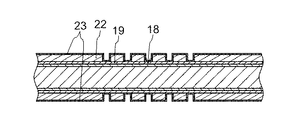
まず、図2Aに示されるように、金属膜19上に第1のめっきレジスト膜21のパターンが形成される。具体的には、まず、ダミー基板18aの両面に、キャリア銅箔のようなキャリア金属箔18bが貼り付けられた金属膜19のキャリア金属箔18b側がダミー基板18aに貼り付けられて、ダミー基板18aとキャリア金属箔18bとで支持基板18が形成され、その支持基板18の表面に金属膜19が貼り付けられたものが準備される。この例では、キャリア金属箔18bと金蔵膜19とが先に接着され、その後にダミー基板18a側にキャリア金属箔18bを向けて、熱圧着により接合される。この金属膜19の表面にめっきレジスト膜が設けられ、パターニングされることにより第1のめっきレジスト膜21が形成される。この第1のめっきレジスト膜21は、前述のパッド12cのポスト部12c2に相当する部分であるので、そのパターンに合せてパターニングされる。しかし、後述するニッケルめっき膜23(図2D参照)の厚さ分だけ大きく形成される。
First, as shown in FIG. 2A, a pattern of the first plating resist
図2Aに示される例では、支持基板18の両面に金属膜19が、接着剤等により貼り付けられる。ダミー基板18aおよびキャリア金属箔18bは、後で除去して廃棄されるものなので、支持基板18の両面に金属膜19が形成されることにより、材料の有効利用が図られている。しかし、片面だけで製造されてもよいし、両面で異なるプリント配線板が形成されてもよい。この実施例では、支持基板18の両面に金属膜19が設けられても、図の支持基板18の上側と下側は全く同じ構造のプリント配線板が形成されており、以下の説明では、主として上側だけについての説明がなされ、図面の符号も下側の部分については適当に省略されている。また、支持基板18は、廃棄されるものであるため、材料も特に限定されないが、キャリア金属箔18bとしては、たとえば銅、ニッケルなどが用いられる。このキャリア金属箔18bと金属膜19とは、後で分離されるため、分離しやすい接着剤、たとえば熱可塑性樹脂により全面が接着されてもよい。このような接着剤で接着されることにより、後の工程で温度を上昇させて引き剥されることにより、金属膜19と支持基板18とは容易に分離される。
In the example shown in FIG. 2A,
または、たとえば支持基板18の周囲だけで通常の接着剤により貼り付けられてもよい。周囲が切断除去されることにより、容易に分離されるからである。以下に説明される実施形態では、前者の方法を採用している。この支持基板18と金属膜19の両者間には、熱膨張率などの差が無いことが望ましいため、金属膜19にニッケルが用いられるのであれば、支持基板18の表面に設けられる金属箔もニッケルが望ましい。しかし、これには制約されない。また、この支持基板18の金属膜19が設けられる面には、適宜、剥離層が設けられても良い。
Or, for example, it may be attached with a normal adhesive only around the
次に、図2Bに示されるように、第1のめっきレジスト膜21のパターンから露出する金属膜19の表面に電気めっき膜22が形成される。具体的には、金属膜19を給電層として、たとえば銅の電気めっきを行うことにより、第1のめっきレジスト膜21が形成されないで金属膜19が露出する部分だけ電気めっき膜22が形成される。この電気めっきは、通常の方法で行われる。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2B, an
次に、図2Cに示されるように、第1のめっきレジスト膜21が除去される。具体的には、たとえばレジスト剥離液に浸漬することにより、第1のめっきレジスト膜21のみが除去されて、電気めっき膜22のパターンのみが残る。このパターンは、前述の第1のめっきレジスト膜21のパターンと逆のパターン、すなわち第1のめっきレジスト膜21のパターンのなかったところに電気めっき膜22のパターンが形成され、第1のめっきレジスト膜21のパターンの部分がなくなったものである。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2C, the first plating resist
その後、図2Dに示されるように、第1のめっきレジスト膜21の除去により露出する金属膜19および電気めっき膜22の表面にバリア層23が形成される。具体的には、たとえば電気めっき膜22と金属膜19を給電層としてニッケルなどの電気めっきを行うことにより、露出面の全面にニッケル膜からなるバリア層23が形成される。このバリア層23は、後述する電気めっき膜22がエッチングにより除去される際(図2N参照)に、下層のパッド部12c2などの第1導体層12がエッチングされないようにするものであるため、ニッケルめっきでなくても、電気めっき膜22と異なる材料であればよい。また、このバリア層23の厚さは、数μm程度あれば充分である。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2D, a
その後、図2Eに示されるように、バリア層23上に第2のめっきレジスト膜24のパターンが形成される。この第2のめっきレジスト膜24のパターンは、第1導体層12のパターンを形成するもので、前述の第1パターン12a、配線パターン12b、パッド12cが形成される部分が露出するようにパターニングされる。すなわち、第1導体層12のパターンの部分のみが除去されて、第1導体層12のパターンのない部分のみに第2のめっきレジスト膜24のパターンが形成される。具体的には、めっきレジスト用フィルムの積層または塗付により全面にめっきレジスト膜が形成され、写真食刻により所望のパターンが形成される。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2E, a pattern of the second plating resist
その後、図2Fに示されるように、第2のめっきレジスト膜24のパターンから露出するバリア層23上に電気めっき膜が形成されることにより、パッド12cなどのパターンを含む第1導体層12が形成される。具体的には、バリア層23を給電層として電気めっきが施されることにより、バリア層23の露出面、すなわち、前述の電気めっき膜22のパターンの凹部内およびそのパターンの表面上に、バリア層23を介して電気めっき膜が形成され、第1導体層12が形成される。この第1導体層12は、前述のように、ビア導体15が接続される第1パターン12aと、配線パターン12bと、パッド12cとが形成されている。すなわち、このパターンが形成されるように、前述の第2のめっきレジスト膜24のパターンが形成されている。このパッド12cのパターンは、前述のように、電気めっき膜22の凹部内に形成されたポスト部12c2と、第1パターン12aなどと同一層に形成されるベース部12c1とで一体に形成されている。この電気めっき膜は、電気抵抗が小さいことから銅が好ましいが、銅に限定されるものではない。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2F, an electroplating film is formed on the
次に、図2Gに示されるように、第2のめっきレジスト膜24が除去される。この第2のめっきレジスト膜24の除去も、前述の第1のめっきレジスト膜21の除去と同様に、することにより、第2のめっきレジスト膜22のみが簡単に除去される。その結果、図2Gに示されるように、第1導体層12のパターンが顕在化する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2G, the second plating resist
次に、図2Hに示されるように、第1導体層12のパターンの間隙部および第1導体層12の表面に樹脂絶縁層11が形成され、第1導体層12側を第1面11a、その第1面11aと反対面を第2面11bとする樹脂絶縁層11とされる。具体的には、樹脂フィルム状のプリプレグと第2導体層14の一部となる金属箔14aが積層されて接着される。このプリプレグおよび金属箔14aの接着は、加圧および加熱して貼り合わせる方法が用いられる。この金属箔14aは、無くても構わない。設けられる場合でも、薄くてよく、2〜5μm程度の厚さがあれば充分である。なお、樹脂絶縁層11と面する側の第1導体層12などの面は粗面に形成されていることが望ましいが、図では省略されている。粗面にする方法としては、ソフトエッチング処理や、黒化(酸化)−還元処理などが例示される。また、粗化処理の前に、粗化を安定させるために電気めっき銅の結晶を成長させるアニール処理が行われてもよい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2H, a
次に、図2Iに示されるように、樹脂絶縁層11の第2面11b側から開口11dが形成される。この開口11dを形成する方法は、レーザ光照射の方法が用いられる。すなわち、第1樹脂絶縁層11の両面に設けられる第1導体層12と第2導体層14とが接続される部分に形成され、第2導体層14の一部となる第2金属箔14aの表面から第1導体層12の第1パターン12aの底面に向けて、CO2レーザ光等が照射されることにより加工される。その結果、樹脂絶縁層11に、ビア導体15用の開口11dが形成される。
Next, as illustrated in FIG. 2I, an
その後、図2Jに示されるように、開口11dの内面および第2金属箔14a上に無電解めっき膜等の金属被膜14bが形成される。この金属被膜14bは、開口11d内の樹脂絶縁層11上に電気めっき膜を形成するための給電層とするためである。この金属被膜14bは、無電解メッキ法でなくても、スパッタリングや真空蒸着などで形成されてもよい。そして、その表面にレジスト膜25が形成される。このレジスト膜25は、第2導体層14のパターン以外のところに電気めっき膜が付着しないように、カバーするもので、このようなアディティブ法を用いないで、後からパターニングをするサブトラクト法を用いるなら、このレジスト膜25の形成は不要である。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2J, a
その後、図2Kに示されるように、金属被膜14bを給電層としてその表面に、たとえば電気めっきにより、開口11d内にビア導体15が形成されると共に、金属箔14a上の金属被膜14bの表面に電気めっき膜14cの層が形成される。この電気めっき膜14cは、たとえば全面に形成されて、第2導体層14の形成と共に同時にパターニングされてもよいが、この例では、前述の図2Jに示されるように、レジスト膜25が形成され、第2導体層14のパターンの部分だけを開口して、その開口部のみに電気めっきが施されることにより、パターンめっきが施されている。本実施形態では、この金属箔14a、金属被膜14bおよび電気めっき膜14cにより第2導体層14が構成され、図1では、これらをまとめて1層で第2導体層14として示されている。なお、図2Kにおいては、金属箔14aと金属被膜14bがまだ全面に設けられたままで、完全にはパターニングされていないが、便宜上第2導体層14とされている。
After that, as shown in FIG. 2K, the
その後、たとえば図2Lに示されるように、支持基板18が除去される。なお、支持基板18が除去されることにより2個の積層体が得られるが、図2Lにおいて、支持基板18の下側の積層体のみが示されている。前述のように、支持基板18(ダミー基板18aの表面に貼り付けられるキャリア銅箔18b)と金属膜19とは、たとえば温度を上昇させてずらせることにより剥離することができるような熱可塑性樹脂により接着されているだけであるため、温度を上昇させて力が加えられるだけで、支持基板18は簡単に分離される。その結果、図2Lに示されるように、金属膜19の支持基板18との接合面が露出する。なお、このダミー基板18と金属膜13とがその周囲で接着されている場合には、その接着されている部分の内側(製品群側)で切断されることにより、簡単に分離され得る。
Thereafter, for example, as shown in FIG. 2L, the
次に、図2Mに示されるように、第2導体層14側の全面に、たとえばPETフィルムなどからなる保護フィルム26が貼り付けられる。次の工程での金属膜19および電気めっき膜22のエッチング除去の際に第2導体層14もエッチングされないように、保護するためである。従って、エッチング液から第2導体層14が保護されれば、PETフィルムに限定されず、他の材料からなる保護フィルムであってもよい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2M, a
その後、金属膜19および金属膜19上に形成された電気めっき膜22を除去する。具体的には、金属膜19および電気めっき膜22は、通常銅により形成されているので、たとえば銅をエッチングするエッチング液に浸漬することにより、金属膜19および電気めっき膜22をエッチング除去する。エッチング液により、金属膜19および電気めっき膜22の銅が溶解して除去される。しかし、その下のバリア層23は、たとえばニッケルなどの異なる金属により形成されているので、エッチングされず、バリア層23が露出すると、エッチングは止まる。このバリア層23はニッケルでなくても、金属膜19や電気めっき膜22に用いられる材料と異なる材料であれば、他の材料でもよい。要は、金属膜19および電気めっき膜22のエッチングの際に、その境界部でエッチングが止まる材料であればよい。
Thereafter, the
その後、図2Oに示されるように、バリア層23が全面に亘って除去される。具体的には、バリア層23がニッケルで形成されている場合、ニッケルをエッチングし、銅をエッチングしない、たとえば硫酸と過酸化水素を含むエッチング液に浸漬することにより、バリア層23のみが溶解して除去され、第1導体層12が露出する。第1導体層12は、全くエッチングされないため、バリア層23の面に並んでいた樹脂絶縁層11の第1面11aと第1導体層12の各パターンの露出面とは面一になって露出する。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2O, the
その後、保護フィルム26が剥離され、さらに、軽く銅をエッチングするエッチング液に全体を浸漬する。第2導体層の金属箔14aと金属被膜14bが全面に形成されて第2導体層の各パターンを連結している状態になっているので、第2導体層14の各パターン間をエッチングして除去し、各パターンを分離するためである。なお、このエッチングは、金属箔14aおよび金属被膜14bが共に非常に薄く、数μm程度であるため、他の部分をマスクすることなく、全体をエッチング液に浸漬することにより、各パターンを分離独立させることができる。その状態が図1に示されている。なお、この図1では、第2導体層14の金属箔14aおよび金属被膜14bの区別は図示されていない。
Thereafter, the
なお、この第2導電層14側に、さらに樹脂絶縁層や導体層が積層され、多層プリント配線板とされることもできる。さらに、最外層にはソルダーレジスト層が設けられ、接続部だけに開口部が形成されるが、上記実施例では省略されている。なお、図示しないソルダーレジスト層の開口部から露出するパッド12cや配線パターン12bの露出部の表面には、OSP、Ni/Au、Ni/Pd/Au、Snなどの表面処理が行われる。パッド12cには、前述のようにOSPが塗布されることが好ましい。
A resin insulating layer and a conductor layer may be further laminated on the second
1 プリント配線板
11 樹脂絶縁層
11a 第1面
11b 第2面
11d 開口
12 第1導体層
12a 第1パターン
12b 配線パターン
12c パッド
12c1 ベース部
12c2 ポスト部
14 第2導体層
14a 金属箔
14b 金属被膜
14c 電気めっき膜
15 ビア導体
18 支持基板
19 金属膜
21 第1のめっきレジスト膜
22 電気めっき膜
23 バリア層
24 第2のめっきレジスト膜
25 レジスト膜
26 保護フィルム
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Printed
Claims (11)
前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第1面側に形成されている、電子部品を搭載するためのパッドおよび配線パターンを含む第1導体層と、
前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面に形成される第2導体層と、
前記樹脂絶縁層を貫通して形成され、前記パッドと前記第2導体層とを接続するビア導体と、
を有するプリント配線板であって、
前記パッドは、前記樹脂絶縁層内に埋め込まれるベース部と前記樹脂絶縁層から突出しているポスト部とからなると共に、前記ポスト部の幅は前記ベース部の幅より小さく、かつ、前記ベース部の前記ポスト側の面が前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第1面と面一であり、
前記パッドは、前記ベース部と前記ポスト部とが一体に形成された電気めっき膜である。 A resin insulation layer having a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface;
A first conductor layer formed on the first surface side of the resin insulation layer, including a pad and a wiring pattern for mounting an electronic component;
A second conductor layer formed on the second surface of the resin insulation layer;
A via conductor formed through the resin insulating layer and connecting the pad and the second conductor layer;
A printed wiring board having
The pad includes a base portion embedded in the resin insulating layer and a post portion protruding from the resin insulating layer, and the width of the post portion is smaller than the width of the base portion, and The post-side surface is flush with the first surface of the resin insulation layer;
The pad is an electroplated film in which the base portion and the post portion are integrally formed.
金属膜上に第1のめっきレジスト膜のパターンを形成することと、
前記第1のめっきレジスト膜のパターンから露出する前記金属膜の表面に電気めっき膜を形成することと、
前記第1のめっきレジスト膜を除去することと、
前記第1のめっきレジスト膜の除去により露出する前記金属膜および前記電気めっき膜の表面にバリア層を形成することと、
前記バリア層上に第2のめっきレジスト膜のパターンを形成することと、
前記第2のめっきレジスト膜のパターンから露出する前記バリア層上に電気めっき膜を形成することにより、パッドのパターンを含む第1導体層を形成することと、
前記第2のめっきレジスト膜を除去することと、
前記第1導体層のパターンの間隙部および表面に形成され、前記第1導体層側を第1面、該第1面と反対面を第2面とする樹脂絶縁層を形成することと、
前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面側から開口を形成し、該開口内にビア導体を形成すると共に、前記樹脂絶縁層の前記第2面に、前記ビア導体を介して前記第1導体層と接続される第2導体層を形成することと、
前記金属膜および該金属膜上に形成された前記電気めっき膜を除去することと、
前記バリア層を全面に亘って除去することと、
を含む。 A method of manufacturing a printed wiring board,
Forming a pattern of a first plating resist film on the metal film;
Forming an electroplating film on the surface of the metal film exposed from the pattern of the first plating resist film;
Removing the first plating resist film;
Forming a barrier layer on the surface of the metal film and the electroplating film exposed by removing the first plating resist film;
Forming a pattern of a second plating resist film on the barrier layer;
Forming a first conductor layer including a pad pattern by forming an electroplating film on the barrier layer exposed from the pattern of the second plating resist film;
Removing the second plating resist film;
Forming a resin insulation layer formed on a gap and a surface of the pattern of the first conductor layer, the first conductor layer side being a first surface, and a surface opposite to the first surface being a second surface;
An opening is formed from the second surface side of the resin insulating layer, a via conductor is formed in the opening, and the first conductor layer is formed on the second surface of the resin insulating layer via the via conductor. Forming a second conductor layer to be connected;
Removing the metal film and the electroplated film formed on the metal film;
Removing the barrier layer over the entire surface;
including.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014233625A JP2016100352A (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2014-11-18 | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014233625A JP2016100352A (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2014-11-18 | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016100352A true JP2016100352A (en) | 2016-05-30 |
Family
ID=56078106
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014233625A Pending JP2016100352A (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2014-11-18 | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2016100352A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021097103A (en) * | 2019-12-16 | 2021-06-24 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Wiring board and semiconductor device |
| CN114073171A (en) * | 2019-08-20 | 2022-02-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Circuit embedded substrate, chip packaging structure and substrate preparation method |
| CN114900994A (en) * | 2022-04-18 | 2022-08-12 | 广州广芯封装基板有限公司 | Embedded circuit type circuit board and preparation method thereof |
-
2014
- 2014-11-18 JP JP2014233625A patent/JP2016100352A/en active Pending
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114073171A (en) * | 2019-08-20 | 2022-02-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Circuit embedded substrate, chip packaging structure and substrate preparation method |
| JP2021097103A (en) * | 2019-12-16 | 2021-06-24 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Wiring board and semiconductor device |
| CN114900994A (en) * | 2022-04-18 | 2022-08-12 | 广州广芯封装基板有限公司 | Embedded circuit type circuit board and preparation method thereof |
| CN114900994B (en) * | 2022-04-18 | 2023-03-28 | 广州广芯封装基板有限公司 | Embedded circuit type circuit board and preparation method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5010737B2 (en) | Printed wiring board | |
| JP5100081B2 (en) | Electronic component-mounted multilayer wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US9698094B2 (en) | Wiring board and electronic component device | |
| JP2016063130A (en) | Printed wiring board and semiconductor package | |
| JP2015211194A (en) | Printed wiring board, semiconductor package and printed wiring board manufacturing method | |
| JP2018032657A (en) | Printed wiring board and method for manufacturing printed wiring board | |
| JP2017152536A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2016021534A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JPWO2007069427A1 (en) | Electronic component built-in module and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2015225895A (en) | Printed wiring board, semiconductor package and printed wiring board manufacturing method | |
| US10211119B2 (en) | Electronic component built-in substrate and electronic device | |
| JP2015226013A (en) | Printed wiring board and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2018082084A (en) | Printed circuit board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2016021535A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP2018032659A (en) | Printed wiring board and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2016100352A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP5539453B2 (en) | Electronic component-mounted multilayer wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2015195308A (en) | Printed wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5315447B2 (en) | Wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US20140201992A1 (en) | Circuit board structure having embedded electronic element and fabrication method thereof | |
| JP5363377B2 (en) | Wiring board and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN107305849B (en) | Packaging structure and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR102141102B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor package substrate and semiconductor package substrate manufactured using the same | |
| JP2015204379A (en) | Printed wiring board | |
| TWI420989B (en) | Printed circuit board and method of manufacturing the same |