JP2013185856A - Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect - Google Patents
Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013185856A JP2013185856A JP2012049081A JP2012049081A JP2013185856A JP 2013185856 A JP2013185856 A JP 2013185856A JP 2012049081 A JP2012049081 A JP 2012049081A JP 2012049081 A JP2012049081 A JP 2012049081A JP 2013185856 A JP2013185856 A JP 2013185856A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sound wave
- position measurement
- sound
- doppler effect
- wind speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 39
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 88
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000009333 weeding Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241000209094 Oryza Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000012271 agricultural production Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Velocity Or Position Using Acoustic Or Ultrasonic Waves (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、測定分野における、特に精度よく位置測定できるドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法および風速測定方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a position measuring method and a wind speed measuring method using the Doppler effect capable of measuring a position with high accuracy in the measurement field.
近年、日本の農業において、農業従事者の減少や高齢化に伴い、農業生産、管理作業等の省力化や低コスト化がますます重要な課題となっている。その中で自動化が進んでいない作業の中で、畦畔での除草作業が挙げられる。特に、中山間地の棚田や段畑においては、刈払い機など人力に依存しているのが現状で、この重労働かつ危険な除草作業を自動で行うために小型除草ロボットの開発が進められている。 In recent years, labor reduction and cost reduction of agricultural production, management work, etc. are becoming more and more important issues in agriculture in Japan as the number of agricultural workers decreases and the population ages. Among the tasks that are not being automated, weeding on the shore is one example. In particular, rice terraces and terraced fields in hilly and mountainous areas depend on human power such as brush cutters, and the development of small weeding robots is underway to automatically perform this heavy labor and dangerous weeding work. Yes.
ロボットが自動で草刈作業をするときに、経路生成や位置検出にはGPSを用いることが考えられる。しかし、精度の高いGPSは、高価であり、また中山間地域では必ずしも必要な数のGPS衛星を補足できないこともあり、低価格の実用機を目指すのは困難である。 When the robot automatically performs mowing work, it is conceivable to use GPS for route generation and position detection. However, high-accuracy GPS is expensive, and it may not always be possible to supplement the required number of GPS satellites in hilly and mountainous areas, so it is difficult to aim for a low-priced practical aircraft.
また、屋外等で音波を利用して位置測定する場合、風の吹く環境下では風による音速の変化に伴う測定精度の低下があり、精度よく位置測定できないものであった。 In addition, when performing position measurement using sound waves outdoors or the like, there is a decrease in measurement accuracy due to changes in sound speed due to wind in an environment where wind blows, and position measurement cannot be performed accurately.
特許調査の結果、特表2005−516190号公報のように、各デバイス間で音波を相互に送受信することで、風速の影響を相殺することが提案されている。また、ドップラー効果を利用することにより風速を測定することが知られている。 As a result of patent research, it has been proposed to cancel the influence of wind speed by transmitting and receiving sound waves between devices as in Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 2005-516190. It is also known to measure wind speed by utilizing the Doppler effect.
しかし、前者では、各デバイス間で音波を相互に送受信させているため、デバイスや処理が複雑となり、コストが増大する。また、後者のドップラー効果により風速を測定する方法では、スピーカとマイクを固定して設置したもので、スピーカとマイクを固定する必要があり、移動する物体の位置測定システムに応用することが難しい。 However, in the former, since sound waves are transmitted and received between the devices, the devices and processing become complicated, and the cost increases. In the latter method of measuring the wind speed by the Doppler effect, the speaker and the microphone are fixed, and the speaker and the microphone need to be fixed. Therefore, it is difficult to apply the method to a moving object position measurement system.
そのため、屋外等の風の吹く環境下でも、風による音速の変化に伴う測定精度を低下することなく、移動する物体の位置等を精度よく測定することが課題であった。 Therefore, it has been a problem to accurately measure the position and the like of a moving object without degrading the measurement accuracy associated with the change in sound speed due to the wind even in an environment where the wind blows, such as outdoors.
本発明は、上記のような点に鑑みたもので、上記の課題を解決するために、ドップラー効果を利用した風速の測定結果に基づき音速変化の補償を行う位置測定方法であって、被位置測定体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体に受信させ、その受信時刻と送信時刻から上記音波の伝搬時間を算出するとともに、ドップラー効果に基づく風による音速変化の補償を行って位置測定体からの被位置測定体の距離を算出して位置測定することを特徴とするドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法を提供するにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and in order to solve the above problems, the present invention is a position measurement method for compensating for a change in sound speed based on a wind speed measurement result using the Doppler effect. A sound wave of a predetermined frequency is transmitted from the measurement body and received by the position measurement body, and the propagation time of the sound wave is calculated from the reception time and the transmission time, and the position of the sound wave is compensated for by the wind based on the Doppler effect. An object of the present invention is to provide a position measuring method using the Doppler effect, characterized in that the position is measured by calculating the distance of the position measuring body from the measuring body.
また、移動する被位置測定体から位置測定用の音波と風速補償用の一定の周波数の音波を交互にスピーカから送信し、位置測定体のマイクで受信して被位置測定体の距離を逐次算出して位置測定するドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法を提供するにある。 In addition, the sound wave for position measurement and the sound wave of constant frequency for wind speed compensation are alternately transmitted from the speaker from the moving position measurement object and received by the microphone of the position measurement object, and the distance of the position measurement object is calculated sequentially. The present invention provides a position measuring method using the Doppler effect for position measurement.
さらに、被位置測定体から送信される位置測定用の音波がスペクトル拡散音のM系列符号の音波であって、当該音波を受信した位置測定体が行う距離算出方法が当該音波のM系列符号について相関処理を行って同期処理するものであるドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法を提供するにある。 Further, the position measurement sound wave transmitted from the position measurement object is an M-sequence code sound wave of spread spectrum sound, and the distance calculation method performed by the position measurement body that has received the sound wave is the M-sequence code of the sound wave. An object of the present invention is to provide a position measurement method using the Doppler effect, which performs a correlation process and performs a synchronization process.
さらにまた、位置測定体を1個以上とし、移動する被位置測定体との距離を数十m以上離した状態となる位置に設置したドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法を提供するにある。 Still another object of the present invention is to provide a position measuring method using the Doppler effect that is installed at a position where the number of position measuring bodies is one or more and the distance from the moving position measuring body is several tens of meters or more.
さらにまた、被位置測定体を含む音波送信体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体を含む音波受信体に受信させ、その音波を周波数解析してそのスペクトル成分の帯域幅より音波送信体から音波受信体間の風速を測定することを特徴とするドップラー効果を利用した風速測定方法を提供するにある。 Furthermore, a sound wave having a predetermined frequency is transmitted from a sound wave transmitting body including a position measurement body and received by a sound wave receiving body including a position measurement body, and the sound wave is frequency-analyzed and transmitted from the bandwidth of the spectral component. An object of the present invention is to provide a wind speed measuring method using the Doppler effect, characterized by measuring a wind speed between a body and a sound wave receiver.
本発明のドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法は、特許請求の範囲の請求項1のように、ドップラー効果を利用した風速の測定結果に基づき音速変化の補償を行う位置測定方法であって、被位置測定体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体に受信させ、その受信時刻と送信時刻から上記音波の伝搬時間を算出するとともに、ドップラー効果に基づく風による音速変化の補償を行って位置測定体からの被位置測定体の距離を算出して位置測定することによって、装置を複雑にすることなく、被位置測定体の位置を測定することができるものであり、ドップラー効果に基づく風による音速変化の補償を行って、屋外等の風の吹く環境下でも、風による音速の変化に伴う測定精度を低下することなく、被位置測定体の位置を精度よく測定することができる。
The position measurement method using the Doppler effect according to the present invention is a position measurement method for compensating for the change in sound speed based on the measurement result of the wind speed using the Doppler effect, as in
また、請求項2のように、移動する被位置測定体から位置測定用の音波と風速補償用の一定の周波数の音波を交互にスピーカから送信し、位置測定体のマイクで受信して被位置測定体の距離を逐次算出して位置測定することによって、装置を簡単化できて、上記したようにドップラー効果に基づく風による音速変化の補償を行って、屋外等の風の吹く環境下でも、風による音速の変化に伴う測定精度を低下することなく、移動する被位置測定体の位置を精度よく測定することができる。 According to another aspect of the present invention, a sound wave for position measurement and a sound wave having a constant frequency for wind speed compensation are alternately transmitted from a speaker and received by a microphone of the position measurement body. By calculating the distance of the measuring body sequentially and measuring the position, the device can be simplified, and as described above, the compensation of the sound speed change due to the wind based on the Doppler effect is performed, even under the wind blowing environment such as outdoors, The position of the moving position-measuring object can be accurately measured without degrading the measurement accuracy associated with the change in sound velocity due to the wind.
さらに、請求項3のように、被位置測定体から送信される位置測定用の音波がスペクトル拡散音のM系列符号の音波であって、当該音波を受信した位置測定体が行う距離算出方法が当該音波のM系列符号について相関処理を行って同期処理することによって、スペクトル拡散音のM系列符号の優れた自己相関特性と雑音耐性を利用して、屋外等の風の吹く環境の雑音下でも、高精度に上記のように位置測定できるとともに、無線ネットワークなので置測定体の追加や除去が容易で、かつその配置も自由に行なえて位置測定することができる。 Further, according to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a distance calculation method performed by the position measurement body that receives the sound wave when the position measurement sound wave transmitted from the position measurement body is an M-sequence code sound wave of spread spectrum sound. By performing correlation processing on the M-sequence code of the sound wave and performing synchronization processing, the excellent autocorrelation characteristics and noise resistance of the M-sequence code of the spread spectrum sound can be used, even under the noise of the wind blowing environment such as outdoors. In addition to being able to measure the position with high accuracy as described above, since it is a wireless network, it is easy to add or remove the measuring object, and the position can be measured freely.
さらにまた、請求項4のように、位置測定体を1個以上とし、移動する被位置測定体との距離を数十m以上離した状態となる位置に設置したことによって、測定距離が数十m以上の測定であっても、位置測定体からの算出距離で移動する被位置測定体を位置測定することができるとともに、数cm位の誤差で位置測定することができる。
Furthermore, as described in
さらにまた、請求項5のように、被位置測定体を含む音波送信体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体を含む音波受信体に受信させ、その音波を周波数解析してそのスペクトル成分の帯域幅より音波送信体から音波受信体間の風速を測定することによって、ドップラー効果を利用して音波送信体から音波受信体間の風速を測定することができる。
Furthermore, as described in
本発明の位置測定方法は、ドップラー効果を利用した風速の測定結果に基づき音速変化の補償を行う位置測定方法であって、被位置測定体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体に受信させ、その受信時刻と送信時刻から上記音波の伝搬時間を算出するとともに、ドップラー効果に基づく風による音速変化の補償を行って位置測定体からの被位置測定体の距離を算出して位置測定することを特徴としている。 The position measurement method of the present invention is a position measurement method that compensates for changes in sound speed based on the measurement result of wind speed using the Doppler effect, and transmits a sound wave of a predetermined frequency from the position measurement object to the position measurement object. Calculate the propagation time of the sound wave from the reception time and transmission time, and compensate for the change in sound velocity due to the wind based on the Doppler effect to calculate the distance of the position measurement object from the position measurement object It is characterized by doing.
ドップラー効果を利用した位置測定方法は、図1のように移動する被位置測定体1のまわりに1個以上(図上4個)の位置測定体2を所定の距離を隔てて配設し、位置測定体2から被位置測定体1の距離を逐次測定して被位置測定体1の位置を測定するようにしている。
In the position measuring method using the Doppler effect, one or more (four in the figure)
図2のように上記移動する被位置測定体1には、装着したプロセッサ3によって位置測定用のスペクトル拡散音を含む音波と風速補償用の一定の周波数の音波を交互に作成し、D/A変換してオーディオアンプ4により増幅し、スピーカ5から位置測定体2側へ送信される。また、この送信するタイミングで、プロセッサ3より同期信号を無線デバイス6に出力して位置測定体2側へ送信して通知するようにしている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the moving position-
そして、位置測定体2では、図2のように装着した無線デバイス7で上記同期信号を受信して検出した後、プロセッサ8に同期信号を出力し、同期信号を検出した後、上記マイク9から出力される音波信号をA/D変換する。そして、バッファに音波データが溜まった時点で相関処理して相関ピーク検出等の所要の処理を行い、スペクトル拡散音等の音波によってスピーカ5―マイク9間の距離を上記プロセッサ8で算出し、その結果を無線デバイス7を介して被位置測定体1に送信して通知するようにして、その距離情報を基に音速にその伝播時間を乗算して被位置測定体1の位置を測定するようにしている。
The
1次元では1個の位置測定体2で位置測定でき、2次元では2個の位置測定体2でも位置測定できるが、その際2つの円の交点の一の位置を選択して位置測定できる。図1のように3個以上では、これらの円の交点ないし重なり合う近傍点として位置測定される。
In one dimension, the position can be measured with one
音波は、障害物があっても回り込みやすく、かつ測定手段が安価である利点がある。スペクトル拡散音は雑音耐性を有して精度よく位置測定できるものであり、その音源としてM系列符号を音波として用いることで、M系列符号の優れた自己相関特性と雑音耐性を有していることから測定精度および雑音耐性を向上できる。また、位置測定器2側で相関処理および距離計算を行うことで、相関処理等の演算コストを分散でき、被位置測定体1の負荷が減り、全体のプロセッサを安価に構築できる。さらに、上記のように被位置測定体1と位置測定体2とを無線デバイス6、7を用いて同期制御処理するので、高精度に位置測定ができる。
Sound waves have the advantage that they can easily go around even if there are obstacles, and the measuring means is inexpensive. Spread spectrum sound has noise tolerance and can measure the position with high accuracy. By using the M-sequence code as a sound wave, it has excellent autocorrelation characteristics and noise tolerance of the M-sequence code. Measurement accuracy and noise resistance can be improved. Further, by performing the correlation process and the distance calculation on the
しかし、屋外等の風の影響があるところでは、上記のように音波による位置測定をすると測定に誤差が生じる。その主な誤差要因は、風によって音速が変化して測定精度が低下することにある。そのため、風による音速変化の補償を行って補正する必要がある。 However, where there is an influence of wind, such as outdoors, an error occurs in the measurement when the position is measured by the sound wave as described above. The main error factor is that the sound speed changes due to the wind and the measurement accuracy decreases. For this reason, it is necessary to compensate for the change in sound velocity due to the wind.
風が吹く環境下では、音波による距離D(m)は、スピーカ5からマイク9までの音の伝搬時間△T(s)、音速Vs(m/s)、温度t(℃)、風速Vw(m/s)とすると、次式で求められる。
D =Vs×ΔT
Vs=331.5+0.61×t+Vw
ここに、風速Vwはスピーカ5からマイク9に吹く追風のときはプラス、逆風のときはマイナスになる。
In an environment where wind blows, the distance D (m) by sound waves is the sound propagation time ΔT (s) from the
D = Vs × ΔT
Vs = 331.5 + 0.61 × t + Vw
Here, the wind speed Vw becomes positive when the wind is blown from the
上式より距離Dの精度向上には、風速Vwと温度も正確に測定する必要があり、風速と温度の影響を含んだ音速Vs(m/s)に修正できて、音波の風速変化による補償が可能となる。 In order to improve the accuracy of the distance D from the above equation, it is necessary to accurately measure the wind speed Vw and temperature, and it can be corrected to the sound speed Vs (m / s) including the influence of the wind speed and temperature, and compensated by the change in the wind speed of the sound wave Is possible.
本発明では、ドップラー効果を利用した風速による音速変化の補償するもので、図3はその原理を示すものである。図3のようにマイク9とスピーカ5を配置し、スピーカ5から周波数fの音波を放射する。このとき、音速cは速度Vで移動する微粒子に散乱反射し、次式のようにドップラー現象によりマイク9の受音する周波数f''は、次のように求められる。ここに、f’は、微粒子に衝突したときの音の周波数である。
(c − Vcosθ1 ) c
f’=────────────f f''=────────────f’
c (c − Vcosθ2 )
(c − Vcosθ1 )
f''=────────────f
(c − Vcosθ2 )
In the present invention, the change in the sound speed due to the wind speed using the Doppler effect is compensated, and FIG. 3 shows the principle thereof. As shown in FIG. 3, the
(C−Vcos θ 1 ) c
f '= ────────────f f''= ──────────── f'
c (c−Vcos θ 2 )
(C−Vcos θ 1 )
f '' = ──────────── f
(C−Vcos θ 2 )
上記の式から、周波数f、f''、c、θ1 、θ2 が既知もしくは測定可能であれば、風速Vを求めることができる。しかし、位置測定する場合、スピーカ5またはマイク9の位置は定まらず、よってθ1 、θ2 も一定値にならない。そこで、一定周波数の音を出力したとき、マイク9は、0°<θ1 <90°、0°<θ2 <90°の範囲内でドップラー効果が起きた音を受信していると考え、風速により周波数がどのように変化するか、上式に代入して計算した。たとえば、ロボットに設置したスピーカ5からの音を利用して距離を計測するとすれば、0°<θ1 <90°、0°<θ2 <90°の範囲内でドップラー効果が起きた音をマイク9で拾っていると考えられる。ここで、音速c=340m/s、送信音波の周波数f=24KHz とした。
From the above formula, if the frequencies f, f ″, c, θ 1 , θ 2 are known or measurable, the wind speed V can be obtained. However, when the position is measured, the position of the
その結果は、図4(a)、(b)、(c)であり、各グラフはx軸がθ1 、y軸がθ2 、z軸が受信周波数を表している。図5は、風速とそのときの受信周波数の最大値と最小値を表したものである。図4、図5のように風速が強くなると、計測周波数の幅が広がっている。 The results are shown in FIGS. 4A, 4B, and 4C. In each graph, the x-axis represents θ 1 , the y-axis represents θ 2 , and the z-axis represents the reception frequency. FIG. 5 shows the maximum and minimum values of the wind speed and the reception frequency at that time. As the wind speed increases as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, the width of the measurement frequency increases.
このような結果、たとえば図5の関係から、風速Vwは、次式のように求めることができる。
1 1
Vw=────fmax − 342.8 Vw=−────fmin + 342.8
70 70
fmax 、fmin は、受信音波信号をフーリエ変換ときのパワースペクトルがある一定値以上の最大周波数と最小周波数の値である。
As a result, for example, the wind speed Vw can be obtained from the relationship shown in FIG.
1 1
Vw = ------ fmax-342.8 Vw = ------- fmin + 342.8
70 70
fmax and fmin are values of a maximum frequency and a minimum frequency that are equal to or higher than a certain value in the power spectrum when the received sound wave signal is Fourier-transformed.
しかし、θ1 、θ2 の全ての範囲を同音圧レベルでじ受信できないため、一意に最大周波数と最小周波数を決めることが困難となる。そこで、受信音波信号をフーリエ変換等の周波数解析し、中心周波数fc のパワースペクトルFcを基準とした差分値が最大となる周波数fmのパワースペクトルFmを求め、その差分値を特徴量df として用いて、風速Vwを次式のように算出した。
Fm− Fc df −1.69
df =─────── Vw=────────
fm−fc −0.173
However, since it is impossible to receive all the ranges of θ 1 and θ 2 at the same sound pressure level, it is difficult to uniquely determine the maximum frequency and the minimum frequency. Therefore, the received sound wave signal is subjected to frequency analysis such as Fourier transform, the power spectrum Fm of the frequency fm with the maximum difference value with respect to the power spectrum Fc of the center frequency fc is obtained, and the difference value is used as the feature value df. The wind speed Vw was calculated as follows:
Fm- Fc df -1.69
df = ─────── Vw = ─────────
fm-fc -0.173
したがって、本発明は、ドップラー効果を利用して風速測定することができ、上記のような被位置測定体のスピーカ等を含む音波送信体から所定の周波数の音波を送信して位置測定体のマイク等を含む音波受信体に受信させ、その音波を周波数解析してそのスペクトル成分の帯域幅より音波送信体から音波受信体間の広範囲の平均的な風速を測定することができる。スピーカ等の音波送信体とマイク等の音波受信体の安価な装置で上記したように風速測定することが可能で、別途デバイスを付加することなく、プロセッサで受信した音波を周波数解析して風速を知ることができ、安価な風速測定システムを構築することができる。 Therefore, the present invention can measure the wind speed by utilizing the Doppler effect, and transmits a sound wave having a predetermined frequency from the sound wave transmitter including the speaker of the position measurement body as described above to thereby measure the microphone of the position measurement body. The sound wave receiving body including the sound wave is received, the sound wave is subjected to frequency analysis, and the average wind speed in a wide range between the sound wave transmitting body and the sound wave receiving body can be measured from the bandwidth of the spectral component. It is possible to measure the wind speed with an inexpensive device such as a sound wave transmitter such as a speaker and a sound wave receiver such as a microphone as described above, and without adding a separate device, frequency analysis of the sound wave received by the processor An inexpensive wind speed measurement system can be constructed.
そしてまた、上記したようにして位置計測用の音波の出力の直後に風速測定用の音波を出力することで、位置計測用の音波が受けたほぼ同じ風の影響を測定することができ、位置計測用の音波の出力と風速測定用の音波を交互に出力することで、移動する被位置測定体1の位置を逐次測定していくことができる。なお、温度計を設けて音速を補償することもできる。
In addition, by outputting the sound wave for wind speed measurement immediately after the output of the sound wave for position measurement as described above, it is possible to measure the influence of almost the same wind received by the sound wave for position measurement. By alternately outputting the sound wave for measurement and the sound wave for wind speed measurement, the position of the moving position-
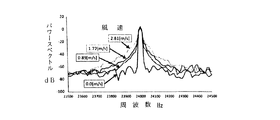
このようなことからドップラー効果を確かめるために、実験を行った。図6に示しているようにスピーカ5とマイク9を1mの距離に設置し、扇風機を用いて、4.46m/s 、2.99m/s 、2.23m/s の風をスピーカ5側からマイク9方向に向かって発生させた。スピーカ5からは、周波数24KHz の音波を送信し、マイク9で受信した音波を周波数解析した。図6に受信した周波数成分を示す。図6より、原理通り風速が大きくなる程、受信音波の周波数幅が増大している。よって、ドップラー効果を利用して、周波数帯域幅から風速を上記した算出式から風速Vwを決定することができる。表1は、このようにして算出した風速Vwと既製品の風速計を用いて計測した風速を比較して示したもので、本発明のドップラー効果を利用して風速測定することが十分可能であることが実証できた。
Experiments were conducted to confirm the Doppler effect. As shown in FIG. 6, the
表1 ドップラー効果を利用した風速測定と既製品の風速計による風速結果表
また、スペクトル拡散音と周波数を24KHz に固定した一定周波数の音を交互にスピーカ5から放射し、屋内と屋外とで実験した。その結果、屋内における風速を変えたそれぞれのパターンのマイク9が受信した音の周波数とそのパワースペクトルの関係は、それぞれ図7、図8のものであった。これにより、風速は強くなるほど周波数の幅が広がっていることが分かる。図9は、ピークとなる24KHz からのパワースペクトルの差分が一番大きくなる点に注目した結果を示すもので、風速と差分の間に相関が見られる。
In addition, a spectrum spread sound and a constant frequency sound with a fixed frequency of 24 KHz were alternately emitted from the
図10は、屋外実験における結果を示す。風向は、マイク9からスピーカ5に向かって吹いていた。上記のように屋内において相関関係が見られ、屋外でも風速と差分の間に相関関係が見られる。屋外では、風速計を同期のためにスピーカとマイクの上に置いて計測したため、実際の風速とずれが生じていたことが考えられるが、風速による音速変化が生じることが分かり、その補償を行うことは有効であると判断できる。
FIG. 10 shows the results of an outdoor experiment. The wind direction was blowing from the
なお、参考用に、暗騒音40dB(F)、出力音圧レベル80dB(F)、測定距離0.5、5、10、20,、0、40、50mとして実験を行った。パソコンによりスペクトル拡散音のM系列符号の音波、周波数24KHz の音波、同期信号を作成し、メディアプロセッサにより出力した。図1、図2で説明したように、スペクトル拡散音は、移動する被位置測定体1のオーディオアンプを通してスピーカにより出力される。同期信号は、無線デバイスに入力され、位置測定体2側へ送信して通知する。
For reference, the experiment was performed with a background noise of 40 dB (F), an output sound pressure level of 80 dB (F), and a measurement distance of 0.5, 5, 10, 20, 0, 40, and 50 m. The sound wave of the M series code of the spread spectrum sound, the sound wave of frequency 24KHz, and the synchronization signal were created by a personal computer and outputted by the media processor. As described in FIGS. 1 and 2, the spread spectrum sound is output from the speaker through the audio amplifier of the moving position-
位置測定体2では、無線デバイスで上記同期信号を受信して検出した後、プロセッサに同期信号を出力し、同期信号を認識するとマイク9から出力される音波信号をA/D変換する。そして、録音バッファに音波データが溜まると相関処理し、スピーカ5―マイク9間の距離を算出し、その結果を無線デバイスを介して被位置測定体1のパソコンに送信して表示する。距離取得間隔は350msである。
In the
その結果を図11に示す。□は実測測定誤差、◇は風速のデータを用いて補償したときの測定誤差である。□は20m以降の誤差は線形に悪くなる。これは、20〜50mの間で風が0.3m/s程度マイクからスピーカ方向に吹いていたためである。この風速を音速に足し合せて再計算した結果は◇のプロットである。風の影響を考慮すれば、50m以内でも誤差20mm以内であり、風による音速変化の補償によって、かなりの精度で位置測定することが可能である。 The result is shown in FIG. □ is an actual measurement error, and ◇ is a measurement error when compensated by using wind speed data. For □, the error after 20m becomes linearly worse. This is because the wind was blowing about 0.3 m / s from the microphone toward the speaker between 20 and 50 m. The result of recalculation by adding this wind speed to the sound speed is a plot of ◇. If the influence of wind is taken into consideration, the error is within 20 mm even within 50 m, and the position can be measured with considerable accuracy by compensating for the change in sound velocity due to the wind.
このことは、上記したドップラー効果を利用した風速の測定結果に基づき音速変化の補償を行う位置測定方法に適用できるものであり、特に被位置測定体から送信される位置測定用の音波がスペクトル拡散音のM系列符号の音波であって、当該音波を受信した位置測定体が行う距離算出方法が当該音波のM系列符号について相関処理を行って同期処理することによって、スペクトル拡散音としてM系列符号を介して優れた自己相関特性と雑音耐性を利用して高精度に位置測定できるものである。 This can be applied to a position measurement method that compensates for a change in sound speed based on the measurement result of wind speed using the Doppler effect described above, and in particular, a sound wave for position measurement transmitted from a position measurement object is spread spectrum. A sound wave of an M-sequence code of a sound, and a distance calculation method performed by a position measurement body that has received the sound wave performs a correlation process on the M-sequence code of the sound wave and performs a synchronization process, thereby obtaining an M-sequence code as a spread spectrum sound. The position can be measured with high accuracy by utilizing the excellent autocorrelation characteristics and noise resistance.
そして、上記のように無線ネットワークの構築によって、位置測定体の追加や除去が容易で、かつその配置も自由に行なうことができ、さらに障害物にも位置測定体を所定位置に適宜数設置して対処することができる。 As described above, the construction of the wireless network makes it easy to add and remove position measuring bodies, and can freely place them. In addition, an appropriate number of position measuring bodies are installed at predetermined positions on obstacles. Can be dealt with.
なお、上記したように位置測定体は1次元では1個の位置測定体でよく、2次元では2個の位置測定体でも測定可能である。また、異なるM系列符号の音波を利用することによって、同時に2以上の移動する被位置測定体の位置測定を行うことができる。そして、上記のようにして被位置測定体を数十m以上離れて移動しても、数cm位の誤差で精度よく位置測定することができる。 As described above, the position measuring body may be one position measuring body in one dimension, and two position measuring bodies can be measured in two dimensions. In addition, by using sound waves of different M-sequence codes, it is possible to perform position measurement of two or more moving position measurement objects at the same time. And even if the position-measuring object is moved several tens of meters or more as described above, the position can be accurately measured with an error of several centimeters.
本発明は、精度よく位置測定や風速測定できて、農業分野での畦畔や中山間地の棚田や段畑でのロボット等による除草処理、ドーム、工場や屋外での物流、搬送の自走台車走行や清掃ロボット、空港等での自走台車配送や清掃ロボット、除草ロボット、その他の航法システム、屋内、屋外での風循環のモニタリング、気象データ観測、道路通行風速情報システムなどに広く利用することができる。 The present invention enables accurate position measurement and wind speed measurement, weeding treatment by robots, etc. on terraced rice fields and terraced fields and terraced fields in agricultural fields, dome, logistics in the factory and outdoors, transportation self-propelled Widely used for bogie running and cleaning robots, self-running cart delivery and cleaning robots at airports, weeding robots, other navigation systems, indoor and outdoor wind circulation monitoring, meteorological data observation, road traffic wind speed information system, etc. be able to.
1…被位置測定体 2…位置測定体 3…プロセッサ 5…スピーカ 6,7…無線デバイス 8…プロセッサ 9…マイク
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012049081A JP2013185856A (en) | 2012-03-06 | 2012-03-06 | Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012049081A JP2013185856A (en) | 2012-03-06 | 2012-03-06 | Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013185856A true JP2013185856A (en) | 2013-09-19 |
Family
ID=49387421
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012049081A Ceased JP2013185856A (en) | 2012-03-06 | 2012-03-06 | Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013185856A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014145654A (en) * | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Position determination method and position determination device |
| CN106908765A (en) * | 2017-02-27 | 2017-06-30 | 广东小天才科技有限公司 | Spatial positioning method and system based on ultrasonic signal and VR (virtual reality) equipment |
| CN112074758A (en) * | 2018-05-02 | 2020-12-11 | 罗伯特·博世有限公司 | Method and device for identifying road conditions |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS58189562A (en) * | 1982-04-29 | 1983-11-05 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Method and apparatus for detecting moving speed of fluid in accordance with extraction of doppler frequency |
| JPS59224582A (en) * | 1983-06-02 | 1984-12-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Distance measuring method |
| JPH02102477A (en) * | 1988-10-08 | 1990-04-16 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Ultrasonic distance measuring instrument |
| JPH05186189A (en) * | 1992-01-08 | 1993-07-27 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | Device for detecting approach of long-size body to obstacle |
| JPH0759774A (en) * | 1993-08-09 | 1995-03-07 | Hewlett Packard Co <Hp> | Fluid flow detecting method |
| JPH11326513A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Furuno Electric Co Ltd | Distance measuring apparatus |
| JP2011038799A (en) * | 2009-08-06 | 2011-02-24 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Position detection device, position detection method and program |
-
2012
- 2012-03-06 JP JP2012049081A patent/JP2013185856A/en not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS58189562A (en) * | 1982-04-29 | 1983-11-05 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Method and apparatus for detecting moving speed of fluid in accordance with extraction of doppler frequency |
| JPS59224582A (en) * | 1983-06-02 | 1984-12-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Distance measuring method |
| JPH02102477A (en) * | 1988-10-08 | 1990-04-16 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Ultrasonic distance measuring instrument |
| JPH05186189A (en) * | 1992-01-08 | 1993-07-27 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | Device for detecting approach of long-size body to obstacle |
| JPH0759774A (en) * | 1993-08-09 | 1995-03-07 | Hewlett Packard Co <Hp> | Fluid flow detecting method |
| JPH11326513A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Furuno Electric Co Ltd | Distance measuring apparatus |
| JP2011038799A (en) * | 2009-08-06 | 2011-02-24 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Position detection device, position detection method and program |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014145654A (en) * | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Position determination method and position determination device |
| CN106908765A (en) * | 2017-02-27 | 2017-06-30 | 广东小天才科技有限公司 | Spatial positioning method and system based on ultrasonic signal and VR (virtual reality) equipment |
| CN106908765B (en) * | 2017-02-27 | 2019-07-09 | 广东小天才科技有限公司 | Spatial positioning method and system based on ultrasonic signal and VR (virtual reality) equipment |
| CN112074758A (en) * | 2018-05-02 | 2020-12-11 | 罗伯特·博世有限公司 | Method and device for identifying road conditions |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU112446U1 (en) | PASSIVE RADIOELECTRONIC COMPLEX FOR ONE-POINT DETERMINATION OF HORIZONTAL COORDINATES AND OBJECTS OF MOTION OF THE OBJECT BY THE LINE-FILTRATION CALMAN-BUSSI METHOD | |
| CN105044676A (en) | Energy-based sound source localization method | |
| CN101907678A (en) | Cable fault test system and determining method of fault point | |
| Mukhopadhyay et al. | Novel RSSI evaluation models for accurate indoor localization with sensor networks | |
| CN102508204A (en) | Indoor noise source locating method based on beam forming and transfer path analysis | |
| KR101374589B1 (en) | Method of tracking position and apparatus performing the same | |
| Huang et al. | A sound-based positioning system with centimeter accuracy for mobile robots in a greenhouse using frequency shift compensation | |
| WO2017124678A1 (en) | Indoor positioning method based on propagation of sound wave in solid body | |
| RU2557808C1 (en) | Method of determining inclined range to moving target using passive monostatic direction-finder | |
| JP2013185856A (en) | Methods for measuring position and wind speed utilizing doppler effect | |
| Huang et al. | Position and orientation measurement system using spread spectrum sound for greenhouse robots | |
| Hammer et al. | An acoustic position estimation prototype system for underground mining safety | |
| RU2649073C1 (en) | Method for determining coordinates of the underwater object by the hydroacoustic system of underwater navigation with an alignment beacon | |
| JP2017142180A (en) | Method and system for estimating position | |
| Chen et al. | TDOA/FDOA mobile target localization and tracking with adaptive extended Kalman filter | |
| KR20150028106A (en) | Indoor positioning based on inaudible sound's droppler effects | |
| RU2631906C1 (en) | Device for determining location of signal source | |
| RU2545068C1 (en) | Measurement method of changes of heading angle of movement of source of sounding signals | |
| KR20160050119A (en) | Appratus and method for measuring velocity and direction of wind using ultrasonic | |
| Finn et al. | The feasibility of unmanned aerial vehicle-based acoustic atmospheric tomography | |
| Shiigi et al. | Temperature compensation method using base-station for spread spectrum sound-based positioning system in green house | |
| Ardakani et al. | A hybrid adaptive approach to improve position tracking measurements | |
| JP5593062B2 (en) | Measuring device, measuring system, and measuring method | |
| CN108332749A (en) | A kind of interior dynamic tracing localization method | |
| Gao et al. | Underwater acoustic positioning system based on propagation loss and sensor network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20141127 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20141127 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150918 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150929 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151111 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160419 |
|
| A045 | Written measure of dismissal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A045 Effective date: 20160830 |