JP2011125843A - Acceleration generation device - Google Patents
Acceleration generation device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011125843A JP2011125843A JP2010187047A JP2010187047A JP2011125843A JP 2011125843 A JP2011125843 A JP 2011125843A JP 2010187047 A JP2010187047 A JP 2010187047A JP 2010187047 A JP2010187047 A JP 2010187047A JP 2011125843 A JP2011125843 A JP 2011125843A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coil
- acceleration
- movable part
- generating device
- frequency
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02K—DYNAMO-ELECTRIC MACHINES
- H02K33/00—Motors with reciprocating, oscillating or vibrating magnet, armature or coil system
- H02K33/16—Motors with reciprocating, oscillating or vibrating magnet, armature or coil system with polarised armatures moving in alternate directions by reversal or energisation of a single coil system
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Reciprocating, Oscillating Or Vibrating Motors (AREA)
- Apparatuses For Generation Of Mechanical Vibrations (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、加速度発生デバイスに関し、特に、可動部を備え、ユーザに擬似力覚を知覚させる加速度発生デバイスに関する。 The present invention relates to an acceleration generating device, and more particularly to an acceleration generating device that includes a movable part and allows a user to perceive a pseudo force sense.
従来、可動部を備え、ユーザに擬似力覚を知覚させる加速度発生デバイスが知られている(たとえば、特許文献1参照)。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, there is known an acceleration generating device that includes a movable part and makes a user perceive a pseudo force sensation (for example, see Patent Document 1).
上記特許文献1には、コイルが巻回される円筒状のボビン(可動部)と、円筒状のボビンの一方端部側に取り付けられる第1永久磁石(可動部)と、ボビンの他方側にボビンと別個に設けられる第2永久磁石と、コイル、ボビン、第1永久磁石および第2永久磁石を収納する円筒状のフレームと、第1永久磁石とフレームとの間に設けられるバネとを備える加速度発生装置が開示されている。なお、上記特許文献1に開示されている加速度発生装置では、第1永久磁石の移動方向(円筒状のボビンが延びる方向)の一方側にバネが配置されるとともに、他方側に第2永久磁石が配置されているので、第1永久磁石の移動方向の中心に対して、加速度発生装置は構造的に非対称な形状を有する。
In
また、この加速度発生装置では、コイルに正弦波状の交流電流(交流電圧)が供給されることにより磁界が発生する。そして、第1永久磁石の一方側にはバネの弾性力が働くとともに、他方側にはコイルの磁界と第2永久磁石の磁界とが働く。そして、第1永久磁石の一方側および他方側に働く力の大きさが第1永久磁石およびボビンの位置によって異なっており、第1永久磁石(ボビン)の加速度の波形が第1永久磁石(ボビン)の移動方向の一方側と他方側とで異なるように構成されている。これにより、ユーザは、加速度発生装置を把持した場合に、所定の方向に引っ張られるような力覚(擬似力覚)を知覚することが可能となる。 In this acceleration generator, a magnetic field is generated by supplying a sinusoidal alternating current (alternating voltage) to the coil. The elastic force of the spring acts on one side of the first permanent magnet, and the magnetic field of the coil and the magnetic field of the second permanent magnet act on the other side. The magnitude of the force acting on one side and the other side of the first permanent magnet differs depending on the positions of the first permanent magnet and the bobbin, and the acceleration waveform of the first permanent magnet (bobbin) is the first permanent magnet (bobbin). ) In the moving direction in FIG. 3 is different from the other side. As a result, the user can perceive a force sense (pseudo force sense) that is pulled in a predetermined direction when holding the acceleration generator.
しかしながら、上記特許文献1に開示された加速度発生装置では、正弦波状の電流がコイルに流されている一方、波形を反転させた電流(電圧)をコイルに流しても、加速度発生装置を把持した場合に得られる擬似力覚の方向は、電流の波形(電圧の波形)を反転させる前後において変わらないという問題点がある。
However, in the acceleration generator disclosed in
この発明は、上記のような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、この発明の1つの目的は、印加する電圧の波形を反転させた場合に、電圧の波形の反転の前後において、装置を把持した場合に得られる力覚の方向を変化させることが可能な加速度発生デバイスを提供することである。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and one object of the present invention is to provide a device before and after the reversal of the voltage waveform when the voltage waveform to be applied is reversed. It is an object of the present invention to provide an acceleration generating device capable of changing the direction of the force sense obtained when the user grasps the finger.
上記目的を達成するために、この発明の第1の局面における加速度発生デバイスは、渦巻状のコイルと、渦巻状のコイルが発生する磁界により往復移動する可動部と、可動部が収納されるとともに可動部の往復移動によって振動する筐体と、可動部と筐体との間に設けられるバネ部とを備え、渦巻状のコイルには、波形が非対称な交流状の電圧が印加され、筐体の振動方向の加速度の波形は、加速度が0の基準線に対して一方方向側と他方方向側とで非対称になるように構成されている。 In order to achieve the above object, an acceleration generating device according to a first aspect of the present invention includes a spiral coil, a movable part that reciprocates by a magnetic field generated by the spiral coil, and a movable part is housed. A casing that vibrates by the reciprocating movement of the movable part and a spring part provided between the movable part and the casing are provided, and an alternating voltage with an asymmetric waveform is applied to the spiral coil, and the casing The waveform of the acceleration in the vibration direction is configured to be asymmetric between the one direction side and the other direction side with respect to the reference line where the acceleration is zero.
この発明の第2の局面における加速度発生デバイスは、永久磁石をそれぞれ含む第1の可動部および第2の可動部と、第1の可動部に対向して配置され、第1の可動部を第1の方向および第2の方向に往復移動させる第1のコイルと、第2の可動部に対向して配置され、第2の可動部を第1の方向および第2の方向に往復移動させる第2のコイルと、第1の可動部および第2の可動部を収納する筐体と、第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルに流れる電流をそれぞれ独立して制御する制御部とを備え、制御部は、第1の可動部および第2の可動部の一往復中における加速度の波形が、第1の方向に対する移動と第2の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルに流れる電流を制御するように構成されている。 The acceleration generating device according to the second aspect of the present invention is arranged to face the first movable portion, the first movable portion and the second movable portion each including a permanent magnet, and the first movable portion is the first movable portion. A first coil that reciprocates in a first direction and a second direction, and a second coil that is disposed opposite to the second movable portion and reciprocates the second movable portion in the first direction and the second direction. A control unit that independently controls the currents flowing through the first coil and the second coil, respectively, and a housing that houses the first movable unit and the second movable unit. The first coil and the second coil are arranged so that the acceleration waveform during one reciprocation of the first movable part and the second movable part is asymmetric between movement in the first direction and movement in the second direction. The current flowing through the two coils is controlled.
この発明の第3の局面における加速度発生デバイスは、永久磁石を含む可動部と、可動部と対向して配置されており、可動部を第1の方向および第2の方向に往復移動させる第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルと、可動部を収納する筐体と、第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルに流れる電流をそれぞれ独立して制御する制御部とを備え、制御部は、可動部の一往復中における加速度の波形が、第1の方向に対する移動と第2の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルに流れる電流を制御するように構成されている。 The acceleration generating device according to the third aspect of the present invention is arranged such that a movable part including a permanent magnet and a movable part are opposed to the movable part, and the movable part is reciprocated in a first direction and a second direction. Coil and the second coil, a housing that houses the movable part, and a control part that independently controls the currents flowing through the first coil and the second coil. The current flowing in the first coil and the second coil is controlled so that the acceleration waveform during one reciprocation is asymmetric between the movement in the first direction and the movement in the second direction. Yes.
上記の構成により、印加する電圧の波形を反転させた場合でも、電圧の波形の反転の前後において、装置を把持した場合に得られる力覚の大きさを略同じにすることができる。 With the above configuration, even when the waveform of the applied voltage is reversed, the magnitude of the force sense obtained when the device is held can be made substantially the same before and after the voltage waveform is reversed.
また、上記の構成により、簡易な構成で任意の方向に擬似力覚を発生させることができる。 Further, with the above configuration, it is possible to generate a pseudo force sense in an arbitrary direction with a simple configuration.
以下、本発明の実施形態を図面に基づいて説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(第1実施形態)
本発明の第1実施形態によるリニアモータ(リニア駆動型振動モータ)100は、図1および図2に示すように、枠体1と、枠体1内に収納された可動部2と、可動部2を支持する一対のバネ部3aおよび3bと、可動部2と対向するように配置された平面コイル4とを備えている。なお、リニアモータ100は、本発明の「加速度発生デバイス」の一例である。また、平面コイル4は、本発明の「コイル」の一例である。
(First embodiment)
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, a linear motor 100 (linear drive vibration motor) 100 according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes a
枠体1は、平面的に見て、略矩形形状に形成されているとともに、枠体1は、上下方向(矢印Z1方向および矢印Z2方向)に貫通する略矩形形状の開口部1aを有する。また、図2に示すように、枠体1には、上方向側(矢印Z1方向側)の開口部1aを塞ぐようにプリント基板5が配置されているとともに、下方向側(矢印Z2方向側)の開口部1aを塞ぐように底板6が配置されている。また、枠体1、プリント基板5および底板6は、ガラスエポキシ樹脂等により形成されている。そして、枠体1、プリント基板5および底板6によって筐体7が構成されている。
The
可動部2は、図1および図2に示すように、平面的に見て略矩形形状に形成されているとともに、平板状の永久磁石(フェライトやネオジウムなどの強磁性材料からなる磁石)により構成されている。また、可動部2は、平面的に見て、枠体1の開口部1aの略中央に位置するように一対のバネ部3aおよび3bにより側面が支持されている。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the
可動部2は、図2に示すように、第1磁石2aおよび第2磁石2bからなる2つの永久磁石により構成されている。具体的には、可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1近傍(図1参照)を境界として矢印X1方向側に第1磁石2aが配置されるとともに、矢印X2方向側に第2磁石2bが配置されるように構成されている。第1磁石2aのプリント基板5に対向する側には、厚み方向にN極に着磁されたN極面21aが設けられている。また、第1磁石2aの底板6に対向する側には、厚み方向にS極に着磁されたS極面22aが設けられている。また、第2磁石2bのプリント基板5に対向する側には、厚み方向にS極に着磁されたS極面21bが設けられている。また、第2磁石2bの底板6に対向する側には、厚み方向にN極に着磁されたN極面22bが設けられている。そして、第1磁石2aと第2磁石2bとは、接着剤などにより互いに固定されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
図1および図2に示すように、バネ部3aおよび3bは、板バネやコイルバネなどからなり、可動部2の矢印X1方向側と矢印X2方向側とにそれぞれ配置されている。なお、バネ部3aおよび3bは、可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して、略対称になるように配置されている。そして、筐体7(枠体1、プリント基板5および底板6)も、可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して、略対称な形状を有する。また、バネ部3aおよび3bは、同じ物である。つまり、バネ部3aおよび3bは、同じ材料からなり、同じバネ特性を有する。これにより、リニアモータ100は、全体として可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して、構造的に略対称な形状を有する。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the
図2に示すように、平面コイル4は、プリント基板5の内部に配置されている。平面コイル4は、平面的に見て、略矩形形状の輪郭を有するとともに、内側から外側に向かってXY面方向に広がるように渦巻状に形成されている。また、平面コイル4は、Y方向に延びるとともに、可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1よりも矢印X1方向側に配置される第1部分4aと、Y方向に延びるとともに、中心線C1よりも矢印X2方向側に配置される第2部分4bとを有している。なお、平面コイル4には、正側と負側とで非対称な波形を有する交流状の電圧が印加されるように構成されている。ここで、正側と負側とで非対称な波形を有する交流状の電圧とは、電圧が0の点に対して、電圧の波形が点対称(たとえば正弦波)になっていないことを意味する。たとえば、電圧の正側と負側とで電圧が異なる極大値を有する場合(図6参照)などを意味する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
次に、図1および図2を参照して、第1実施形態によるリニアモータ100の往復移動の動作を説明する。
Next, with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the operation | movement of the reciprocating movement of the
まず、平面コイル4に電圧を印加する。そして、図1に示すように、A1方向に電流が供給されるとする。これにより、可動部2のN極面21aにおいて発生する矢印Z1方向の磁界と、平面コイル4の第1部分4aを矢印Y1方向に流れる電流とによって、平面コイル4の第1部分4aには、矢印X2方向にローレンツ力が働く。また、可動部2のS極面21bにおいて発生する矢印Z2方向の磁界と、平面コイル4の第2部分4bを矢印Y2方向に流れる電流とによって、平面コイル4の第2部分4bには、矢印X2方向にローレンツ力が働く。なお、平面コイル4は、プリント基板5に固定されているので、可動部2が平面コイル4が受けるローレンツ力の向きと逆の矢印X1方向に直線移動する。そして、所定時間後、A2方向に電流を供給することによって、上記と同様に、可動部2が矢印X2方向に直線移動する。このようにして、所定の周波数で駆動電流の方向を切り替えることによって、可動部2は、矢印X1方向と矢印X2方向とに交互に直線移動(往復移動)する。その結果、リニアモータ100は、矢印X1方向と矢印X2方向とに交互に往復移動する。
First, a voltage is applied to the
次に、図3〜図13を参照して、第1実施形態によるリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加する電圧を調整する方法について説明する。
Next, a method for adjusting the voltage applied to the
図3に示すように、リニアモータ100の理想的な加速度の形状を仮定する。第1実施形態では、1周期がT(sec)であり、加速度の最大値がGP(G)であるとともに最小値がGN(G)である矩形波からなる加速度を仮定する。なお、図3において、h×Tとk×Tとは、それぞれ、加速度が最小(GN)から最大(GP)になる時間と、加速度が最大(GP)から最小(GN)になる時間とを示している。また、加速度の1周期において、正側の加速度の面積S1と、負側の加速度の面積S2とが略等しくなるように、理想的な加速度の形状が仮定されている。なお、図3に示す加速度の形状は、下記の式(1)および(2)によって表される。
As shown in FIG. 3, an ideal acceleration shape of the
そして、上記式(1)および(2)をフーリエ余弦級数展開することにより、下記の式(3)、式(4)および式(5)を得る。 Then, the following formulas (3), (4), and (5) are obtained by expanding the above formulas (1) and (2) into a Fourier cosine series.
次に、上記式(3)に示される加速度について時間積分を2回行うことにより、下記の式(6)により表されるリニアモータ100の変位y(t)が得られる。なお、y(0)=0、dy(0)/dt=0とした。
Next, the displacement y (t) of the
そして、上記式(6)により表される変位y(t)を出力とするとともに、電圧V(t)を入力とする伝達関数をGy(s)とすると、下記の式(7)を得る。 When the displacement y (t) represented by the above equation (6) is output and the transfer function having the voltage V (t) as input is G y (s), the following equation (7) is obtained. .
また、上記の式(7)が成り立つように、電圧V(t)は、下記の式(8)のようになれば良い。なお、a0≠0の場合、電圧V(t)は、発散する。ここで、電圧V(t)が発散するとは、電圧V(t)の大きさが時間とともに徐々に大きくなってゆき、最終的に電圧V(t)の大きさが無限大になってしまうことを意味する。このため、|a0|≪1が望ましい。この場合、下記の式(9)が成り立つ。そして、下記の式(9)が成り立つ場合は、加速度の波形の1周期における時間積分の値が略0になる。 Further, the voltage V (t) may be expressed by the following expression (8) so that the above expression (7) is established. Note that when a 0 ≠ 0, the voltage V (t) diverges. Here, when the voltage V (t) diverges, the voltage V (t) gradually increases with time, and eventually the voltage V (t) becomes infinite. Means. Therefore, | a 0 | << 1 is desirable. In this case, the following formula (9) is established. When the following equation (9) holds, the value of the time integration in one cycle of the acceleration waveform becomes substantially zero.
次に、図1に示すリニアモータ100において、加速度が0の基準線に対して非対称な波形を有する加速度を実現するように、リニアモータ100の伝達関数を求める。なお、非対称な加速度の波形とは、加速度が0の基準線に対して、加速度の波形が線対称になっていないことを意味する。たとえば、加速度の正側の最大値と負側の最大値とが異なる場合(図3参照)などである。リニアモータ100の伝達関数は、下記の式(10)により表される電圧方程式、下記の式(11)により表される可動部2の運動方程式、および、下記の式(12)により表される筐体7の運動方程式から求めることができる。
Next, in the
ここで、yおよびxは、それぞれ、筐体7および可動部2の変位を表す。また、Mおよびmは、それぞれ、筐体7の質量および可動部2の質量を表す。また、k1およびk2は、それぞれ、バネ部3aのバネ定数およびバネ部3bのバネ定数を表す。また、κ1およびκ2は、それぞれ、バネ部3aの減衰係数およびバネ部3bの減衰係数を表す。また、V(t)およびI(t)は、それぞれ、電圧および電流を表す。また、RおよびLは、それぞれ、コイルの抵抗およびコイルの自己インダクタンスを表す。また、KeおよびKfは、それぞれ、誘起電圧定数および推力定数を表す。
Here, y and x represent the displacement of the
ここで、コイルの自己インダクタンスLが0の場合には、リニアモータ100の伝達関数は、下記の式(13)および式(14)により表される。なお、バネ部3aおよび3bの減衰係数と角周波数ω0との関係は、下記の式(15)により表される。なお、角周波数ω0は、後述する図4に示されるリニアモータ100のインピーダンスの周波数特性において、インピーダンスが最大になる際の角周波数(共振角周波数)を表す。
Here, when the self-inductance L of the coil is 0, the transfer function of the
また、コイルの自己インダクタンスLが0の場合には、|Gy(j×n×ω)|と∠Gy(j×n×ω)とは、下記の式(16)、式(17)および式(18)により表される。 When the coil self-inductance L is 0, | G y (j × n × ω) | and ∠G y (j × n × ω) are expressed by the following equations (16) and (17). And represented by equation (18).
次に、図4に示されるリニアモータ100のインピーダンスの周波数特性から、上記式(16)により表される|Gy(j×n×ω)|と、上記式(17)および式(18)により表される∠Gy(j×n×ω)とを算出する。なお、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスの周波数特性は、一般的には、角周波数ω0においてピークを有する曲線となる。具体的には、まず、下記の式(19)により、r1を計算する。
Next, from the frequency characteristics of the impedance of the
次に、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスZ(ω)が、下記の式(20)を満たす角周波数γ1およびγ2を求める。
Next, the angular frequencies γ 1 and γ 2 in which the impedance Z (ω) of the
また、バネ部3aおよびバネ部3bの減衰係数の和(κ1+κ2)と、角周波数γ1およびγ2との関係は、下記の式(21)により表される。また、誘起電圧定数および推力定数の積Kf×Keと、角周波数γ1およびγ2との関係は、下記の式(22)により表される。また、換算質量μは、下記の式(23)により表される。
The relationship between the sum of the damping coefficients of the
そして、上記式(16)〜(18)と、上記式(21)〜(23)とによって、下記の式(24)〜式(26)が得られる。 Then, the following formulas (24) to (26) are obtained by the above formulas (16) to (18) and the above formulas (21) to (23).
そして、上記式(4)で求められるa0、式(5)で求められるan、式(14)で求められるGy(0)、式(24)で求められる|Gy(j×n×ω)|、および、式(25)、式(26)で求められる∠Gy(j×n×ω)を上記式(8)に代入することにより、電圧V(t)が得られる。 Then, a 0 obtained by the above equation (4), a n obtained by the equation (5), G y (0) obtained by the equation (14), and | G y (j × n) obtained by the equation (24). The voltage V (t) is obtained by substituting ωG y (j × n × ω) obtained by (× ω) | and equations (25) and (26) into the above equation (8).
次に、上記の方法によって求められた電圧V(t)と、電圧V(t)を入力することによって得られる加速度について行ったシミュレーションについて説明する。 Next, a simulation performed on the voltage V (t) obtained by the above method and the acceleration obtained by inputting the voltage V (t) will be described.
まず、リニアモータ100のパラメータを定義する。ここでは、可動部2の質量mおよび筐体7の質量Mを、それぞれ、5gおよび100gとした。これにより、換算質量μは、上記式(23)を用いて、4.761904762と算出された。また、バネ部3aのバネ定数k1およびバネ部3bのバネ定数k2を、それぞれ、0.28N/mmおよび0.28N/mmとした。また、インピーダンスが最大となる角周波数ω0を、342.9rad/sとした。また、平面コイル4の抵抗Rを、2Ωとした。また、バネ部3aの減衰係数κ1およびバネ部3bの減衰係数κ2を、それぞれ、0.216および0.216とした。また、推力定数Kfおよび誘起電圧定数Keを、それぞれ、0.29N/Aおよび0.29V/(m/s)とした。上記のパラメータから、図5に示すように、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスと加速度の周波数特性とが求められた。ここで、リニアモータ100の共振周波数は55Hzであった。
First, parameters of the
そして、上記のように、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスの周波数特性から、式(19)によってr1を計算した。次に、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスZ(ω)が、式(20)を満たす角周波数γ1およびγ2を求めた。そして、式(24)〜式(26)によって、|Gy(j×n×ω)|、および、∠Gy(j×n×ω)を求めた。なお、電圧V(t)の式(8)に含まれる係数a0は、図3に示す理想的な加速度の波形と式(4)とから求めた。同様に、係数anは、図3に示す理想的な加速度の波形と式(5)とから求めた。さらに、伝達関数Gy(0)は、上記の定義されたパラメータ(Kf、M、R、ω0)と、式(14)とから求めた。そして、a0、an、Gy(0)、|Gy(j×n×ω)|、および、∠Gy(j×n×ω)の値を式(8)に代入することにより、電圧V(t)が得られた。
Then, as described above, r 1 was calculated from the frequency characteristic of the impedance of the
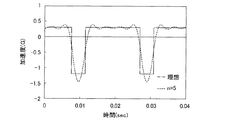
上記のシミュレーションの結果、図6に示す電圧V(t)の波形が得られた。なお、図6では、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)において、a1〜a5(n=1〜5)の5次の次数までを加算した。図6に示すように、電圧V(t)の波形は、正(+)側と負(−)側とで非対称な形状を有する交流状になることが確認された。また、図6に示す電圧V(t)をリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加するシミュレーションにより、図7に示すリニアモータ100の加速度の波形が得られた。なお、図7において、1点鎖線により表される矩形状の波形は、リニアモータ100の加速度の理想的な波形(図3参照)である。図7に示すように、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)においてa1〜a5(n=1〜5)の5次の次数までを加算した場合、理想的な加速度の波形(1点鎖線)と、シミュレーションによって得られた加速度の波形(点線)とは、少しずれていることが判明した。なお、図7に示すリニアモータ100の加速度の波形の1周期を時間積分した場合、時間積分の値は略0になる。つまり、図7において斜線により示される領域S3および領域S4の面積は、略等しい。
As a result of the above simulation, the waveform of the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 6 was obtained. In FIG. 6, up to the fifth order of a 1 to a 5 (n = 1 to 5) are added to the voltage V (t) shown in the equation (8). As shown in FIG. 6, it was confirmed that the waveform of the voltage V (t) was an alternating shape having an asymmetric shape between the positive (+) side and the negative (−) side. Moreover, the waveform of the acceleration of the
次に、図6に示す電圧V(t)の波形を反転させた図8に示す電圧V(t)をリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加したシミュレーションにより、図9に示す加速度の波形が得られた。そして、図9に示す加速度の波形は、加速度が0の基準線に対して、図7に示す加速度の波形と略対称な形状になることが判明した。つまり、第1実施形態では、平面コイル4に印加する電圧V(t)の波形を反転させた場合、電圧V(t)の反転の前後で、加速度が0の基準線に対して、加速度の波形が略対称な形状になることが確認された。
Next, an acceleration waveform shown in FIG. 9 is obtained by simulation in which the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 8 obtained by inverting the waveform of the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 6 is applied to the
次に、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)において、a1〜a10(n=1〜10)の10次の次数までを加算した場合、図10に示す電圧V(t)の波形がシミュレーションにより得られた。そして、図10に示す電圧V(t)をリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加したシミュレーションにより、図11に示す加速度の波形が得られた。図11に示すように、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)においてa1〜a10(n=1〜10)の10次の次数までを加算した場合では、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)においてa1〜a5(n=1〜5)の5次の次数までを加算した場合(図7参照)と比べて、シミュレーションによって得られた加速度の波形(点線)が理想的な加速度の波形(1点鎖線)により近づくことが確認された。これにより、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)において、加算する次数(n)を大きくすればするほど、シミュレーションによって得られる加速度の波形が理想的な加速度の波形により近づくと考えられる。
Next, in the voltage V (t) shown in Expression (8), when the 10th order of a 1 to a 10 (n = 1 to 10) is added, the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. The waveform was obtained by simulation. Then, the acceleration waveform shown in FIG. 11 was obtained by a simulation in which the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 10 was applied to the
また、図10に示す電圧V(t)の波形を反転させた図12に示す電圧V(t)をリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加したシミュレーションにより、図13に示す加速度の波形が得られた。そして、図13に示す加速度の波形は、加速度が0の基準線に対して、図11に示す加速度の波形と略対称な形状になることが判明した。つまり、平面コイル4に印加する電圧V(t)の波形を反転させた場合、電圧V(t)の反転の前後で、加速度が0の基準線に対して、加速度の波形が略対称な形状になることが確認された。
Moreover, the waveform of the acceleration shown in FIG. 13 is obtained by the simulation in which the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 12 obtained by inverting the waveform of the voltage V (t) shown in FIG. 10 is applied to the
次に、図14を参照して、リニアモータ100が消費する電力P(W)の周波数特性について行ったシミュレーションについて説明する。
Next, with reference to FIG. 14, a simulation performed on the frequency characteristics of the electric power P (W) consumed by the
まず、このシミュレーションでは、リニアモータ100の共振周波数は55(Hz)であり、共振周波数55(Hz)の共振周波数に対応する共振角周波数ω0は、2π×55(rad/s)である。また、このシミュレーションでは、式(8)に示される電圧V(t)においてa1〜a5(n=1〜5)の5次の次数までを加算した場合と、a1〜a10(n=1〜10)の10次の次数までを加算した場合とについて、電力P(W)のシミュレーションを行った。そして、図14に示すように、5次の次数までを加算した場合または10次の次数までを加算した場合のいずれにおいても、振動数が52Hz(角周波数ωが2π×52rad/s)より小さい範囲では、電力P(W)は、振動数が増加するにつれて、急減に減少していることが判明した。また、周波数が52Hz(角周波数ωが2π×52rad/s)以上の範囲では、電力P(W)は、振動数が増加するにつれて、徐々に増加していることが判明した。つまり、周波数が52Hz(角周波数ωが2π×52rad/s)の場合、電力P(W)が極小になることが確認された。また、リニアモータ100が消費する電力P(W)の極小値の2倍までをリニアモータ100が消費する電力P(W)として許容すると仮定した場合、許容される角周波数ωは、共振角周波数ω0の3分の2倍以上でかつ共振角周波数ω0の2倍以下(2ω0/3≦ω≦2ω0)であることが確認された。
First, in this simulation, the resonance frequency of the
第1実施形態によるリニアモータ100では、以下の効果を得ることができる。
In the
(1)平面コイル4に波形が非対称な交流状の電圧を印加して、筐体7(リニアモータ100)の振動方向の加速度の波形を加速度が0の基準線に対して一方方向側と他方方向側とで非対称になるように構成した。これにより、平面コイル4に印加する電圧の波形を反転させた場合、平面コイル4に印加する電圧の波形が非対称であるので、電圧の波形の反転の前後において、筐体7(リニアモータ100)を把持した場合に得られる力覚の方向を変化させることができる。
(1) An AC voltage having an asymmetric waveform is applied to the
(2)交流状の電圧の波形を反転させた電圧を平面コイル4に印加した場合に、電圧V(t)の波形の反転の前後で筐体7(リニアモータ100)の加速度の波形が、加速度が0の基準線に対して略対称になるように、平面コイル4に印加する電圧V(t)を調整した。これにより、平面コイル4に印加する交流状の電圧の波形を反転させて、リニアモータ100の一方方向側に引っ張られるように感じる力覚を、他方方向側に引っ張られるように感じる力覚に切り替えた場合、把持したリニアモータ100の一方方向側と他方方向側とで略同じ大きさの力覚を得ることができる。その結果、リニアモータ100の一方方向側に力覚を得る際と他方方向側に力覚を得る際とのそれぞれにおいて電圧の波形を求める場合と異なり、リニアモータ100の一方方向側と他方方向側とで略同じ大きさの力覚を容易に得ることができる。
(2) When a voltage obtained by inverting the waveform of the AC voltage is applied to the
(3)平面コイル4に印加する電圧の波形を、正側と負側とで非対称になるように構成した。これにより、正弦波状の交流電圧のように正側と負側とで点対称な電圧を平面コイル4に印加する場合と異なり、リニアモータ100の構成を非対称にしなくても、容易に、リニアモータ100の振動方向の加速度の波形を、加速度が0の基準線に対して一方方向側と他方方向側とで非対称にすることができる。その結果、リニアモータ100の構成を非対称にしなくても、容易に、一方方向側または他方方向側の力覚を付与することができる。
(3) The waveform of the voltage applied to the
(4)バネ部3aおよび3bを、可動部2の移動方向に沿った方向の一方側と他方側とにそれぞれ配置するとともに、バネ部3aおよび3bを、可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して略対称になるように配置した。これにより、バネ部が可動部2の移動方向に沿った方向の一方側または他方側のいずれか一方に配置される場合や、バネ部3aおよび3bが可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して非対称に配置される場合と異なり、リニアモータ100の形状を可動部2の往復移動の中心線C1に対して対称にしやすくすることができる。なお、可動部の往復移動の中心線に対して非対称な形状を有するリニアモータ(たとえば、可動部の一方側にはバネの弾性力が働き、他方側には永久磁石の磁界が働く場合など)に、非対称な波形を有する電圧を反転させて印加した場合、電圧の波形の反転の前後において、リニアモータの加速度は、加速度が0になる基準線に対して対称にならない。その結果、リニアモータを把持した場合に感じる力覚の大きさが、電圧の波形を反転させる前後において異なってしまう。
(4) The
(5)リニアモータ100の加速度の波形を、加速度が0の基準線に対して正側と負側とに変動するように構成し、周期性を有するリニアモータ100の加速度の波形の1周期Tにおける時間積分の値を略0になるように構成した。これにより、上記式(8)により表される電圧V(t)が発散するのを抑制することができる。
(5) The acceleration waveform of the
(6)理想的な形状を有するリニアモータ100(筐体7)の加速度の波形と、リニアモータ100のインピーダンスの周波数特性から導かれるインピーダンスZ(ω0)および角周波数(ω0、γ1、γ2)とに基づいて、平面コイル4に印加する電圧V(t)の波形を求めた。これにより、理想的な形状を有する加速度の波形と、インピーダンスの周波数特性とから求められる電圧V(t)をリニアモータ100の平面コイル4に印加することにより、容易に、理想的な形状に近いリニアモータ100の加速度を得ることができる。
(6) Impedance Z (ω 0 ) and angular frequency (ω 0 , γ 1 ) derived from the acceleration waveform of the linear motor 100 (housing 7) having an ideal shape and the frequency characteristics of the impedance of the
(7)振動するリニアモータ100(筐体7)の角周波数ωを、振動するリニアモータ100の共振角周波数ω0の3分の2倍以上でかつ2倍以下になるように構成した。これにより、上記図14に示したように、リニアモータ100が消費する電力P(W)を極小値の2倍以下に抑制することができる。
(7) The angular frequency ω of the vibrating linear motor 100 (housing 7) is configured to be not less than two-thirds and not more than twice the resonance angular frequency ω 0 of the vibrating
(8)平面コイル4を可動部2の移動方向に沿って扁平状になるように渦巻状に形成した。これにより、コイルの巻き面が可動部の移動方向に対して直交する方向に配置される場合と比べて、コイルの巻き面による高さ方向への領域を設ける必要がなくなり、Z方向の厚みを小さくすることができる。その結果、ユーザに擬似力覚を知覚させるリニアモータ100の薄型化を実現することができる。
(8) The
(第2実施形態)
次に、図15〜図18を参照して、第2実施形態について説明する。この第2実施形態では、1つの可動部2が設けられる上記第1実施形態と異なり、2つの第1可動部204および第2可動部205が設けられている。なお、第1可動部204および第2可動部205は、それぞれ、本発明の「第1の可動部」および「第2の可動部」の一例である。
(Second Embodiment)
Next, a second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. In the second embodiment, unlike the first embodiment in which one
第2実施形態による加速度発生デバイス201は、図15に示すように、上側筐体202と、下側筐体203と、第1可動部204と、第2可動部205と、バネ部材206と、第1コイル基板207と、第2コイル基板208とから構成されている。上側筐体202および下側筐体203は、互いの開口部を嵌め合わせることにより直方体の筐体209を形成する。筐体209の内部には、第1可動部204、第2可動部205およびバネ部材206が収納されている。また、第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208は、下側筐体203に固定されている。
As shown in FIG. 15, the
加速度発生デバイス201は、第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208に電流を流すことにより、筐体209内において第1可動部204および第2可動部205を往復移動させ、バネ部材206で可動部の移動を受け止めて振動するように構成されている。上側筐体202および下側筐体203は、磁性材料から構成されており、第1可動部204および第2可動部205から生じる磁束が筐体209から外部へ漏出することを抑制している。
The
上側筐体202は、矩形状の底面202aと、底面202aの長手方向に沿った側面202bと、底面202aの短手方向に沿った側面202cとから構成されている。また、下側筐体203は、略矩形状の底面203aと、底面203aの長手方向に沿った側面203bとから構成されている。上側筐体202および下側筐体203は、上側筐体202の側面202bおよび側面202cと、下側筐体203の側面203bとが嵌め合わされることにより筐体209を形成している。
The
下側筐体203の底面203aには、矩形状の第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208と略同一形状を有する開口部231および232が形成されている。また、下側筐体203の2つの側面203bには、それぞれ、第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208の厚みに応じた開口部233および234が形成されている。第1コイル基板207は、開口部231および233に嵌め込まれることにより、下側筐体203に固定されている。また、第2コイル基板208は、開口部232および234に嵌め込まれることにより、下側筐体203に固定されている。
また、下側筐体203の底面203aの上面には、上側に突出した一対のレール210が形成されている。一対のレール210は、下側筐体203の長手方向(X方向)に沿って、X方向の一端から開口部231までの間と、開口部231から開口部232までの間と、開口部232から他端までの間とに形成されている。レール210の断面形状は、角が削られた略円弧形状に形成されている。
A pair of
なお、上側筐体202、レール210および下側筐体203の表面には、フッ素樹脂加工が施されている。具体的には、ニムフロン処理(ニムフロンは登録商標)が施されている。ニムフロン処理とは、摩擦係数の低いテフロン(登録商標)(ポリテトラフルオロエチレン:PTFE)と無電解Niとの双方の特性を併せ持つメッキ処理である。ニムフロン処理は、無電解メッキ液にPTFE粒子を混ぜてメッキすることにより行われる。
In addition, the fluororesin process is given to the surface of the upper housing | casing 202, the
図16に示すように、第1可動部204および第2可動部205は、それぞれ永久磁石211と、おもり212と、磁石カバー213とから構成されている。永久磁石211は、直方体形状を有し、フェライトやネオジウム等の強磁性材料から構成されている。永久磁石211は、その厚み方向(Y方向)に一対の磁極が着磁された第1磁石211aおよび第2磁石211bから構成されており、第1磁石211aと第2磁石211bとは互いに磁極が逆方向となっている。
As shown in FIG. 16, the first
おもり212は、直方体形状を有しており、おもり212の長手方向(X方向)および短手方向(Z方向)の幅は、永久磁石211の長手方向(X方向)および短手方向(Z方向)の幅よりも大きい。また、おもり212には、永久磁石211と略同一の形状を有したY方向に貫通する貫通孔212aが形成されている。貫通孔212aの内部には、永久磁石211が嵌め込まれており、永久磁石211は、接着剤等により貫通孔212aに固定されている。おもり212は、たとえば比重の大きい材料であるタングステン等から形成されている。なお、おもり212のY方向の厚みは、永久磁石211のY方向の厚みと略同一である。
The
磁石カバー213は、非磁性材料から構成されており、永久磁石211およびおもり212の上面を覆うとともに、X方向側の両端部がおもり212のX方向側の側面およびおもり212の下面の一部まで延びるように形成されている。磁石カバー213は、永久磁石211およびおもり212と接着剤等により固定されている。磁石カバー213は、たとえばりん青銅等により形成されている。なお、磁石カバー213の外面には、ニムフロン処理が施されている。
The
バネ部材206は、非磁性材料から構成されており、2つの皿部206aおよび206bと、同一のバネ定数を有する3つの板バネ206c、206dおよび206eとが一体的に形成されている。バネ部材206の皿部206aには、第1可動部204が固定されるとともに、皿部206bには、第2可動部205が固定されている。また、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の移動方向(X方向)における両側面は、板バネ206c、206dおよび206eによって挟みこんで支持されている。これにより、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の移動が、板バネ206c、206dおよび206eにより受け止められる。また、バネ部材206は、たとえばSUS301またはSUS304等により形成されている。なお、板バネ206c、206dおよび206eは、それぞれ、本発明の「第1弾性部材」、「第2弾性部材」および「第3弾性部材」の一例である。
The
皿部206aおよび206bは、磁石カバー213の上面と略同一の形状を有した皿状の部材であり、皿部206aおよび206bのそれぞれの下面と第1可動部204および第2可動部205の上面とが接着されて固定されている。皿部206aおよび206bの中央部には、それぞれ、永久磁石211の磁極面と略同一の形状を有する開口部261および262が形成されている。
The
板バネ206cは、第1可動部204のX2方向側の側面と上側筐体202の側面202cとの間に設けられるとともに、板バネ206dは、第1可動部204のX1方向側の側面と第2可動部205のX2方向側の側面との間に設けられている。また、板バネ206eは、第2可動部205のX1方向側の側面と上側筐体202の側面202cとの間に設けられている。また、板バネ206c、206dおよび206eは、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の移動を受け止めるために、それぞれ1つの屈曲点Xを有している。
The
次に、図17および図18を参照して、第1コイル基板207の構成について説明する。第1コイル基板207は、第1可動部204の永久磁石211の磁極面と平行になるように下側筐体203に配置されている。ここで、平行とは、互いに平行な状態だけでなく、永久磁石211を含む第1可動部204が往復移動する際の妨げにならない程度に平行な状態からずれた状態を含んでいる。
Next, the configuration of the
第1コイル基板207は、上層コイル271および下層コイル272が積層された平面コイル273と、配線層274と、ヨーク275とを含んでいる。第1コイル基板207の各構成要素は、上側からこの順に積層された絶縁性樹脂層276、277および278によって一体的に形成されている。なお、平面コイル273は、本発明の「第1のコイル」の一例である。
The
具体的には、絶縁性樹脂層276は上層コイル271を覆うとともに、絶縁性樹脂層277は下層コイル272およびヨーク275を覆っている。また、絶縁性樹脂層278は配線層274の一部を覆っている。絶縁性樹脂層278の下面には開口部278a(図18参照)が形成されており、開口部278aから配線層274が露出している。
Specifically, the insulating
平面コイル273の上層コイル271は、第1コイル基板207の外側から内側に向かって反時計回りに渦巻状に巻回されている。下層コイル272は、第1コイル基板207の内側から外側に向かって反時計回りに渦巻状に巻回されている。上層コイル271の内側の端部と、下層コイル272の内側の端部とは、第1コイル基板207の中心部近傍において互いに接続されている。上層コイル271の外側の端部は、第1コイル基板207の厚み方向に延びる接続線279を介して配線層274に接続されている。下層コイル272の外側の端部は、第1コイル基板207の厚み方向に延びる接続線280を介して配線層274に接続されている。平面コイル273は、第1コイル基板207の長手方向に沿って延びる複数のコイル線を含む領域273Aおよび273Bを有しており、領域ごとに同じ方向に電流が流れるように形成されている。
The
配線層274は、平面コイル273の上層コイル271および下層コイル272に駆動電流を供給するためのものであり、配線層274は、駆動電流を制御するための駆動電流制御回路290に接続されている。駆動電流制御回路290は、所定の周期で平面コイル273に供給する駆動電流の方向を切り替える。なお、駆動電流制御回路290は、本発明の「制御部」の一例である。
The
また、第2コイル基板208は、第1コイル基板207と平行に並んで、第2可動部205の永久磁石211の磁極面と対向して下側筐体203に配置されている。第2コイル基板208は、第1コイル基板207と同一の構成であり、上層コイル281および下層コイル282が積層された平面コイル283と、配線層284と、ヨーク285とを含んでいる。また、平面コイル283の上層コイル281および下層コイル282の外側の端部は、駆動電流制御回路290に接続されている。駆動電流制御回路290は、第1コイル基板207の平面コイル273および第2コイル基板208の平面コイル283に供給する駆動電流を独立して制御するように構成されている。なお、平面コイル283は、本発明の「第2のコイル」の一例である。
Further, the
以上のように、加速度発生デバイス201では、第1可動部204および第2可動部205において磁石カバー213がおもり212の下面まで延びているとともに、下側筐体203にレール210が形成されている。上述したように、下側筐体203の表面および磁石カバー213の外面にはニムフロン処理が施されているため、第1可動部204および第2可動部205が移動する場合に、磁石カバー213とレール210とが接触したとしても生じる摩擦を低減することができる。その結果、加速度発生デバイス201は、効率良く第1可動部204および第2可動部205を移動させることができるので、振動量を増大させることが可能となる。
As described above, in the
また、加速度発生デバイス201は、第1コイル基板207がヨーク275を備えているとともに、第2コイル基板208がヨーク285を備えており、上側筐体202および下側筐体203は磁性材料で構成されているので、永久磁石211が生じる磁束はヨークおよび筐体内を選択的に通過する。これにより、永久磁石211の磁束が筐体209の外部まで漏出することを抑制することが可能となる。
In the
次に、図19および図20を参照して、加速度発生デバイス201の動作について説明する。なお、図20の横軸は平面コイル273および283に駆動電流を供給してからの時間を示すとともに、縦軸は加速度発生デバイス201の振動量(加速度)を示している。また、縦軸の振動量は、X1方向の振動量を正、X2方向の振動量を負としている。
Next, the operation of the
まず、第1可動部204の移動について説明する。駆動電流制御回路290(図18参照)は、第1コイル基板207の平面コイル273に対し、配線層274を介して図18に示すA方向に駆動電流を供給する。これにより、図19に示すように、平面コイル273の領域273Aには、第1コイル基板207の長手方向に沿って紙面奥側から手前側、すなわちZ2方向に電流が流れる。また、平面コイル273の領域273Bには、第1コイル基板207の長手方向に沿って紙面手前側から奥側、すなわちZ1方向に電流が流れる。
First, the movement of the first
ここで、第1可動部204の永久磁石211の第1コイル基板207と対向する面のN極面211AとS極面211Bとの間において発生する磁界の向きは、N極面211A下においては、N極面211Aの表面から第1コイル基板207に向かった方向、すなわちY2方向となる。また、S極面211B下においては、第1コイル基板207からS極面211Bに向かった方向、すなわちY1方向となる。このように、第1可動部204の永久磁石211が発生する磁界は、第1コイル基板207の平面コイル273の領域273Aおよび273Bを流れる電流の方向と直交することとなる。
Here, the direction of the magnetic field generated between the N-
そのため、平面コイル273の各領域を流れる電流は、永久磁石211の磁界からX1方向への力を受ける。すなわち、第1コイル基板207には、X1方向への力が作用する。しかし、第1コイル基板207は下側筐体203に固定されているので、第1可動部204は反作用によりX2方向への力を受け、X2方向に移動する。
Therefore, the current flowing through each region of the
また、第2可動部205についても、第1可動部204と同様に、駆動電流制御回路290が第2コイル基板208の平面コイル283に対し、配線層284を介して図18に示すA方向に駆動電流を供給することにより、第2可動部205は、X2方向へ移動する。そして、所定時間後、駆動電流制御回路290が平面コイル273および283に供給する駆動電流の方向をA方向からB方向へ切り替えることにより、第1可動部204および第2可動部205がX1方向に移動する。
Also for the second
このようにして、駆動電流制御回路290が所定の周波数で駆動電流の方向を切り替えることによって、第1可動部204および第2可動部205は、X1方向とX2方向とに交互に往復移動する。
In this way, when the drive
このとき、駆動電流制御回路290は、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍になるよう制御する。これにより、図20に示すように、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の一往復中における加速度の波形(時間変化)が、X1方向(正の方向)に対する移動とX2方向(負の方向)に対する移動とで非対称となる。その結果、ユーザに対してX1方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。これは、第1可動部204の加速度と第2可動部205の加速度とが、互いに強め合ったり弱め合ったりすることを交互に繰り返すことにより生じる現象である。
At this time, the drive
ここで、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧と、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧との位相差を調整することにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向の所望の方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。つまり、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧と、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧との位相差を調整することにより、加速度の波形が、加速度が0の基準線に対して、図20に示される波形の正負を反転させた波形を得ることが可能となる。
Here, by adjusting the phase difference between the AC voltage applied to the
第2実施形態による加速度発生デバイス201では、以下の効果を得ることができる。
The
(9)加速度発生デバイス201を、平面コイル273および平面コイル283と、バネ部材206と、永久磁石211とにより構成した。これにより、加速度発生デバイスを、バネ、永久磁石、ボビンおよびコイルなどにより構成する場合と異なり、構成を簡易にすることができる。また、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の一往復中における加速度の波形が、正の方向に対する移動と負の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、平面コイル273および平面コイル283に流れる電流を制御するように駆動電流制御回路290を構成した。これにより、加速度発生デバイスを、バネ、永久磁石、ボビンおよびコイルなどにより構成して、バネ、永久磁石およびボビンなどの相対的な位置を調整して擬似力覚を発生させる場合と異なり、容易に、任意の方向に擬似力覚を発生させることができる。
(9) The
(10)平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍にした。これにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向に明確な擬似力覚を提示することができる。なお、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧の周波数は、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍に限られず、1.5倍以上2.5倍以下の間であればよい。また、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧の周波数の1.5倍以上2.5倍以下としてもよい。平面コイル273および283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率を1.5倍以上2.5倍以下とすることにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向に明確な擬似力覚を提示することができる。
(10) The frequency of the alternating voltage applied to the
また、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧および平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数を同一とし、位相差を調整することによっても上述した効果と同一の効果を得ることができる。
Also, the same effect as described above can be obtained by adjusting the phase difference by setting the frequency of the AC voltage applied to the
さらに、平面コイル273および283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率を1.5倍以上2.5倍以下に固定しつつ、各周波数を連続的に変化させる構成であっても上述した効果と同一の効果を得ることができる。
Furthermore, even if the frequency ratio of the AC voltage applied to the
(第3実施形態)
次に、図21を参照して、本発明の第3実施形態について説明する。この第3実施形態では、第1コイル基板207と第2コイル基板208とが隣接するように配置されている上記第2実施形態と異なり、第1コイル基板207と第2コイル基板208とが互いに積層されている。なお、第2実施形態の加速度発生デバイス201と同一の機能を有する構成要素については、同一の符号を付して説明は省略する。
(Third embodiment)
Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In the third embodiment, unlike the second embodiment in which the
第3実施形態による加速度発生デバイス301は、図21に示すように、第1コイル基板207と第2コイル基板208とが互いに積層されている。第1コイル基板207の第2コイル基板208と接触している面とは反対側の面と対向するように、第1可動部204が配置されており、第2コイル基板208の第1コイル基板207と接触している面とは反対側の面と対向するように、第2可動部205が配置されている。ここで、第1コイル基板207と第2コイル基板208とは、配線層274および284が露出している面(図18参照)が重ね合わされるように積層されている。
As shown in FIG. 21, the
また、加速度発生デバイス301は、第1バネ部材361と、第2バネ部材362とを備えている。第1バネ部材361は、非磁性材料から構成されており、1つの皿部361aと、2つの板バネ361bおよび361cとが一体的に形成されている。第1バネ部材361では、皿部361aには、第1可動部204が固定されているとともに、第1可動部204の移動方向(X方向)における両側面が板バネ361bおよび361cによって挟みこんで支持されている。これにより、第1可動部204の移動が第1バネ部材361により受け止められる。また、第2バネ部材362も、第1バネ部材361と同様の構成であり、第2可動部205の移動が第2バネ部材362により受け止められる。なお、第1バネ部材361および第2バネ部材362は、それぞれ同一のバネ定数を有している。また、第1バネ部材361および第2バネ部材362は、それぞれ、本発明の「第4弾性部材」および「第5弾性部材」の一例である。
The
なお、加速度発生デバイス301のその他の構成および動作は、第2実施形態の加速度発生デバイス201と同一であるので、ここでは説明は省略する。また、第3実施形態の加速度発生デバイス301の効果は、上記第2実施形態の加速度発生デバイス201と同様である。
Since the other configuration and operation of the
ただし、加速度発生デバイス301では、第1可動部204、第2可動部205、第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208の位置関係を調整することにより、第1可動部204および第2可動部205に対し、X1方向およびX2方向への移動に加え、Y1方向およびY2方向への移動も生じさせることが可能である。これにより、加速度発生デバイス301は、ユーザに対し、より多様な疑似力覚を提示することができる。
However, in the
(第4実施形態)
次に、図22を参照して、本発明の第4実施形態について説明する。この第4実施形態では、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが移動する方向に沿って配置されている上記第2実施形態と異なり、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが移動する方向と交差する方向に沿って配置されている。
(Fourth embodiment)
Next, a fourth embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In the fourth embodiment, the first
加速度発生デバイス302は、第2実施形態の加速度発生デバイス201のように、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが直列に配置された構成ではなく、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが並列に配置されている。つまり、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが、第1可動部204と第2可動部205とが移動するZ方向と交差するX方向に沿って配置されている。なお、第1可動部204および第2可動部205は、第1バネ部材361および第2バネ部材362にそれぞれ支持されている。
The
また、加速度発生デバイス302のその他の構成および動作は、上記第2実施形態の加速度発生デバイス201と同一であるので、ここでは説明は省略する。また、加速度発生デバイス302は、加速度発生デバイス201と同一の効果を奏する。
Further, since the other configuration and operation of the
(第5実施形態)
次に、図23〜図26を参照して、本発明の第5実施形態について説明する。この第5実施形態では、1つの可動部2に対して、1つの平面コイル4が設けられている上記第1実施形態と異なり、1つの可動部404に対して、2つの平面コイル463と平面コイル473とが設けられている。
(Fifth embodiment)
Next, a fifth embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In the fifth embodiment, unlike the first embodiment in which one
加速度発生デバイス401は、図23および図24に示すように、上側筐体402と、下側筐体403と、可動部404と、バネ部材405と、第1コイル基板406と、第2コイル基板407とから構成されている。上側筐体402および下側筐体403は、互いの開口部を嵌め合わせることにより直方体の筐体408を形成する。筐体408の内部には、可動部404およびバネ部材405が収納されている。また、筐体408の内側において、第1コイル基板406は上側筐体402に固定されているとともに、第2コイル基板407は下側筐体403に固定されている。
As shown in FIGS. 23 and 24, the
加速度発生デバイス401は、第1コイル基板406および第2コイル基板407に電流を流すことにより、筐体408内において可動部404を往復移動させ、バネ部材405で可動部404の移動を受け止めて振動する構成である。上側筐体402および下側筐体403は磁性材料から構成されており、可動部404から発生する磁束が筐体408から外部へ漏出することを抑制している。
The
上側筐体402は、矩形状の底面402aと、底面402aの長手方向に沿った側面402bと、底面402aの短手方向に沿った側面402cとから構成されている。また、下側筐体403は、略矩形状の底面403aと、底面403aの長手方向に沿った側面403bとから構成されている。上側筐体402および下側筐体403は、上側筐体402の側面402bおよび側面402cと、下側筐体403の側面403bとが嵌め合わされることにより筐体408を形成している。
The
上側筐体402の底面402aには、矩形状の第1コイル基板406と略同一形状を有する開口部402dが形成されている。また、上側筐体402の側面402bには、第1コイル基板406の厚みに応じた開口部402eが形成されている。第1コイル基板406は、開口部402dおよび402eに嵌め込まれることにより、上側筐体402に固定されている。
An
同様に、下側筐体403の底面403aには、矩形状の第2コイル基板407と略同一形状を有する開口部403dが形成されている。また、下側筐体403の側面403bには、第2コイル基板407の厚みに応じた開口部403eが形成されている。第2コイル基板407は、開口部403dおよび403eに嵌め込まれることにより、下側筐体403に固定されている。
Similarly, an
また、下側筐体403の底面403aの上面には、上側に突出した一対のレール409が形成されている。一対のレール409は、下側筐体403の長手方向(X方向)に沿って、X方向の一端から開口部403dまでの間と、開口部403dから他端までの間とに形成されている。また、一対のレール409は、並行に延びるように形成されている。レール409の断面形状は、角が削られた略円弧形状に形成されている。
A pair of
なお、上側筐体402、レール409および下側筐体403の表面は、フッ素樹脂加工が施されている。具体的には、ニムフロン処理(ニムフロンは登録商標)が施されている。ニムフロン処理とは、摩擦係数の低いテフロン(登録商標)(ポリテトラフルオロエチレン:PTFE)と無電解Niとの双方の特性を併せ持つメッキ処理である。ニムフロン処理は、無電解メッキ液にPTFE粒子を混ぜてメッキすることにより行われる。
Note that the surfaces of the
図24に示すように、可動部404は、永久磁石410と、おもり411と、磁石カバー412とから構成されている。永久磁石410は、直方体形状を有し、フェライトやネオジウム等の強磁性材料から構成されている。永久磁石410は、その厚み方向(Y方向)に一対の磁極が着磁された第1磁石410aおよび第2磁石410bから構成されており、第1磁石410aと第2磁石410bとは互いに磁極が逆方向となっている。
As shown in FIG. 24, the
おもり411は、直方体形状を有し、おもり411の長手方向(X方向)および短手方向(Z方向)の幅は、永久磁石410の長手方向(X方向)および短手方向(Z方向)の幅よりも大きい。また、おもり411には、永久磁石410と略同一の形状を有し、Y方向に貫通する貫通孔411aが形成されている。貫通孔411aの内部には、永久磁石410が嵌め込まれており、接着剤等により固定されている。おもり411は、たとえば比重の大きい材料であるタングステン等から形成されている。なお、おもり411のY方向の厚みは、永久磁石410のY方向の厚みと同一である。
The
磁石カバー412は、非磁性材料から構成されており、永久磁石410およびおもり411の上面を覆うとともに、X方向側の両端部がおもり411のX方向側の側面およびおもり411の下面の一部まで延びるように形成されている。磁石カバー412は、永久磁石410およびおもり411と接着剤等により固定されている。磁石カバー412は、たとえばりん青銅等により形成されている。なお、磁石カバー412の外面には、ニムフロン処理が施されている。
The
バネ部材405は、非磁性材料から構成されており、皿部405aと、2つの板バネ405bおよび405cとが一体的に形成されている。バネ部材405は、皿部405aと可動部404とを固定し、可動部404の移動方向(X方向)における両側面を板バネ405bおよび405cによって挟みこんで支持している。これにより、可動部404の移動がバネ部材405により受け止められる。バネ部材405は、たとえばSUS301またはSUS304等により形成されている。なお、板バネ405cおよび405bは、それぞれ、本発明の「第1弾性部材」および「第2弾性部材」の一例である。
The
皿部405aは、磁石カバー412の上面と略同一の形状を有した皿状の部材であり、皿部405aの下面と可動部404の上面とが接着されることにより固定されている。皿部405aの中央部には、永久磁石410の磁極面と略同一の形状を有する開口部451が形成されている。
The
板バネ405bおよび405cは、可動部404のX方向の両側面と上側筐体402の側面402c(図23参照)との間に設けられている。具体的には、板バネ405bおよび405cは、板バネ405bおよび405cの一端側において皿部405aに接続されており、他端側において上側筐体402の側面402cに固定されている。また、板バネ405bおよび405cは、可動部404の移動を受け止めるために、可動部404の側面と上側筐体402の側面402cとの間で、1つの屈曲点Xを有している。これにより、板バネ405bおよび405cは、可動部404に対して、X方向に沿って互いに逆方向に付勢し合う。
The leaf springs 405b and 405c are provided between both side surfaces in the X direction of the
図23に示すように、第1コイル基板406は、永久磁石410の一方の磁極面と平行になるように上側筐体402に配置されている。ここで、平行とは、互いに平行な状態だけでなく、永久磁石410を含む可動部404が往復移動する際の妨げにならない程度に平行な状態からずれた状態を含んでいる。
As shown in FIG. 23, the
図25に示すように、第1コイル基板406は、上層コイル461および下層コイル462が積層された平面コイル463と、配線層464と、ヨーク465とを含んでいる。第1コイル基板406の各構成要素は、上側からこの順に積層された絶縁性樹脂層466、467および468によって一体的に形成されている。なお、平面コイル463は、本発明の「第1のコイル」の一例である。
As shown in FIG. 25, the
具体的には、絶縁性樹脂層466は配線層464の一部を覆っているとともに、絶縁性樹脂層467はヨーク465および上層コイル461を覆っている。また、絶縁性樹脂層468は下層コイル462を覆っている。図26に示すように、絶縁性樹脂層466の上面には開口部466aが形成されており、開口部466aから配線層464が露出している。
Specifically, the insulating
平面コイル463の上層コイル461は、第1コイル基板406の外側から内側に向かって反時計回りに渦巻状に巻回されている。下層コイル462は、第1コイル基板406の内側から外側に向かって反時計回りに渦巻状に巻回されている。上層コイル461の内側の端部と、下層コイル462の内側の端部とは、第1コイル基板406の中心部近傍において互いに接続されている。上層コイル461の外側の端部は、第1コイル基板406の厚み方向に延びる接続線469を介して配線層464に接続されている。下層コイル462の外側の端部は、第1コイル基板406の厚み方向に延びる接続線470を介して配線層464に接続されている。また、図26に示すように、平面コイル463は、第1コイル基板406の長手方向に沿って延びる複数のコイル線を含む領域463Aおよび463Bを有しており、領域ごとに同じ方向に電流が流れるように形成されている。
The
配線層464は、平面コイル463の上層コイル461および下層コイル462に駆動電流を供給するためのものであり、駆動電流を制御するための駆動電流制御回路490と接続されている。駆動電流制御回路490は、所定の周期で平面コイル463に供給する駆動電流の方向を切り替える。
The
また、図25に示すように、第2コイル基板407は、第1コイル基板406と同一の構成であり、第1コイル基板406とは上下逆向きの状態で永久磁石410の他方の磁極面と平行になるように下側筐体403に配置(図23参照)されている。具体的には、第2コイル基板407は、上層コイル471および下層コイル472が積層された平面コイル473と、配線層474と、ヨーク475とを含んでいる。また、平面コイル473の上層コイル471および下層コイル472の外側の端部は、配線層474を介して駆動電流制御回路490に接続されている。駆動電流制御回路490は、平面コイル463に供給する駆動電流と平面コイル473に供給する駆動電流とを独立して制御しており、所定の周期で平面コイル473に供給する駆動電流の方向を切り替える。なお、平面コイル473は、本発明の「第2のコイル」の一例である。
Also, as shown in FIG. 25, the
また、図26に示すように、平面コイル473は、第2コイル基板407の長手方向に沿って延びる複数のコイル線を含む領域473Aおよび473Bを有しており、領域ごとに同じ方向に電流が流れるように形成されている。なお、平面コイル463の領域463Aと463Bとは、それぞれ、平面コイル473の領域473Aと473Bとに重畳するように配置されている。
Further, as shown in FIG. 26, the
以上のように、加速度発生デバイス401では、可動部404において磁石カバー412がおもり411の下面まで延びているとともに、下側筐体403にレール409が形成されている。上述したように、下側筐体403の表面および磁石カバー412の外面にはニムフロン処理が施されているため、可動部404が移動する場合に、磁石カバー412とレール409とが接触したとしても生じる摩擦を低減することが可能となる。その結果、加速度発生デバイス401は、可動部404を効率良く移動させることができ、振動量を増大させることが可能となる。
As described above, in the
また、加速度発生デバイス401は、第1コイル基板406がヨーク465を備えるとともに、第2コイル基板407がヨーク475を備えており、上側筐体402および下側筐体403は磁性材料で構成されているため、永久磁石410が生じる磁束はヨークおよび筐体内を選択的に通過する。そのため、永久磁石410の磁束が筐体408の外部まで漏出することを抑制することが可能となる。
In the
次に、図20、図26および図27を参照して、加速度発生デバイス401の動作について説明する。
Next, the operation of the
まず、駆動電流制御回路490は、第1コイル基板406の平面コイル463に対し、配線層464を介して図26に示すA方向に駆動電流を供給する。これにより、平面コイル463の領域463Aには、第1コイル基板406の長手方向に沿って紙面奥側から手前側、すなわちZ2方向に電流が流れる。また、平面コイル463の領域463Bには、第1コイル基板406の長手方向に沿って紙面手前側から奥側、すなわちZ1方向に電流が流れる。
First, the drive
また、駆動電流制御回路490は、第2コイル基板407の平面コイル473に対し、配線層474を介して図26に示すB方向に駆動電流を供給する。これにより、平面コイル473の領域473Aには、第2コイル基板407の長手方向に沿って紙面手前側から奥側、すなわちZ1方向に電流が流れる。また、平面コイル473の領域473Bには、第2コイル基板407の長手方向に沿って紙面奥側から手前側、すなわちZ2方向に電流が流れる。
In addition, the drive
ここで、永久磁石410の第1コイル基板406と対向する面のN極面410AとS極面410Bとの間において発生する磁界の向きは、N極面410A上においては、N極面410Aの表面から第1コイル基板406に向かった方向(Y1方向)となる。また、S極面410B上においては、第1コイル基板406からS極面410Bに向かった方向(Y2方向)となる。
Here, the direction of the magnetic field generated between the N-
また、永久磁石410の第2コイル基板407と対向する面のN極面410CとS極面410Dとの間において発生する磁界の向きは、N極面410C下においては、N極面410Cの表面から第2コイル基板407に向かった方向(Y2方向)となる。また、S極面410D下においては、第2コイル基板407からS極面410Dに向かった方向(Y1方向)となる。このように、永久磁石410が発生する磁界は、平面コイル463および473の各領域を流れる電流の方向と直交することとなる。
The direction of the magnetic field generated between the N-
これにより、平面コイル463および473の各領域を流れる電流は、永久磁石410の磁界からX2方向への力を受ける。すなわち、第1コイル基板406および第2コイル基板407には、X2方向への力が作用する。しかし、第1コイル基板406は上側筐体402に固定されており、第2コイル基板407は下側筐体403に固定されているので、可動部404は反作用によりX1方向への力を受け、X1方向に移動する。
As a result, the current flowing through the regions of the
そして、所定時間後、駆動電流制御回路490が平面コイル463に供給する駆動電流の方向をA方向からB方向へ切り替えるとともに、平面コイル473に供給する駆動電流の方向をB方向からA方向へ切り替えることにより、可動部404がX2方向に移動する。このようにして、駆動電流制御回路490が所定の周波数で駆動電流の方向を切り替えることによって、可動部404はX1方向とX2方向とに交互に往復移動する。
After a predetermined time, the direction of the drive current supplied to the
このとき、駆動電流制御回路490は、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍になるよう制御する。これにより、図20に示すように、可動部404の一往復中における加速度の波形(時間変化)が、X1方向(正の方向)に対する移動とX2方向(負の方向)に対する移動とで非対称となる。その結果、ユーザに対してX1方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。これは、平面コイル463に駆動電流を供給することにより生じる可動部404の加速度と、平面コイル473に電流を流すことにより生じる可動部404の加速度とが、互いに強め合ったり弱め合ったりすることを交互に繰り返すことにより生じる現象である。
At this time, the drive
ここで、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧と、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧との位相差を調整することにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向の所望の方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。
Here, by adjusting the phase difference between the AC voltage applied to the
第5実施形態による加速度発生デバイス401では、以下の効果を得ることができる。
The
(11)加速度発生デバイス401を、平面コイル463および平面コイル473と、バネ部材405と、永久磁石410とにより構成した。これにより、加速度発生デバイスを、バネ、永久磁石、ボビンおよびコイルなどにより構成する場合と異なり、構成を簡易にすることができる。また、可動部404の一往復中における加速度の波形が、正の方向に対する移動と負の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、平面コイル463および平面コイル473に流れる電流を制御するように駆動電流制御回路490を構成した。これにより、加速度発生デバイスを、バネ、永久磁石、ボビンおよびコイルなどにより構成して、バネ、永久磁石およびボビンなどの相対的な位置を調整して擬似力覚を発生させる場合と異なり、容易に、任意の方向に擬似力覚を発生させることができる。
(11) The
(12)平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍にした。これにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向に明確な擬似力覚を提示することができる。なお、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧の周波数は、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約2倍に限られず、1.5倍以上2.5倍以下の間であればよい。また、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧の周波数の約1.5倍以上2.5倍以下としてもよい。平面コイル463および473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率を1.5倍以上2.5倍以下とすることにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向に明確な擬似力覚を提示することができる。
(12) The frequency of the AC voltage applied to the
また、平面コイル463および473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率を1.5倍以上2.5倍以下に固定しつつ、各周波数を連続的に変化させる構成であっても上述した効果と同一の効果を得ることができる。
The same effect as described above can be obtained even when the frequency ratio of the AC voltage applied to the
(第6実施形態)
次に、図28を参照して、本発明の第6実施形態について説明する。この第6実施形態では、第1コイル基板406と第2コイル基板407とが、それぞれ、永久磁石410のY1方向側とY2方向側とに配置されている上記第5実施形態と異なり、第1コイル基板406が、永久磁石410のX2方向側に配置されるとともに、第2コイル基板407が、永久磁石410のY2方向側に配置されている。
(Sixth embodiment)
Next, a sixth embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In the sixth embodiment, unlike the fifth embodiment in which the
加速度発生デバイス402は、図28に示すように、第5実施形態の加速度発生デバイス401と異なり、第1コイル基板406が筐体408の上面ではなく側面に配置されている。なお、その他の構成は加速度発生デバイス401と同一であるので、ここでは説明は省略する。なお、第1コイル基板406と可動部404との間に設けられる板バネ405bは、本発明の「第3弾性部材」の一例である。
As shown in FIG. 28, the
次に、加速度発生デバイス402の動作について説明する。駆動電流制御回路490は、第2コイル基板407の平面コイル473に対し、図26に示すB方向に駆動電流を供給する。この場合、第5実施形態と同様に、平面コイル473を流れる電流が永久磁石410の磁束からX2方向の力を受けるとともに、電流が受ける力の反作用により可動部404をX1方向に移動させる力が働く。
Next, the operation of the
また、駆動電流制御回路490は、第1コイル基板406の平面コイル463に対し、図26に示すA方向に駆動電流を供給する。このとき、平面コイル463を流れる電流は、永久磁石410の磁束と斜めに交わる。そのため、平面コイル463を流れる電流は、永久磁石410の磁束からX2方向、Y1方向およびY2方向の力を受ける。Y1方向の力とY2方向の力とは互いに打ち消しあうため、平面コイル463を流れる電流はX2方向にのみ力を受けて、電流が受ける力の反作用により可動部404をX1方向に移動させる力が働く。
Further, the drive
このようにして、平面コイル463に対して図26に示すA方向に駆動電流を供給するとともに、平面コイル473に対して図26に示すB方向に駆動電流を供給することにより、可動部404はX1方向へ移動する。そして、所定時間後、駆動電流制御回路490が平面コイル463に供給する駆動電流の方向をA方向からB方向へ切り替えるとともに、平面コイル473に供給する駆動電流の方向をB方向からA方向へ切り替えることにより、可動部404がX2方向に移動する。
In this way, the drive current is supplied to the
このとき、上記第5実施形態と同様に、駆動電流制御回路490は、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧の周波数を、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧の周波数の1.5倍以上2.5倍以下、特に約2倍になるよう制御する。これにより、可動部404の一往復中における加速度の波形(時間変化)が、X1方向に対する移動とX2方向に対する移動とで非対称となる。
At this time, similarly to the fifth embodiment, the drive
ここで、平面コイル463に印加する交流電圧と、平面コイル473に印加する交流電圧との位相差を調整することにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向の所望の方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。
Here, by adjusting the phase difference between the AC voltage applied to the
また、第6実施形態では、筐体408のX2方向側の側面にのみコイル基板が配置された構成であるが、筐体408のX1方向側およびX2方向側の両側面にコイル基板が配置された構成であってもよい。
In the sixth embodiment, the coil substrate is disposed only on the side surface of the
なお、今回開示された実施形態は、すべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本発明の範囲は、上記した実施形態の説明ではなく特許請求の範囲によって示され、さらに特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれる。 The embodiment disclosed this time should be considered as illustrative in all points and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is shown not by the above description of the embodiments but by the scope of claims for patent, and further includes all modifications within the meaning and scope equivalent to the scope of claims for patent.
たとえば、上記第1実施形態では、理想的な加速度の波形として矩形状の波形を用いる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。本発明では、加速度の波形が、加速度が0の基準線に対して非対称であればよい。 For example, in the first embodiment, an example in which a rectangular waveform is used as an ideal acceleration waveform has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this. In the present invention, the acceleration waveform may be asymmetric with respect to a reference line with zero acceleration.
また、上記第1実施形態では、理想的な形状を有する加速度の波形と、リニアモータのインピーダンスの周波数特性とから、電圧V(t)を求める例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。本発明では、理想的な形状を有する加速度の波形が再現できるように、インピーダンスの周波数特性以外から電圧V(t)を求めてもよい。 In the first embodiment, the example in which the voltage V (t) is obtained from the acceleration waveform having an ideal shape and the frequency characteristics of the impedance of the linear motor has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this. Absent. In the present invention, the voltage V (t) may be obtained from a frequency characteristic other than the impedance so that an acceleration waveform having an ideal shape can be reproduced.
また、上記第1実施形態では、1つの平面コイルと1つの可動部とを有するリニアモータを用いる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、可動部の移動方向に隣接して配置される2つの平面コイルと、1つの可動部とを有するリニアモータを用いてもよい。この場合、2つの平面コイルにより発生する磁界の向きはそれぞれ異なる。また、可動部は、平面コイルと対向する側がN極またはS極の一方であり、平面コイルと対向する側と反対側がN極またはS極の他方である永久磁石からなる。 Moreover, although the example which uses the linear motor which has one planar coil and one movable part was shown in the said 1st Embodiment, this invention is not limited to this. For example, you may use the linear motor which has two planar coils arrange | positioned adjacent to the moving direction of a movable part, and one movable part. In this case, the directions of the magnetic fields generated by the two planar coils are different from each other. Further, the movable part is formed of a permanent magnet whose side facing the planar coil is one of the N or S poles and whose side opposite to the planar coil is the other of the N or S poles.
また、上記第1実施形態では、本発明の渦巻状のコイルの一例として平面コイルを用いる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、可動部の移動方向と直交する方向に所定の厚みを有するコイルでもよい。 Moreover, although the example which uses a planar coil as an example of the spiral coil of this invention was shown in the said 1st Embodiment, this invention is not limited to this. For example, a coil having a predetermined thickness in a direction orthogonal to the moving direction of the movable part may be used.
また、上記第1実施形態では、1つの平面コイルを有するリニアモータを用いる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、可動部の移動方向と直交する方向に複数の平面コイルを積層してもよい。 Moreover, although the example which uses the linear motor which has one planar coil was shown in the said 1st Embodiment, this invention is not limited to this. For example, you may laminate | stack a several planar coil in the direction orthogonal to the moving direction of a movable part.
また、上記第1実施形態では、可動部の移動方向に沿った方向の一方側と他方側とにそれぞれバネ部が配置される例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、可動部の移動方向に沿った方向の一方側または他方側のいずれか一方にだけバネ部を配置してもよい。 Moreover, in the said 1st Embodiment, although the spring part was each arrange | positioned at the one side and the other side of the direction along the moving direction of a movable part, this invention is not limited to this. For example, the spring part may be arranged only on one side or the other side in the direction along the moving direction of the movable part.
また、上記第1実施形態では、リニアモータが可動部の往復移動の中心線に対して構造的に略対称な形状を有する例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。本発明では、可動部の往復移動の中心線に対して構造的に非対称な形状を有するリニアモータにも適用可能である。 In the first embodiment, the linear motor has an example of a substantially symmetrical shape with respect to the center line of the reciprocating movement of the movable part. However, the present invention is not limited to this. The present invention is also applicable to a linear motor having a shape that is structurally asymmetric with respect to the center line of the reciprocating movement of the movable portion.
また、上記第1実施形態では、可動部の移動方向に沿った方向の一方側と他方側とにそれぞれ配置されるバネ部3aおよび3bのバネ定数(k1およびk2)が等しい例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、バネ部3aおよび3bのバネ定数を異ならせてもよい。
In the first embodiment, the
また、上記第1実施形態では、平面コイルの表面に沿った方向に沿って往復移動する可動部が設けられる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、図29に示すように、円筒形の筐体11と、筐体11の内部に収納され、X方向側に磁極面(N極、S極)を有する永久磁石12と、筐体11の外周に巻回され、互いに逆方向の電圧(電流)が印加されるコイル13およびコイル14とを備えるリニアモータ101にも適用可能である。そして、コイル13およびコイル14が発生する磁界と、永久磁石12の磁界とによって、永久磁石12がX方向に往復移動するように構成されている。
In the first embodiment, the example in which the movable portion that reciprocates along the direction along the surface of the planar coil is shown, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, as shown in FIG. 29, a
また、上記第2実施形態では、バネ部材206の板バネ206c、206dおよび206eは、同一のバネ定数を有している例を示したが、本発明はこれに限られない。たとえば、板バネ206cと板バネ206eとが異なるバネ定数を有していてもよい。そして、加速度発生デバイス201は、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の2つの可動部を備えているため、板バネ206cと板バネ206eとのバネ定数を異ならせた場合、第1可動部204および第2可動部205は、それぞれ異なる周波数で共振する。そのため、第1可動部204の共振周波数と第2可動部205の共振周波数との比率を約2倍とするとともに、平面コイル273および283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率を約2倍とした場合、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の一往復中における加速度の波形(時間変化)が、X1方向に対する移動とX2方向に対する移動とで非対称となる。
Moreover, in the said 2nd Embodiment, although the leaf | plate springs 206c, 206d, and 206e of the
ここで、駆動電流制御回路290が、平面コイル273に印加する交流電圧の周波数と、平面コイル283に印加する交流電圧の周波数との位相差を調整することにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向の所望の方向への擬似力覚を提示することが可能となる。
Here, the drive
なお、第1可動部204の共振周波数は、板バネ206cのバネ定数に関係しているとともに、第2可動部205の共振周波数は、板バネ206eのバネ定数に関係している。したがって、平面コイル273および283に同一の周波数を有する交流電圧を印加した場合において、板バネ206cおよび206eのバネ定数を、第1可動部204の共振周波数と第2可動部205の共振周波数との比率が約2倍となるように設定する。このとき、板バネ206dのバネ定数は、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向の所望の方向への擬似力覚を提示するという効果には影響を与えない。
Note that the resonance frequency of the first
このように、板バネ206cおよび206eのバネ定数を異ならせることにより、第2実施形態と比較して、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の加速度の非対称性を大きくすることができる。
Thus, by making the spring constants of the
なお、第1可動部204の共振周波数と第2可動部205の共振周波数との比率は約2倍に限られず、1.5倍以上2.5倍以下の間であればよい。また、平面コイル273および283に印加する交流電圧の周波数の比率も約2倍に限られず、1.5倍以上2.5倍以下の間であればよい。これらの範囲内で調整することにより、ユーザに対してX1方向またはX2方向に明確な擬似力覚を提示することができる。
Note that the ratio between the resonance frequency of the first
また、上記第2実施形態では、第1可動部204および第2可動部205の移動を受け止めるために、板バネ206c、206dおよび206eを用いる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限らない。たとえば、ねじりバネ等の他の構成のバネを用いてもよい。また、第1可動部204および第2可動部205のX方向における両側面と、上側筐体202の両側面202cとにそれぞれ磁石を設け、磁石間の反発力により第1可動部204および第2可動部205の移動を受け止めるようにしてもよい。
Moreover, in the said 2nd Embodiment, in order to catch the movement of the 1st
また、上記第2実施形態では、平面コイル273および283を用いているが、本発明はこれに限られず、たとえば、スパイラルコイルのように第1コイル基板207および第2コイル基板208の厚み方向に厚みのあるコイルを用いてもよい。
In the second embodiment, the
また、上記第3実施形態では、第1コイル基板207と第2コイル基板208とが積層されている例を示したが、本発明はこれに限らない。たとえば、第1コイル基板207が上側筐体202の底面202aに配置されているとともに、第2コイル基板208が下側筐体203の底面203aに配置されていてもよい。
In the third embodiment, the example in which the
また、上記第3および第4実施形態においても、第2実施形態の板バネ206c、206eのバネ定数と同様に、第1バネ部材361と第2バネ部材362とのバネ定数を異ならせることにより、第2実施形態の変形例と同一の効果を得ることができる。
Also in the third and fourth embodiments, the spring constants of the
また、上記第5実施形態では、可動部404の移動を受け止めるために、板バネ405bおよび405cを用いている例を示したが、本発明はこれに限らない。たとえば、ねじりバネ等の他の構成のバネを用いてもよい。また、可動部404のX方向における両側面と、上側筐体402の両側面402cとにそれぞれ磁石を設け、磁石間の反発力により可動部404の移動を受け止める構成であってもよい。
Moreover, in the said 5th Embodiment, in order to catch the movement of the
また、上記第5実施形態では、平面コイル463および473を用いている例を示したが、本発明はこれに限らない。たとえば、スパイラルコイルのように第1コイル基板406および第2コイル基板407の厚み方向に厚みのあるコイルを用いてもよい。
Moreover, in the said 5th Embodiment, although the example which uses the
また、上記第2〜第4実施形態では、2つの可動部にそれぞれ対向するように、2つの平面コイルが設けられる例を示すとともに、上記第5および第6実施形態では、1つの可動部に対向するように、2つの平面コイルが設けられる例を示したが、本発明はこれに限らない。たとえば、3つ以上の可動部にそれぞれ対向するように、3つ以上の平面コイルが設けられていてもよいし、1つの可動部に対向するように、3つ以上の平面コイルが設けられていてもよい。この場合、3つ以上の平面コイルのうち、1つの平面コイルに、上記の式(8)に示される波形が非対称な交流状の電圧V(t)を印加するとともに、他の平面コイルに波形が対称な正弦波状の電圧を印加するようにしてもよい。このように複数の平面コイルのうちの1つの平面コイルに波形が非対称な交流状の電圧を印加することにより、非対称な形状の加速度の波形を得ることができる。また、3つ以上の平面コイルのうち、1つの平面コイルに、上記の式(8)に示される波形のうち、たとえばnが1次から10次までの波形を印加するとともに、他の平面コイルのうちの1つの平面コイルにnが11次から20次までの波形を印加することによっても、非対称な形状の加速度の波形を得ることができる。さらに、3つ以上の平面コイルのうち、2つの平面コイルに、それぞれ、周波数が異なる正弦波状の電圧を印加することによっても、非対称な形状の加速度の波形を得ることができる。 In the second to fourth embodiments, two planar coils are provided so as to face the two movable parts, respectively. In the fifth and sixth embodiments, one movable part is provided. Although the example in which two planar coils are provided so as to face each other is shown, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, three or more planar coils may be provided so as to face three or more movable parts, respectively, or three or more planar coils may be provided so as to face one movable part. May be. In this case, an AC voltage V (t) having an asymmetric waveform shown in the above equation (8) is applied to one of the three or more planar coils, and the waveform is applied to the other planar coils. A sine wave-like voltage may be applied. Thus, by applying an alternating voltage with an asymmetric waveform to one of the plurality of planar coils, an asymmetrical acceleration waveform can be obtained. In addition, among the three or more planar coils, one of the waveforms represented by the above formula (8) is applied to one planar coil, for example, n is a waveform from the first to the tenth, and another planar coil. A waveform of acceleration having an asymmetric shape can also be obtained by applying a waveform of nth to 20th order to one of the planar coils. Furthermore, an asymmetrical acceleration waveform can also be obtained by applying sinusoidal voltages having different frequencies to two of the three or more planar coils.
1 枠体(筐体)
2、404 可動部
3a、3b バネ部
4 平面コイル(コイル)
5 プリント基板(筐体)
6 底板(筐体)
100 リニアモータ(加速度発生デバイス)
201、301、401、402 加速度発生デバイス
211、410 永久磁石
204 第1可動部(第1の可動部)
205 第2可動部(第2の可動部)
206c、405c 板バネ(第1弾性部材)
206d、405b 板バネ(第2弾性部材)
206e、405b 板バネ(第3弾性部材)
209、408 筐体
273、463 平面コイル(第1のコイル)
283、473 平面コイル(第2のコイル)
290、490 駆動電流制御回路(制御部)
361 第1バネ部材(第4弾性部材)
362 第2バネ部材(第5弾性部材)
1 frame (housing)
2, 404
5 Printed circuit board (housing)
6 Bottom plate (housing)
100 linear motor (acceleration generating device)
201, 301, 401, 402
205 2nd movable part (2nd movable part)
206c, 405c Leaf spring (first elastic member)
206d, 405b Leaf spring (second elastic member)
206e, 405b Leaf spring (third elastic member)
209, 408
283, 473 Planar coil (second coil)
290, 490 Drive current control circuit (control unit)
361 First spring member (fourth elastic member)
362 Second spring member (fifth elastic member)
Claims (21)
前記渦巻状のコイルが発生する磁界により往復移動する可動部と、
前記可動部が収納されるとともに前記可動部の往復移動によって振動する筐体と、
前記可動部と前記筐体との間に設けられるバネ部とを備え、
前記渦巻状のコイルには、波形が非対称な交流状の電圧が印加され、
前記筐体の振動方向の加速度の波形は、加速度が0の基準線に対して一方方向側と他方方向側とで非対称になるように構成されている、加速度発生デバイス。 A spiral coil,
A movable part that reciprocates by a magnetic field generated by the spiral coil;
A housing that houses the movable portion and vibrates by reciprocating movement of the movable portion;
A spring portion provided between the movable portion and the housing;
An alternating voltage with an asymmetric waveform is applied to the spiral coil,
The acceleration generating device is configured such that an acceleration waveform in a vibration direction of the housing is asymmetrical on one side and the other side with respect to a reference line where acceleration is zero.
振動する前記筐体の角周波数は、前記振動する筐体の共振角周波数の3分の2倍以上でかつ2倍以下になるように構成されている、請求項1〜4のいずれか1項に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 The waveform of the voltage applied to the spiral coil is determined based on the acceleration waveform of the casing having a desired shape and the impedance and angular frequency derived from the frequency characteristics of the impedance of the casing. Configured,
The angular frequency of the casing that vibrates is configured to be not less than two-thirds and not more than twice the resonance angular frequency of the casing that vibrates. The acceleration generating device described in 1.
前記第1の可動部に対向して配置され、前記第1の可動部を第1の方向および第2の方向に往復移動させる第1のコイルと、
前記第2の可動部に対向して配置され、前記第2の可動部を前記第1の方向および前記第2の方向に往復移動させる第2のコイルと、
前記第1の可動部および前記第2の可動部を収納する筐体と、
前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに流れる電流をそれぞれ独立して制御する制御部とを備え、
前記制御部は、前記第1の可動部および前記第2の可動部の一往復中における加速度の波形が、前記第1の方向に対する移動と前記第2の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに流れる電流を制御するように構成されている、加速度発生デバイス。 A first movable part and a second movable part each including a permanent magnet;
A first coil disposed opposite to the first movable part and reciprocatingly moving the first movable part in a first direction and a second direction;
A second coil that is disposed opposite to the second movable part and moves the second movable part back and forth in the first direction and the second direction;
A housing that houses the first movable part and the second movable part;
A control unit for independently controlling the currents flowing through the first coil and the second coil,
The control unit is configured so that an acceleration waveform during one reciprocation of the first movable unit and the second movable unit is asymmetric between movement in the first direction and movement in the second direction. An acceleration generating device configured to control a current flowing through the first coil and the second coil.
前記筐体と前記第1の可動部との間に設けられる第1弾性部材と、前記第1の可動部と前記第2の可動部との間に設けられる第2弾性部材と、前記第2の可動部と前記筐体との間に設けられる第3弾性部材とをさらに備え、
前記第1弾性部材のバネ定数と前記第3弾性部材のバネ定数とが異なるように構成されている、請求項6に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 The first movable part and the second movable part are arranged along the moving direction of the first movable part and the second movable part,
A first elastic member provided between the housing and the first movable part; a second elastic member provided between the first movable part and the second movable part; A third elastic member provided between the movable part and the housing,
The acceleration generating device according to claim 6, wherein the first elastic member has a spring constant different from that of the third elastic member.
前記第1の可動部および前記第2の可動部の移動方向に沿って、前記筐体と前記第1の可動部との間に設けられる第4弾性部材と、前記筐体と前記第2の可動部との間に設けられる第5弾性部材とをさらに備え、
前記第4弾性部材のバネ定数と前記第5弾性部材のバネ定数とが異なるように構成されている、請求項6に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 The first movable part and the second movable part are arranged along a direction intersecting a moving direction of the first movable part and the second movable part,
A fourth elastic member provided between the casing and the first movable section along a moving direction of the first movable section and the second movable section; and the casing and the second movable section. A fifth elastic member provided between the movable portion and the movable portion;
The acceleration generating device according to claim 6, wherein the fourth elastic member has a spring constant different from that of the fifth elastic member.
前記可動部と対向して配置されており、前記可動部を第1の方向および第2の方向に往復移動させる第1のコイルおよび第2のコイルと、
前記可動部を収納する筐体と、
前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに流れる電流をそれぞれ独立して制御する制御部とを備え、
前記制御部は、前記可動部の一往復中における加速度の波形が、前記第1の方向に対する移動と前記第2の方向に対する移動とで非対称となるように、前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに流れる電流を制御するように構成されている、加速度発生デバイス。 A movable part including a permanent magnet;
A first coil and a second coil that are arranged to face the movable part, and reciprocate the movable part in a first direction and a second direction;
A housing that houses the movable part;
A control unit for independently controlling the currents flowing through the first coil and the second coil,
The control unit includes the first coil and the second coil such that an acceleration waveform during one reciprocation of the movable unit is asymmetric between movement in the first direction and movement in the second direction. An acceleration generating device configured to control the current flowing in the coil of the.
前記制御部は、前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに印加する交流電圧の周波数を異ならせるように構成されている、請求項14に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 The first coil is disposed to face one magnetic pole surface of the permanent magnet, and the second coil is disposed to face the other magnetic pole surface of the permanent magnet,
The acceleration generating device according to claim 14, wherein the control unit is configured to vary the frequency of an alternating voltage applied to the first coil and the second coil.
前記可動部の第2の方向側の側面と前記筐体との間に配置された第2弾性部材とをさらに備える、請求項15に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 A first elastic member disposed between a side surface on the first direction side of the movable portion and the housing;
The acceleration generating device according to claim 15, further comprising a second elastic member disposed between a side surface on the second direction side of the movable portion and the housing.
前記制御部は、前記第1のコイルおよび前記第2のコイルに印加する交流電圧の周波数を異ならせるように構成されている、請求項14に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 The first coil is disposed to face one magnetic pole surface of the permanent magnet, and the second coil is disposed to face a side surface on the second direction side of the permanent magnet. And
The acceleration generating device according to claim 14, wherein the control unit is configured to vary the frequency of an alternating voltage applied to the first coil and the second coil.
前記可動部の第2の方向側の側面と前記第2のコイルとの間に配置された第3弾性部材とをさらに備える、請求項17に記載の加速度発生デバイス。 A first elastic member disposed between a side surface on the first direction side of the movable portion and the housing;
The acceleration generating device according to claim 17, further comprising a third elastic member disposed between a side surface on the second direction side of the movable portion and the second coil.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010187047A JP2011125843A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2010-08-24 | Acceleration generation device |
| PCT/JP2010/066760 WO2011040382A1 (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2010-09-28 | Acceleration generating device |
Applications Claiming Priority (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009224132 | 2009-09-29 | ||
| JP2009224132 | 2009-09-29 | ||
| JP2009224131 | 2009-09-29 | ||
| JP2009224131 | 2009-09-29 | ||
| JP2009261234 | 2009-11-16 | ||
| JP2009261234 | 2009-11-16 | ||
| JP2009261984 | 2009-11-17 | ||
| JP2009261984 | 2009-11-17 | ||
| JP2010187047A JP2011125843A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2010-08-24 | Acceleration generation device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011125843A true JP2011125843A (en) | 2011-06-30 |
Family
ID=43826197
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010187047A Pending JP2011125843A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2010-08-24 | Acceleration generation device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2011125843A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011040382A1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018189914A1 (en) * | 2017-04-14 | 2018-10-18 | 富士通株式会社 | Tactile sensation presentation device and simulation system |
| CN109613973A (en) * | 2017-10-04 | 2019-04-12 | 意美森公司 | Tactile actuator with intellectual material actuating member and Electromagnetically actuated component |
| WO2020105539A1 (en) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-05-28 | オムロン株式会社 | Key input device having vibration mechanism |
| WO2024209841A1 (en) * | 2023-04-07 | 2024-10-10 | アルプスアルパイン株式会社 | Vibration generation device, tactile sensation imparting device, and seat system |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012034561A (en) * | 2010-04-21 | 2012-02-16 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Vibration device and electronic apparatus equipped with the same |
| CN106959112A (en) * | 2017-03-22 | 2017-07-18 | 信利光电股份有限公司 | A kind of oscillatory type motion perception equipment |
| CN111344936A (en) * | 2017-11-20 | 2020-06-26 | 阿尔卑斯阿尔派株式会社 | Vibration generating device |
| CN110417230A (en) * | 2019-07-11 | 2019-11-05 | 重庆汝新动力科技股份有限公司 | A kind of d. c reciprocating formula linear motor and its application apparatus |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08308201A (en) * | 1995-04-27 | 1996-11-22 | Foster Electric Co Ltd | Vibration actuator |
| JP2001213509A (en) * | 2000-02-03 | 2001-08-07 | Shinko Electric Co Ltd | Vibrating feeder |
| JP2004202327A (en) * | 2002-12-24 | 2004-07-22 | Teikoku Tsushin Kogyo Co Ltd | Vibration generator |
| WO2007086426A1 (en) * | 2006-01-24 | 2007-08-02 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Acceleration generating apparatus and pseudo tactile-force generating apparatus |
| JP2008271742A (en) * | 2007-04-24 | 2008-11-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Oscillating device and cell phone including oscillating device |
-
2010
- 2010-08-24 JP JP2010187047A patent/JP2011125843A/en active Pending
- 2010-09-28 WO PCT/JP2010/066760 patent/WO2011040382A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08308201A (en) * | 1995-04-27 | 1996-11-22 | Foster Electric Co Ltd | Vibration actuator |
| JP2001213509A (en) * | 2000-02-03 | 2001-08-07 | Shinko Electric Co Ltd | Vibrating feeder |
| JP2004202327A (en) * | 2002-12-24 | 2004-07-22 | Teikoku Tsushin Kogyo Co Ltd | Vibration generator |
| WO2007086426A1 (en) * | 2006-01-24 | 2007-08-02 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Acceleration generating apparatus and pseudo tactile-force generating apparatus |
| JP2008271742A (en) * | 2007-04-24 | 2008-11-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Oscillating device and cell phone including oscillating device |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018189914A1 (en) * | 2017-04-14 | 2018-10-18 | 富士通株式会社 | Tactile sensation presentation device and simulation system |
| JPWO2018189914A1 (en) * | 2017-04-14 | 2020-02-20 | 富士通株式会社 | Tactile sense providing device and simulation system |
| CN109613973A (en) * | 2017-10-04 | 2019-04-12 | 意美森公司 | Tactile actuator with intellectual material actuating member and Electromagnetically actuated component |
| JP2019067409A (en) * | 2017-10-04 | 2019-04-25 | イマージョン コーポレーションImmersion Corporation | Tactile actuator having smart material working component and electromagnetic working component |
| WO2020105539A1 (en) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-05-28 | オムロン株式会社 | Key input device having vibration mechanism |
| JP2020086649A (en) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-06-04 | オムロン株式会社 | Key input device |
| JP7124665B2 (en) | 2018-11-19 | 2022-08-24 | オムロン株式会社 | key input device |
| WO2024209841A1 (en) * | 2023-04-07 | 2024-10-10 | アルプスアルパイン株式会社 | Vibration generation device, tactile sensation imparting device, and seat system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2011040382A1 (en) | 2011-04-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2011040382A1 (en) | Acceleration generating device | |
| CN110875680B (en) | Vibration actuator and portable electronic device provided with same | |
| WO2010026883A1 (en) | Linear motor and portable device provided with linear motor | |
| US20090267423A1 (en) | Electromagnetic exciter | |
| JP2011072856A (en) | Acceleration generation device and composite type acceleration generation device | |
| JP7057494B2 (en) | Vibration actuator and vibration presentation device | |
| WO2010050285A1 (en) | Linear motor and mobile device having linear motor | |
| WO2017088359A1 (en) | Linear vibration motor | |
| KR101790895B1 (en) | A multi-directional driving module | |
| WO2017088367A1 (en) | Linear vibration motor | |
| JP2018074781A (en) | Linear vibration motor | |
| KR20130018409A (en) | Haptic actuator systems and methods thereof | |
| US20180287477A1 (en) | Self-adaptive control miniature motor | |
| WO2017133132A1 (en) | Linear vibration motor | |
| WO2010026709A1 (en) | Vibration motor and portable terminal device using same | |
| JP2010069470A (en) | Linear motor and portable apparatus equipped with linear motor | |
| JP2010089061A (en) | Vibration motor and portable terminal device using the same | |
| JP2010082508A (en) | Vibrating motor and portable terminal using the same | |
| WO2010103929A1 (en) | Vibration motor and portable apparatus | |
| US11949310B2 (en) | Vibration actuator with movable body with tip part of the core oscillating and a shaft part supporting the movable body on a side of a base | |
| CN211908616U (en) | Linear vibration motor with four permanent magnet structures and damping coil | |
| JP2010099642A (en) | Vibration motor and portable digital terminal device using the same | |
| CN111049351A (en) | Linear vibration motor with four permanent magnet structures and damping coil | |
| JP2010051163A (en) | Linear motor | |
| KR20190057947A (en) | Vibration motor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130822 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140930 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20141107 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20141112 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20141114 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20150303 |