JP2010060397A - Magnetic balance type current sensor - Google Patents
Magnetic balance type current sensor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010060397A JP2010060397A JP2008225487A JP2008225487A JP2010060397A JP 2010060397 A JP2010060397 A JP 2010060397A JP 2008225487 A JP2008225487 A JP 2008225487A JP 2008225487 A JP2008225487 A JP 2008225487A JP 2010060397 A JP2010060397 A JP 2010060397A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- ring
- magnetic core
- negative feedback
- shaped magnetic
- current sensor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Instrument Details And Bridges, And Automatic Balancing Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、例えばハイブリットカーや電気自動車のバッテリー電流やモータ駆動電流、工作機械のモータに流れる電流をホール素子等の磁気検出素子を用いて測定する磁気平衡式電流センサに関する。 The present invention relates to a magnetic balance type current sensor that measures a battery current of a hybrid car or an electric vehicle, a motor drive current, and a current flowing through a motor of a machine tool using a magnetic detection element such as a Hall element.
ホール素子等の磁気検出素子を用いてバスバーに流れる電流(被測定電流)を非接触状態で検出する電流センサとして、磁気比例式のものが従来から知られている。磁気比例式電流センサは、図11(A)に例示のように、ギャップGを有するリング状の磁気コア820(高透磁率で残留磁気が少ない珪素鋼板やパーマロイコア等)と、ギャップGに配置されたホール素子816(磁気検出素子の例示)とを有する。磁気コア820は、被測定電流Iinの流れるバスバー810が貫通する配置である。したがって、被測定電流IinによってギャップG内に磁界が発生し、これがホール素子816の感磁面に印加される。磁界の強さは被測定電流Iinに比例するので、ホール素子816の出力電圧から被測定電流Iinが求められる。
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, a magnetic proportional sensor is known as a current sensor that detects a current (current to be measured) flowing through a bus bar in a non-contact state using a magnetic detection element such as a Hall element. As shown in FIG. 11A, the magnetic proportional current sensor is arranged in the gap G with a ring-shaped magnetic core 820 having a gap G (such as a silicon steel plate or a permalloy core with high permeability and low residual magnetism). Hall element 816 (an example of a magnetic detection element). The magnetic core 820 is arranged so that the
一方、磁気平衡式電流センサは、図11(B)に例示のように、磁気比例式電流センサの構成に加え、磁気コア820に巻線を設けてなる負帰還用コイルLFBを有する。この構成においては、被測定電流IinによってギャップG内に第1の磁界が発生してこれがホール素子816の感磁面に印加される一方、ホール素子816の感磁面に印加される前記第1の磁界を相殺する(ゼロにする)第2の磁界を発生するように負帰還用コイルLFBに電流が供給される。この供給した電流から被測定電流Iinが求められる。 On the other hand, as illustrated in FIG. 11B, the magnetic balanced current sensor has a negative feedback coil L FB in which a winding is provided on the magnetic core 820 in addition to the configuration of the magnetic proportional current sensor. In this configuration, a first magnetic field is generated in the gap G by the measured current I in and applied to the magnetosensitive surface of the Hall element 816, while being applied to the magnetosensitive surface of the Hall element 816. A current is supplied to the negative feedback coil LFB so as to generate a second magnetic field that cancels (makes zero) the magnetic field of 1. A current to be measured I in is obtained from the supplied current.
図11(B)に例示のような磁気平衡式電流センサでは、ギャップ部Gを有するリング状磁気コア820にトロイダル巻線するのが一般的であるが、これには特殊な巻線機が必要となり、また巻線スピードが遅いという問題があった。この問題の解決を目的とする公知文献として、下記特許文献1及び2が挙げられる。
特許文献1の電流検出器は、例えば4分割された円弧状のボビン片の各々に自動巻作業にて導電線を巻回して複数のコイル体を形成し、その後、2分割された半円弧状のコア片を各ボビン片の内側に貫入し、円環状を成すように双方のコア片を接続固定したものである。特許文献2にも同様の技術が開示されている。
For example, the current detector of Patent Document 1 forms a plurality of coil bodies by winding a conductive wire around each of arc-shaped bobbin pieces divided into four parts by an automatic winding operation, and then divided into two semi-arc-shaped parts. These core pieces are inserted into the inside of each bobbin piece, and both core pieces are connected and fixed so as to form an annular shape.
特許文献1及び2の技術によれば、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機を使用する必要がなく、巻線スピードも改善することが可能と考えられる。しかし、2分割された半円弧状のコア片を円環状を成すように組み合わせる必要があるため、分割されていないリング状磁気コアを用いることができない。したがって、分割されたコアを組み合わせる際にギャップ部の長さがばらついたり、組合せ後の振動等によりギャップ部の長さが変動することにより、電流検出精度が悪化することが懸念される。
According to the techniques of
本発明はこうした状況を認識してなされたものであり、その目的は、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機の使用を不要としつつ、分割されていないリング状磁気コアを用いることを可能とすることにより、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機を使用する場合と比較して巻線スピードを改善するとともに、分割されたコアを組み合わせる場合と比較して電流検出精度の悪化のリスクが少ない磁気平衡式電流センサを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in recognition of such a situation, and the purpose thereof is to make it possible to use an undivided ring-shaped magnetic core while obviating the use of a special winding machine for toroidal winding. As a result, the winding speed is improved compared to the case of using a special winding machine for toroidal winding, and the risk of deterioration in current detection accuracy compared to the case of combining divided cores. It is an object of the present invention to provide a magnetic balance type current sensor with a small amount.
本発明のある態様は、磁気平衡式電流センサである。この磁気平衡式電流センサは、
被測定電流の経路を囲む、ギャップ部を有する分割されていないリング状磁気コアと、
前記ギャップ部に位置する磁気検出素子と、
前記リング状磁気コアが内側を貫通する負帰還用コイルとを備え、
前記負帰還用コイルの軸方向の長さは少なくとも一部で前記リング状磁気コアの前記ギャップ部の長さよりも短く、これにより前記負帰還用コイルは前記ギャップ部から前記リング状磁気コアに実装可能とされている。
One embodiment of the present invention is a magnetically balanced current sensor. This magnetic balanced current sensor
An undivided ring-shaped magnetic core having a gap surrounding the path of the current to be measured;
A magnetic sensing element located in the gap portion;
The ring-shaped magnetic core comprises a negative feedback coil that penetrates the inside,
The length of the negative feedback coil in the axial direction is at least partially shorter than the length of the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core, whereby the negative feedback coil is mounted on the ring-shaped magnetic core from the gap portion. It is possible.
ある態様の磁気平衡式電流センサにおいて、前記負帰還用コイルは、巻軸方向の長さが少なくとも一部で前記リング状磁気コアの前記ギャップ部の長さよりも短いボビンに巻線を施したものであり、前記ボビンの内側を前記リング状磁気コアが貫通しているとよい。 In the magnetically balanced current sensor according to an aspect, the negative feedback coil is obtained by winding a bobbin having a length in the winding axis direction that is at least partly shorter than the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core. It is preferable that the ring-shaped magnetic core penetrates the inside of the bobbin.
ある態様の磁気平衡式電流センサにおいて、前記負帰還用コイルは複数存在し、前記リング状磁気コアの周方向に関して磁気的極性が同一となるように複数の前記負帰還用コイルが直列に接続されているとよい。 In one aspect of the magnetic balanced current sensor, there are a plurality of the negative feedback coils, and the plurality of negative feedback coils are connected in series so that the magnetic polarity is the same in the circumferential direction of the ring-shaped magnetic core. It is good to have.
この場合、複数の前記負帰還用コイルはそれぞれ、
巻軸方向の長さが少なくとも一部で前記リング状磁気コアの前記ギャップ部の長さよりも短く、内側を前記リング状磁気コアが貫通するボビンと、
前記ボビンに施され、前記ボビンから突き出たピンに端末が電気的に接続された巻線とを有するものであり、
各ピンはプリント基板のスルーホールに挿通されて前記プリント基板上の導電パターンと電気的に接続され、
複数の前記負帰還用コイルは、前記リング状磁気コアの周方向に関して磁気的極性が同一となるように、前記プリント基板上の前記導電パターンにより相互に電気的に接続されているとよい。
In this case, each of the plurality of negative feedback coils is
A bobbin whose length in the winding axis direction is at least partly shorter than the length of the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core and through which the ring-shaped magnetic core passes;
A winding that is applied to the bobbin and has a terminal electrically connected to a pin protruding from the bobbin;
Each pin is inserted into a through hole of the printed circuit board and electrically connected to the conductive pattern on the printed circuit board,
The plurality of negative feedback coils may be electrically connected to each other by the conductive pattern on the printed circuit board so that the magnetic polarities are the same in the circumferential direction of the ring-shaped magnetic core.
ある態様の磁気平衡式電流センサにおいて、前記被測定電流の経路は前記被測定電流を所定の比率で分流するように高抵抗電流路と低抵抗電流路とに分岐したバスバーであり、前記リング状磁気コアが前記高抵抗電流路を囲んでいるとよい。 In the magnetically balanced current sensor of one aspect, the path of the current to be measured is a bus bar that branches into a high resistance current path and a low resistance current path so as to shunt the current to be measured at a predetermined ratio, and the ring shape A magnetic core may surround the high resistance current path.
この場合、前記負帰還用コイルは、前記低抵抗電流路から離れた位置となるように前記リング状磁気コアに実装されているとよい。 In this case, the negative feedback coil may be mounted on the ring-shaped magnetic core so as to be positioned away from the low resistance current path.
あるいは、前記高抵抗電流路は、前記低抵抗電流路の幅内において前記低抵抗電流路の上方又は下方のいずれかに位置し、
前記負帰還用コイルは、前記低抵抗電流路に対して前記高抵抗電流路よりも離れた位置となるように前記リング状磁気コアに実装されているとよい。
Alternatively, the high resistance current path is located either above or below the low resistance current path within the width of the low resistance current path,
The negative feedback coil may be mounted on the ring-shaped magnetic core such that the negative feedback coil is located farther from the high resistance current path than the low resistance current path.
なお、以上の構成要素の任意の組合せ、本発明の表現を方法やシステムなどの間で変換したものもまた、本発明の態様として有効である。 It should be noted that any combination of the above-described constituent elements, and those obtained by converting the expression of the present invention between methods and systems are also effective as aspects of the present invention.
本発明によれば、負帰還用コイルの軸方向の長さを少なくとも一部でリング状磁気コアのギャップ部の長さよりも短いものとし、これにより前記負帰還用コイルを前記ギャップ部から前記リング状磁気コアに実装可能としているため、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機の使用を不要としつつ、分割されていないリング状磁気コアを用いることが可能となり、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機を使用する場合と比較して巻線スピードを改善するとともに、分割されたコアを組み合わせる場合と比較して電流検出精度の悪化のリスクが少ない磁気平衡式電流センサを実現することができる。 According to the present invention, the length of the negative feedback coil in the axial direction is at least partly shorter than the length of the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core, whereby the negative feedback coil is moved from the gap portion to the ring. It is possible to use an undivided ring-shaped magnetic core while eliminating the need to use a special winding machine for toroidal winding. To achieve a magnetically balanced current sensor that improves the winding speed compared to using a simple winding machine and has a lower risk of deterioration of current detection accuracy compared to combining split cores. it can.
以下、図面を参照しながら本発明の好適な実施の形態を詳述する。なお、各図面に示される同一または同等の構成要素、部材等には同一の符号を付し、適宜重複した説明は省略する。また、実施の形態は発明を限定するものではなく例示であり、実施の形態に記述されるすべての特徴やその組み合わせは必ずしも発明の本質的なものであるとは限らない。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the same or equivalent component, member, etc. which are shown by each drawing, and the overlapping description is abbreviate | omitted suitably. In addition, the embodiments do not limit the invention but are exemplifications, and all features and combinations thereof described in the embodiments are not necessarily essential to the invention.
(第1の実施の形態)
図1は、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る磁気平衡式電流センサ100の正断面図(図3のI-I'断面図)である。図2は、図1のII-II'断面図である。図3は、同磁気平衡式電流センサ100の平面図である。図4は、同磁気平衡式電流センサ100の例示的な回路図である。
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a front sectional view (II ′ sectional view of FIG. 3) of a magnetic balanced current sensor 100 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line II-II ′ of FIG. FIG. 3 is a plan view of the magnetic balance type current sensor 100. FIG. 4 is an exemplary circuit diagram of the magnetically balanced current sensor 100.
磁気平衡式電流センサ100は、被測定電流の経路としてのバスバー12と、リング状磁路を成すリング状磁気コア15と、磁気検出素子としてのホール素子25と、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10と、プリント基板26と、絶縁板29とを備える。
The magnetic balance type current sensor 100 includes a
バスバー12は、平板形状(例えば銅板)であり、長手方向の両端部に位置する取付け孔(図示せず)を介して例えばネジやリベットによって被測定電流の経路を成すように取り付けられる。バスバー12の長手方向の中間部を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15(高透磁率で残留磁気が少ない珪素鋼板やパーマロイコア、アモルファス等からなる)が配置され、リング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gにホール素子25が位置し、リング状磁気コア15が内側を貫通するように負帰還用コイルL1〜L10が実装される。ここで、リング状磁気コア15は、上記特許文献1及び2のコアと異なり、分割されていないものである。また、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の軸方向の長さLcはリング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さLgよりも短い(Lc<Lg)。したがって、リング状磁気コア15が特許文献1及び2のコアのように分割されていなくても、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10をギャップ部Gからリング状磁気コア15に実装することができる。
The
負帰還用コイルL1は好ましくは図2にも示されるようにボビン17に巻線18を施したものであり、巻線18の端末はボビン17から突き出たピン19に例えば絡げて半田付けすることで電気的に接続されている。ボビン17の巻軸方向の長さ(すなわち負帰還用コイルL1の長さLc)はリング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さLgよりも短い。ボビン17の内側をリング状磁気コア15が貫通する。負帰還用コイルL2〜L10も同様の構成である。ここで、リング状磁気コア15は好ましくは図1に示されるような方形リング状(長方形リング状)であり、ギャップ部Gの存在する直線状部16が負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の内側を貫通するとよい。
The negative feedback coil L1 is preferably a
プリント基板26は負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の鍔部端面上に配置され、各ボビン17から突き出たピン19がプリント基板26のスルーホールに挿通されてプリント基板26上の導電パターン(図3参照)と例えば半田付けにより電気的に接続される。またホール素子25の各ピンもプリント基板26のスルーホールに挿通されて同様に接続される。なお、図3においては、プリント基板26上に負帰還用コイルL1〜L10を接続する導電パターンのみを図示し、その他の回路部品及び接続の図示は省略している。プリント基板26上の前記導電パターンにより負帰還用コイルL1〜L10は、図3及び図4に示されるように、リング状磁気コア15の周方向に関して磁気的極性が同一となるように(同じ向きの磁束を発生するように)直列に接続される。
The printed
図4に示される回路において、ホール素子25は等価的に4つの抵抗のブリッジ接続で表され、端子a,c間に一定のホール素子駆動電流を流しておくことにより出力端子b,d間にホール素子25に印加された磁界に比例した(換言すれば被測定電流Iinに比例した)電圧を得る構成としている。なお、抵抗R1及びR2(電流制限用抵抗器)によって電源(電圧Vcc)からホール素子25への供給電流が制限される。ホール素子25の出力端子b,dは、負帰還用差動増幅器35の入力端子にそれぞれ接続される。負帰還用差動増幅器35の出力端子と基準電圧端子(例えば2.5V)とを接続する経路に負帰還用コイルL1〜L10と検出抵抗RSとが直列接続される。検出抵抗RSと並列に電圧計37が接続される。
In the circuit shown in FIG. 4, the
ホール素子25の出力電圧VHは負帰還用差動増幅器35に入力される。負帰還用差動増幅器35は、出力端子から電流を吸い込む又は吐き出すことにより、端子b、d間の電位差が常にゼロとなるように、すなわちホール素子25の感磁面において被測定電流Iinによって発生する第1の磁界と負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の発生する第2の磁界とが相殺するように、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10に負帰還電流IFBを供給する。供給された負帰還電流IFBは検出抵抗RSで電圧に変換されて電圧計37によって検出(モニタ)される(又はセンサ出力として外部に取り出される)。被測定電流Iinは負帰還用コイルL1〜L10への供給電流と巻線総和とから「等アンペアターンの原理」により求めることができる。
The output voltage V H of the
本実施の形態によれば、下記の効果を奏することができる。 According to the present embodiment, the following effects can be achieved.
(1) 負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の軸方向の長さLcがリング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さLgよりも短い(Lc<Lg)ため、リング状磁気コア15が特許文献1及び2のコアのように分割されていなくても、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10をギャップ部Gからリング状磁気コア15に実装することができる。したがって、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機の使用を不要としつつ、分割されていないリング状磁気コア15を用いることが可能となり、トロイダル巻線のための特殊な巻線機を使用する場合と比較して巻線スピードを改善するとともに、分割されたコアを組み合わせる場合と比較して電流検出精度の悪化のリスクが少ない。
(1) Since the axial length Lc of the negative feedback coils L1 to L10 is shorter than the length Lg of the gap portion G of the ring-shaped magnetic core 15 (Lc <Lg), the ring-shaped
(2) 複数の負帰還用コイルL1〜L10を直列に接続しているので、負帰還用コイルが1つの場合と比較して、被測定電流Iinが大きい場合に適している。 (2) Since the connecting multiple negative feedback coil L1~L10 in series, as compared with the case of one negative feedback coil, it is suitable for the case the measured current I in is large.
(3) リング状磁気コア15を方形リング状(長方形リング状)とし、ギャップ部Gの存在する直線状部16が負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の内側を貫通しているので、リング状磁気コア15への負帰還用コイルL1〜L10の実装作業が容易である。また、負帰還用コイルL1〜L10とプリント基板26との接続もしやすい。
(3) Since the ring-shaped
(4) 電流センサを「磁気平衡式」としているため、「磁気比例式」の場合と比較して高精度の電流検出が可能となる。すなわち、温度特性(−40℃〜+100℃)を含む精度が「磁気比例式」の場合は例えば±400A(F.S.)において±3%であったのが、「磁気平衡式」にしたことにより、±1%以下に高精度化できた。その原因は、「磁気比例式」の場合、±400A(F.S.)時にはコア内ギャップに発生する磁束密度が最大となり、ホール素子に例えば20mT(F.S.)が印加され、そのときのホール素子の温度特性がそのまま電流センサの精度悪化に影響するためである。これに対し「磁気平衡式」の場合には、ギャップ内磁束密度が常時0mTで動作するため、原理的にホール素子のオフセットの温度特性のみしか精度に影響せず、比較的高精度なセンサが構成可能となる。 (4) Since the current sensor is of the “magnetic balance type”, the current can be detected with higher accuracy than the “magnetic proportional type”. That is, when the accuracy including the temperature characteristic (−40 ° C. to + 100 ° C.) is “magnetic proportional type”, for example, ± 3% at ± 400 A (FS) is changed to “magnetic equilibrium type”. The accuracy was improved to ± 1% or less. The reason for this is that, in the case of “magnetic proportional type”, the magnetic flux density generated in the gap in the core becomes maximum at ± 400 A (FS), and for example, 20 mT (FS) is applied to the Hall element. This is because it affects the accuracy deterioration of the current sensor as it is. On the other hand, in the case of the “magnetic balance type”, since the magnetic flux density in the gap always operates at 0 mT, in principle, only the temperature characteristic of the offset of the Hall element affects the accuracy, and a relatively high accuracy sensor can be obtained. It becomes configurable.
(第2の実施の形態)
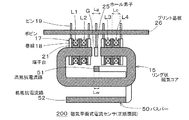
図5は、本発明の第2の実施の形態に係る磁気平衡式電流センサ200の概略斜視図である。但し、本図においてホール素子及びプリント基板の図示は省略している。図6は、同磁気平衡式電流センサ200の正断面図である。本実施の形態の磁気平衡式電流センサ200は、第1の実施の形態の磁気平衡式電流センサ100と比較して、バスバー50が2つの経路に分岐していてリング状磁気コア15が一方の経路を囲むように配置されている点において主に相違し、その他の点で一致している。以下、相違点を中心に説明する。
(Second embodiment)
FIG. 5 is a schematic perspective view of a magnetic balanced current sensor 200 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. However, in this figure, illustration of a Hall element and a printed circuit board is omitted. FIG. 6 is a front sectional view of the magnetic balanced current sensor 200. Compared with the magnetic balance type current sensor 100 of the first embodiment, the magnetic balance type current sensor 200 of the present embodiment has a
バスバー50は、後述のように長手方向の中間部で部分的に高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52とに分岐しており、長手方向の両端部に位置する取付け孔91,92を介して例えばネジやリベットによって被測定電流の経路を成すように取り付けられる。リング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さLgは高抵抗電流路51の幅Lwよりも長く、高抵抗電流路51を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15が配置され、リング状磁気コア15に負帰還用コイルL1〜L4が実装される。ここで、負帰還用コイルL1〜L4は、鍔部端面から端子台21(ピン19の植設部分)が出っ張っていて軸方向の長さがリング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さよりも長くなっているが、端子台21を除いた軸方向の長さLcはギャップ部Gの長さLgよりも短い(Lc<Lg)。したがって、第1の実施の形態と同様に、リング状磁気コア15が特許文献1及び2のコアのように分割されていなくても、負帰還用コイルL1〜L4をギャップ部Gからリング状磁気コア15に実装することができる。
As will be described later, the
図7は、同磁気平衡式電流センサ200の組立過程を示す斜視図である。但し、本図においてホール素子及びプリント基板の図示は省略している。まず、負帰還用コイルL1〜L4をリング状磁気コア15にギャップ部Gから順次実装する(同図(A)→(C))。そして、バスバー50の高抵抗電流路51を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15を配置する(同図(C)→(D))。ここで、高抵抗電流路51の幅Lwはギャップ部Gの長さLgよりも短い(Lw<Lg)。このため、バスバー50が一体形成されかつリング状磁気コア15が分割されていなくても、高抵抗電流路51をギャップ部Gに通すことで、高抵抗電流路51を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15を配置することができる。その後、図6に示されるように負帰還用コイルL1〜L4とホール素子25の各ピンをプリント基板26のスルーホールに挿通して半田付け等によりプリント基板26上の導電パターンと接続する。
FIG. 7 is a perspective view showing an assembly process of the magnetic balance type current sensor 200. However, in this figure, illustration of a Hall element and a printed circuit board is omitted. First, the negative feedback coils L1 to L4 are sequentially mounted on the ring-shaped
図8は、第2の実施の形態におけるバスバー50の組立過程を示す斜視図である。バスバー50は、同図(A)に示されるように、折曲げ前においては一体形成された平板形状(例えば銅板)であり、長手方向の中間部に前記長手方向に沿う所定長の開口57が形成されている。開口57によってバスバー50は長手方向の中間部で部分的に高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52とに分岐している。換言すれば、被測定電流Iinの全てが流れる未分岐電流路(バスバー50の両端部の分岐していない電流路)の間に高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52とが挟まれている。したがって、被測定電流Iinは所定の比率で高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52とに分流される。このため、本実施の形態では、高抵抗電流路51に流れる電流は負帰還用コイルL1〜L4への供給電流と巻線総和とから「等アンペアターンの原理」により求められ、それに基づいて被測定電流Iinが分流比より算出される。なお、バスバー50は図9に示す回路図で等価的に表され、分流比は高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52の抵抗の逆数の比に等しい。
FIG. 8 is a perspective view showing an assembly process of the
高抵抗電流路51は好ましくは、バスバー50の長手方向の中間部にコの字型に形成され、コの字型の先端側(第1の折曲げ部53)及び中間部(第2の折曲げ部54)の2カ所で折り曲げられて庇状になっている(図8(A)→(B))。そしてコの字型の高抵抗電流路51の底辺(底部55)は低抵抗電流路52の幅内(例えば幅方向の中間部)で低抵抗電流路52の上方(又は下方)に位置し、その部分をリング状磁気コア15が図5及び図6に示されるように囲む。
The high resistance
本実施の形態によれば、被測定電流Iinよりも小さな電流が流れる高抵抗電流路51をリング状磁気コア15で囲む構成としているので、被測定電流Iinの全てが流れる電流路を囲む場合と比較して、リング状磁気コア15が小型で済み、負帰還用コイルの巻線数も少なくてよいため、コスト安である。
According to this embodiment, since a configuration to surround the high-resistance
また、高抵抗電流路51は折り曲げられて低抵抗電流路52に対して庇状とされ、高抵抗電流路51のうち低抵抗電流路52の上方(又は下方)に位置する部分をリング状磁気コア15が囲むため、リング状磁気コア15がバスバー50の幅方向に関してはみ出る量を減らすことができ、電流センサを幅狭に構成できる。
Further, the high resistance
さらに、バスバー50が一体形成されているため、すなわち高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52、及びそれらの両側の分岐していない部分がネジやリベット等による結合ではなく一体形成されているため、分岐箇所をネジやリベット等で結合する分離構造のバスバーを用いる場合と比較して、分岐箇所の接触抵抗の変化による分流割合への影響がないので、分流割合の変化による電流検出精度の悪化を防止して高精度に電流検出することが可能となる。
Further, since the
さらに、負帰還用コイルL1〜L4は低抵抗電流路52から離れた位置となるようにリング状磁気コア15に実装されている(例えば低抵抗電流路52に対して高抵抗電流路51よりも離れた位置となるようにリング状磁気コア15に実装されている)ため、大電流が流れる低抵抗電流路52からの熱の影響を受けにくく、信頼性が高いといえる。また、負帰還用コイルL1〜L4がリング状磁気コア15の上側部分に実装されているので、各コイルのピンをそのままプリント基板26のスルーホールに挿通することができて実装容易である。
Further, the negative feedback coils L1 to L4 are mounted on the ring-shaped
(第3の実施の形態)
図10は、本発明の第3の実施の形態に係る磁気平衡式電流センサ300の正断面図である。本実施の形態の磁気平衡式電流センサ300は、第2の実施の形態の磁気平衡式電流センサ200と比較して、リング状磁気コア15がコアホルダ70に保持されている点と、全体がケース(ケース本体80及び蓋85)で覆われている点とにおいて相違し、その他の点で一致している。以下、相違点を中心に説明する。
(Third embodiment)
FIG. 10 is a front sectional view of a magnetic balanced current sensor 300 according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Compared with the magnetic balance type current sensor 200 of the second embodiment, the magnetic balance type current sensor 300 of the present embodiment has a point that the ring-shaped
樹脂等からなるコアホルダ70は、コの字型形状の内側にリング状磁気コア15を収容し、コの字型の両脚71,72でリング状磁気コア15を挟み込む。また、コの字型の底部73の外面には2カ所の平行な凸条74,75が形成され、凸条74,75で低抵抗電流路52を幅方向両側から挟み込む。なお、コアホルダ70の底部73の外面に凸条74,75に替えて所定数のボスを形成しておき、それらを低抵抗電流路52に形成した所定数の穴に圧入する構成としてもよい。
The
樹脂等からなるケース本体80は、上方が開口した直方体形状であり、底部の内面の凹部81に凸条74,75で挟まれた低抵抗電流路52が嵌るようになっている。プリント基板26はケース本体80の上辺に載置され、樹脂等からなる蓋85がケース本体80に例えば嵌合して被せられる。
The case
本実施の形態によれば、第2の実施の形態の効果に加え、コアホルダ70によってバスバー50とリング状磁気コア15との位置決めが容易かつ確実となり、組み立てやすい。
According to the present embodiment, in addition to the effects of the second embodiment, the positioning of the
以上、実施の形態を例に本発明を説明したが、実施の形態の各構成要素には請求項に記載の範囲で種々の変形が可能であることは当業者に理解されるところである。以下、変形例について触れる。 The present invention has been described above by taking the embodiment as an example. However, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications can be made to each component of the embodiment within the scope of the claims. Hereinafter, modifications will be described.
負帰還用コイルを第1の実施の形態では10個とし、第2及び第3の実施の形態では4個としたが、負帰還用コイルの個数は任意であり、被測定電流Iinの大きさや1個あたりの巻線数によって適宜決定される。 Although the number of negative feedback coils is 10 in the first embodiment and 4 in the second and third embodiments, the number of negative feedback coils is arbitrary, and the magnitude of the current I in to be measured is large. It is determined appropriately depending on the number of windings per sheath.
実施の形態では負帰還用コイルはボビンに巻線を施したものとしたが、変形例ではボビンレス、例えば自己融着導線(セメントワイヤ)をボビンレスで巻回したもの、としてもよい。 In the embodiment, the negative feedback coil is formed by winding a bobbin. However, in a modified example, a bobbinless, for example, a self-bonding conductive wire (cement wire) wound by a bobbinless may be used.
実施の形態ではプリント基板上の導電パターンにより負帰還用コイル同士を直列に電気的に接続したが、変形例では負帰還用コイル同士の接続にリード線を用いてもよい。 In the embodiment, the negative feedback coils are electrically connected in series by the conductive pattern on the printed circuit board. However, in a modified example, a lead wire may be used to connect the negative feedback coils.
第2及び第3の実施の形態ではリング状磁気コア15のギャップ部Gの長さが高抵抗電流路51の幅よりも長い場合を説明したが、ギャップ部Gの長さが高抵抗電流路51の厚み又は幅の少なくともいずれかよりも長ければ、高抵抗電流路51をギャップ部Gに通すことで、高抵抗電流路51を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15を配置することができる。
In the second and third embodiments, the case where the length of the gap portion G of the ring-shaped
第2及び第3の実施の形態では高抵抗電流路51を2カ所で折り曲げて庇状とする場合を説明したが、変形例では高抵抗電流路51を湾曲させることにより部分的に低抵抗電流路52の上方(又は下方)に位置するようにしてもよく、この場合も同様の効果を奏する。なお、電流センサの幅方向の大きさの制約が緩い場合は高抵抗電流路51を折り曲げずにリング状磁気コア15を実装してもよい。
In the second and third embodiments, the case has been described in which the high resistance
第2及び第3の実施の形態ではバスバー50が一体形成されている場合を説明したが、変形例では、高抵抗電流路51と低抵抗電流路52、及びそれらの両側の分岐していない部分を別体としてネジやリベット等により接続してもよい。この場合、リング状磁気コア15のギャップ部の長さが高抵抗電流路51の厚み及び幅の双方よりも短くても、高抵抗電流路51を囲むようにリング状磁気コア15を配置することができる。
In the second and third embodiments, the case where the
12,50 バスバー
15 リング状磁気コア
16 直線状部
17 ボビン
18 巻線
19 ピン
25 ホール素子
26 プリント基板
29 絶縁板
51 高抵抗電流路
52 低抵抗電流路
70 コアホルダ
80 ケース
85 蓋
100,200,300 磁気平衡式電流センサ
L1〜L10 負帰還用コイル
12, 50
Claims (7)
前記ギャップ部に位置する磁気検出素子と、
前記リング状磁気コアが内側を貫通する負帰還用コイルとを備え、
前記負帰還用コイルの軸方向の長さは少なくとも一部で前記リング状磁気コアの前記ギャップ部の長さよりも短く、これにより前記負帰還用コイルは前記ギャップ部から前記リング状磁気コアに実装可能とされている、磁気平衡式電流センサ。 An undivided ring-shaped magnetic core having a gap surrounding the path of the current to be measured;
A magnetic sensing element located in the gap portion;
The ring-shaped magnetic core comprises a negative feedback coil that penetrates the inside,
The length of the negative feedback coil in the axial direction is at least partially shorter than the length of the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core, whereby the negative feedback coil is mounted on the ring-shaped magnetic core from the gap portion. A magnetic balance type current sensor is possible.
複数の前記負帰還用コイルはそれぞれ、
巻軸方向の長さが少なくとも一部で前記リング状磁気コアの前記ギャップ部の長さよりも短く、内側を前記リング状磁気コアが貫通するボビンと、
前記ボビンに施され、前記ボビンから突き出たピンに端末が電気的に接続された巻線とを有するものであり、
各ピンはプリント基板のスルーホールに挿通されて前記プリント基板上の導電パターンと電気的に接続され、
複数の前記負帰還用コイルは、前記リング状磁気コアの周方向に関して磁気的極性が同一となるように、前記プリント基板上の前記導電パターンにより相互に電気的に接続されている、磁気平衡式電流センサ。 The magnetically balanced current sensor according to claim 3,
Each of the plurality of negative feedback coils is
A bobbin whose length in the winding axis direction is at least partly shorter than the length of the gap portion of the ring-shaped magnetic core and through which the ring-shaped magnetic core passes;
A winding that is applied to the bobbin and has a terminal electrically connected to a pin protruding from the bobbin;
Each pin is inserted into a through hole of the printed circuit board and electrically connected to the conductive pattern on the printed circuit board,
The plurality of negative feedback coils are electrically connected to each other by the conductive pattern on the printed circuit board so as to have the same magnetic polarity in the circumferential direction of the ring-shaped magnetic core. Current sensor.
前記高抵抗電流路は、前記低抵抗電流路の幅内において前記低抵抗電流路の上方又は下方のいずれかに位置し、
前記負帰還用コイルは、前記低抵抗電流路に対して前記高抵抗電流路よりも離れた位置となるように前記リング状磁気コアに実装されている、磁気平衡式電流センサ。 The magnetic balance type current sensor according to claim 5,
The high resistance current path is located either above or below the low resistance current path within the width of the low resistance current path,
The magnetic feedback type current sensor, wherein the negative feedback coil is mounted on the ring-shaped magnetic core so as to be located farther from the high resistance current path than the low resistance current path.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008225487A JP2010060397A (en) | 2008-09-03 | 2008-09-03 | Magnetic balance type current sensor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008225487A JP2010060397A (en) | 2008-09-03 | 2008-09-03 | Magnetic balance type current sensor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010060397A true JP2010060397A (en) | 2010-03-18 |
Family
ID=42187350
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008225487A Withdrawn JP2010060397A (en) | 2008-09-03 | 2008-09-03 | Magnetic balance type current sensor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010060397A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010085228A (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2010-04-15 | Tdk Corp | Current sensor |
-
2008
- 2008-09-03 JP JP2008225487A patent/JP2010060397A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010085228A (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2010-04-15 | Tdk Corp | Current sensor |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2010071822A (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP5067574B2 (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP4788922B2 (en) | Current sensor | |
| US7365535B2 (en) | Closed-loop magnetic sensor system | |
| JP2008215970A (en) | Bus bar integrated current sensor | |
| JP7522129B2 (en) | Magnetic Sensors | |
| US9804203B2 (en) | Compensation current sensor arrangement | |
| WO2017125728A1 (en) | Measurement device | |
| EP2860535B1 (en) | Hall effect sensor core with multiple air gaps | |
| JP2009210406A (en) | Current sensor and watthour meter | |
| WO1995020167A1 (en) | Current sensor including magnetic sensors | |
| JP6384677B2 (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP2010038750A (en) | Magnetic balance type current sensor | |
| JP2009058451A (en) | Current sensor-use magnetic core and current sensor employing the same | |
| CN107103982B (en) | Magnetic core for sensor | |
| JP6492693B2 (en) | Current sensor unit | |
| JP4816980B2 (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP2009156802A (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP2010101635A (en) | Magnetic balance type current sensor | |
| JP4623289B2 (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP2010060397A (en) | Magnetic balance type current sensor | |
| JP2010112767A (en) | Current sensor | |
| JP5257811B2 (en) | Fast response and low current consumption non-contact DC current sensor | |
| JP2012198053A (en) | Magnetic sensor and current sensor using the same | |
| JP2005221342A (en) | Coil-type current sensor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A300 | Withdrawal of application because of no request for examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A300 Effective date: 20111206 |